Vitexin Regulates Heat Shock Protein Expression by Modulating ROS Levels Thereby Protecting against Heat-Stress-Induced Apoptosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
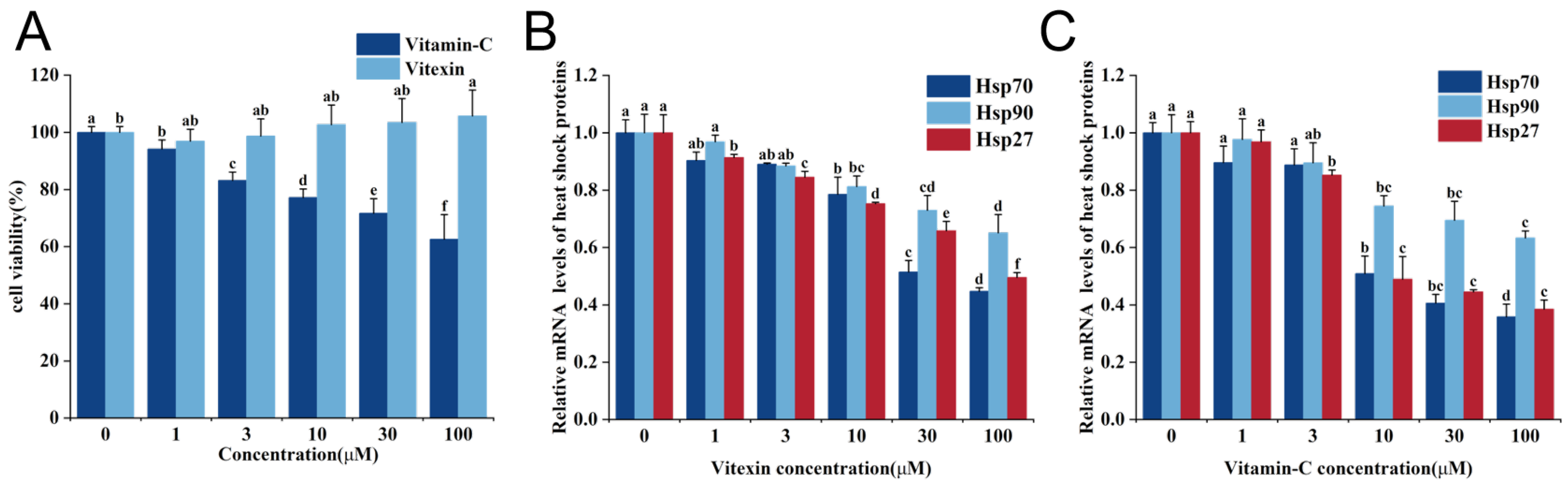
2.1. Vitexin Promotes Caco-2 Cell Proliferation
2.2. Effects of Different Vitexin Concentrations on Relative mRNA Expression of HSPA1A, HSP90AB1, and HSPB1
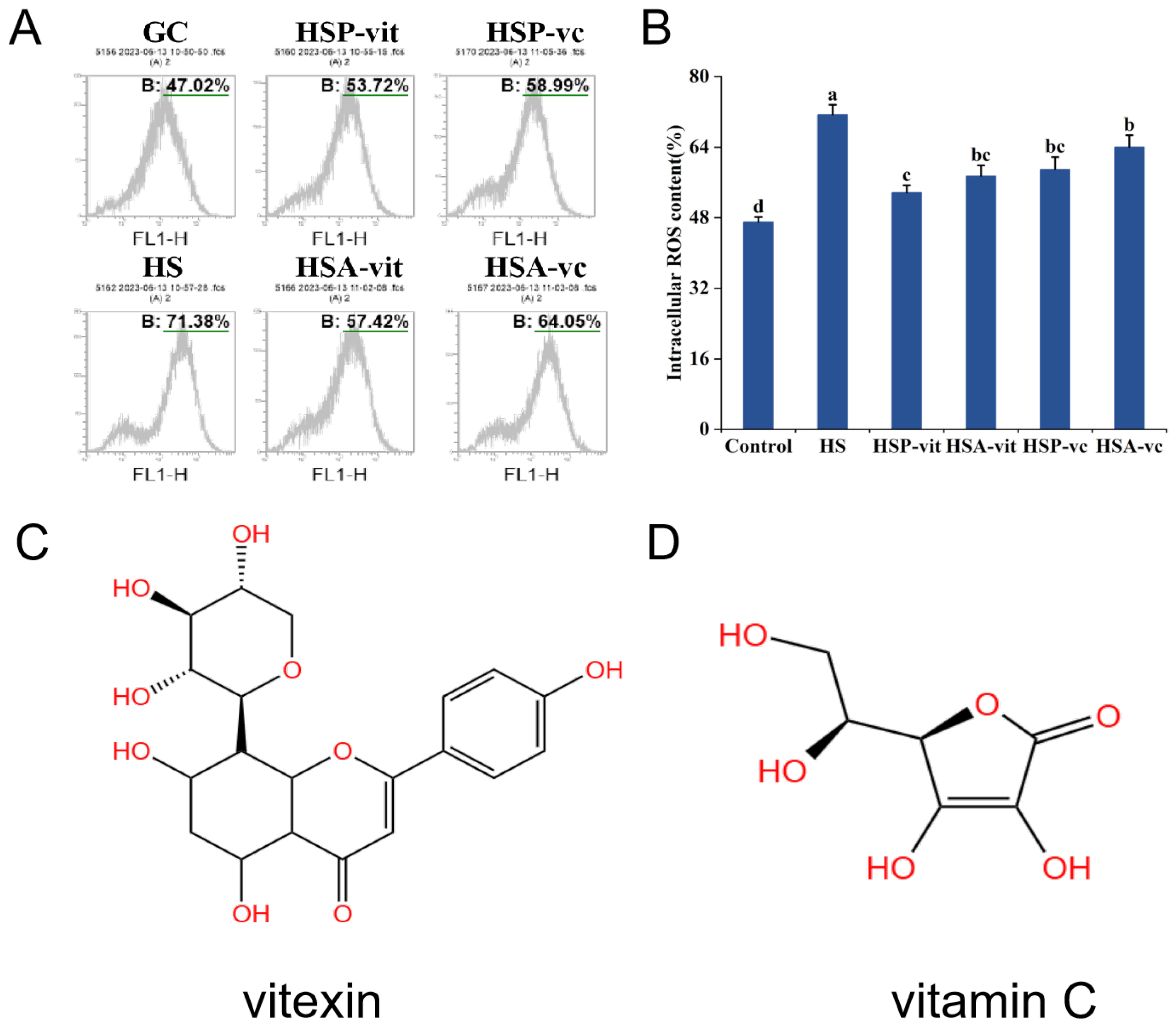
2.3. Vitexin Inhibits Heat-Stress-Induced ROS Production
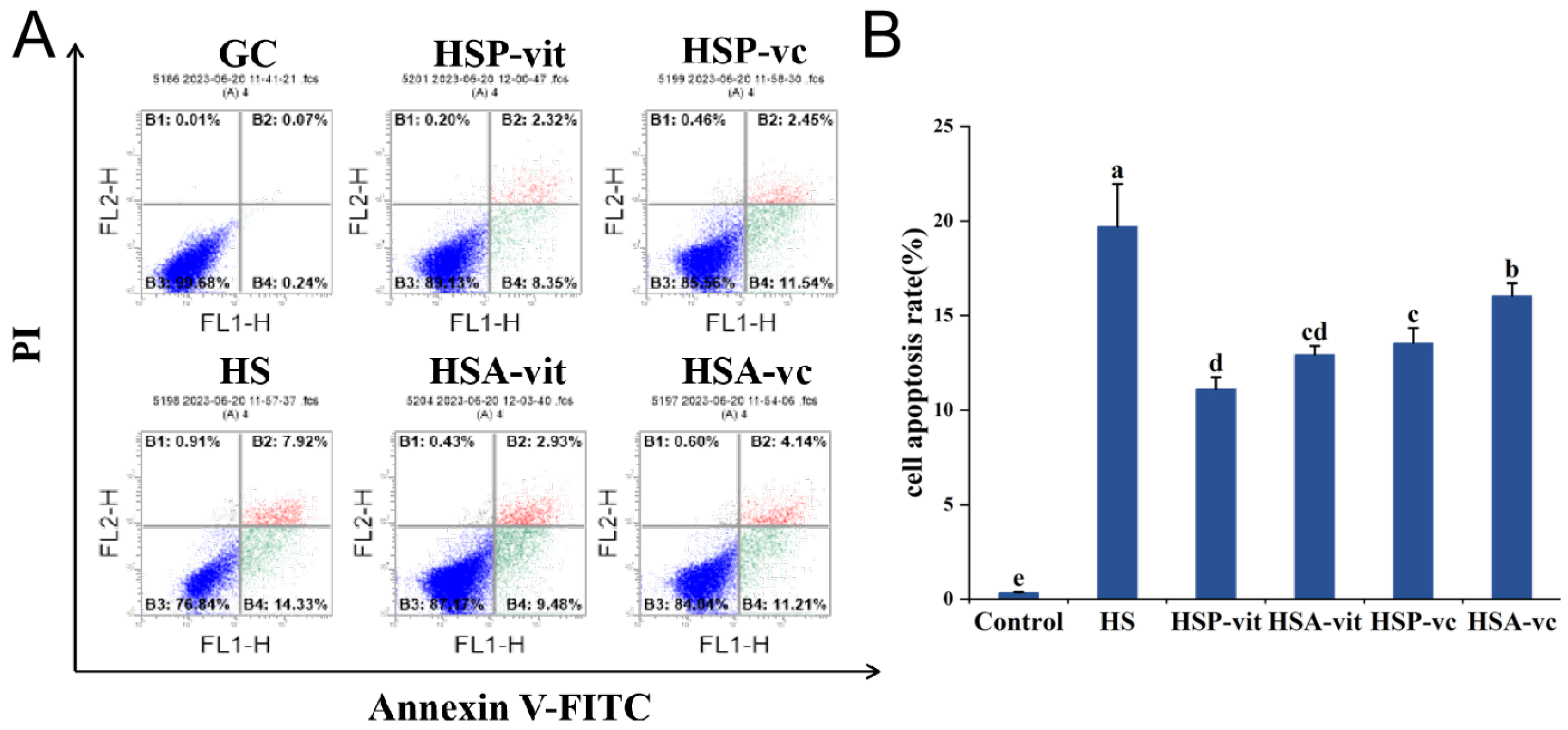
2.4. Vitexin Reduces Heat Shock Protein Expression and Apoptosis Induced by Heat Stress
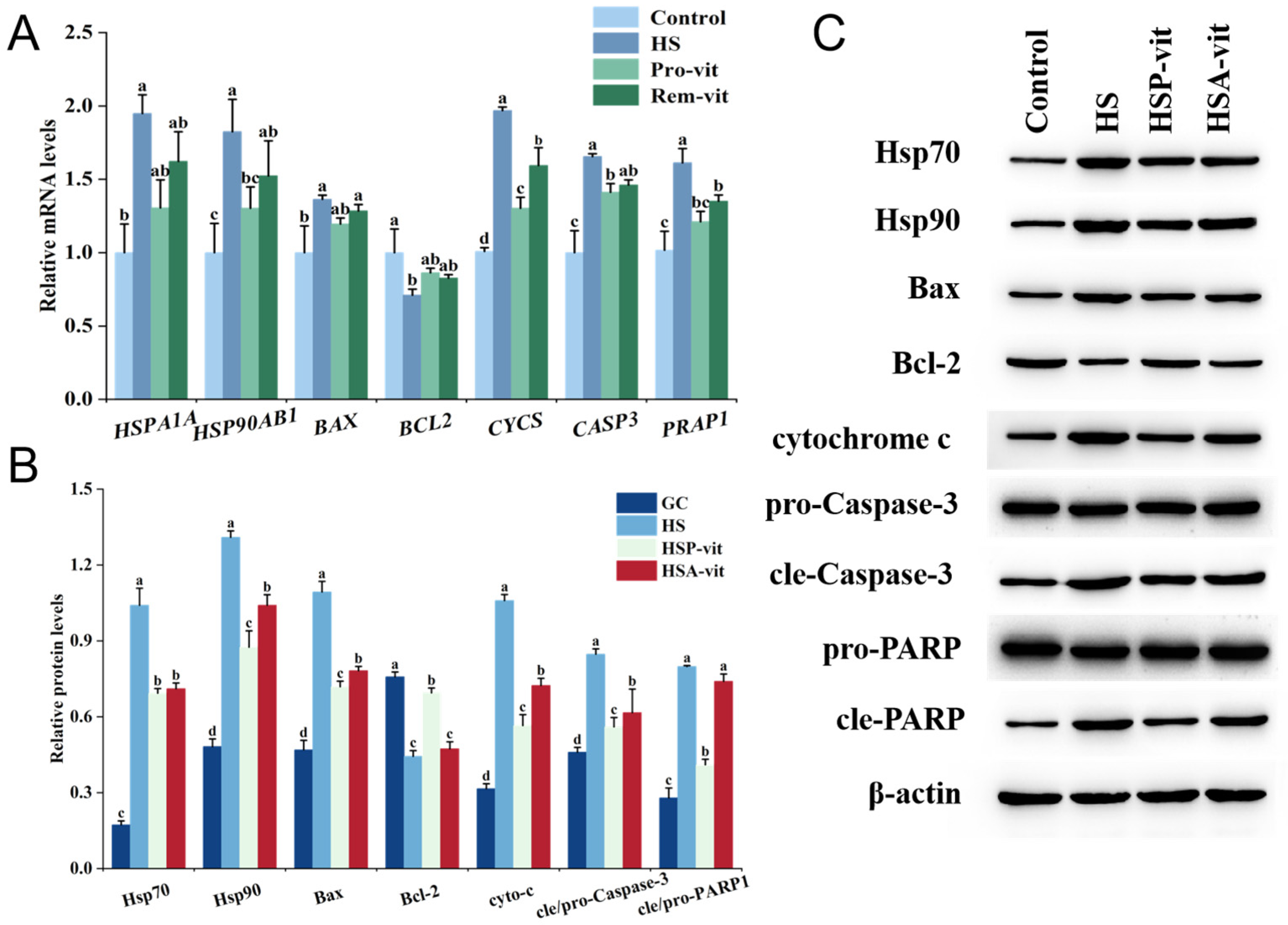
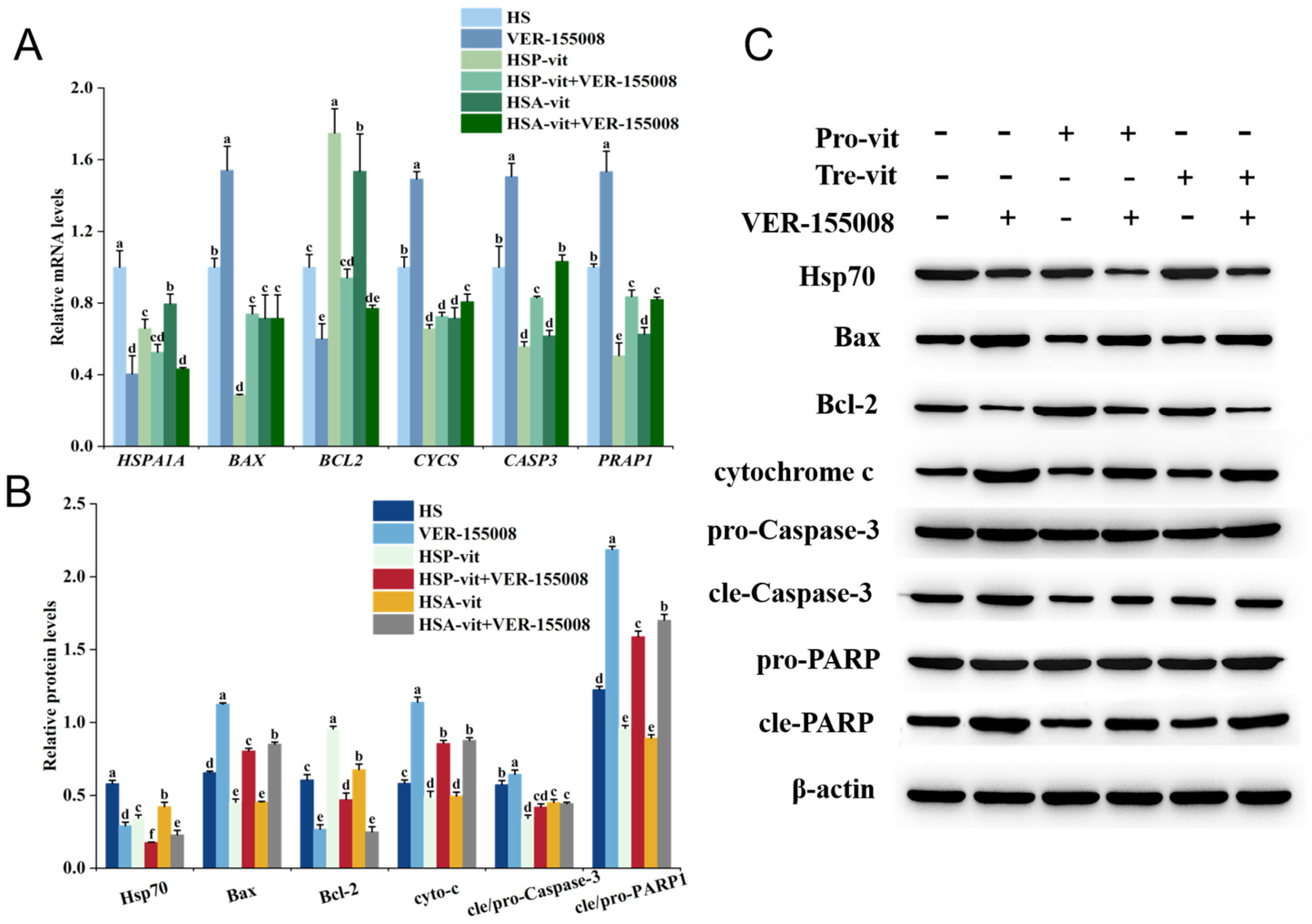
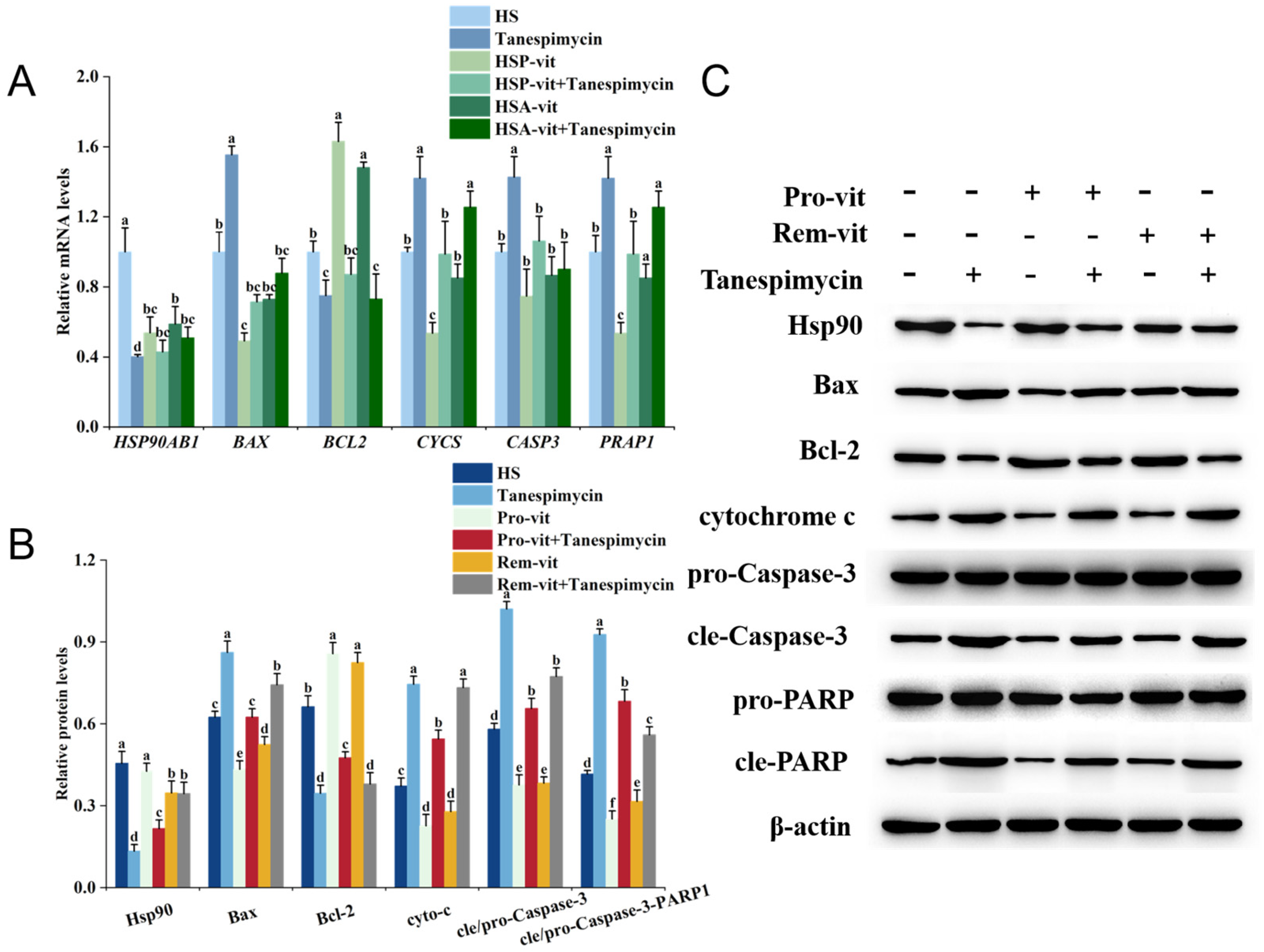
2.5. Vitexin Inhibited Apoptosis by Regulating Heat Shock Protein Expression
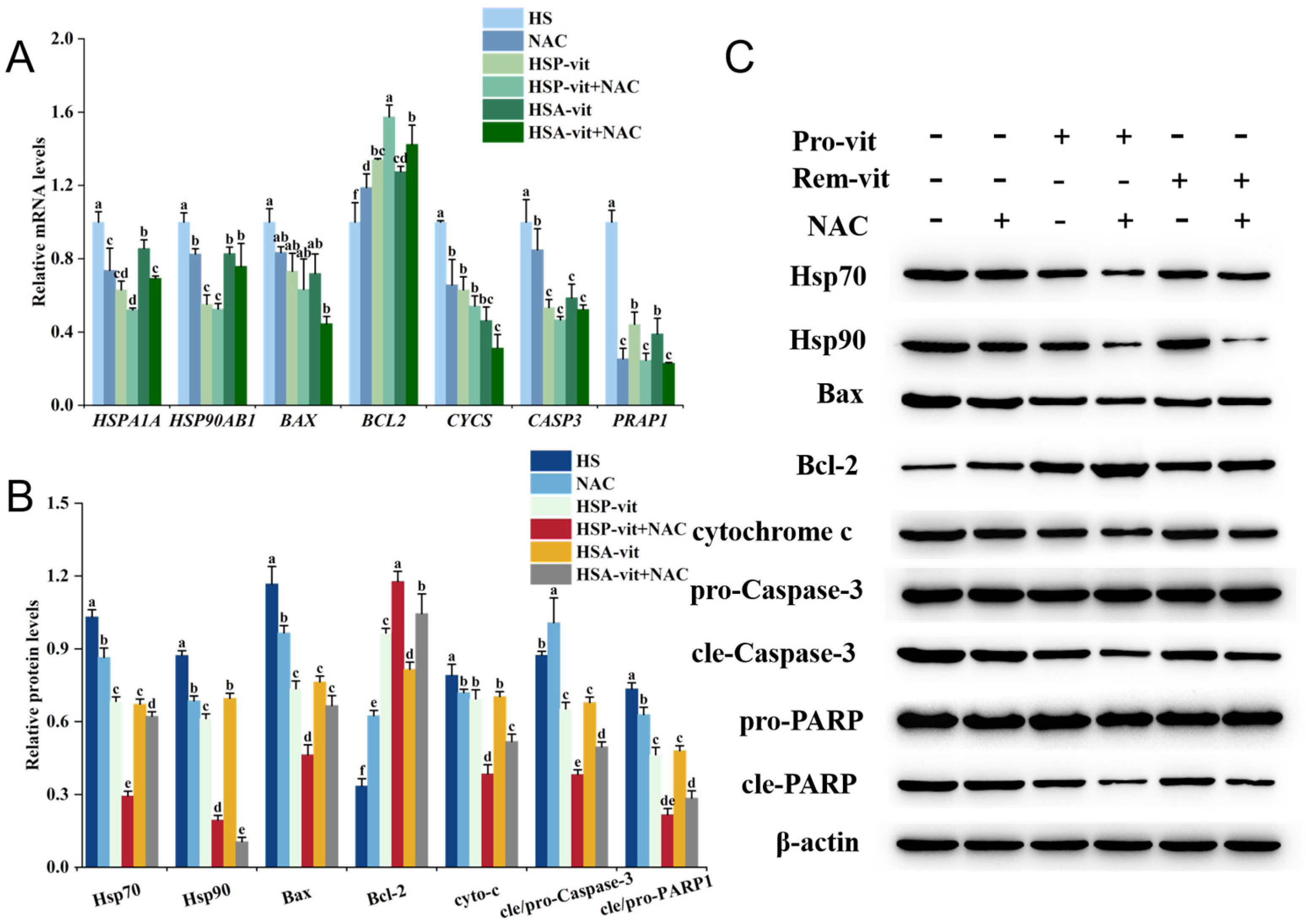
2.6. Vitexin Regulates Heat Shock Protein Expression by Reducing ROS Levels thereby Alleviating Apoptosis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Cell Culture and Compound Treatment
3.3. Cell Viability Assay
3.4. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
3.5. Measurement of ROS Levels
3.6. Cell Apoptosis Analysis
3.7. Western Blot Analysis
3.8. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, Y.; Lin, L.; Liu, K.; Liu, E.; Han, S.; Gong, Z.; Xiao, W. L-Theanine alleviates heat stress-induced impairment of immune function by regulating the p38 MAPK signalling pathway in mice. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagath, M.; Krishnan, G.; Devaraj, C.; Rashamol, V.P.; Pragna, P.; Lees, A.M.; Sejian, V. The impact of heat stress on the immune system in dairy cattle: A review. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 126, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Périard, J.D.; Eijsvogels, T.M.H.; Daanen, H.A.M. Exercise under heat stress: Thermoregulation, hydration, performance implications, and mitigation strategies. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 1873–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkes, B.; Buzan, J.R.; Huber, M. Heat stress in Africa under high intensity climate change. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2022, 66, 1531–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.A. Heat related illnesses. Review of an ongoing challenge. Saudi Med. J. 2019, 40, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salata, F.; Golasi, I.; Petitti, D.; de Lieto Vollaro, E.; Coppi, M.; de Lieto Vollaro, A. Relating microclimate, human thermal comfort and health during heat waves: An analysis of heat island mitigation strategies through a case study in an urban outdoor environment. