Quorum Sensing Inhibitors: An Alternative Strategy to Win the Battle against Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) Bacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Quorum Sensing: General Overview
4. Initial Explanations of the Quorum Sensing Mechanism
4.1. Quorum Sensing System in Gram-Negative Bacteria
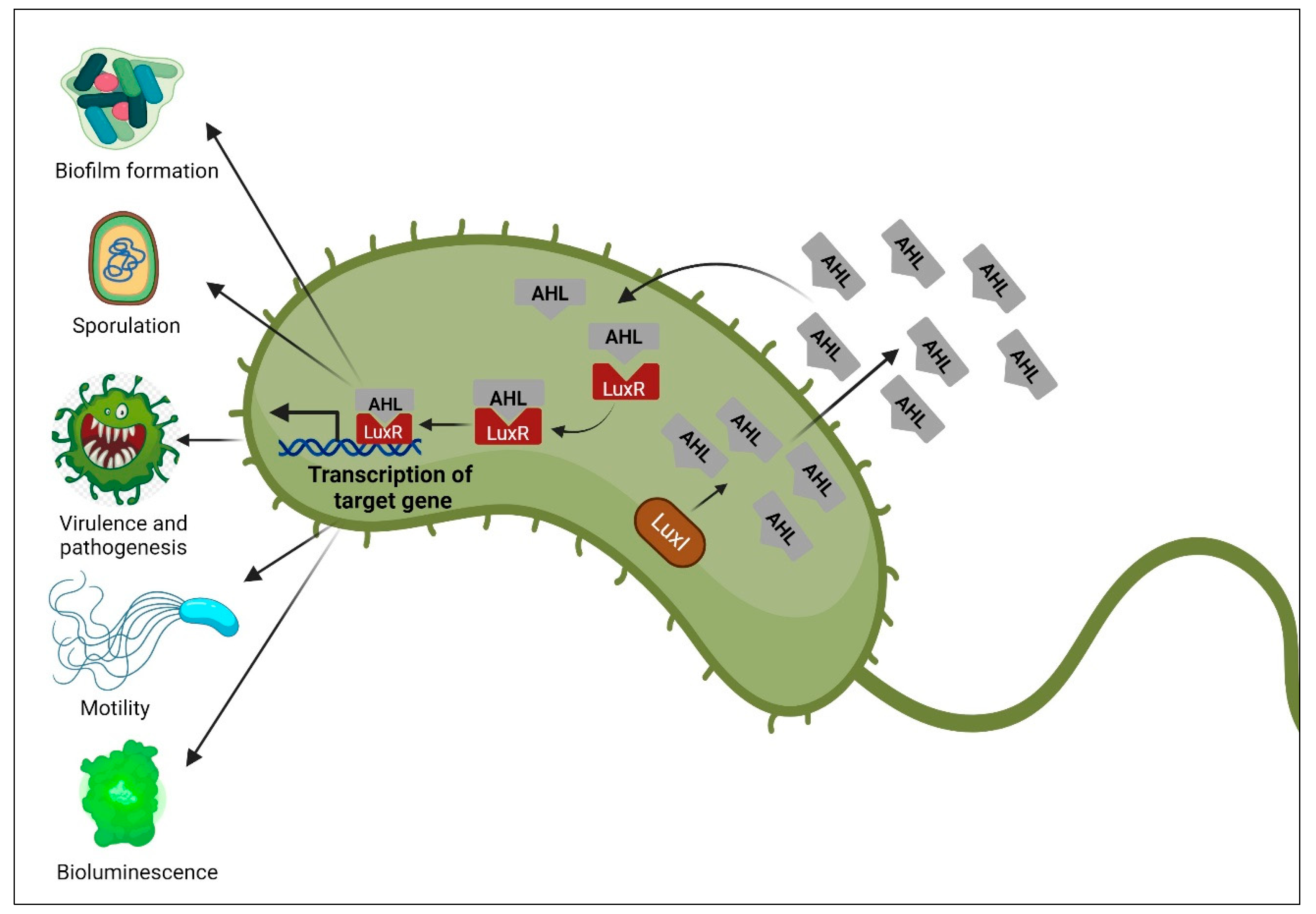
4.2. Quorum Sensing System in Gram-Positive Bacteria
| Microorganism | QS | Regulated Phenotypes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| P. aeruginosa | Las, Rhl, PQS, IQS | Factors contributing to virulence include elastase, alkaline protease, rhamnolipids, pyocyanin, pyoverdine, motility, and biofilm formation. | [70] |
| V. fischeri | LuxI, Ain, LuxS | Motility, colonization within the host, and bioluminescence expression | [38] |
| E. coli | SdiA | Biofilm formation and motility | [64] |
| A. baumannii | Lux, abaI/abaR | Biofilm formation and motility, growth characteristics, and morphology | [65] |
| Legionella | LqsA-LqsR | The formation of a transmissive L. pneumophila Subpopulation at the Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV) periphery and phenotypic heterogeneity. | [78] |
| B. cepacia | CepI/CepR | Siderophore and protease production | [81] |
| P. aureofaciens | PhrI/PhrR | phz (phenazine antibiotic biosynthesis) | [82] |
| M. xanthus | SasSRN | sporulation | [83] |
| Microorganism | QS | Regulated Phenotypes | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | Agr | Synthesis of nucleases, lipases, and proteases | [84] |
| S. pneumoniae | LUX | Autolysis and biofilm formation | [75] |
| C. botulinum | Agr | Sporulation and Production of botulinum toxin | [76] |
| B. subtilis | ComQXPA | Production of biofilm and surfactin | [77] |
| C. maltaromaticum | AMP-like peptide pheromone (CS) | Synthesis of Class II bacteriocin | [85] |
| C. piscicola | AMP-like peptide pheromones (CbnS, CbaX) | Synthesis of Class II bacteriocin | [86,87] |
| E. faecalis | GBAP, FsrB, CyIL AMP-like peptide pheromone (EntF) | Synthesis of Class II bacteriocin | [87,88] |
| L. plantarum | LamD558 AMP-like peptide pheromone (PlnA) | Synthesis of exo-polysaccharides synthesis, cell membrane proteins | [87,89,90] |
| L. sakei | AMP-like peptide pheromone (SppIP) | Synthesis of Class II bacteriocin | [87,91] |
| L. lactis | Nisin | Synthesis of lantibiotic | [87] |
| S. mutans | CSP (ComC) XIP (ComS) | Synthesis of bacteriocins and biofilm | [92,93] |
5. QS Inhibition
6. Standards for Choosing QSIs
7. Possible Mechanisms of QSIs
7.1. Targeting AIs Biosynthesis
| Bacteria | QSI | Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| P. aeruginosa | Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) | Interfering with N-(3-oxododecanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone (3-oxo-C12AHL) autoinducers | [126] |
| AHL-lactonase AiiA | Degradation of AHL signaling molecules | [127] | |
| Boronic acid derivatives | Reduction in signal molecule production | [128] | |
| 3-Hydroxy-2-methyl-4(1H)-quinolone 2,4-dioxygenase | Decrease in the PQS-signal molecule expression | [129] | |
| S.suis serotype 2 | TNRHNPHHLHHV (peptide) | Binding to LuxS enzyme and inactivate production of AI-2 signals | [117] |
| S. pneumoniae | Sinefungin | LuxS downregulation to inhibit the synthesis of AI-2 | [130] |
| Using S. pneumoniae LuxS mutant strain | Use of LuxS/AI-2 mutant strain that lacks LuxS/AI-2 signalling | [75] | |
| E. coli (AK-117) | CRISPRi | Suppression of LuxS synthase and AI-2 synthesis | [131] |
| B. cepacia | Diketopiperazines | disrupting the signal | [132] |
| E. carotovora and P. fluorescens | Hexanal | Lowering AI-2 Signals | [133] |
| H. parasuis | The LuxS mutant strain of H. parasuis | Utilizing the LuxS/AI-2 signaling mutant strain of H. parasuis | [113] |
7.2. Preventing the Production of AHLs in Gram-Negative Bacteria
7.3. Preventing the Synthesis of AIPs in Gram-Positive Bacteria
7.4. Targeting the AI-2 Synthases
7.5. Targeting AI Receptors
| Bacteria | QSI | Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| P. aeruginosa | Morin (3,5,7,2’,4’-Pentahydroxyflavone | Inhibition of the receptor RhlR and LasR | [157] |
| Meta-bromo-thiolactone | Inhibition of the receptor RhlR and LasR | [140] | |
| Flavonoids | LasR and RhlR receptors’ antagonistic interactions | [144] | |
| V-06-018 | LasR receptor antagonistic interactions | [158] | |
| P. aeruginosa and E. coli | Thiolactone derivatives | LasR receptor’s antagonistic interactions | [159] |
| PQS R antagonist | PQS R receptor’s antagonistic interactions | [159] | |
| P. aeruginosa and B. cenocepacia | 3-Azidodihydrofuran-2(3H)-one (2) | AHL analogs | [160] |
| P. fluorescens | Cinnamaldehyde | LasR receptor’s antagonistic interactions | [161] |
| K802NR strain of E. coli | Steviol glycosides and aglycon steviol | LasR receptor’s antagonistic interactions | [162] |
| A. hydrophila | Vanillin (4-hydroxy-3-methoxy benzaldehyde) | AHL receptor interference | [163] |
| C. violaceum CV026 C. violaceum and others | 2(5H)-Furanone | Interfering with different AHL signaling molecules | [164] |
| Senegalia nigrescens | directing QS signal binding to the appropriate receptors | [161] | |
| F. nucleatum | Brominated furanone derivative | Antagonist of the AI-2 signal | [165] |
| S. mutans | Extracts of embelin and piperine | suppressing the QS-related receptors’ activity | [149] |
| L.monocytogenes | Furanone derivative | removing QS signaling molecules from their corresponding receptors | [166] |
7.6. Targeting the AHL Receptors on Gram-Negative Bacteria
7.6.1. AHL Analogs
7.6.2. Structurally Unrelated AHLs
7.6.3. Natural Analogues of QS Inhibitors
7.7. Histidine Kinase Receptor Targeting in Gram-Positive Bacteria
7.8. Targeting LuxP Receptors
7.9. Enzymatic Inactivation of AIs
7.9.1. Lactonase Enzyme
7.9.2. Acylase Enzyme
7.9.3. Oxidoreductase Enzyme
7.10. Active Uptake of AI Signaling Molecules by Beneficial Bacteria
8. Applications on QSIs in Combating Bacterial Biofilm Formation
9. Polyphenols as QSIs
10. Novel Approaches Using QSIs to Combat Resistant Bacteria
10.1. QSIs-NPs
10.2. Combination of QSIs with Traditional Antibiotics through Linkers
10.3. Repurposing of Previously Known Drugs as QSIs
11. Clinical Trials
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalia, V.C. Quorum sensing inhibitors: An overview. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 224–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Baky, R.M.; Masoud, S.M.; Mohamed, D.S.; Waly, N.G.; Shafik, E.A.; Mohareb, D.A.; Elkady, A.; Elbadr, M.M.; Hetta, H.F. Prevalence and some possible mechanisms of colistin resistance among multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kadmy, I.M.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Al-Saryi, N.; Aziz, S.N.; Besinis, A.; Hetta, H.F. Prevalence of genes involved in colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: First report from Iraq. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 26, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nageeb, W.M.; Al Harbi, N.; Alrehaili, A.A.; Zakai, S.A.; Elfadadny, A.; Hetta, H.F. Global genomic epidemiology of chromosomally mediated non-enzymatic carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: On the way to predict and modify resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1271733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nageeb, W.M.; Hetta, H.F. Pangenome analysis of Corynebacterium striatum: Insights into a neglected multidrug-resistant pathogen. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, I. Biofilm-specific antibiotic tolerance and resistance. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Uehara, T.; Bernhardt, T.G. Beta-lactam antibiotics induce a lethal malfunctioning of the bacterial cell wall synthesis machinery. Cell 2014, 159, 1300–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mina, G.; Chbib, C. Recent progresses on synthesized LuxS inhibitors: A mini-review. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, S.B.; Marshall, B. Antibacterial resistance worldwide: Causes, challenges and responses. Nat. Med. 2004, 10 (Suppl. S12), S122–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. Antimicrobial (AR) Threats Report. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/antimicrobial-resistance/data-research/threats/?CDC_AAref_Val= (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- Algammal, A.; Hetta, H.F.; Mabrok, M.; Behzadi, P. Emerging multidrug-resistant bacterial pathogens “superbugs”: A rising public health threat. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1135614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algammal, A.M.; Abo Hashem, M.E.; Alfifi, K.J.; Al-Otaibi, A.S.; Alatawy, M.; ElTarabili, R.M.; Abd El-Ghany, W.A.; Hetta, H.F.; Hamouda, A.M.; Elewa, A.A. Sequence analysis, antibiogram profile, virulence and antibiotic resistance genes of XDR and MDR Gallibacterium anatis isolated from layer chickens in Egypt. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 2022, 4321–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algammal, A.M.; Alfifi, K.J.; Mabrok, M.; Alatawy, M.; Abdel-Moneam, D.A.; Alghamdi, S.; Azab, M.M.; Ibrahim, R.A.; Hetta, H.F.; El-Tarabili, R.M. Newly Emerging MDR B. cereus in Mugil seheli as the First report commonly harbor nhe, hbl, cytK, and pc-plc virulence genes and bla1, bla2, tetA, and ermA resistance genes. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 2167–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algammal, A.M.; Eid, H.M.; Alghamdi, S.; Ghabban, H.; Alatawy, R.; Almanzalawi, E.A.; Alqahtani, T.M.; Elfouly, S.G.; Mohammed, G.M.; Hetta, H.F.; et al. Meat and meat products as potential sources of emerging MDR Bacillus cereus: GroEL gene sequencing, toxigenic and antimicrobial resistance. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algammal, A.M.; Eidaroos, N.H.; Alfifi, K.J.; Alatawy, M.; Al-Harbi, A.I.; Alanazi, Y.F.; Ghobashy, M.O.I.; Khafagy, A.R.; Esawy, A.M.; El-Sadda, S.S.; et al. oprL Gene sequencing, resistance patterns, virulence genes, quorum sensing and antibiotic resistance genes of XDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from broiler Chickens. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 853–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algammal, A.M.; El-Tarabili, R.M.; Abd El-Ghany, W.A.; Almanzalawi, E.A.; Alqahtani, T.M.; Ghabban, H.; Al-Otaibi, A.S.; Alatfeehy, N.M.; Abosleima, N.M.; Hetta, H.F. Resistance profiles, virulence and antimicrobial resistance genes of XDR S. enteritidis and S. typhimurium. AMB Express 2023, 13, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algammal, A.M.; Hashem, H.R.; Al-Otaibi, A.S.; Alfifi, K.J.; El-Dawody, E.M.; Mahrous, E.; Hetta, H.F.; El-Kholy, A.W.; Ramadan, H.; El-Tarabili, R.M. Emerging MDR-Mycobacterium avium subsp. avium in house-reared domestic birds as the first report in Egypt. