The Application of Hydrogen Sulfide Fluorescent Probe in Food Preservation, Detection and Evaluation
Abstract
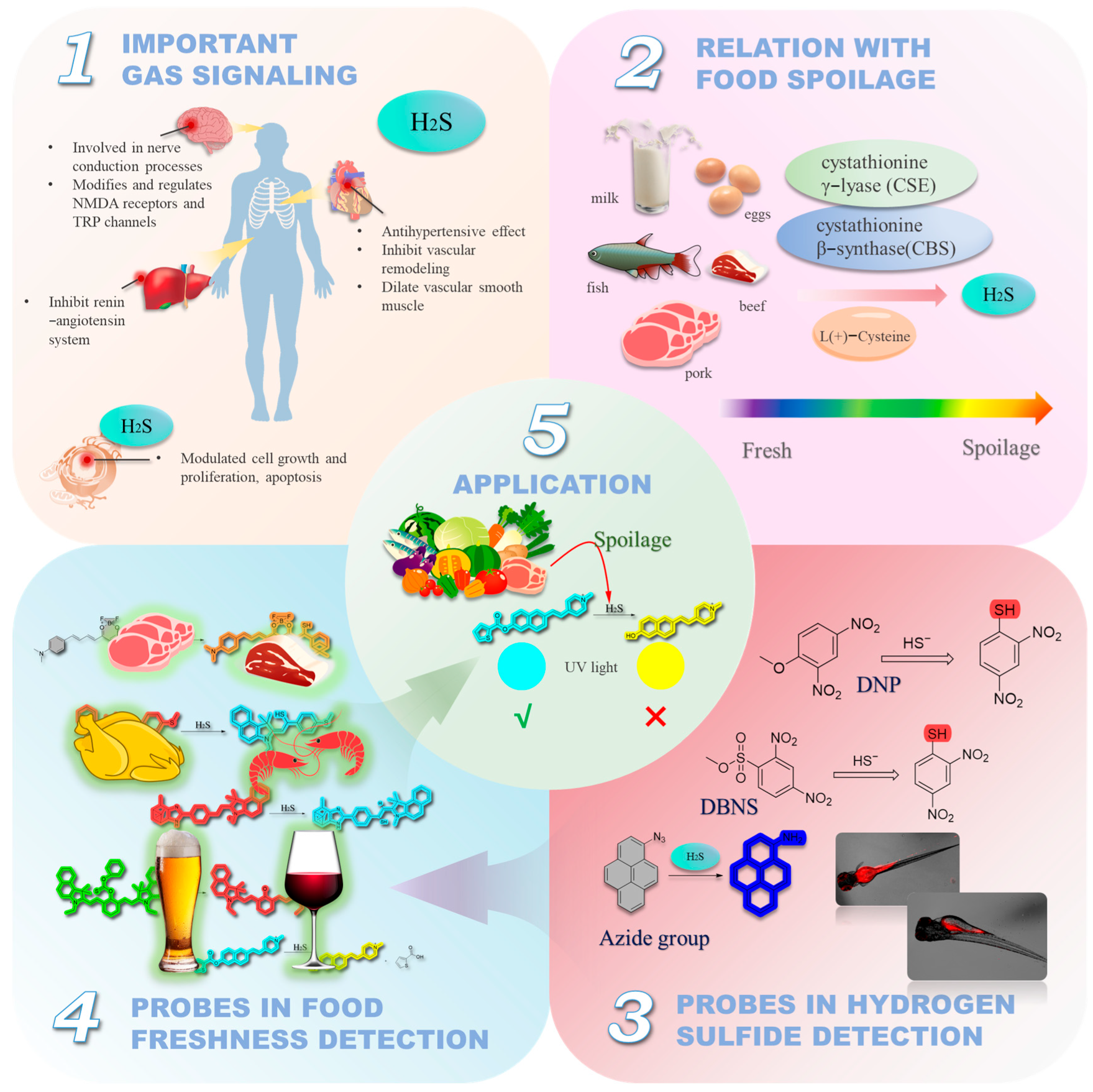
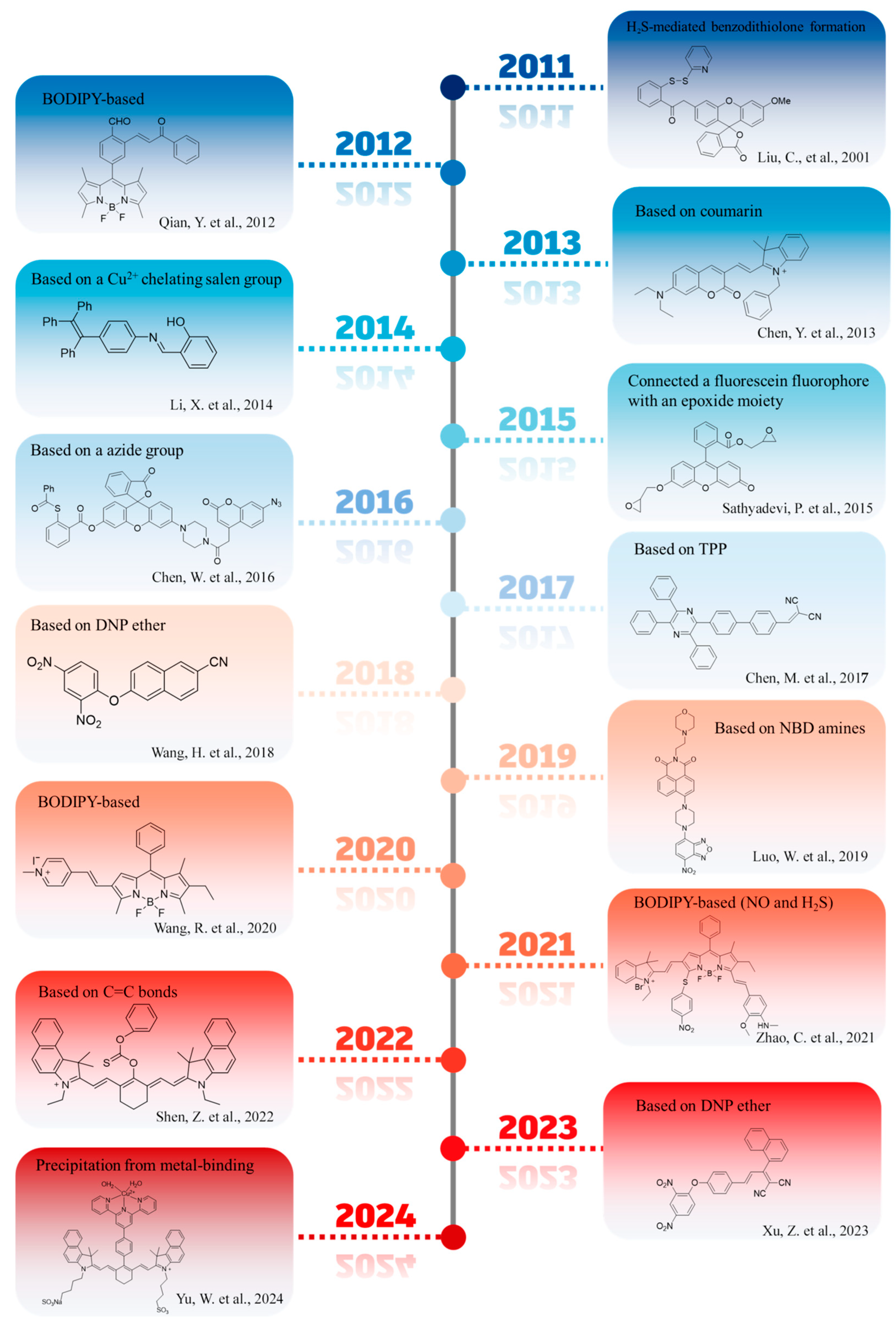
1. Introduction
2. Fluorescent Probes for the Detection of H2S in Foods
2.1. Thiolysis Reactions Based on 2,4-dinitrophenyl (DNP)
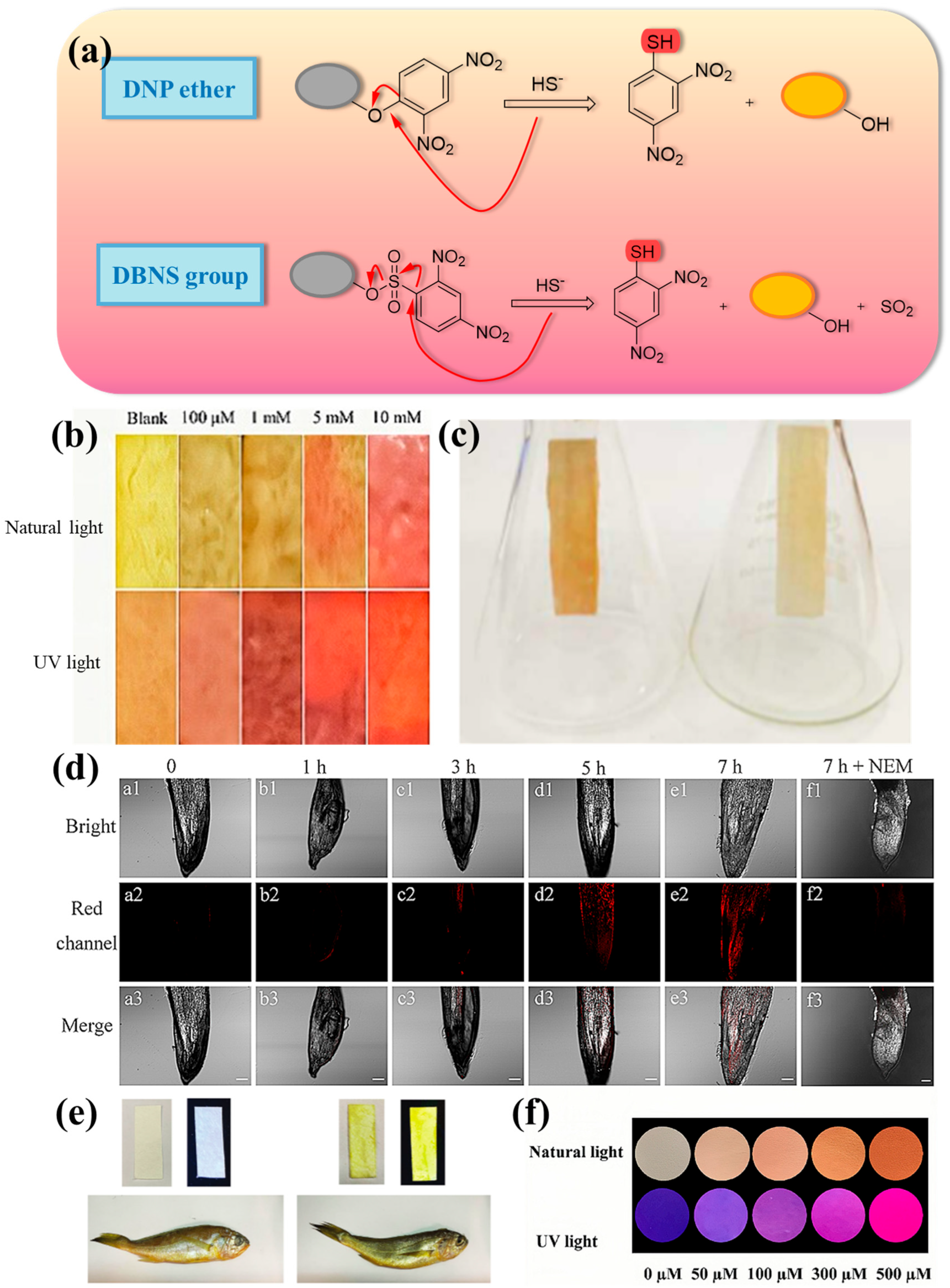
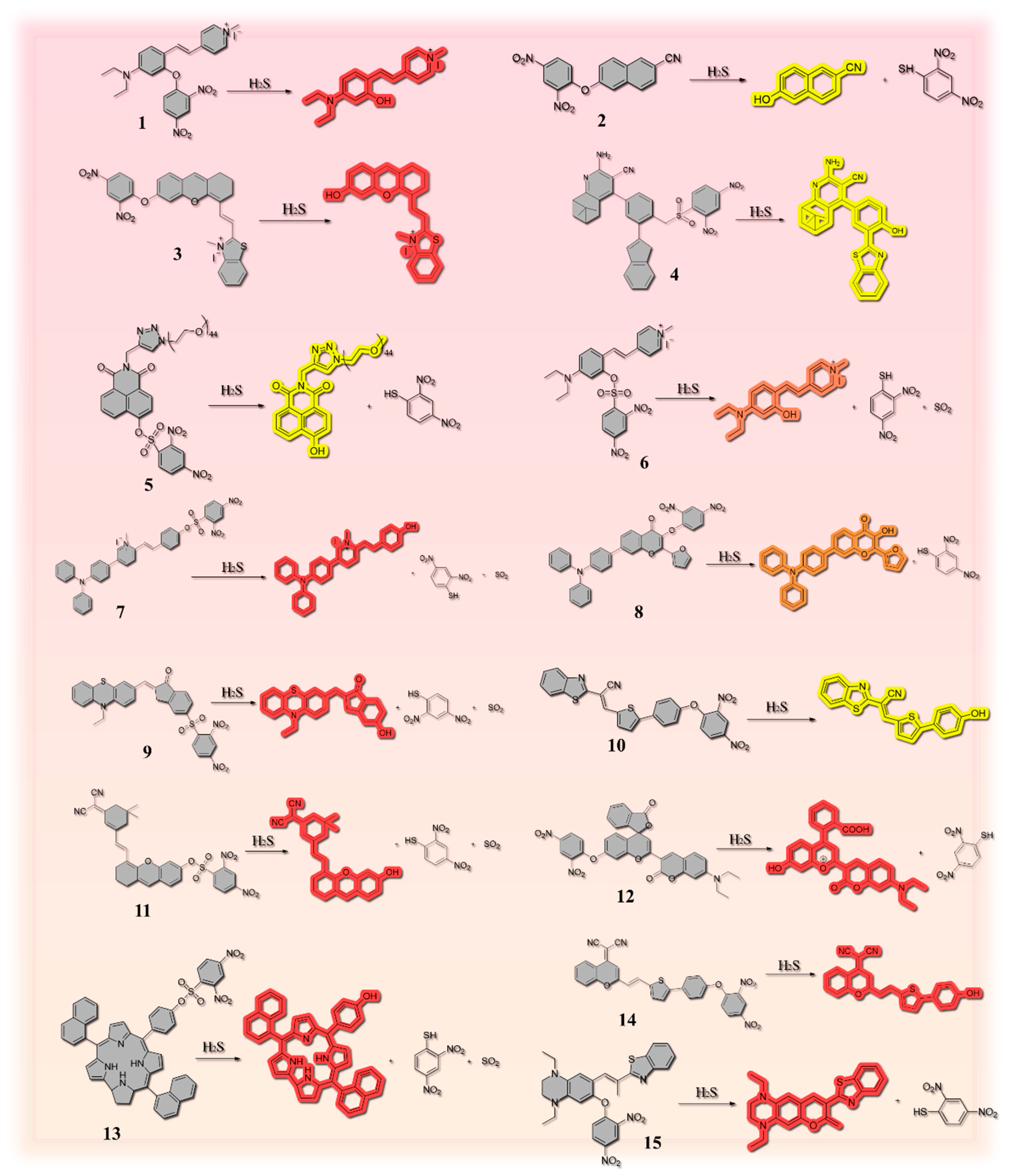
| Number | Response Time | LOD | Stokes Shift | Fluorescent Chromophore | H2S Reporter | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | / | 10.5 µM | 111 nm | 4-diethylaminosalicylaldehyde | 2,4-dinitrophenyl (DNP) | Red wine and beer | [29] |
| 2 | 30 min | 76 nM | / | 6-hydroxy-2-naphthonitrile | 2,4-dinitrophenyl (DNP) | Red wine and beer | [31] |
| 3 | / | 104 nM | / | benzothiazole | 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene | Rice and lake water | [32] |
| 4 | / | 79 nM | / | nopinone | 2,4- dinitrobenzenesulfonyl ester group | River water, lake water, stream water, red wine, beer, hen egg, duck egg, quail egg, and pigeon egg | [34] |