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 30, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovats, R.S.; Hajat, S. Heat stress and public health: A critical review. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2008, 29, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, C.; Hess, J. Treatment and Prevention of Heat-Related Illness. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1404–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; He, Y.; Arowolo, M.A.; Wu, S.; He, J. Polyphenols as Potential Attenuators of Heat Stress in Poultry Production. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ibtisham, F.; Niu, Y.F.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.H.; Zhao, Y.; Nawab, A.; Xiao, M.; An, L. Curcumin inhibits heat-induced oxidative stress by activating the MAPK-Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway in chicken fibroblasts cells. J. Therm. Biol. 2019, 79, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, X.; Song, J.; Wang, N.; Liu, Q. Ferulic acid protects against heat stress-induced intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in IEC-6 cells via the PI3K/Akt-mediated Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Int. J. Hyperth. 2019, 35, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putics, A.; Vegh, E.M.; Csermely, P.; Sőti, C. Resveratrol induces the heat-shock response and protects human cells from severe heat stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Lian, R.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Sun, C.; Lin, S.; et al. Tea Polyphenols Enhanced the Antioxidant Capacity and Induced Hsps to Relieve Heat Stress Injury. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9615429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Fu, C.; Yan, M.; Xie, H.; Li, S.; Yu, Q.; He, S.; He, J. Resveratrol modulates intestinal morphology and HSP70/90, NF-κB and EGF expression in the jejunal mucosa of black-boned chickens on exposure to circular heat stress. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Shen, H.; Tian, Z.; Kang, M.; Ma, J.; He, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wang, D. Protective effect of hawthorn vitexin on the ethanol-injured DNA of BRL-3A hepatocytes. Medicine 2021, 100, e28228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Ning, T.; Wang, H. Vitexin alleviates inflammation and enhances apoptosis through the regulation of the JAK/STAT/SOCS signaling pathway in the arthritis rat model. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e23201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, M.; Paul, S.; Jakhar, R.; Kang, S.C. Potential role of vitexin in alleviating heat stress-induced cytotoxicity: Regulatory effect of Hsp90 on ER stress-mediated autophagy. Life Sci. 2015, 142, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Fan, X.; Suo, D.; Zhang, S.