Photocatalytic Bacterial Destruction and Mineralization by TiO2-Based Photocatalysts: A Mini Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Mechanisms of Photocatalytic Bacterial Inactivation—Fundamentals
3. Photocatalytic Bacterial Mineralization
3.1. Photocatalytic Bacterial Mineralization in Air
3.2. Photocatalytic Bacterial Mineralization in Aqueous Solutions
4. The Proposed Mechanism of Photocatalytic Bacterial Mineralization
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, G. Photocatalytic advanced oxidation processes for water treatment: Recent advances and perspective. Chem. Asian J. 2020, 15, 3239–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Al-Dossari, M.; Singh, J.; Rawat, M.; Kordy, M.G.M.; Shaban, M. A Review on green synthesis of TiO2 NPs: Photocatalysis and antimicrobial applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidsvåg, H.; Bentouba, S.; Vajeeston, P.; Yohi, S.; Velauthapillai, D. TiO2 as a photocatalyst for water splitting—An experimental and theoretical review. Molecules 2021, 26, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Zhou, W. Recent progress in defective TiO2 photocatalysts for energy and environmental applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 156, 111980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Pillai, S.C. Self-cleaning applications of TiO2 by photo-induced hydrophilicity and photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 176, 396–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Jitan, S.; Palmisano, G.; Garlisi, C. Synthesis and surface modification of TiO2-based photocatalysts for the conversion of CO2. Catalysts 2020, 10, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, M.; Hajra, S.; Irshad, M.; Usman, M.; Imran, M.; Assiri, M.A.; Ashraf, W.M. Hydrogen production using TiO2-based photocatalysts: A comprehensive review. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 25640–25648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, N.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Huo, S.; Cheng, P.; Peng, P.; Zhang, R.; et al. Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants using TiO2-based photocatalysts: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 121725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeshan, M.; Bhatti, I.A.; Mohsin, M.; Iqbal, M.; Amjed, N.; Nisar, J.; Al Masoud, L.; Alomar, T.S. Remediation of pesticides using TiO2 based photocatalytic strategies: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, B.; Liu, F.; Gao, T.; Zhou, G. TiO2-based S-scheme photocatalysts for solar energy conversion and environmental remediation. Sci. China Mater. 2024, 67, 424–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Mahyad, B.; Hashemzadeh, H.; Janfaza, S.; Gholikhani, T.; Tayebi, L. Biomedical applications of TiO2 nanostructures: Recent advances. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 3447–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodithuwakku, P.; Jayasundara, D.R.; Munaweera, I.; Jayasinghe, R.; Thoradeniya, T.; Weerasekera, M.; Ayajan, P.A.; Kottegoda, N. A review on recent developments in structural modification of TiO2 for food packaging applications. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2022, 67, 100369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.V.L.; Kavitha, B.; Reddy, P.A.K.; Kim, K.H. TiO2-based photocatalytic disinfection of microbes in aqueous media: A review. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, C.S.U.; Birben, N.C.; Bekbolet, M. A comprehensive review on the use of second generation TiO2 photocatalysts: Microorganism inactivation. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 420–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.R.; Alavi, M.; Taran, M.; Kahrizi, D. Antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, and photocatalytic activities of TiO2 nanoparticles, nanocomposites, and bio-nanocomposites: Recent advances and challenges. J. Public Health Res. 2022, 11, 22799036221104151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, N.; Ponti, F.; Punta, C.; Candiani, G. Effect of UV Irradiation and TiO2-photocatalysis on airborne bacteria and viruses: An overview. Materials 2021, 14, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pasquale, I.; Porto, C.L.; Dell’Edera, M.; Curri, M.L.; Comparelli, R. TiO2-based nanomaterials assisted photocatalytic treatment for virus inactivation: Perspectives and applications. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2021, 34, 100716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacoby, W.A.; Maness, P.C.; Wolfrum, E.J.; Blake, D.M.; Fennell, J.A. Mineralization of bacterial cell mass on a photocatalytic surface in air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2650–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudhoo, A.; Paliya, S.; Goswami, P.; Singh, M.; Lofrano, G.; Carotenuto, M.; Libralato, G.; Guida, M.; Usman, M.; Kumar, S. Fabrication, functionalization and performance of doped photocatalysts for dye degradation and mineralization: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1825–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, J.O.; Ajiboye, T.; Onwudiwe, D.C. Mineralization of antibiotics in wastewater via photocatalysis. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, R.; Gupta, A.; Dubey, K.K.; Khan, A.M.; Singhal, R.; Kumar, R.; Bharti, A.; Singh, P.; Kant, R.; et al. TiO2 based Photocatalysis membranes: An efficient strategy for pharmaceutical mineralization. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlova, E.A.; Safatov, A.S.; Kiselev, S.A.; Marchenko, V.Y.; Sergeev, A.A.; Skarnovich, M.O.; Emelyanova, E.K.; Smetannikova, M.A.; Buryak, G.A.; Vorontsov, A.V. Inactivation and mineralization of aerosol deposited model pathogenic microorganisms over TiO2 and Pt/TiO2. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5121–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taddese, R.; Belzer, C.; Aalvink, S.; de Jonge, M.I.; Nagtegaal, I.D.; Dutilh, B.E.; Boleij, A. Production of inactivated gram-positive and gram-negative species with preserved cellular morphology and integrity. J. Microbiol. Methods 2021, 184, 106208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, H.A.; Ditta, I.B.; Varghese, S.; Steele, A. Photocatalytic disinfection using titanium dioxide: Spectrum and mechanism of antimicrobial activity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 90, 1847–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, T.; Tomoda, R.; Nakajima, T.; Wake, H. Photochemical sterilization of microbial cells by semiconductor powder. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1985, 1, 211–214. [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple, O.K.; Stefanakos, E.; Trotz, M.A.; Goswami, D.Y. A review of the mechanisms and modeling of photocatalytic disinfection. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 98, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnout, C.; Jomini, S.; Dadhwal, M.; Caillet, C.; Thomas, F.; Bauda, P. Role of electrostatic interactions in the toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles toward Escherichia coli. Colloids Surf. B 2012, 92, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.L.; Wu, G.S.; Liao, B.Q. Zeta potential of shape-controlled TiO2 nanoparticles with surfactants. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 348, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.H.; Rather, M.A. Effect of calcination temperature on the crystallite size, particle size and zeta potential of TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized via polyol-mediated method. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Iwase, T.; Horie, J.; Morioka, T. Mode of photocatalytic bactericidal action of powdered semiconductor TiO2 on mutans streptococci. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 1992, 14, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Guo, J.; Qu, J.; Hu, X. Photocatalytic degradation of pathogenic bacteria with AgI/TiO2 under visible light irradiation. Langmuir 2007, 23, 4982–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogniat, G.; Thyssen, M.; Denis, M.; Pulgarin, C.; Dukan, S. The bactericidal effect of TiO2 photocatalysis involves adsorption onto catalyst and the loss of membrane integrity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 258, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maness, P.C.; Smolinski, S.; Blake, D.M.; Huang, Z.; Wolfrum, E.J.; Jacoby, W.A. Bactericidal activity of photocatalytic TiO2 reaction: Toward an understanding of its killing mechanism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 4094–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiwi, J.; Nadtochenko, V. New evidence for TiO2 photocatalysis during bilayer lipid peroxidation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 17675–17684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carré, G.; Hamon, E.; Ennahar, S.; Estner, M.; Lett, M.C.; Horvatovich, P.; Gies, J.P.; Andre, P. TiO2 photocatalysis damages lipids and proteins in Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2573–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koizumi, Y.; Yamada, R.; Nishioka, M.; Matsumura, Y.; Tsuchido, T.; Taya, M. Deactivation kinetics of Escherichia coli cells correlated with intracellular superoxide dismutase activity in photoreaction with titanium dioxide particles. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2002, 77, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Pandey, A.K.; Singh, S.S.; Shanker, R.; Dhawan, A. Engineered ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and DNA damage leading to reduced viability of Escherichia coli. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1872–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokicka-Konieczna, P.; Wanag, A.; Sienkiewicz, A.; Kusiak-Nejman, E.; Morawski, A.W. Effect of APTES modified TiO2 on antioxidant enzymes activity secreted by Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 534, 1064–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Cao, J.; Tang, B.P.; Wang, T.G. Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on the structure and activity of catalase. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 19, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogniat, G.; Dukan, S. TiO2 photocatalysis causes DNA damage via Fenton reaction-generated hydroxyl radicals during the recovery period. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7740–7743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Feng, X.; Li, H. Thermal-sprayed photocatalytic coatings for biocidal applications: A review. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2021, 30, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vohra, A.; Goswami, D.Y.; Deshpande, D.A.; Block, S.S. Enhanced photocatalytic disinfection of indoor air. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 64, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.G.; Kumar, A.; Wong, J.S.; Shridhar, R.; Goswami, D.Y. Effect of a novel photoelectrochemical oxidation air purifier on nasal and ocular allergy symptoms. Ther. Adv. Allergy Rhinol. 2018, 9, 2152656718781609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, D.Y. A review of engineering developments of aqueous phase solar photocatalytic detoxification and disinfection processes. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 1997, 119, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, T.K.; Hingorani, S.K.; Greist, H.; Goswami, D.Y.; Block, S.S. Photocatalytic system to destroy bioaerosols in air. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 1999, 4, 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfrum, E.J.; Huang, J.; Blake, D.M.; Maness, P.C.; Huang, Z.; Fiest, J.; Jacoby, W.A. Photocatalytic oxidation of bacteria, bacterial and fungal spores, and model biofilm components to carbon dioxide on titanium dioxide-coated surfaces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3412–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiwi, J.; Nadtochenko, V. Evidence for the mechanism of photocatalytic degradation of the bacterial wall membrane at the TiO2 interface by ATR-FTIR and laser kinetic spectroscopy. Langmuir 2005, 21, 4631–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadtochenko, V.A.; Sarkisov, O.M.; Nikandrov, V.V.; Chubukov, P.A.; Denisov, N.N. Inactivation of pathogenic microorganisms in the photocatalytic process on nanosized TiO2 crystals. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 2, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.E.O.; Jacoby, W.A. Microfibrous mesh coated with titanium dioxide: A self-sterilizing, self-cleaning filter. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2002, 52, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sökmen, M.; Candan, F.; Sümer, Z. Disinfection of E. coli by the Ag-TiO2/UV system: Lipidperoxidation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2001, 143, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.D.; Tay, J.H.; Tan, K.M. Photocatalytic degradation of E. coliform in water. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3452–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraji, M.; Mohaghegh, N.; Abedini, A. Ternary composite of TiO2 nanotubes/Ti plates modified by g-C3N4 and SnO2 with enhanced photocatalytic activity for enhancing antibacterial and photocatalytic activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2018, 178, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.W.; Chan, R.C.; Wong, P.K. Disinfection of Legionella pneumophila by photocatalytic oxidation. Water Res. 2007, 41, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youji, L.I.; Mingyuan, M.A.; Xiaohu, W.A.N.G.; Xiaohua, W.A.N.G. Inactivated properties of activated carbon-supported TiO2 nanoparticles for bacteria and kinetic study. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, E.; Wei, Z.; Karabiyik, B.; Herissan, A.; Janczarek, M.; Endo, M.; Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Remita, H.; Ohtani, B. Silver-modified titania with enhanced photocatalytic and antimicrobial properties under UV and visible light irradiation. Catal. Today 2015, 252, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, M.; Wei, Z.; Wang, K.; Karabiyik, B.; Yoshiiri, K.; Rokicka, P.; Ohtani, B.; Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Kowalska, E. Noble metal-modified titania with visible-light activity for the decomposition of microorganisms. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokicka-Konieczna, P.; Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Kusiak-Nejman, E.; Morawski, A.W. Photocatalytic water disinfection under the artificial solar light by fructose-modified TiO2. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Li, G.; Sun, H.; An, T.; Zhao, H.; Wong, P.K. Visible-light-driven photocatalytic inactivation of E. coli by Ag/AgX-CNTs (X = Cl, Br, I) plasmonic photocatalysts: Bacterial performance and deactivation mechanism. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 158, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Yin, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, Y.; Zou, Q.; Luo, L.; Li, H.; Huo, Y.; Li, H. Synergistic Ag/TiO2-N photocatalytic system and its enhanced antibacterial activity towards Acinetobacter baumannii. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 224, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, M.; Mazierski, P.; Żebrowska, J.; Klimczuk, T.; Lisowski, W.; Żak, A.M.; Skowron, P.M.; Zaleska-Medynska, A. Detailed insight into photocatalytic inactivation of pathogenic bacteria in the presence of visible-light-active multicomponent photocatalysts. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.W.; Chang, H.H. Bactericidal effects and mechanisms of visible light-responsive titanium dioxide photocatalysts on pathogenic bacteria. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2012, 60, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, J.W.; Gu, M.H.; Chen, Y.K.; Chen, W.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Tseng, Y.H.; Hung, J.L.; Chang, H.H. Visible light responsive photocatalyst induces progressive and apical-terminus preferential damages on Escherichia coli surfaces. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Modak, J. Bacterial lysis via photocatalysis-A critical mechanistic review. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 2148–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
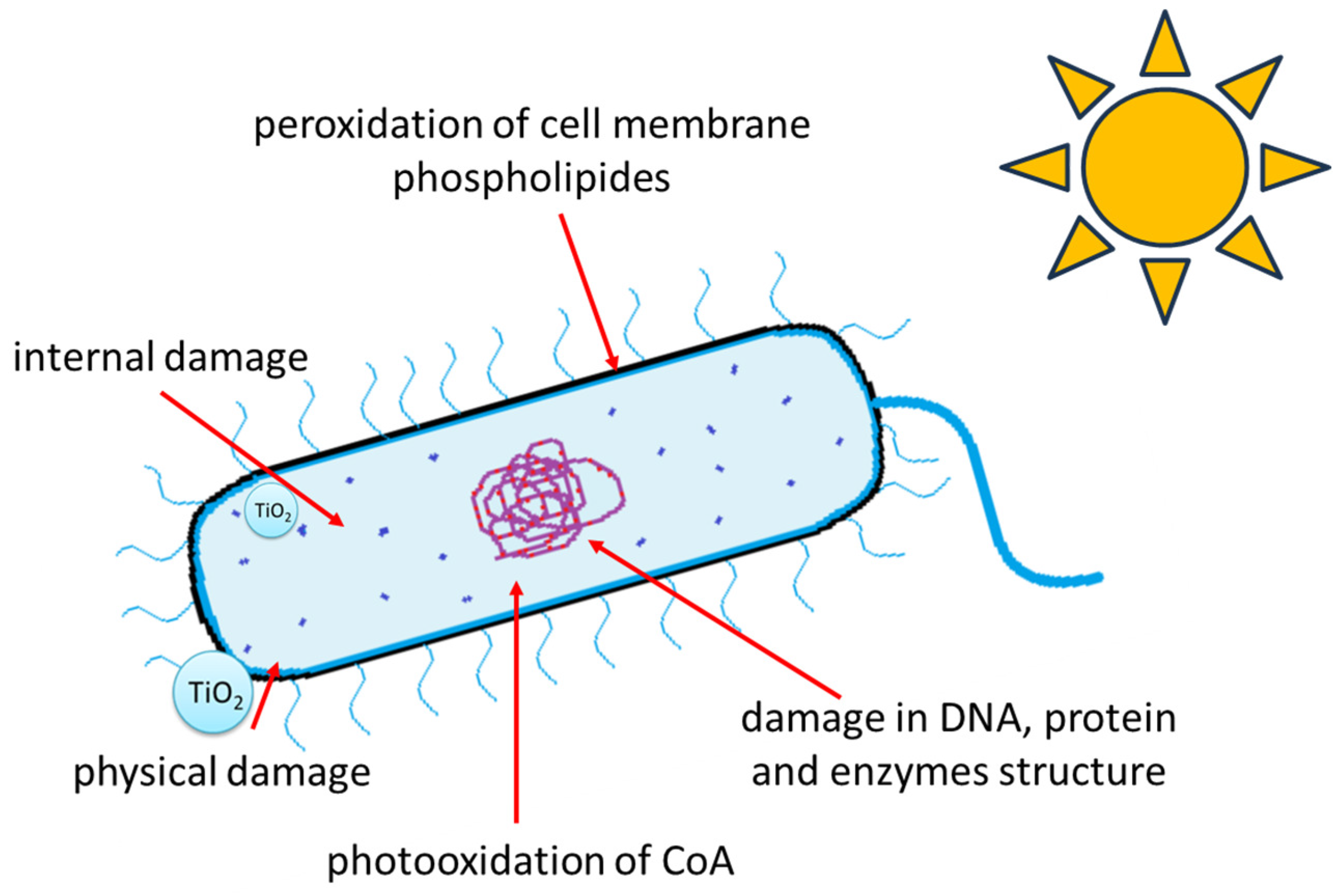
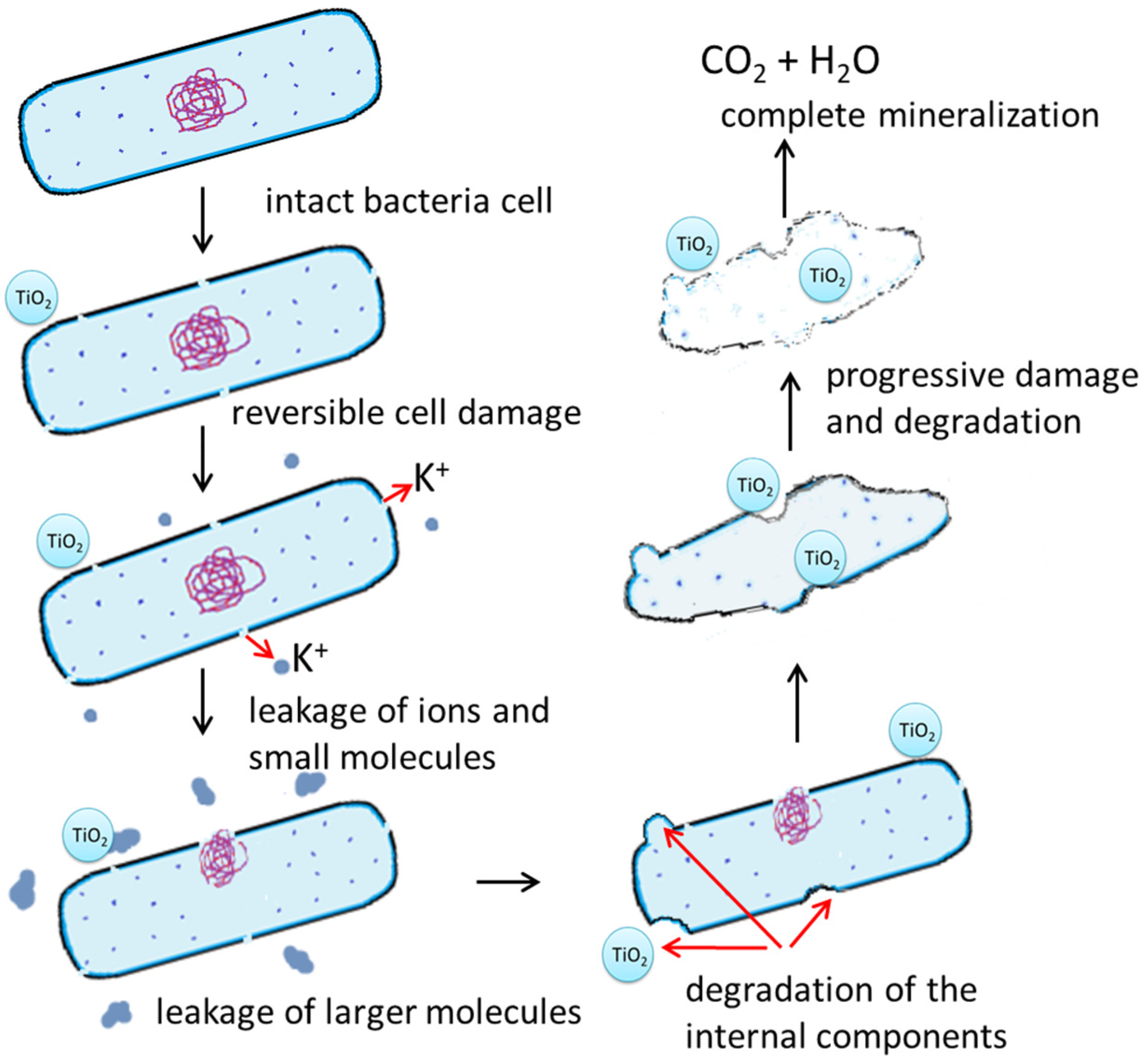
| Research Methods | Photocatalyst | Radiation Type | Used Microorganisms | Experiment Time | Results/Observations | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC—CO2 measurements, 14C radioisotope labelling SEM analysis | P25 coated on glass | UV | E. coli | 75 h | mineralization of bacteria | [18] |
