Carbohydrate-Binding Mechanism of the Coagulant Lectin from Moringa oleifera Seeds (cMoL) Is Related to the Dimeric Protein Structure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Lectin Purification
3.2. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
3.3. Molecular Quenching
3.4. Urea-Induced Denaturation Experiments
3.4.1. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
3.4.2. Circular Dichroism (CD)
3.4.3. Hemagglutinating Activity (HA)
3.5. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baptista, A.T.A.; Silva, M.O.; Gomes, R.G.; Bergamasco, R.; Vieira, M.F.; Vieira, A.M.S. Protein fractionation of seeds of Moringa oleifera Lam. and its application in superficial water treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 180, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Baes, A.U.; Nishijima, W.; Okada, M. Isolation and characterization of coagulant extracted from Moringa oleifera seed by salt solution. Water Res. 2001, 35, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lossio, C.F.; Moreira, C.G.; Amorim, R.M.; Nobre, C.S.; Silva, M.T.; Neto, C.C.; Pinto-Junior, V.R.; Silva, I.B.; Campos, J.; Assreuy, A.M.S. Lectin from Canavalia villosa seeds: A glucose/mannose-specific protein and a new tool for inflammation studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, I.J. What should be called a lectin? Nature 1980, 66, 285–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Fakharany, E.M.; Saad, M.H.; Salem, M.S.; Sidkey, N.M. Biochemical characterization and application of a novel lectin from the cyanobacterium Lyngabya confervoides MK012409 as an antiviral and anticancer agent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klafke, G.B.; Moreira, G.M.S.G.; Monte, L.G.; Pereira, J.L.; Brandolt, T.M.; Xavier, M.O.; Pinto, L.S. Assessment of plant lectin antifungal potential against yeasts of major importance in medical mycology. Mycopathologia 2013, 175, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, M.L.R.; Oliveira, C.F.; Oliveira, C.T. Insecticidal activity of plant lectins and potential application in crop protection. Molecules 2015, 20, 2014–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.F.S.; Luz, L.A.; Argolo, A.C.C.; Teixeira, J.A.