| 5 | 2 min | 9.95 nM | / | naphthalimide | dinitrobenzenesulfonyl | Fish | [36] |
| 6 | 3 min | 41.95 nM | 111 nm | combining N, N-diethyl-4- vinylaniline with a 1-methylpyridinium iodide moiety | 2,4- dinitrobenzenesulfonyl group | Beer | [4] |
| 7 | 3 min | 41.9 nM | / | styrylpyridinium scaffold | 2,4-dinitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride | Chicken, pork, beef | [27] |
| 8 | 3 min | 96 nM | 210 nm | natural product flavonol | 2,4-dinitrophenyl (DNP) | Red wine, beer, eggs, milk, and sour bamboo shoots | [44] |
| 9 | Within 90 s | 0.14 μM | 220 nm | phenothiazine derivative | 2,4-dinitrobenzene sulfonyl chloride | Pork, chicken, beef and fish | [36] |
| 10 | Within 90 s | 76 nM | 145 nm | benzothiazole derivative | 2,4-dinitrophenyl (DNP) | Pork, chicken and shrimp | [45] |
| 11 | 60 s | 1.27 μM | 190 nm | (E)-2-(3-(2-(6-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-1H-xanthen-4-yl)vinyl)-5,5-dimethylcyclohex-2-en-1-ylidene)malononitrile | 2,4-dinitrobenzenesulfonyl ester group | Chicken, eggs, and fish | [47] |
