A Bicyclic Analog of the Linear Peptide Arodyn Is a Potent and Selective Kappa Opioid Receptor Antagonist
Abstract
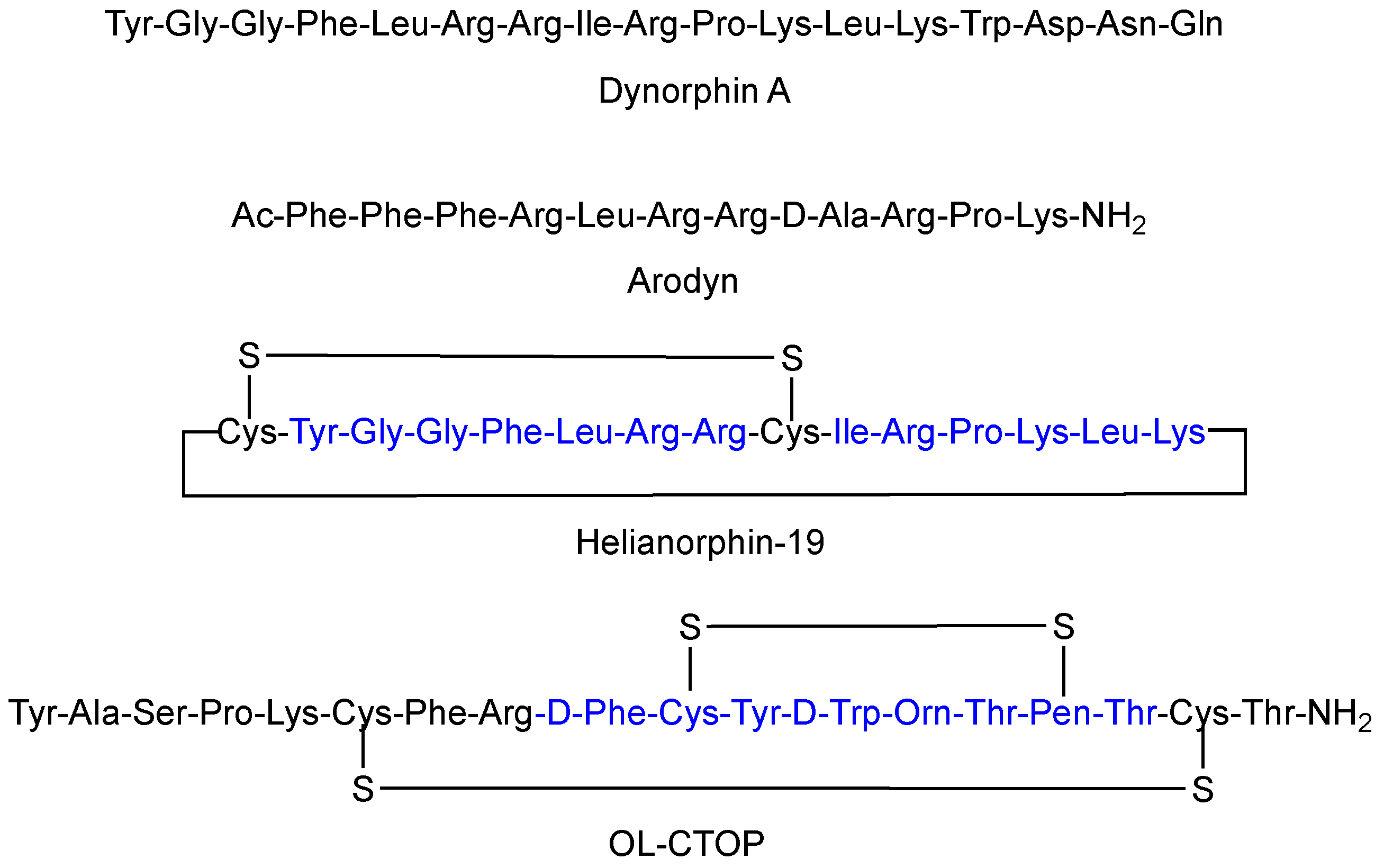
1. Introduction
2. Results
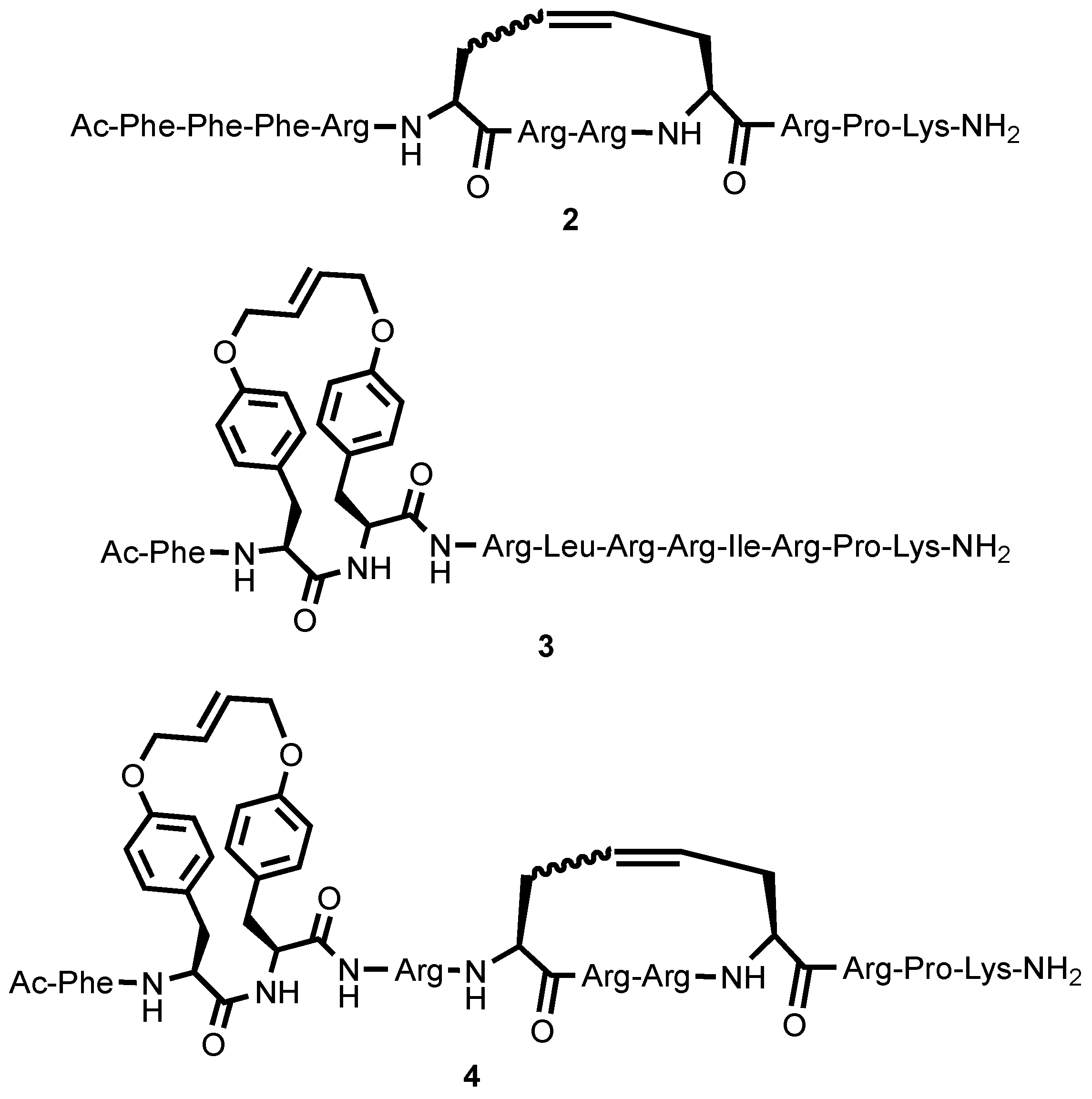
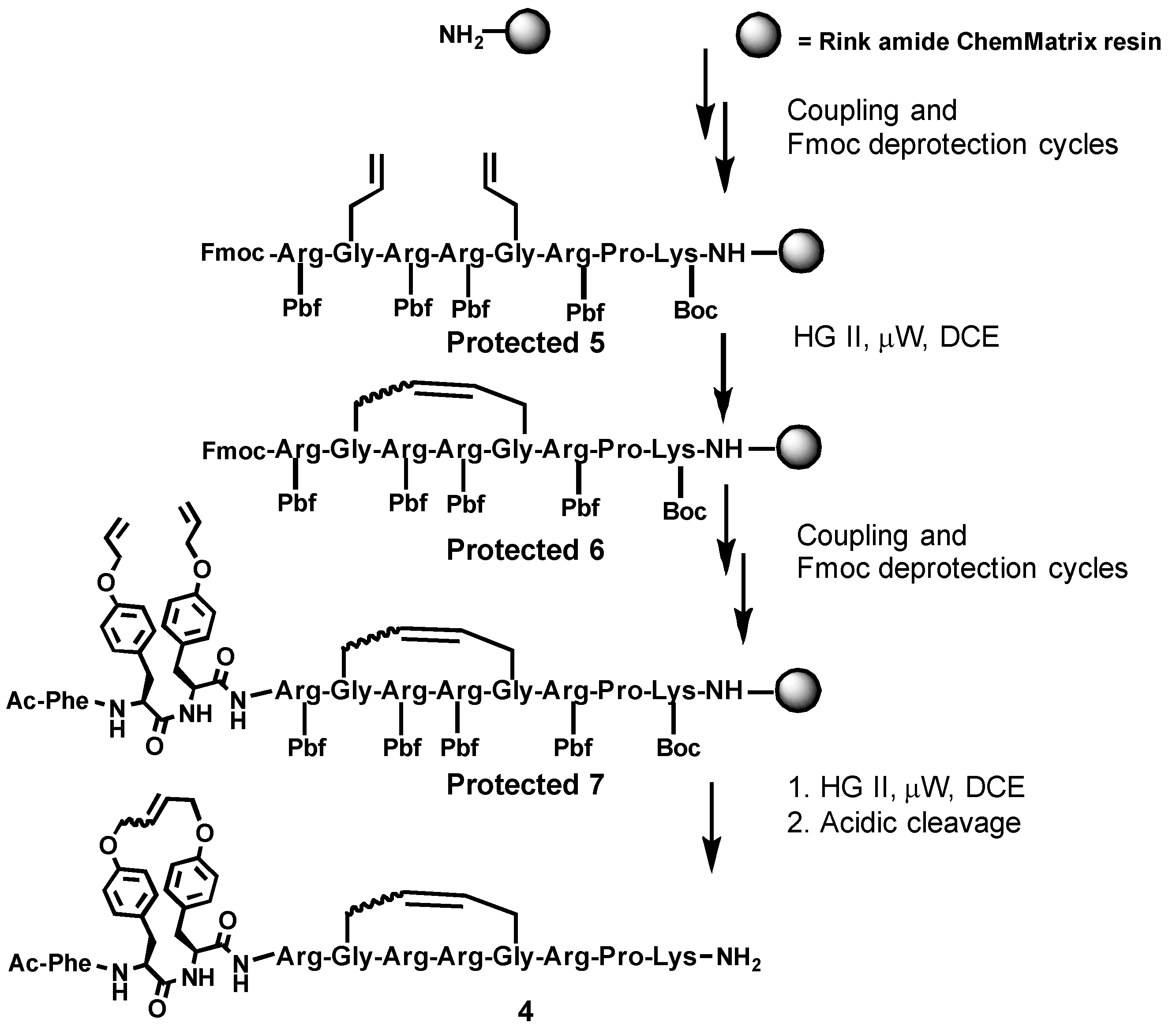
2.1. Synthesis
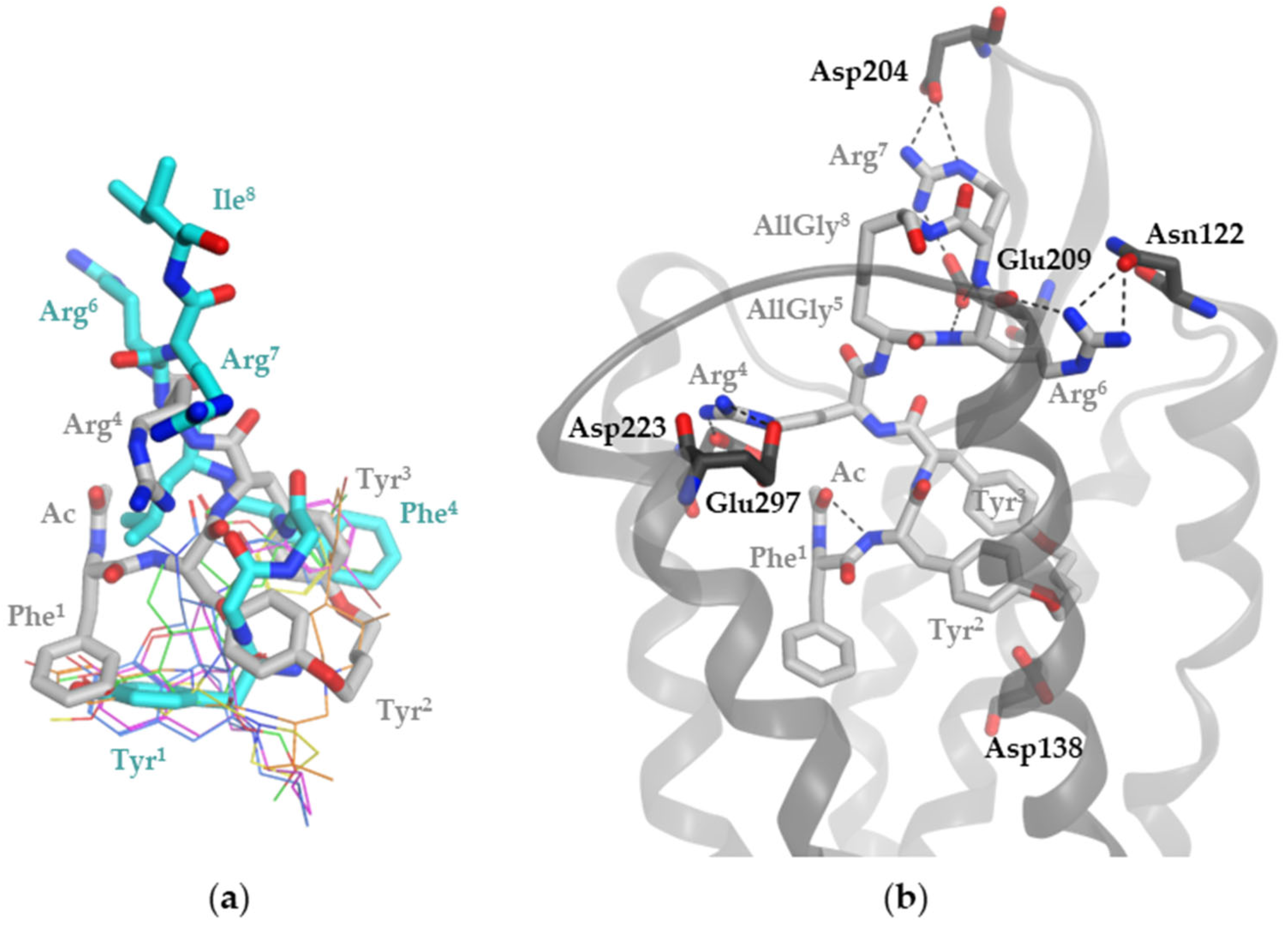
2.2. Molecular Modeling
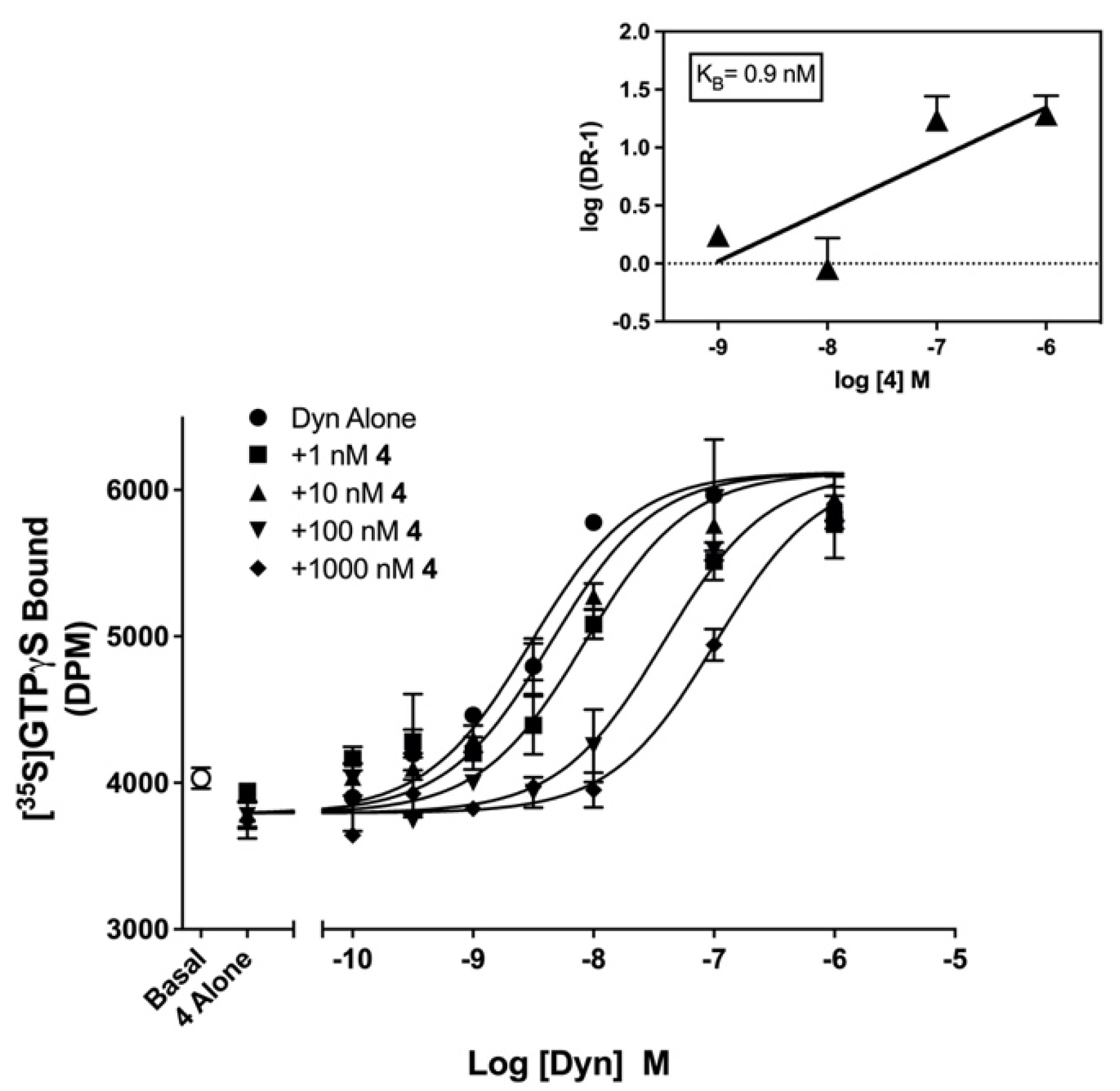
2.3. Pharmacological Evaluation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Instruments
4.3. Synthesis
4.3.1. Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis
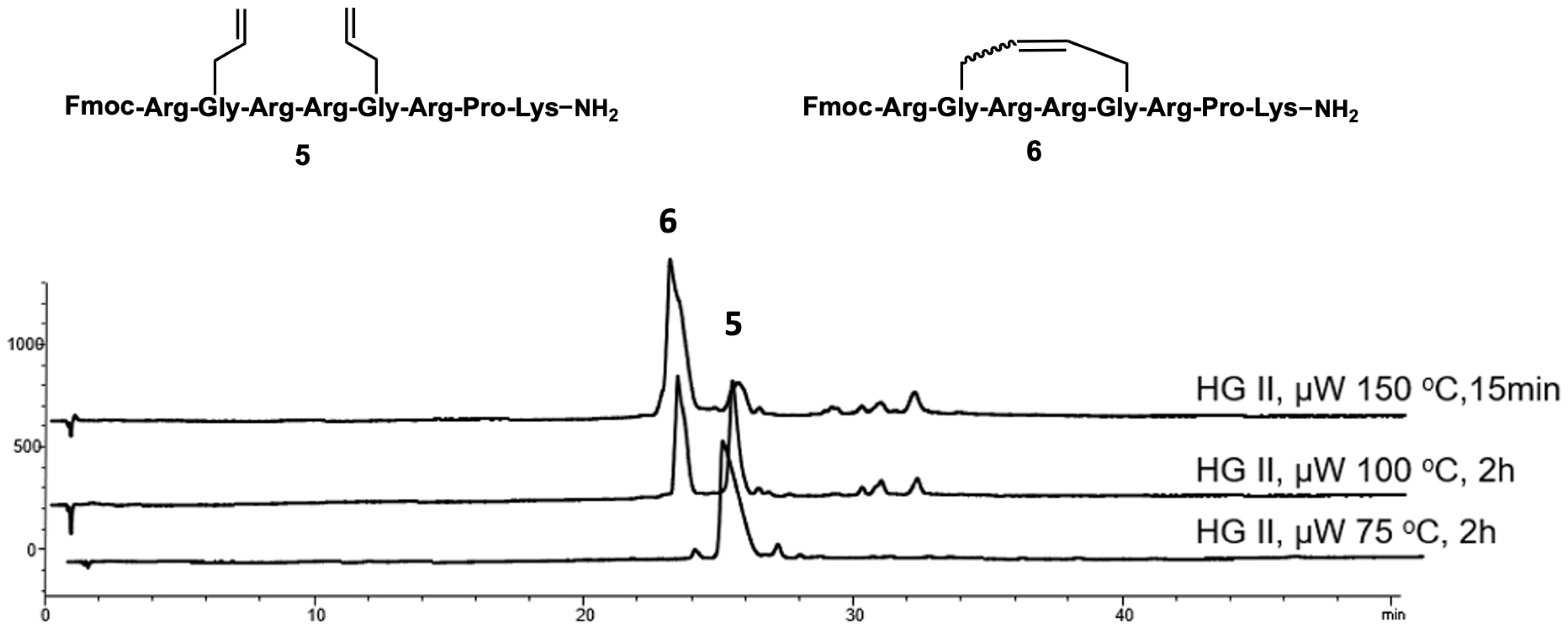
4.3.2. Ring-Closing Metathesis
4.3.3. Synthesis and Purification of Bicyclic Arodyn Analog 4
4.4. Molecular Modeling
4.5. Pharmacological Evaluation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carlezon, W.A., Jr.; Krystal, A.D. Kappa-Opioid Antagonists for Psychiatric Disorders: From Bench to Clinical Trials. Depress. Anxiety 2016, 33, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, M.A.; Habib, E.S.; Chittiboyina, A.G. Selective κ opioid antagonists for treatment of addiction, are we there yet? Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 141, 632–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, M.L.; Browne, C.A.; Lucki, I. Kappa Opioid Receptor Antagonists as Potential Therapeutics for Stress-Related Disorders. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 60, 615–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrich, J.V.; McLaughlin, J.P. Peptide Kappa Opioid Receptor Ligands and Their Potential for Drug Development. In Kappa Opioid Receptor. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 271, pp. 197–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, B.; Butelman, E.R.; Kreek, M.J. Kappa Opioid Receptor Antagonists as Potential Therapeutics for Mood and Substance Use Disorders. In Kappa Opioid Receptor. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.A.; Murray, T.F.; Aldrich, J.V. Identification of Arodyn, a Novel Acetylated Dynorphin A-(1–11) Analogue, as a κ Opioid Receptor Antagonist. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 5617–5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, A.N.; Borozny, K.; Aldrich, J.V.; McLaughlin, J.P. Reinstatement of cocaine place-conditioning prevented by the peptide κ-opioid receptor antagonist arodyn. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 569, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzi, A.; Deyle, K.; Heinis, C. Cyclic Peptide Therapeutics: Past, Present and Future. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2017, 38, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, Y.S.; Gao, L.; Kalesh, K.A.; Yu, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Sun, H.; Lee, S.S. Recent Advances in Synthesis and Identification of Cyclic Peptides for Bioapplications. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 2302–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaofi, A.; On, N.; Kiptoo, P.; Williams, T.D.; Miller, D.W.; Siahaan, T.J. Comparison of Linear and Cyclic His-Ala-Val Peptides in Modulating the Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability: Impact on Delivery of Molecules to the Brain. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nielsen, D.S.; Shepherd, N.E.; Xu, W.; Lucke, A.J.; Stoermer, M.J.; Fairlie, D.P. Orally Absorbed Cyclic Peptides. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8094–8128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piekielna, J.; Perlikowska, R.; Gach, K.; Janecka, A. Cyclization in opioid peptides. Curr. Drug Targets 2013, 14, 798–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remesic, M.; Lee, Y.S.; Hruby, J.V. Cyclic Opioid Peptides. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 1288–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berezowska, I.; Chung, N.N.; Lemieux, C.; Wilkes, B.C.; Schiller, P.W. Cyclic dermorphin tetrapeptide analogues obtained via ring-closing metathesis. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2006, 53, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berezowska, I.; Chung, N.N.; Lemieux, C.; Wilkes, B.C.; Schiller, P.W. Dicarba analogues of the cyclic enkephalin peptides H-Tyr-c[D-Cys-Gly-Phe-D(or L)-Cys]NH2 retain high opioid activity. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 1414–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollica, A.; Guardiani, G.; Davis, P.; Ma, S.W.; Porreca, F.; Lai, J.; Mannina, L.; Sobolev, A.P.; Hruby, V.J. Synthesis of Stable and Potent δ/μ Opioid Peptides: Analogues of H-Tyr-c[D-Cys-Gly-Phe-D-Cys]-OH by Ring-Closing Metathesis. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 3138–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezowska, I.; Lemieux, C.; Chung, N.N.; Wilkes, B.C.; Schiller, P.W. Cyclic opioid peptide agonists and antagonists obtained via ring-closing metathesis. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2009, 74, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.J.; Cui, Y.; Murray, T.F.; Aldrich, J.V. Design, synthesis, and pharmacological activities of dynorphin A analogues cyclized by ring-closing metathesis. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5619–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanucci, A.; Lei, W.; Pieretti, S.; Dimmito, M.P.; Luisi, G.; Novellino, E.; Nowakowski, M.; Kozminski, W.; Mirzaie, S.; Zengin, G.; et al. Novel Cyclic Biphalin Analogues by Ruthenium-Catalyzed Ring Closing Metathesis: In Vivo and In Vitro Biological Profile. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, C.A.; Pei, D. Bicyclic Peptides as Next-Generation Therapeutics. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 12690–12703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtler, C.; Lamers, C. Macrocyclization strategies for cyclic peptides and peptidomimetics. RSC Med. Chem. 2021, 12, 1325–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; DiBerto, J.F.; Zhou, X.E.; Schmitz, G.P.; Yuan, Q.; Jain, M.K.; Liu, W.; Melcher, K.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Structures of the entire human opioid receptor family. Cell 2023, 186, 413–427.e417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratspahic, E.; Tomasevic, N.; Koehbach, J.; Duerrauer, L.; Hadzic, S.; Castro, J.; Schober, G.; Sideromenos, S.; Clark, R.J.; Brierley, S.M.; et al. Design of a Stable Cyclic Peptide Analgesic Derived from Sunflower Seeds that Targets the κ-Opioid Receptor for the Treatment of Chronic Abdominal Pain. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 9042–9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayala, R.; Tiller, A.; Majumder, S.A.; Stacy, H.M.; Eans, S.O.; Nedovic, A.; McLaughlin, J.P.; Cudic, P. Solid-Phase Synthesis of the Bicyclic Peptide OL-CTOP Containing Two Disulfide Bridges, and an Assessment of Its In Vivo μ-Opioid Receptor Antagonism after Nasal Administration. Molecules 2023, 28, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.