Quercetin: A Potential Polydynamic Drug
Abstract
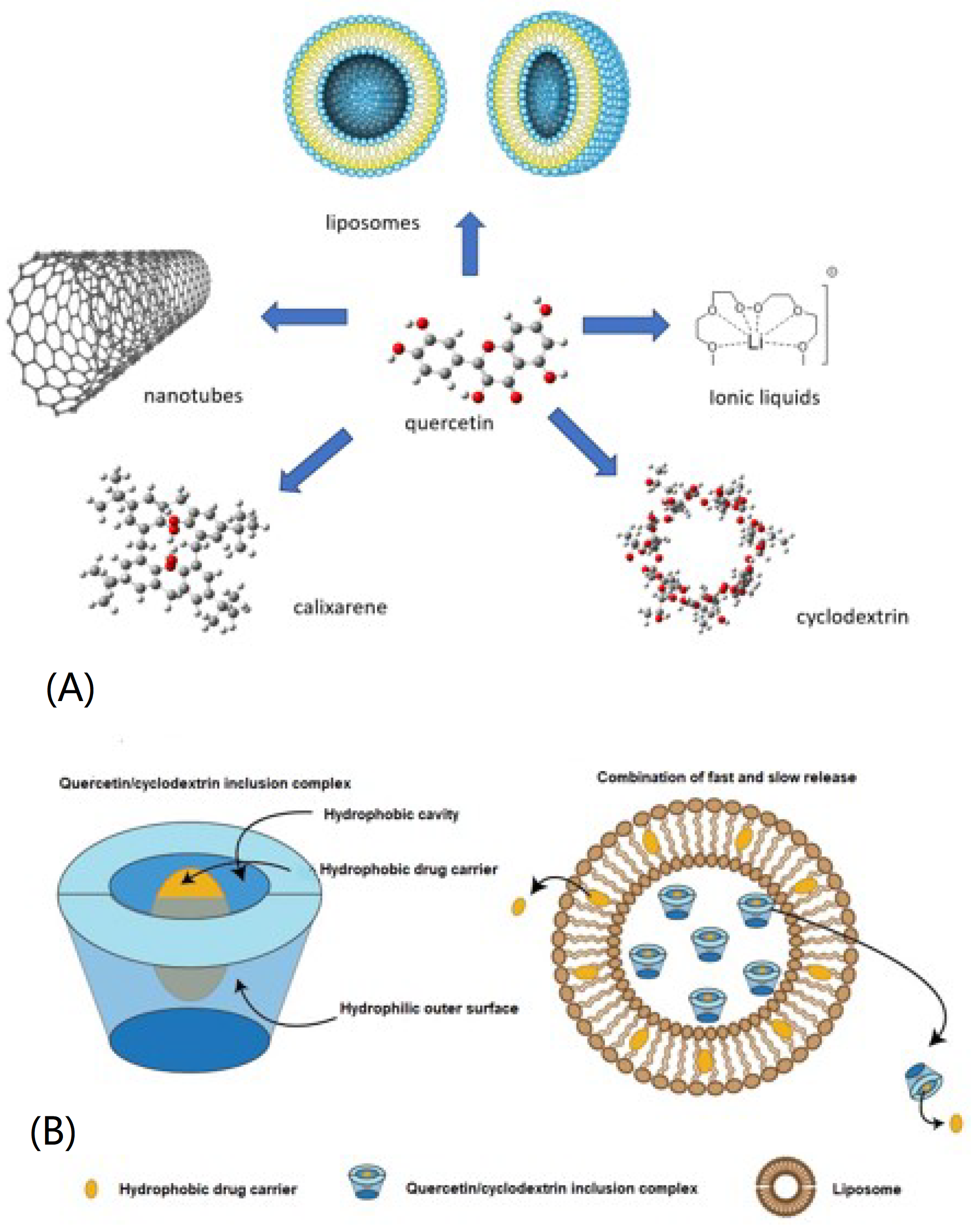
:1. Introduction
2. Polydynamic Biological Activity of Quercetin
2.1. Mental Activity
2.2. Ultraviolet (UV) Activity
2.3. Antiviral Activity
2.4. Anticancer Activity
2.5. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
2.6. Neurological Activity
2.7. Antioxidant Activity
2.8. Anti-Cardiovascular Disease
2.9. Skin Sensitivity
2.10. Anti-Tuberculosis
2.11. Antidiabetic Activity
2.12. Antimalaria Activity
2.13. Antichagas Activity
2.14. Antifungal Activity
2.15. Combination of Quercetin with Other Drugs
2.16. Anti-Rhinitis Activity
2.17. Antidrug Resistance
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pallag, A.; Bungau, S.; Tit, D.M.; Jurca, T.; Sirbu, V.; Honiges, A.; Horhogea, C. Comparative Study of Polyphenols, Flavonoids and Chlorophylls in Equisetum arvense L. Populations. Rev. Chim. 2016, 67, 530–533. [Google Scholar]
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: An Overview. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yao, J.; Han, C.; Yang, J.; Chaudhry, M.T.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y. Quercetin, Inflammation and Immunity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formica, J.V.; Regelson, W. Review of the Biology of Quercetin and Related Bioflavonoids. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1995, 33, 1061–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Wang, T.; Long, M.; Li, P. Quercetin: Its Main Pharmacological Activity and Potential Application in Clinical Medicine. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8825387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Park, S.U. Quercetin and Its Role in Biological Functions: An Updated Review. EXCLI J. 2018, 17, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Arif, Y.; Bajguz, A.; Hayat, S. The Role of Quercetin in Plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 166, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanzadeh, E.; Esmaeili, A.; Rahgozar, S.; Nourbakhshnia, M. Application of Quercetin in Neurological Disorders: From Nutrition to Nanomedicine. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 30, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Mendoza, E.; Burd, R. Quercetin as a Systemic Chemopreventative Agent: Structural and Functional Mechanisms. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2012, 11, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A Free Web Tool to Evaluate Pharmacokinetics, Drug-Likeness and Medicinal Chemistry Friendliness of Small Molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.E.V.; Blundell, T.L.; Ascher, D.B. PkCSM: Predicting Small-Molecule Pharmacokinetic and Toxicity Properties Using Graph-Based Signatures. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viana Nunes, A.M.; das Chagas Pereira de Andrade, F.; Filgueiras, L.A.; de Carvalho Maia, O.A.; Cunha, R.L.O.R.; Rodezno, S.V.A.; Maia Filho, A.L.M.; de Amorim Carvalho, F.A.; Braz, D.C.; Mendes, A.N. PreADMET Analysis and Clinical Aspects of Dogs Treated with the Organotellurium Compound RF07: A Possible Control for Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis? Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 80, 103470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, L.; Yang, H.; Cai, Y.; Sun, L.; Di, P.; Li, W.; Liu, G.; Tang, Y. ADMET-Score—A Comprehensive Scoring Function for Evaluation of Chemical Drug-Likeness. Medchemcomm 2019, 10, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiou, N.; Chontzopoulou, E.; Cheilari, A.; Katsogiannou, A.; Karta, D.; Vavougyiou, K.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Javornik, U.; Plavec, J.; Tzeli, D.; et al. Thiocarbohydrazone and Chalcone-Derived 3,4-Dihydropyrimidinethione as Lipid Peroxidation and Soybean Lipoxygenase Inhibitors. ACS Omega 2022, 8, 11966–11977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiou, N.; Gouleni, N.; Chontzopoulou, E.; Skoufas, G.S.; Gkionis, A.; Tzeli, D.; Vassiliou, S.; Mavromoustakos, T. Structure Assignment, Conformational Properties and Discovery of Potential Targets of the Ugi Cinnamic Adduct NGI25. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 41, 1253–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiou, N.; Cheilari, A.; Karta, D.; Chontzopoulou, E.; Plavec, J.; Tzeli, D.; Vassiliou, S.; Mavromoustakos, T. Conformational Properties and Putative Bioactive Targets for Novel Thiosemicarbazone Derivatives. Molecules 2022, 27, 4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, N.; Katsogiannou, A.; Skourtis, D.; Iatrou, H.; Tzeli, D.; Vassiliou, S.; Javornik, U.; Plavec, J.; Mavromoustakos, T. Conformational Properties of New Thiosemicarbazone and Thiocarbohydrazone Derivatives and Their Possible Targets. Molecules 2022, 27, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginex, T.; Vazquez, J.; Gilbert, E.; Herrero, E.; Luque, F.J. Lipophilicity in Drug Design: An Overview of Lipophilicity Descriptors in 3D-QSAR Studies. Future Med. Chem. 2019, 11, 1177–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veber, D.F.; Johnson, S.R.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Smith, B.R.; Ward, K.W.; Kopple, K.D. Molecular Properties That Influence the Oral Bioavailability of Drug Candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Fei, T.; Wu, D.; Tao, L. Application of Quercetin or Quercetin Derivative for Relieving Smoke Harm.