| GC—CO2 measurements + kinetic data and carbon mass balance | P25 coated on quartz disks | UV | E. coli, M. luteus, B. cereus, A. niger | 72–144 h | mineralization of microorganisms | [46] |
| FTIR spectrometer fitted with a gas cell—CO2 measurements, SEM analysis | metal microfibrous mesh coated with TiO2 (P25) | UV | E. coli | 168 h | total remove bacteria from mesh | [49] |
| ATR-FTIR spectroscopy | P25 porous film | UV-A | E. coli | 44 h | changes in spectral bands suggesting the mineralization | [47] |
| ATR-FTIR spectroscopy | P25 porous film | UV-A | E. coli | 16 h | total oxidation of cell organic matter | [48] |
| GC—CO2 measurements | TiO2 (Hombifine N) and Pt/TiO2 on glass plates | UV | B. thuringiensis | 50–150 h | full photocatalytic bacterial mineralization | [22] |
| Research Methods | Photocatalyst | Radiation Type | Used Microorganisms | Experiment Time | Results/Observations | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA formation GC—CO2 measurements | TiO2 or Ag-TiO2 | UV | E. coli | 40 min | complete mineralization of E. coli | [50] |
| GC—CO2 measurements, SEM analysis | TiO2–Fe2O3 powder | UV | E. coli | 75 h | E. coli mineralization | [51] |
| TEM analysis, TOC analysis | P25 | UV | L. pneumophila | 2 h | bacterial mineralization | [53] |
| SEM analysis | TiO2/AC composites | UV | E. coli | 250 min | nearly total bacterial decomposition | [54] |
| FT-IR analysis | Ag/AgX-CNTs (X = Cl, Br, I) | VL | E. coli | 2 h | destruction of E. coli to large biomolecules | [58] |
| GC—CO2 measurements | Ag@TiO2 | UV | E. coli | 6 h | initial stage of bacterial mineralization | [55] |
| TOC analysis | Ag/TiO2-N | VL | A. baumannii | 0.5 h | initial stage of bacterial mineralization | [59] |
| GC—CO2 measurements, SEM analysis | g-C3N4-SnO2/TiO2 nanotubes/Ti plates | VL | E. coli | 32 h | complete mineralization of E. coli | [52] |
| FID-GC—CO2 measurements | Ag/TiO2 | VL | E. coli | 3 h | initial stage of bacterial mineralization | [56] |
| GC—CO2 measurements | TiO2 modified by carbon | UVA ASL | E. coli S. epidermidis | 3 h | initial stage of bacterial mineralization | [57] |
| GC—CO2 measurements | TiO2/Ag2O/AuO NTs | VL | S. aureus | 4 h | initial stage of bacterial mineralization | [60] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rokicka-Konieczna, P.; Morawski, A.W. Photocatalytic Bacterial Destruction and Mineralization by TiO2-Based Photocatalysts: A Mini Review. Molecules 2024, 29, 2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102221
Rokicka-Konieczna P, Morawski AW. Photocatalytic Bacterial Destruction and Mineralization by TiO2-Based Photocatalysts: A Mini Review. Molecules. 2024; 29(10):2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102221
Chicago/Turabian StyleRokicka-Konieczna, Paulina, and Antoni W. Morawski. 2024. "Photocatalytic Bacterial Destruction and Mineralization by TiO2-Based Photocatalysts: A Mini Review" Molecules 29, no. 10: 2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102221
APA StyleRokicka-Konieczna, P., & Morawski, A. W. (2024). Photocatalytic Bacterial Destruction and Mineralization by TiO2-Based Photocatalysts: A Mini Review. Molecules, 29(10), 2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102221