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algammal, A.M.; Hashem, H.R.; Alfifi, K.J.; Hetta, H.F.; Sheraba, N.S.; Ramadan, H.; El-Tarabili, R.M. atpD gene sequencing, multidrug resistance traits, virulence-determinants, and antimicrobial resistance genes of emerging XDR and MDR-Proteus mirabilis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algammal, A.M.; Hetta, H.F.; Batiha, G.E.; Hozzein, W.N.; El Kazzaz, W.M.; Hashem, H.R.; Tawfik, A.M.; El-Tarabili, R.M. Virulence-determinants and antibiotic-resistance genes of MDR-E. coli isolated from secondary infections following FMD-outbreak in cattle. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algammal, A.M.; Hetta, H.F.; Elkelish, A.; Alkhalifah, D.H.H.; Hozzein, W.N.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; El Nahhas, N.; Mabrok, M.A. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): One health perspective approach to the bacterium epidemiology, virulence factors, antibiotic-resistance, and zoonotic impact. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algammal, A.M.; Mabrok, M.; Sivaramasamy, E.; Youssef, F.M.; Atwa, M.H.; El-Kholy, A.W.; Hetta, H.F.; Hozzein, W.N. Emerging MDR-Pseudomonas aeruginosa in fish commonly harbor oprL and toxA virulence genes and blaTEM, blaCTX-M, and tetA antibiotic-resistance genes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kazzaz, W.; Metwally, L.; Yahia, R.; Al-Harbi, N.; El-Taher, A.; Hetta, H.F. Antibiogram, prevalence of OXA carbapenemase encoding genes, and RAPD-genotyping of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii incriminated in hidden community-acquired infections. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.A.; Ahmed, F.A.; Elkhateeb, A.F.; Mahmoud, E.E.; Ahmed, M.I.; Ahmed, R.I.; Hosni, A.; Alghamdi, S.; Kabrah, A.; Dablool, A.S. Virulence characteristics of biofilm-forming Acinetobacter baumannii in clinical isolates using a Galleria mellonella Model. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makharita, R.R.; El-Kholy, I.; Hetta, H.F.; Abdelaziz, M.H.; Hagagy, F.I.; Ahmed, A.A.; Algammal, A.M. Antibiogram and genetic characterization of carbapenem-resistant gram-negative pathogens incriminated in healthcare-associated infections. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3991–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Baky, R.M.; Farhan, S.M.; Ibrahim, R.A.; Mahran, K.M.; Hetta, H.F. Antimicrobial resistance pattern and molecular epidemiology of ESBL and MBL producing Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from hospitals in Minia, Egypt. Alex. J. Med. 2020, 56, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Baky, R.M.; Sandle, T.; John, J.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.-D.A.; Hetta, H.F. A novel mechanism of action of ketoconazole: Inhibition of the NorA efflux pump system and biofilm formation in multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, S.M.; Ibrahim, R.A.; Mahran, K.M.; Hetta, H.F.; Abd El-Baky, R.M. Antimicrobial resistance pattern and molecular genetic distribution of metallo-β-lactamases producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from hospitals in Minia, Egypt. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetta, H.F.; Ramadan, Y.N.; Al-Harbi, A.I.A.; Ahmed, E.; Battah, B.; Abd Ellah, N.H.; Zanetti, S.; Donadu, M.G. Nanotechnology as a promising approach to combat multidrug resistant bacteria: A comprehensive review and future perspectives. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mokhtar, M.A.; Hetta, H.F. Ambulance vehicles as a source of multidrug-resistant infections: A multicenter study in Assiut City, Egypt. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhawaga, A.A.; Hetta, H.F.; Osman, N.S.; Hosni, A.; El-Mokhtar, M.A. Emergence of Cronobacter sakazakii in cases of neonatal sepsis in upper Egypt: First report in North Africa. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, S.M.; Al-Kadmy, I.M.; Kazaal, S.S.; Ali, A.N.M.; Aziz, S.N.; Makharita, R.R.; Algammal, A.M.; Al-Rejaie, S.; Behl, T.; Batiha, G.E.-S. Detection of gyra and parc mutations and prevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadakkan, K.; Choudhury, A.A.; Gunasekaran, R.; Hemapriya, J.; Vijayanand, S. Quorum sensing intervened bacterial signaling: Pursuit of its cognizance and repression. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subhadra, B.; Kim, D.H.; Woo, K.; Surendran, S.; Choi, C.H. Control of biofilm formation in healthcare: Recent advances exploiting quorum-sensing interference strategies and multidrug efflux pump inhibitors. Materials 2018, 11, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soukarieh, F.; Williams, P.; Stocks, M.J.; Camara, M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing systems as drug discovery targets: Current position and future perspectives. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 10385–10402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manner, S.; Fallarero, A. Screening of natural product derivatives identifies two structurally related flavonoids as potent quorum sensing inhibitors against gram-negative bacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.; Ahmad, F.; Dar, S.A.; Jawed, A.; Mandal, R.K.; Wahid, M.; Lohani, M.; Khan, S.; Singh, V.; Akhter, N. Developments in strategies for Quorum Sensing virulence factor inhibition to combat bacterial drug resistance. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 121, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetta, H.F.; Rashed, Z.I.; Ramadan, Y.N.; Al-Kadmy, I.M.S.; Kassem, S.M.; Ata, H.S.; Nageeb, W.M. Phage Therapy, a salvage treatment for multidrug-resistant bacteria causing infective endocarditis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Juárez, I.; Maeda, T.; Mandujano-Tinoco, E.A.; Tomás, M.; Pérez-Eretza, B.; García-Contreras, S.J.; Wood, T.K.; García-Contreras, R. Role of quorum sensing in bacterial infections. World J. Clin. Cases 2015, 3, 575–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, J. Quorum sensing by super bugs and their resistance to antibiotics, a short review. Glob. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 3, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenfort, K.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing signal–response systems in gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koul, S.; Prakash, J.; Mishra, A.; Kalia, V.C. Potential emergence of multi-quorum sensing inhibitor resistant (MQSIR) bacteria. Indian J. Microbiol. 2016, 56, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnet, V.; Juillard, V.; Gardan, R. Peptide conversations in Gram-positive bacteria. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, M.; Sexton, D.J.; Diggle, S.P.; Greenberg, E.P. Acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing: From evolution to application. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flavier, A.B.; Ganova-Raeva, L.M.; Schell, M.A.; Denny, T.P. Hierarchical autoinduction in Ralstonia solanacearum: Control of acyl-homoserine lactone production by a novel autoregulatory system responsive to 3-hydroxypalmitic acid methyl ester. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 7089–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.H.; Cámara, M.; He, Y.W. The DSF family of quorum sensing signals: Diversity, biosynthesis, and turnover. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiaden, A.; Hilbi, H. α-hydroxyketone synthesis and sensing by Legionella and Vibrio. Sensors 2012, 12, 2899–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, M.M.; Sperandio, V. Quorum sensing by enteric pathogens. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 23, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heeb, S.; Fletcher, M.P.; Chhabra, S.R.; Diggle, S.P.; Williams, P.; Cámara, M. Quinolones: From antibiotics to autoinducers. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 247–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesci, E.C.; Milbank, J.B.; Pearson, J.P.; McKnight, S.; Kende, A.S.; Greenberg, E.P.; Iglewski, B.H. Quinolone signaling in the cell-to-cell communication system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 11229–11234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nageeb, W.M.; Hetta, H.F. The predictive potential of different molecular markers linked to amikacin susceptibility phenotypes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, A.D. Genetic networks controlling the initiation of sporulation and the development of genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1995, 29, 477–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.L.; Bassler, B.L. Bacterial quorum-sensing network architectures. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2009, 43, 197–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, H.B.; Greenberg, E.P. Diffusion of autoinducer is involved in regulation of the Vibrio fischeri luminescence system. J. Bacteriol. 1985, 163, 1210–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherford, S.T.; Bassler, B.L. Bacterial quorum sensing: Its role in virulence and possibilities for its control. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a012427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novick, R.P.; Projan, S.J.; Kornblum, J.; Ross, H.F.; Ji, G.; Kreiswirth, B.; Vandenesch, F.; Moghazeh, S. The agr P2 operon: An autocatalytic sensory transduction system in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Gen. Genet. MGG 1995, 248, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seed, P.C.; Passador, L.; Iglewski, B.H. Activation of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa lasI gene by LasR and the Pseudomonas autoinducer PAI: An autoinduction regulatory hierarchy. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Yu, Z.; Ding, T. Quorum-sensing regulation of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasz, A. Control of the competent state in Pneumococcus by a hormone-like cell product: An example for a new type of regulatory mechanism in bacteria. Nature 1965, 208, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nealson, K.H.; Platt, T.; Hastings, J.W. Cellular control of the synthesis and activity of the bacterial luminescent system. J. Bacteriol. 1970, 104, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engebrecht, J.; Silverman, M. Identification of genes and gene products necessary for bacterial bioluminescence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1984, 81, 4154–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhard, A.; Burlingame, A.L.; Eberhard, C.; Kenyon, G.L.; Nealson, K.H.; Oppenheimer, N. Structural identification of autoinducer of Photobacterium fischeri luciferase. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 2444–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuqua, W.C.; Winans, S.C.; Greenberg, E.P. Quorum sensing in bacteria: The LuxR-LuxI family of cell density-responsive transcriptional regulators. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Contreras, R. Is quorum sensing interference a viable alternative to treat Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections? Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, E.; Cimdins, A.; Lüthje, P.; Brauner, A.; Sjöling, Å.; Landini, P.; Römling, U. “It’s a gut feeling”–Escherichia coli biofilm formation in the gastrointestinal tract environment. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Y.; Song, F.; Guo, F.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, C.; Xiang, J.; Huan, J. Acinetobacter baumannii quorum-sensing signalling molecule induces the expression of drug-resistance genes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 4061–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeki, E.K.; Kobayashi, R.K.T.; Nakazato, G. Quorum sensing system: Target to control the spread of bacterial infections. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 142, 104068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, N.B.; Chormey, D.S.; Büyükpınar, Ç.; Engin, G.O.; Bakirdere, S. Quorum sensing: Little talks for an effective bacterial coordination. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 91, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, M.; Sperandio, V. Quorum sensing in Escherichia coli and Salmonella. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 296, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boban, T.; Nadar, S.; Tauro, S. Breaking down bacterial communication: A review of quorum quenching agents. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 9, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Wu, J.; Deng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Chang, C.; Dong, Y.; Williams, P.; Zhang, L.-H. A cell-cell communication signal integrates quorum sensing and stress response. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Zhang, L. The hierarchy quorum sensing network in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Protein Cell 2015, 6, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyahya, A.; Dakka, N.; Et-Touys, A.; Abrini, J.; Bakri, Y. Medicinal plant products targeting quorum sensing for combating bacterial infections. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghaddam, M.; Khodi, S.; Mirhosseini, A. Quorum sensing in bacteria and a glance on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clin. Microb. 2014, 3, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-R.; Yeon, K.-M. Quorum sensing as language of chemical signals. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 81, pp. 57–94. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, M.K.; Vidal, J.E.; Go, Y.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Chae, S.-W.; Song, J.-J. The LuxS/AI-2 quorum-sensing system of Streptococcus pneumoniae is required to cause disease, and to regulate virulence-and metabolism-related genes in a rat model of middle ear infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Vidal, J.E.; McClane, B.A. The Agr-like quorum-sensing system regulates sporulation and production of enterotoxin and beta2 toxin by Clostridium perfringens type A non-food-borne human gastrointestinal disease strain F5603. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogsa, I.; Oslizlo, A.; Stefanic, P.; Mandic-Mulec, I. Social interactions and biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 52, 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- Striednig, B.; Lanner, U.; Niggli, S.; Katic, A.; Vormittag, S.; Brülisauer, S.; Hochstrasser, R.; Kaech, A.; Welin, A.; Flieger, A.; et al. Quorum sensing governs a transmissive Legionella subpopulation at the pathogen vacuole periphery. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22, e52972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobbetti, M.; De Angelis, M.; Di Cagno, R.; Minervini, F.; Limitone, A. Cell–cell communication in food related bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 120, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-H.; Tian, X. Quorum sensing and bacterial social interactions in biofilms. Sensors 2012, 12, 2519–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewenza, S.; Conway, B.; Greenberg, E.; Sokol, P.A. Quorum sensing in Burkholderia cepacia: Identification of the LuxRI homologs CepRI. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.W.; Gong, F.; Daykin, M.M.; Williams, P.; Pierson, L., 3rd. N-acyl-homoserine lactone-mediated regulation of phenazine gene expression by Pseudomonas aureofaciens 30–84 in the wheat rhizosphere. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 7663–7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.B.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2001, 55, 165–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter, K.; Steinbach, A.; Helms, V. Interfering with bacterial quorum sensing. Perspect. Med. Chem. 2016, 8, S13209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohde, B.H.; Quadri, L.E. Functional characterization of a three-component regulatory system involved in quorum sensing-based regulation of peptide antibiotic production in Carnobacterium maltaromaticum. BMC Microbiol. 2006, 6, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadri, L.; Kleerebezem, M.; Kuipers, O.P.; de Vos, W.M.; Roy, K.L.; Vederas, J.C.; Stiles, M.E. Characterization of a locus from Carnobacterium piscicola LV17B involved in bacteriocin production and immunity: Evidence for global inducer-mediated transcriptional regulation. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 6163–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleerebezem, M.; Quadri, L.E. Peptide pheromone-dependent regulation of antimicrobial peptide production in Gram-positive bacteria: A case of multicellular behavior. Peptides 2001, 22, 1579–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, G.J.; Muir, T.W. Chemical signaling among bacteria and its inhibition. Chem. Biol. 2003, 10, 1007–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sturme, M.H.; Nakayama, J.; Molenaar, D.; Murakami, Y.; Kunugi, R.; Fujii, T.; Vaughan, E.E.; Kleerebezem, M.; De Vos, W.M. An agr-like two-component regulatory system in Lactobacillus plantarum is involved in production of a novel cyclic peptide and regulation of adherence. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 5224–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diep, D.B.; Håvarstein, L.S.; Nes, I.F. Characterization of the locus responsible for the bacteriocin production in Lactobacillus plantarum C11. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 4472–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eijsink, V.; Brurberg, M.B.; Middelhoven, P.H.; Nes, I.F. Induction of bacteriocin production in Lactobacillus sake by a secreted peptide. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 2232–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashburn-Warren, L.; Morrison, D.A.; Federle, M.J. A novel double-tryptophan peptide pheromone controls competence in Streptococcus spp. via an Rgg regulator. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 78, 589–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemme, A.; Gröbe, L.; Reck, M.; Tomasch, J.; Wagner-Döbler, I. Subpopulation-specific transcriptome analysis of competence-stimulating-peptide-induced Streptococcus mutans. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 1863–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, V.C.; Raju, S.C.; Purohit, H.J. Genomic analysis reveals versatile organisms for quorum quenching enzymes: Acyl-homoserine lactone-acylase and-lactonase. Open Microbiol. J. 2011, 5, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, N.; Morohoshi, T.; Nozawa, T.; Matsumoto, H.; Ikeda, T. Control of gram-negative bacterial quorum sensing with cyclodextrin immobilized cellulose ether gel. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2006, 56, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, N.; Tanaka, T.; Nakagawa, S.; Morohoshi, T.; Hiratani, K.; Ikeda, T. Control of virulence factor expression in opportunistic pathogens using cyclodextrin immobilized gel. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2007, 57, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morohoshi, T.; Tokita, K.; Ito, S.; Saito, Y.; Maeda, S.; Kato, N.; Ikeda, T. Inhibition of quorum sensing in gram-negative bacteria by alkylamine-modified cyclodextrins. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 116, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jagasia, R.; Kaufmann, G.F.; Mathison, J.C.; Ruiz, D.I.; Moss, J.A.; Meijler, M.M.; Ulevitch, R.J.; Janda, K.D. Infection control by antibody disruption of bacterial quorum sensing signaling. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetzner, S. Quorum quenching enzymes. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 201, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, W.D.; Robinson, J.B. Disruption of bacterial quorum sensing by other organisms. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givskov, M.; de Nys, R.; Manefield, M.; Gram, L.; Maximilien, R.; Eberl, L.; Molin, S.; Steinberg, P.D.; Kjelleberg, S. Eukaryotic interference with homoserine lactone-mediated prokaryotic signalling. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 6618–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackman, G.; Defoirdt, T.; Miyamoto, C.; Bossier, P.; Van Calenbergh, S.; Nelis, H.; Coenye, T. Cinnamaldehyde and cinnamaldehyde derivatives reduce virulence in Vibrio spp. by decreasing the DNA-binding activity of the quorum sensing response regulator LuxR. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, N.; Choudhary, G.; Li, M.; Wang, B. Pyrogallol and its analogs can antagonize bacterial quorum sensing in Vibrio harveyi. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teplitski, M.; Merighi, M.; Gao, M.; Robinson, J. Integration of cell-to-cell signals in soil bacterial communities. Biocommunication Soil Microorg. 2011, 23, 369–401. [Google Scholar]