- Daina, A.; Zoete, V. A BOILED-Egg to Predict Gastrointestinal Absorption and Brain Penetration of Small Molecules. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, B.; Carradori, S.; Guglielmi, P.; Uddin, M.S.; Kim, H. New Aspects of Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors: The Key Role of Halogens to Open the Golden Door. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 266–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Funk, C.D. Lipoxygenase Pathways in Atherogenesis. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2004, 14, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, A.; Razavi, B.M.; Banach, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Quercetin and Metabolic Syndrome: A Review. Phyther. Res. 2021, 35, 5352–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, B.H.; Jung, J.W.; Lee, J.-J.; Cho, Y.-W.; Jang, C.-G.; Jin, C.; Oh, T.H.; Ryu, J.H. Anxiolytic-like Effects of Sinapic Acid in Mice. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, A.R.; Vieira, Í.G.P.; Queiroz, D.B.; Leal, A.L.A.B.; Maia Morais, S.; Muniz, D.F.; Calixto-Junior, J.T.; Coutinho, H.D.M. Use of Flavonoids and Cinnamates, the Main Photoprotectors with Natural Origin. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 2018, 5341487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogaça, L.A.; Feuser, P.E.; Ricci-Júnior, E.; Hermes de Araújo, P.H.; Sayer, C.; da Costa, C. ZnO and Quercetin Encapsulated Nanoparticles for Sun Protection Obtained by Miniemulsion Polymerization Using Alternative Co-Stabilizers. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 015096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, J.D.; Doms, R.W. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 2. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 1253–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, P.M.; Hahn, B.H. The Evolution of HIV-1 and the Origin of AIDS. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 2487–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Petrillo, A.; Orrù, G.; Fais, A.; Fantini, M.C. Quercetin and Its Derivates as Antiviral Potentials: A Comprehensive Review. Phyther. Res. 2022, 36, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Gu, W.; Zhao, S.; Shen, Z.; Lin, Z.; Liu, W.; Yan, T. Pharmacological Activity of Quercetin: An Updated Review. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 3997190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, P.K.; Agrawal, C.; Blunden, G. Quercetin: Antiviral Significance and Possible COVID-19 Integrative Considerations. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15, 1934578X20976293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschovou, K.; Antoniou, M.; Chontzopoulou, E.; Papavasileiou, K.D.; Melagraki, G.; Afantitis, A.; Mavromoustakos, T. Exploring the Binding Effects of Natural Products and Antihypertensive Drugs on SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Investigation of Main Protease and Spike Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oz, M.; Selcuk, I.; Arik, Z.; Gungor, T. Targeted Agents in Ovarian Carcinoma. Med. Sci. 2016, 5, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, S.; Turkekul, K.; Dibirdik, I.; Doganlar, O.; Doganlar, Z.B.; Bilir, A.; Oktem, G. Midkine Downregulation Increases the Efficacy of Quercetin on Prostate Cancer Stem Cell Survival and Migration through PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK Pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.B.; Mir, H.; Kapur, N.; Gales, D.N.; Carriere, P.P.; Singh, S. Quercetin Inhibits Prostate Cancer by Attenuating Cell Survival and Inhibiting Anti-Apoptotic Pathways. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 16, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisaka, T.; Sakai, H.; Sato, T.; Goto, Y.; Nomura, Y.; Fukutomi, S.; Fujita, F.; Mizobe, T.; Nakashima, O.; Tanigawa, M.; et al. Quercetin Suppresses Proliferation of Liver Cancer Cell Lines In Vitro. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 4695–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazvand, F.; Orazizadeh, M.; Khorsandi, L.; Abbaspour, M.; Mansouri, E.; Khodadadi, A. Effects of Quercetin-Loaded Nanoparticles on MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Medicina (B. Aires) 2019, 55, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.N.D.; Stempel, S.; Shields, M.A.; Spaulding, C.; Kumar, K.; Bentrem, D.J.; Matsangou, M.; Munshi, H.G. Quercetin Enhances the Anti-Tumor Effects of BET Inhibitors by Suppressing HnRNPA1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturza, A.; Pavel, I.; Ancușa, S.; Danciu, C.; Dehelean, C.; Duicu, O.; Muntean, D. Quercetin Exerts an Inhibitory Effect on Cellular Bioenergetics of the B164A5 Murine Melanoma Cell Line. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 447, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, J.; Liu, T.; Li, S.; Feng, J.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ji, J.; et al. Quercetin Shows Anti-tumor Effect in Hepatocellular Carcinoma LM3 Cells by Abrogating JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 4806–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caro, C.; Pourmadadi, M.; Eshaghi, M.M.; Rahmani, E.; Shojaei, S.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Rahdar, A.; Behzadmehr, R.; García-Martín, M.L.; Díez-Pascual, A.M. Nanomaterials Loaded with Quercetin as an Advanced Tool for Cancer Treatment. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 78, 103938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y. Inflammation and Regeneration Rheumatoid Arthritis. BioMed Cent. 2020, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, K.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, Q.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, M.; Li, X.; Huang, G.; Xu, A. Quercetin Alleviates Rheumatoid Arthritis by Inhibiting Neutrophil Inflammatory Activities. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 84, 108454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chontzopoulou, E.; Papaemmanouil, C.D.; Chatziathanasiadou, M.V.; Kolokouris, D.; Kiriakidi, S.; Konstantinidi, A.; Gerogianni, I.; Tselios, T.; Kostakis, I.K.; Chrysina, E.D.; et al. Molecular Investigation of Artificial and Natural Sweeteners as Potential Anti-Inflammatory Agents. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 40, 12608–12620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnova, E.O.; Egorova, A.M.; Lantsova, N.V.; Chechetkin, I.R.; Toporkova, Y.Y.; Grechkin, A.N. Recombinant Soybean Lipoxygenase 2 (GmLOX2) Acts Primarily as a ω 6 (S)-Lipoxygenase. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 2, 6283–6295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheltens, P.; De Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chételat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s Disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruwizhi, N.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Cinnamic Acid Derivatives and Their Biological Efficacy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, P.; Yan, Y.; Sun, H.; Liu, W.; Feng, F.; Qu, W. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Carboline-Cinnamic Acid Hybrids as Multifunctional Agents for Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 99, 103844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.S.; Hou, J.W.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, T. Design, Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Cinnamic Acid Derivatives Bearing N-Benzyl Pyridinium Moiety as Multifunctional Cholinesterase Inhibitors for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Machin, L.; Monzote, L.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Ezzat, S.M.; Salem, M.A.; Merghany, R.M.; El Mahdy, N.M.; Klllç, C.S.; Sytar, O.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin: New Insights and Perspectives for Human Health. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 11849–11872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Hu, M.-J.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Cui, Y.-L. Antioxidant Activities of Quercetin and Its Complexes for Medicinal Application. Molecules 2019, 24, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiailanis, A.D.; Renziehausen, A.; Kiriakidi, S.; Vrettos, E.I.; Markopoulos, G.S.; Sayyad, N.; Hirmiz, B.; Aguilar, M.-I.; Del Borgo, M.P.; Kolettas, E.; et al. Enhancement of Glioblastoma Multiforme Therapy through a Novel Quercetin-Losartan Hybrid. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 160, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulusoy, H.G.; Sanlier, N. A Minireview of Quercetin: From Its Metabolism to Possible Mechanisms of Its Biological Activities. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3290–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroto, J.Á.M. Synergic Polyphenol Combination ES2391211B1. ES2391211B1, 2 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- De, P.; Bedos-Belval, F.; Vanucci-Bacque, C.; Baltas, M. Cinnamic Acid Derivatives in Tuberculosis, Malaria and Cardiovascular Diseases—A Review. Curr. Org. Chem. 2012, 16, 747–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.; Ivanova, S.; Roomi, W.; Niedzwicki, A.; Rath, M. Novel Composition and Method for the Treatment of Hypertension. US2004242504A1, 30 May 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jalili, T. Quercetin Supplementation to Treat Hypertenstion. US2004258674A1, 12 April 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, A.J.; Symons, J.D.; Jalili, T. Quercetin: A Treatment for Hypertension?—A Review of Efficacy and Mechanisms. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, B.P.; Parimelazhagan, T.; Sajeesh, T.; Saravanan, S. Antitumor and Wound Healing Properties of Rubus Niveus Thunb. Root. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2014, 33, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polera, N.; Badolato, M.; Perri, F.; Carullo, G.; Aiello, F. Quercetin and Its Natural Sources in Wound Healing Management. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 5825–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, S.M.; Choucry, M.A.; Kandil, Z.A. Antibacterial, Antioxidant, and Topical Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Bergia Ammannioides: A Wound-Healing Plant. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorino, G.; Marchetti, C.; Borghesi, B.; Cornara, L.; Ribulla, S.; Burlando, B. Biological Activities of the Legume Crops Melilotus Officinalis and Lespedeza Capitata for Skin Care and Pharmaceutical Applications. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 96, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodhi, S.; Jain, A.; Jain, A.P.; Pawar, R.S.; Singhai, A.K. Effects of Flavonoids from Martynia Annua and Tephrosia Purpurea on Cutaneous Wound Healing. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2016, 6, 578–591. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Diao, P.; Shu, X.; Li, L.; Xiong, L. Quercetin and Quercitrin Attenuates the Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells: In Vitro Assessment and a Theoretical Model. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7039802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, L.; Ji, Y.; Yan, C.; Zhang, X. Protective Effects of Quercetin against Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in a Rabbit Model of Knee Osteoarthritis. Drug Dev. Res. 2019, 80, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sul, O.-J.; Ra, S.W. Quercetin Prevents LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation by Modulating NOX2/ROS/NF-KB in Lung Epithelial Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Fukuma, Y.; Notsu, K.; Kono, M. Quercetin and HSC70 Coregulate the Anti-Inflammatory Action of the Ubiquitin-like Protein MNSFβ. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, G.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; He, X. Quercetin Inhibits TNF-α Induced HUVECs Apoptosis and Inflammation via Downregulating NF-KB and AP-1 Signaling Pathway in vitro. Medicine 2020, 99, e22241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.-Q.; Li, Z.; Xie, W.-R.; Liu, C.-M.; Liu, S.