A Comprehensive Analysis of Fel Ursi and Its Common Adulterants Based on UHPLC-QTOF-MSE and Chemometrics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
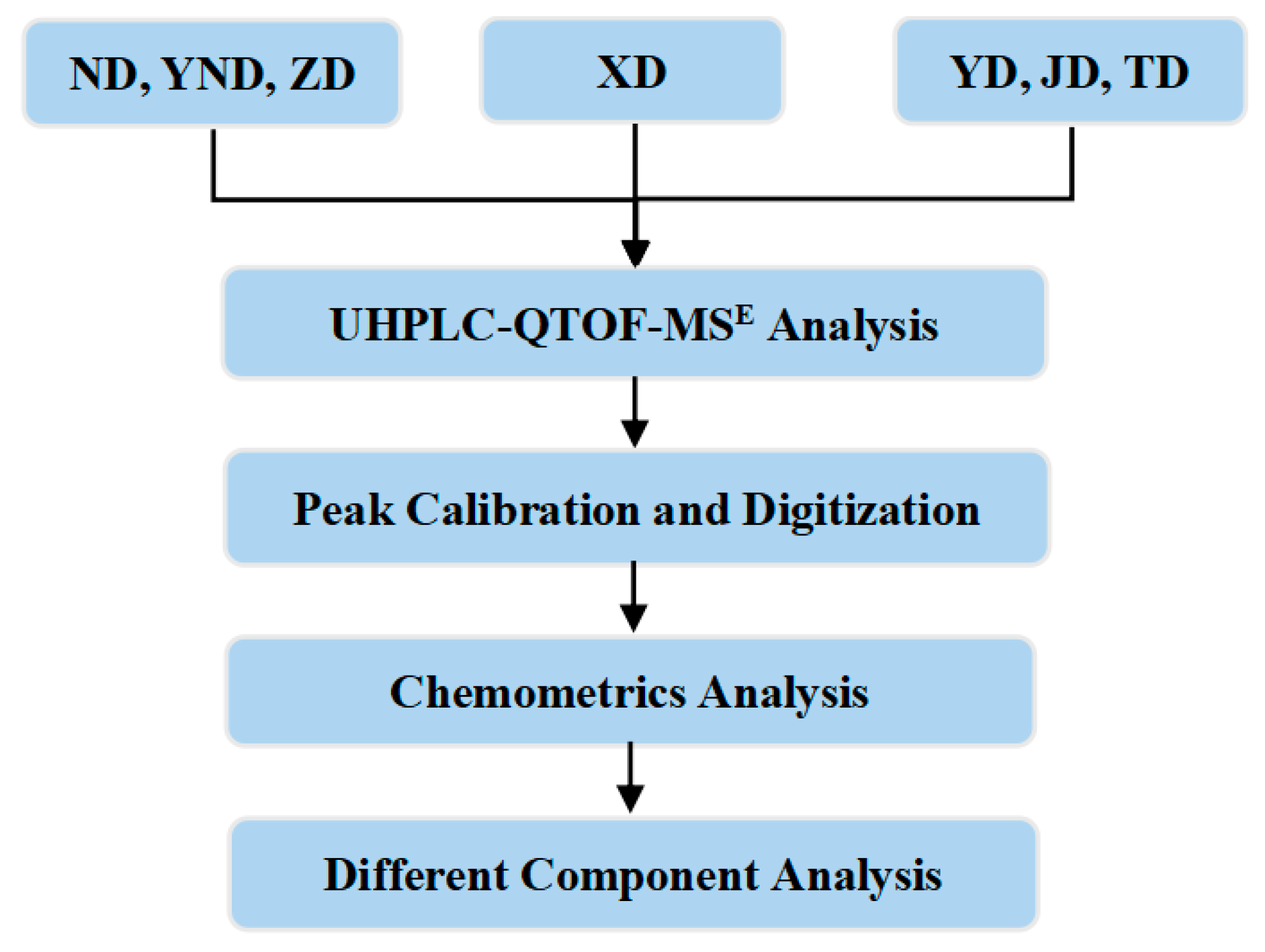
2.1. UHPLC-QTOF-MSE Analysis
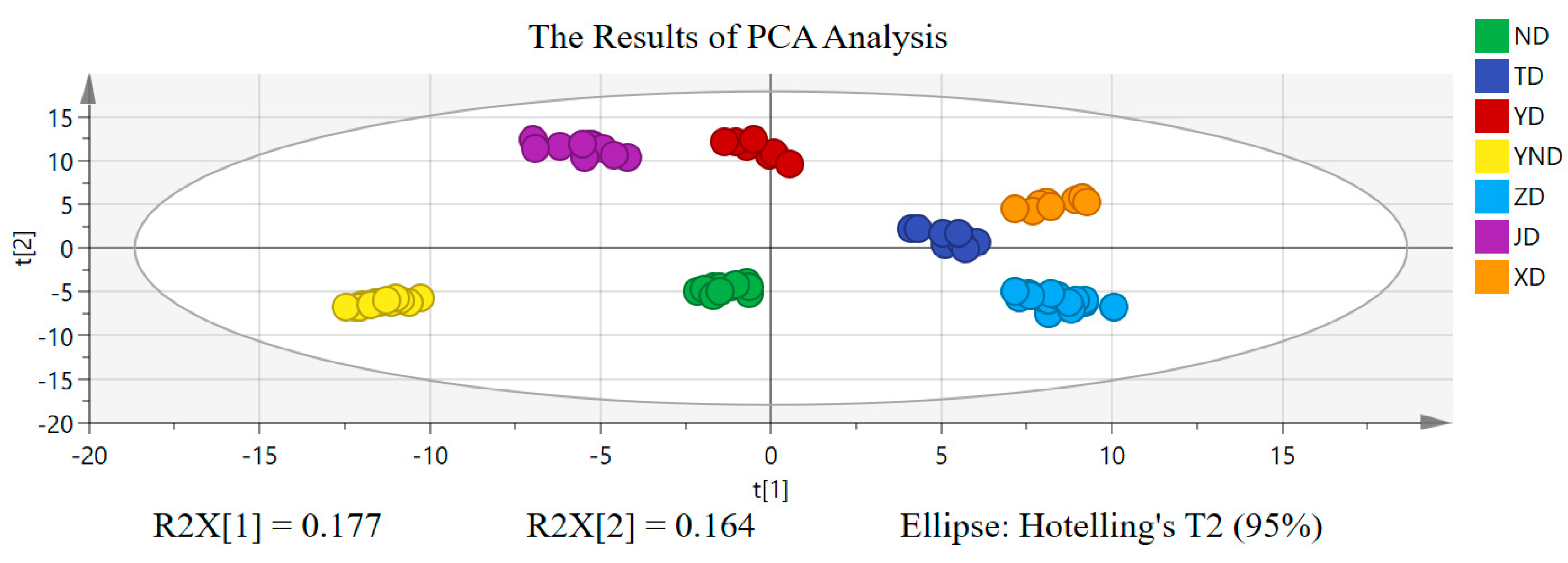
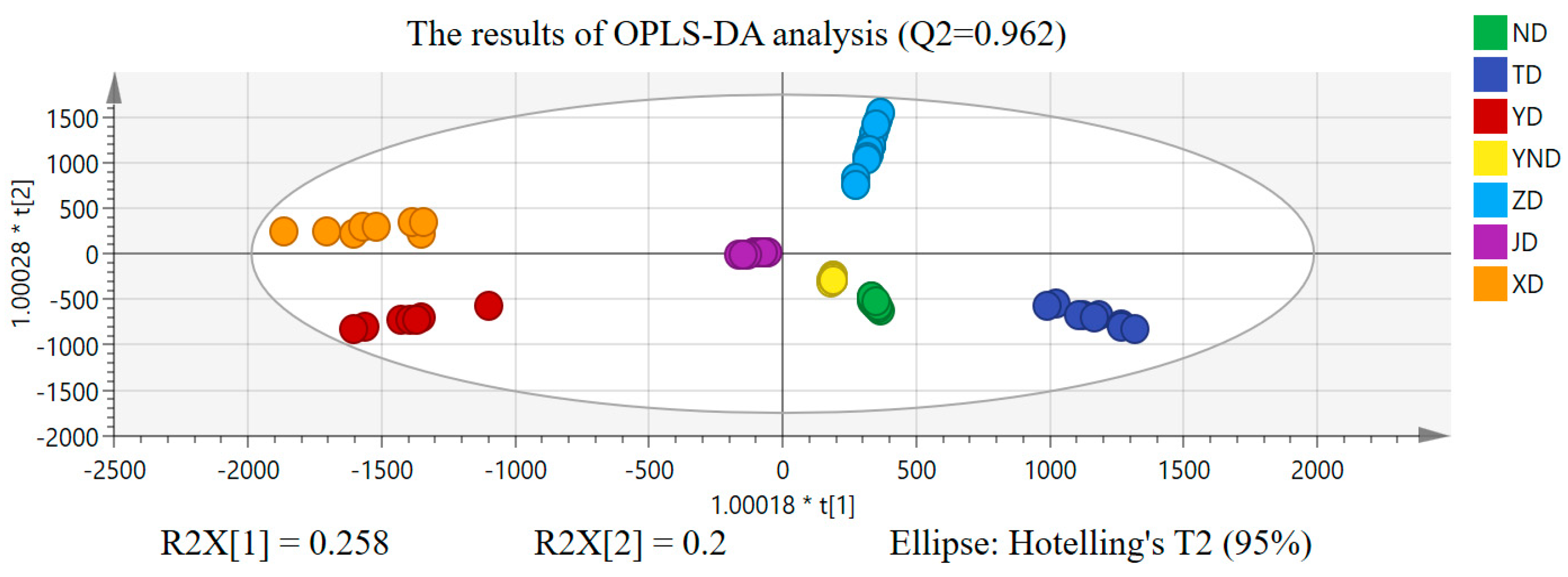
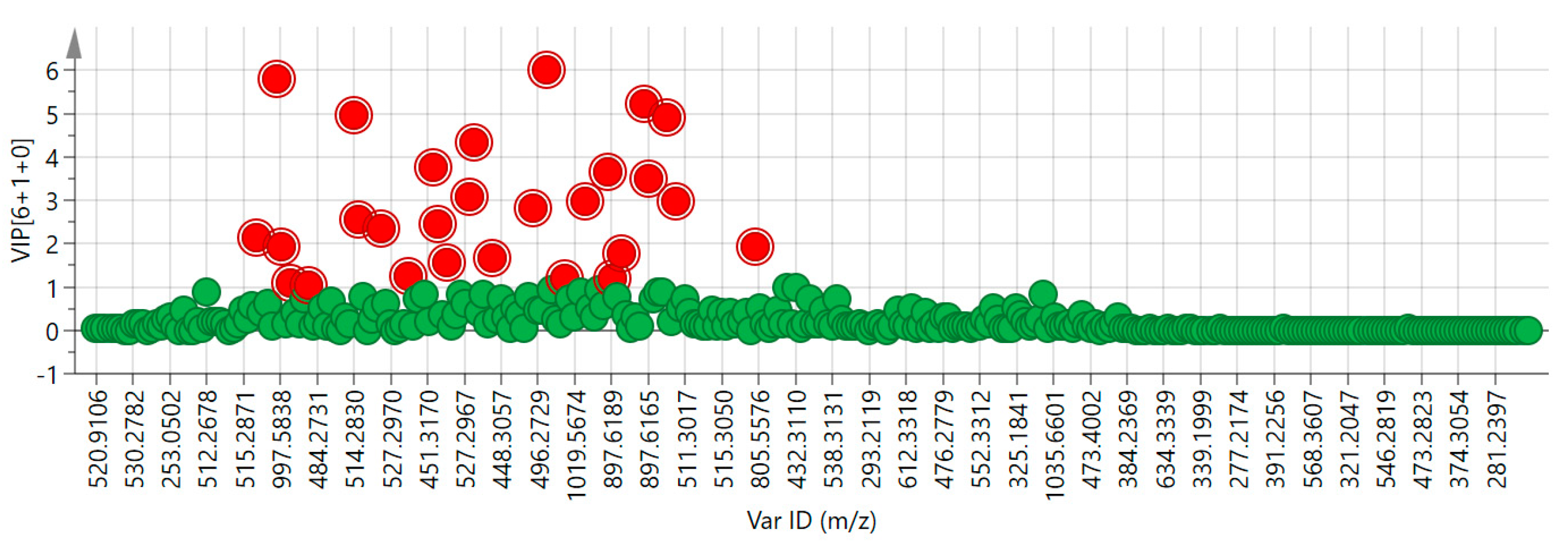
2.2. Chemometric Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Herbal Materials and Chemical Reference Substances
4.2. Reagent Materials
4.3. Sample Pretreatment and UHPLC-QTOF-MSE Analysis
4.4. Data Processing and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.Y.; Su, F.F.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, F.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, G. Development history and prospect of Fel Urs. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2022, 47, 4284–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Qian, Z.Z.; Nohara, T. Bile acids of Fel Ursi. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 46, 1653–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.W.; Zhu, X.Y.; But, P.P.; Yeung, H.W. Ethnopharmacology of bear gall bladder: I. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1995, 23, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.W.; Hwang, J.H. Anticancer Effects of Ursi Fel Extract and Its Active Compound, Ursodeoxycholic Acid, in FRO Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.L.; Chang, H.C.; Chang, C.P.; Chen, C.Y. Identification and differentiation of bear bile used in medicinal products in Taiwan. J. Forensic Sci. 1997, 42, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.L.; Xing, L.H.; Xue, D.S.; Qu, H.B. An authentication method of bear bile powder based on the near infrared spectroscopy. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen. Xi 2011, 31, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.Z.; Zhao, C.Z.; Peng, X.F.; Yang, J.C. Study on qualitation and quantitation method of Xiongdan pills. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2012, 32, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Zheng, T.J.; Shi, Y.; Wei, F.; Ma, S.C.; He, L.; Wang, S.C.; Liu, X.S. Analysis of the fingerprint profile of bioactive constituents of traditional Chinese medicinal materials derived from animal bile using the HPLC-ELSD and chemometric methods: An application of a reference scaleplate. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 10, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Yuan, M.; Li, S.; Zhou, Q.; Li, M.; Zeng, D.; Guo, Y.; Guo, L. Performance evaluation of E-nose and E-tongue combined with machine learning for qualitative and quantitative assessment of bear bile powder. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 3503–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Ye, M.; Pan, D.L.; Miao, W.J.; Xiang, C.; Han, J.; Guo, D.A. Differentiation of various traditional Chinese medicines derived from animal bile and gallstone: Simultaneous determination of bile acids by liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahetjan, Y.; Muhaxi, M.; Pang, K.; Kizaibek, M.; Tang, H.; Sefidkon, F.; Yang, X. Chemistry, Bioactivity, and Prediction of the Quality Marker (Q-Marker) of Ferula Plants in China: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, S.; Zeng, J.; Cai, R.; Liang, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, B.; Li, C. Database-aided UHPLC-Q-orbitrap MS/MS strategy putatively identifies 52 compounds from Wushicha Granule to propose anti-counterfeiting quality-markers for pharmacopoeia. Chin. Med. 2023, 18, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Gao, R.; Wang, F.; Shan, G.; Gao, H. Identification of Chemical Constituents in Zhizhu Pills Based on UPLC-QTOF-MSE. J. AOAC Int. 2022, 105, 1555–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; Li, S.; Yao, S.; Qi, P.; Yang, Z.; Feng, Z.; Hou, J.; Cai, L.; Yang, M.; et al. An intelligentized strategy for endogenous small molecules characterization and quality evaluation of earthworm from two geographic origins by ultra-high performance HILIC/QTOF MS(E) and Progenesis QI. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 3881–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Salem, K.; Ben Abdelaziz, A. Principal Component Analysis (PCA). Tunis Med. 2021, 99, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, K.; Liang, T.; Liu, Q.; Yan, J.; Yang, Y.; Qiao, K.; Ma, S.; Wang, D. Comparative Analysis of Acanthopanacis Cortex and Periplocae Cortex Using an Electronic Nose and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Coupled with Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Molecules 2022, 27, 8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Shu, Y.; Xu, Y. Metabolomics analyses of traditional Chinese medicine formula Shuang Huang Lian by UHPLC-QTOF-MS/MS. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Cao, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Lai, X.; Sun, L.; Chen, R.; Wen, S.; Sun, S.; Lai, Z. HS-SPME and GC/MS volatile component analysis of Yinghong No. 9 dark tea during the pile fermentation process. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, M.; Hellman, U.; Wixner, J.; Anan, I. Metabolomics analysis for diagnosis and biomarker discovery of transthyretin amyloidosis. Amyloid 2021, 28, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Wang, H.; Lan, Y.; Miao, J.; Pan, C.; Sun, W.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Blood biomarkers of post-stroke depression after minor stroke at three months in males and females. BMC Psychiatry 2022, 22, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.X.; Xiao, Z.J.; Yang, X.X.; Guan, Y.L.; Qu, W.H.; Ma, C.H. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of major cholic acids in Suis Fellis Pulvis. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2019, 44, 1842–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Guo, A.; Oler, E. HMDB 5.0: The Human Metabolome Database for 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D622–D631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Lin, S.; Xu, W.; Huang, M.; Chu, J.; Xiao, F.; Lin, J.; Peng, J. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of the Major Constituents in Shexiang Tongxin Dropping Pill by HPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS and UPLC-QqQ-MS/MS. Molecules 2015, 20, 18597–18619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Wu, H.; Yu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, L.; Li, Z. Rapid identification of chemical