- Vattem, D.A.; Mihalik, K.; Crixell, S.H.; McLean, R.J. Dietary phytochemicals as quorum sensing inhibitors. Fitoterapia 2007, 78, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Teplitski, M.; Robinson, J.B.; Bauer, W.D. Production of substances by Medicago truncatula that affect bacterial quorum sensing. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2003, 16, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girennavar, B.; Cepeda, M.L.; Soni, K.A.; Vikram, A.; Jesudhasan, P.; Jayaprakasha, G.; Pillai, S.D.; Patil, B.S. Grapefruit juice and its furocoumarins inhibits autoinducer signaling and biofilm formation in bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 125, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathesius, U.; Mulders, S.; Gao, M.; Teplitski, M.; Caetano-Anollés, G.; Rolfe, B.G.; Bauer, W.D. Extensive and specific responses of a eukaryote to bacterial quorum-sensing signals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, C.; Afre, S.; Gilbert, E.S. Subinhibitory concentrations of cinnamaldehyde interfere with quorum sensing. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudrappa, T.; Bais, H.P. Curcumin, a known phenolic from Curcuma longa, attenuates the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 in whole plant and animal pathogenicity models. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1955–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, T.B.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Skindersoe, M.E.; Hentzer, M.; Kristoffersen, P.; Kote, M.; Nielsen, J.; Eberl, L.; Givskov, M. Screening for quorum-sensing inhibitors (QSI) by use of a novel genetic system, the QSI selector. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 1799–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Sarre, B.; Federle, M.J. Exploiting quorum sensing to confuse bacterial pathogens. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 73–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ku, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, F.; Zeng, W.; Li, J.; Zhu, L.; He, Q. The AI-2/luxS quorum sensing system affects the growth characteristics, biofilm formation, and virulence of Haemophilus parasuis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.; Yin, Y.; Yao, K. Quorum sensing: A prospective therapeutic target for bacterial diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2015978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhoads, M.K.; Hauk, P.; Terrell, J.; Tsao, C.Y.; Oh, H.; Raghavan, S.R.; Mansy, S.S.; Payne, G.F.; Bentley, W.E. Incorporating LsrK AI-2 quorum quenching capability in a functionalized biopolymer capsule. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2018, 115, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamin, A.; Kaksonen, A.H.; Cole, I.S.; Chen, X.-B. Quorum sensing inhibitors applications: A new prospect for mitigation of microbiologically influenced corrosion. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 145, 108050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Lu, C. Biological activity and identification of a peptide inhibitor of LuxS from Streptococcus suis serotype 2. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 294, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, M. Analysis of the antibacterial effect of an Edwardsiella tarda LuxS inhibitor. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, Q.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X. LuxS/AI-2 quorum sensing system in Edwardsiella piscicida promotes biofilm formation and pathogenicity. Infect. Immun. 2020, 88, e00907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Yeo, S.; Ji, Y.; Lee, J.; Yang, J.; Park, S.; Shin, H.; Holzapfel, W. Autoinducer-2 associated inhibition by Lactobacillus sakei NR28 reduces virulence of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157: H7. Food Control 2014, 45, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Lee, K.; Yeo, S.; Shin, H.; Holzapfel, W.H. Autoinducer-2 quorum sensing influences viability of Escherichia coli O157: H7 under osmotic and in vitro gastrointestinal stress conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, V.; Adams, B.L.; Bentley, W.E. Developing next generation antimicrobials by intercepting AI-2 mediated quorum sensing. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2011, 49, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medarametla, P.; Gatta, V.; Kajander, T.; Laitinen, T.; Tammela, P.; Poso, A. Structure-Based Virtual Screening of LsrK Kinase Inhibitors to Target Quorum Sensing. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 2400–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatta, V.; Tomašič, T.; Ilaš, J.; Zidar, N.; Peterlin Mašič, L.; Barančoková, M.; Frlan, R.; Anderluh, M.; Kikelj, D.; Tammela, P. A new cell-based AI-2-mediated quorum sensing interference assay in screening of LsrK-targeted inhibitors. ChemBioChem 2020, 21, 1918–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stotani, S.; Gatta, V.; Medarametla, P.; Padmanaban, M.; Karawajczyk, A.; Giordanetto, F.; Tammela, P.; Laitinen, T.; Poso, A.; Tzalis, D. DPD-inspired discovery of novel LsrK kinase inhibitors: An opportunity to fight antimicrobial resistance. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 2720–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Feng, S.; Fuente-Núñez, C.S.D.L.; Hancock, R.E.; Lu, X. Development of molecularly imprinted polymers to block quorum sensing and inhibit bacterial biofilm formation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 18450–18457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anandan, K.; Vittal, R.R. Quorum quenching activity of AiiA lactonase KMMI17 from endophytic Bacillus thuringiensis KMCL07 on AHL-mediated pathogenic phenotype in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 132, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppoloni, S.; Pericolini, E.; Colombari, B.; Pinetti, D.; Cermelli, C.; Fini, F.; Prati, F.; Caselli, E.; Blasi, E. The β-lactamase inhibitor boronic acid derivative SM23 as a new anti-Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pustelny, C.; Albers, A.; Büldt-Karentzopoulos, K.; Parschat, K.; Chhabra, S.R.; Cámara, M.; Williams, P.; Fetzner, S. Dioxygenase-mediated quenching of quinolone-dependent quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chem. Biol. 2009, 16, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.K.; Park, S.-W.; Chae, S.-W.; Song, J.-J. Sinefungin, a natural nucleoside analogue of S-adenosylmethionine, inhibits Streptococcus pneumoniae biofilm growth. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 156987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuberi, A.; Misba, L.; Khan, A.U. CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) inhibition of luxS gene expression in E. coli: An approach to inhibit biofilm. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buroni, S.; Scoffone, V.C.; Fumagalli, M.; Makarov, V.; Cagnone, M.; Trespidi, G.; De Rossi, E.; Forneris, F.; Riccardi, G.; Chiarelli, L.R. Investigating the mechanism of action of diketopiperazines inhibitors of the Burkholderia cenocepacia quorum sensing synthase CepI: A site-directed mutagenesis study. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kong, J.; Xie, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Qian, H.; Shi, R.; Yao, W. Quorum-sensing inhibition by hexanal in biofilms formed by Erwinia carotovora and Pseudomonas fluorescens. LWT 2019, 109, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleitas Martínez, O.; Cardoso, M.H.; Ribeiro, S.M.; Franco, O.L. Recent advances in anti-virulence therapeutic strategies with a focus on dismantling bacterial membrane microdomains, toxin neutralization, quorum-sensing interference and biofilm inhibition. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churchill, M.E.; Chen, L. Structural basis of acyl-homoserine lactone-dependent signaling. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentzer, M.; Givskov, M. Pharmacological inhibition of quorum sensing for the treatment of chronic bacterial infections. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, N.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, B. Inhibitors and antagonists of bacterial quorum sensing. Med. Res. Rev. 2009, 29, 65–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Luo, Y. Bacterial quorum-sensing systems and their role in intestinal bacteria-host crosstalk. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 611413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-C.J.; Wang, M.C. Microbial metabolites regulate host lipid metabolism through NR5A–Hedgehog signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Loughlin, C.T.; Miller, L.C.; Siryaporn, A.; Drescher, K.; Semmelhack, M.F.; Bassler, B.L. A quorum-sensing inhibitor blocks Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence and biofilm formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17981–17986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, T.; Lee, B.W.; Cannon, L.M.; Ritter, K.A.; Dai, S.; Ren, D.; Wood, T.K.; Zhou, Z.S. A naturally occurring brominated furanone covalently modifies and inactivates LuxS. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 6200–6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benneche, T.; Hussain, Z.; Scheie, A.A.; Lönn-Stensrud, J. Synthesis of 5-(bromomethylene) furan-2 (5 H)-ones and 3-(bromomethylene) isobenzofuran-1 (3 H)-ones as inhibitors of microbial quorum sensing. New J. Chem. 2008, 32, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Z. Surfactin effectively inhibits Staphylococcus aureus adhesion and biofilm formation on surfaces. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 4565–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paczkowski, J.E.; Mukherjee, S.; McCready, A.R.; Cong, J.-P.; Aquino, C.J.; Kim, H.; Henke, B.R.; Smith, C.D.; Bassler, B.L. Flavonoids suppress Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence through allosteric inhibition of quorum-sensing receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4064–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proctor, C.R.; McCarron, P.A.; Ternan, N.G. Furanone quorum-sensing inhibitors with potential as novel therapeutics against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asfour, H.Z. Anti-quorum sensing natural compounds. J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 2018, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, H.A.; Shaldam, M.A.; Eldamasi, D. Curtailing quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by sitagliptin. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, M.; D’morris, S.; Paul, V.; Warrier, S.; Vasudevan, A.K.; Vanuopadath, M.; Nair, S.S.; Paul-Prasanth, B.; Mohan, C.G.; Biswas, R. Mechanistic understanding of Phenyllactic acid mediated inhibition of quorum sensing and biofilm development in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 8223–8236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, D.; Singh, V. Effects of the natural compounds embelin and piperine on the biofilm-producing property of Streptococcus mutans. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2016, 6, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, L.-X.; Yang, Y.-X.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Wang, L.-H. A new synthetic ligand that activates QscR and blocks antibiotic-tolerant biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 2565–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-X.; Xu, Z.-H.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Tian, J.; Weng, L.-X.; Wang, L.-H. A new quorum-sensing inhibitor attenuates virulence and decreases antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swem, L.R.; Swem, D.L.; O’Loughlin, C.T.; Gatmaitan, R.; Zhao, B.; Ulrich, S.M.; Bassler, B.L. A quorum-sensing antagonist targets both membrane-bound and cytoplasmic receptors and controls bacterial pathogenicity. Mol. Cell 2009, 35, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capilato, J.N.; Philippi, S.V.; Reardon, T.; McConnell, A.; Oliver, D.C.; Warren, A.; Adams, J.S.; Wu, C.; Perez, L.J. Development of a novel series of non-natural triaryl agonists and antagonists of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasR quorum sensing receptor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.; Lee, J.-W.; Javaid, A.; Park, S.-K.; Kim, Y.-M. Inhibition of biofilm and virulence properties of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by sub-inhibitory concentrations of aminoglycosides. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 146, 104249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernando-Amado, S.; Alcalde-Rico, M.; Gil-Gil, T.; Valverde, J.R.; Martínez, J.L. Naringenin inhibition of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing response is based on its time-dependent competition with N-(3-Oxo-dodecanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone for LasR binding. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sully, E.K.; Malachowa, N.; Elmore, B.O.; Alexander, S.M.; Femling, J.K.; Gray, B.M.; DeLeo, F.R.; Otto, M.; Cheung, A.L.; Edwards, B.S.; et al. Selective chemical inhibition of agr quorum sensing in Staphylococcus aureus promotes host defense with minimal impact on resistance. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annapoorani, A.; Umamageswaran, V.; Parameswari, R.; Pandian, S.K.; Ravi, A.V. Computational discovery of putative quorum sensing inhibitors against LasR and RhlR receptor proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2012, 26, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manson, D.E.; O’Reilly, M.C.; Nyffeler, K.E.; Blackwell, H.E. Design, synthesis, and biochemical characterization of non-native antagonists of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing receptor LasR with nanomolar IC50 values. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnis, C.E.; Blackwell, H.E. Thiolactone modulators of quorum sensing revealed through library design and screening. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 4820–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brackman, G.; Risseeuw, M.; Celen, S.; Cos, P.; Maes, L.; Nelis, H.J.; Van Calenbergh, S.; Coenye, T. Synthesis and evaluation of the quorum sensing inhibitory effect of substituted triazolyldihydrofuranones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 4737–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Wang, D.; Liu, N.; Ma, Y.; Ding, T.; Mei, Y.; Li, J. Inhibition of quorum sensing-controlled virulence factors and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens by cinnamaldehyde. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 269, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, V.; Share, O.; Teralı, K.; Ozer, N.; Marks, R.S.; Kushmaro, A.; Golberg, K. Anti-quorum sensing activity of stevia extract, Stevioside, Rebaudioside a and their Aglycon Steviol. Molecules 2020, 25, 5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, K.; Paul, D.; Kweon, J.H. Inhibition of quorum sensing mechanism and Aeromonas hydrophila biofilm formation by vanillin. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2009, 26, 1359–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, K.; Paul, D.; Kim, Y.S.; Kweon, J.H. 2 (5H)-Furanone: A prospective strategy for biofouling-control in membrane biofilm bacteria by quorum sensing inhibition. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2010, 41, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Ryu, E.-J.; Li, L.; Choi, B.-K.; Kim, B.M. New bicyclic brominated furanones as potent autoinducer-2 quorum-sensing inhibitors against bacterial biofilm formation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 137, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-López, P.; Barrenengoa, A.E.; Pascual-Sáez, S.; Cabo, M.L. Efficacy of synthetic furanones on listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation. Foods 2019, 8, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naga, N.G.; El-Badan, D.E.; Ghanem, K.M.; Shaaban, M.I. It is the time for quorum sensing inhibition as alternative strategy of antimicrobial therapy. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2023, 21, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geske, G.D.; Mattmann, M.E.; Blackwell, H.E. Evaluation of a focused library of N-aryl L-homoserine lactones reveals a new set of potent quorum sensing modulators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 5978–5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naga, N.G.; El-Badan, D.E.; Rateb, H.S.; Ghanem, K.M.; Shaaban, M.I. Quorum Sensing Inhibiting Activity of Cefoperazone and Its Metallic Derivatives on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 716789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soheili, V.; Bazzaz, B.S.F.; Abdollahpour, N.; Hadizadeh, F. Investigation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing signaling system for identifying multiple inhibitors using molecular docking and structural analysis methodology. Microb. Pathog. 2015, 89, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Mishra, N. Antiquorum sensing activity of Copper nanoparticle in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An in silico approach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 91, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.G.; Ansari, M.A.; Sajid Jamal, Q.M.; Khan, H.M.; Jalal, M.; Ahmad, H.; Mahdi, A.A. Antiquorum sensing activity of silver nanoparticles in P. aeruginosa: An in silico study. Silico Pharmacol. 2017, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, T.; Saha, T.; Sarkar, P.; Hoque, K.M.; Chatterjee, B.K.; Chakrabarti, P. The gold nanoparticle reduces Vibrio cholerae pathogenesis by inhibition of biofilm formation and disruption of the production and structure of cholera toxin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 204, 111811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciardi, M.C.; Blázquez, M.A.; Cartagena, E.; Bardón, A.; Arena, M.E. Mandarin essential oils inhibit quorum sensing and virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 68, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luís, Â.; Duarte, A.; Gominho, J.; Domingues, F.; Duarte, A.P. Chemical composition, antioxidant, antibacterial and anti-quorum sensing activities of Eucalyptus globulus and Eucalyptus radiata essential oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 79, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, B.D.Á.; Rodrigues, A.C.; Cardoso, B.M.I.; Ramos, A.L.C.C.; Bertoldi, M.C.; Taylor, J.G.; da Cunha, L.R.; Pinto, U.M. Antioxidant, antimicrobial and anti-quorum sensing activities of Rubus rosaefolius phenolic extract. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 84, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasavi, H.; Arun, A.; Rekha, P. Anti-quorum sensing activity of flavonoid-rich fraction from Centella asiatica L. against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2016, 49, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naga, N.G.; Zaki, A.A.; El-Badan, D.E.; Rateb, H.S.; Ghanem, K.M.; Shaaban, M.I. Methoxyisoflavan derivative from Trigonella stellata inhibited quorum sensing and virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattnaik, A.; Sarkar, R.; Sharma, A.; Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, A.; Roy, P.; Mazumder, A.; Karmakar, S.; Sen, T. Pharmacological studies on Buchanania lanzan Spreng.-A focus on wound healing with particular reference to anti-biofilm properties. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 3, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.R.T.; Lou, Z.; Yu, F.; Wang, P.; Wang, H. Anti-quorum sensing and anti-biofilm activity of Amomum tsaoko (Amommum tsao-ko Crevost et Lemarie) on foodborne pathogens. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsen, T.H.; van Gennip, M.; Phipps, R.K.; Shanmugham, M.S.; Christensen, L.D.; Alhede, M.; Skindersoe, M.E.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Friedrich, K.; Uthe, F. Ajoene, a sulfur-rich molecule from garlic, inhibits genes controlled by quorum sensing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2314–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pederson, D.B.; Dong, Y.; Blue, L.B.; Smith, S.V.; Cao, M. Water-soluble cranberry extract inhibits Vibrio cholerae biofilm formation possibly through modulating the second messenger 3’, 5’—Cyclic diguanylate level. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Z.; Wang, H.; Ding, T.; Zhu, W.; Zhuang, X.; Chu, W. Azithromycin reduces the production of α-hemolysin and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus. Indian J. Microbiol. 2014, 54, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gestel, J.; Bareia, T.; Tenennbaum, B.; Dal Co, A.; Guler, P.; Aframian, N.; Puyesky, S.; Grinberg, I.; D’Souza, G.G.; Erez, Z. Short-range quorum sensing controls horizontal gene transfer at micron scale in bacterial communities. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimi, S.; Klementiev, A.D.; Whiteley, M.; Diggle, S.P. Bacterial quorum sensing during infection. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 74, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.S.; Thompson, J.A.; Xavier, K.B. AI-2-mediated signalling in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 156–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Gamby, S.; Zheng, Y.; Sintim, H.O. Small molecule inhibitors of AI-2 signaling in bacteria: State-of-the-art and future perspectives for anti-quorum sensing agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 17694–17728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Cheng, Y.; Ni, N.; Li, M.; Choudhary, G.; Chou, H.T.; Lu, C.D.; Tai, P.C.; Wang, B. Synthesis and evaluation of new antagonists of bacterial quorum sensing in Vibrio harveyi. ChemMedChem Chem. Enabl. Drug Discov. 