Expression Profiles of ITGA8 and VANGL2 Are Altered in Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract (CAKUT)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
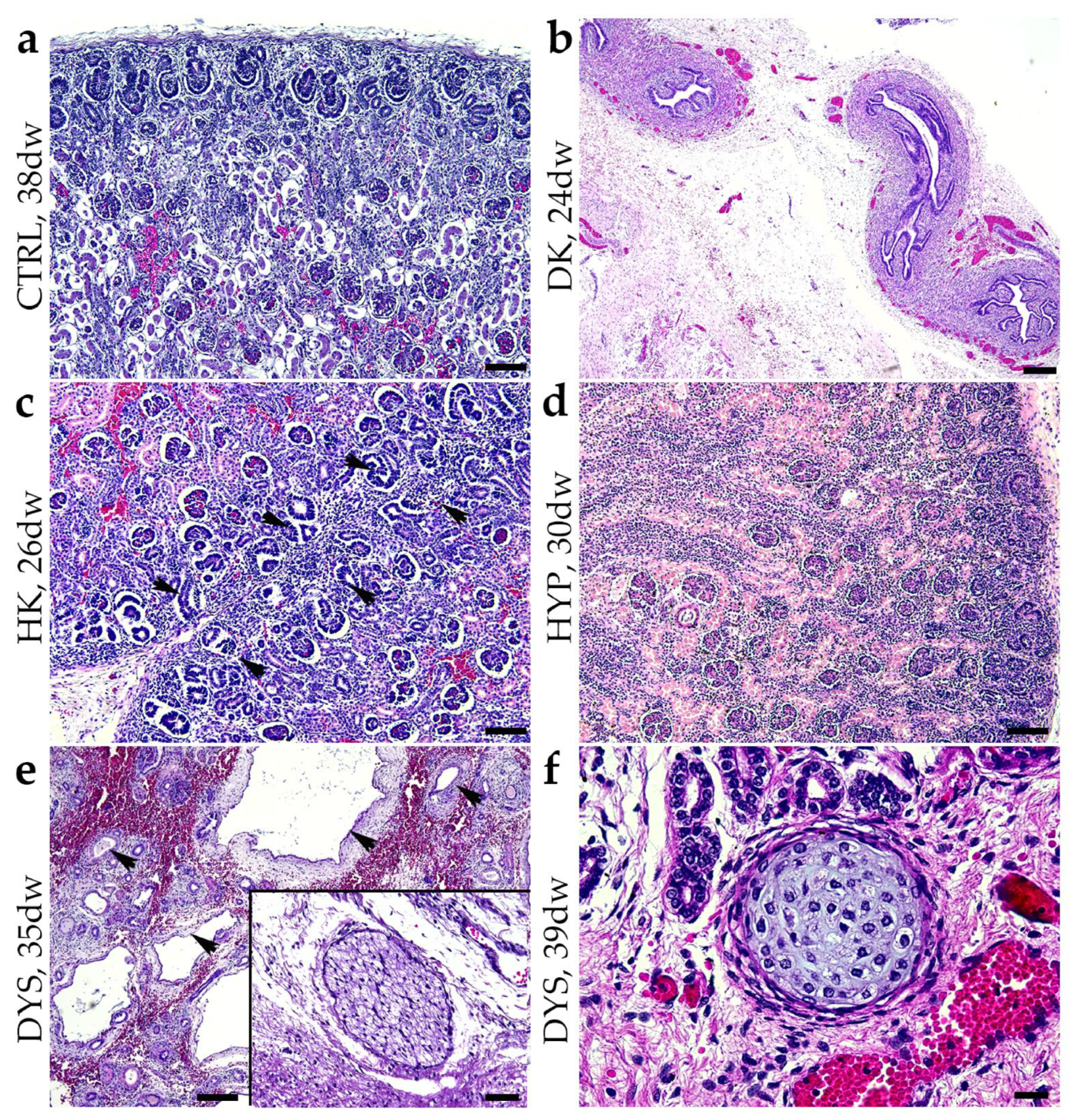
2.1. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining (H&E) of Normal Healthy Kidneys and CAKUT-Affected Kidneys
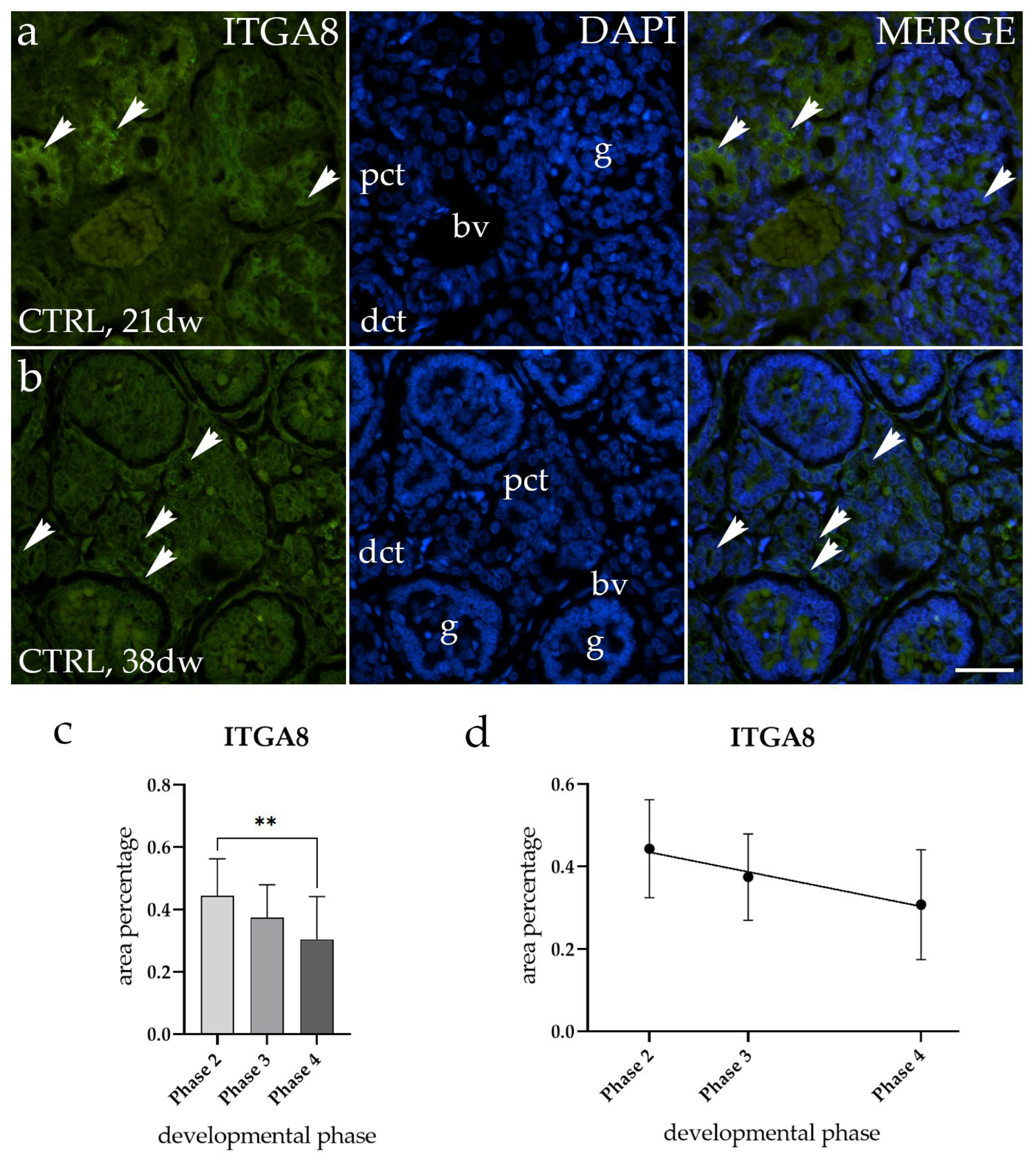
2.2. ITGA8 Expression Declines with Fetal Age in Normal Healthy Kidney
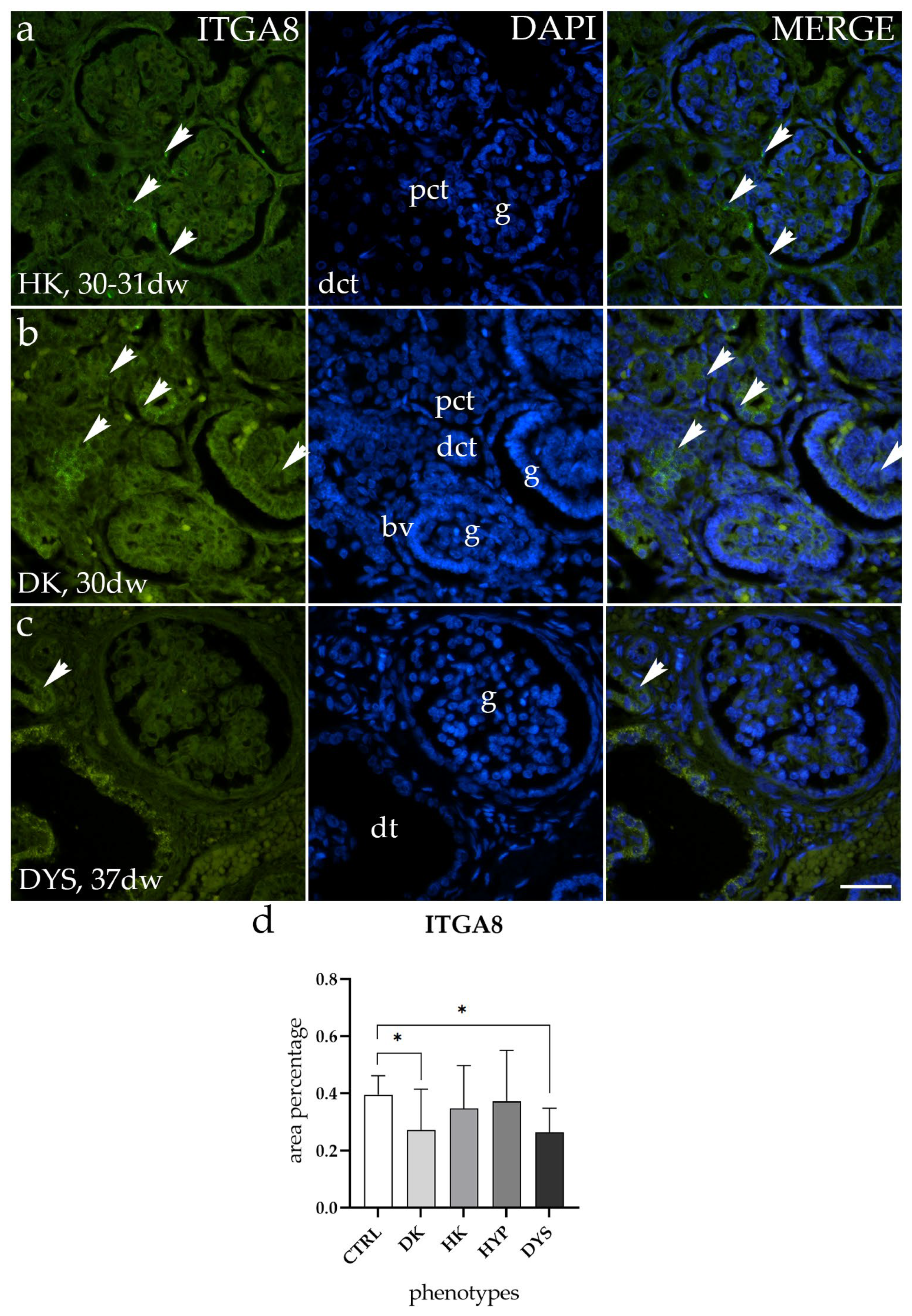
2.3. ITGA8 Expression Is Altered in DK and DYS
2.4. VANGL2 Shows Consistent Expression throughout All Stages of Normal Healthy Kidney Development
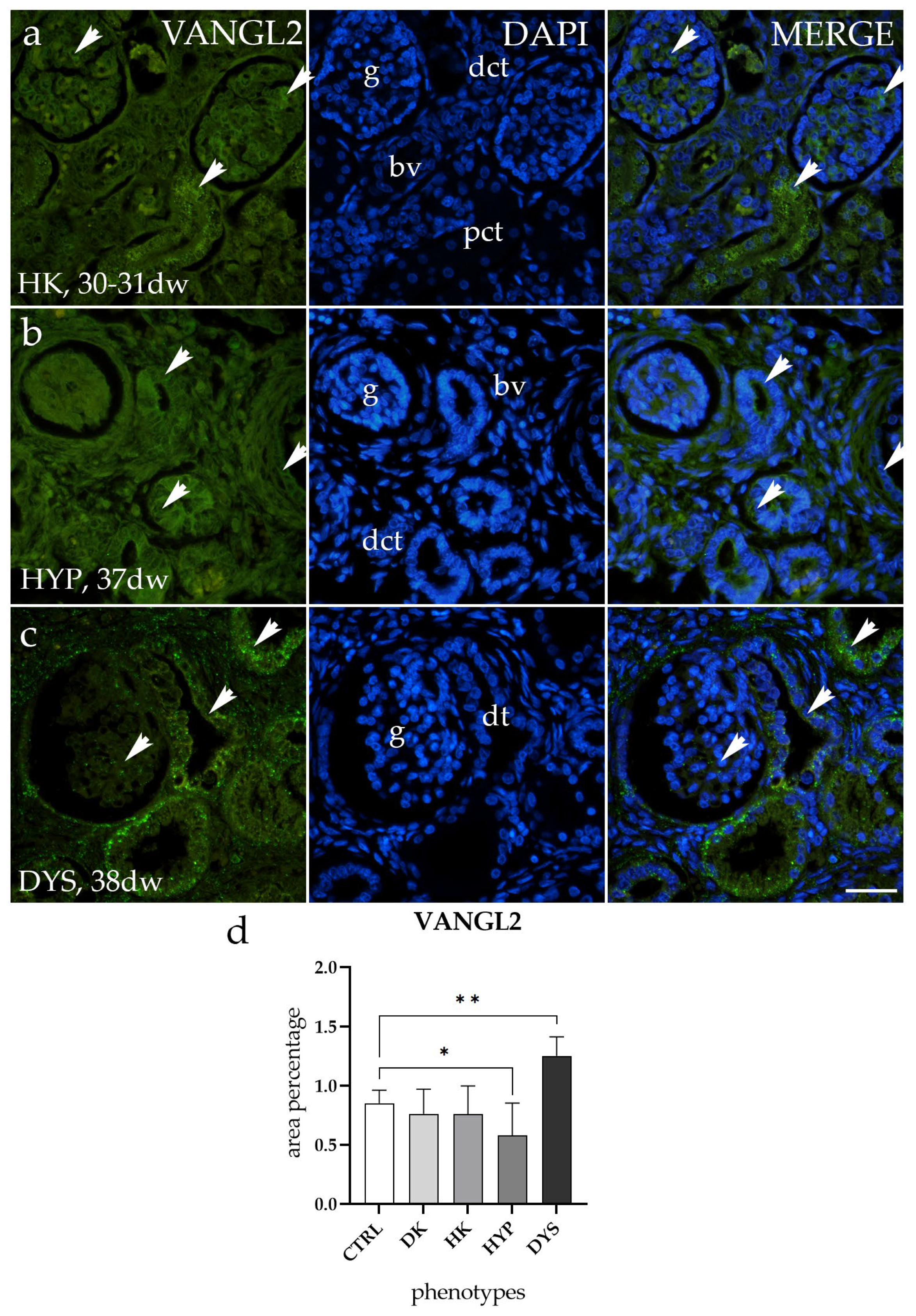
2.5. VANGL2 Expression Is Altered in HYP and DYS
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Fetal Kidney Tissue
4.2. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
4.3. Immunofluorescence (IF) on Postmortem Human Prenatal Renal Tissue
4.4. Data Collection & Image Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chan, K.; Li, X. Current Epigenetic Insights in Kidney Development. Genes 2021, 12, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelam, N.; Racetin, A.; Polovic, M.; Benzon, B.; Ogorevc, M.; Vukojevic, K.; Glavina Durdov, M.; Dunatov Huljev, A.; Kuzmic Prusac, I.; Caric, D.; et al. Aberrations in FGFR1, FGFR2, and RIP5 Expression in Human Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract (CAKUT). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virth, J.; Mack, H.G.; Colville, D.; Crockett, E.; Savige, J. Ocular manifestations of congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract (CAKUT). Pediatr. Nephrol. 2024, 39, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolvenbach, C.M.; Shril, S.; Hildebrandt, F. The genetics and pathogenesis of CAKUT. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, S.; Habbig, S.; Weber, L.T.; Liebau, M.C. Molecular causes of congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract (CAKUT). Mol. Cell. Pediatr. 2021, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaou, N.; Renkema, K.Y.; Bongers, E.M.; Giles, R.H.; Knoers, N.V. Genetic, environmental, and epigenetic factors involved in CAKUT. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 720–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derish, I.; Lee, J.K.H.; Wong-King-Cheong, M.; Babayeva, S.; Caplan, J.; Leung, V.; Shahinian, C.; Gravel, M.; Deans, M.R.; Gros, P.; et al. Differential role of planar cell polarity gene Vangl2 in embryonic and adult mammalian kidneys. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, S.; Ahmed, D. Embryology, Kidney, Bladder, and Ureter. In StatPearls; Ineligible Companies. Disclosure: Danish Ahmed Declares no Relevant Financial Relationships with Ineligible Companies; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Little, M.H.; Brennan, J.; Georgas, K.; Davies, J.A.; Davidson, D.R.; Baldock, R.A.; Beverdam, A.; Bertram, J.F.; Capel, B.; Chiu, H.S.; et al. A high-resolution anatomical ontology of the developing murine genitourinary tract. Gene Expr. Patterns GEP 2007, 7, 680–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekblom, P. Renal development. In Kidney Physiology and Pathophysiology; Seldin, D.W., Giebisch, G., Eds.; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 475–501. [Google Scholar]
- Talati, A.N.; Webster, C.M.; Vora, N.L. Prenatal genetic considerations of congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract (CAKUT). Prenat. Diagn. 