components in Qi-Yu-San-Long decoction by ultra high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Se Pu 2021, 39, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, J.D.; Richardson, S.J.; Moghaddam, M.F. Implementation of a novel ultra fast metabolic stability analysis method using exact mass TOF-MS. Bioanalysis 2017, 9, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.H. Principal component analysis of hybrid functional and vector data. Stat. Med. 2021, 40, 5152–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Qi, J.; Zhao, W.; Gu, J.; Guo, W.; Li, Y. Screening of specific quantitative peptides of beef by LC-MS/MS coupled with OPLS-DA. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Xu, F.; Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Huang, S.; Sheng, Y.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Establishment of Male and Female Eucommia Fingerprints by UPLC Combined with OPLS-DA Model and Its Application. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202201054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Chen, Z.; Guan, Z.; Zhao, C.; Cui, H.; Shang, H. Variable importance for projection (VIP) scores for analyzing the contribution of risk factors in severe adverse events to Xiyanping injection. Chin. Med. 2023, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Compositions | Ions | Abbreviation | Compositions | Ions | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tauroursodeoxycholic acid | 8.71 min_m/z 498.29 | TUDCA | Taurocholic acid | 11.08 min_m/z 514.28 | TCA |
| Taurohyodeoxycholic acid | 9.54 min_m/z 498.30 | THDCA | Glycocholic acid | 15.52 min_m/z 464.30 | GCA |
| Glycoursodeoxycholic acid | 12.73 min_m/z 498.30 | GUDCA | Taurodeoxycholic acid | 19.78 min_m/z 498.29 | TDCA |
| Glycohyodeoxycholic acid | 14.07 min_m/z 448.30 | GHDCA | Ursodeoxycholic acid | 21.81 min_m/z 437.30 | UDCA |
| Taurochenodeoxycholic acid | 16.90 min_m/z 498.29 | TCDCA | Hyodeoxycholic acid | 26.72 min_m/z 437.29 | HDCA |
| Glycochenodeoxycholic acid | 26.94 min_m/z 448.30 | GCDCA | Cholic acid | 27.33 min_m/z 407.30 | CA |
| Glycodeoxycholic acid | 30.14 min_m/z 448.30 | GDCA | Taurolithocholic acid | 31.56 min_m/z 482.29 | TLCA |
