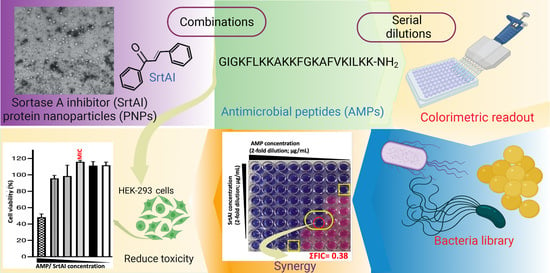
Sortase A Inhibitor Protein Nanoparticle Formulations Demonstrate Antibacterial Synergy When Combined with Antimicrobial Peptides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
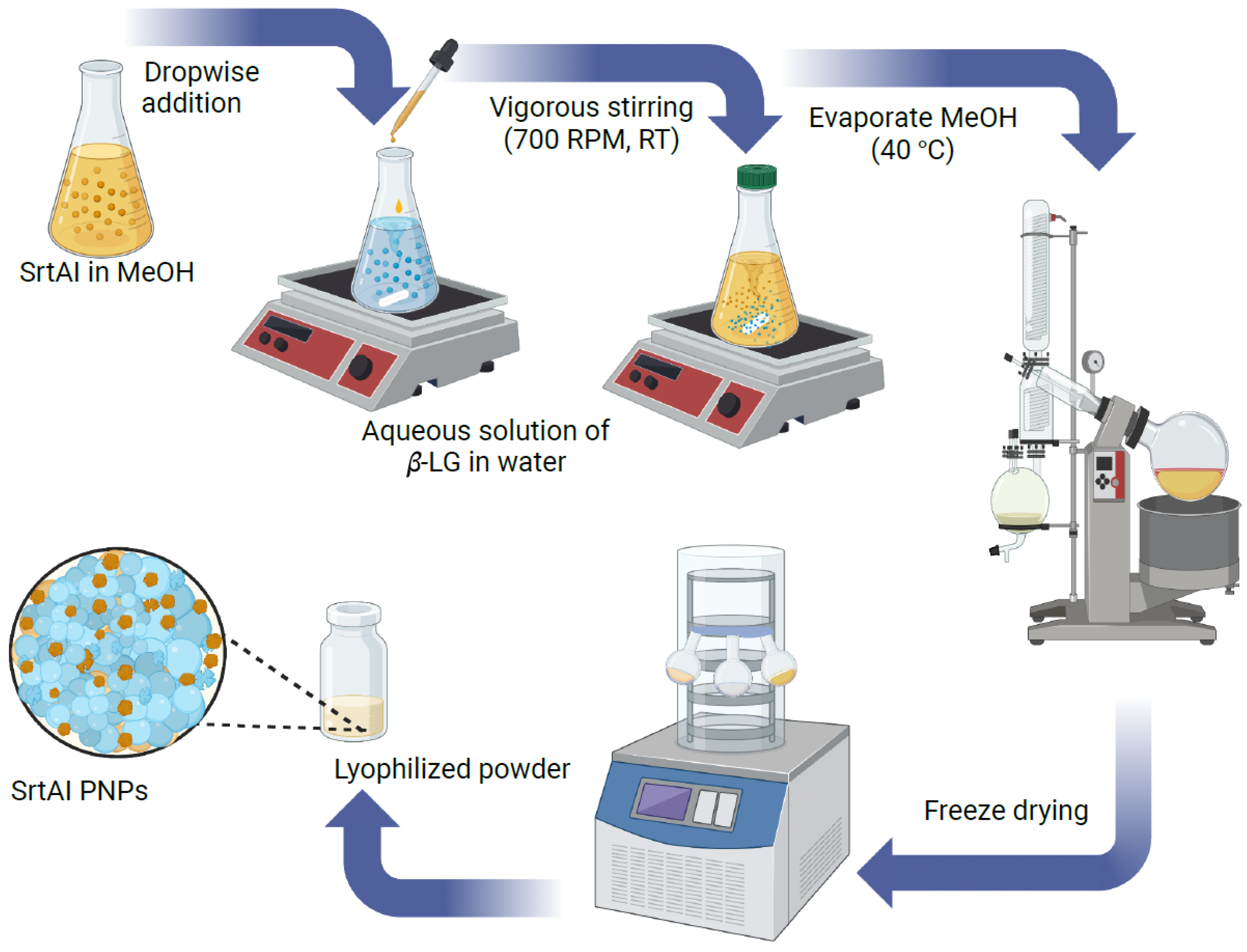
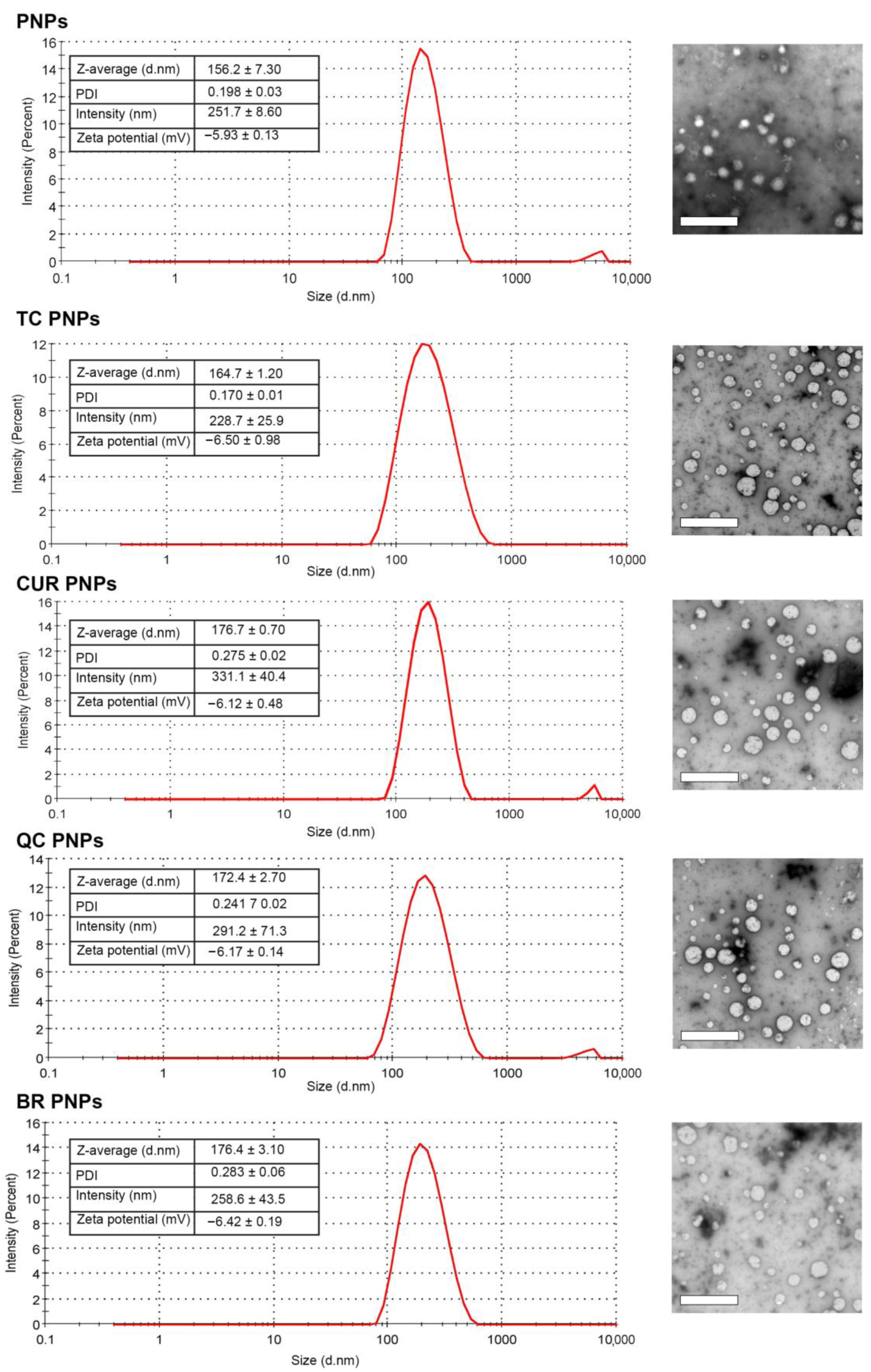
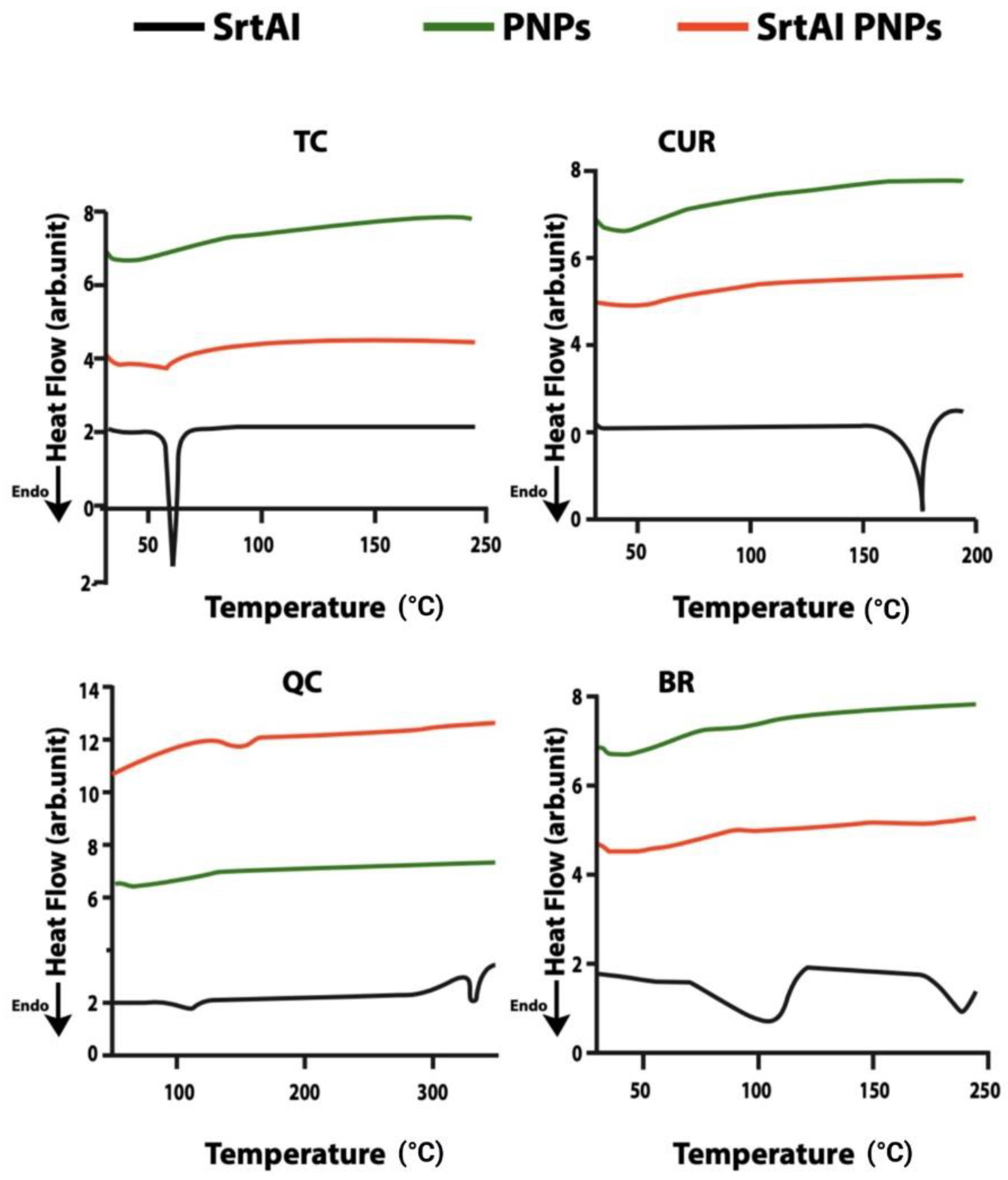
2.1. Characterization of SrtAI PNPs
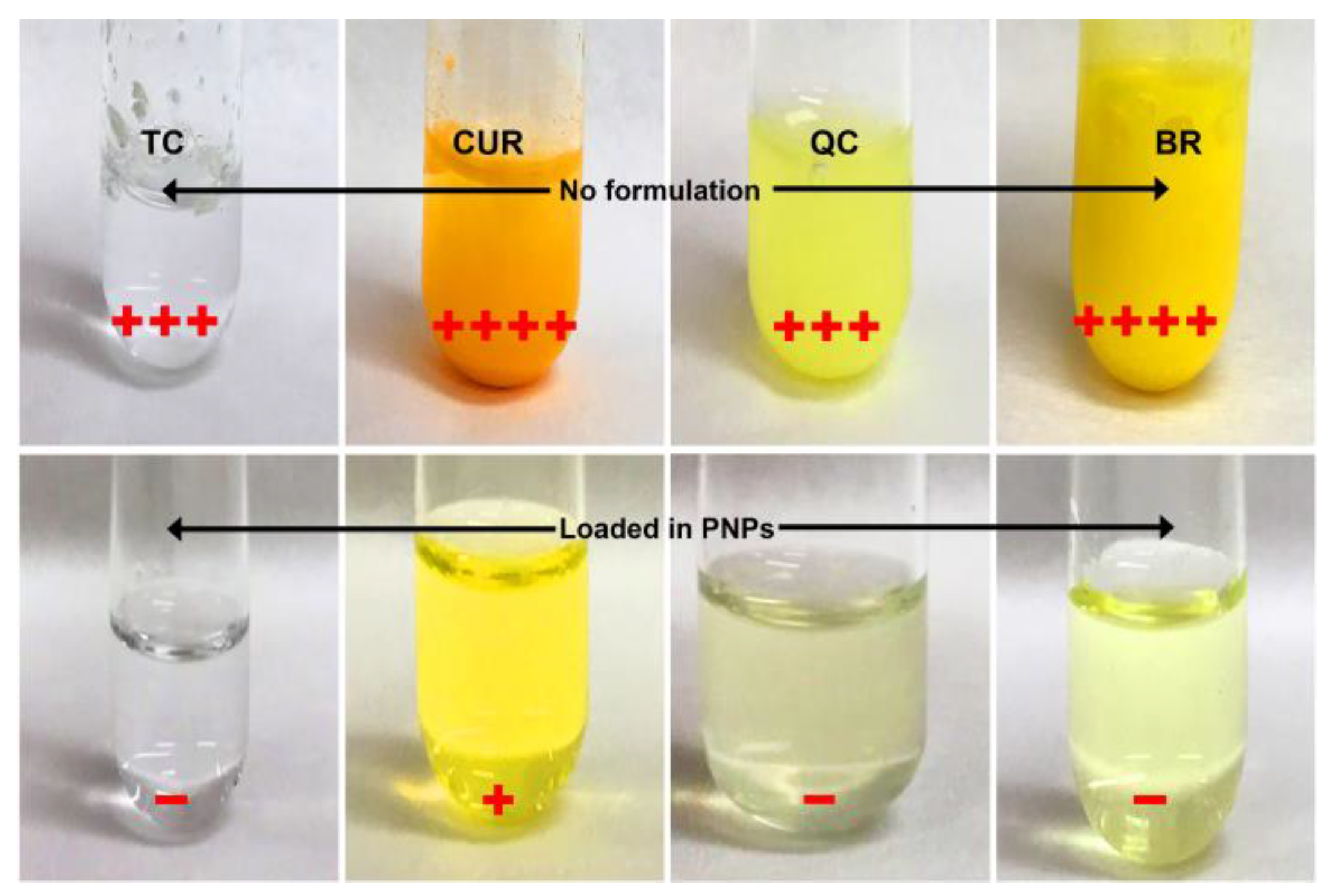
2.2. β -LG PNP SrtAI-Loading Capacity
2.3. Antibacterial Activity of Each SrtAI PNP Formulation
2.4. Identification of Synergistic SrtAI PNP Combinations with AMPs
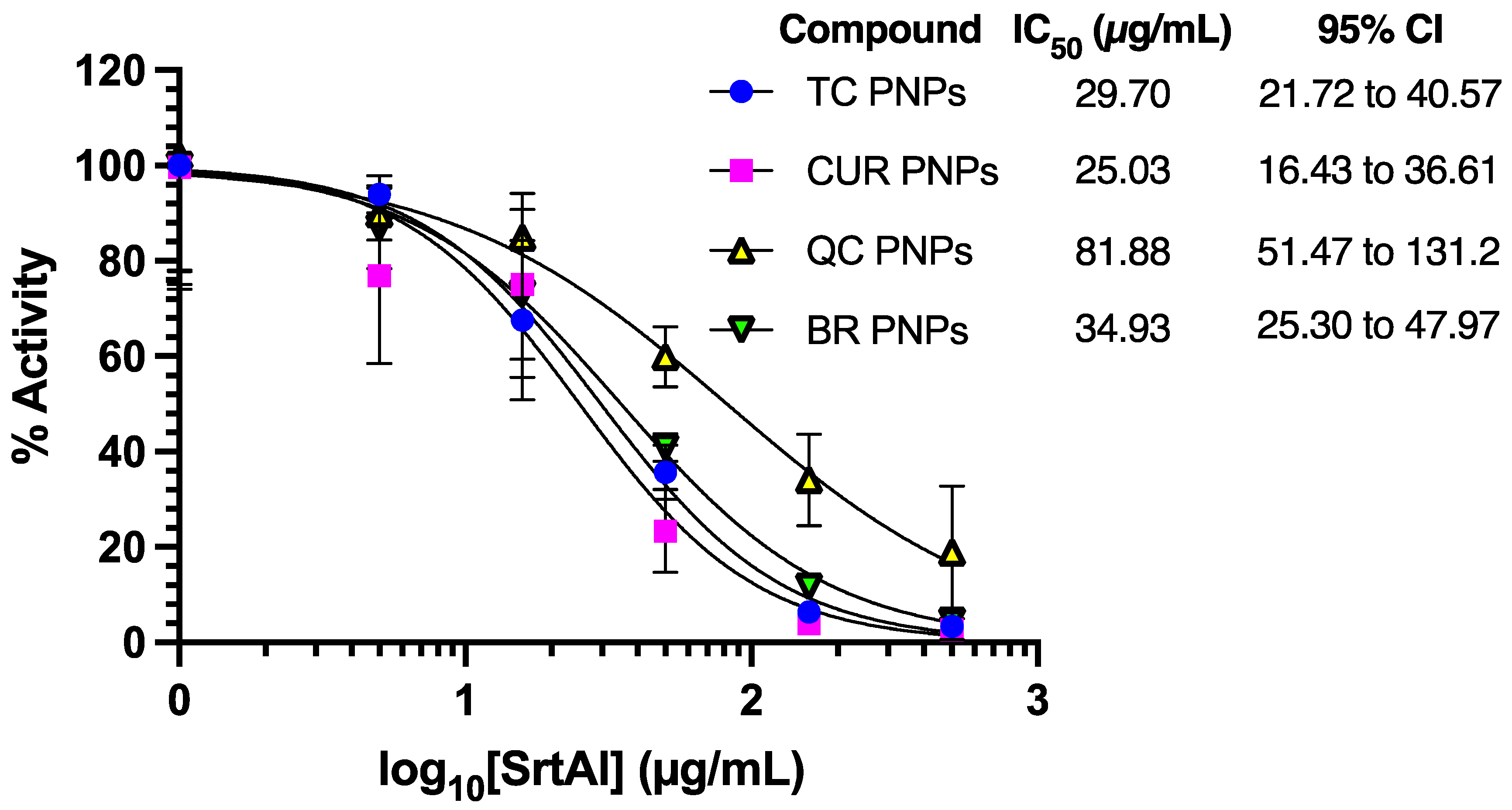
2.5. Assessment of SrtA Inhibition
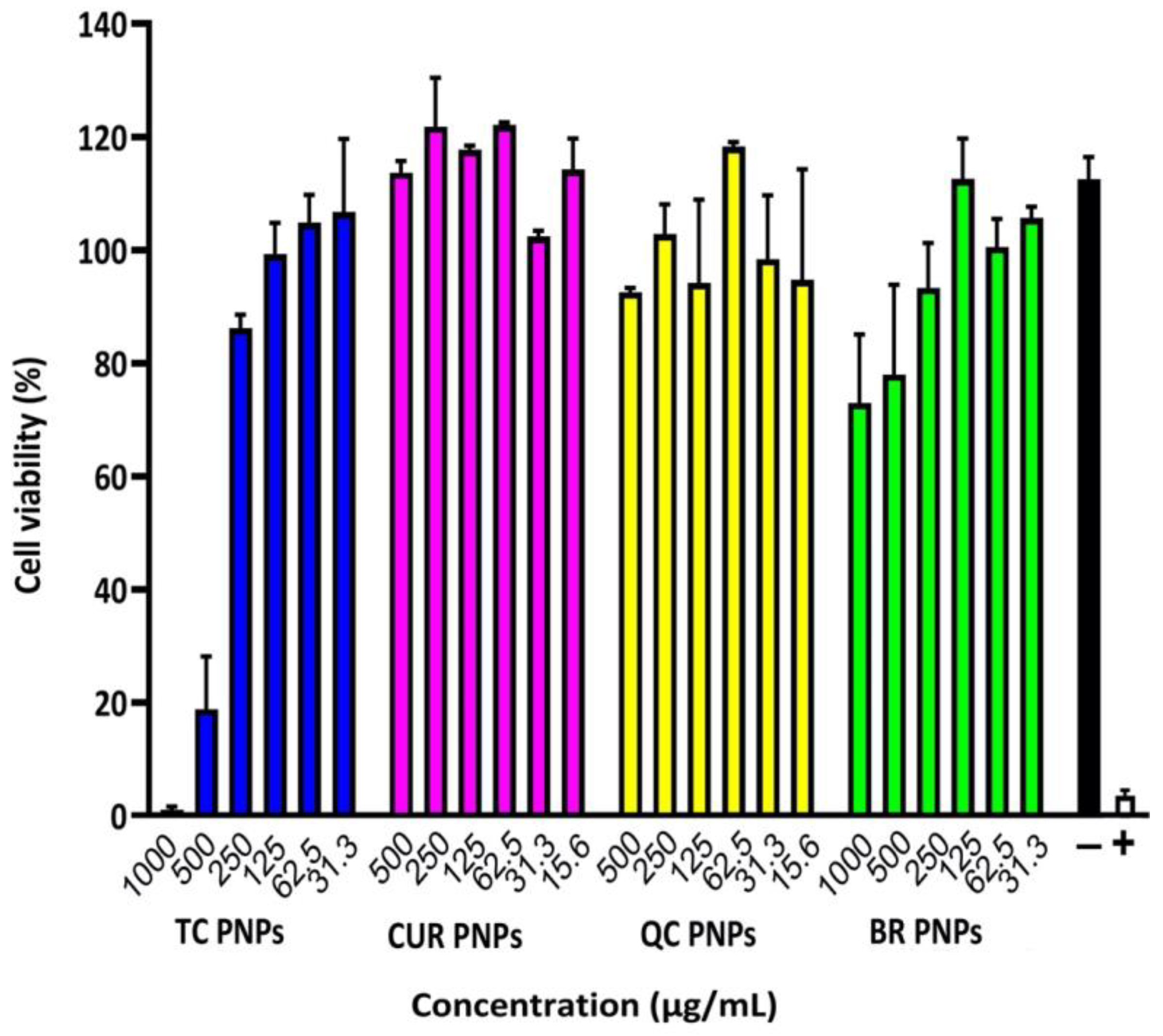
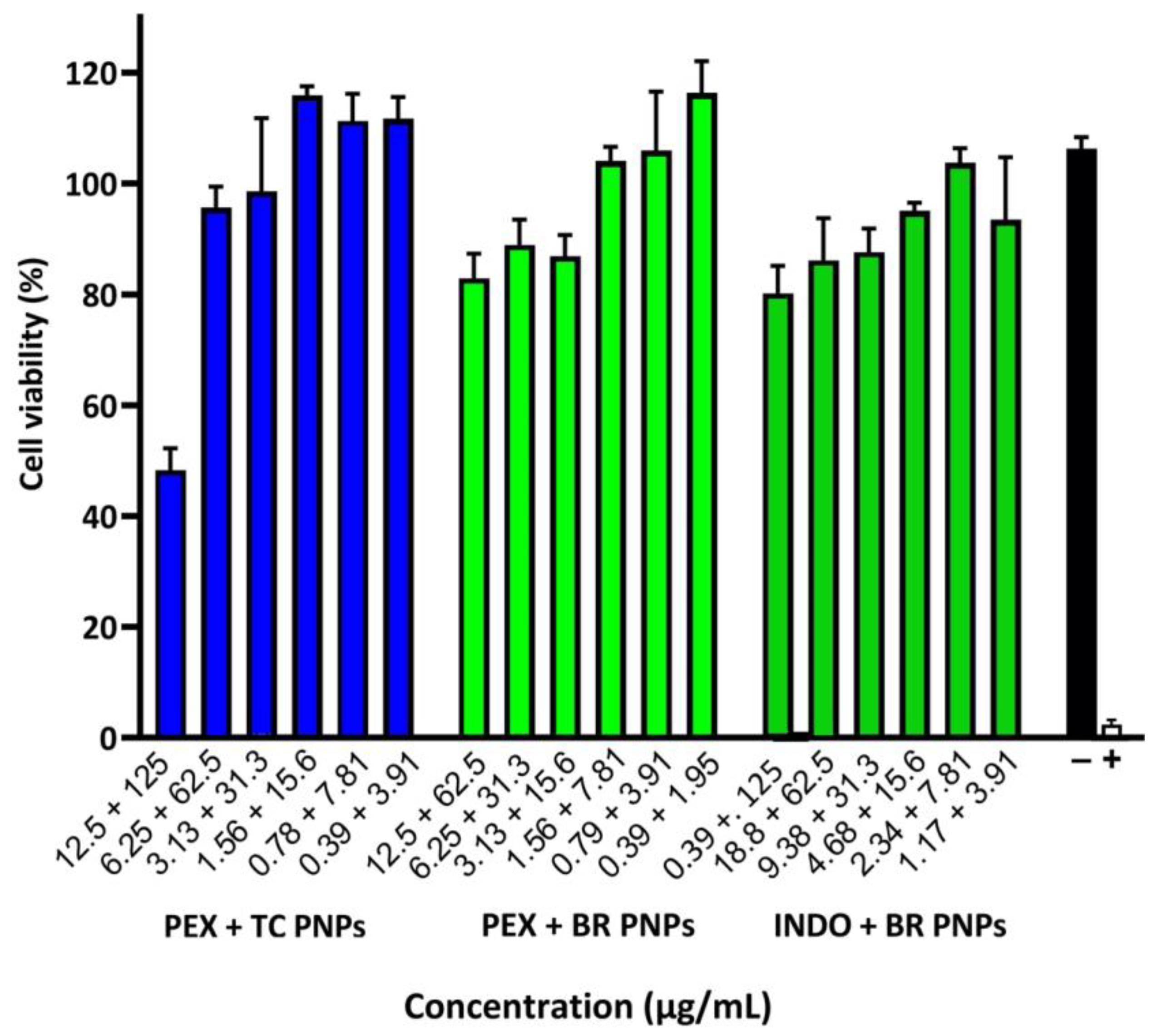
2.6. Cell Viability
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Equipment
3.3. Preparation of SrtAI-Loaded PNPs
3.4. Characterization of SrtAI-Loaded PNPs
3.5. Loading Capacity Determination
3.6. Preparation of Bacterial Inoculums
3.7. Broth Microdilution Assays
3.8. Checkerboard Assay
3.9. SrtA Inhibition Assay
3.10. Cell Viability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, B.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Harris, P.N.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Walker, M.