Heteronuclear Complexes of Hg(II) and Zn(II) with Sodium Monensinate as a Ligand
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
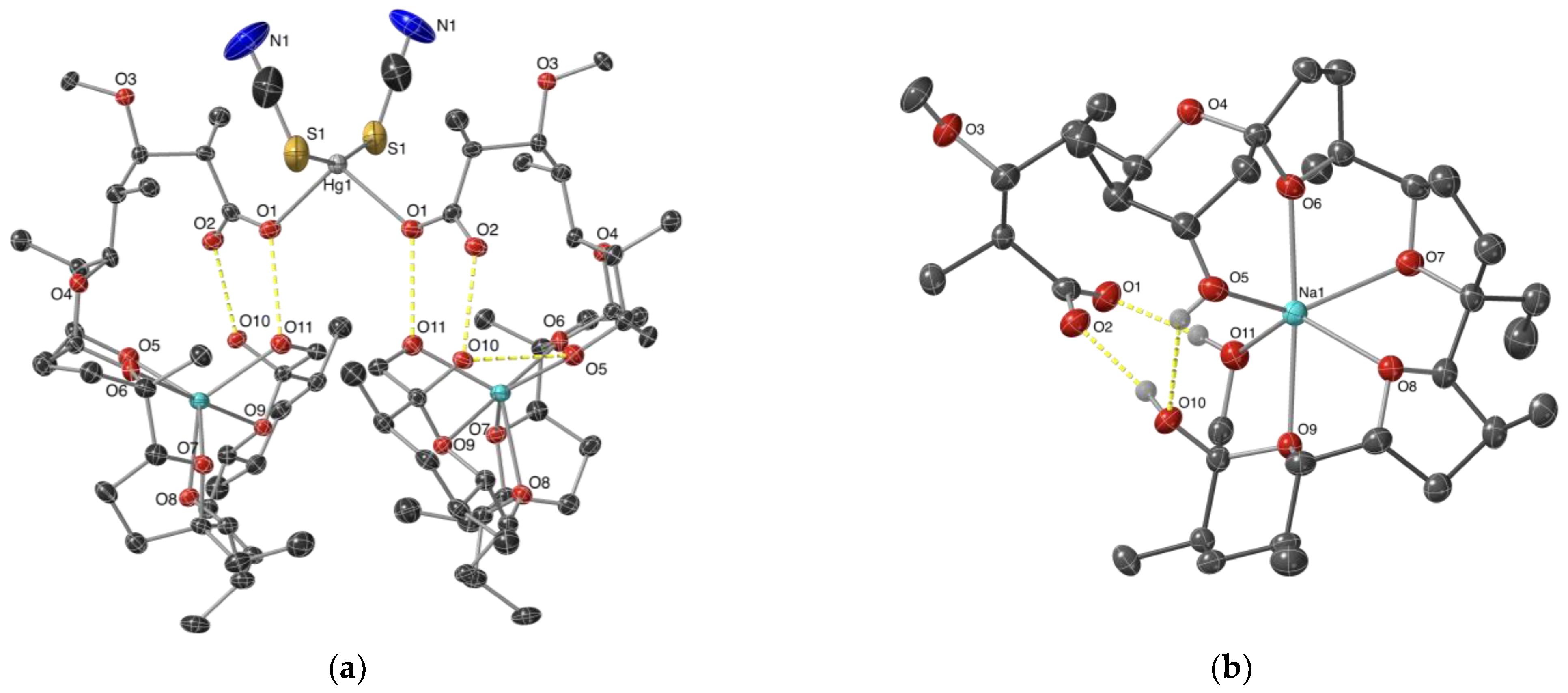
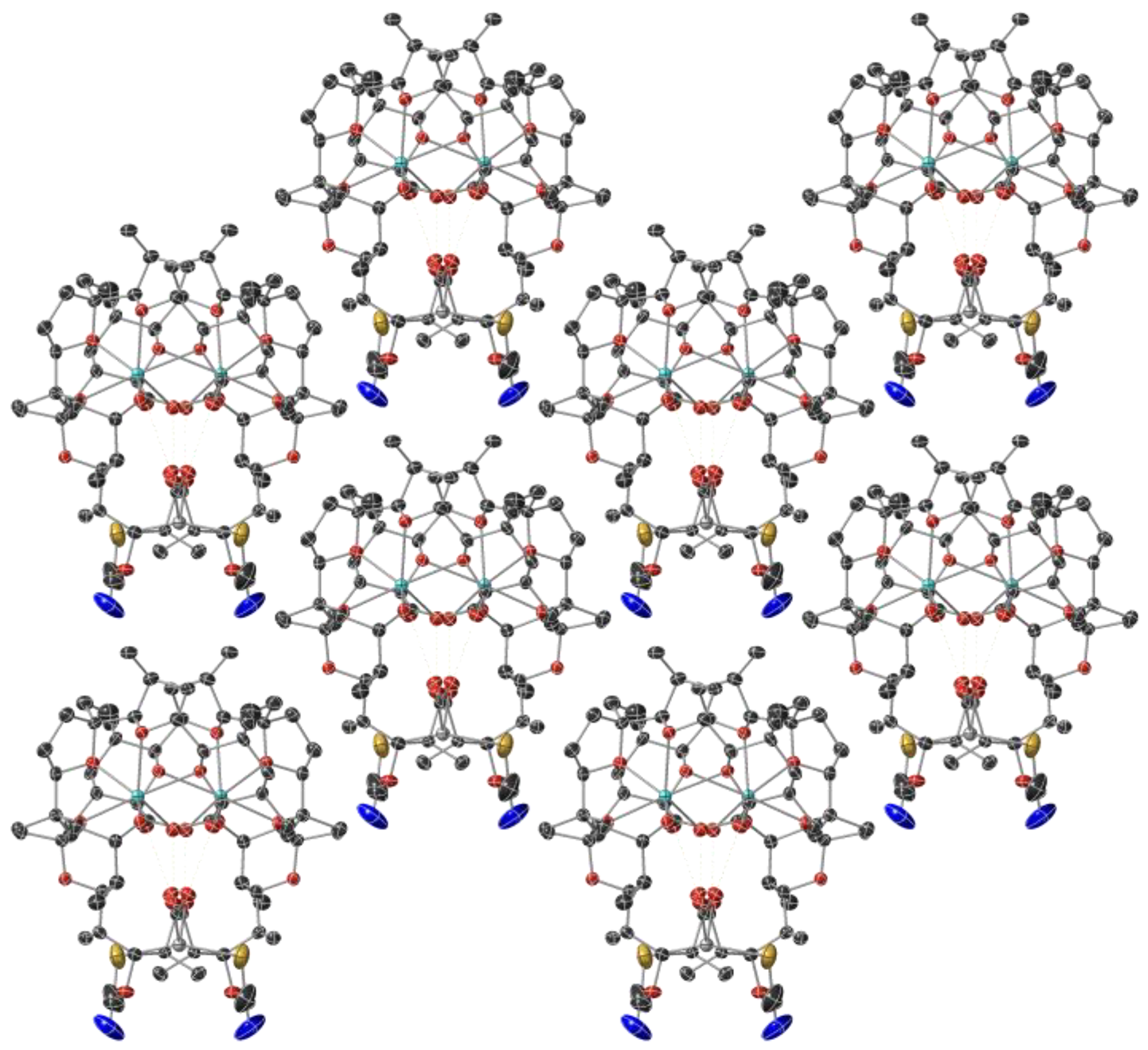
2.1. Description of the Crystal Structure of Complex 1
| Hg-O1 | 2.429(4) | Na-O5 | 2.328(5) |
| Hg-S1 | 2.375(2) | Na-O6 | 2.350(5) |
| O1-Hg-O1 11 | 102.60(20) | Na-O7 | 2.447(5) |
| S11-Hg-S1 | 159.13(11) | Na-O8 | 2.400(8) |
| S1-Hg-O1 | 91.42(12) | Na-O | 2.457(5) |
| S11-Hg-O1 | 101.64(11) | Na-O11 | 2.339(5) |
| Ligand/Complex | Core Unit | Bond Length [Å] | Refs. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hg-O | Hg-N | Hg-S | |||
| quinoline-2-carboxylic acid/[HgL2X], X = H2O, EtOH | HgN2O3 | 2.31–2.52 | 2.19–2.26 | − | [39] |
| picolinic acid/[HgL2Cl] | HgN2O2Cl | 2.49–2.54 | 2.12–2.35 | − | [40] |
| pyridine-2-thione/[HgL2] | HgS4 | − | − | 2.56–2.68 | [43] |
| biquinoline/[HgL2(SCN)2] | HgN2S2 | − | 2.30–2.50 | 2.44–2.47 | [44] |
| bipyridyl-based carbazoles/[HgL2(SCN)2] | HgN2S2 | − | 2.30–2.45 | 2.44–2.45 | [45] |
| nicotinamide/[HgL2(SCN)2] | HgN2S2 | − | 2.33–2.39 | 2.42–2.46 | [46] |
| 4,5-diazafluoren-9-one/[HgL2(SCN)2] | HgN2S2 | − | 2.48 | 2.4 | [47] |
| 3-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-sulfanylpropenoic acid | [41] | ||||
| [HgL2]2− | HgO2S2 | 2.55–2.61 | − | 2.34 | |
| [HgL(HL)]− | HgO2S2 | 2.54–2.67 | − | 2.34 | |