| Chenodeoxycholic acid | 34.57 min_m/z 448.30 | CDCA | Deoxycholic acid | 35.05 min_m/z 391.28 | DCA |
| Lithocholic acid | 37.67 min_m/z 448.30 | LCA | — | — | — |
| Ions/Neutral Mass | VIP | Ions/Neutral Mass | VIP |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16.94_498.2881 m/z | 6.00 | 14.12_897.6177 m/z | 2.45 |
| 8.73_498.2887 m/z | 5.82 | 11.75_464.3007 m/z | 2.34 |
| 29.63_448.3053 m/z | 5.23 | 8.46_997.5836 m/z | 2.13 |
| 11.02_514.2830 m/z | 4.98 | 8.73_997.5838 m/z | 1.92 |
| 30.22_448.3058 m/z | 4.92 | 34.60_437.2897 m/z | 1.91 |
| 15.48_464.3006 m/z | 4.33 | 27.28_407.2764 m/z | 1.79 |
| 14.12_448.3053 m/z | 3.76 | 15.73_496.2733 m/z | 1.66 |
| 27.17_448.3059 m/z | 3.64 | 15.06_446.2897 m/z | 1.57 |
| 29.64_897.6165 m/z | 3.52 | 13.75_446.2899 m/z | 1.25 |
| 15.48_929.6074 m/z | 3.07 | 18.82_555.3085 m/z | 1.22 |
| 19.55_498.2885 m/z | 2.96 | 27.20_897.6189 m/z | 1.19 |
| 30.25_897.6189 m/z | 2.96 | 9.11_462.2856 m/z | 1.10 |
| 16.82_997.5822 m/z | 2.79 | 9.79_448.3058 m/z | 1.04 |
| 11.02_1029.5717 m/z | 2.55 | — | — |
| Compositions | Molecular Formula | Ions/Neutral Mass | Ionic Forms | VIP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taurochenodeoxycholic acid | C26H45NO6S | 16.94_498.2881 m/z | [M−H]− | 6.00 |
| Tauroursodeoxycholic acid | C26H45NO6S | 8.73_498.2887 m/z | [M−H]− | 5.82 |
| Taurocholic acid | C26H45NO7S | 11.02_514.2830 m/z | [M−H]− | 4.98 |
| Glycodeoxycholic acid | C26H43NO5 | 30.22_448.3058 m/z | [M−H]− | 4.92 |
| Glycocholic acid | C26H43NO6 | 15.48_464.3006 m/z | [M−H]− | 4.33 |
| Glycohyodeoxycholic acid | C26H43NO5 | 14.12_448.3053 m/z | [M−H]− | 3.76 |
| Glycochenodeoxycholic acid | C26H43NO5 | 27.17_448.3059 m/z | [M−H]− | 3.64 |
| Taurodeoxycholic acid | C26H44NO6S | 19.55_498.2885 m/z | [M−H]− | 2.96 |
| Chenodeoxycholic acid | C24H40O4 | 34.60_437.2897 m/z | [M+HCOO]− | 1.91 |
| Cholic acid | C24H40O5 | 27.28_407.2764 m/z | [M−H]− | 1.79 |
| Compositions | Molecular Formula | Ions/Neutral Mass | Ionic Forms | Specific Attribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tauroursodeoxycholic acid | C26H45NO6S | 8.73_498.2887 m/z | [M−H]− | XD |