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; Guan, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, C. Screening of heat stress-regulating active fractions in mung beans. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1102752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthamilan, S.; Aggarwal, A.; Grewal, S.; Rani, S.; Vats, P.; Pal, P.; Jaswal, S.; Arya, A.; Alhussien, M.N. Pre-treatment but not co-treatment with vitexin alleviates hyperthermia induced oxidative stress and inflammation in buffalo mammary epithelial cells. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2023, 158, 103979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Song, Z.; Li, S.; Yan, E.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, T. Effects of resveratrol on intestinal oxidative status and inflammation in heat-stressed rats. J. Therm. Biol. 2019, 85, 102415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, Q.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y. L-arginine reduces injury from heat stress to bovine intestinal epithelial cells by improving antioxidant and inflammatory response. Anim. Biotechnol. 2021, 34, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swank, G.M.; Lu, Q.; Xu, D.Z.; Michalsky, M.; Deitch, E.A. Effect of acute-phase and heat-shock stress on apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). Crit. Care Med. 1998, 26, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo, Z.; Seiquer, I. Supplemental Zinc exerts a positive effect against the heat stress damage in intestinal epithelial cells: Assays in a Caco-2 model. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 83, 104569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengartner, M.O. The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 2000, 407, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, E. Life, death, and the pursuit of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Y.N.; Luo, Y.H.; Liu, S.B.; Xu, W.T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Xue, H.; Zuo, W.B.; Li, Y.N.; Wang, C.Y.; et al. Zeaxanthin Induces Apoptosis via ROS-Regulated MAPK and AKT Signaling Pathway in Human Gastric Cancer Cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 10995–11006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xie, W.; Gu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Su, L. Oxidative stress regulates mitogen-activated protein kinases and c-Jun activation involved in heat stress and lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 2579–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, Y.; Suh, D.H.; Lee, C.H.; Yoo, S.