Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Association between the Pathways of Glutathione and α-Linolenic Acid Metabolism and Lanthanum Accumulation in Tea Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
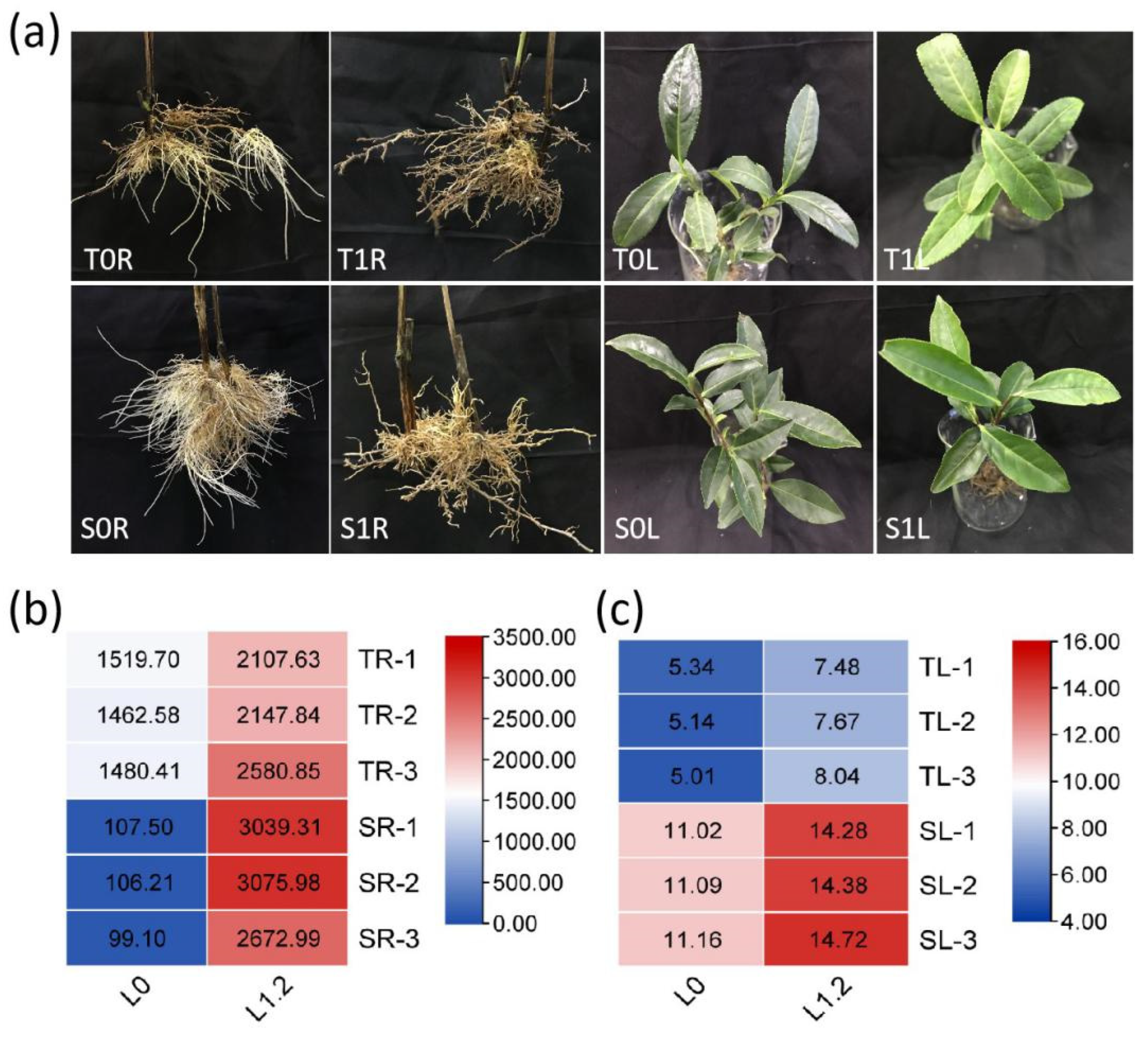
2.1. Effect of La on Tea Growth and La Accumulation
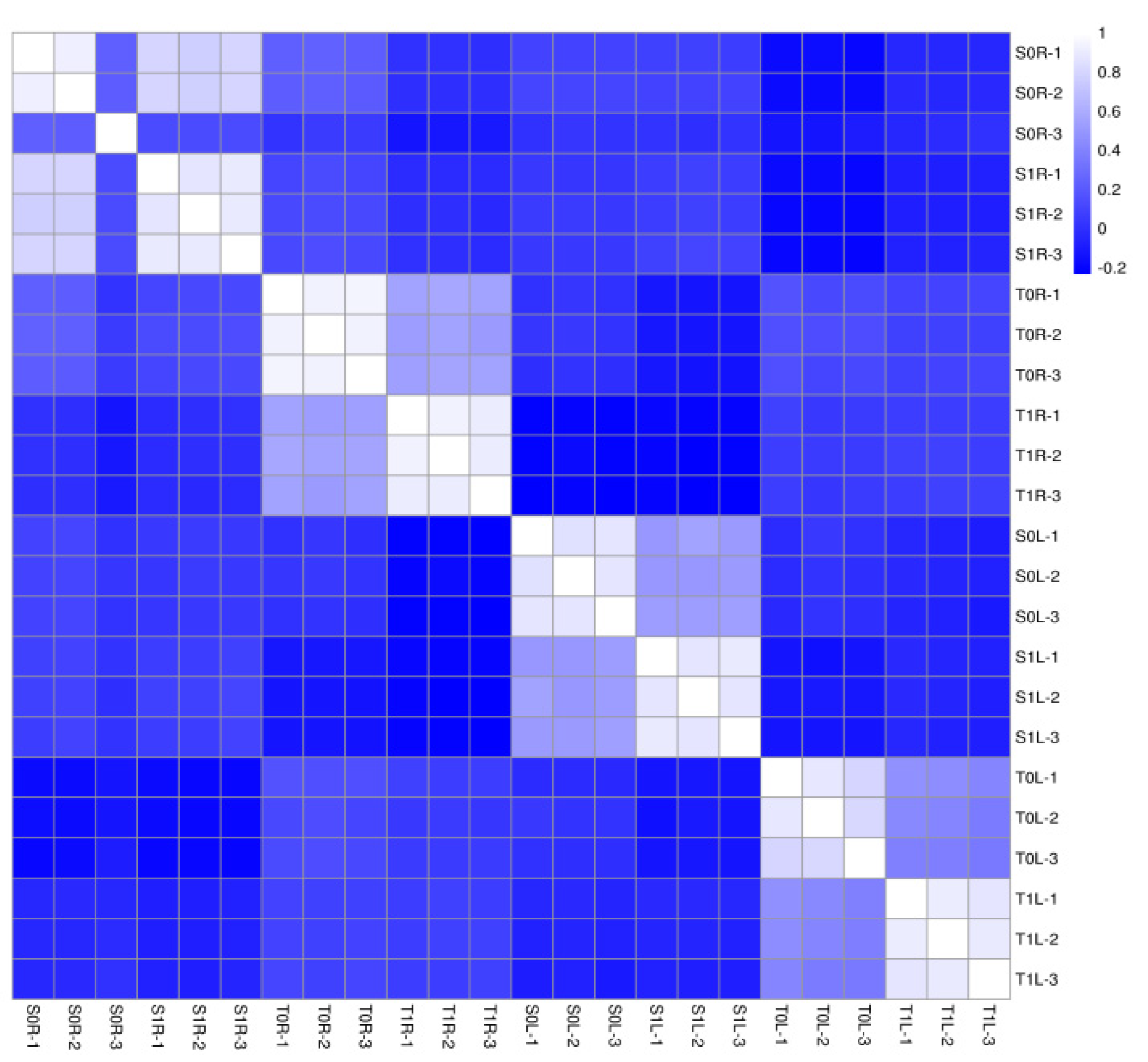
2.2. Qualitative Assessment of Protein Assay Data
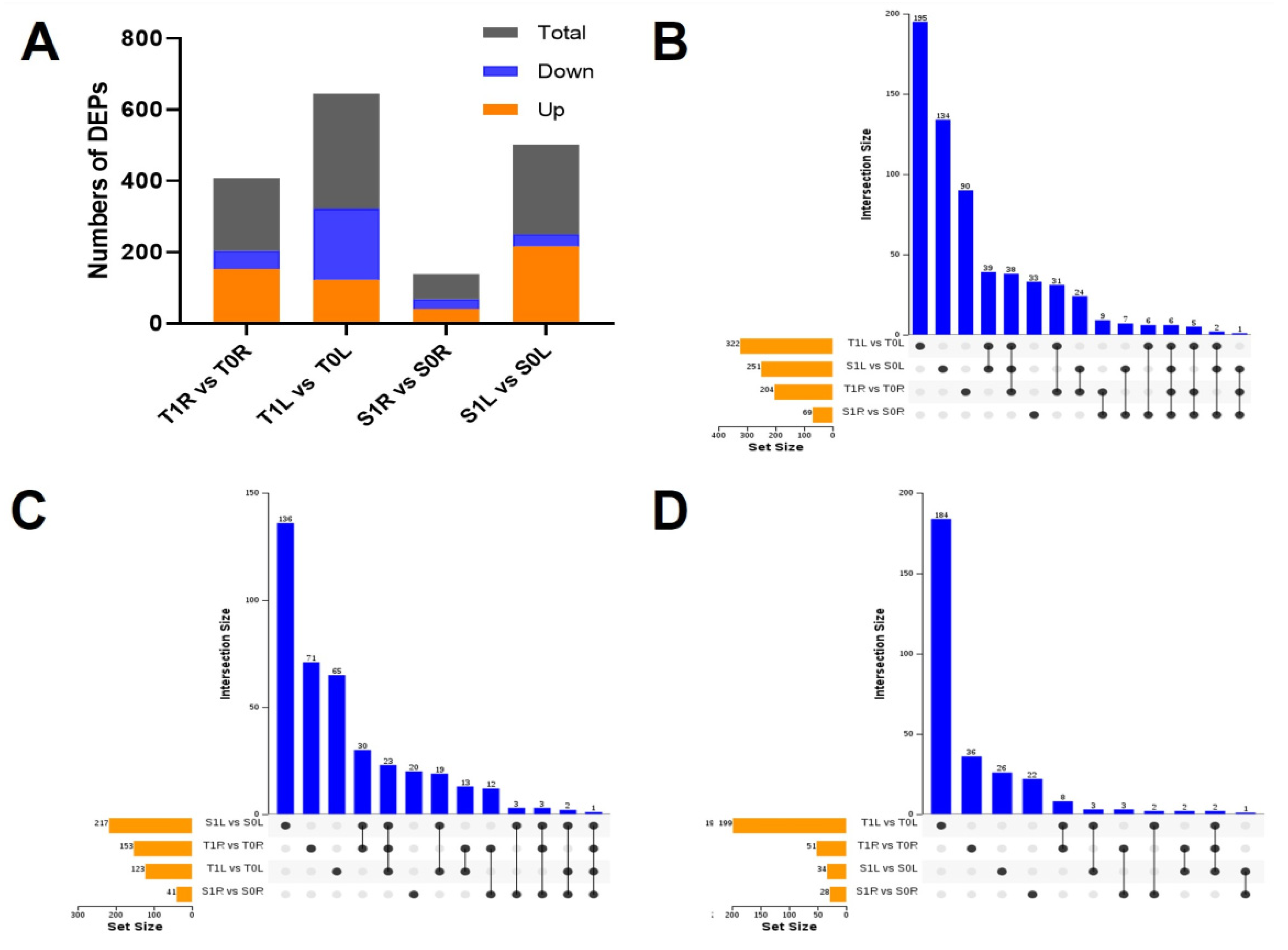
2.3. Differential Protein Analysis of the Roots and Leaves of TGY and SX under La Treatment
2.4. Bioinformatic Analysis of DEPs in the Roots and Leaves of TGY and SX under La Treatment
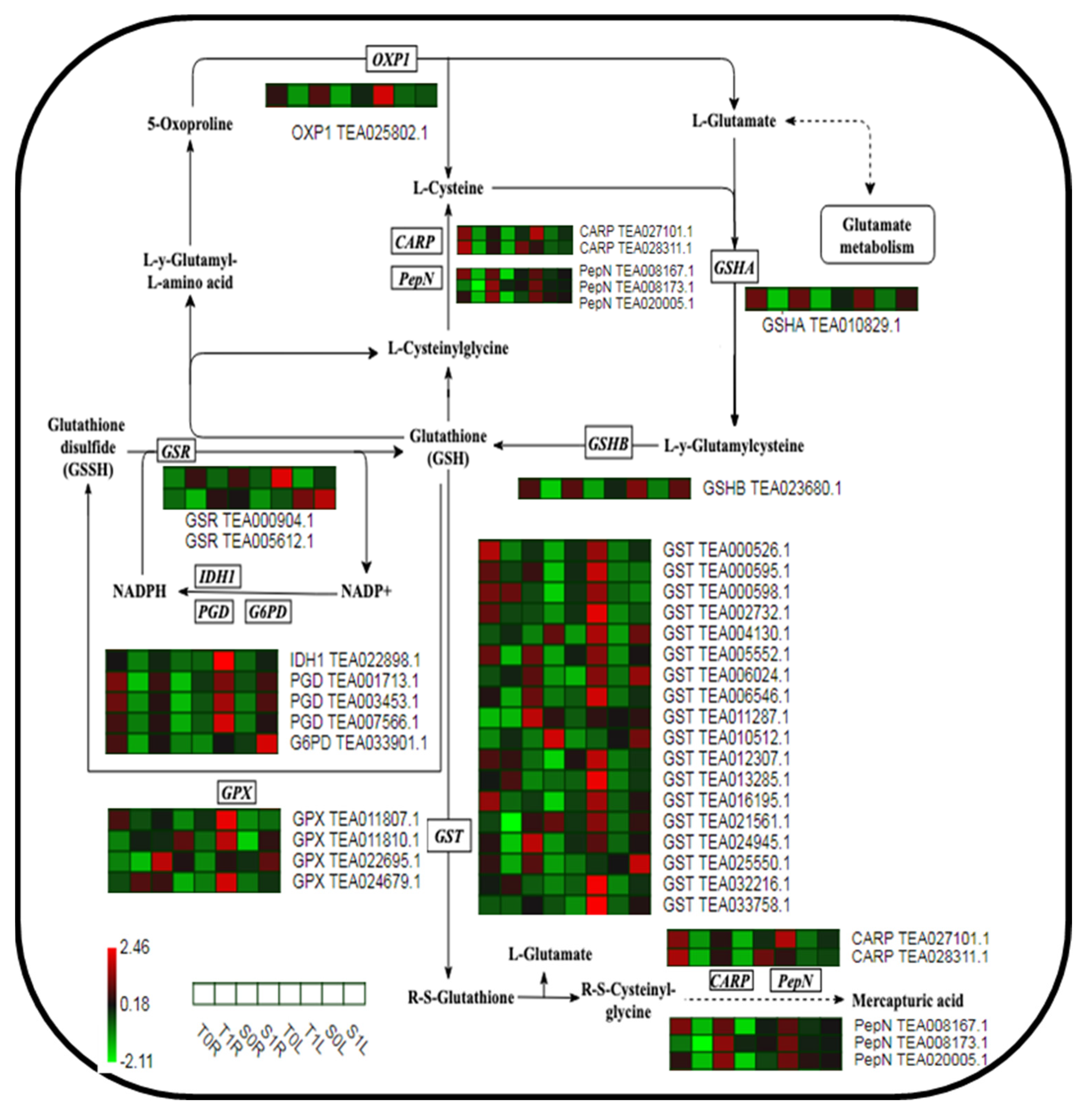
2.5. Analysis of the Expression of Key Proteins in the GSH Metabolic Pathway in Different TGY and SX Sites in Response to La
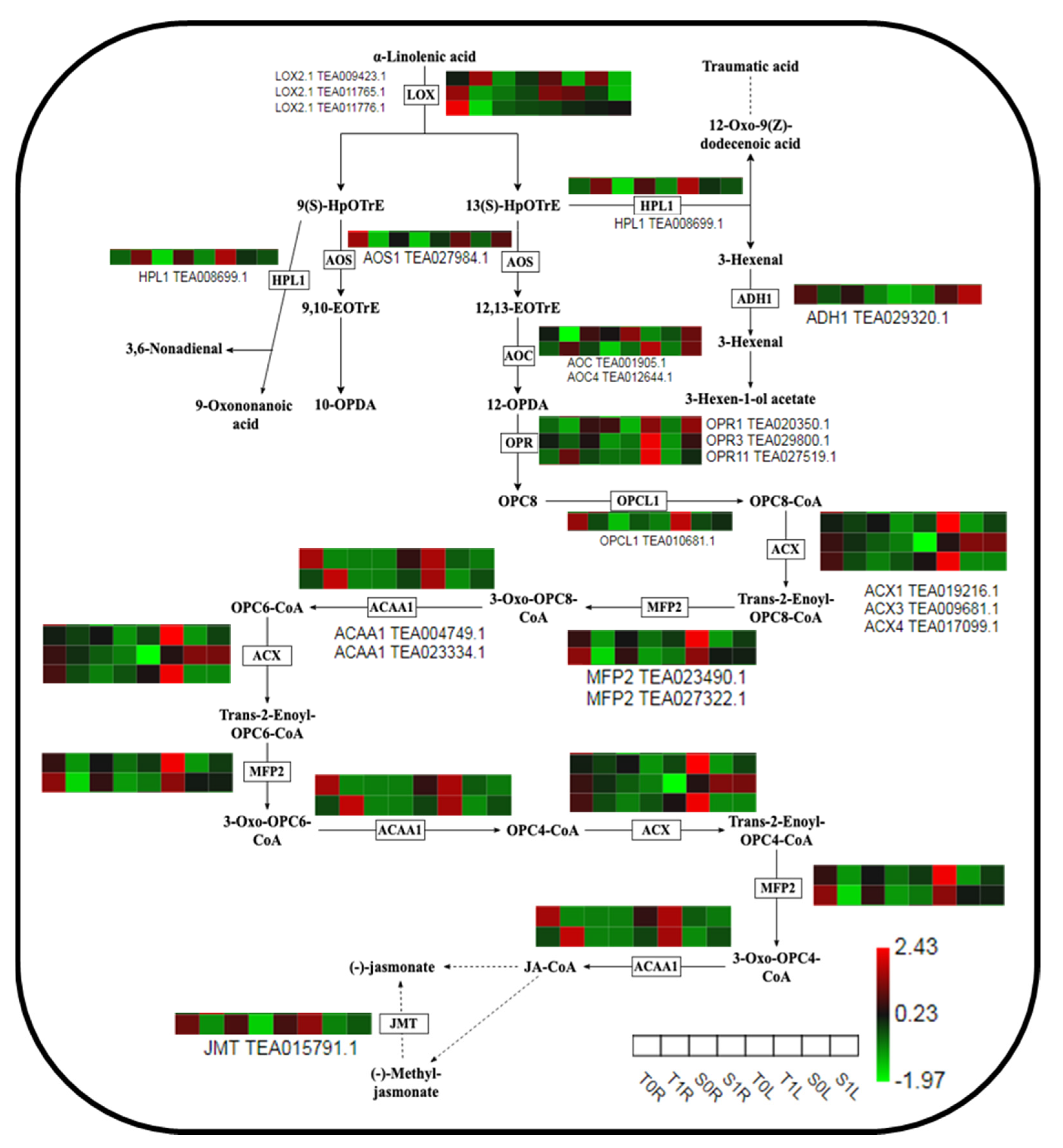
2.6. Analysis of the Expression of Key Proteins in Theα-Linolenic Acid Metabolism Pathway in Different TGY and SX Sites in Response to La
3. Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Differential Protein Enrichment in the Roots and Leaves of TGY and SX Treated with La
3.2. Different Parts of TGY and SX Respond to La via the Protein Regulation Mechanism of the GSH Metabolic Pathway
3.3. Different Parts of TGY and SX Respond to La via the Protein Regulation Mechanism of the α-Linolenic Acid Metabolic Pathway
4. Materials
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Hydroponic Culture of Tea Seedlings
4.3. La Treatment
4.4. Determination of La in Roots and Leaves
4.5. Identification and Analysis of Protein Using Mass Spectrometry
4.5.1. Protein Extraction and Trypsin Digestion
4.5.2. Peptide Identification by LC-MS/MS