-S. Quercetin Protects Mouse Liver against CCl4-Induced Inflammation by the TLR2/4 and MAPK/NF-ΚB Pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairwa, R.; Kakwani, M.; Tawari, N.R.; Lalchandani, J.; Ray, M.K.; Rajan, M.G.R.; Degani, M.S. Novel Molecular Hybrids of Cinnamic Acids and Guanylhydrazones as Potential Antitubercular Agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 1623–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotgiu, G.; Centis, R.; D’Ambrosio, L.; Tadolini, M.; Castiglia, P.; Migliori, G.B. Do We Need a New Fleming Époque: The Nightmare of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2013, 2, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikumar, K.; Ghosh, A.R.; Dusthackeer, A. Antimycobacterial Potentials of Quercetin and Rutin against Mycobacterium Tuberculosis H37Rv. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Czech, M.P. The GLUT4 Glucose Transporter. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanya, R. Quercetin for Managing Type 2 Diabetes and Its Complications, an Insight into Multitarget Therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 146, 112560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrens, M.J.; Thompson, D.L.; Atm Metabolics Lllp. Composition for Treating Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders with Quercetin, Myrcetin and Chlorogenic Acid. EP2129371B1, 11 March 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kruthiventi, A.; Javed, I. Pharmaceutical Co-Crystals of Quercetin. US20120258170A1, 30 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, P.; Choudhury, S.T.; Seidel, V.; Rahman, A.B.; Aziz, M.A.; Richi, A.E.; Rahman, A.; Jafrin, U.H.; Hannan, J.M.A.; Abdel-Wahab, Y.H.A. Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin in the Management of Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus. Life 2022, 12, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.H.; Sudi, S.; Shi-Jing, N.; Rozianoor, W.; Hassan, M.; Basir, R.; Agustar, H.K.; Embi, N.; Sidek, H.M.; Latip, J. Dual Anti-Malarial and GSK3 β-Mediated Cytokine-Modulating Activities of Quercetin Are Requisite of Its Potential as a Plant-Derived Therapeutic in Malaria. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, A.A.; Maia, P.I.d.S.; Lopes, C.D.; de Albuquerque, S.; Valle, M.S. Synthesis, Characterization and Antichagasic Evaluation of Thiosemicarbazones Prepared from Chalcones and Dibenzalacetones. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1232, 130014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasdemir, D.; Kaiser, M.; Brun, R.; Yardley, V.; Schmidt, T.J.; Tosun, F.; Ru, P. Antitrypanosomal and Antileishmanial Activities of Flavonoids and Their Analogues: In Vitro, In Vivo, Structure-Activity Relationship, and Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Studies. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1352–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fábio, M.; Rocha, G.; Sales, J.A.; Gleiciane, M.; Galdino, L.M.; Aguiar, L.D.; Pereira-Neto, W.D.A.; Cordeiro, R.D.A.; Souza, D.D.; Maia, C. Antifungal Effects of the Flavonoids Kaempferol and Quercetin: A Possible Alternative for the Control of Fungal Biofilms. Biofouling 2019, 35, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebbi, C.K. Sickle Cell Disease: A Review. Hemato 2022, 3, 341–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, R.; Azarang, A.; Wilaisakditipakorn, T.; Hagerman, R.J. Fragile X Syndrome: A Review of Clinical Management. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2016, 5, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodoeva, R. Quercetin-Based Composition for Treating Rhinosinusitis. US2021000787A1, 15 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tiboc-Schnell, C.N.; Filip, G.A.; Man, S.C.; Decea, N.; Moldovan, R.; Opris, R.; Sas, V.; Tabaran, F. Quercetin Attenuates Naso-Sinusal Inflammation and Inflammatory Response in Lungs and Brain on an Experimental Model of Acute Rhinosinusitis in Rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 71, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedipour, F.; Kesharwani, P.; Sahebkar, A. Mechanisms of Multidrug Resistance in Cancer. In Aptamers Engineered Nanocarriers for Cancer Therapy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 51–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.S.; Aggarwal, P.; Hiprara, V.K.; Jaggi, M.; Singh, A.; Awasthi, A.; Verma, R. Novel Quercetin Derivatives as Anti-Cancer Agents. US2011034413A1, 8 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka, Y.; Egawa, K.; Kanzaki, N.; Izumo, T.; Rogi, T.; Shibata, H. Quercetin Glycosides Prevent Dexamethasone-Induced Muscle Atrophy in Mice. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2019, 18, 100618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaboga, A.S.; Perez-Neuno, V.I.; Souchet, M.; Decaudin, D. Muscle Atrophy Inhibitor Containing Quercetin Glycoside. CN106255500A, 2 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Leonis, G.; Vakali, V.; Zoupanou, N.; Georgiou, N.; Diamantis, D.A.; Tzakos, A.G.; Mavromoustakos, T.; Tzeli, D. Computational and Spectroscopic Analysis of the Quercetin Encapsulation in (2HP-β-CD)2 and (2,6Me-β-CD)2 Complexes. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1294, 136430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakali, V.; Papadourakis, M.; Georgiou, N.; Zoupanou, N.; Diamantis, D.A.; Javornik, U.; Papakyriakopoulou, P.; Plavec, J.; Valsami, G.; Tzakos, A.G.; et al. Comparative Interaction Studies of Quercetin with 2-Hydroxyl-Propyl-β-Cyclodextrin and 2,6-Methylated-β-Cyclodextrin. Molecules 2022, 27, 5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manta, K.; Papakyriakopoulou, P.; Nikolidaki, A.; Balafas, E.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Banella, S.; Colombo, G.; Valsami, G. Comparative Serum and Brain Pharmacokinetics of Quercetin after Oral and Nasal Administration to Rats as Lyophilized Complexes with β-Cyclodextrin Derivatives and Their Blends with Mannitol/Lecithin Microparticles. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savic, I.M.; Nikolic, V.D.; Savic-Gajic, I.; Nikolic, L.B.; Radovanovic, B.C.; Mladenovic, J.D. Investigation of Properties and Structural Characterization of the Quercetin Inclusion Complex with (2-Hydroxypropyl)-β-Cyclodextrin. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2015, 82, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manta, K.; Papakyriakopoulou, P.; Chountoulesi, M.; Diamantis, D.A.; Spaneas, D.; Vakali, V.; Naziris, N.; Chatziathanasiadou, M.V.; Andreadelis, I.; Moschovou, K.; et al. Preparation and Biophysical Characterization of Quercetin Inclusion Complexes with β-Cyclodextrin Derivatives to Be Formulated as Possible Nose-to-Brain Quercetin Delivery Systems. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 4241–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palli, V.; Leonis, G.; Zoupanou, N.; Georgiou, N.; Chountoulesi, M.; Naziris, N.; Tzeli, D.; Demetzos, C.; Valsami, G.; Marousis, K.D.; et al. Losartan Interactions with 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-CD. Molecules 2022, 27, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kfoury, M.; Landy, D.; Ruellan, S.; Auezova, L.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Fourmentin, S. Determination of Formation Constants and Structural Characterization of Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes with Two Phenolic Isomers: Carvacrol and Thymol. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caira, M.R.; Bourne, S.A.; Samsodien, H.; Smith, V.J. Inclusion Complexes of 2-Methoxyestradiol with Dimethylated and Permethylated β-Cyclodextrins: Models for Cyclodextrin-Steroid Interaction. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 2616–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haimhoffer, Á.; Rusznyák, Á.; Réti-Nagy, K.; Vasvári, G.; Váradi, J.; Vecsernyés, M.; Bácskay, I.; Fehér, P.; Ujhelyi, Z.; Fenyvesi, F. Cyclodextrins in Drug Delivery Systems and Their Effects on Biological Barriers. Sci. Pharm. 2019, 87, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, G.; Tiwari, R.; Rai, A. Cyclodextrins in Delivery Systems: Applications. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2010, 2, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wüpper, S.; Lüersen, K.; Rimbach, G. Cyclodextrins, Natural Compounds, and Plant Bioactives—A Nutritional Perspective. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Chang, C.E.; Gilson, M.K. Calculation of Cyclodextrin Binding Affinities: Energy, Entropy, and Implications for Drug Design. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 3035–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liossi, A.S.; Ntountaniotis, D.; Kellici, T.F.; Chatziathanasiadou, M.V.; Megariotis, G.; Mania, M.; Becker-Baldus, J.; Kriechbaum, M.; Krajnc, A.; Christodoulou, E.; et al. Exploring the Interactions of Irbesartan and Irbesartan–2-Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Complex with Model Membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantis, D.A.; Ramesova, S.; Chatzigiannis, C.M.; Degano, I.; Gerogianni, P.S.; Karadima, K.E.; Perikleous, S.; Rekkas, D.; Gerothanassis, I.P.; Galaris, D.; et al. Exploring the Oxidation and Iron Binding Profile of a Cyclodextrin Encapsulated Quercetin Complex Unveiled a Controlled Complex Dissociation through a Chemical Stimulus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 1913–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, E.; Barbiric, D. Molecular Modeling and Cyclodextrins: A Relationship Strengthened By Complexes. Curr. Org. Chem. 2006, 10, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellici, T.F.; Chatziathanasiadou, M.V.; Diamantis, D.; Chatzikonstantinou, A.V.; Andreadelis, I.; Christodoulou, E.; Valsami, G.; Mavromoustakos, T.; Tzakos, A.G. Mapping the Interactions and Bioactivity of Quercetin(2-Hydroxypropyl)-β-Cyclodextrin Complex. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellici, T.F.; Chatziathanasiadou, M.V.; Lee, M.S.; Sayyad, N.; Geromichalou, E.G.; Vrettos, E.I.; Tsiailanis, A.D.; Chi, S.W.; Geromichalos, G.D.; Mavromoustakos, T.; et al. Rational Design and Structure-Activity Relationship Studies of Quercetin-Amino Acid Hybrids Targeting the Anti-Apoptotic Protein Bcl-XL. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 7956–7976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, K.; Jana, N.R.; Jana, N.R. Quercetin Encapsulated Polymer Nanoparticle for Inhibiting Intracellular Polyglutamine Aggregation. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 5298–5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jullian, C.; Moyano, L.; Yañez, C.; Olea-Azar, C. Complexation of Quercetin with Three Kinds of Cyclodextrins: An Antioxidant Study. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2007, 67, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Dong, L.; Chen, A.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, B. Inclusion Complexes of Quercetin with Three β-Cyclodextrins Derivatives at Physiological PH: Spectroscopic Study and Antioxidant Activity. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 115, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangpheak, W.; Kicuntod, J.; Schuster, R.; Rungrotmongkol, T.; Wolschann, P.; Kungwan, N.; Viernstein, H.; Mueller, M.; Pongsawasdi, P. Physical Properties and Biological Activities of Hesperetin and Naringenin in Complex with Methylated P-Cyclodextrin. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 2763–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kicuntod, J.; Khuntawee, W.; Wolschann, P.; Pongsawasdi, P.; Chavasiri, W.; Kungwan, N.; Rungrotmongkol, T. Inclusion Complexation of Pinostrobin with Various Cyclodextrin Derivatives. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2016, 63, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Pakade, Y.B.; Singh, B.; Yadav, S.C. Development of Biodegradable Nanoparticles for Delivery of Quercetin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 80, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwicker, J.I.; Furie, B.; Flaumenhaft, R. Method for Treating Sickle Cell Disease Using Quercetin-Containing Compositions. WO 2023/288044 A1, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Renjit, S. Sickle Cell Anemia Treatment. US 2006/0115459 A1, 26 November 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Trimboli, D.; Gatti, V.; Naccari, G.C. Combination of Catechin and Quercetin for Pharmaceutical or Dietary Use. WO 02/34262 A1, 11 October 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, B. New Application of Quercetin and Kaempferol. CN113018293A, 10 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Antipruritic Composition Containing Astragalin and Quercetin. KR20120121684A, 27 April 2011.
