MD Simulation Reveals Regulation of Mechanical Force and Extracellular Domain 2 on Binding of DNAM-1 to CD155
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
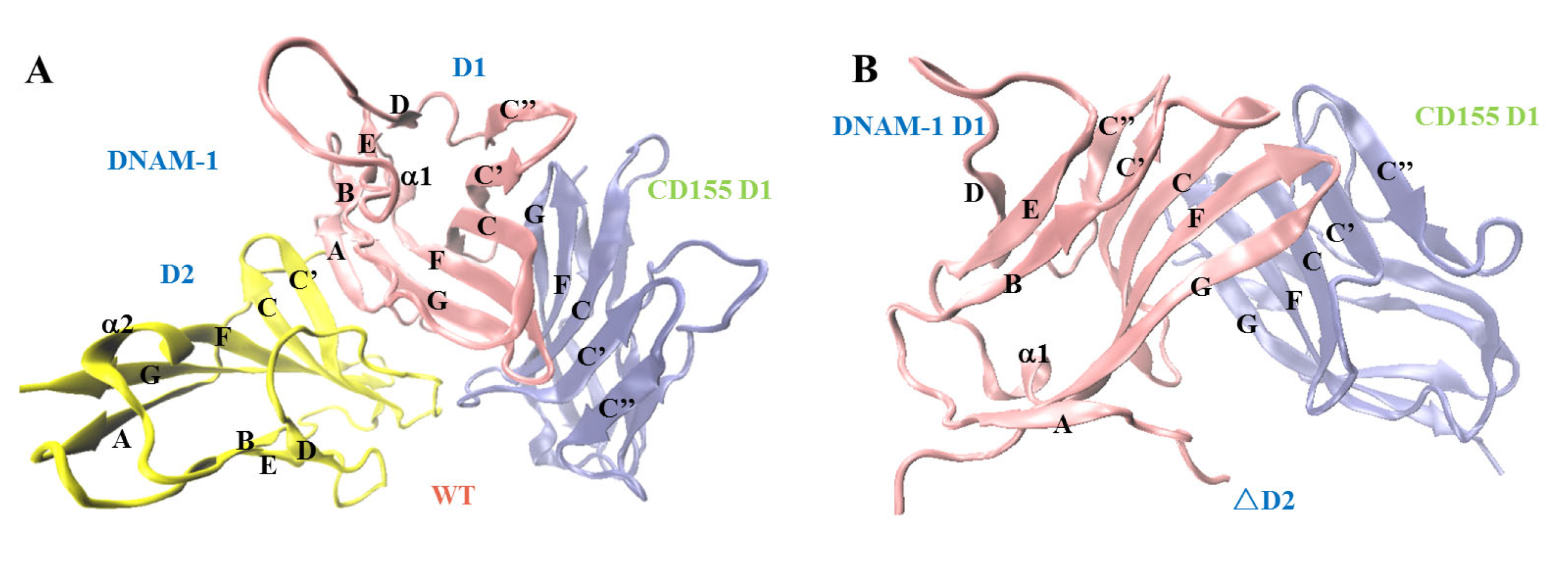
2.1. The Second Extracellular Domain D2 Improved DNAM-1 Affinity to CD155
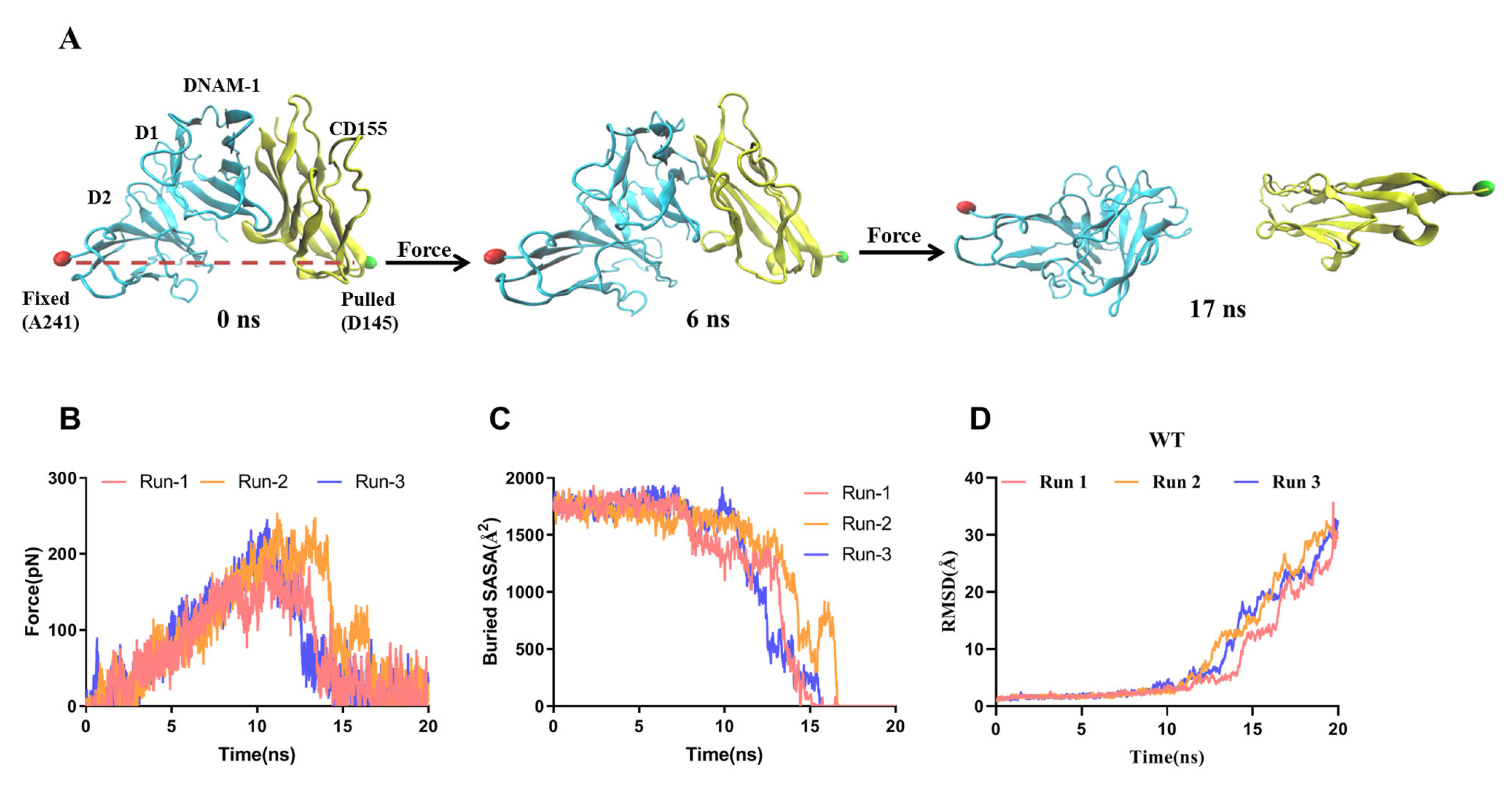
2.2. Dissociation of the Stretched DNAM-1/CD155 Complex Was Biphasic Force-Dependent
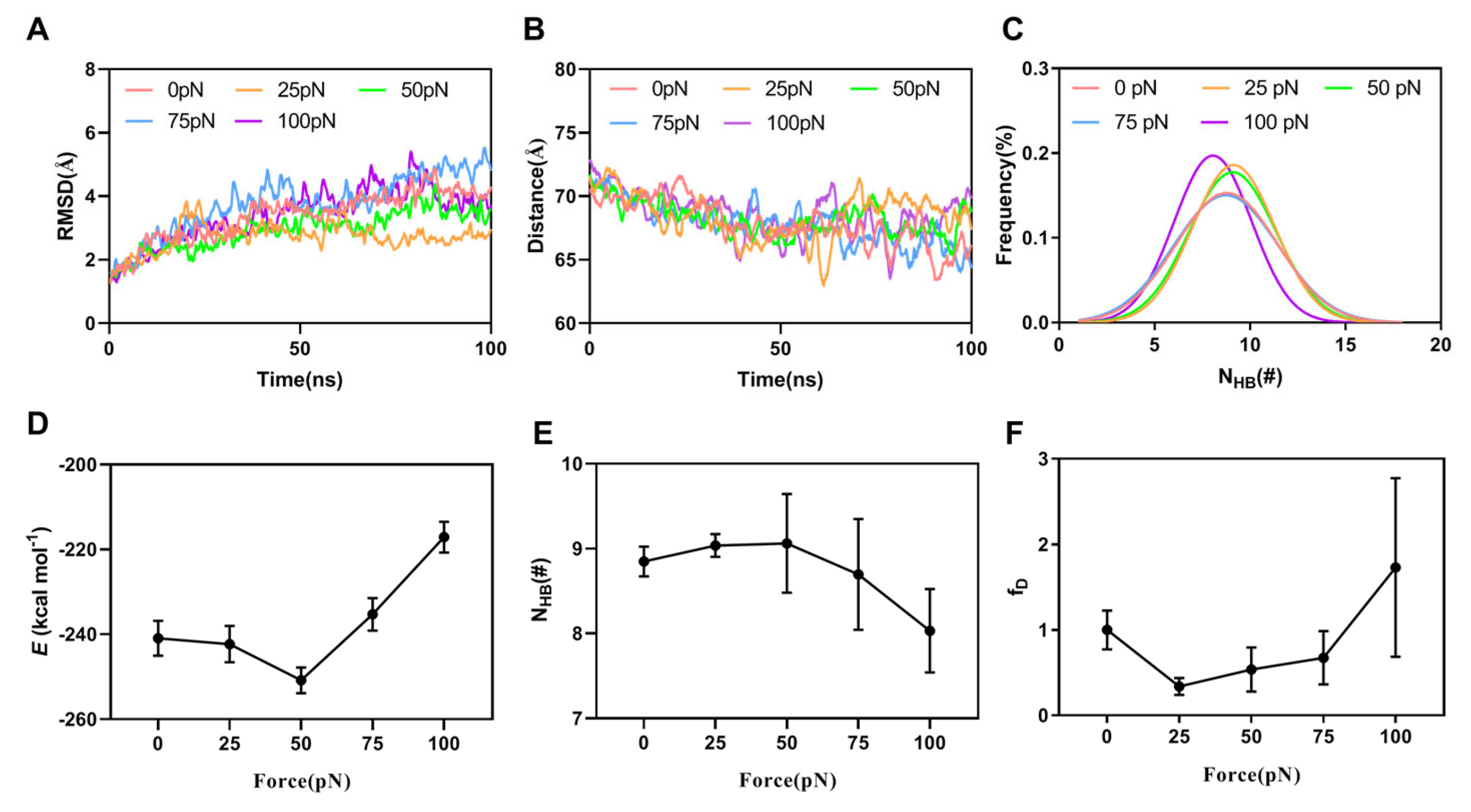
2.3. Force-Induced Allostery of the DNAM-1/CD155 Complex
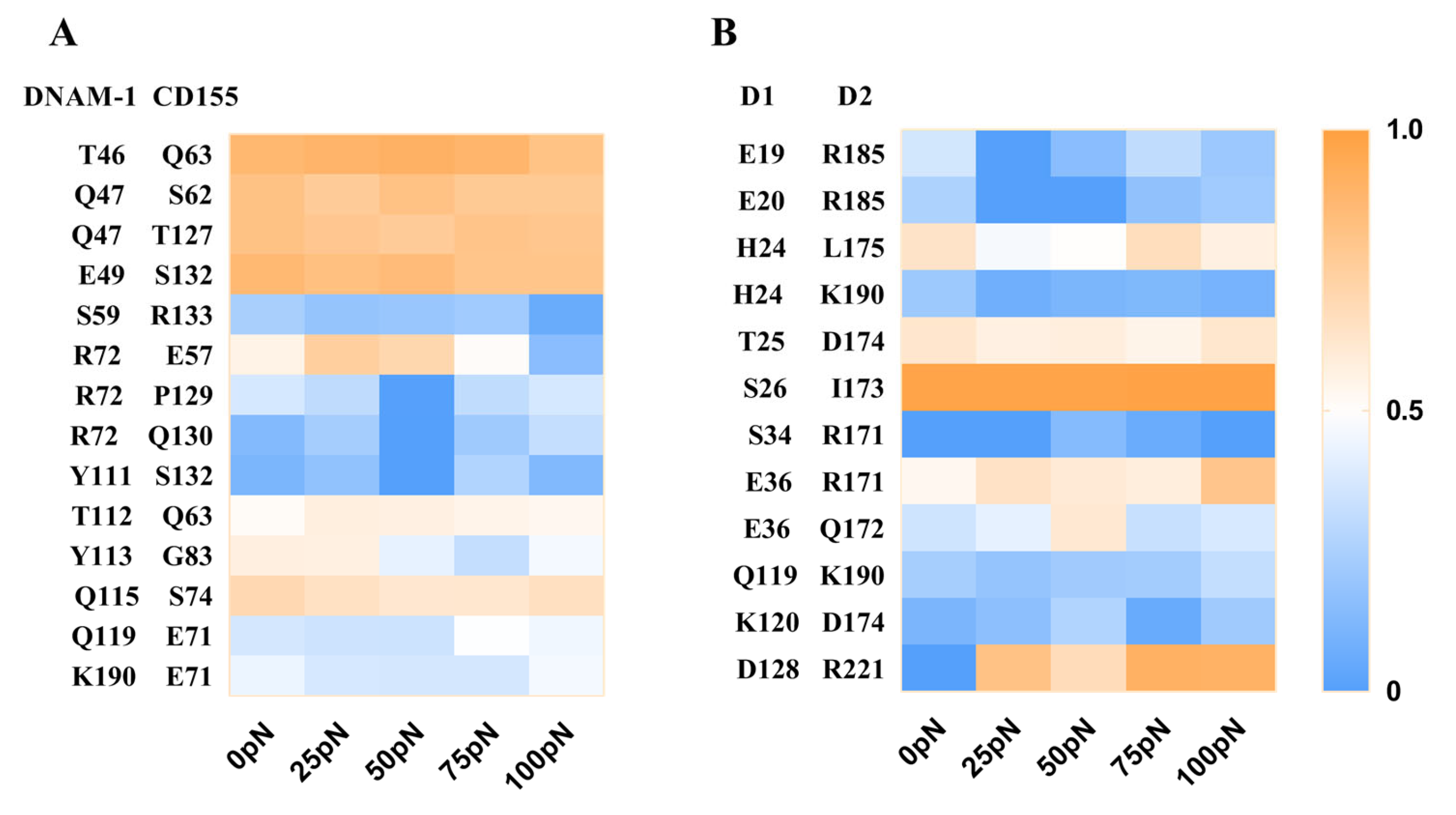
2.4. The Key Residues in the Binding of DNAM-1 to CD155 under Tensile Force
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. System Setup
4.2. MD Simulation
4.3. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Swann, J.B.; Smyth, M.J. Immune surveillance of tumors. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinchieri, G. Biology of natural killer cells. Adv. Immunol. 1989, 47, 187–376. [Google Scholar]
- Cerwenka, A.; Lanier, L.L. Ligands for natural killer cell receptors: Redundancy or specificity. Immunol. Rev. 2001, 181, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, G.P.; Koebel, C.M.; Schreiber, R.D. Interferons, immunity and cancer immunoediting. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, W.M. Natural killer cell receptors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1998, 10, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, G.F.; Triglia, T.; Werkmeister, J.A.; Begley, C.G.; Boyd, A.W. TLiSA1, a human T lineage-specific activation antigen involved in the differentiation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and anomalous