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Coelho, L.C.B.B. Isolation of a seed coagulant Moringa oleifera lectin. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, L.A.; Silva, M.C.C.; Ferreira, R.S.; Santana, L.A.; Silva-Lucca, R.A.; Mentele, R.; Oliva, M.L.V.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Coelho, L.C.B.B. Structural characterization of coagulant Moringa oleifera lectin and its effect on hemostatic parameters. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 58, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agra-Neto, A.C.; Napoleão, T.H.; Pontual, E.V.; Santos, N.D.L.; Andrade, L.L.; Oliveira, C.M.F.; Melo-Santos, M.A.V.; Coelho, L.C.B.B.; Navarro, D.M.A.F.; Paiva, P.M.G. Effect of Moringa oleifera lectins on survival and enzyme activities of Aedes aegypti larvae susceptible and resistant to organophosphate. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.F.R.; Luz, L.A.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Coelho, L.C.B.B.; Marangoni, S.; Macedo, M.L.R. Evaluation of seed coagulant Moringa oleifera lectin (cMoL) as a bioinsecticidal tool with potential for the control of insects. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, L.A.; Rossato, F.A.; Costa, R.A.P.; Napoleão, T.H.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Coelho, L.C.B.B. Cytotoxicity of the coagulant Moringa oleifera lectin (cMoL) to B16-F10 melanoma cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2017, 44, 94–99. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, L.C.C.; Aguiar, J.S.; Napoleão, T.H.; Mota, F.V.B.; Barros, A.L.S.; Moura, M.C.; Coriolano, M.C.; Coelho, L.C.B.B.; Silva, T.G.; Paiva, P.M.G. Evaluation of cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory activities of extracts and lectins from Moringa oleifera seeds. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 81973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, M.L.; Alves, R.R.V.; Oliveira, B.F.; Napoleão, T.H.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Coelho, L.C.B.B.; Bezerra, A.C.; Silva, M.D.C. In vitro effects of Moringa oleifera seed lectins on Haemonchus contortus in larval and adult stages. Exper. Parasitol. 2020, 218, 108004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, B.F.; Araújo, H.D.A.; Neves, E.F.; Napoleão, T.H.