| [Hg(HL)2] | HgO2S2 | 2.65 | − | 2.36 | |
| thiol (L′) & carboxylic acid (L″)/[HgL′2L″] | HgO2S2 * | 2.46–27 | 2.33–2.41 | [42] | |
2.2. Spectral Characterization of 1 and 2
2.3. Structure Elucidation of Complex 2
2.4. Antibacterial Properties of MonNa and Complex 2
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Synthesis of 1 and 2
3.3. Methods
3.3.1. X-ray Crystallography
3.3.2. Physical Measurements
3.3.3. Antibacterial Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berger, J.; Rachlin, A.I.; Scott, W.E.; Sternbach, L.H.; Goldberg, M. W 1951. The isolation of three new crystalline antibiotics from Streptomyces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 5295–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harned, R.L.; Hidy, P.H.; Corum, C.J.; Jones, K.L. Nigericin, a new crystalline antibiotic from an unidentified Streptomyces. Antibiot. Chemother. 1951, 1, 594–596. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24541690 (accessed on 8 May 2024).
- Agtarap, A.; Chamberlin, J.W.; Pinkerton, M.; Steinrauf, L.K. The structure of monensic acid, a new biologically active compound. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967, 89, 5737–5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haney, M.E.; Hoehn, M.M. Monensin, a new biologically active compound. I. Discovery and isolation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1967, 7, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, W.M.; Knox, N.G.; Westhead, J.E. Monensin, a new biologically active compound. II. Fermentation studies. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1967, 7, 353–358. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/5596159/ (accessed on 8 May 2024).
- Agtarap, A.; Chamberlin, J.W. Monensin, a new biologically active compound. IV. Chemistry. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1967, 7, 359–362. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/5596160/ (accessed on 8 May 2024).
- Shumard, R.F.; Callender, M.E. Monensin, a new biologically active compound. VI. Anticoccidial activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1967, 7, 369–377. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/5596162/ (accessed on 8 May 2024).
- Donoho, A.L.; Kline, R.M. Monensin, a new biologically active compound. VII. Thin-layer bioautographic assay for monensin in chick tissues. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1967, 7, 763–766. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4970208/ (accessed on 8 May 2024).
- Estrada, S.; Rightmire, B.; Lardy, H.A. Antibiotics as tools for metabolic studies. X1. Specific inhibition of ion transport in mitochondria by the monensins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1967, 7, 279–288. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/5596149/ (accessed on 8 May 2024).