killer cells from their precursors. J. Exp. Med. 1985, 161, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xie, X.; Zhang, X.; Jia, W.; Jian, J.; Song, C.; Jin, B. The expression, regulation and adhesion function of a novel CD molecule, CD226, on human endothelial cells. Life Sci. 2003, 73, 2373–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.L.; Dunn, S.M.; Jin, B.; Hillam, A.J.; Walton, S.; Berndt, M.C.; Murray, A.W.; Krissansen, G.W.; Burns, G.F. Characterization of a novel membrane glycoprotein involved in platelet activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 13475–13482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibuya, A.; Campbell, D.; Hannum, C.; Yssel, H.; Franz-Bacon, K.; McClanahan, T.; Kitamura, T.; Nicholl, J.; Sutherland, G.R.; Lanier, L.L.; et al. DNAM-1, a novel adhesion molecule involved in the cytolytic function of T lymphocytes. Immunity 1996, 4, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, A.; Colonna, M. The role of NK cell recognition of nectin and nectin-like proteins in tumor immunosurveillance. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2006, 16, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zheng, Q.; Xin, N.; Wang, W.; Zhao, C. CD155, an onco-immunologic molecule in human tumors. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1934–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castriconi, R.; Dondero, A.; Corrias, M.V.; Lanino, E.; Pende, D.; Moretta, L.; Bottino, C.; Moretta, A. Natural killer cell-mediated killing of freshly isolated neuroblastoma cells: Critical role of DNAX accessory molecule-1-poliovirus receptor interaction. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 9180–9184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huse, M. Mechanical forces in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuss, F.A.; Watson, G.M.; Goodall, K.J.; Leece, I.; Chatterjee, S.; Fu, Z.; Thaysen-Andersen, M.; Andrews, D.M.; Rossjohn, J.; Berry, R. Structural basis for the recognition of nectin-like protein-5 by the human-activating immune receptor, DNAM-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 12534–12546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Mueller, S.; Morais, M.C.; Bator, C.M.; Bowman, V.D.; Hafenstein, S.; Wimmer, E.; Rossmann, M.G. Crystal structure of CD155 and electron microscopic studies of its complexes with polioviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18284–18289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.; Ge, K.; Zheng, X.; Wei, H.; Sun, R.; Tian, Z. CD226 protein is involved in immune synapse formation and triggers Natural Killer (NK) cell activation via its first extracellular domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 6969–6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qi, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Tan, S.; Gao, G.F. Binding mode of the side-by-side two-IgV molecule CD226/DNAM-1 to its ligand CD155/Necl-5. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Fang, Y.; Wu, J. Biphasic Force-Regulated Phosphorylation Site Exposure and Unligation of ERM Bound with PSGL-1: A Novel Insight into PSGL-1 Signaling via Steered Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Huang, B.; Pan, Y.; Fang, J.; Wang, H.; Ji, Y.; Ling, Y.; Guo, P.; Lin, J.; Li, Q.; et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics of P-selectin-induced β(2) integrin activation of human neutrophils under flow. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1023865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yago, T.; Lou, J.; Wu, T.; Yang, J.; Miner, J.J.; Coburn, L.; López, J.A.; Cruz, M.A.; Dong, J.F.; McIntire, L.V.; et al. Platelet glycoprotein Ibalpha forms catch bonds with human WT vWF but not with type 2B von Willebrand disease vWF. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3195–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yago, T.; Wu, J.; Wey, C.D.; Klopocki, A.G.; Zhu, C.; McEver, R.P. Catch bonds govern adhesion through L-selectin at threshold shear. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 166, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Sun, X.; Lin, J.; Ling, Y.; Fang, Y.; Wu, J. MD Simulations on a Well-Built Docking Model Reveal Fine Mechanical Stability and Force-Dependent Dissociation of Mac-1/GPIbalpha Complex. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 638396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Chen, W.; Evavold, B.D.; Zhu, C.J.C. Accumulation of Dynamic Catch Bonds between TCR and Agonist Peptide-MHC Triggers T Cell Signaling. Cell 2014, 157, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Fang, Y.; Wu, J. Tension Enhances the Binding Affinity of beta1 Integrin by Clamping Talin Tightly: An Insight from Steered Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2022, 62, 5688–5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Wu, J.; Fang, Y. Moderate Constraint Facilitates Association and Force-Dependent Dissociation of HA-CD44 Complex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wayman, A.; Lin, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Wu, J. Flow-Enhanced Stability of Rolling Adhesion through E-Selectin. Biophys. J. 2016, 111, 686–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, B.T.; Long, M.; Piper, J.W.; Yago, T.; McEver, R.P.; Zhu, C. Direct observation of catch bonds involving cell-adhesion molecules. Nature 2003, 423, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Lin, J.; Cruz, M.A.; Dong, J.F.; Zhu, C. Force-induced cleavage of single VWFA1A2A3 tridomains by ADAMTS-13. Blood 2010, 115, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGibbon, R.T.; Schwantes, C.R.; Pande, V.S. Statistical model selection for Markov models of biomolecular dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 6475–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aricescu, A.R.; Jones, E.Y. Immunoglobulin superfamily cell adhesion molecules: Zippers and signals. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2007, 19, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottino, C.; Castriconi, R.; Pende, D.; Rivera, P.; Nanni, M.; Carnemolla, B.; Cantoni, C.; Grassi, J.; Marcenaro, S.; Reymond, N.; et al. Identification of PVR (CD155) and Nectin-2 (CD112) as cell surface ligands for the human DNAM-1 (CD226) activating molecule. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Qi, G.; Miller, J.S.; Zheng, S.G. CD226: An Emerging Role in Immunologic Diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.J.; Tiede, C.; Penswick, N.; Tang, A.A.; Trinh, C.H.; Mandal, U.; Zajac, K.Z.; Gaule, T.; Howell, G.; Edwards, T.A.; et al. Generation of specific inhibitors of SUMO-1- and SUMO-2/3-mediated protein-protein interactions using Affimer (Adhiron) technology. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, eaaj2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.C.; Braun, R.; Wang, W.; Gumbart, J.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Villa, E.; Chipot, C.; Skeel, R.D.; Kalé, L.; Schulten, K. Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1781–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKerell, A.D.; Bashford, D.; Bellott, M.; Dunbrack, R.L.; Evanseck, J.D.; Field, M.J.; Fischer, S.; Gao, J.; Guo, H.; Ha, S.; et al. All-atom empirical potential for molecular modeling and dynamics studies of proteins. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 3586–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Z. Characterization of the structural ensembles of p53 TAD2 by molecular dynamics simulations with different force fields. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. PCCP 2018, 20, 8676–8684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoreishi, D.; Cerutti, D.S.; Fallon, Z.; Simmerling, C.; Roitberg, A.E. Fast Implementation of the Nudged Elastic Band Method in AMBER. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019, 15, 4699–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

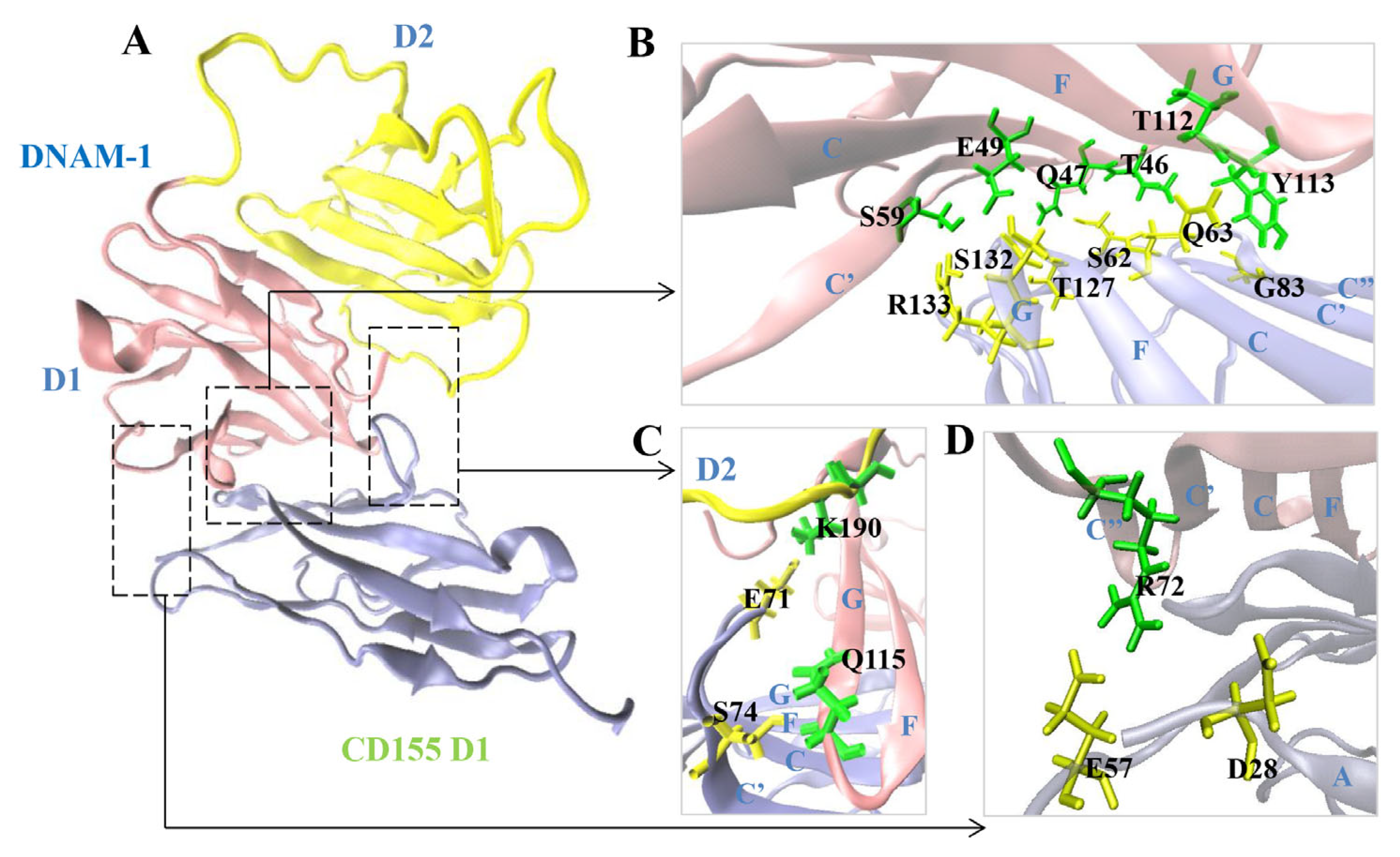

| No. | DNAM-1 | CD155 | WT | ΔD2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residue | Residue | Occupancy | Occupancy | |
| 1 | E49 | S132 | 0.90 ± 0.02 | 0.86 ± 0.07 |