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Yoon, S.H. Heat-responsive and time-resolved transcriptome and metabolome analyses of Escherichia coli uncover thermo-tolerant mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukay, B.; Csoboz, B.; Tóth, M.E. Heat-Shock Proteins in Neuroinflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jing, J.; Ye, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jing, Y.; Li, S.; Hong, W.; Ruan, H.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Q.; et al. Characterization of the dual functional effects of heat shock proteins (HSPs) in cancer hallmarks to aid development of HSP inhibitors. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, W. Heat shock proteins and viral infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 947789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastaki, N.K.; Albarjas, T.A.; Almoosa, F.A.; Al-Adsani, A.M. Chronic heat stress induces the expression of HSP genes in the retina of chickens (Gallus gallus). Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1085590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Wu, R.; Long, Y.; Peng, L.; Yang, T.; Zhang, B.; Shi, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X. Role of Fe, Transferrin and Transferrin Receptor in Anti-Tumor Effect of Vitamin C. Cancers 2022, 14, 4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Chowdhury, V.S.; Han, G.; Zhang, R.; Furuse, M. Flavangenol regulates gene expression of HSPs, anti-apoptotic and anti-oxidative factors to protect primary chick brain cells exposed to high temperature. J. Therm. Biol. 2019, 81, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.; Sezgin-Bayindir, Z.; Losada-Barreiro, S.; Paiva-Martins, F.; Saso, L.; Bravo-Díaz, C. Polyphenols as Antioxidants for Extending Food Shelf-Life and in the Prevention of Health Diseases: Encapsulation and Interfacial Phenomena. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Qiao, X. The Alleviative Effects of Quercetin on Cadmium-Induced Necroptosis via Inhibition ROS/iNOS/NF-κB Pathway in the Chicken Brain. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 1584–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Li, D. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Responsive Nanomedicine for Solving Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xi, X.; Mei, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, L.; Ma, M.; Liu, S.; Zha, X.; Yang, Y. High-glucose induces retinal pigment epithelium mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis and inhibits mitophagy by regulating ROS/PINK1/Parkin signal pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 1315–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Shi, Z.; Li, J.; Tang, D.; Qin, S.; Guo, Y. Protective Effect of Manganese on Apoptosis and