- Dutton, C.J.; Banks, B.J.; Cooper, C.B. Polyether ionophores. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1995, 12, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaway, T.R.; Edrington, T.S.; Rychlik, J.L.; Genovese, K.J.; Poole, T.L.; Jung, Y.S.; Bischoff, K.M.; Anderson, R.C.; Nisbet, D.J. Ionophores: Their use as ruminant growth promotants and impact on food safety. Curr. Issues Intest. Microbiol. 2003, 4, 43–51. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14503688/ (accessed on 8 May 2024). [PubMed]
- Allèaume, M.; Busetta, B.; Farges, C.; Gachon, P.; Kergomard, A.; Staron, T. X-Ray structure of alborixin, a new antibiotic ionophore. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Comm. 1975, 411–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otake, N.; Ogita, T.; Nakayama, H.; Miyamae, H.; Sato, S.; Saito, Y. X-Ray crystal structure of the thallium salt of antibiotic-6016, a new polyether ionophore. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Comm. 1978, 875–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangborn, W.; Duax, W.L.; Langs, D. The hydrated potassium complex of the ionophore monensin A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 2163–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oscarson, J.R.; Bordner, J.; Celmer, W.D.; Cullen, W.P.; Huang, L.H.; Maeda, H.; Moshier, P.M.; Nishiyama, S.; Presseau, L.; Shibakawa, R.; et al. Endusamycin, a novel polycyclic ether antibiotic produced by a strain of Streptomyces endus subsp. aureus. J. Antib. 1989, 42, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Ogata, R.; Matsuda, M.; Hamada, M.; Naganawa, H.; Takita, T.; Iitaka, Y.; Sato, K.; Takeuchi, T. Kijimicin, a polyether antibiotic. J. Antib. 1990, 43, 441–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Paulus, E.F.; Kurz, M.; Matter, H.; Vertesy, L. Solid-state and solution structure of the salinomycin-sodium complex: Stabilization of different conformers for an ionophore in different environments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 8209–8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huczynski, A.; Ratajczak-Sitarz, M.; Katrusiak, A.; Brzezinski, B. Molecular structure of the 1:1 inclusion complex of monensin A sodium salt with acetonitrile. J. Mol. Struct. 2007, 832, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huczynski, A.; Ratajczak-Sitarz, M.; Katrusiak, A.; Brzezinski, B. Molecular structure of the 1:1 inclusion complex of monensin A lithium salt with acetonitrile. J. Mol. Struct. 2007, 871, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, S.O.; McKee, V.; Khardli, F.Z.; Mimouni, M.; Hadda, T.B. Rubidium (I) monensinate dihydrate. Acta Cryst. 2008, E64, m154–m155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.M.; Russell, J.B. Effect of ionophores and pH on growth of Streptococcus bovis in batch and continuous culture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1588–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirase, N.K.; Greene, L.W.; Schelling, G.T.; Byers, F.M. Effect of magnesium and potassium on microbial fermentation in a continuous culture fermentation system with different levels of monensin or lasalocid. J. Anim. Sci. 1987, 65, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidinia, S.A.; Shimelis, O.I.; Tan, B.; Erdahl, W.L.; Chapman, C.J.; Renkes, G.D.; Taylor, R.W.; Pfeiffer, D.R. Monensin mediates a rapid and selective transport of Pb2+: Possible application of monensin for the treatment of Pb2+ intoxication. J. Biol. Chem 2002, 277, 38111–38120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidinia, S.A.; Erdahl, W.L.; Chapman, C.J.; Steinbaugh, G.E.; Taylor, R.W.; Pfeiffer, D.R. Monensin improves the effectiveness of meso-dimercaptosuccinate when used to treat lead intoxication in rats. Environm. Health Persp. 2006, 114, 484–493. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/3650926 (accessed on 10 May 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantcheva, I.N.; Ivanova, J.; Zhorova, R.; Mitewa, M.; Simova, S.; Mayer-Figge, H.; Sheldrick, W.S. Nickel(II) and zinc(II) dimonensinates: Crystal structure, spectral properties and bactericidal activity. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2010, 363, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, J.; Pantcheva, I.N.; Mitewa, M.; Simova, S.; Mayer-Figge, H.; Sheldrick, W.S. Crystal structures and spectral properties of new Cd(II) and Hg(II) complexes of monensic acid with different coordination modes of the ligand. Centr. Eur. J. Chem. 2010, 8, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantcheva, I.; Dimitrova, R.; Ivanova, V.; Nedzhib, A.; Dorkov, P.; Dinev, D.; Spasov, R.; Alexandrova, R. Spectral properties and biological activity of La(III) and Nd(III) monensinates. Open Chem. 2019, 17, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkov, N.; Pantcheva, I.; Ivanova, A.; Stoyanova, R.; Kukeva, R.; Alexandrova, R.; Abudalleh, A.; Dorkov, P. Novel cerium(IV) coordination compounds of monensin and salinomycin. Molecules 2023, 28, 4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petkov, N.; Tadjer, A.; Encheva, E.; Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z.; Paneva, D.; Stoyanova, R.; Kukeva, R.; Dorkov, P.; Pantcheva, I. Experimental and DFT study of monensinate and salinomycinate complexes containing {Fe3(µ3–O)}7+ core. Molecules 2024, 26, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkov, N.; Tadjer, A.; Simova, S.; Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z.; Paneva, D.; Stoyanova, R.; Kukeva, R.; Dorkov, P.; Pantcheva, I. Synthesis, spectral characterization and structural modelling of di- and trinuclear iron(III) monensinates with different bridging patterns. Inorganics 2024, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldin, Z.; Matković-Čalogović, D.; Pavlović, G.; Popović, J.; Vinković, M.; Vikić-Topić, D.; Popović, Z. Various coordination modes in mercury(II) complexes with quinoline-2-carboxylic acid: Preparation and structural characterization. Polyhedron 2009, 28, 2735–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldin, Z.; Kukovec, B.-M.; Matković-Čalogović, D.; Popović, Z. The solvent effect on composition and dimensionality of mercury(II) complexes with picolinic acid. Molecules 2021, 26, 5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, J.S.; Collazo, R.; Couce, M.D.; García-Vega, M.; Sánchez, A.; Sordo, J.; Vázquez-López, E.M. Mercury(II) complexes containing the [Hg(L)2]2−, [Hg(L)(HL)]−, and [Hg(HL)2] units [H2L = 3-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-sulfanylpropenoic acid]. Structural and spectroscopic effects of the different degrees of ligand protonation. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 5370–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.-Y.; Zheng, A.-X.; Shang, H.; Yuan, R.-X.; Li, H.-X.; Ren, Z.-G.; Lang, J.-P. Binding of a coordinatively unsaturated mercury(II) thiolate compound by carboxylate anions. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popović, Z.; Matković-Čalogović, D.; Hasić, J.; Vikić-Topić, D. Preparation and spectroscopic properties of the complexes of mercuric thiocyanate with pyridine-2-thione and pyridine-2-carboxylic acid.: Crystal and molecular structure of two polymorphs of Hg(SCN)2(C5H5NS)2. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1999, 285, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsali, A.; Mahjoub, A.R.; Ramazani, A. Zn(II), Cd(II) and Hg(II) complexes with 2,2′-biquinoline, syntheses and X-ray crystal structures of [Hg(bq)(SCN)2]. J. Coord. Chem. 2004, 57, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.-P.; Tian, Y.-P.; Wu, J.-Y.; Zhang, J.-Z.; Li, D.-M.; Zhu, Y.-M.; Hu, Z.-J.; Tao, X.-T.; Jiang, M.-H.; Xie, Y. Synthesis, crystal structures and photoluminescence of mercury(II) complexes with two homologous novel functional rigid ligands. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 2005, 4976–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đaković, M.; Popović, Z.; Giester, G.; Rajić-Linarić, M. Synthesis, spectroscopic and structural investigation of Zn(NCS)2(nicotinamide)2 and [Hg(SCN)2(nicotinamide)]n. Polyhedron 2008, 27, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machura, B.; Wolff, M.; Palion, J.; Świtlicka, A.; Nawrot, I.; Michalik, K. Cu(II), Ni(II), and Hg(II) thiocyanate complexes incorporating 4,5-diazafluoren-9-one: Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, X-ray studies, and magnetic properties. Struct. Chem. 2011, 22, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, J.; Beauchamp, A.L.; Rivets, R. Crystal and molecular structure of dithiocyanato(triphenylarsine)mercury(II). Can. J. Chem. 1975, 53, 3383–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, A.; Rajarajan, K.; Nizam-Mohideen, M.; Sagayaraj, P. Crystal structure of bis-(thio-cyanato-κS)bis-(thio-urea-κS)mercury(II). Acta Cryst. E Cryst. Commun. 2015, 71, m28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duax, W.L.; Smith, G.D.; Strong, P.D. Complexation of metal ions by monensin. Crystal and molecular structure of hydrated and anhydrous crystal forms of sodium monensin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 6725–6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, F.A.A.; Gates, P.J.; Fowler, S.; Gallimore, A.; Harvey, B.; Lopes, N.P.; Stark, C.B.W.; Staunton, J.; Klinowski, J.; Spencer, J.B. Sodium monensin dihydrate. Acta Cryst. E 2003, 59, m1050–m1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorkov, P.; Pantcheva, I.N.; Sheldrick, W.S.; Mayer-Figge, H.; Petrova, R.; Mitewa, M. Synthesis, structure and antimicrobial activity of manganese(II) and cobalt(II) complexes of the polyether ionophore antibiotic sodium monensin A. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2008, 102, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gertenbach, G.; Popov, A.I. Solution chemistry of monensin and its alkali metal ion complexes. Potentiometric and spectroscopic studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 4738–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, K. Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds, 5th ed.; Wiley: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, C.T.; Siqueira, A.B.; Rodrigues, E.C.; Ionashiro, M. Synthesis, characterization and thermal behaviour of solid-state compounds of 2-methoxybenzoate with some bivalent transition metal ions. Ecl. Quim. 2005, 30, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vučković, G.; Stanić, V.; Sovilj, S.P.; Antonijević-Nikolić, M.; Mrozinski, J. Cobalt(II) complexes with aromatic carboxylates and N-functionalized cyclam bearing 2-pyridylmethyl pendant arms. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2005, 70, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramer, A. Spectra and structure of thiocyanate complexes. In Theory and Structure of Complex Compounds; Jezowska-Trzebiatowska, B., Ed.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1964; pp. 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.A.; Kozak, S.L.; Michelsen, T.W.; Mills, W.N. Infrared spectra of complexes of the thiocyanate and related ions. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1971, 6, 407–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, C.; Pike, J. Infrared spectroscopic analysis of linkage isomerism in metal-thiocyanate complexes. J. Chem. Edu. 2010, 87, 724–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertini, I.; Sabatini, A. Infrared spectra of substituted thiocyanate complexes. The effect of the substituent on bond type. II. Inorg. Chem. 1966, 5, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escard, J.; Mavel, G.; Guerchais, J.E.; Kergoat, R. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of some metal(II) halide and pseudohalide complexes. Inorg. Chem. 1974, 13, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Hua, Y.; Yan, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Y. Sulfhydryl functionalized carbon quantum dots as a turn-off fluorescent probe for sensitive detection of Hg2+. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 36310–36318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awan, S.U.; Hasanain, S.K.; Bertino, M.F.; Jaffari, G.H. Ferromagnetism in Li doped ZnO nanoparticles: The role of interstitial Li. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 103924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengo, N.; Vittadini, A.; Natile, M.M.; Gross, S. In-depth study of ZnS nanoparticle surface properties with a combined experimental and theoretical approach. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 7777–7789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Fu, K.-L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Deng, Y.; Xie, R.; Ju, X.-J.; Wang, W.; et al. Zinc-coordinated polydopamine surface with a nanostructure and superhydrophilicity for antibiofouling and antibacterial applications. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 5476–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, R.A. X-ray photoelectron spectra of inorganic molecules [1]. XXIII. On the question of the usefulness of XPS in studying the ambidentate nature of the thiocyanate ligand. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1979, 37, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, S.A.; Walton, R.A. X-ray photoelectron spectra of inorganic molecules. XIX. Thiocyanato and isothiocyanato complexes of the transition metals: Carbon 1s, nitrogen ls and sulfur 2p binding energies and their possible correlation with the mode of thiocyanate bonding. Isr. J. Chem. 1976, 15, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J.; Levason, W.; McAuliffe, C.A. The preparation of some mercury(II) complexes of group VB donors and preliminary toxicity studies towards lysozyme. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1976, 38, 1919–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.E.; Germida, J.J.; Huang, P.M. Effects of chemical speciation in growth media on the toxicity of mercury(II). Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, P.L.; Lu, G.L.; Choi, K.H.; Lin, Z.; Kok, S.H.L.; Lee, K.K.H.; Lam, K.H.; Li, H.; Gambari, R.; Bian, Z.X.; et al. Antimicrobial and toxicological evaluations of binuclear mercury(II) bis(alkynyl) complexes containing oligothiophenes and bithiazoles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 16736–16744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajaz, A.A.; Robinson, J.A. Biosynthesis of the polyether ionophore antibiotic monensin A: Assignment of the carbon-I3 and proton N.M.R. spectra of monensin A by two-dimensional spectroscopy. Incorporation of oxygen-18 labelled molecular oxygen. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1987, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruker Analytical X-ray Systems, SADABS version 2016/2; Bruker: Madison, WI, USA, 2016.
- Bruker Analytical X-ray Systems; SAINTV8.38A; Bruker: Madison, WI, USA, 2018.
- Bruker Analytical X-ray Systems; SHELXTL 2018; Bruker: Madison, WI, USA, 2018.
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.; Puschmann, H.J. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Cryst. A 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst. A 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, S.; Flack, H.D.; Wagner, T. Use of intensity quotients and differences in absolute structure refinement. Acta Cryst. B 2013, 69, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| C Atom | MonNa | Hg(II) Complex, 1 | Zn(II) Complex, 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ, ppm | δ1, ppm | Δ1, ppm | δ2, ppm | Δ2, ppm | |
| 1C | 181.3 | 181.3 | 0.0 | 181.9 | −0.6 |
| 9C | 107.2 | 107.1 | 0.1 | 107.1 | 0.1 |
| 25C | 98.4 | 98.4 | 0.0 | 98.6 | −0.2 |