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00181-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezzoagli, C.; Archetti, M.; Mignot, I.; Baumgartner, M.; Kümmerli, R. Combining antibiotics with antivirulence compounds can have synergistic effects and reverse selection for antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharthi, S.; Ziora, Z.M.; Janjua, T.; Popat, A.; Moyle, P.M. Formulation and Biological Evaluation of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Combinations of Sortase A Inhibitors and Antimicrobial Peptides. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marraffini, L.A.; DeDent, A.C.; Schneewind, O. Sortases and the Art of Anchoring Proteins to the Envelopes of Gram-Positive Bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2006, 70, 192–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosschalk, J.E.; Chang, C.; Sue, C.K.; Siegel, S.D.; Wu, C.; Kattke, M.D.; Yi, S.W.; Damoiseaux, R.; Jung, M.E.; Ton-That, H.; et al. A Cell-based Screen in Actinomyces oris to Identify Sortase Inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitulescu, G.; Margina, D.; Zanfirescu, A.; Olaru, O.; Nitulescu, G. Targeting Bacterial Sortases in Search of Anti-virulence Therapies with Low Risk of Resistance Development. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, S.; Alavi, S.E.; Moyle, P.M.; Ziora, Z.M. Sortase A (SrtA) inhibitors as an alternative treatment for superbug infections. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 2164–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.W.; Yi, S.W.; Paek, S.-M. Design and Synthesis of Small Molecules as Potent Staphylococcus aureus Sortase A Inhibitors. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, S.; Ziora, Z.M.; Moyle, P.M. Optimized protocols for assessing libraries of poorly soluble sortase A inhibitors for antibacterial activity against medically-relevant bacteria, toxicity and enzyme inhibition. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2021, 52, 116527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Guliani, A.; Shukla, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Acharya, A. Green surfactant based synthesis of curcumin loaded poly lactic-co-glycolic acid nanoparticles with enhanced solubility, photo-stability and anti-biofilm activity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Dongave, S.M.; Date, T.; Kushwah, V.; Mahajan, R.R.; Pujara, N.; Kumeria, T.; Popat, A. Succinylated β-Lactoglobuline-Functionalized Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes with Improved Colloidal Stability and Biocompatibility. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 3361–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulakkat, S.; Balaji, S.A.; Rangarajan, A.; Raichur, A.M. Surface Engineered Protein Nanoparticles With Hyaluronic Acid Based Multilayers for Targeted Delivery of Anticancer Agents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 23437–23449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanin, I.A.; Elzoghby, A.O. Self-assembled non-covalent protein-drug nanoparticles: An emerging delivery platform for anti-cancer drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 1437–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Wang, L.; You, X.; Wu, J. Nano and microscale delivery platforms for enhanced oral peptide/protein bioavailability. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 5804–5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.P.; Gandhi, V.V.; Singh, B.G.; Kunwar, A.; Kumar, N.N.; Priyadarsini, K. Preparation of albumin nanoparticles: Optimum size for cellular uptake of entrapped drug (Curcumin). Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 567, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohcharoenkal, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.C.; Rojanasakul, Y. Protein Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Carriers for Cancer Therapy. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 180549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, M.; Sousa, J.; Pais, A.; Vitorino, C. Clinical applications of nanostructured drug delivery systems. In Core-Shell Nanostructures for Drug Delivery and Theranostics; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 43–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujara, N.; Wong, K.Y.; Qu, Z.; Wang, R.; Moniruzzaman; Rewatkar, P.; Kumeria, T.; Ross, B.P.; McGuckin, M.; Popat, A. Oral Delivery of β-Lactoglobulin-Nanosphere-Encapsulated Resveratrol Alleviates Inflammation in Winnie Mice with Spontaneous Ulcerative Colitis. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 18, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Wahed, A.A.; Yosri, N.; Sakr, H.; Du, M.; Algethami, A.; Zhao, C.; Abdelazeem, A.; Tahir, H.; Masry, S.; Abdel-Daim, M.; et al. Wasp Venom Biochemical Components and Their Potential in Biological Applications and Nanotechnological Interventions. Toxins 2021, 13, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Guo, M. Interactions between β-Lactoglobulin and 3,3′-Diindolylmethane in Model System. Molecules 2019, 24, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.-K.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, M.-R.; Jun, W.; Lee, W.-J. Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity of β-Lactoglobulin Nanoparticles: The Effects of Particle Size and Surface Charge. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 28, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Wehling, R.L.; Ciftci, O.; Zhang, Y. Formation of complexes between tannic acid with bovine serum albumin, egg ovalbumin and bovine beta-lactoglobulin. Food Res. Int. 2017, 102, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; Saini, M. Formulation and evaluation of curcumin microsponges for oral and topical drug delivery. Prog. Biomater. 2018, 7, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tang, K.; Hu, X.; Zou, G. Physicochemical characterization and antioxidant activity of quercetin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 107, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battu, S.K.; Repka, M.A.; Maddineni, S.; Chittiboyina, A.; Avery, M.; Majumdar, S. Physicochemical Characterization of Berberine Chloride: A Perspective in the Development of a Solution Dosage Form for Oral Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banun, V.J.; Rewatkar, P.; Chaudhary, Z.; Qu, Z.; Janjua, T.; Patil, A.; Wu, Y.; Ta, H.T.; Bansal, N.; Miles, J.A.; et al. Protein Nanoparticles for Enhanced Oral Delivery of Coenzyme-Q10: In Vitro and in Silico Studies. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarihamy, M.; Tripathi, S.K.; Khan, S.; Muhammad, I. Schottiin, a new prenylated isoflavones from Psorothamnus schottii and antibacterial synergism studies between methicillin and fremontone against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ATCC. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 36, 2984–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awang, A.F.I.; Ahmed, Q.U.; Shah, S.A.A.; Jaffri, J.M.; Ghafoor, K.; Uddin, A.B.M.H.; Ferdosh, S.; Sarker, Z.I. Isolation and characterization of novel antibacterial compound from an untapped plant, Stereospermum fimbriatum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 34, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshikh, M.; Ahmed, S.; Funston, S.; Dunlop, P.; McGaw, M.; Marchant, R.; Banat, I.M. Resazurin-based 96-well plate microdilution method for the determination of minimum inhibitory concentration of biosurfactants. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 1015–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, M.W.; Antos, J.M.; Ploegh, H.L. Site-Specific Protein Labeling via Sortase-Mediated Transpeptidation. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2009, 56, 15.3.1–15.3.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Präbst, K.; Engelhardt, H.; Ringgeler, S.; Hübner, H. Basic Colorimetric Proliferation Assays: MTT, WST, and Resazurin. In Cell Viability Assays; Gilbert, D.F., Friedrich, O., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1601, pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]

| Bacteria | MIC Values for SrtAI PNPs (µg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC | CUR | QC | BR | |
| S. aureus (MSSA) | 125 | 62.5 | 62.5 | 125 |
| E. coli | 500 | 31.3 | 31.3 | 250 |
| P. aeruginosa | 500 | 31.3 | 31.3 | 500 |
| S. aureus (MRSA) | 125 | 62.5 | 62.5 | 125 |
| FIC Index (ΣFIC) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus (MSSA) | S. aureus (MRSA) | E. coli | P. aeruginosa | |||||||||
| PEX | INDO | MASTO | PEX | INDO | MASTO | PEX | INDO | MASTO | PEX | INDO | MASTO | |
| TC PNPs | 0.38 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.38 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.37 | 0.63 | 0.75 | 0.50 | 0.75 | 1.00 |