2019, 39, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozic, M.; Minarik, L.; Racetin, A.; Filipovic, N.; Saraga Babic, M.; Vukojevic, K. CRKL, AIFM3, AIF, BCL2, and UBASH3A during Human Kidney Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartner, A.; Dotsch, J. Lessons in congenital and acquired renal disease from alpha8 integrin mutant mice. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2002, 17, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, U.; Bossy, B.; Venstrom, K.; Reichardt, L.F. Integrin alpha 8 beta 1 promotes attachment, cell spreading, and neurite outgrowth on fibronectin. Mol. Biol. Cell 1995, 6, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schedl, A. Renal abnormalities and their developmental origin. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marek, I.; Hilgers, K.F.; Rascher, W.; Woelfle, J.; Hartner, A. A role for the alpha-8 integrin chain (itga8) in glomerular homeostasis of the kidney. Mol. Cell. Pediatr. 2020, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, C.; Silbermann, F.; Morar, B.; Parisot, M.; Zarhrate, M.; Masson, C.; Tores, F.; Blanchet, P.; Perez, M.J.; Petrov, Y.; et al. Integrin alpha 8 recessive mutations are responsible for bilateral renal agenesis in humans. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 94, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Song, H.; Bishop, K.; Elliot, G.; Garrett, L.; English, M.A.; Andre, P.; Robinson, J.; Sood, R.; Minami, Y.; et al. Wnt signaling gradients establish planar cell polarity by inducing Vangl2 phosphorylation through Ror2. Dev. Cell 2011, 20, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, I.; Wei, A.; Awamleh, Z.; Singh, M.; Ning, A.; Herrera, A.; Russell, B.E.; Weksberg, R.; Arboleda, V.A. Multiomics of Bohring-Opitz syndrome truncating ASXL1 mutations identify canonical and noncanonical Wnt signaling dysregulation. JCI Insight 2023, 8, 167744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Lu, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; Zeng, K.; et al. VANGL2 inhibits antiviral IFN-I signaling by targeting TBK1 for autophagic degradation. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna-Cherchi, S.; Westland, R.; Ghiggeri, G.M.; Gharavi, A.G. Genetic basis of human congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnapp, L.M.; Breuss, J.M.; Ramos, D.M.; Sheppard, D.; Pytela, R. Sequence and tissue distribution of the human integrin alpha 8 subunit: A beta 1-associated alpha subunit expressed in smooth muscle cells. J. Cell Sci. 1995, 108, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Conde, S.; Dunand, O.; Hummel, A.; Moriniere, V.; Gauthier, M.; Mesnard, L.; Heidet, L. Bi-allelic pathogenic variants in ITGA8 cause slowly progressive renal disease of unknown etiology. Clin. Genet. 2023, 103, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, U.; Wang, D.; Denda, S.; Meneses, J.J.; Pedersen, R.A.; Reichardt, L.F. Integrin alpha8beta1 is critically important for epithelial-mesenchymal interactions during kidney morphogenesis. Cell 1997, 88, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linton, J.M.; Martin, G.R.; Reichardt, L.F. The ECM protein nephronectin promotes kidney development via integrin alpha8beta1-mediated stimulation of Gdnf expression. Development 2007, 134, 2501–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babayeva, S.; Rocque, B.; Aoudjit, L.; Zilber, Y.; Li, J.; Baldwin, C.; Kawachi, H.; Takano, T.; Torban, E. Planar cell polarity pathway regulates nephrin endocytosis in developing podocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 24035–24048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, L.L.; Papakrivopoulou, J.; Long, D.A.; Goggolidou, P.; Connolly, J.O.; Woolf, A.S.; Dean, C.H. The planar cell polarity gene Vangl2 is required for mammalian kidney-branching morphogenesis and glomerular maturation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 4663–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.P.; Zhang, T.; Li, H.; Wu, B.L.; Jin, L.; Wang, H.Y. VANGL2 mutations in human cranial neural-tube defects. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2232–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papakrivopoulou, E.; Vasilopoulou, E.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Pacheco, S.; Brzoska, H.L.; Price, K.L.; Kolatsi-Joannou, M.; White, K.E.; Henderson, D.J.; Dean, C.H.; et al. Vangl2, a planar cell polarity molecule, is implicated in irreversible and reversible kidney glomerular injury. J. Pathol. 2018, 246, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puvirajesinghe, T.M.; Bertucci, F.; Jain, A.; Scerbo, P.; Belotti, E.; Audebert, S.; Sebbagh, M.; Lopez, M.; Brech, A.; Finetti, P.; et al. Identification of p62/SQSTM1 as a component of non-canonical Wnt VANGL2-JNK signalling in breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzoska, H.L.; d’Esposito, A.M.; Kolatsi-Joannou, M.; Patel, V.; Igarashi, P.; Lei, Y.; Finnell, R.H.; Lythgoe, M.F.; Woolf, A.S.; Papakrivopoulou, E.; et al. Planar cell polarity genes Celsr1 and Vangl2 are necessary for kidney growth, differentiation, and rostrocaudal patterning. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelam, J.; Kelam, N.; Filipovic, N.; Komic, L.; Racetin, A.; Komic, D.; Kostic, S.; Kuzmic Prusac, I.; Vukojevic, K. Expression of Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract (CAKUT) Candidate Genes EDA2R, PCDH9, and TRAF7 in Normal Human Kidney Development and CAKUT. Genes 2024, 15, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosin, M.; Kelam, N.; Juric, I.; Racetin, A.; Ogorevc, M.; Corre, B.; Caric, D.; Filipovic, N.; Vukojevic, K. Syndecans, Exostosins