| 16C | 86.0 | 85.9 | 0.1 | 85.9 | 0.1 |
| 12C | 85.4 | 85.3 | 0.1 | 85.5 | −0.1 |
| 17C | 85.1 | 85.1 | 0.0 | 84.9 | 0.2 |
| 3C | 83.2 | 83.0 | 0.2 | 82.3 | 0.9 |
| 13C | 82.7 | 82.6 | 0.1 | 82.2 | 0.5 |
| 20C | 76.6 | 76.5 | 0.1 | 76.4 | 0.2 |
| 21C | 74.6 | 74.6 | 0.0 | 74.8 | −0.2 |
| 7C | 70.6 | 70.5 | 0.1 | 70.4 | 0.2 |
| 5C | 68.5 | 68.4 | 0.1 | 68.3 | 0.2 |
| 26C | 65.1 | 65.0 | 0.1 | 65.6 | −0.5 |
| 28C | 58.0 | 58.0 | 0.0 | 58.1 | −0.1 |
| 2C | 45.2 | 45.0 | 0.2 | 44.3 | 0.9 |
| 10C | 39.4 | 39.3 | 0.1 | 39.3 | 0.1 |
| 4C | 37.6 | 37.5 | 0.1 | 37.5 | 0.1 |
| 24C | 36.7 | 36.6 | 0.1 | 36.2 | 0.5 |
| 23C | 35.9 | 35.7 | 0.2 | 35.4 | 0.5 |
| 6C | 35.0 | 34.9 | 0.1 | 35.2 | −0.2 |
| 18C | 34.5 | 34.4 | 0.1 | 34.3 | 0.2 |
| 8C | 33.7 | 33.6 | 0.1 | 33.5 | 0.2 |
| 19C | 33.5 | 33.4 | 0.1 | 33.5 | 0.0 |
| 11C | 33.4 | 33.3 | 0.1 | 33.3 | 0.1 |
| 22C | 32.0 | 31.9 | 0.1 | 31.9 | 0.1 |
| 32C | 30.7 | 30.7 | 0.0 | 30.6 | 0.1 |
| 15C | 30.0 | 29.9 | 0.1 | 30.2 | −0.2 |
| 31C | 27.6 | 27.5 | 0.1 | 27.6 | 0.0 |
| 14C | 27.4 | 27.4 | 0.0 | 27.3 | 0.1 |
| 35C | 16.9 | 16.9 | 0.0 | 16.8 | 0.1 |
| 27C | 16.9 | 16.8 | 0.1 | 16.4 | 0.5 |
| 36C | 16.2 | 16.2 | 0.0 | 16.3 | −0.1 |
| 34C | 14.7 | 14.7 | 0.0 | 14.7 | 0.0 |
| 29C | 11.1 | 11.2 | −0.1 | 11.4 | −0.3 |
| 30C | 10.6 | 10.6 | 0.0 | 10.7 | −0.1 |
| 33C | 8.3 | 8.3 | 0.0 | 8.3 | 0.0 |
| Compound | Concentration | Bacterial Strain | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BS | BC | KR | SA | SS | ||
| MonNa | µg/mL | 62.50 | 1.95 | 125.0 | 31.25 | 31.25 |
| µM | 90 | 2.8 | 180 | 45 | 45 | |
| 2 | µg/mL | 31.25 | 3.91 | 125.0 | 61.25 | 15.63 |
| µM | 20 | 2.5 | 80 | 40 | 10 | |
| Crystal Data | |
| Chemical formula | C74H122HgN2Na2O22S2 |
| Mr | 1702.42 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, C2 |
| Temperature (K) | 107.01 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 19.3234(7), 15.4753(5), 13.5120(5) |
| V (Å3) | 4039.2(2) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type, λ [Å] | Cu Kα, 1.54178 |
| µ (mm−1) | 4.594 |
| Crystal size (mm3) | 0.169 × 0.163 × 0.073 |
| Data Collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEX-II CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan |
| Tmin, Tmax | 0.549, 0.753 |
| No. of measured, independent andobserved [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 27485, 7140, 7136 |
| Rint | 0.0441 |
| Resolution (Å−1) | 0.84 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)], wR(F2), S | 0.0351, 0.0883, 1.072 |
| No. of reflections | 7140 |
| No. of parameters | 477 |
| No. of restraints | 1 |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 1.86, −0.51 |
| Absolute structure | Flack x determined using quotients [(I+)−(I−)]/[(I+)+(I−)] [70] |
| Absolute structure parameter | −0.026(5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pantcheva, I.; Petkov, N.; Encheva, E.; Kolev, S.; Simova, S.; Tsanev, A.; Dorkov, P.; Ugrinov, A. Heteronuclear Complexes of Hg(II) and Zn(II) with Sodium Monensinate as a Ligand. Molecules 2024, 29, 3106. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133106
Pantcheva I, Petkov N, Encheva E, Kolev S, Simova S, Tsanev A, Dorkov P, Ugrinov A. Heteronuclear Complexes of Hg(II) and Zn(II) with Sodium Monensinate as a Ligand. Molecules. 2024; 29(13):3106. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133106
Chicago/Turabian StylePantcheva, Ivayla, Nikolay Petkov, Elzhana Encheva, Stiliyan Kolev, Svetlana Simova, Aleksandar Tsanev, Petar Dorkov, and Angel Ugrinov. 2024. "Heteronuclear Complexes of Hg(II) and Zn(II) with Sodium Monensinate as a Ligand" Molecules 29, no. 13: 3106. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133106
APA StylePantcheva, I., Petkov, N., Encheva, E., Kolev, S., Simova, S., Tsanev, A., Dorkov, P., & Ugrinov, A. (2024). Heteronuclear Complexes of Hg(II) and Zn(II) with Sodium Monensinate as a Ligand. Molecules, 29(13), 3106. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133106