4.5.3. Proteome Data and Bioinformatics Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alagawany, M.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Saeed, M.; Naveed, M.; Arain, M.A.; Arif, M.; Tiwari, R.; Khandia, R.; Khurana, S.K.; Karthik, K.; et al. Nutritional applications and beneficial health applications of green tea and l-theanine in some animal species: A review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, T. Condensed catechins and their potential health-benefits. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 765, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musial, C.; Kuban-Jankowska, A.; Gorska-Ponikowska, M. Beneficial properties of green tea catechins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Türközü, D.; Şanlier, N. L-theanine, unique amino acid of tea, and its metabolism, health effects, and safety. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1681–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, D.; Sun, P.; Bucheli, P.; Li, L.; Hou, Y.; Wang, J. Effects of soluble tea polysaccharides on hyperglycemia in alloxan-diabetic mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 5523–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.E.; Yoo, S.H.; Chung, J.O.; Park, M.Y.; Hong, Y.D.; Park, S.H.; Park, T.S.; Shim, S.M. Hypoglycemic effect of soluble polysaccharide and catechins from green tea on inhibiting intestinal transport of glucose. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3979–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.Z.; Qiu-Man, X.U. A review on rare earth elements in botany. Food Res. Dev. 2015, 36, 176–179. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.F.; Shao, X.G.; Fang, N.H.; Wang, C.H.; Zhao, G.W. Analysis on effects of spraying rare ethers in tea garden on tea output and quality. Acta Agron. Sin. 2000, 26, 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Wang, C.; Ye, S.; Qi, H.; Zhao, G. Effects of spraying rare earths on contents of rare Earth elements and effective components in tea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6731–6735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ommasi, F.; Thomas, P.J.; Pagano, G.; Perono, G.A.; Oral, R.; Lyons, D.M.; Toscanesi, M.; Trifuoggi, M. Review of rare earth elements as fertilizers and feed additives: A knowledge gap analysis. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 81, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.B.; Zhu, J.G.; Chu, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zeng, Q.; Ma, H.L.; Cao, Z.L. Effect of lanthanum on rice production, nutrient uptake, and distribution. J. Plant Nutr. 2002, 25, 2315–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Z.; Witkamp, G. Accumulation of rare earth elements in maize plants (Zea mays L.) after application of mixtures of rare earth elements and lanthanum. Plant Soil. 2003, 252, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.B.; Chen, X.T.; Ye, J.H.; Jia, X.L.; Zhang, Q.; He, H. Analysis of the absorption and accumulation characteristics of rare earth elements in Chinese tea. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3360–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.Y.; Li, X.; Wan, X.; Cai, H.M.C. Research progress of rare earth elements in tea. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2015, 6, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, L.P.; Wang, A.; Luo, Y.W.; Zhou, S.J.; Qin, Z. Content characteristics of rare earth elements in Guizhou green tea. Hubei Agr. Sci. 2014, 53, 197–199. [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers, A.; Hausman, J.F.; Sergeant, K. Long-term cadmium exposure influences the abundance of proteins that impact the cell wall structure in Medicago sativa stems. Plant Biol. 2018, 20, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Gutsch, A.; Zouaghi, S.; Renaut, J.; Cuypers, A.; Hausman, J.F.; Sergeant, K. Changes in the proteome of Medicago sativa leaves in response to long-term cadmium exposure using a cell-wall targeted approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 24, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, N.; Renaut, J.; Komatsu, S. Recent developments in the application of proteomics to the analysis of plant responses to heavy metals. Proteomics 2009, 9, 2602–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Q.; Xue, Z.H.; Lin, W.; Chen, Z.; Sun, W. Study of accumulation and distribution of the rare earth elements in different tea cultivars. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2017, 44, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Z.H.; Wang, X.Z.; Zhao, J.; Tzuhsing, K.O.; Sun, W. Shoot morphology and leaf ultrastructure of two tea genotypes and their effects on rare earth lanthanum adsorption. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2020, 26, 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Z.H.; Zhou, Z.; Shang, H.; He, X.Y.; Huang, H.S.; Sun, W.J. Effects of different concentrations of lanthanum on root antioxidant enzyme activities and root cells ultrastructure in tea (Camellia sinensis) plant. J. South. Agric. 2022, 53, 324–333. [Google Scholar]