| 12 | / | 35.70 nM | / | functional coumarin-benzopyrylium platform (FC-OH) | 2,4-dinitrophenyl moiety | Pork, chicken and shrimp | [30] |
| 13 | 10 s | 61 nM | / | 5,15-bis(naphthyl)3-10-(4-hydroxylphenyl) corrole (NPC–OH) | 2,4-dinitrobenzenesulfonyl group (DNBS) | Chicken, beef, pork, cracked egg and fish | [35] |
| 14 | Within 30 s | 58 nM | 175 nm | dicyanomethylene-4H-pyran (DCM) | 2,4-dinitrophenyl group | Shrimp, pork, and chicken | [37] |
| 15 | / | 38.30 nM | 126 nm | 1,4-diethylpiperazine-modified iminocoumarin-benzothiazole | 2,4-dinitrophenyl group | River water and red wine | [44] |
| 16 | 6 min | 0.44 μM | 220 nm | β-diketone boron difluoride complex | C=C bonds | Red wine | [48] |
| 17 | 50 s | 19.43 nM | / | α-Pinenecombined with imidazole ring | C=C bonds | Pork, fish, and shrimp | [10] |
| 18 | / | 0.22 µM | / | benzo-hemicyanine | C=C bonds | Egg, raw meat and fish | [49] |