| CUR PNPs | 1.12 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 1.50 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| QC PNPs | 0.75 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.75 | 2.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.75 | 1.50 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.50 |
| BR PNPs | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.75 | 0.31 | 0.50 | 0.62 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alharthi, S.; Popat, A.; Ziora, Z.M.; Moyle, P.M. Sortase A Inhibitor Protein Nanoparticle Formulations Demonstrate Antibacterial Synergy When Combined with Antimicrobial Peptides. Molecules 2023, 28, 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052114
Alharthi S, Popat A, Ziora ZM, Moyle PM. Sortase A Inhibitor Protein Nanoparticle Formulations Demonstrate Antibacterial Synergy When Combined with Antimicrobial Peptides. Molecules. 2023; 28(5):2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052114
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlharthi, Sitah, Amirali Popat, Zyta Maria Ziora, and Peter Michael Moyle. 2023. "Sortase A Inhibitor Protein Nanoparticle Formulations Demonstrate Antibacterial Synergy When Combined with Antimicrobial Peptides" Molecules 28, no. 5: 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052114
APA StyleAlharthi, S., Popat, A., Ziora, Z. M., & Moyle, P. M. (2023). Sortase A Inhibitor Protein Nanoparticle Formulations Demonstrate Antibacterial Synergy When Combined with Antimicrobial Peptides. Molecules, 28(5), 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052114