- Lines, T. Reducing Cholesterol Levels with Combined Use of Quercetin and Statin. WO2010027572A2, 23 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Won, L.K.; Joo, L.H.; Jun, L.S.; Young, C.J.; Ju, K.N.; Hoon, K.J.; Hyuk, L.J. Composition for Inhibiting Liver Cancer Containing Doxorubicin and Quercetin. KR100553266B1, 20 February 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Marchi, D.; Feige, J.; Horcajada, M. Compositions and Methods Using a Combination of Oleuropein and Quercetin for Use in Cartilage Degeneration. WO2022106410A1, 11 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, D. Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome with Ibudilast in Combination with Metformin, Cannbidiol, Sertraline or Quercetin. WO2021044158A1, 4 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lines, T. Quercetin-Containing Compositions for Use in Treating Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. WO2022243942A1, 19 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.B.; Tae, S.J.; Ki, H.B.; Yong, B.P.; Myung, S.C.; Sik, M.S.; Yong, K.K.; Lee, E.S.; Byung, H.H.; Yang, K.C.; et al. Composition Containing Rutin and Quercetin for Preventing or Treating Elevated Blood Lipid Level-Related Diseases. WO0015237A1, 15 September 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, W.; Ernst, L.G.; Schroder, H.-C.; Wilhelm, F.; Wang, X. Synergistic Composition Comprising Quercetin and Polyphosphate for Treatment of Bone Disorders. WO2015132304A1, 4 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sang-Chan, K.I.M.; Park, S.M.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, E.O.; PARK, C.A.; Sung-Hui, B.Y.U.N.; Sook-Jahr, P.A.R.K. Composition for Preventing or Treating Liver Disease, Comprising Icaritin and Quercetin. WO2022065550A1, 25 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jeung-Hye, P. Composition Containing Quercetin and Vitamin D for Alleviation of Acnegenic Skin. WO2018230824A1, 9 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, A.R.; Granger, S.P.; Scott, I.R. Skin Care Compositions Containing Naringenin and/or Quercetin and a Retinoid. US5665367A, 27 September 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Jeung-Hye, P. Composition, Containing Quercetin, Genistein, and Alpha-Lipoic Acid, for Relieving Acne Skin. WO2020111757A1, 27 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vasquez Garzon, V.R.; Carrasco Torres, G.; Andrade Jorge, E.; Trujillo Ferrara, J.G.; Trevino Villa, S. Quercetin and Maleic Anhydride Derivatives for The Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. MX2018008239A, 3 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez Munoz, F.J.; Espinosa Juarez, J.V.; Jaramilo Morales, O.A. Pharmaceutical Composition of Haloperidol and Quercetin with Analgesic Effect In Neuropathic Pain. MX2017007166A, 5 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mi-La, C.; Min-Jung, P.; Seon-Yeong, L.; Sung-Hee, L.; Eun-Ji, Y.; Hye-Jin, S. Composition for Preventing or Treating Immune Disease Comprising Metformin and Quercetin as Active Ingredients. KR20140132932A, 9 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gwonhwa, S.; Whasun, L.; Sunwoo, P. Pharmaceutical Composition for Preventing or Treating Endometriosis Comprising Quercetin Luteolin Delphinidin or Mixture Thereof. KR20210044409A, 15 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kuebler, U. Medicament, Useful to Treat or Prevent Malignantly Transformed Cells, e.g., Adeno-Carcinoma, Prostate Carcinoma and Breast Carcinoma, Comprises a Mixture of Quercetin and Myrecetin and/or Anisomycin and Rapamycin as Kinase Inhibitors. DE102006036307A1, 3 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Polifenoles, C, Combinación Sinérgica de Polifenoles. WO2012150370A1, 2 May 2012.
- Nday, C.M.; Halevas, E.; Jackson, G.E.; Salifoglou, A. Quercetin Encapsulation in Modified Silica Nanoparticles: Potential Use against Cu(II)-Induced Oxidative Stress in Neurodegeneration. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2015, 145, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Luan, X.; Luo, Z. Quercetin Derivatives and Their Medical Usages. US2004132671A1, 26 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira-Silva, M.; Faria-Silva, C.; Carvalheiro, M.C.; Simões, S.; Marinho, H.S.; Marcelino, P.; Campos, M.C.; Metselaar, J.M.; Fernandes, E.; Baptista, P.V.; et al. Quercetin Liposomal Nanoformulation for Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonio Tamayo-Ramos, J.; Martel, S.; Barros, R.; Bol, A.; Atilhan, M.; Aparicio, S. On the Behavior of Quercetin + Organic Solvent Solutions and Their Role for C60 Fullerene Solubilization. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 345, 117714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Torre, M.D.L.; Tomé, A.C.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S. Synthesis of [60]Fullerene–Quercetin Dyads. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 4617–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Saha, M.; Mahata, L.C.; China, A.; Chatterjee, N.; Das Saha, K. Quercetin and 5-Fu Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Trigger Cell-Cycle Arrest and Induce Apoptosis in HCT116 Cells via Modulation of the P53/P21 Axis. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 36893–36905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.A.; Syeda, J.T.M.; Wasan, K.M.; Wasan, E.K. An Overview of Chitosan Nanoparticles and Its Application in Non-Parenteral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Lazcano, A.A.; Hassan, D.; Pourmadadi, M.; Shamsabadipour, A.; Behzadmehr, R.; Rahdar, A.; Medina, D.I.; Díez-Pascual, A.M. 5-Fluorouracil Nano-Delivery Systems as a Cutting-Edge for Cancer Therapy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 246, 114995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, Y.J.; Wang, X.; Morris, M.E. Dietary Flavonoids: Effects on Xenobiotic and Carcinogen Metabolism. Toxicol. Vitr. 2006, 20, 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Liu, B.; Gao, J. The Application of Nanoparticles in Diagnosis and Theranostics of Gastric Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017, 386, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugazhendhi, A.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Karuppusamy, I.; Kathirvel, B. Inorganic Nanoparticles: A Potential Cancer Therapy for Human Welfare. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 539, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Khan, A.A.P.; Asiri, A.M.; Rub, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Ghani, S.A. In Vitro Studies of Carbon Fiber Microbiosensor for Dopamine Neurotransmitter Supported by Copper-Graphene Oxide Composite. Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, J.M.; Teixeira, M.R.; Ferronato, K.; Teixeira, H.F.; Koester, L.S.; Simões, C.M.O. Preparation, Characterization, and In Vitro Intestinal Permeability Evaluation of Thalidomide–Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Complexes. AAPS PharmSciTech 2012, 13, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Khan, A.A.P.; Asiri, A.M. Toward Design and Measurement of Electrical Conductivity and Thermal Properties of Silver Nanoparticle Embedded Poly(o-anisidine) Molybdophosphate Nanocomposite and Its Application as Microbiosensor. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, E237–E245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Khan, A.A.P.; Asiri, A.M.; Rub, M.A.; Azum, N.; Rahman, M.M.; Khan, S.B.; Ghani, S.A. A New Trend on Biosensor for Neurotransmitter Choline/Acetylcholine—An Overview. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 169, 1927–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, F.; Su, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, W. Nanoparticles Designed to Regulate Tumor Microenvironment for Cancer Therapy. Life Sci. 2018, 201, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, G.; Garrick, B.G.; Lalitha, K.; Chamundeeswari, M. Gold Nanoparticle Mediated Delivery of Fungal Asparaginase against Cancer Cells. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 44, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alban, L.; Monteiro, W.F.; Diz, F.M.; Miranda, G.M.; Scheid, C.M.; Zotti, E.R.; Morrone, F.B.; Ligabue, R. New Quercetin-Coated Titanate Nanotubes and Their Radiosensitization Effect on Human Bladder Cancer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 110, 110662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Down, C.J.; Nair, R.; Thurairaja, R. Bladder Cancer. Surgery 2016, 34, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.; Karanastasis, A.A.; Chatziathanasiadou, M.V.; Oguz, M.; Kougioumtzi, A.; Clemente, N.; Kellici, T.F.; Zafeiropoulos, N.E.; Avgeropoulos, A.; Mavromoustakos, T.; et al. Inclusion of Quercetin in Gold Nanoparticles Decorated with Supramolecular Hosts Amplifies Its Tumor Targeting Properties. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 2715–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, F.R.; Abdallah, I.A.; Bedair, A.; Hamed, M. Analytical Methods for the Determination of Quercetin and Quercetin Glycosides in Pharmaceuticals and Biological Samples. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2023, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmedova, A.; Paradowska, K.; Wawer, I. 1H, 13C MAS NMR and DFT GIAO Study of Quercetin and Its Complex with Al(III) in Solid State. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 110, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehranfar, F.; Bordbar, A.-K.; Parastar, H. A Combined Spectroscopic, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamic Simulation Study on the Interaction of Quercetin with β-Casein Nanoparticles. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2013, 127, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, N.; Karim, N.; Abdel-Halim, H.; Khan, I.; Wadood, S.F.; Nisar, M. Phytochemical Analysis, Molecular Docking and Antiamnesic Effects of Methanolic Extract of Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn Seeds in Scopolamine Induced Memory Impairment in Mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 210, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkhasian, A.Y.S.; Howlin, B.J. Docking and DFT Studies on Ligand Binding to Quercetin 2,3-Dioxygenase. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 34, 2453–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.-P.; Wang, X.-D.; Peng, Z.-Y.; Huang, S.; Yang, P.; Li, Q.-S.; Zhou, L.-H.; Hu, X.-J.; Wu, L.-J.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Molecular Docking, Kinetics Study, and Structure–Activity Relationship Analysis of Quercetin and Its Analogous as Helicobacter Pylori Urease Inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10572–10577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Selvaraj, C.; Knowar, B.K.; Singh, S.K.; Singh, C.B.; Sahoo, D. Competitive Inhibition of Quercetin and Apigenin at the ATP Binding Site of D-Alanine-D-Alanine Ligase of Helicobacter Pylori—A Molecular Modeling Approach. Curr. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Sarmah, P.; Patel, H.; Mukerjee, N.; Mishra, R.; Alkahtani, S.; Varma, R.S.; Baishya, D. Nonlinear Molecular Dynamics of Quercetin in Gynocardia Odorata and Diospyros Malabarica Fruits: Its Mechanistic Role in Hepatoprotection. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikiowo, B.; Ahmad, I.; Alade, A.A.; Ijatuyi, T.T.; Iwaloye, O.; Patel, H.M. Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Pharmacokinetics Studies of Ombuin and Quercetin against Human Pancreatic α-Amylase. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 10388–10395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maran, M.; Gangadharan, S.; Emerson, I.A. Molecular Dynamics Study of Quercetin Families and Its Derivative Compounds from Carica Papaya Leaf as Breast Cancer Inhibitors. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2022, 793, 139470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omirin, E.S.; Omotuyi, O.; Afokhume, O.G.; Okoh, E.F.; Boboye, S.O.; Olugbogi, E.A.; Adelegan, O.O.; Ibitoye, B.O.; Aderiye, M.A.; Agosile, O.O. Molecular Dynamics Simulations on Quercetin-3-(6-Malonylglucoside) From Morus Alba Shows Optimal Inhibition of Bcl-2 with Favorable Anti-Tumor Activities. bioRxiv 2015, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anusuya, S.; Gromiha, M.M. Quercetin Derivatives as Non-Nucleoside Inhibitors for Dengue Polymerase: Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics Simulation, and Binding Free Energy Calculation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2017, 35, 2895–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lokhande, K.B.; Ballav, S.; Yadav, R.S.; Swamy, K.V.; Basu, S. Probing Intermolecular Interactions and Binding Stability of Kaempferol, Quercetin and Resveratrol Derivatives with PPAR-γ: Docking, Molecular Dynamics and MM/GBSA Approach to Reveal Potent PPAR-γ Agonist against Cancer. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-Y.; Li, Y.-C.; Yu, D.-G.; Liao, Y.-Z.; Wang, X. Fast Disintegrating Quercetin-Loaded Drug Delivery Systems Fabricated Using Coaxial Electrospinning. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21647–21659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, N.G.; Kakran, M.; Shaal, L.A.; Li, L.; Müller, R.H.; Pal, M.; Tan, L.P. Preparation and Characterization of Quercetin Nanocrystals. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 2379–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Gao, W. Preparation, Physicochemical Characterization and in Vitro Digestibility on Solid Complex of Maize Starches with Quercetin. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koontz, J.L.; Marcy, J.E.; O’Keefe, S.F.; Duncan, S.E. Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex Formation and Solid-State Characterization of the Natural Antioxidants α-Tocopherol and Quercetin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, B.; Sengupta, P.K. The Interaction of Quercetin with Human Serum Albumin: A Fluorescence Spectroscopic Study. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 299, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, A.C.; Gehlen, M.H. Time Resolved Fluorescence Spectroscopy of Quercetin and Morin Complexes with Al3+. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2002, 58, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poór, M.; Boda, G.; Kunsági-Máté, S.; Needs, P.W.; Kroon, P.A.; Lemli, B. Fluorescence Spectroscopic Evaluation of the Interactions of Quercetin, Isorhamnetin, and Quercetin-3′-Sulfate with Different Albumins. J. Lumin. 2018, 194, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabri, Z.K.; Hussain, J.; Mabood, F.; Rehman, N.U.; Ali, L.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Hamaed, A.; Khan, A.L.; Rizvi, T.S.; Jabeen, F.; et al. Fluorescence Spectroscopy-Partial Least Square Regression Method for the Quantification of Quercetin in Euphorbia Masirahensis. Measurement 2018, 121, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wu, D.; Du, Z.; Li, R.; Chen, X.; Li, X. Spectroscopy Study on the Interaction of Quercetin with Collagen. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 3431–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wybranowski, T.; Kruszewski, S. Optical Spectroscopy Study of the Interaction between Quercetin and Human Serum Albumin. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2014, 125, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham-Hoang, B.; Winckler, P.; Waché, Y. Fluorescence Lifetime and UV-Vis Spectroscopy to Evaluate the Interactions between Quercetin and Its Yeast Microcapsule. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 13, 1700389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, J.; Rehman, N.U.; Mabood, F.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Ali, L.; Rizvi, T.S.; Khan, A.; Rafiq, K.; Al-Rabaani, H.; Jabeen, F. Application of Fluorescence Spectroscopy Coupled with PLSR for the Estimation of Quercetin in Four Medicinal Plants. Chem. Data Collect. 2019, 21, 100228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, J.; Kaur Lamba, A.; Lamba, H.S. Development, Characterization and Solubility Study of Solid Dispersion of Quercetin by Solvent Evaporation Method. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 10128–10133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.; Trehan, N. HPLC Analysis of Methanolic Extract of Herbs for Quercetin Content. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2013, 2, 159–162. [Google Scholar]