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Freitas, K.C.S.; Souza, S.R.; Coelho, L.C.B.B. Electrochemical Characterization Using Biosensors with the Coagulant Moringa oleifera Seed Lectin (cMoL). Biosensors 2023, 13, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.L.S. Lectin biosensors in cancer glycan biomarker detection. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2019, 93, 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- Serra, B.; Gamella, M.; Reviejo, A.J.; Pingarron, J.M. Lectin-modified piezoelectric biosensors for bacteria recognition and quantification. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Inokoshi, J.; Hachiya, A.H.; Oka, S.; Omura, S.; Tanaka, H. The high mannose-type glycan binding lectin actinohivin: Dimerization greatly improves anti-HIV activity. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loris, R.; Hamelryck, T.; Bouckaert, J.; Wyns, L. Legume lectin structure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1383, 9–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varejão, N.; Correia, M.T.S.; Foguel, D. Characterization of the unfolding process of the tetrameric and dimeric forms of Cratylia mollis seed lectin (CRAMOLL 1): Effects of natural fragmentation on protein stability. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 7330–7340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Holle, S.; Van Damme, E.J. Messages from the past: New insights in plant lectin evolution. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameel, N.I.A.; Wong, Y.H.; Shuib, A.S.; Tayyab, S. Conformational analysis of champedak galactose-binding lectin under different urea concentrations. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 98, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 331–348. [Google Scholar]
- Whitmore, L.; Wallace, B. DICHROWEB, an online server for protein secondary structure analyses from circular dichroism spectroscopic data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, D.C.; Barros, M.R.; Menezes, T.M.; Neves, J.L.