and Sulfotransferases as Potential Synovial Inflammation Moderators in Patients with Hip Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicchetti, D. Guidlines, Criteria, and Rules of Thumb for Evaluating Normed and Standardized Assessment Instrument in Psychology. Psychol. Assess. 1994, 6, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Groups | Developmental Phase | Renal and Associated Pathology | Gestational Week | Number of Kidney Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy kidney (CTRL) | Phase 2 | N/A | 15 | 1 |
| N/A | 16 | 1 | ||
| N/A | 17 | 1 | ||
| N/A | 18 | 2 | ||
| N/A | 21 | 1 | ||
| Phase 3 | N/A | 23 | 2 | |
| N/A | 28 | 3 | ||
| N/A | 29 | 1 | ||
| N/A | 32 | 1 | ||
| N/A | 35 | 1 | ||
| Phase 4 | N/A | 37 | 1 | |
| N/A | 38 | 1 | ||
| Horseshoe kidney (HK) | Ren concreatus arcuatus, cystae multiplices corticales | 22 | 1 | |
| Ren concreatus arcuatus, tetras Fallot | 26 | 1 | ||
| Syndroma Edwards, Ren arcuatus | 30–31 | 1 | ||
| Syndroma Edwards, Ren arcuatus | 34 | 1 | ||
| Dysplastic kidneys (DYS) | Megaureter lateris dextri, Dysplasia renis | 21 | 1 | |
| Dysplasia multicystica renis dextri | 27 | 1 | ||
| Cystes parvae focales | ||||
| Renes dysplastici cystici, Syndroma Potter | 35 | 1 | ||
| Agenesis renis dextri et dysplasia renis sinistri cum ureter duplex | 37 | 1 | ||
| Dysplasia hypoplastica, renis bilateralis, syndroma Down, syndroma Potter | 38 | 1 | ||
| Hypoplastic kidneys (HYP) | Hypoplasia renis lateris sinistri | 37 | 1 | |
| Hypoplasia renis | 38 | 1 | ||
| Duplex kidneys (DKs) | Ureter duplex lateris dextri | 24 | 1 | |
| Ureter duplex lateris sinistri | 30 | 1 | ||
| Pyelon et ureter duplex bilateralis | 41 | 1 | ||