Mitochondrial Function of Heat-Stressed Primary Chick Embryonic Myocardial Cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 4419–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Kong, W.; Qi, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, W.; Lin, X.; Lai, J.; Yu, Z.; et al. Icariin induces apoptosis of human lung adenocarcinoma cells by activating the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Life Sci. 2019, 239, 116879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lončar, A.; Negrojević, L.; Dimitrić-Marković, J.; Dimić, D. The reactivity of neurotransmitters and their metabolites towards various nitrogen-centered radicals: Experimental, theoretical, and biotoxicity evaluation. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2021, 95, 107573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, J.; Mckenna, Z.J.; Atkins, W.C.; Jarrard, C.P.; Crandall, C.G. Aging Increases Enterocyte Damage during a 3-Hour Exposure to Very Hot and Dry Heat: A Preliminary Study. Biology 2023, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, M.; Yi, W.; Murong, M.; Peng, N.; Tong, H.; Jiang, M.; Jin, D.; Peng, S.; Liang, W.; Quan, J.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila improves heat stress-impaired intestinal barrier function by modulating HSP27 in Caco-2 cells. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 177, 106028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, M.A.; Rollo, I.; Baker, L.B. Nutritional considerations to counteract gastrointestinal permeability during exertional heat stress. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 130, 1754–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, W.; Huang, J.; Ding, Y.; Pan, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Hu, B.; Zeng, X. In vitro extraction and fermentation of polyphenols from grape seeds (Vitis vinifera) by human intestinal microbiota. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavefve, L.; Howard, L.R.; Carbonero, F. Berry polyphenols metabolism and impact on human gut microbiota and health. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Liang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, K.; Yang, S.; Lv, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Guan, X. Vitexin alleviates high-fat diet induced brain oxidative stress and inflammation via anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and gut microbiota modulating properties. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 171, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, V.B.; Siletsky, S.A.; Nastasi, M.R.; Forte, E. ROS Defense Systems and Terminal Oxidases in Bacteria. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimić, D.; Milenković, D.; Marković, J.D.; Marković, Z. Antiradical activity of catecholamines and metabolites of dopamine: Theoretical and experimental study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 12970–12980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasaka, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Nagashima, U.; Nagaoka, S.I. Potential energy curve for singlet-oxygen quenching reaction by vitamin E. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2023, 442, 114749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanaraman, B.; Hardy, M.; Podsiadly, R.; Cheng, G.; Zielonka, J. Recent developments in detection of superoxide radical anion and hydrogen peroxide: Opportunities, challenges, and implications in redox signaling. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 617, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Tang, S.; Tian, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y. Thermodynamics, kinetics and structure-activity relationship of hydroxyanthraquinones scavenging free radicals. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Gu, X.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H. Mitochondrial Mechanisms of Apoptosis and Necroptosis in Liver Diseases. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2021, 2021, 8900122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, W.; Chen, L.; Tong, Q.; Ming, Y. Corilagin induces the apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the mitochondrial apoptotic and death receptor pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 2545–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shao, S.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, X.; Qin, Y.; Ren, Q.; Xiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Sun, Y. Reversible phase separation of HSF1 is required for an acute transcriptional response during heat shock. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogvadze, V.; Orrenius, S.; Zhivotovsky, B. Multiple pathways of cytochrome c release from mitochondria in apoptosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1757, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Yi, H.K.; Yun, B.S.; Lee, D.Y.; Hwang, P.H.; Park, H.R.; Kim, M.S. The extract of the immature fruit of Poncirus trifoliata induces apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells via mitochondrial autophagy. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2020, 9, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zarei, M.F.; Alseaf, A.M.; Alhaidary, A.A.; Mousa, E.F.; Okab, A.B.; Samara, E.M.; Abdoun, K.A. Short-term heat shock proteins 70 and 90 mRNA expression profile and its relation to thermo-physiological parameters in goats exposed to heat stress. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2019, 63, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yenari, M.A.; Cheng, D.; Sapolsky, R.M.; Steinberg, G.K. Bcl-2 overexpression protects against neuron loss within the ischemic margin following experimental stroke and inhibits cytochrome c translocation and caspase-3 activity. J. Neurochem. 2003, 85, 1026–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, E.; Eftekhari, A.; Babaei, H.; Nayebi, A.M.; Eghbal, M.A. Anti-Cancer Effects of Citalopram on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Occur via Cytochrome C Release and the Activation of NF-kB. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1570–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.; Jäger, R.; Mosser, D.D.; Samali, A. Regulation of apoptosis by heat shock proteins. IUBMB Life 2014, 66, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, S.S.; Kurade, N.P.; Bhendarkar, M.P.; Bhosale, S.V.; Nirmale, A.V.; Kochewad, S.A. Modulation of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) gene expression ex vivo in response to heat stress in chicken. Anim. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, Y.Y.; Tse, T.J.; Saini, A.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Reaney, M.J. Uptake of Flaxseed Dietary Linusorbs Modulates Regulatory Genes Including Induction of Heat Shock Proteins and Apoptosis. Foods 2022, 11, 3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Chowdhury, V.S.; Bahry, M.A.; Tran, P.V.; Do, P.H.; Han, G.; Zhang, R.; Tagashira, H.; Tsubata, M.; Furuse, M. Chronic oral administration of pine bark extract (flavangenol) attenuates brain and liver mRNA expressions of HSPs in heat-exposed chicks. J. Therm. Biol. 2016, 60, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.; Myung, S.C.; Kim, W.; Lee, C.S. 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid potentiates Hsp90 inhibition-induced apoptosis in human epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells via activation of death receptor and mitochondrial pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 370, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelnour, S.A.; Swelum, A.A.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Khafaga, A.F.; Taha, A.E.; Abdo, M. Cellular and functional adaptation to thermal stress in ovarian granulosa cells in mammals. J. Therm. Biol. 2020, 92, 102688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Gong, W.; Wu, S.; Perrett, S. Hsp70 in Redox Homeostasis. Cells 2022, 11, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Li, S.M.; Li, Y.N.; Cao, J.L.; Xue, H.; Wang, C.; Jin, C.H. Atractylodin Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits the Migration of A549 Lung Cancer Cells by Regulating ROS-Mediated Signaling Pathways. Molecules 2022, 27, 2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Sequences 5′–3′(Forward/Reverse) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSPA1A | TTGAAGAGCAACAGCAGCAG GCTGATTCTCGATTGGCAGG | 60 | 248 |