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Silva, T.G.; Napoleão, T.H.; Coriolano, M.C.; Correia, M.T.S. A new lectin from the floral capitula of Egletes viscosa (EgviL): Biochemical and biophysical characterization and cytotoxicity to human cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbani, G.; Baig, M.H.; Lee, E.J.; Cho, W.K.; Ma, J.Y.; Choi, I. Biophysical study on the interaction between eperisone hydrochloride and human serum albumin using spectroscopic, calorimetric, and molecular docking analyses. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1656–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neco, A.H.B.; Pinto-Junior, V.R.; Araripe, D.A.; Santiago, M.Q.; Osterne, V.J.S.; Lossio, C.F.; Nobre, C.A.S.; Oliveira, M.V.; Silva, M.T.L.; Martins, M.G.Q. Structural analysis, molecular docking and molecular dynamics of an edematogenic lectin from Centrolobium microchaete seeds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, Z.; Sun, Q.; Yang, H.; Tang, P.; Gan, R.; Xiong, X.; Li, H. Combined spectroscopy methods and molecular simulations for the binding properties of trametinib to human serum albumin. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 4742–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenoth, R.; Sreekumar, A.K.; Sukanya, A.; Prabu, A.; Kamlekar, R.K. Interaction of sugar stabilised silver nanoparticles with Momordica charantia seed lectin, a type II ribosome inactivating protein. Glycoconj. J. 2023, 40, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, P.P.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Singha, S.; Mandal, S.; Mondal, G.; Gupta, P.; Chatterjee, B.P. A glucose/mannose binding lectin from litchi (Litchi chinensis) seeds: Biochemical and biophysical characterizations. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2016, 6, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.B.; Franciscato, D.S.; Toledo, K.C.; Souza, J.R.B.; Nakatani, H.S.; Souza, V.R.D. Investigação da supressão de fluorescência de soro albumina bovina e humana por complexo de rutênio. Quím. Nova 2015, 38, 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Sahasrabuddhe, A.A.; Gaikwad, S.M.; Krishnasastry, M.; Khan, M.I. Studies on recombinant single chain Jacalin lectin reveal reduced affinity for saccharides despite normal folding like native Jacalin. Prot. Sci. 2004, 13, 3264–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, K.Y.; Zou, X. Carbohydrate-Protein Interactions: Advances and Challenges. Commun. Inf. Syst. 2021, 21, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, M.I. Interaction of Fusarium solani lectin with monosaccharides and oligosaccharides: A fluorometric study. Photochem. Photobiol. 