| 19 | / | 0.98 μM | / | coumarin dye | C=C bonds | Pork, chicken sample, and garlic sample | [50] |
| 20 | 30 s | 99.68 nM | / | benzothiazole | C=C bonds | Beer | [51] |
| 21 | / | 0.37 µM | / | combined the naphthalimide with a morpholine moiety | 7-nitro-1,2,3-benzoxadiazole (NBD) amines | Beer | [52] |
| 22 | / | 18 nM | / | coumarin | thenoic acid | Red wine | [53] |
| 23 | / | 54 nM | / | / | quinolinium-phenol vinylic conjugate | Eggs and pork | [54] |
| 24 | / | 80 nM | 205 nm | coumarin2212dicyanoisophorone conjugate | 7-nitro-1,2,3-benzoxadiazole (NBD) | Pork, shrimp, and eggs | [55] |
| 25 | Within 5 s | 87.5 nM | 147 nm | / | the alkenyl group | Beef, shrimp | [56] |
| 26 | / | 0.10 mM (S/N = 3) | / | naphthofluorescein | thiophenecarboxylic ester | Red wine | [57] |
| 27 | Within 10 s | 4.3 nM | / | 6,8-dichloro-7-hydroxy-9,9-dimethylacridin-2(9H)-one | oxygen-nitrile bond | Crucian chicken, shrimp, pork and egg | [58] |
| 28 | / | 54 nM | / | merocyanine | 2-thiophenecarbonyl group | Beef, pork, and chicken | [59] |