2009, 4, 1457–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Li, X. Quorum quenching enzymes and their application in degrading signal molecules to block quorum sensing-dependent infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 17477–17500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-H.; Wang, L.-H.; Xu, J.-L.; Zhang, H.-B.; Zhang, X.-F.; Zhang, L.-H. Quenching quorum-sensing-dependent bacterial infection by an N-acyl homoserine lactonase. Nature 2001, 411, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Momb, J.; Thomas, P.W.; Moulin, A.; Petsko, G.A.; Fast, W.; Ringe, D. Mechanism of the quorum-quenching lactonase (AiiA) from Bacillus thuringiensis. 1. Product-bound structures. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 7706–7714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps, J.; Pujol, I.; Ballester, F.; Joven, J.; Simó, J.M. Paraoxonases as potential antibiofilm agents: Their relationship with quorum-sensing signals in Gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1325–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, P.; Rai, V.R. Inhibition of QS-regulated virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and Pectobacterium carotovorum by AHL-lactonase of endophytic bacterium Bacillus cereus VT96. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2016, 7, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergonzi, C.; Schwab, M.; Naik, T.; Daudé, D.; Chabrière, E.; Elias, M. Structural and biochemical characterization of AaL, a quorum quenching lactonase with unusual kinetic properties. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paluch, E.; Rewak-Soroczyńska, J.; Jędrusik, I.; Mazurkiewicz, E.; Jermakow, K. Prevention of biofilm formation by quorum quenching. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Sun, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, C.; Zhou, S. Quorum quenching mediated bacteria interruption as a probable strategy for drinking water treatment against bacterial pollution. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustine, N.; Kumar, P.; Thomas, S. Inhibition of Vibrio cholerae biofilm by AiiA enzyme produced from Bacillus spp. Arch. Microbiol. 2010, 192, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Reis Ponce, A.; Martins, M.L.; de Araujo, E.F.; Mantovani, H.C.; Vanetti, M.C.D. AiiA quorum-sensing quenching controls proteolytic activity and biofilm formation by Enterobacter cloacae. Curr. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leadbetter, J.R.; Greenberg, E.P. Metabolism of acyl-homoserine lactone quorum-sensing signals by Variovorax paradoxus. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 6921–6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Byun, T.; Dussen, H.-J.; Duke, K.R. Degradation of N-acylhomoserine lactones, the bacterial quorum-sensing molecules, by acylase. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 101, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.J.; Han, J.-I.; Zhang, L.-H.; Leadbetter, J.R. Utilization of acyl-homoserine lactone quorum signals for growth by a soil pseudomonad and Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5941–5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Xu, J.L.; Hu, J.; Wang, L.H.; Ong, S.L.; Leadbetter, J.R.; Zhang, L.H. Acyl-homoserine lactone acylase from Ralstonia strain XJ12B represents a novel and potent class of quorum-quenching enzymes. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhove, M.; Jimenez, P.N.; Quax, W.J.; Dijkstra, B.W. The quorum-quenching N-acyl homoserine lactone acylase PvdQ is an Ntn-hydrolase with an unusual substrate-binding pocket. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.-W.; Koh, C.-L.; Sam, C.-K.; Yin, W.-F.; Chan, K.-G. Quorum quenching revisited—From signal decays to signalling confusion. Sensors 2012, 12, 4661–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, K.B.; Bassler, B.L. Interference with AI-2-mediated bacterial cell—Cell communication. Nature 2005, 437, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallós, P.; Gajdács, M.; Urbán, E.; Szabados, Y.; Szalai, K.; Hevesi, L.; Horváth, A.; Kuklis, A.; Morjaria, D.; Iffat, W.; et al. Characterization of antibiotic and disinfectant susceptibility in biofilm-forming Acinetobacter baumannii: A focus on environmental isolates. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2024, 14, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kadmy, I.M.; Aziz, S.N.; Suhail, A.; Abid, S.A.; Naji, E.N.; Al-Kadmy, Z.; Algammal, A.M.; Ahmed, H.R.; Khodeer, D.M.; Batiha, G.E.-S. Enhancing the anti-biofilm activity of novel keratinase isolated from Acinetobacter baumannii using Reduced Graphene oxide: A way to recycle feather waste pollution. Clean. Waste Syst. 2023, 5, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kadmy, I.M.S.; Abid, S.A.; Aziz, S.N.; Al-Kadmy, Z.; Suhail, A.; Al-Jubori, S.S.; Naji, E.N.; Alhomaidi, E.; Yahia, R.; Algammal, A.M.; et al. The secrets of environmental Pseudomonas aeruginosa in slaughterhouses: Antibiogram profile, virulence, and antibiotic resistance genes. Folia Microbiol. 2023; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kadmy, I.M.S.; Aziz, S.N.; Hussein, N.H.; El-Shafeiy, S.N.; Hamzah, I.H.; Suhail, A.; Alhomaidi, E.; Algammal, A.M.; El-Saber Batiha, G.; ElBadre, H.M.; et al. Sequencing analysis and efficient biodiesel production by lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salah, M.; Badr, G.; Hetta, H.F.; Khalifa, W.A.; Shoreit, A.A. Fig latex inhibits the growth of pathogenic bacteria invading human diabetic wounds and accelerates wound closure in diabetic mice. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utari, P.D.; Setroikromo, R.; Melgert, B.N.; Quax, W.J. PvdQ quorum quenching acylase attenuates Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence in a mouse model of pulmonary infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcelik, B.; Ho, K.K.K.; Glattauer, V.; Willcox, M.; Kumar, N.; Thissen, H. Poly (ethylene glycol)-based coatings combining low-biofouling and quorum-sensing inhibiting properties to reduce bacterial colonization. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.-J.; Zhou, J.-W.; Zhang, P.-P.; Luo, H.-Z.; Tang, S.; Li, J.-J.; Deng, S.-M.; Jia, A.-Q. Quorum sensing inhibition and tobramycin acceleration in Chromobacterium violaceum by two natural cinnamic acid derivatives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 5025–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Chowdhury, G.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Dutta, S.; Basu, S. Convergence of Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii Infection. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 793615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, C.; Muras, A.; Parga, A.; Romero, M.; Rumbo-Feal, S.; Poza, M.; Ramos-Vivas, J.; Otero, A. Quorum Sensing as a Target for Controlling Surface Associated Motility and Biofilm Formation in Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC® 17978TM. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 565548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nait Chabane, Y.; Mlouka, M.B.; Alexandre, S.; Nicol, M.; Marti, S.; Pestel-Caron, M.; Vila, J.; Jouenne, T.; Dé, E. Virstatin inhibits biofilm formation and motility of Acinetobacter baumannii. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.H.; Choi, C.H. Role of LuxIR Homologue AnoIR in Acinetobacter nosocomialis and the Effect of Virstatin on the Expression of anoR Gene. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambanthamoorthy, K.; Luo, C.; Pattabiraman, N.; Feng, X.; Koestler, B.; Waters, C.M.; Palys, T.J. Identification of small molecules inhibiting diguanylate cyclases to control bacterial biofilm development. Biofouling 2014, 30, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacy, D.M.; Welsh, M.A.; Rather, P.N.; Blackwell, H.E. Attenuation of quorum sensing in the pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii using non-native N-Acyl homoserine lactones. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, P.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Mabood Husain, F.; Tabish Rehman, M.; Alajmi, M.F.; Noman, O.M.; El Gamal, A.A.; Al-Massarani, S.M.; Shavez Khan, M. Siphonocholin isolated from red sea sponge Siphonochalina siphonella attenuates quorum sensing controlled virulence and biofilm formation. Saudi Pharm. J. SPJ 2020, 28, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Zhou, C.; Yu, K.H.; Lin, Y.S.; Wang, L.B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.X.; Xu, W.Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, T.L.; et al. Glabridin Functions as a Quorum Sensing Inhibitor to Inhibit Biofilm Formation and Swarming Motility of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 5697–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.Y.; Yang, Y.; Tay, S.B.; Chua, K.L.; Yew, W.S. Disruption of biofilm formation by the human pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii using engineered quorum-quenching lactonases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1802–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odularu, A.T.; Afolayan, A.J.; Sadimenko, A.P.; Ajibade, P.A.; Mbese, J.Z. Multidrug-Resistant Biofilm, Quorum Sensing, Quorum Quenching, and Antibacterial Activities of Indole Derivatives as Potential Eradication Approaches. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 9048245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beenker, W.A.G.; Hoeksma, J.; Bannier-Hélaouët, M.; Clevers, H.; den Hertog, J. Paecilomycone Inhibits Quorum Sensing in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0509722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, S.; Borges, A.; Gomes, I.B.; Sousa, S.F.; Simões, M. Curcumin and 10-undecenoic acid as natural quorum sensing inhibitors of LuxS/AI-2 of Bacillus subtilis and LasI/LasR of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, A.A.; Khan, S.; Powell, L.C.; Pritchard, M.F.; Beck, K.; Sadh, H.; Sutton, L.; Cavaliere, A.; Florance, H.; Rye, P.D.; et al. Alginate Oligosaccharide-Induced Modification of the lasI-lasR and rhlI-rhlR Quorum-Sensing Systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 2018, 62, 416–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathinam, P.; Viswanathan, P. Anti-virulence potential of eugenol-rich fraction of Syzygium aromaticum against multidrug resistant uropathogens isolated from catheterized patients. Avicenna J. Phytomedicine 2018, 8, 416–431. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.S.; Zahin, M.; Hasan, S.; Husain, F.M.; Ahmad, I. Inhibition of quorum sensing regulated bacterial functions by plant essential oils with special reference to clove oil. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulghesu, L.; Giallorenzo, C.; Savoia, D. Evaluation of different compounds as quorum sensing inhibitors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Chemother. 2007, 19, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, J.; Sun, F.; Feng, W.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, X.; Xiong, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Quercetin is an effective inhibitor of quorum sensing, biofilm formation and virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetrivel, A.; Vetrivel, P.; Dhandapani, K.; Natchimuthu, S.; Ramasamy, M.; Madheswaran, S.; Murugesan, R. Inhibition of biofilm formation, quorum sensing and virulence factor production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 by selected LasR inhibitors. Int. Microbiol. 2023, 26, 851–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, T.H.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Jensen, P.; Givskov, M.; Høiby, N. Targeting quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms: Current and emerging inhibitors. Future Microbiol. 2013, 8, 901–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.H.; She, M.T.; Zhang, Y.H.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhong, D.X.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zheng, J.X.; Sun, N.; Wong, W.L.; Lu, Y.J. Novel quinoline-based derivatives as the PqsR inhibitor against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 2167–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, S.; Das, T.; Kuppusamy, R.; Yu, T.T.; Willcox, M.D.P.; Black, D.S.; Kumar, N. Novel quinazolinone disulfide analogues as pqs quorum sensing inhibitors against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 130, 106226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, W.; Ma, Y.-C.; Bai, B.; Sun, G.; Zhang, S.; Chang, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, X.; et al. Design and Synthesis of 4-Fluorophenyl-5-methylene-2(5H)-furanone Derivatives as Potent Quorum Sensing Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 8441–8463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, P.; Guo, T.; Gu, X.; Bai, B.; Zhang, S.; Chang, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, S. Design, synthesis and evaluation of oxazolopyridinone derivatives as quorum sensing inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 130, 106266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Srivastava, N.; Devi, B.; Kumar, L.; Kumar, R.; Kumar Yadav, A. Synthesis, Biological evaluation and in silico study of N-(2- and 3-Pyridinyl)benzamide derivatives as quorum sensing inhibitors against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202201191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soukarieh, F.; Gurnani, P.; Romero, M.; Halliday, N.; Stocks, M.; Alexander, C.; Cámara, M. Design of Quorum Sensing Inhibitor–Polymer Conjugates to Penetrate Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. ACS Macro Lett. 2023, 12, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Saafin, B.A.; Al-Bakri, A.G.; Abdelrazig, S.; Dahabiyeh, L.A. Investigating the effect of the probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum and the prebiotic fructooligosaccharides on Pseudomonas aeruginosa metabolome, virulence factors and biofilm formation as potential quorum sensing inhibitors. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 177, 106057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Pagedar Singh, A. Antibiofilm Effect of DNase against Single and Mixed Species Biofilm. Foods 2018, 7, 7030042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lu, H.; Chu, X.; Lou, T.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, B.; Chu, W. Tea polyphenols inhibits biofilm formation, attenuates the quorum sensing-controlled virulence and enhances resistance to Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in Caenorhabditis elegans model. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, M.M.; Russell, R.; Moreira, C.G.; Adebesin, A.M.; Wang, C.; Williams, N.S.; Taussig, R.; Stewart, D.; Zimmern, P.; Lu, B.; et al. QseC Inhibitors as an Antivirulence Approach for Gram-Negative Pathogens. mBio 2014, 5, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinothkannan, R.; Muthu Tamizh, M.; David Raj, C.; Adline Princy, S. Fructose furoic acid ester: An effective quorum sensing inhibitor against uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 79, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, N.; Subramaniam, S.; Christena, L.R.; Muthuraman, M.S.; Subramanian, N.S.; Pemiah, B.; Sivasubramanian, A. Antimicrobial flavonoids isolated from Indian medicinal plant Scutellaria oblonga inhibit biofilms formed by common food pathogens. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 2002–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameswaran, S.; Gujjala, S.; Zhang, S.; Kondeti, S.; Mahalingam, S.; Bangeppagari, M.; Bellemkonda, R. Quenching and quorum sensing in bacterial bio-films. Res. Microbiol. 2023, 175, 104085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouarab-Chibane, L.; Forquet, V.; Lantéri, P.; Clément, Y.; Léonard-Akkari, L.; Oulahal, N.; Degraeve, P.; Bordes, C. Antibacterial properties of polyphenols: Characterization and QSAR (Quantitative structure–activity relationship) models. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, L.; Sleiman, A.; Abdel-Massih, R.M. Antimicrobial activity of polyphenols and alkaloids in middle eastern plants. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, B.; Eberl, L.; Feucht, W.; Polster, J. Influence of polyphenols on bacterial biofilm formation and quorum-sensing. Z. Für Naturforschung C 2003, 58, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, I.; Abbas, H.A.; Ashour, M.L.; Yasri, A.; El-Shazly, A.M.; Wink, M.; Sobeh, M. Polyphenols from Salix tetrasperma impair virulence and inhibit quorum sensing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecules 2020, 25, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Deng, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Zhuang, X.; Chu, W. Tea polyphenols as an antivirulence compound disrupt quorum-sensing regulated pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Lee, S.-J.; Park, N.-H.; Mechesso, A.F.; Birhanu, B.T.; Kang, J.; Reza, M.A.; Suh, J.-W.; Park, S.-C. Impact of phenolic compounds in the acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing regulatory pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Rui, X.; Wang, L.; Guan, Y.; Sun, X.; Dong, M. Polyphenolic extract from Rosa rugosa tea inhibits bacterial quorum sensing and biofilm formation. Food Control 2014, 42, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, F.M.; Ansari, A.A.; Khan, A.; Ahmad, N.; Albadri, A.; Albalawi, T.H. Mitigation of acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) based bacterial quorum sensing, virulence functions, and biofilm formation by yttrium oxide core/shell nanospheres: Novel approach to combat drug resistance. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Shama, U.H.; El-Gendy, H.; Mousa, W.S.; Hamouda, R.A.; Yousuf, W.E.; Hetta, H.F.; Abdeen, E.E. Synergistic and antagonistic effects of metal nanoparticles in combination with antibiotics against some reference strains of pathogenic microorganisms. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kadmy, I.M.S.; Aziz, S.N.; Rheima, A.M.; Abid, S.A.; Suhail, A.; Hamzah, I.H.; Naji, E.N.; Besinis, A.; Hetta, H.F. Anti-capsular activity of CuO nanoparticles against Acinetobacter baumannii produce efflux pump. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 181, 106184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.N.; Al-Kadmy, I.M.S.; Rheima, A.M.; Al-Sallami, K.J.; Abd Ellah, N.H.; El-Saber Batiha, G.; El-Bouseary, M.M.; Algammal, A.M.; Hetta, H.F. Binary CuO\CoO nanoparticles inhibit biofilm formation and reduce the expression of papC and fimH genes in multidrug-resistant Klebsiella oxytoca. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 5969–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetta, H.F.; Al-Kadmy, I.; Khazaal, S.S.; Abbas, S.; Suhail, A.; El-Mokhtar, M.A.; Ellah, N.H.A.; Ahmed, E.A.; Abd-Ellatief, R.B.; El-Masry, E.A. Antibiofilm and antivirulence potential of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Qing, Y.A.; Cheng, L.; Li, R.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Qin, Y. Potential antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and the optimization of orthopedic implants by advanced modification technologies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 5, 3311–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagtap, S.; Priolkar, K. Evaluation of ZnO nanoparticles and study of ZnO–TiO2 composites for lead free humidity sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 183, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.A.; Khan, A.; Labis, J.P.; Alam, M.; Manthrammel, M.A.; Ahamed, M.; Akhtar, M.J.; Aldalbahi, A.; Ghaithan, H. Mesoporous multi-silica layer-coated Y2O3: Eu core-shell nanoparticles: Synthesis, luminescent properties and cytotoxicity evaluation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 96, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindran, D.; Ramanathan, S.; Arunachalam, K.; Jeyaraj, G.; Shunmugiah, K.; Arumugam, V. Phytosynthesized silver nanoparticles as antiquorum sensing and antibiofilm agent against the nosocomial pathogen Serratia marcescens: An in vitro study. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1425–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.S.A.S.; Nag, M.; Kalagara, T.; Singh, S.; Manorama, S.V. Silver on PEG-PU-TiO2 polymer nanocomposite films: An excellent system for antibacterial applications. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 2455–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Singh, B.R.; Adholeya, A. Intracellular synthesis of gold nanoparticles using an ectomycorrhizal strain EM-1083 of Laccaria fraterna and its nanoanti-quorum sensing potential against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Indian J. Microbiol. 2017, 57, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shabib, N.A.; Husain, F.M.; Hassan, I.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmed, F.; Qais, F.A.; Oves, M.; Rahman, M.; Khan, R.A.; Khan, A. Biofabrication of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle fromOchradenus baccatusLeaves: Broad-Spectrum Antibiofilm Activity, Protein Binding Studies, andIn VivoToxicity and Stress Studies. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoj, G.; Pati, R.; Sonawane, A.; Vaseeharan, B. In vitro cytotoxic effects of gold nanoparticles coated with functional acyl homoserine lactone lactonase protein from Bacillus licheniformis and their antibiofilm activity against Proteus species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, G.F.; Sartorio, R.; Lee, S.-H.; Rogers, C.J.; Meijler, M.M.; Moss, J.A.; Clapham, B.; Brogan, A.P.; Dickerson, T.J.; Janda, K.D. Revisiting quorum sensing: Discovery of additional chemical and biological functions for 3-oxo-N-acylhomoserine lactones. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, F.; Han, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.-H. Disruption of quorum sensing in Vibrio harveyi by the AiiA protein of Bacillus thuringiensis. Aquaculture 2008, 274, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, K.; Kowshik, M. Anti-quorum sensing activity of AgCl-TiO2 nanoparticles with potential use as active food packaging material. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 972–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, K.P. Bacterial Communication and Its Role as a Target for Nanoparticlebased Antimicrobial Therapy; University of South Carolina: Columbia, SC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- García-Lara, B.; Saucedo-Mora, M.; Roldán-Sánchez, J.; Pérez-Eretza, B.; Ramasamy, M.; Lee, J.; Coria-Jimenez, R.; Tapia, M.; Varela-Guerrero, V.; García-Contreras, R. Inhibition of quorum-sensing-dependent virulence factors and biofilm formation of clinical and environmental Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains by ZnO nanoparticles. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 61, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, D.; Nag, M.; Sheikh, H.I.; Sarkar, T.; Edinur, H.A.; Pati, S.; Ray, R.R. Microbiologically-synthesized nanoparticles and their role in silencing the biofilm signaling cascade. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 636588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yako, Y.Y.; Madubedube, J.H.; Kengne, A.P.; Erasmus, R.T.; Pillay, T.S.; Matsha, T.E. Contribution of ENPP1, TCF7L2, and FTO polymorphisms to type 2 diabetes in mixed ancestry ethnic population of South Africa. Afr. Health Sci. 2015, 15, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.F.; Husain, F.M.; Zia, Q.; Ahmad, E.; Jamal, A.; Alaidarous, M.; Banawas, S.; Alam, M.M.; Alshehri, B.A.; Jameel, M. Anti-quorum sensing and anti-biofilm activity of zinc oxide nanospikes. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 32203–32215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilk, S.; Sağlam, N.; Özgen, M.; Korkusuz, F. Chitosan nanoparticles enhances the anti-quorum sensing activity of kaempferol. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 94, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, T.B.; Givskov, M. Quorum-sensing inhibitors as anti-pathogenic drugs. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 296, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, M.Y.; Ahmad, A. Non-Traditional Approaches to Combat Antimicrobial Drug Resistance; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wani, M.Y.; Malik, M.A.; Rather, I.A. Quorum sensing-mediated targeted delivery of antibiotics. In Non-Traditional Approaches to Combat Antimicrobial Drug Resistance; Wani, M.Y., Ahmad, A., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 249–269. [Google Scholar]
- Nolting, B. Linker technologies for antibody-drug conjugates. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1045, 71–100. [Google Scholar]
- Dal Corso, A.; Cazzamalli, S.; Gébleux, R.; Mattarella, M.; Neri, D. Protease-cleavable linkers modulate the anticancer activity of noninternalizing antibody-drug conjugates. Bioconj. Chem. 2017, 28, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisbal Lopez, L.; Ravazza, D.; Bocci, M.; Zana, A.; Principi, L.; Dakhel Plaza, S.; Galbiati, A.; Gilardoni, E.; Scheuermann, J.; Neri, D.; et al. Ex vivo mass spectrometry-based biodistribution analysis of an antibody-Resiquimod conjugate bearing a protease-cleavable and acid-labile linker. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1320524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brackman, G.; Cos, P.; Maes, L.; Nelis, H.J.; Coenye, T. Quorum sensing inhibitors increase the susceptibility of bacterial biofilms to antibiotics in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 2655–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Sun, H.; Yin, C.; Lin, Z. Combination of sulfonamides, silver antimicrobial agents and quorum sensing inhibitors as a preferred approach for improving antimicrobial efficacy against Bacillus subtilis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 181, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Romero, M.; Travanut, A.; Monteiro, P.F.; Jordana-Lluch, E.; Hardie, K.R.; Williams, P.; Alexander, M.R.; Alexander, C. Dual bioresponsive antibiotic and quorum sensing inhibitor combination nanoparticles for treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in vitro and ex vivo. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 4099–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K. A review of computational drug repurposing. Transl. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 27, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudrapal, M.; Khairnar, S.J.; Jadhav, A.G. Drug Repurposing (DR): An Emerging Approach in Drug Discovery; Intechopen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Konreddy, A.K.; Rani, G.U.; Lee, K.; Choi, Y. Recent Drug-Repurposing-Driven Advances in the Discovery of Novel Antibiotics. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 5363–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farha, M.A.; Brown, E.D. Drug repurposing for antimicrobial discovery. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.A.; Elsherbini, A.M.; Shaldam, M.A. Repurposing metformin as a quorum sensing inhibitor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Afr. Health Sci. 2017, 17, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, W.A.H.; Khayat, M.T.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Nassar, M.S.; Bakhrebah, M.A.; Abdulaal, W.H.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Bendary, M.M. Repurposing Anti-diabetic Drugs to Cripple Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayat, M.T.; Abbas, H.A.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Elbaramawi, S.S.; Khayyat, A.N.; Alharbi, M.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Yehia, F.A.A. Synergistic Benefits: Exploring the Anti-Virulence Effects of Metformin/Vildagliptin Antidiabetic Combination against Pseudomonas aeruginosa via Controlling Quorum Sensing Systems. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayat, M.T.; Abbas, H.A.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Khayyat, A.N.; Alharbi, M.; Darwish, K.M.; Elhady, S.S.; Khafagy, E.S.; Safo, M.K.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities of Gliptins against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho Sui, S.J.; Lo, R.; Fernandes, A.R.; Caulfield, M.D.; Lerman, J.A.; Xie, L.; Bourne, P.E.; Baillie, D.L.; Brinkman, F.S. Raloxifene attenuates Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyocyanin production and virulence. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 40, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imperi, F.; Massai, F.; Ramachandran Pillai, C.; Longo, F.; Zennaro, E.; Rampioni, G.; Visca, P.; Leoni, L. New life for an old drug: The anthelmintic drug niclosamide inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Bhatia, S. In silico identification of albendazole as a quorum sensing inhibitor and its in vitro verification using CviR and LasB receptors based assay systems. BioImpacts BI 2018, 8, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Kumar, A.; Ozkan, J.; Bandara, R.; Ding, A.; Perera, I.; Steinberg, P.; Kumar, N.; Lao, W.; Griesser, S.S.; et al. Fimbrolide-coated antimicrobial lenses: Their in vitro and in vivo effects. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2008, 85, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, A.R.; Cifelli, P.M.; Ortori, C.A.; Righetti, K.; Lewis, S.; Erskine, P.; Holland, E.D.; Givskov, M.; Williams, P.; Cámara, M.; et al. Garlic as an inhibitor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing in cystic fibrosis—A pilot randomized controlled trial. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2010, 45, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Delden, C.; Köhler, T.; Brunner-Ferber, F.; François, B.; Carlet, J.; Pechère, J.-C. Azithromycin to prevent Pseudomonas aeruginosa ventilator-associated pneumonia by inhibition of quorum sensing: A randomized controlled trial. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, J.; Mortensen, K.T.; Nørskov, A.; Qvortrup, K.; Yang, L.; Tan, C.H.; Nielsen, T.E.; Givskov, M. Itaconimides as Novel Quorum Sensing Inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
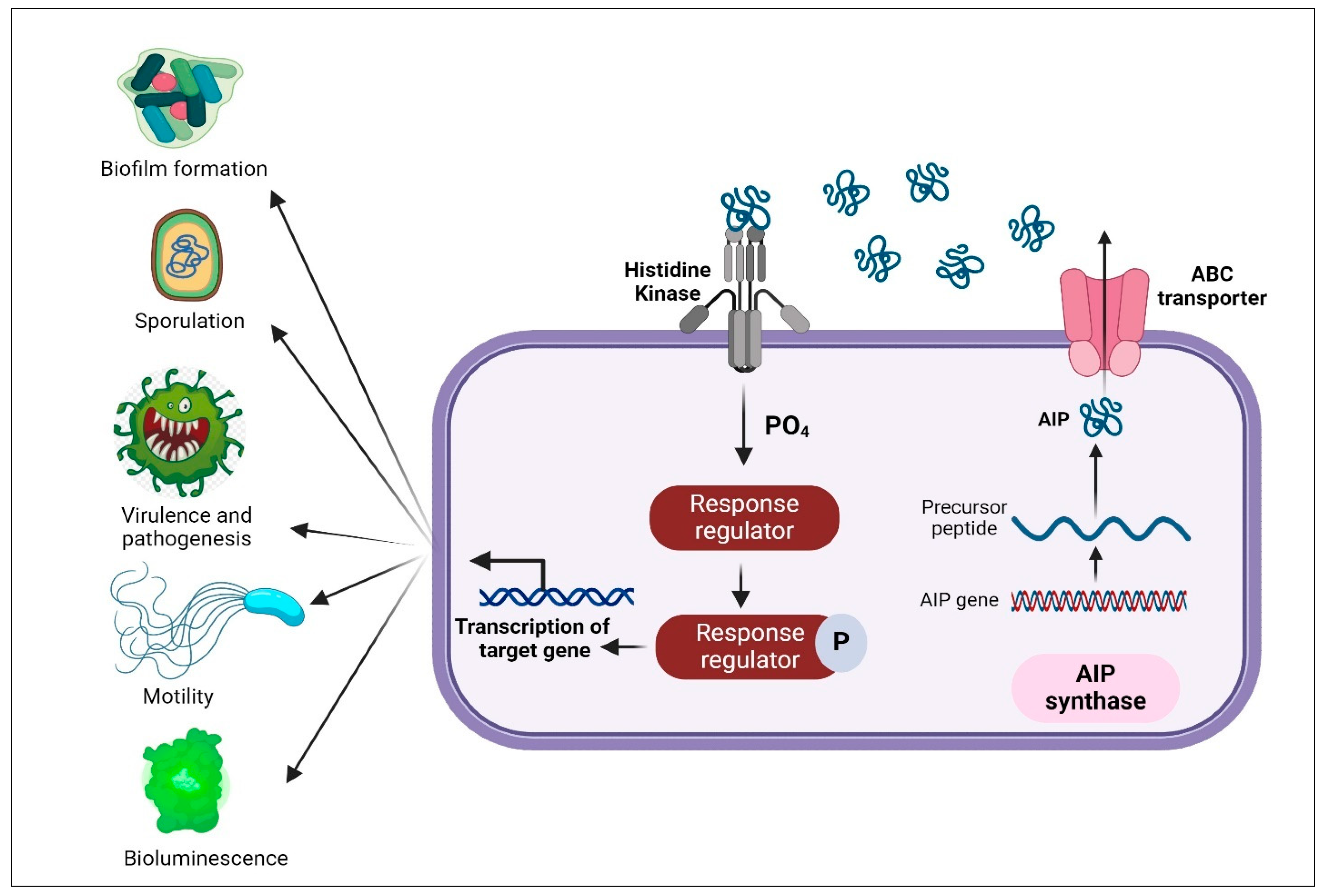
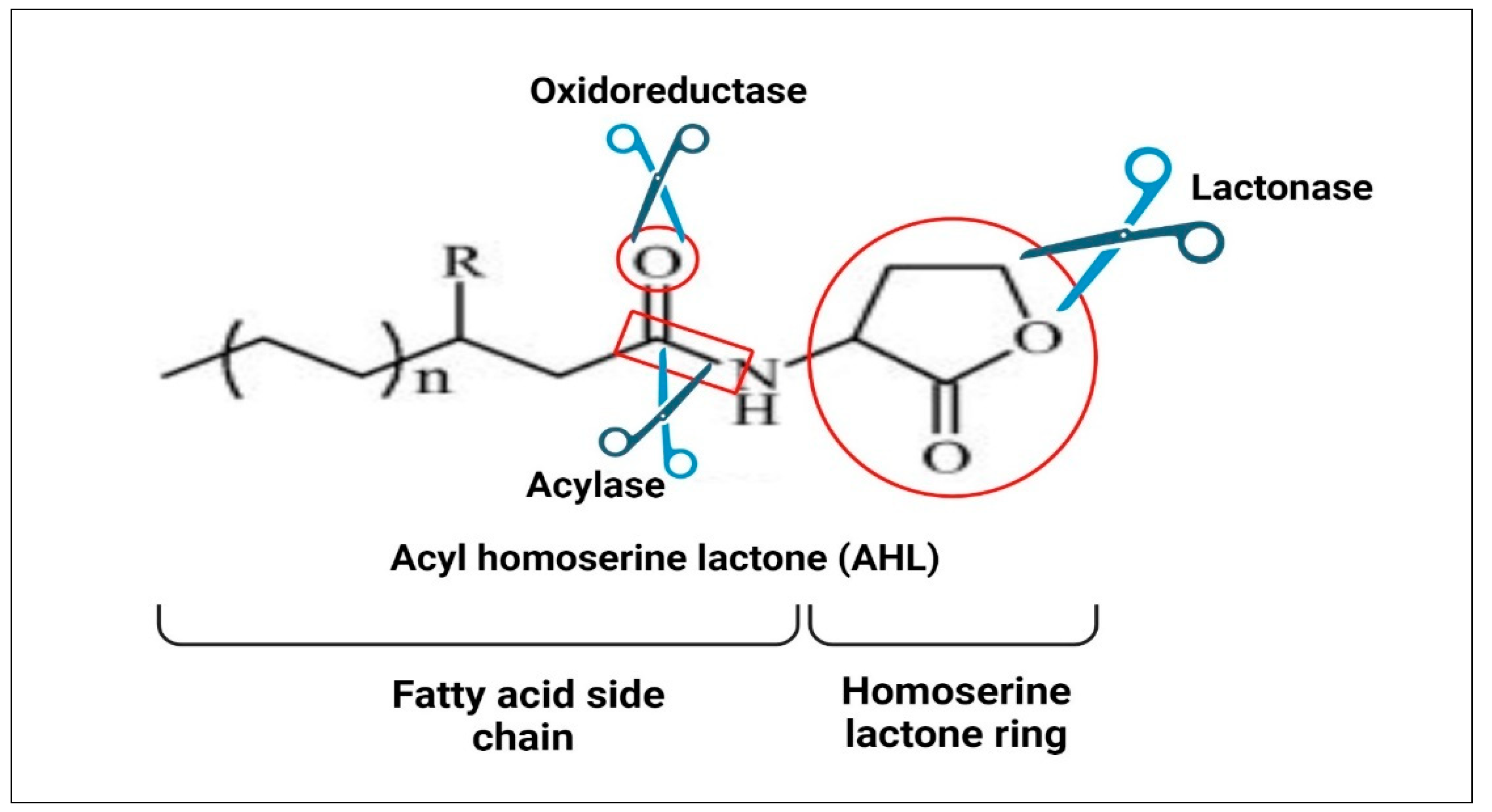

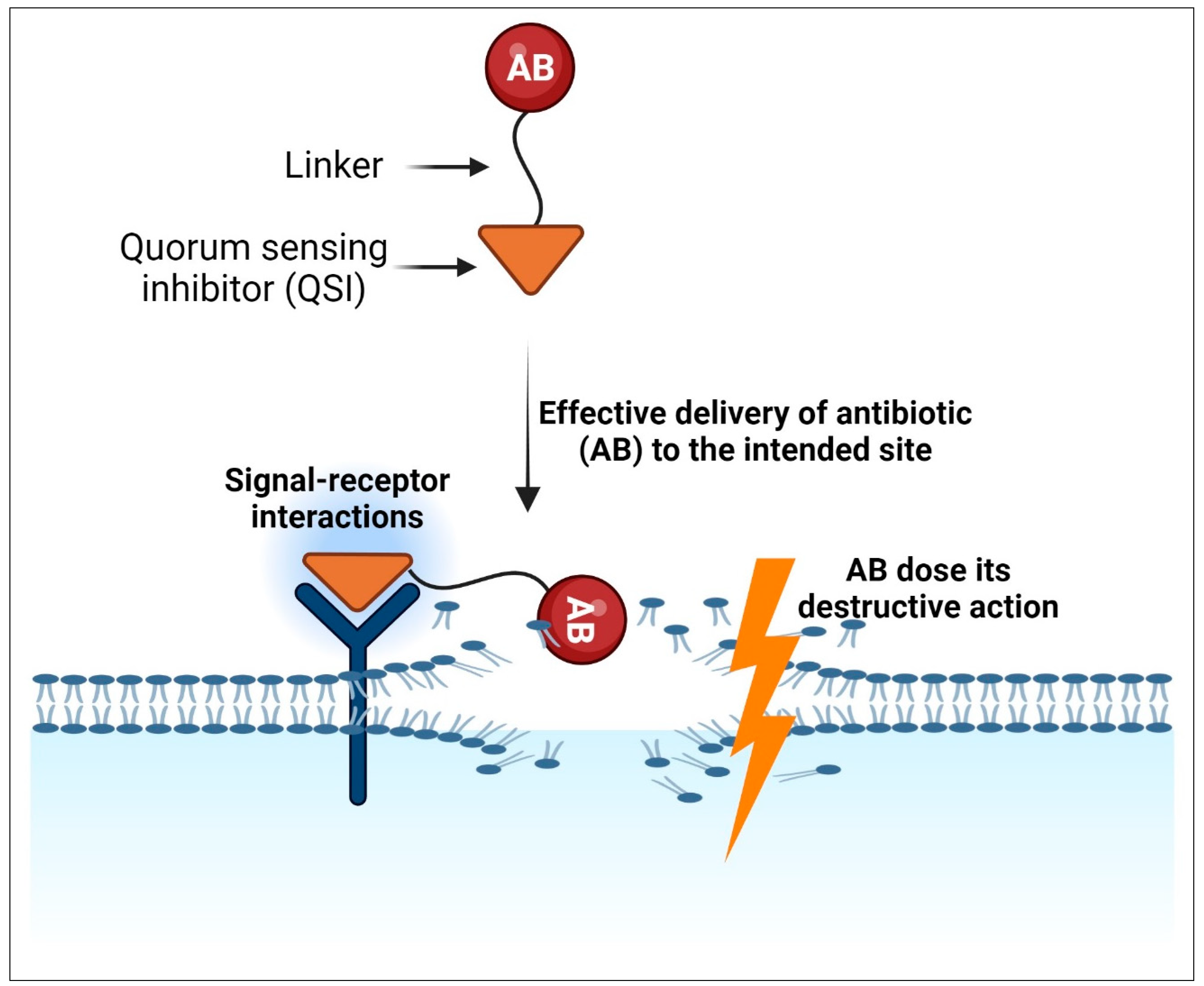
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hetta, H.F.; Ramadan, Y.N.; Rashed, Z.I.; Alharbi, A.A.; Alsharef, S.; Alkindy, T.T.; Alkhamali, A.; Albalawi, A.S.; Battah, B.; Donadu, M.G. Quorum Sensing Inhibitors: An Alternative Strategy to Win the Battle against Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) Bacteria. Molecules 2024, 29, 3466. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153466
Hetta HF, Ramadan YN, Rashed ZI, Alharbi AA, Alsharef S, Alkindy TT, Alkhamali A, Albalawi AS, Battah B, Donadu MG. Quorum Sensing Inhibitors: An Alternative Strategy to Win the Battle against Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) Bacteria. Molecules. 2024; 29(15):3466. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153466
Chicago/Turabian StyleHetta, Helal F., Yasmin N. Ramadan, Zainab I. Rashed, Ahmad A. Alharbi, Shomokh Alsharef, Tala T. Alkindy, Alanoud Alkhamali, Abdullah S. Albalawi, Basem Battah, and Matthew G. Donadu. 2024. "Quorum Sensing Inhibitors: An Alternative Strategy to Win the Battle against Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) Bacteria" Molecules 29, no. 15: 3466. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153466
APA StyleHetta, H. F., Ramadan, Y. N., Rashed, Z. I., Alharbi, A. A., Alsharef, S., Alkindy, T. T., Alkhamali, A., Albalawi, A. S., Battah, B., & Donadu, M. G. (2024). Quorum Sensing Inhibitors: An Alternative Strategy to Win the Battle against Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) Bacteria. Molecules, 29(15), 3466. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153466