2007, 83, 966–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dam, T.K.; Roy, R.; Pagé, D.; Brewer, C.F. Negative cooperativity associated with binding of multivalent carbohydrates to lectins. Thermodynamic analysis of the “multivalency effect”. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoitsova, S.R.; Boteva, R.N.; Doyle, R.J. Binding of hydrophobic ligands by Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA-I lectin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1619, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulal, H.P.; Adachi, Y.; Ohno, N.; Yamaguchi, Y. β-Glucan-induced cooperative oligomerization of Dectin-1 C-type lectin-like domain. Glycobiology 2018, 28, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, E.P.; Dima, R.I.; Brooks, B.; Thirumalai, D. Interactions between hydrophobic and ionic solutes in aqueous guanidinium chloride and urea solutions: Lessons for protein denaturation mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7346–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagle, L.B.; Zhang, Y.; Litosh, V.A.; Chen, X.; Cho, Y.; Cremer, P.S. Investigating the hydrogen-bonding model of urea denaturation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 9304–9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.M.; Qadeer, A.; Ahmad, E.; Ashraf, R.; Bhushan, B.; Chaturvedi, S.K.; Rabbani, G.; Khan, R.H. Monomeric banana lectin at acidic pH overrules conformational stability of its native dimeric form. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 9304–9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Mandal, D.K. Denaturant-induced equilibrium unfolding of concanavalin A is expressed by a three-state mechanism and provides an estimate of its protein stability. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Prot. Proteom. 2003, 1648, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorakshakar, A.C.; Ghosh, K. Use of lectins in immunohematology. Asian J. Transfus. Sci. 2016, 10, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Zhang, B.; Qi, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, N.; Wu, C. Conformational study reveals amino acid residues essential for hemagglutinating and anti-proliferative activities of Clematis montana lectin. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2014, 46, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folowosele, M.T.; Odekanyin, O.O.; Adefila, A.O.; Oyepitan, S.P.; Owolabi, E.R.; Alobaloye, A.I. Chemical Modification and Denaturation Effects on the Hemagglutinating Activity of Two Pterocarpus Species Seeds Lectins. Chem. Sci. Int. J. 2024, 33, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, Y.; Koga, H.; Yamada, H.; Ueda, T.; Imoto, T. Effective renaturation of reduced lysozyme by gentle removal of urea. Protein Eng. 1995, 8, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Junior, V.R.; Osterne, V.J.S.; Santiago, M.Q.; Correia, J.L.A.; Pereira-Junior, F.N.; Leal, R.B.; Pereira, M.G.; Chicas, L.S.; Nagano, C.S.; Rocha, B.A.M. Structural studies of a vasorelaxant lectin from Dioclea reflexa Hook seeds: Crystal structure, molecular docking and dynamics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Mariutti, R.B.; Masood, R.; Caruso, I.P.; Costa, G.H.G.; Freita, C.M.; Santos, C.R.; Zanphorlin, L.M.; Mutton, M.J.R.; Murakami, M.T. Crystal structure of mature 2S albumin from Moringa oleifera seeds. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Com. 2015, 468, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, M.; Mossou, E.; Signor, L.; Kieffer-Jaquinod, S.; Kwaambwa, H.; Nermark, F.; Gutfreund, P.; Mitchell, E.; Haertlein, M.; Forsyth, V. Towards a molecular understanding of the water purification properties of Moringa seed proteins. J. Coll. Interf. Sci. 2019, 554, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.F.; Jiang, P.; Zhu, D.Y.; Hu, Y.; Max, M.; Wang, D.C. Crystal structure of Mabinlin II: A novel structural type of sweet proteins and the main structural basis for its sweetness. J. Struct. Biol. 2008, 162, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delatorre, P.; Rocha, B.A.; Souza, E.P.; Oliveira, T.M.; Bezerra, G.A.; Moreno, F.B.; Freitas, B.T.; Santi-Gadelha, T.; Sampaio, A.H.; Azevedo, W.F. Structure of a lectin from Canavalia gladiata seeds: New structural insights for old molecules. BMC Struct. Biol. 