| 29 | Within 8 min | 34 nM | / | cyanine derivative | phenyl chlorothionocarbonate | Pork and shrimp | [60] |
| 30 | Within 3 min | 0.144 µM | / | derivative of Indocyanine green (ICG) | Cu2+ | Red wine, beer, meat, milk, and sweet potato | [61] |
| 31 | 10 min | 56 nM | pyren-1-amine | azido group | Red wine | [62] | |
| 32 | / | 8.12 µM | / | / | Two double bonds between Calix[4]arene and methylpyridinium iodide fragments | Beef and apricot seeds | [63] |
2.2. Based on Double Bond Addition
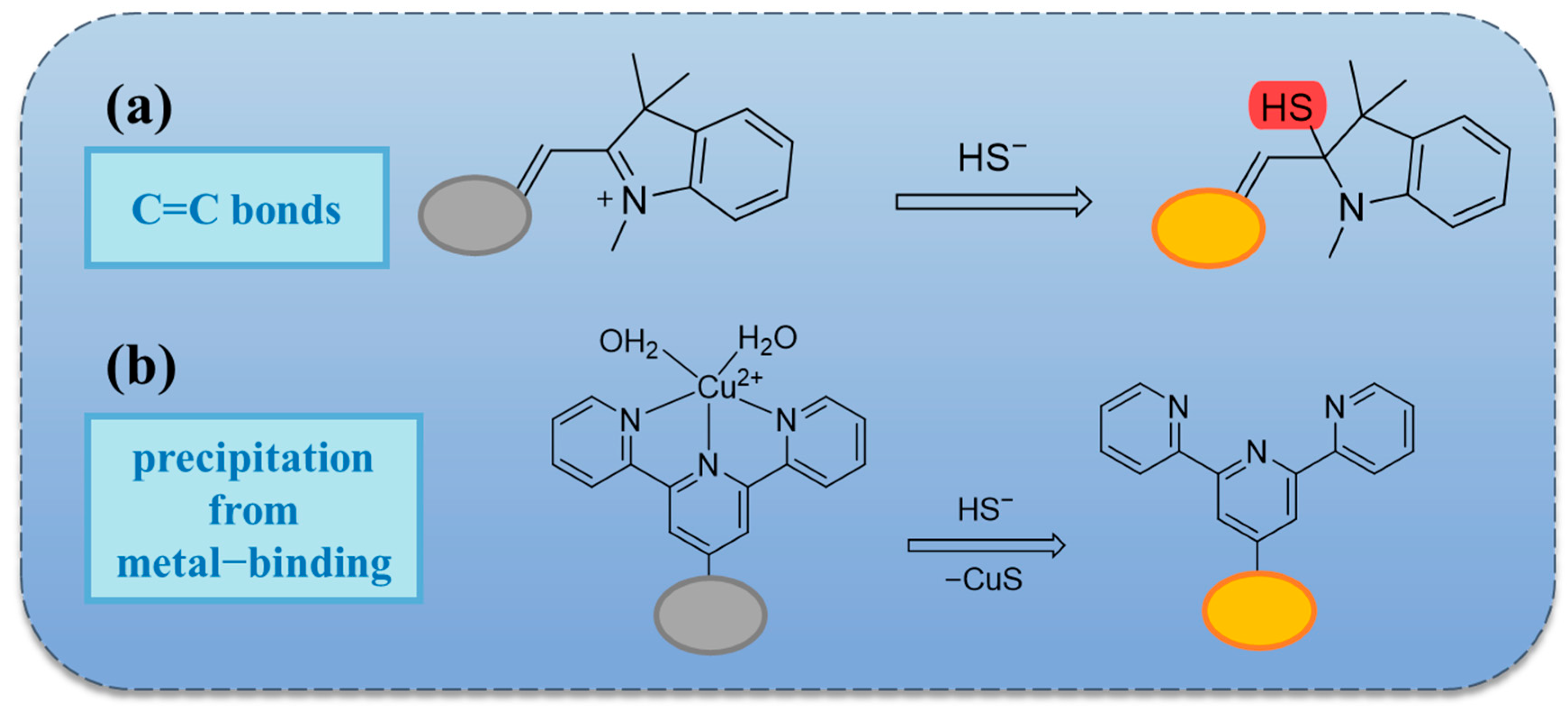
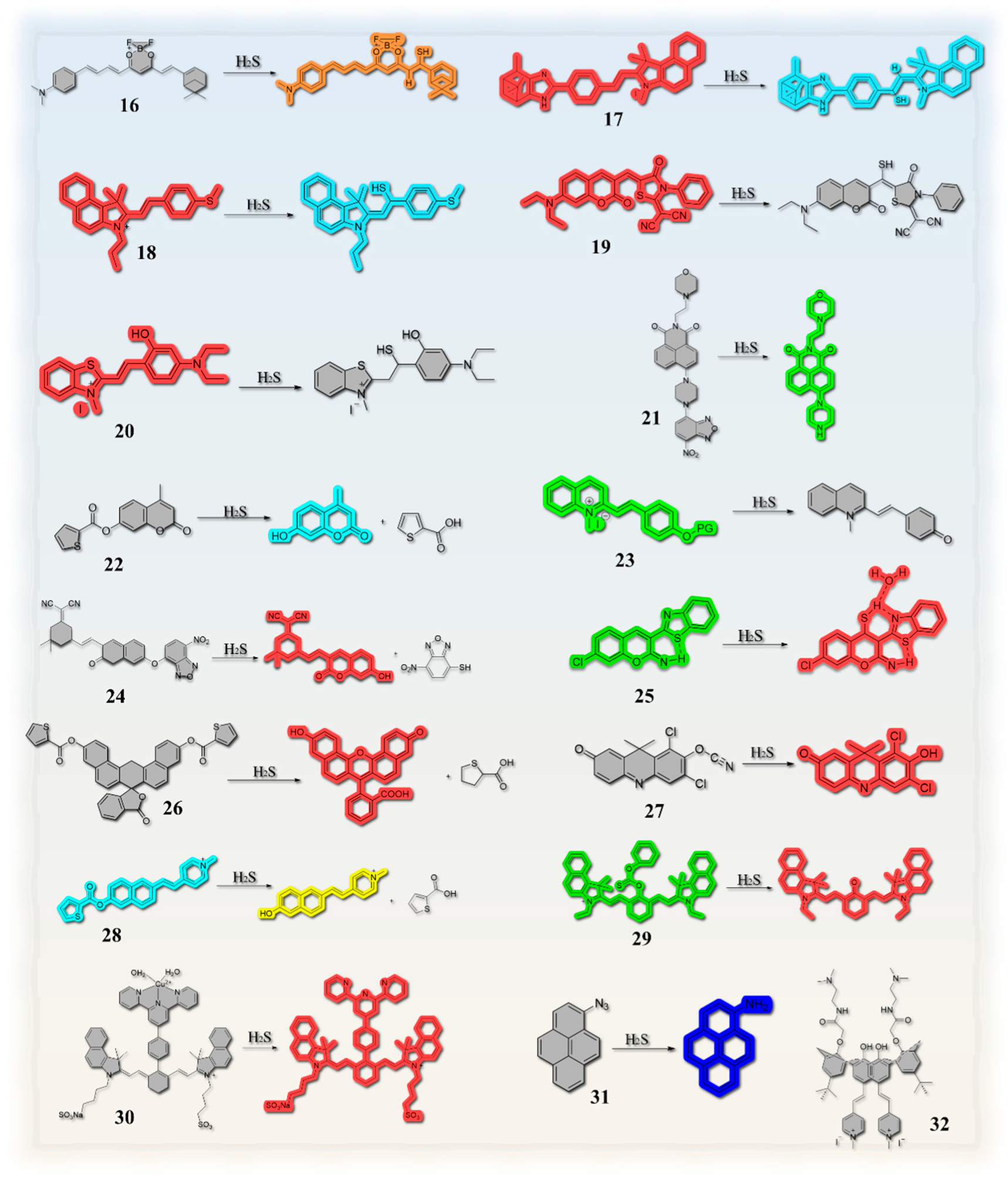
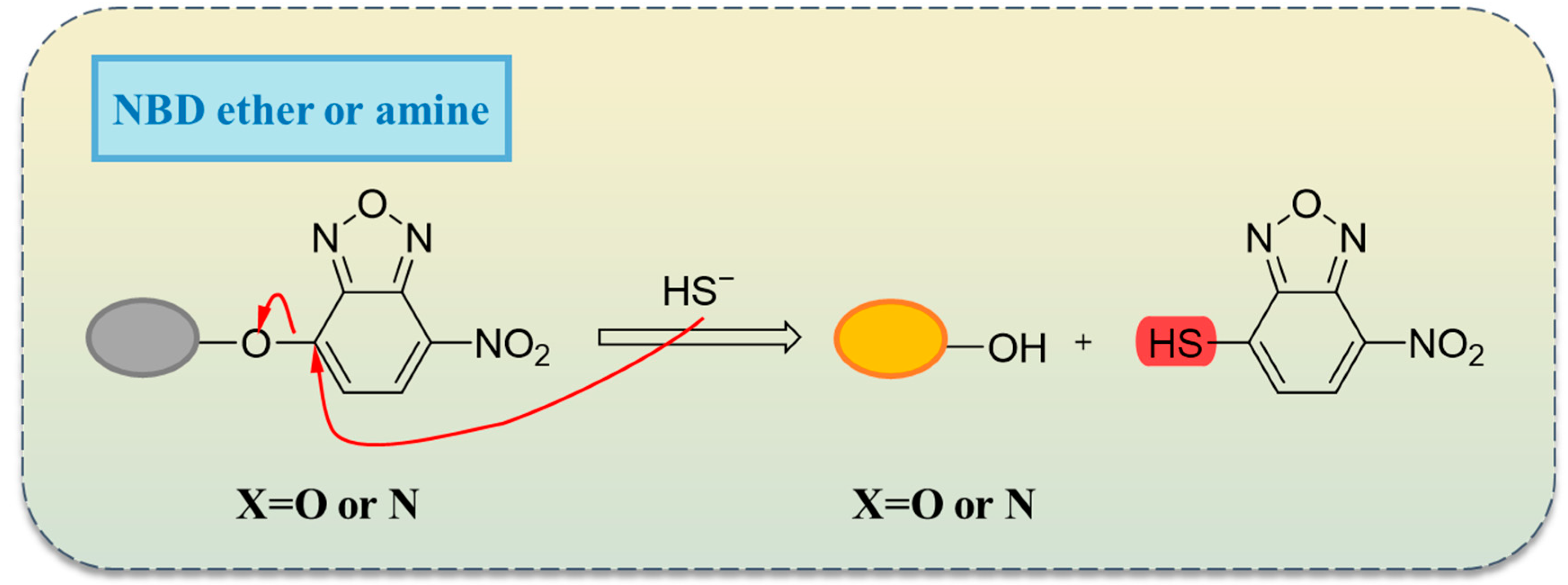
2.3. Thiolation Reactions Based on 7-Nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1,3-diazole (NBD)
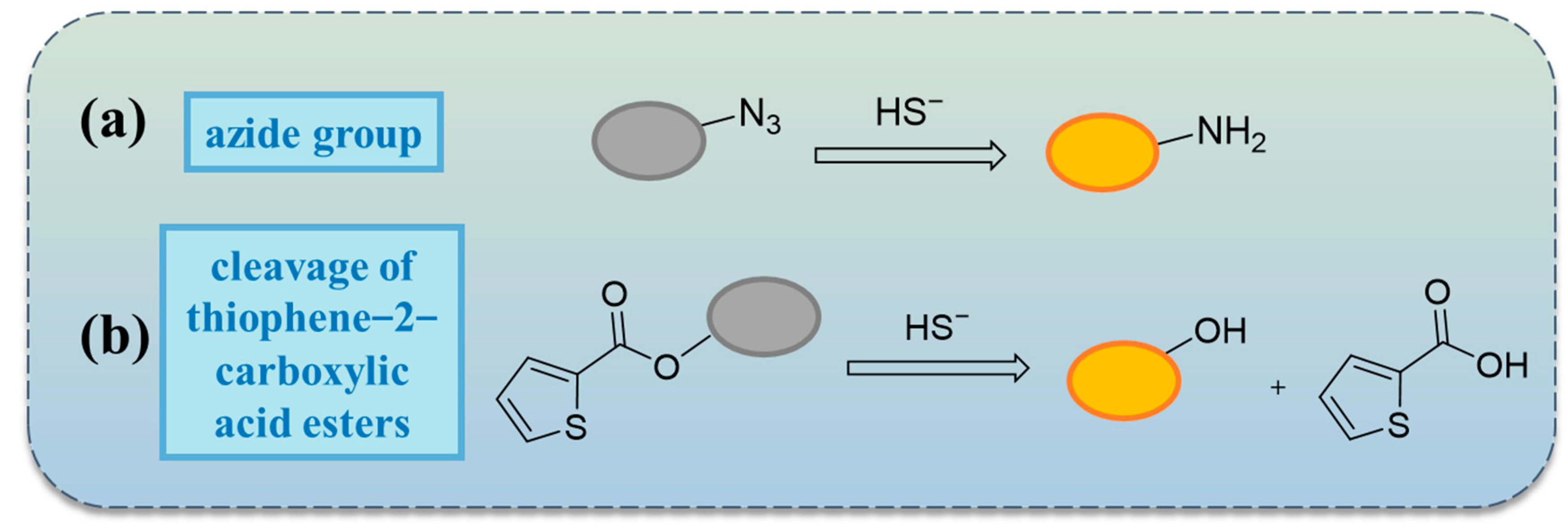
2.4. Reactions Based on Azide Groups
2.5. Others
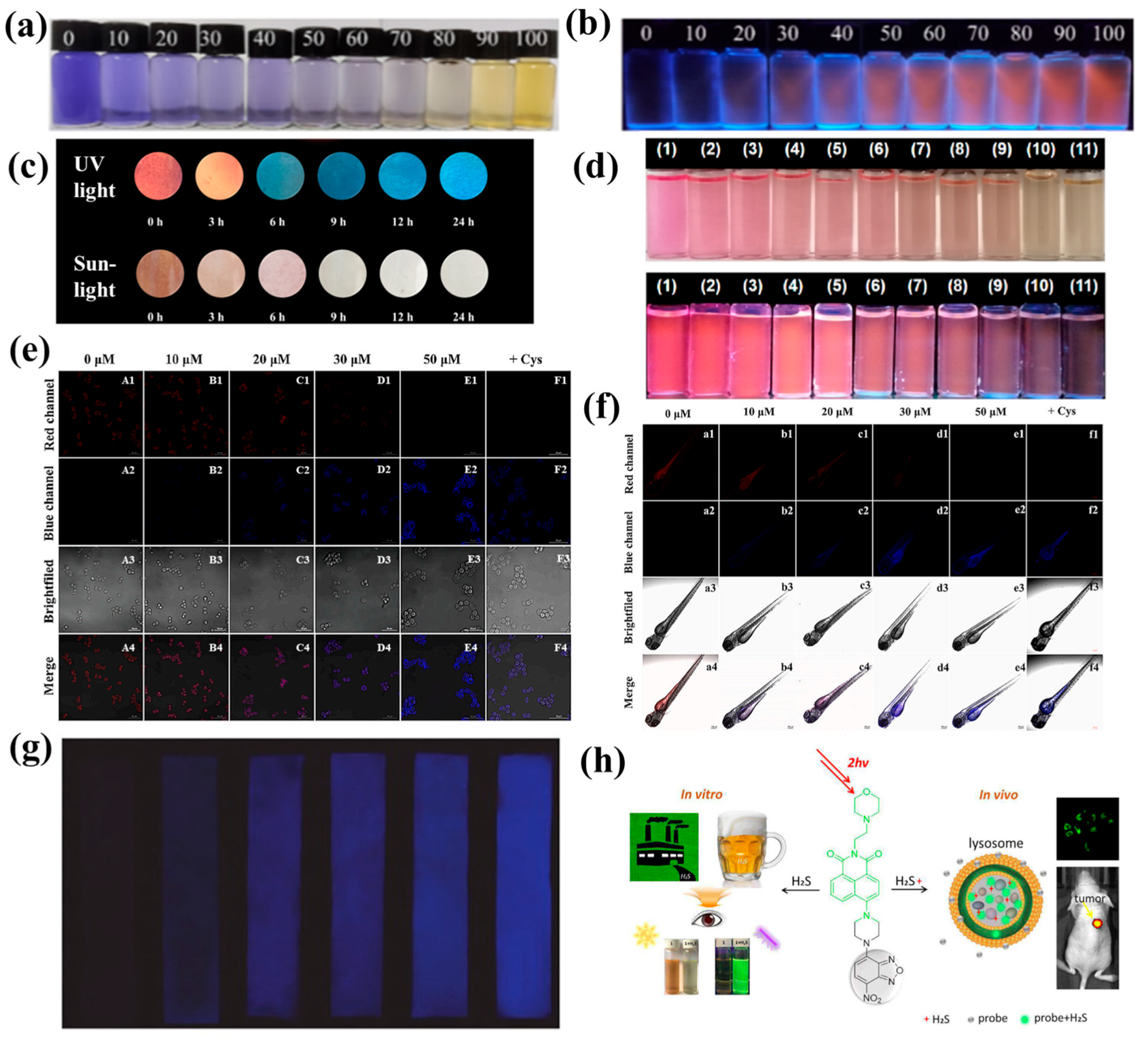
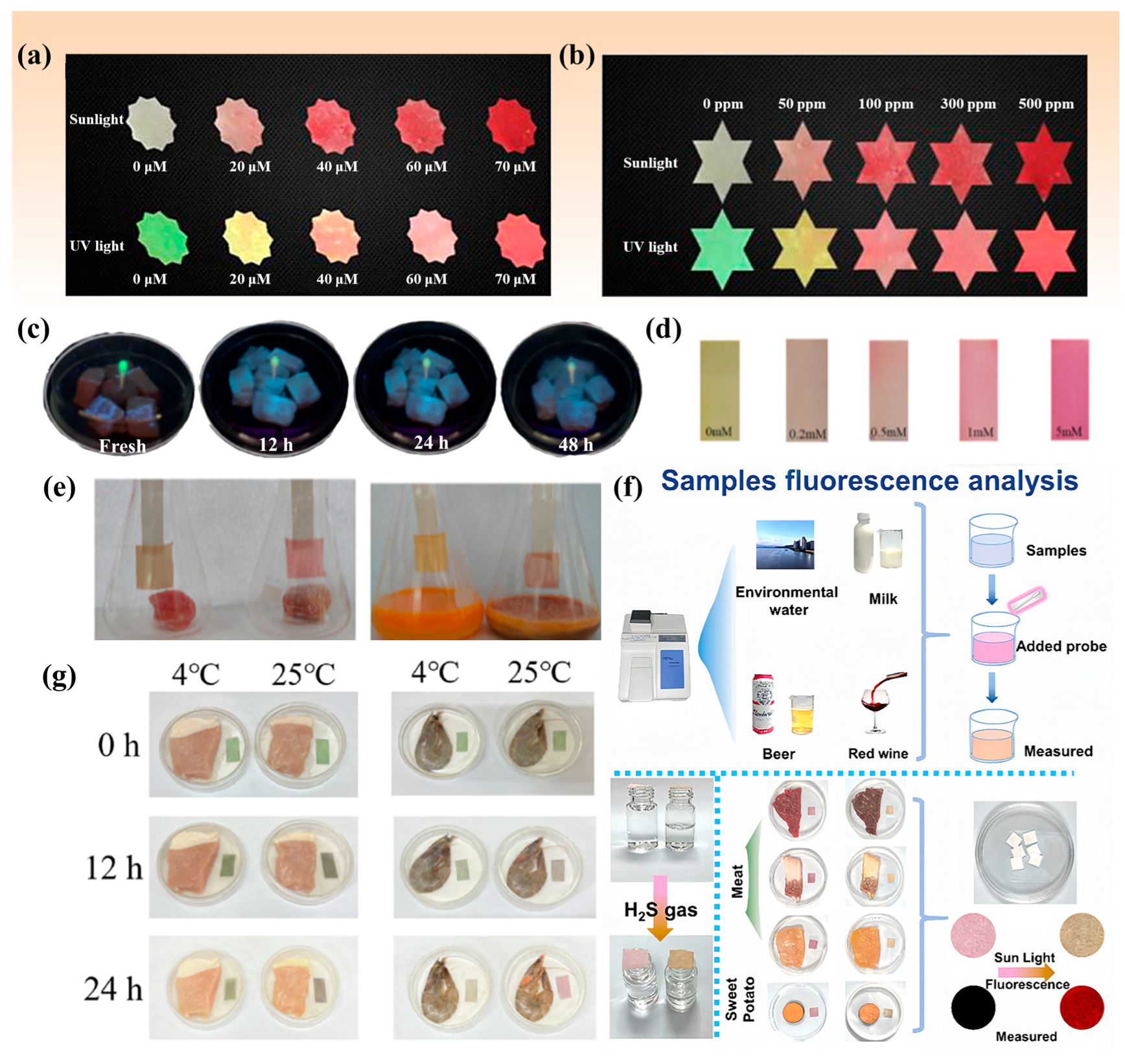
3. Methods for H2S Detection in Foods
3.1. Colorimetric Method