- D’Mello, P.M.; Joshi, U.J.; Shetgiri, P.P.; Dasgupta, T.K.; Darji, K.K. A Simple HPLC Method for Quantitation of Quercetin in Herbal Extracts. J. AOAC Int. 2011, 94, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, M.; Bahar, S.; Heydari, R.; Amininasab, S.M. Determination of Quercetin Using a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer as Solid-Phase Microextraction Sorbent and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Microchem. J. 2019, 148, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefova, M.; Kulevanova, S.; Stafilov, T. Assay of Flavonols and Quantification of Quercetin in Medicinal Plants by Hplc with Uv-Diode Array Detection. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2001, 24, 2283–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewska, M. Separation of Quercetin, Sexangularetin, Kaempferol and Isorhamnetin for Simultaneous HPLC Determination of Flavonoid Aglycones in Inflorescences, Leaves and Fruits of Three Sorbus Species. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 48, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canini, A.; Alesiani, D.; D’Arcangelo, G.; Tagliatesta, P. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Phenolic Compounds from Carica papaya L. Leaf. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2007, 20, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Zito, S.W. Development and Validation of a Gas Chromatographic–Mass Spectrometric Method for Simultaneous Identification and Quantification of Marker Compounds Including Bilobalide, Ginkgolides and Flavonoids in Ginkgo biloba L. Extract and Pharmaceutical Preparatio. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 986, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, M.; Pfeiffer, M.; Martini, M.; Campbell, D.; Slavin, J.; Potter, J. The Quantitation of Metabolites of Quercetin Flavonols in Human Urine. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 1996, 5, 711–720. [Google Scholar]
- Pejic, N.; Kuntic, V.; Vujic, Z.; Micic, S. Direct Spectrophotometric Determination of Quercetin in the Presence of Ascorbic Acid. Il Farm. 2004, 59, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belščak-Cvitanović, A.; Valinger, D.; Benković, M.; Tušek, A.J.; Jurina, T.; Komes, D.; Gajdoš Kljusurić, J. Integrated Approach for Bioactive Quality Evaluation of Medicinal Plant Extracts Using HPLC-DAD, Spectrophotometric, near Infrared Spectroscopy and Chemometric Techniques. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S2463–S2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzawa, M. Determination of Quercetin and Rutin in Selected Herbs and Pharmaceutical Preparations. Anal. Lett. 2010, 43, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligor, M.; Kornyšova, O.; Maruška, A.; Buszewski, B. Determination of Flavonoids in Tea and Rooibos Extracts by TLC and HPLC. J. Planar Chromatogr.—Mod. TLC 2008, 21, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randhawa, K.; Kumar, D.; Jamwal, A.; Kumar, S. Screening of Antidepressant Activity and Estimation of Quercetin from Coccinia Indica Using TLC Densitometry. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, G.A. Stability of Drugs, Drug Candidates, and Metabolites in Blood and Plasma. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2016, 2016, 7.6.1–7.6.12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.A.; Amin, A.A.; Patwari, A.H.; Shah, M.B. Validated High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography Method for Simultaneous Determination of Quercetin and Gallic Acid in Leea Indica. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2017, 27, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, H.; Ye, J. Determination of Rutin and Quercetin in Plants by Capillary Electrophoresis with Electrochemical Detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 423, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Z. Separation and Determination of Rutin and Quercetin in the Flowers of Sophora japonica L. by Capillary Electrophoresis with Electrochemical Detection. Chromatographia 2002, 55, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntornsuk, L.; Kasemsook, S.; Wongyai, S. Quantitative Analysis of Aglycone Quercetin in Mulberry Leaves (Morus alba L.) by Capillary Zone Electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2003, 24, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Han, S. Ultrasensitive Determination of Epicatechin, Rutin, and Quercetin by Capillary Electrophoresis Chemiluminescence. Acta Chromatogr. 2012, 24, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, A.F.; Solangi, A.R.; Memon, S.Q.; Mallah, A.; Memon, N.; Memon, A.A. Simultaneous Determination of Quercetin, Rutin, Naringin, and Naringenin in Different Fruits by Capillary Zone Electrophoresis. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, D.; Wiczkowski, W.; Piskula, M.K. Determination of the Relative Contribution of Quercetin and Its Glucosides to the Antioxidant Capacity of Onion by Cyclic Voltammetry and Spectrophotometric Methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 3524–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddaiah, K.; Reddy, T.M.; Swamy, K. Electrochemical Determination of Quercetin at β–Cyclodextrin Modified Chemical Sensor: A Voltammetric Study. Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem. 2012, 4, 122. [Google Scholar]
- Guss, E.V.; Ziyatdinova, G.K.; Zhupanova, A.S.; Budnikov, H.C. Voltammetric Determination of Quercetin and Rutin on Their Simultaneous Presence on an Electrode Modified with Polythymolphthalein. J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 75, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotkova, E.I.; Voronova, O.A.; Dorozhko, E.V. Study of Antioxidant Properties of Flavonoids by Voltammetry. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2012, 16, 2435–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, Y.; Tanaka, H. Quantitative Analysis of Quercetin Using Raman Spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurasekova, Z.; Domingo, C.; Garcia-Ramos, J.V.; Sanchez-Cortes, S. Effect of PH on the Chemical Modification of Quercetin and Structurally Related Flavonoids Characterized by Optical (UV-Visible and Raman) Spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 12802–12811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paczkowska, M.; Lewandowska, K.; Bednarski, W.; Mizera, M.; Podborska, A.; Krause, A.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Application of Spectroscopic Methods for Identification (FT-IR, Raman Spectroscopy) and Determination (UV, EPR) of Quercetin-3-O-Rutinoside. Experimental and DFT Based Approach. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 140, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurasekova, Z.; Torreggiani, A.; Tamba, M.; Sanchez-Cortes, S.; Garcia-Ramos, J.V. Raman and Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Investigation of the Quercetin Interaction with Metals: Evidence of Structural Changing Processes in Aqueous Solution and on Metal Nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 2009, 918, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornard, J.P.; Merlin, J.C.; Boudet, A.C.; Vrielynck, L. Structural Study of Quercetin by Vibrational and Electronic Spectroscopies Combined with Semiempirical Calculations. Biospectroscopy 1997, 3, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savic, I.M.; Nikolic, V.D.; Savic, I.M.; Nikolic, L.B.; Stankovic, M.Z. Development and Validation of a New RP-HPLC Method for Determination of Quercetin in Green Tea. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 68, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, M.K.; Gautam, B.; Pokhrel, K.P.; Ghani, L.; Bhattarai, A. Quantification of the Quercetin Nanoemulsion Technique Using Various Parameters. Molecules 2023, 28, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh Kumar, V.; Verma, P.R.P.; Singh, S.K. Morphological and in vitro Antibacterial Efficacy of Quercetin Loaded Nanoparticles against Food-Borne Microorganisms. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, M.; Ghoreishi, S.M.; Masoum, S.; Khoobi, A. Determination of Quercetin in the Presence of Tannic Acid in Soft Drinks Based on Carbon Nanotubes Modified Electrode Using Chemometric Approaches. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 272, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savic-Gajic, I.M.; Savic, I.M.; Nikolic, V.D. Modelling and Optimization of Quercetin Extraction and Biological Activity of Quercetin-Rich Red Onion Skin Extract from Southeastern Serbia. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 57, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, T.; Xia, N.; Xia, Q. Nanostructured Lipid Carrier (NLC) as a Strategy for Encapsulation of Quercetin and Linseed Oil: Preparation and in Vitro Characterization Studies. J. Food Eng. 2017, 215, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacek, J.; Papoušková, B.; Vrba, J.; Zatloukalová, M.; Křen, V.; Ulrichová, J. LC–MS Metabolic Study on Quercetin and Taxifolin Galloyl Esters Using Human Hepatocytes as Toxicity and Biotransformation in vitro Cell Model. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 86, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokalj Ladan, M.; Straus, J.; Tavčar Benković, E.; Kreft, S. FT-IR-Based Method for Rutin, Quercetin and Quercitrin Quantification in Different Buckwheat (Fagopyrum) Species. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pralhad, T.; Rajendrakumar, K. Study of Freeze-Dried Quercetin–Cyclodextrin Binary Systems by DSC, FT-IR, X-ray Diffraction and SEM Analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2004, 34, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasongsidh, B.C.; Skurray, G.R. Capillary Electrophoresis Analysis of Trans- and Cis-Resveratrol, Quercetin, Catechin and Gallic Acid in Wine. Food Chem. 1998, 62, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Li, H. Assessing the Anti-inflammatory Effects of Quercetin Using Network Pharmacology and in Vitro Experiments. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 23, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-W.; Chen, J.-Y.; Ouyang, D.; Lu, J.-H. Quercetin in Animal Models of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, T.; Hanssen, H.; Sisic, Z.; Pfeiler, S.; Summo, C.; Schmauss, D.; Hoster, E.; Weis, M. Immunoregulatory Effects of the Flavonol Quercetin in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Nutr. 2011, 50, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekinci, M.S. Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Quercetin from Sumac (Rhus coriaria L.): Effects of Supercritical Extraction Parameters. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Tang, G.; Li, M.; Zhang, T.; Fillet, M.; Crommen, J.; Jiang, Z. Development and Validation of a Fast SFC Method for the Analysis of Flavonoids in Plant Extracts. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 140, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnuszewska, J.; Krogulec, T. Analytica Chimica Acta Application of Hot Platinum Microelectrodes for Determination of Flavonoids in Flow Injection Analysis and Capillary Electrophoresis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 786, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldanha, L.; Vilegas, W.; Dokkedal, A. Characterization of Flavonoids and Phenolic Acids in Myrcia Bella Cambess. Using FIA-ESI-IT-MSn and HPLC-PAD-ESI-IT-MS Combined with NMR. Molecules 2013, 18, 8402–8416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Malik, A.K.; Tewary, D.K. A New Method for Determination of Myricetin and Quercetin Using Solid Phase Microextraction–High Performance Liquid Chromatography–Ultra Violet/Visible System in Grapes, Vegetables and Red Wine Samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 631, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchi, L.; Ieri, F.; Vignolini, P.; Mulinacci, N.; Romani, A. Characterization of Volatile and Flavonoid Composition of Different Cuts of Dried Onion (Allium cepa L.) by HS-SPME-GC-MS, HS-SPME-GC×GC-TOF and HPLC-DAD. Molecules 2020, 25, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, N.; May, R. The Crystal and Molecular Structure of Quercetin: A Biologically Active and Naturally Occurring Flavonoid. Bioorg. Chem. 1986, 69, 55–69. [Google Scholar]
- Han, G.; Zeng, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Xing, T.; Huang, C. Talanta MIL-101 (Cr) as Matrix for Sensitive Detection of Quercetin by Matrix- Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Talanta 2017, 164, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sporns, P. MALDI-TOF MS Analysis of Food Flavonol Glycosides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1657–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frison-Norrie, S.; Sporns, P. Identification and Quantification of Flavonol Glycosides in Almond Seedcoats Using MALDI-TOF MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2782–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroslakova, I.; Pedrussio, S.; Wolfram, E. Direct Coupling of HPTLC with MALDI-TOF MS for Qualitative Detection of Flavonoids on Phytochemical Fingerprints. Phytochem. Anal. 2016, 27, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojković, E.D.; Zdravkovski, Z. Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Quercetin and Rutin from Hyperici Herba Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Quercetin and Rutin from Hyperici Herba. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2007, 26, 2517–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, M.; Abdallah, I.A.; Bedair, A.; Mansour, F.R. Sample Preparation Methods for Determination of Quercetin and Quercetin Glycosides in Diverse Matrices. Microchem. J. 2023, 194, 109233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinelli, A.; Weiss, R.; Mizaikoff, B. Advanced Solid Phase Extraction Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for the Determination of Quercetin in Red Wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1804–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, L. Quercetin Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Preparation, Recognition Characteristics and Properties as Sorbent for Solid-Phase Extraction. Talanta 2009, 80, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, L.R.; Rosa, A.A.; Dias, A.C.B. Synthesis and Characterization of Molecularly Imprinted Silica Mediated by Al for Solid Phase Extraction of Quercetin in Ginkgo biloba L. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 4029–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaram, A.; Arabi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Sadeghi, H.; Ghaedi, M. Simple and Selective Detection of Quercetin in Extracts of Plants and Food Samples by Dispersive-Micro-Solid Phase Extraction Based on Core–Shell Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 16144–16153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