- Noctor, G.; Mhamdi, A.; Chaouch, S.; Han, Y.; Neukermans, J.; Marquez-Garcia, B.; Queval, G.; Foyer, C.H. Glutathione in plants: An integrated overview. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 454–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.K.; Wan, W.F.; Tian, T.; Wang, Y.X.; Liu, Q.L.; Zhang, W.F.; Ai, Y.F.; Xue, L.C.; He, H.Q. Protein complex and proteomic profile in the roots of Oryza sativa L. in response to cadmium toxicity. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2015, 37, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajduch, M.; Rakwal, R.; Agrawal, G.K.; Yonekura, M.; Pretova, A. High-resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis separation of proteins from metal-stressed rice (Oryza sativa L.) leaves: Drastic reductions/fragmentation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase and induction of stress-related proteins. Electrophoresis 2001, 22, 2824–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.N.; Wang, Q.Q.; Sun, W.J.; Xue, Z.H.; Chen, C.C. Transcriptional analysis of responses of tea cultivars with different genotypes to accumulation of rare earth, fluorine and aluminum. Mol. Plant Breed 2020, 20, 2204–2216. [Google Scholar]
- Anjum, N.A.; Ahmad, I.; Mohmood, I.; Pacheco, M.; Duarte, A.C.; Pereira, E.; Umar, S.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, N.A.; Iqbal, M.; et al. Modulation of glutathione and its related enzymes in plants’ responses to toxic metals and metalloids—A review. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2012, 75, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Asif, M.H.; Chakrabarty, D.; Tripathi, R.D.; Dubey, R.S.; Trivedi, P.K. Expression of a rice Lambda class of glutathione S-transferase, OsGSTL2, in Arabidopsis provides tolerance to heavy metal and other abiotic stresses. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 15, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halusková, L.; Valentovicová, K.; Huttová, J.; Mistrík, I.; Tamás, L. Effect of abiotic stresses on glutathione peroxidase and glutathione S-transferase activity in barley root tips. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 47, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noctor, G.; Gomez, L.; Vanacker, H.; Foyer, C.H. Interactions between biosynthesis, compartmentation and transport in the control of glutathione homeostasis and signalling. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 1283–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxas, V.P.; Smith, R.K.; Allen, E.R.; Allen, R.D. Overexpression of glutathione S-transferase glutathione peroxidase enhances the growth of transgenic tobacco seedlings during stress. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 988–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.H.; Li, F.D.; Tong, W.; Li, P.H.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, H.J.; Ge, R.H.; Li, R.P.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.Z.; et al. Tea plant information archive: A comprehensive genomics and bioinformatics platform for tea plant. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1938–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Element | Source | Concentration mmol/L |
|---|---|---|
| Al | Al2(SO4)3·18H2O | 0.25 |
| NH4−N | (NH4)2SO4 | 0.75 |
| NO3−N | NH4NO3 | 0.25 |
| P | KH2PO4 | 0.05 |
| K | K2SO4 | 0.35 |
| Ca | CaCl2 | 0.395 |
| Mg | MgSO4 | 0.21 |
| B | H3BO3 | 3.33 |
| Mn | MnSO4·H2O | 0.5 |