2007, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nubi, T.; Adewole, T.S.; Agunbiade, T.O.; Osukoya, O.A.; Kuku, A. Purification and erythrocyte-membrane perturbing activity of a ketose-specific lectin from Moringa oleifera seeds. Biotechnol. Rep. 2021, 31, e00650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.; O’Neill, M.; Pritzel, A.; Antropova, N.; Senior, A.; Green, T.; Žídek, A.; Bates, R.; Blackwell, S.; Yim, J. Protein complex prediction with AlphaFold-Multimer. Biorxiv 2021, 463034. [Google Scholar]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Belfon, K.A.; Raguette, L.; Huang, H.; Migues, A.N.; Bickel, J.; Wang, Y.; Pincay, J.; Wu, Q. Amino-Acid Specific Protein Backbone Parameters Trained Against Quantum Mechanics Energy Surfaces in Solution. J. Chem. Theor. Comp. 2019, 16, 528–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschner, K.N.; Yongye, A.B.; Tschampel, S.M.; González-Outeiriño, J.; Daniels, C.R.; Foley, B.L.; Woods, R.J. GLYCAM06: A generalizable biomolecular force field. J. Comp. Chem. 2008, 29, 622–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izadi, S.; Anandakrishnan, R.; Onufriev, A.V. Building Water Models: A Different Approach. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 3863–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, D.A.; Aktulga, H.M.; Belfon, K.; Ben-Shalom, I.; Brozell, S.R.; Cerutti, D.S.; Cheatham, T.E.; Cruzeiro, V.W.D.; Darden, T.A.; Duke, R.E. Amber 2021 Reference Manual; University of California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, A.J.; Wallace, B.A. CDtoolX, a Downloadable Software Package for Processing and Analyses of Circular Dichroism Spectroscopic Data. Prot. Sci. 2018, 27, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

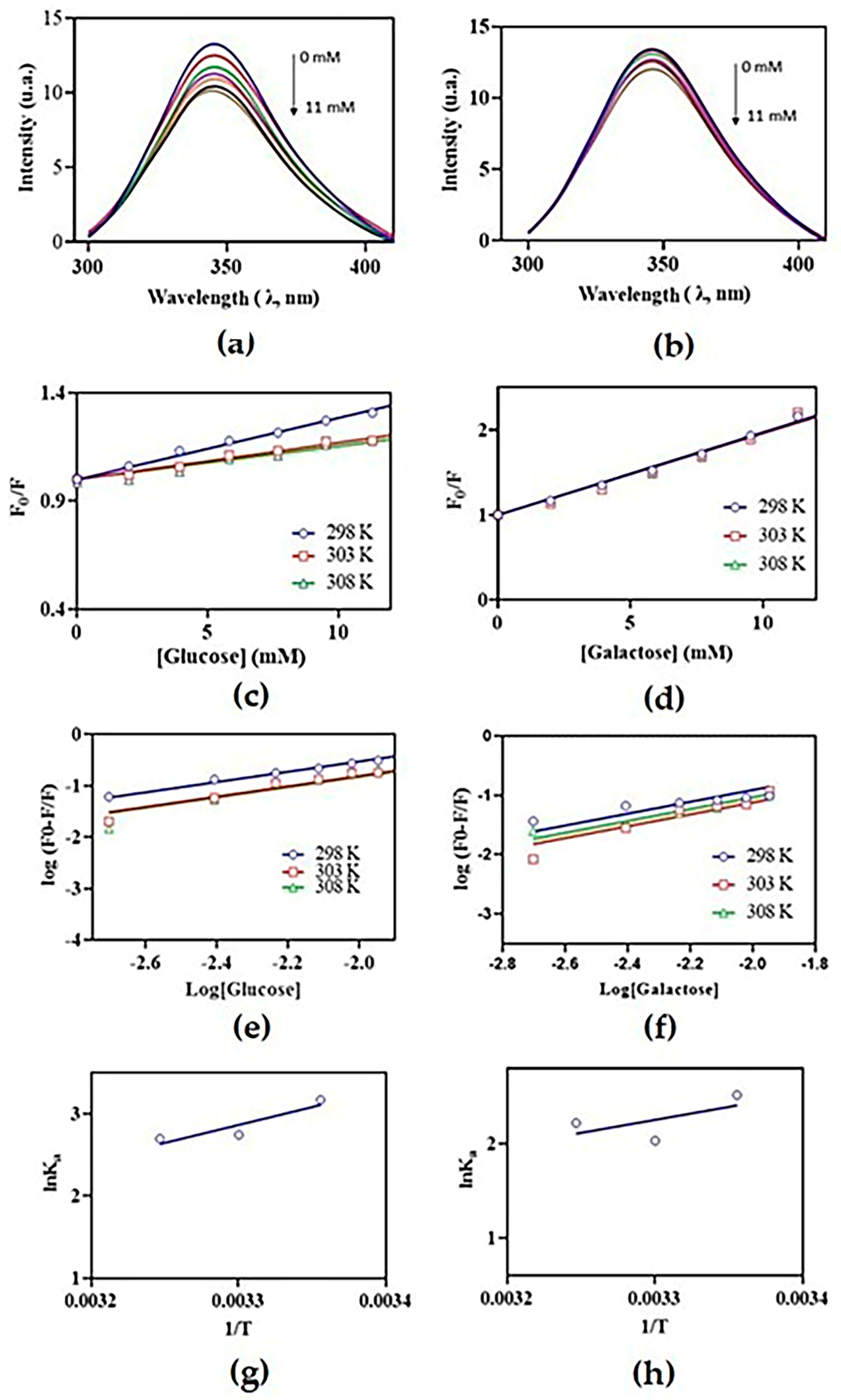
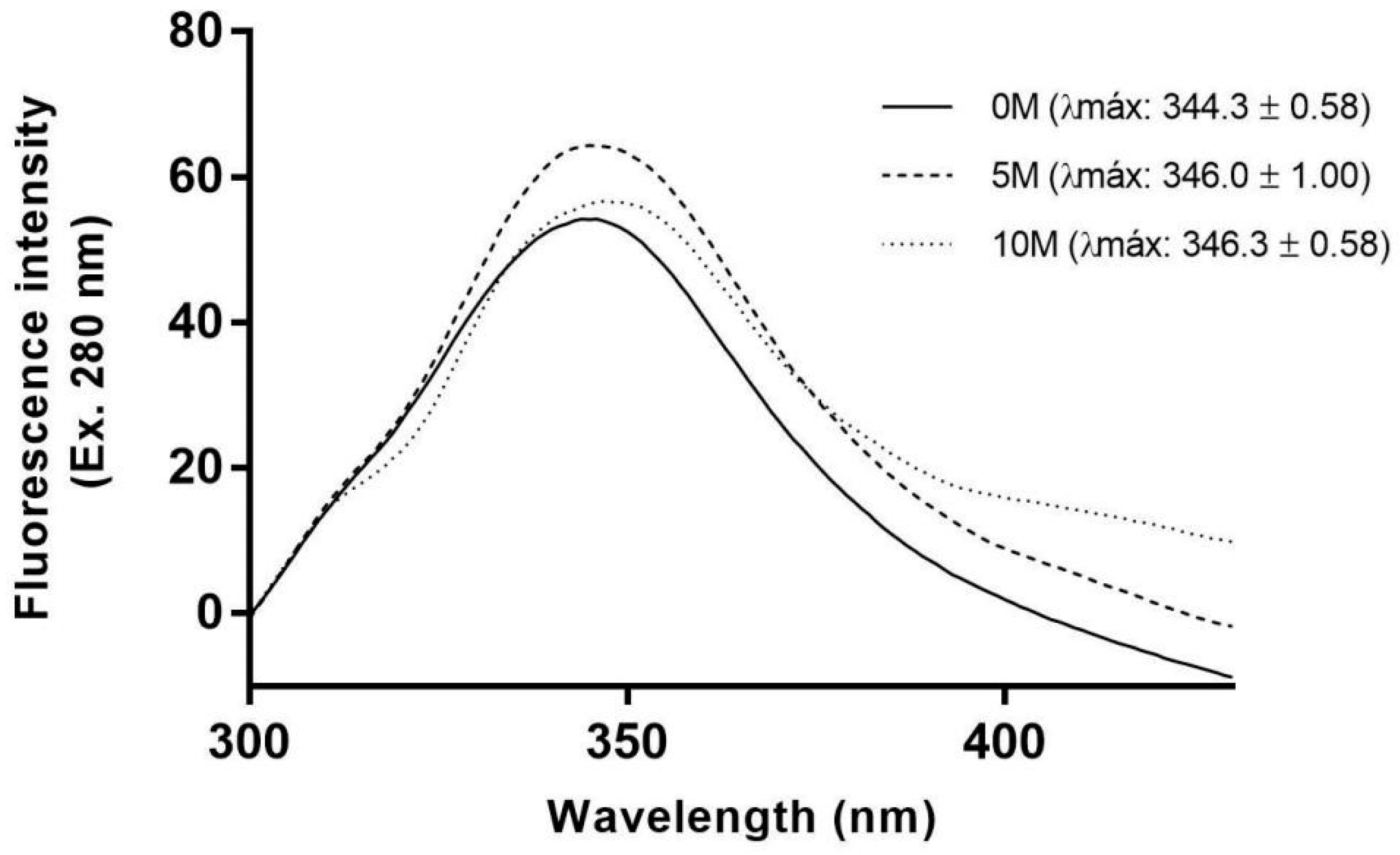
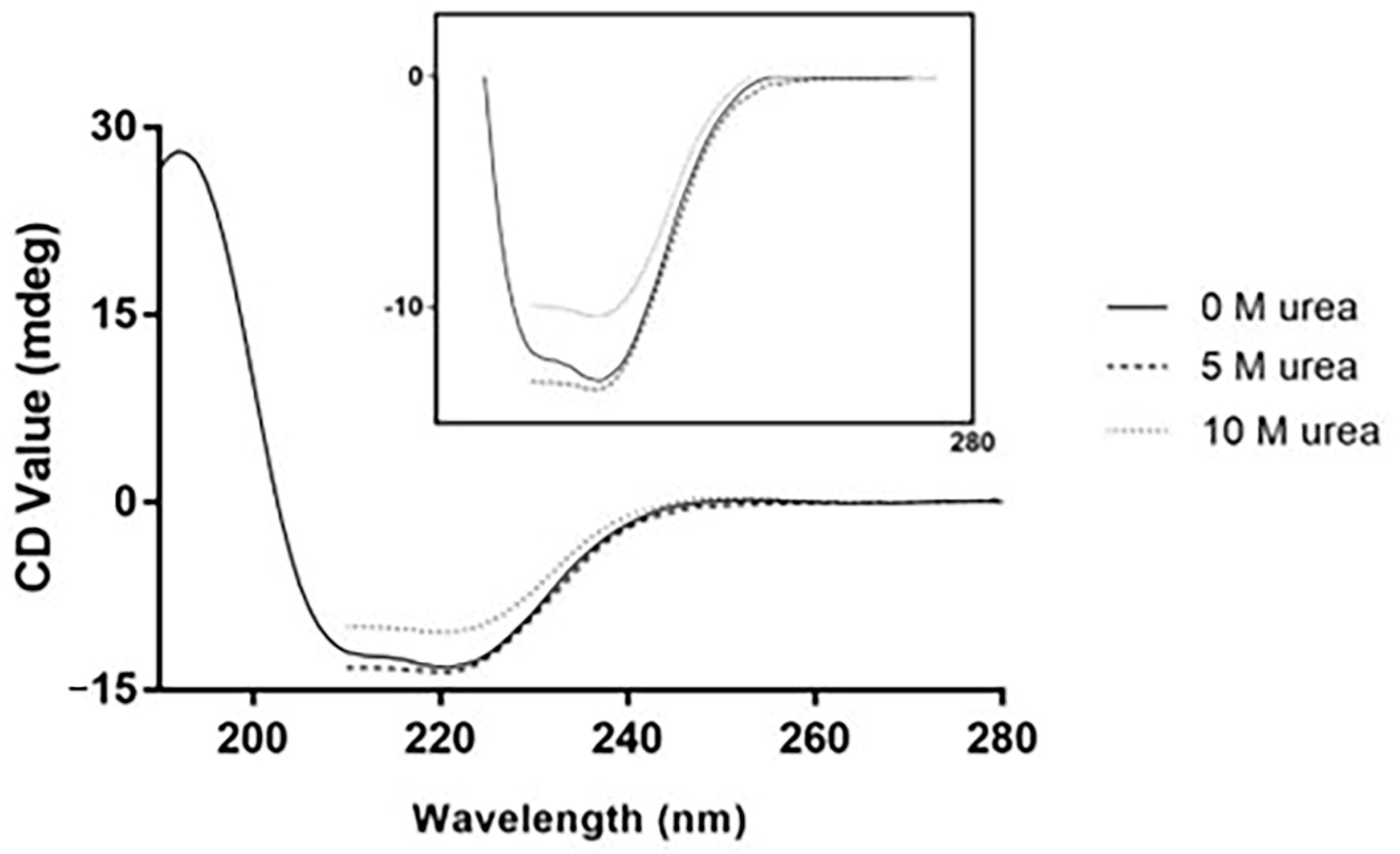

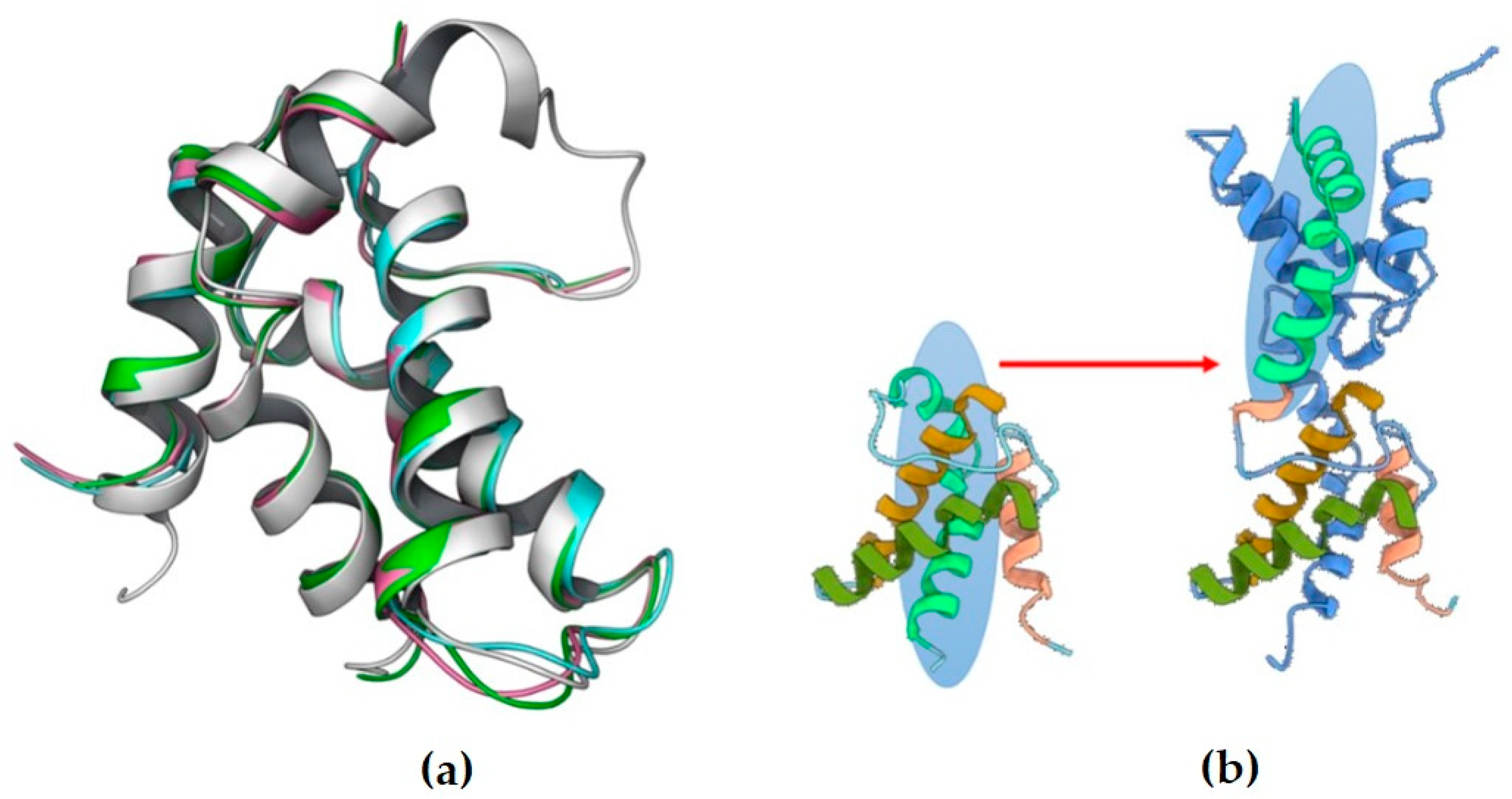

| Carbohydrate | T (K) | Ksv (102 M−1) | Ka (102 M−1) | ∆H (J/mol) | ∆S (J/K·mol) | ∆G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | 298 | 0.2847 ± 0.0020 | 0.29785 ± 0.00007 | 4.358 | −11.51 | −7.681 |
| 303 | 0.1701 ± 0.0014 | 0.15559 ± 0.00005 | −6.764 | |||
| 308 | 0.1542 ± 0.0013 | 0.14825 ± 0.00007 | −6.904 | |||
| Galactose | 298 | 0.9768 ± 0.0007 | 0.12387 ± 0.00004 | 2.752 | −6.82 | −6.371 |