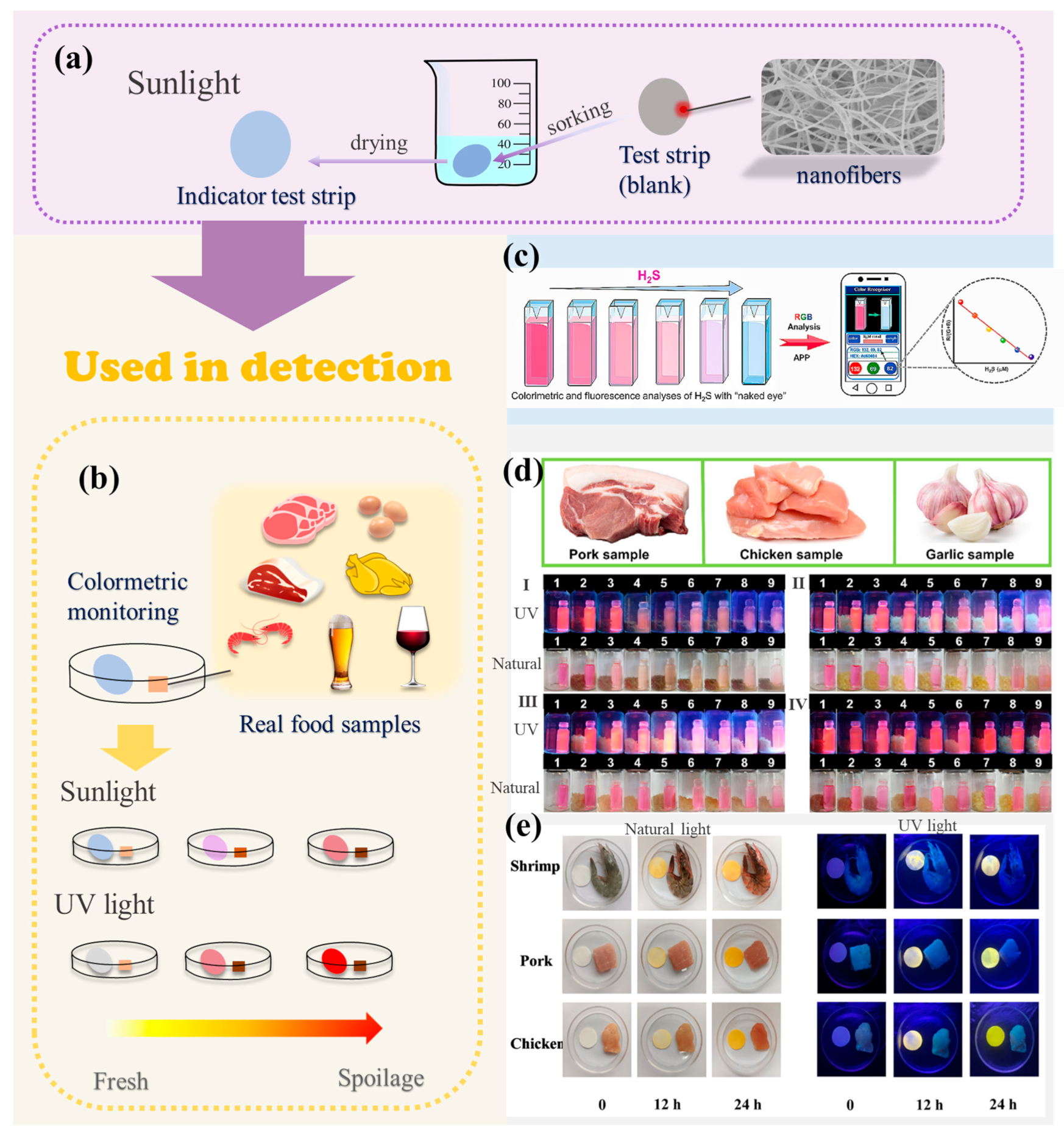
3.2. Spiked Recovery Test
4. Conclusions and Outlook
- (1)
- It remains unclear whether it is possible to achieve complete water solubility without the involvement of organic reagents, which is still the case with only a few probes.
- (2)
- The question thus arises as to whether it is possible to achieve complete water solubility and to detect gaseous H2S.
- (3)
- The objective is to ascertain whether it is feasible to observe a change in color for trace amounts of H2S. This would entail enhancing the sensitivity and color change of the probes for small concentrations.
- (4)
- The objective is to ascertain whether a color change can be observed for trace amounts of H2S. In other words, the sensitivity of the probe must be enhanced for small concentrations, and it must be determined whether the color change is affected by the concentration of H2S. Also, it is essential to pursue continuous improvements in the loading capacity of the probe on the test strip.