| HSP90AB1 | GAAACTGCGCTCCTGTCTTC GAAACTGCGCTCCTGTCTTC | 60 | 239 |
| HSPB1 | GATGGCGTGGTGGAGATCA GGTGACTGGGATGGTGATCT | 60 | 150 |
| BAX | AAGAAGCTGAGCGAGTGTCT GTTCTGATCAGTTCCGGCAC | 60 | 181 |
| BCL2 | GGATAACGGAGGCTGGGATG TGACTTCACTTGTGGCCCAG | 60 | 156 |
| CYCS | ACAGAAACCAGGCAGCCTTT CAGGGACTGTGCTCTGGAAG | 60 | 123 |
| CASP3 | GGCGGTTGTAGAAGAGTTTCG ACACAGCCACAGGTATGAGC | 60 | 53 |
| PRAP1 | AGCGTGTTTCTAGGTCGTGG CATCAAACATGGGCGACTGC | 60 | 194 |
| ACTB | CCCTGGAGAAGAGCTACGAG CGTACAGGTCTTTGCGGATG | 60 | 240 |
| Name of Primary Antibody | Species of Origin | Producer | Article Number | Dilution Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSP90 | Rabbit | Mitaka, Wuhan, China | 13171-1-AP | 1:5000 |
| HSP70 | Rabbit | Affinity, Changzhou, China | AF5466 | 1:1000 |
| Bax | Rabbit | CAT, Danvers, MA, USA | 2772 | 1:1000 |
| Bcl-2 | Rabbit | Mitaka, Wuhan, China | 26593-1-AP | 1:2000 |
| cytochrome c | Rabbit | Mitaka, Wuhan, China | 10993-1-AP | 1:3000 |
| pro-PARP1 | Rabbit | Huaan biology, Hangzhou, China | ET1608-56 | 1:2000 |
| cle-PARP1 | Rabbit | Affinity, Changzhou, China | AF7023 | 1:1000 |
| pro-caspase3 | Rabbit | Abcam, Shanghai, China | ab32150 | 1:1000 |
| cle-caspase3 | Rabbit | Affinity, Changzhou, China | AF7022 | 1:1000 |
| β-actin | Rabbit | Abclonal, Wuhan, China | AC026 | 1:50,000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, T.; Sheng, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, C. Vitexin Regulates Heat Shock Protein Expression by Modulating ROS Levels Thereby Protecting against Heat-Stress-Induced Apoptosis. Molecules 2023, 28, 7639. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227639
Wu T, Sheng Y, Tian Y, Wang C. Vitexin Regulates Heat Shock Protein Expression by Modulating ROS Levels Thereby Protecting against Heat-Stress-Induced Apoptosis. Molecules. 2023; 28(22):7639. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227639
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Tong, Yanan Sheng, Yu Tian, and Changyuan Wang. 2023. "Vitexin Regulates Heat Shock Protein Expression by Modulating ROS Levels Thereby Protecting against Heat-Stress-Induced Apoptosis" Molecules 28, no. 22: 7639. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227639
APA StyleWu, T., Sheng, Y., Tian, Y., & Wang, C. (2023). Vitexin Regulates Heat Shock Protein Expression by Modulating ROS Levels Thereby Protecting against Heat-Stress-Induced Apoptosis. Molecules, 28(22), 7639. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227639