| 303 | 0.9610 ± 0.0009 | 0.07617 ± 0.00001 | −5.124 | |||
| 308 | 0.9584 ± 0.0080 | 0.09212 ± 0.00001 | −5.686 |
| PDB ID | System | Res (Å) | Identity (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6VJ0 | Mo Chitin-binding protein | 1.90 | 81.2 | PDB |
| 5DOM | Mo albumin | 1.69 | 81.2 | [47] |
| 6S3F | Mo seed protein Mo-CBP3-4 | 1.68 | 81.2 | [48] |
| 2DS2 | Mabinlin II | 1.70 | 73.9 | [49] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Barros, M.C.; de Oliveira, A.P.S.; dos Santos, F.G.; Silva, F.A.C.; Menezes, T.M.; Seabra, G.d.M.; Yoneda, J.S.; Coelho, L.C.B.B.; Macedo, M.L.R.; Napoleão, T.H.; et al. Carbohydrate-Binding Mechanism of the Coagulant Lectin from Moringa oleifera Seeds (cMoL) Is Related to the Dimeric Protein Structure. Molecules 2024, 29, 4615. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194615
de Barros MC, de Oliveira APS, dos Santos FG, Silva FAC, Menezes TM, Seabra GdM, Yoneda JS, Coelho LCBB, Macedo MLR, Napoleão TH, et al. Carbohydrate-Binding Mechanism of the Coagulant Lectin from Moringa oleifera Seeds (cMoL) Is Related to the Dimeric Protein Structure. Molecules. 2024; 29(19):4615. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194615
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Barros, Matheus Cavalcanti, Ana Patrícia Silva de Oliveira, Franciane Gonçalves dos Santos, Fabiana Aparecida Cavalcante Silva, Thais Meira Menezes, Gustavo de Miranda Seabra, Juliana Sakamoto Yoneda, Luana Cassandra Breitenbach Barroso Coelho, Maria Lígia Rodrigues Macedo, Thiago Henrique Napoleão, and et al. 2024. "Carbohydrate-Binding Mechanism of the Coagulant Lectin from Moringa oleifera Seeds (cMoL) Is Related to the Dimeric Protein Structure" Molecules 29, no. 19: 4615. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194615
APA Stylede Barros, M. C., de Oliveira, A. P. S., dos Santos, F. G., Silva, F. A. C., Menezes, T. M., Seabra, G. d. M., Yoneda, J. S., Coelho, L. C. B. B., Macedo, M. L. R., Napoleão, T. H., Lima, T. d. A., Neves, J. L., & Paiva, P. M. G. (2024). Carbohydrate-Binding Mechanism of the Coagulant Lectin from Moringa oleifera Seeds (cMoL) Is Related to the Dimeric Protein Structure. Molecules, 29(19), 4615. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194615