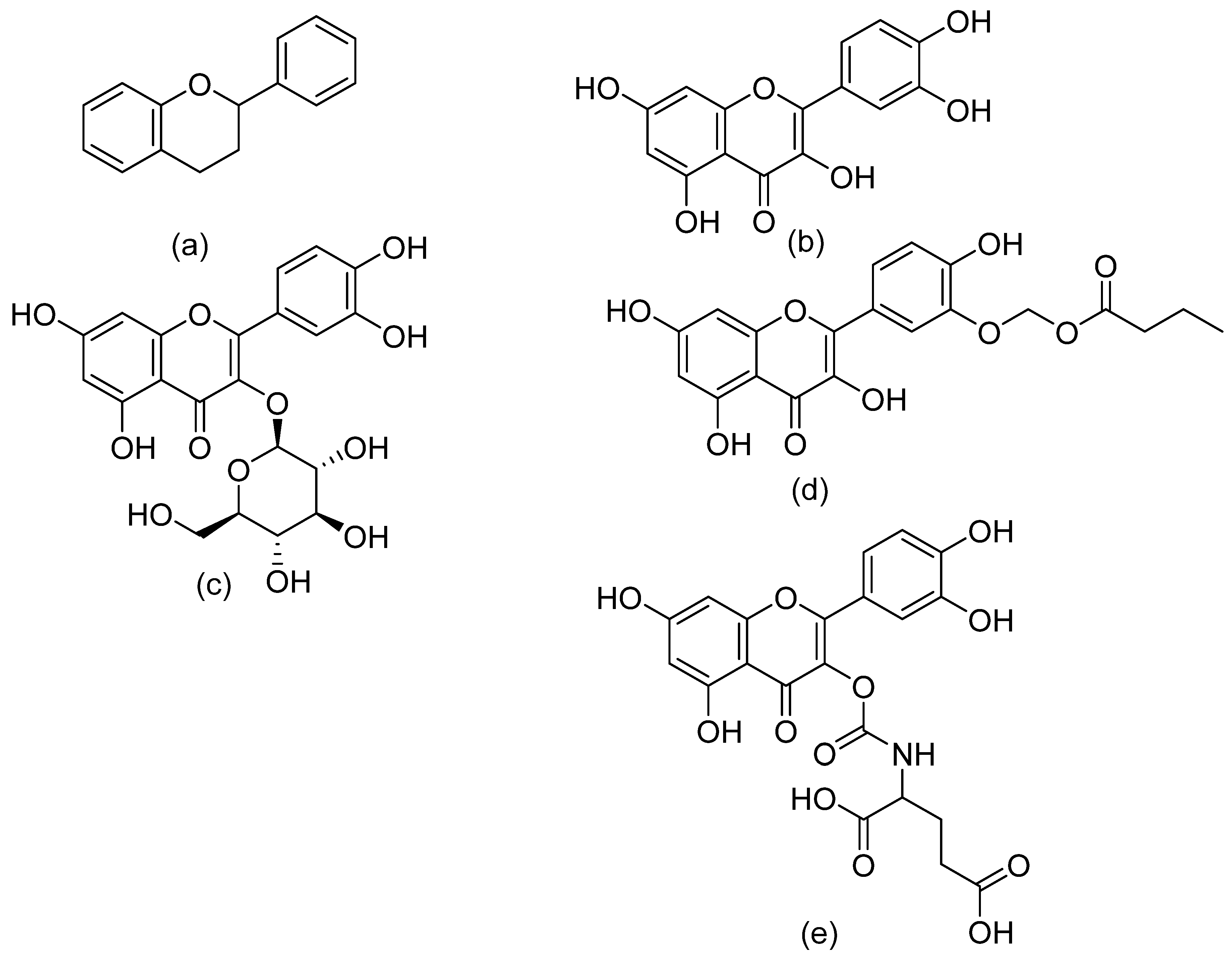
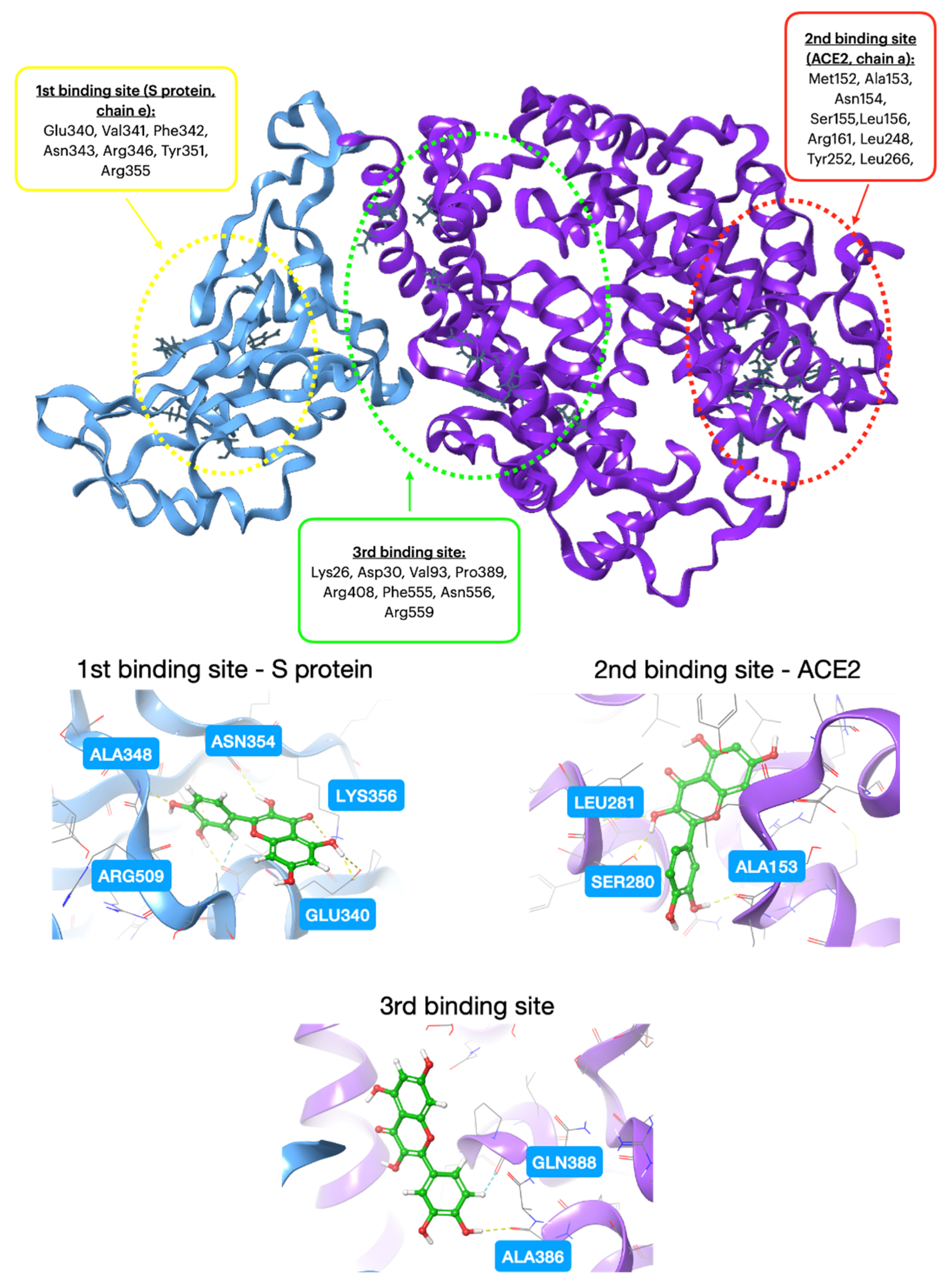

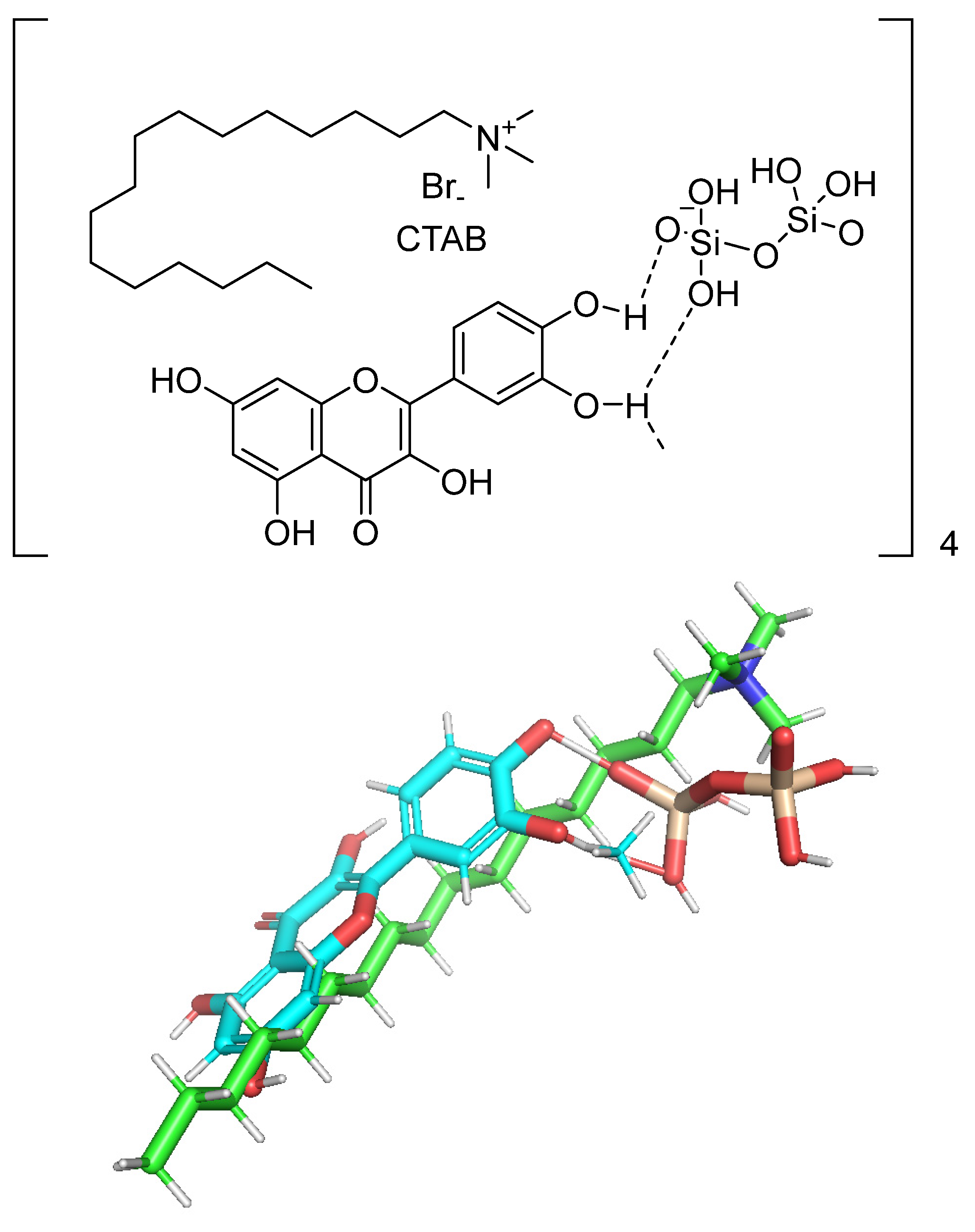
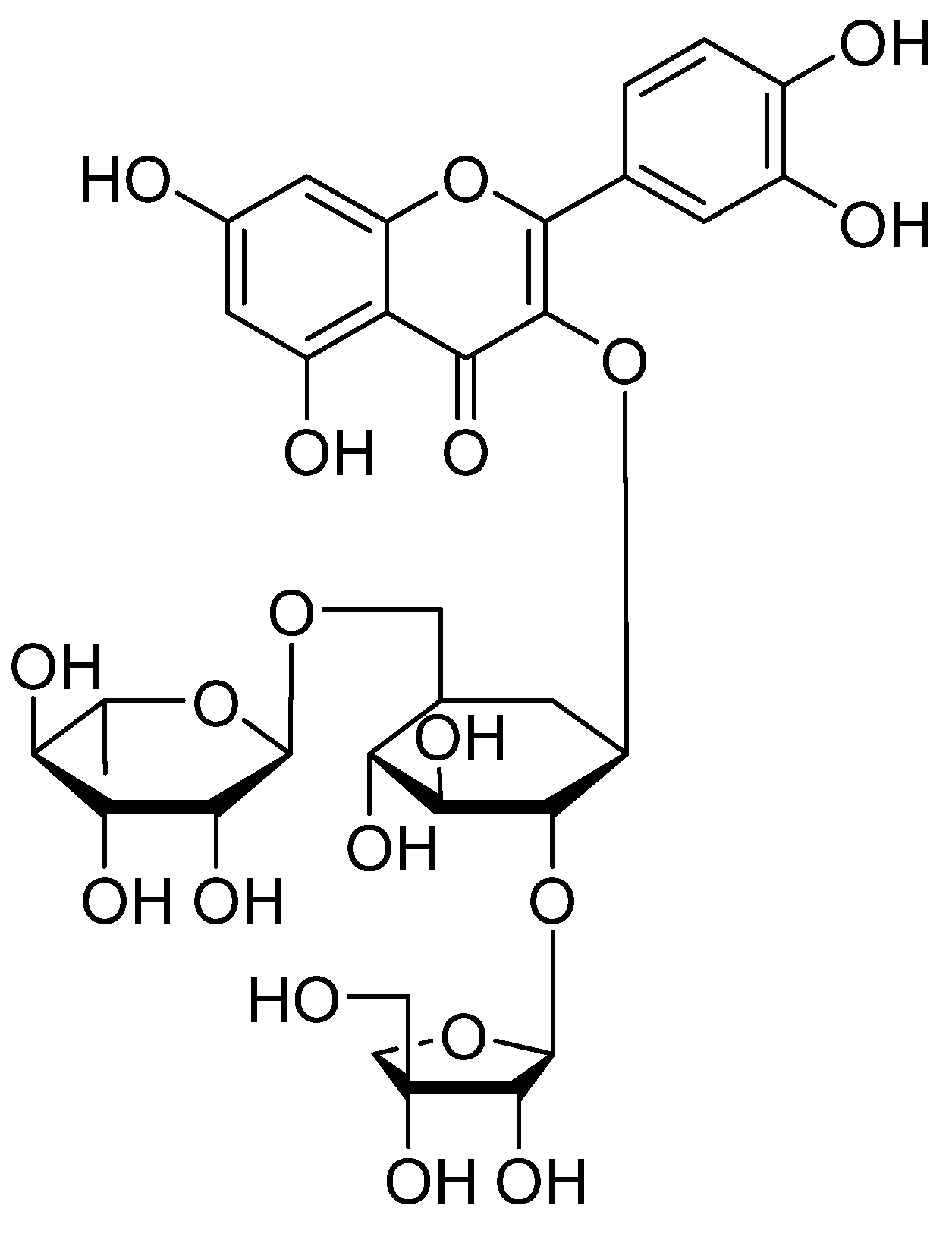


| Additive | Treatment of Disease |
|---|---|
| Vitamin C, vitamin B3, folic acid | Sickle cell disease (SCD) [114,115] |
| Catechin | Synergistic inhibition of the platelet function and dietary use [116] |
| Kaempferol | Prevention and treatment of hereditary cardiomyopathy [117] |
| Astragalin | Treatment of atopic dermatitits [118] |
| Statins | Reducing cholesterol levels [119] |
| Doxorubicin | Inhibiting liver cancer [120] |
| Oleuropein | Preventing and treating joint disorders [121] |
| Ibudilast | Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome [122] |
| Zafirlukast | Treating amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [123] |
| Rutin | Treating elevated blood lipid level-related diseases [124] |
| Polyphosphate | Treating osteoporosis [125] |
| Icaritin | Treatment of liver disease [126] |
| Vitamin D, retinol, and genistein | Improvement of skin conditions [127,128,129] |
| Maleic anhydride derivatives | Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma [130] |
| Haloperidol | Releaving neuropathic pain [131] |
| Metformin | Preventing against immune diseases [132] |
| Luteonil and delphinidin | Treatment of endometriosis [133] |
| Myrecetin | Curing adenocarcinoma, prostate carcinoma, and breast cancer [134] |
| Technique | Reason That It Was Used |
|---|---|
| NMR spectroscopy | Structure elucidation of quercetin with cyclodextrins and observation of their complexation [91,157] |
| 2D-DOSY NMR spectroscopy | Evaluation of the complex formation of quercetin with cyclodextrins [92,158] |
| Induced Fit Docking (IFD) | Evaluation of how effectively quercetin binds to essential viral components or enzymes. For instance, quercetin was used for IFD against acetylcholinesterase and butyrelcholinesterase [159,160,161,162]. |
| Molecular dynamics | To obtain a deeper understanding of the stability and molecular interactions within the complexes formed by the “protein-ligand” pairs identified in the docking studies [92,163,164,165,166,167] |
| Molecular Mechanics Generalized Born Surface Area (MM GBSA) | To highlight the strongest binding capability of quercetin against different macromolecules [92,168] |
| Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) | Validation of the formation of the complexes. For example, it was shown that quercetin was well distributed in the polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) matrix [169,170,171,172,173]. |
| Fluorescence spectroscopic studies | Investigation of the interactions between quercetin and macromolecules. In particular, it was used in the formation of the dimeric assemblies of quercetin with cyclodextrins [91,174,175,176,177,178,179,180]. |
| Solubility studies | Examination of the solubility of quercetin inside macromolecules in different pHs [155,181,182] |
| High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) | Validation of the purity and identification of the components. It was used for the determination of quercetin in herbal extracts [183,184,185,186]. |
| Gas chromatography (GC) | Analysis of quercetin and its separation from different plants, materials, etc. [187,188,189] |
| UV/Vis spectroscopy | Quantification of quercetin in various contexts, encompassing pharmaceutical formulations [190], medicinal plants, beverages [191,192], and food. |
| Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) | Separation of quercetin from other flavonoids in a shared matrix [193,194,195,196] |
| Electrophoresis | Analysis of quercetin [197,198,199,200,201] |
| Cyclic voltammetry (CV) | Determination of the antioxidant activity of quercetin in lyophilized onion tissue of onion var [202,203,204] |
| Pulse voltammetry (DPV) | Determination of the antioxidant activity and the electrochemical parameters of quercetin [205] |
| Raman spectroscopy | Quantitative analysis of quercetin in onion peels [206,207,208,209,210] |
| Limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantitation (LOQ) | Validation of the analytical method by determining quercetin in green tea [211] |
| Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) | Details for structural properties of quercetin in oil-in-water nanoemulsions [212,213] |
| Central Composite Design (CCD) | Evaluation of the effects of pH in determining quercetin in the presence of electroactive tannic acid [214,215] |
| Rheological measurements | Evaluation of the strength of the structure of quercetin with nanostructured lipid carriers in linseed oil [216] |
| Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectroscopy (LC-MS) | Identification and quantification of quercetin in human hepatocytes as in vitro cell models [217] |
| Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) | Analyzing the infrared absorption or emission of the molecule in buckwheat samples [218,219] |
| Capillary electrophoresis (CE) | Analysis of quercetin based on its electrophoretic mobility in red and white wine samples [197,220] |
| Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) | Quantitative analysis of quercetin to determine its anti-inflammatory effects in lipopolysaccharide stimulated cells [221,222,223] |
| Supercritical Fluid Chromatography (SFC) | Separation and extraction of quercetin from sumac fruits [224,225] |
| Flow Injection Analysis (FIA) | Subsequent detection of quercetin using normal and hot platinum microelectrode, showing the utility of Baranski’s method [226,227] |
| Solid-Phase Microextraction (SPME) | Extraction and analysis of quercetin, combined with HPLC-UV detection method, in green and black tea and coffee samples [184,228,229] |
| X-ray crystallography | Determination of the three-dimensional structure of quercetin crystals existing as hydrogen-bonded dimers, contributing to its unique biological activities [230] |
| Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-MS) | Analysis of quercetin utilizing MIL-101(Cr) as surface-assisted matrix for replacing traditional organic matrices [231,232,233,234] |
| Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE) | Extraction of quercetin from Hyperici herba [224,235] |
| Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE) | Preparation of samples for extracting and determining quercetin’s and quercetin glucosides’ concentration in food products [236,237,238,239,240] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Georgiou, N.; Kakava, M.G.; Routsi, E.A.; Petsas, E.; Stavridis, N.; Freris, C.; Zoupanou, N.; Moschovou, K.; Kiriakidi, S.; Mavromoustakos, T. Quercetin: A Potential Polydynamic Drug. Molecules 2023, 28, 8141. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248141
Georgiou N, Kakava MG, Routsi EA, Petsas E, Stavridis N, Freris C, Zoupanou N, Moschovou K, Kiriakidi S, Mavromoustakos T. Quercetin: A Potential Polydynamic Drug. Molecules. 2023; 28(24):8141. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248141
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeorgiou, Nikitas, Margarita Georgia Kakava, Efthymios Alexandros Routsi, Errikos Petsas, Nikolaos Stavridis, Christoforos Freris, Nikoletta Zoupanou, Kalliopi Moschovou, Sofia Kiriakidi, and Thomas Mavromoustakos. 2023. "Quercetin: A Potential Polydynamic Drug" Molecules 28, no. 24: 8141. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248141
APA StyleGeorgiou, N., Kakava, M. G., Routsi, E. A., Petsas, E., Stavridis, N., Freris, C., Zoupanou, N., Moschovou, K., Kiriakidi, S., & Mavromoustakos, T. (2023). Quercetin: A Potential Polydynamic Drug. Molecules, 28(24), 8141. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248141