| Zn | ZnSO4·7H2O | 0.51 |
| Cu | CuSO4·5H2O | 0.13 |
| Mo | Na2MoO4·2H2O | 0.17 |
| Fe | Fe-EDTA | 2.10 |
| Time (min) | A (0.1% FA, H2O) | B (0.08% FA, 80% ACN) | Flow Rate (nL/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 95% | 5% | 600 |
| 16 | 90% | 10% | 600 |
| 51 | 78% | 22% | 600 |
| 71 | 70% | 30% | 600 |
| 72 | 5% | 95% | 600 |
| 78 | 5% | 95% | 600 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, W. Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Association between the Pathways of Glutathione and α-Linolenic Acid Metabolism and Lanthanum Accumulation in Tea Plants. Molecules 2023, 28, 1124. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031124
Xue Z, Chen Z, Wang Y, Sun W. Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Association between the Pathways of Glutathione and α-Linolenic Acid Metabolism and Lanthanum Accumulation in Tea Plants. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1124. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031124
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Zhihui, Zhidan Chen, Yankun Wang, and Weijiang Sun. 2023. "Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Association between the Pathways of Glutathione and α-Linolenic Acid Metabolism and Lanthanum Accumulation in Tea Plants" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1124. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031124
APA StyleXue, Z., Chen, Z., Wang, Y., & Sun, W. (2023). Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Association between the Pathways of Glutathione and α-Linolenic Acid Metabolism and Lanthanum Accumulation in Tea Plants. Molecules, 28(3), 1124. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031124