-J.; Murray, T.F.; Aldrich, J.V. Analogs of the κ Opioid Receptor Antagonist Arodyn Cyclized by Ring-Closing Metathesis Retain κ Opioid Receptor Affinity, Selectivity and κ Opioid Receptor Antagonism. Med. Chem. Res. 2021, 30, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.-J.; Murray, T.F.; Aldrich, J.V. Design, synthesis, and opioid activity of arodyn analogs cyclized by ring-closing metathesis involving Tyr(Allyl). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisemba, S.A.; Ferracane, M.J.; Murray, T.F.; Aldrich, J.V. Conformational Constraint between Aromatic Residue Side Chains in the “Message” Sequence of the Peptide Arodyn Using Ring Closing Metathesis Results in a Potent and Selective Kappa Opioid Receptor Antagonist. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 3153–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattabiraman, V.R.; Stymiest, J.L.; Derksen, D.J.; Martin, N.I.; Vederas, J.C. Multiple On-Resin Olefin Metathesis to Form Ring-Expanded Analogues of the Lantibiotic Peptide, Lacticin 3147 A2. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimartino, G.; Wang, D.; Chapman, R.N.; Arora, P.S. Solid-Phase Synthesis of Hydrogen-Bond Surrogate-Derived α-Helices. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 2389–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, R.N.; Arora, P.S. Optimized Synthesis of Hydrogen-Bond Surrogate Helices: Surprising Effects of Microwave Heating on the Activity of Grubbs Catalysts. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 5825–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisemba, S.A.; Aldrich, J.V. Optimized Ring Closing Metathesis Reaction Conditions to Suppress Desallyl Side Products in the Solid Phase Synthesis of Cyclic Peptides Involving