| 2 | T46 | Q63 | 0.86 ± 0.07 | 0.80 ± 0.14 |
| 3 | Q47 | T127 | 0.78 ± 0.02 | 0.76 ± 0.05 |
| 4 | Q115 | S74 | 0.67 ± 0.02 | 0.45 ± 0.24 |
| 5 | Q47 | S62 | 0.62 ± 0.33 | 0.70 ± 0.14 |
| 6 | T112 | Q63 | 0.49 ± 0.42 | 0.40 ± 0.19 |
| 7 | Y113 | G83 | 0.49 ± 0.07 | 0.44 ± 0.23 |
| 8 | R72 | E57 | 0.33 ± 0.57 | 0.26 ± 0.44 |
| 9 | R72 | D28 | 0.28 ± 0.49 | 0.04 ± 0.07 |
| 10 | S59 | R133 | 0.25 ± 0.38 | 0.08 ± 0.08 |
| 11 | E49 | R133 | 0.24 ± 0.42 | 0.14 ± 0.25 |
| 12 | K190 | E71 | 0.23 ± 0.22 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, P.; Fang, Y.; Wu, J. MD Simulation Reveals Regulation of Mechanical Force and Extracellular Domain 2 on Binding of DNAM-1 to CD155. Molecules 2023, 28, 2847. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062847
Fang L, Zhao Y, Guo P, Fang Y, Wu J. MD Simulation Reveals Regulation of Mechanical Force and Extracellular Domain 2 on Binding of DNAM-1 to CD155. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2847. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062847
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Liping, Yang Zhao, Pei Guo, Ying Fang, and Jianhua Wu. 2023. "MD Simulation Reveals Regulation of Mechanical Force and Extracellular Domain 2 on Binding of DNAM-1 to CD155" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2847. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062847
APA StyleFang, L., Zhao, Y., Guo, P., Fang, Y., & Wu, J. (2023). MD Simulation Reveals Regulation of Mechanical Force and Extracellular Domain 2 on Binding of DNAM-1 to CD155. Molecules, 28(6), 2847. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062847