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, S.; Padovani, D.; Leslie, R.A.; Chiku, T.; Banerjee, R. Relative contributions of cystathionine β-synthase and γ-cystathionase to H2S biogenesis via alternative trans-sulfuration reactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 22457–22466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.J.; Nanduri, J.; Wang, N.; Kumar, G.K.; Bindokas, V.; Paul, B.D.; Chen, X.; Fox, A.P.; Vignane, T.; Filipovic, M.R.; et al. Hypoxia sensing requires H2S-dependent persulfidation of olfactory receptor 78. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadf3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, R.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Qu, C.; Kikuiri, T.; Wang, S.; Zandi, E.; Du, J.; Ambudkar, I.S.; et al. Hydrogen sulfide maintains mesenchymal stem cell function and bone homeostasis via regulation of Ca2+ channel sulfhydration. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 15, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, K.; Hu, X.; Zhou, S.; Liu, X.; Gao, X.; Tang, L. Mitochondria-targeted red-emission fluorescent probe for ultrafast detection of H2S in food and its bioimaging application. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 4628–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuang, T.; Fu, M.; Yang, G.; Wu, L.; Wang, R. The interaction of IGF-1/IGF-1R and hydrogen sulfide on the proliferation of mouse primary vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 149, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodkin, S.; Nwosu, C.; Sannikov, A.; Tyurin, A.; Chulkov, V.S.; Raevskaya, M.; Ermakov, A.; Kirichenko, E.; Gasanov, M. The role of gasotransmitter-dependent signaling mechanisms in apoptotic cell death in cardiovascular, rheumatic, kidney, and neurodegenerative diseases and mental disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Pluth, M.D. ROS-Activated Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) donors exhibit protections in H2O2-induced cellular oxidative damage. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 112, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Feng, W.; Peh, M.T.; Peh, K.; Dymock, B.W.; Moore, P.K. A novel slow-releasing hydrogen sulfide donor, FW1256, exerts anti-inflammatory effects in mouse macrophages and in vivo. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 113, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yang, X.; Guo, M.Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Li, T.; Yan, R.; Yang, Y.S.; Zhu, H.L.; Hu, Z.G. Imaging the dynamic processes of hydrogen sulfide using a rapid “turn-on” mitochondria-targeting fluorescent probe. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 369, 132285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Gao, L.; Liang, Y.; Meng, Z.; Gong, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.F. A ratiometric near-infrared fluorescent probe with a large Stokes shift for rapid and sensitive detection of hydrogen sulfide in food samples and imaging in biological system. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 127, 106005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J.T.; Miao, J.Y.; Zhao, B.X. A new ratiometric fluorescent probe for rapid, sensitive and selective detection of endogenous hydrogen sulfide in mitochondria. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 3131–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Chen, L.; Yan, X.; Tang, Y.; Hou, S.; Li, X.; Tang, L.J. Dual-functional multi-application probe: Rapid detection of H2S and colorimetric recognition of HSO3− in food and cell. Dyes Pigments 2020, 182, 108656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Mu, R.; Fang, M.; Cheng, Y.; Senchyna, F.; Moreno, A.; Banaei, N.; Rao, J.H. A dual-caged resorufin probe for rapid screening of infections resistant to lactam antibiotics. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 9153–9161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, C.; Pang, X.; Peng, X.J. A novel “turn-on” fluorescent probe with a large stokes shift for homocysteine and cysteine: Performance in living cells and zebrafish. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 259, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usama, S.M.; Inagaki, F.; Kobayashi, H.; Schnermann, M.J. Norcyanine-carbamates are versatile near-infrared fluorogenic probes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 5674–5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Q.; Dong, K.; Sun, C.; Huang, Y.; Qiang, Z.; Chen, B.Q.; Chen, M.; Feng, Y.; Meng, X.M. Accurate monitoring and multiple evaluations of mitophagy by a versatile two-photon fluorescent probe. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 9200–9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Tang, B. Cellular fluorescence imaging based on resonance energy transfer. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 123, 115742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słowiński, D.; Świerczyńska, M.; Romański, J.; Podsiadły, R. Sensitive Detection of Various Forms of Hydrogen Sulfide via Highly Selective Naphthalimide-Based Fluorescent Probe. Molecules 2023, 28, 6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gu, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Cheng, P.; Xu, K. A novel near-infrared colorimetric-fluorescent probe for hydrogen sulfide and application in bioimaging. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2023, 437, 114438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Yun, L.; Chen, K.; He, S.; Cheng, P.; Xu, K. A novel near-infrared fluorescence probe for hydrogen sulfide detection and application in cell and mice imaging. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1286, 135576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xu, Z.; Spring, D.R.; Cui, J. A lysosome-targetable fluorescent probe for imaging hydrogen sulfide in living cells. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 2310–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasakura, K.; Hanaoka, K.; Shibuya, N.; Mikami, Y.; Kimura, Y.; Komatsu, T.; Ueno, T.; Terai, T.; Kimura, H.; Nagano, T. Development of a highly selective fluorescence probe for hydrogen sulfide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 18003–18005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, C.; Yang, Z.; Chen, J.; He, Y.; Jiao, Y.; He, W.; Qiu, L.; Cen, J.; Guo, Z. A ratiometric fluorescent probe for rapid detection of hydrogen sulfide in mitochondria. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 1688–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Gong, J.; Li, L.; Lu, H.; Xue, P.; Ren, Z.; Wang, X. A highly selective and sensitive fluorescence probe based on BODIPY-cyclen for hydrogen sulfide detection in living cells and serum. Talanta 2024, 268, 125339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.R.; Zhou, L.Y.; Liu, X.Z.; Tan, G.J.; Yuan, F.; Nezamzadeh, A.; Qi, N.; Liu, J.; Peng, Y. Fluorescence detection platform of metal-organic frameworks for biomarkers. Colloids Surf. B 2023, 229, 113455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.W.; Huang, J.F.; Jian, Y.H.; Singh, A.; Kumar, A.; Liu, J.; Pan, Y.; Ouyang, Q. Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) as apt luminescent probes for the detection of biochemical analytes. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Wang, R.; Fan, C.; Tu, Y.; Liu, G.; Pu, S. Mitochondria-targeted fluorescent probe with long wavelength emission for detecting H2S and its application in foodstuff, water and living cells. Food Chem. 2023, 410, 135411. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, W. Fluorescent and chromogenic probes bearing salicylaldehyde hydrazone functionality for cyanide detection in aqueous solution. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 143, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Zhou, S.; Yan, X.; Li, X.; Hou, S.; Cheng, L.; Gao, X.; Li, Y.; Tang, L. A simple H2S fluorescent probe with long wavelength emission: Application in water, wine, living cells and detection of H2S gas. Dyes Pigments 2020, 174, 108049. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Xing, H.; Gao, Z.; You, M.; Li, B.; Feng, X.; Zhou, B.; Cong, Z.; Zhu, J.; Jin, M. An “off−on” NIR fluorescence probe for visualization of H2S in food spoilage, living cells and zebrafish. Dyes Pigments 2023, 209, 110888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Tian, H.; Liu, Y.; Sun, B. Highly selective and rapidly responsive fluorescent probe for hydrogen sulfide detection in wine. Food Chem. 2018, 257, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.M.; He, Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Hua, F.F.; Liu, X.Y.; Fu, Y.L. Near-infrared fluorescent probe for imaging upregulated hydrogen sulfide levels in rice under salt and drought stress. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 5154–5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, S.; Tian, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. A novel ratiometric fluorescent chemosensor for detecting malononitrile and application assisted with smartphone. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 262, 120135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Gao, M.; Fu, Q.; Chen, X.; Xu, K.; Gong, S.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. Novel 2-Benzo[d]thiazolyl-4-quinolinylphenol skeleton-based turn-on fluorescent probe for H2S detection and its multiple applications in water environment, foodstuffs, and living organisms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fang, Y.; Yan, J.; Ren, X.; Zheng, C.; Wu, B.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Hua, H.; Wang, P.; et al. Small-molecule fluorescent probes for H2S detection: Advances and perspectives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 134, 116117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Tao, F.; Yang, L.; Yuan, G.; Sun, W.; Zhang, X. A color turn-on fluorescent probe for real-time detection of hydrogen sulfide and identification of food spoilage. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 5012–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Xin, T.; Sun, L.; Fan, C.; Liao, G.; Tu, Y.; Liu, G.; Pu, S. Near-infrared fluorescent probe for detection of hydrogen sulfide in water samples and food spoilage. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 316, 124341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Jiang, X.D.; Sun, C.; Li, Q. BODIPY-based naked-eye fluorescent on-off probe with high selectivity for H2S based on thiolysis of dinitrophenyl ether. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 290, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhu, H.; Su, M.; Wang, X.; Rong, X.; Wang, K.; Yu, M.; Sheng, W.; et al. H2S-activated fluorescent probe enables dual-channel fluorescence tracking of drug release in tumor cells. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 135, 106498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhou, L.; Yan, X.; Zhong, K.; Gao, X.; Li, J. A new NIR-emissive fluorescence turn-on probe for Hg2+ detection with a large Stokes shift and its multiple applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2020, 387, 112160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Xia, Q.; Feng, G. Iminocoumarin-based red to near-infrared fluorescent turn-on probe with a large Stokes shift for imaging H2S in living cells and animals. Dyes Pigments 2019, 163, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; He, Y.; Deng, L.; Yan, X.; Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Hou, S.; Tang, L. A near-infrared fluorescent probe for H2S based on tandem reaction to construct iminocoumarin-benzothiazole and its application in food, water, living cells. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1127, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, S.; Qin, A.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, J.; Li, M.; Liang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. Construction of a flavonol-based fluorescent probe with a large stokes shift for highly selective and rapid monitoring of H2S in water, foodstuff, and living systems. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 11, 15114–15123. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, W.; Sun, L.; Xin, T.; Tu, Y.; Liao, G.; Liu, G.; Pu, S.; Fan, C. A turn-on fluorescent probe based on benzothiazole for H2S detection and its multiple applications in water samples and food spoilage. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1307, 137978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zeng, Y.; Ding, H.; Liu, Q.; Mao, L.; Liu, G.; Pu, S. Rapidly responsive and highly selective NIR fluorescent probe for detecting hydrogen sulfide in food samples and living cells. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 320, 124640. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Lu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Du, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Near-infrared fluorescent probe with a large stokes shift for detection of hydrogen sulfide in food spoilage, living cells, and zebrafish. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 3047–3055. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.; Duan, L.; Meng, S.; Cai, P.; Ding, S.; Wang, X. Development of a colorimetric and turn-on fluorescent probe with large Stokes shift for H2S detection and its multiple applications in environmental, food analysis and biological imaging. Dyes Pigments 2023, 220, 111687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Gao, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, K.; Gong, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. Development and application of a novel β-diketone difluoroboron-derivatized fluorescent probe for sensitively detecting H2S. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 281, 121609. [Google Scholar]
- Magesh, K.; Vijay, N.; Wu, S.P.; Velmathi, S. Dual-responsive benzo-hemicyanine-based fluorescent probe for detection of cyanide and hydrogen sulfide: Real-time application in identification of food spoilage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Meng, Q.; Tian, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R. Red-emitting fluorescent probe for hydrogen sulfide detection and its applications in food freshness determination and in vivo bioimaging. Food Chem. 2023, 427, 136701. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Yuan, K.; Tao, B.; Liu, G.; Liao, G.; Chen, S.; Fan, C. Engineering a mitochondria-targeted fluorescent probe with long wavelength for rapid detection of H2S in beer, water and living cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2023, 444, 114993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Xue, H.; Ma, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, W. Molecular engineering of a colorimetric two-photon fluorescent probe for visualizing H2S level in lysosome and tumor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1077, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, S.; Tian, H.; Liu, Y.; Sun, B. A Novel fluorescent probe for detecting hydrogen sulfide in wine. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 1398–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yi, F.; Liu, C. A quinolinium-phenol vinylic conjugated fluorescent probe for H2S detection based on H2S -triggered release of protected group. Tetrahedron 2022, 117–118, 132837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Bao, J.; Pan, X.; Chen, Q.; Yan, J.; Yang, G.; Khan, B.; Zhang, K.; Han, X. A near-infrared fluorescent probe with large stokes shift for sensitive detection of hydrogen sulfide in environmental water, food spoilage, and biological systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2024, 128, 5846–5854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Leng, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, W. Reversible AIE-active fluorescent probe with a large emission peak shift for ratiometric detection of food freshness indicator H2S. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132768. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Xie, P.; Shan, X.; Zhao, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Jin, X. A near-infrared naphthofluorescein-based fluorescent probe for hydrogen sulfide detection. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1207, 127822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Gao, G.; Zhou, X. A water-soluble NIR fluorescent probe capable of rapid response and selective detection of hydrogen sulfide in food samples and living cells. Talanta 2023, 256, 124303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, X.; Zeng, A.; Leng, J.; Zhao, W. Engineering a mitochondria-targeted ratiometric fluorescent probe with a large Stokes shift for H2S -specific assaying in foodstuffs and living cells. Sens. Actuators B 2021, 343, 130095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Cui, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y. A cyanine derivative-based NIR fluorescent probe for hydrogen sulfide bioimaging and food spoilage monitoring. Dyes Pigments 2023, 219, 111644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wu, J.; Wang, F.; Tan, X.; Liu, Y.; Tan, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wu, G. NIR-activated water-soluble molecular probe based on Cu(ii) ion quenching mechanisms and substituted strategies: For in vitro/in vivo H2S detection. Sens. Actuators B 2024, 415, 135875. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Xing, P.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, S. A Selective Fluorescent Sensor for Fast Detection of Hydrogen Sulfide in Red Wine. Chin. J. Chem. 2017, 35, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, A.; Oguz, M.; Kursunlu, A.N.; Yilmaz, M. A fully water-soluble Calix[4]arene probe for fluorometric and colorimetric detection of toxic hydrosulfide and cyanide ions: Practicability in living cells and food samples. Food Chem. 2023, 401, 134132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosnacht, K.G.; Pluth, M.D. Activity-based fluorescent probes for hydrogen sulfide and related reactive sulfur species. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 4124–4257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Chen, S.; Zhong, A.; Sun, R.; Jin, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, D.; Niu, J.; Lu, S. Tuning photophysical properties via positional isomerization of the pyridine ring in donor–acceptorstructured aggregation-induced emission luminogens based on phenylmethylene pyridineacetonitrile derivatives. Molecules 2023, 28, 3282. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Ni, Y.; Tan, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, H.; Xu, B. Recent advances in meat freshness “magnifier”: Fluorescence sensing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Preethichandra, D.M.G.; Gholami, M.D.; Izake, E.L.; O’Mullane, A.P.; Sonar, P. Conducting polymer-based ammonia and hydrogen sulfide chemical sensors and their suitability for detecting food spoilage. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2200841. [Google Scholar]
- GB11607-89; Fishery Water Quality Standard. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1990.
- Xu, J.R.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, T.Z.; Zhao, B.; Wang, K. A turn-on fluorescent probe for the detection of hydrogen sulfide and thiophenol in water and beer samples. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 128, 106038. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Wen, Y.; Zhong, A.; Xua, J.; Shao, S. An HBT-based fluorescent probe for nitroreductase determination and its application in Escherichia coli cell imaging. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 16265–16268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Pan, J.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, L.; Berkman, C.; Whorton, A.R.; Xian, M. Capture and visualization of hydrogen sulfide by a fluorescent probe. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 50, 10327–10329. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ding, S.; Deng, X.; He, C.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, J. A fluorescent probe for rapid detection of hydrogen sulfide in blood plasma and brain tissues in mice. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 2920–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, C.; Wu, K.; Hu, Y.; Han, Y.; Liang, S.H. A highly specific probe for sensing hydrogen sulfide in live cells based on copper-initiated fluorogen with aggregation-induced emission characteristics. Theranostics. 2014, 4, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathyadevi, P.; Chen, Y.; Wu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. Reaction-based epoxide fluorescent probe for in vivo visualization of hydrogen sulfide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Pacheco, A.; Takano, Y.; Day, J.J.; Hanaoka, K.; Xian, M. A single fluorescent probe to visualize hydrogen sulfide and hydrogen polysulfides with different fluorescence signals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 9993–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Chen, R.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, X.; Yan, Y.; Sun, J.Z.; Qin, A.; et al. Malonitrile-functionalized tetraphenylpyrazine: Aggregation-induced emission, ratiometric detection of hydrogen sulfide, and mechanochromism. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 28, 1704689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Gu, X.; Li, Q.; Gao, J.; Shi, B.; Zhu, T.; Tian, H.; Zhao, C. Aggregation enhanced responsiveness of rationally designed probes to hydrogen sulfide for targeted cancer imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 15084–15090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhu, T.; Ren, N.; Dong, Y.; Jinzhu, G.; Sun, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Tian, H.; Li, J.; et al. Probing the intracellular dynamics of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide using an activatable nir ii fluorescence reporter. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 8450–8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Qiao, R.; Cao, S.; Fang, Y.; Bo, X.; Zhu, H.; Ying, C.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, J. Organic fluorescent probe for concurrent imaging and apoptosis induction in cancer cells in vivo and in vitro by utilizing endogenous hydrogen sulfide. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 456, 141000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, L. The Application of Hydrogen Sulfide Fluorescent Probe in Food Preservation, Detection and Evaluation. Molecules 2024, 29, 3973. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163973
Chen S, Zhao X, Zhou L. The Application of Hydrogen Sulfide Fluorescent Probe in Food Preservation, Detection and Evaluation. Molecules. 2024; 29(16):3973. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163973
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Sitong, Xiongjie Zhao, and Liyi Zhou. 2024. "The Application of Hydrogen Sulfide Fluorescent Probe in Food Preservation, Detection and Evaluation" Molecules 29, no. 16: 3973. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163973
APA StyleChen, S., Zhao, X., & Zhou, L. (2024). The Application of Hydrogen Sulfide Fluorescent Probe in Food Preservation, Detection and Evaluation. Molecules, 29(16), 3973. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163973