| Glycohyodeoxycholic acid | C26H43NO5 | 14.12_448.3053 m/z | [M−H]− | ZD |
| Cholic acid | C24H40O5 | 27.28_407.2764 m/z | [M−H]− | YND, JD, ND |
| Glycodeoxycholic acid | C26H43NO5 | 30.22_448.3058 m/z | [M−H]− | TD |
| Glycocholic acid | C26H43NO6 | 15.48_464.3006 m/z | [M−H]− | ND, TD |
| Glycochenodeoxycholic acid | C26H43NO5 | 27.17_448.3059 m/z | [M−H]− | ND, ZD |
| Taurodeoxycholic acid | C26H44NO6S | 19.55_498.2885 m/z | [M−H]− | ND, TD, YND |
| Chemical component F | — | 13.75_446.2899 m/z | [M−H]− | ZD |
| Chemical component G | — | 18.82_555.3085 m/z | [M−H]− | TD |
| Chemical component H | — | 9.11_462.2856 m/z | [M−H]− | ND |
| Time | Flow (mL/min) | %A | %B | %C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.3 | 14.0 | 23.0 | 63.0 |
| 15 | 0.3 | 24.0 | 29.0 | 47.0 |
| 20 | 0.3 | 20.0 | 29.0 | 51.0 |
| 25 | 0.3 | 15.0 | 29.0 | 56.0 |
| 30 | 0.3 | 30.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 |
| 40 | 0.3 | 25.0 | 72.0 | 3.0 |
| 41 | 0.3 | 14.0 | 23.0 | 63.0 |
| 45 | 0.3 | 14.0 | 23.0 | 63.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Li, M.; Guo, X.; Cheng, X.; Jing, W.; Wei, F. A Comprehensive Analysis of Fel Ursi and Its Common Adulterants Based on UHPLC-QTOF-MSE and Chemometrics. Molecules 2024, 29, 3144. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133144
Wang X, Wu H, Li M, Guo X, Cheng X, Jing W, Wei F. A Comprehensive Analysis of Fel Ursi and Its Common Adulterants Based on UHPLC-QTOF-MSE and Chemometrics. Molecules. 2024; 29(13):3144. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133144
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xianrui, Haonan Wu, Minghua Li, Xiaohan Guo, Xianlong Cheng, Wenguang Jing, and Feng Wei. 2024. "A Comprehensive Analysis of Fel Ursi and Its Common Adulterants Based on UHPLC-QTOF-MSE and Chemometrics" Molecules 29, no. 13: 3144. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133144
APA StyleWang, X., Wu, H., Li, M., Guo, X., Cheng, X., Jing, W., & Wei, F. (2024). A Comprehensive Analysis of Fel Ursi and Its Common Adulterants Based on UHPLC-QTOF-MSE and Chemometrics. Molecules, 29(13), 3144. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133144