| Antibodies | Catalog Number | Host | Dilution | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | Anti-ITGA8 antibody | AMAb91468 | Mouse | 1:200 | Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) |
| Anti-VANGL2 antibody | AF4815 | Sheep | 1:50 | R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN, USA) | |
| Secondary | Anti-Mouse IgG, Alexa Fluor® 488 | 711-545-150 | Donkey | 1:300 | Jackson Immuno Research Laboratories, Inc. (Baltimore, PA, USA) |
| Anti-Goat IgG (H + L), Alexa Fluor® 488 | 705-545-003 | Donkey | 1:300 | Jackson Immuno Research Laboratories, Inc. (Baltimore, PA, USA) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pavlović, N.; Kelam, N.; Racetin, A.; Filipović, N.; Pogorelić, Z.; Prusac, I.K.; Vukojević, K. Expression Profiles of ITGA8 and VANGL2 Are Altered in Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract (CAKUT). Molecules 2024, 29, 3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143294
Pavlović N, Kelam N, Racetin A, Filipović N, Pogorelić Z, Prusac IK, Vukojević K. Expression Profiles of ITGA8 and VANGL2 Are Altered in Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract (CAKUT). Molecules. 2024; 29(14):3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143294
Chicago/Turabian StylePavlović, Nikola, Nela Kelam, Anita Racetin, Natalija Filipović, Zenon Pogorelić, Ivana Kuzmić Prusac, and Katarina Vukojević. 2024. "Expression Profiles of ITGA8 and VANGL2 Are Altered in Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract (CAKUT)" Molecules 29, no. 14: 3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143294
APA StylePavlović, N., Kelam, N., Racetin, A., Filipović, N., Pogorelić, Z., Prusac, I. K., & Vukojević, K. (2024). Expression Profiles of ITGA8 and VANGL2 Are Altered in Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract (CAKUT). Molecules, 29(14), 3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143294