Tyrosine(O-allyl). J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wacker, D.; Mileni, M.; Katritch, V.; Han, G.W.; Vardy, E.; Liu, W.; Thompson, A.A.; Huang, X.P.; Carroll, F.I.; et al. Structure of the human κ-opioid receptor in complex with JDTic. Nature 2012, 485, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, T.; Majumdar, S.; Zaidi, S.A.; Ondachi, P.; McCorvy, J.D.; Wang, S.; Mosier, P.D.; Uprety, R.; Vardy, E.; Krumm, B.E.; et al. Structure of the Nanobody-Stabilized Active State of the κ Opioid Receptor. Cell 2018, 172, 55–67.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Daibani, A.; Paggi, J.M.; Kim, K.; Laloudakis, Y.D.; Popov, P.; Bernhard, S.M.; Krumm, B.E.; Olsen, R.H.J.; Diberto, J.; Carroll, F.I.; et al. Molecular mechanism of biased signaling at the κ opioid receptor. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, J.; Nazarova, A.L.; Bernhard, S.M.; Krumm, B.E.; Zhao, L.; Lam, J.H.; Rangari, V.A.; Majumdar, S.; Nichols, D.E.; et al. Ligand and G-protein selectivity in the κ-opioid receptor. Nature 2023, 617, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muratspahic, E.; Deibler, K.; Han, J.; Tomasevic, N.; Jadhav, K.B.; Olive-Marti, A.L.; Hochrainer, N.; Hellinger, R.; Koehbach, J.; Fay, J.F.; et al. Design and structural validation of peptide-drug conjugate ligands of the κ-opioid receptor. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.A.; Murray, T.F.; Aldrich, J.V. Structure-activity relationships of arodyn, a novel acetylated κ opioid receptor antagonist. J. Pept. Res. 2005, 65, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norgren, A.S.; Buttner, F.; Prabpai, S.; Kongsaeree, P.; Arvidsson, P.I. β2-Amino acids in the design of conformationally homogeneous cyclo-peptide scaffolds. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 6814–6821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumberger, M.; Li, X.; Kreutzer, A.G.; Peoples, A.J.; Nitti, A.G.; Cunningham, A.M.; Jones, C.R.; Achorn, C.; Ling, L.L.; Hughes, D.E.; et al. Synthesis and Stereochemical Determination of the Peptide Antibiotic Novo29. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 2214–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loktev, A.; Haberkorn, U.; Mier, W. Multicyclic Peptides as Scaffolds for the Development of Tumor Targeting Agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 2141–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornishbowden, A. Nomenclature and Symbolism for Amino Acids and Peptides. Eur. J. Biochem. 1984, 138, 9–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molecular Operating Environment (MOE). 2022.02 Chemical Computing Group ULC; Chemical Computing Group Inc.: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Weiner, S.J.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A.; Singh, U.C.; Ghio, C.; Alagona, G.; Profeta, S.; Weiner, P. A New Force-Field for Molecular Mechanical Simulation of Nucleic-Acids and Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 765–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arttamangkul, S.; Ishmael, J.E.; Murray, T.F.; Grandy, D.K.; DeLander, G.E.; Kieffer, B.L.; Aldrich, J.V. Synthesis and Opioid Activity of Conformationally Constrained Dynorphin A Analogues. 2. Conformational Constraint in the “Address” Sequence. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Prusoff, W.H. Relationship between the Inhibition Constant (K1) and the Concentration of Inhibitor Which Causes 50 Per Cent Inhibition (IC50) of an Enzymatic Reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1973, 22, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schild, H.O. pA, A New Scale for The Measurement of Drug Antagonism. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1947, 2, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Peptide | KOR Ki ± SEM (nM) | MOR Ki ± SEM (nM) | Ki Ratio (MOR/KOR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1, arodyn 1 | 10.0 ± 3.0 | 1750 ± 130 | 174 |
| 2 2,3 | 54.0 ± 3.9/ 63.0 ± 6.3 | >10,000/ 9370 ± 590 | >185/ 149 |
| 3 4,5 | 55.4 ± 4.1 | 903 ± 34 1 | 16 |
| 4 | 26.4 ± 5.9 | 2570 ± 500 | 97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gisemba, S.A.; Ferracane, M.J.; Murray, T.F.; Aldrich, J.V. A Bicyclic Analog of the Linear Peptide Arodyn Is a Potent and Selective Kappa Opioid Receptor Antagonist. Molecules 2024, 29, 3109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133109
Gisemba SA, Ferracane MJ, Murray TF, Aldrich JV. A Bicyclic Analog of the Linear Peptide Arodyn Is a Potent and Selective Kappa Opioid Receptor Antagonist. Molecules. 2024; 29(13):3109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133109
Chicago/Turabian StyleGisemba, Solomon A., Michael J. Ferracane, Thomas F. Murray, and Jane V. Aldrich. 2024. "A Bicyclic Analog of the Linear Peptide Arodyn Is a Potent and Selective Kappa Opioid Receptor Antagonist" Molecules 29, no. 13: 3109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133109
APA StyleGisemba, S. A., Ferracane, M. J., Murray, T. F., & Aldrich, J. V. (2024). A Bicyclic Analog of the Linear Peptide Arodyn Is a Potent and Selective Kappa Opioid Receptor Antagonist. Molecules, 29(13), 3109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133109






