In Situ Electrospun Porous MIL-88A/PAN Nanofibrous Membranes for Efficient Removal of Organic Dyes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
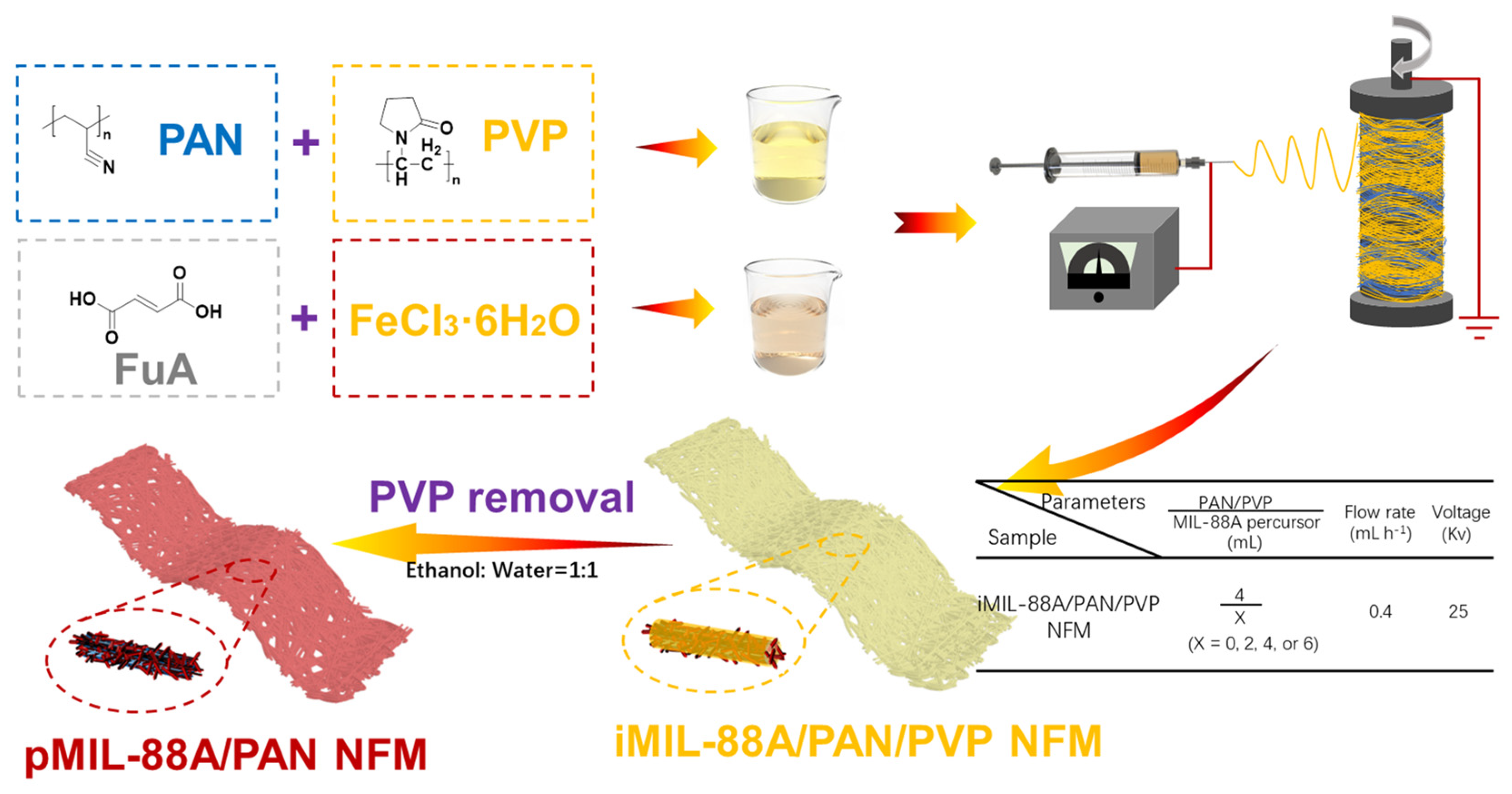
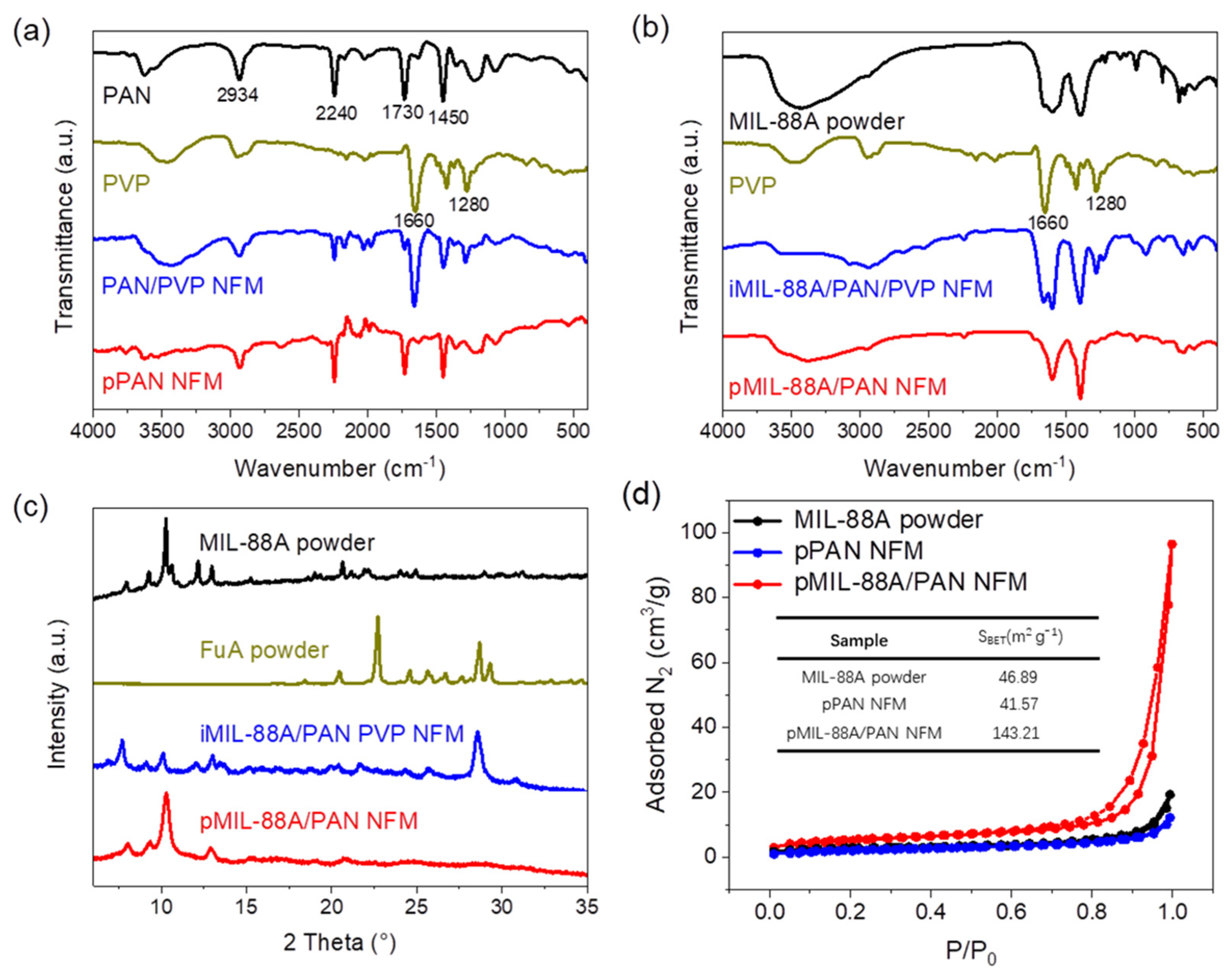
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of the pMIL-88A/PAN NFMs
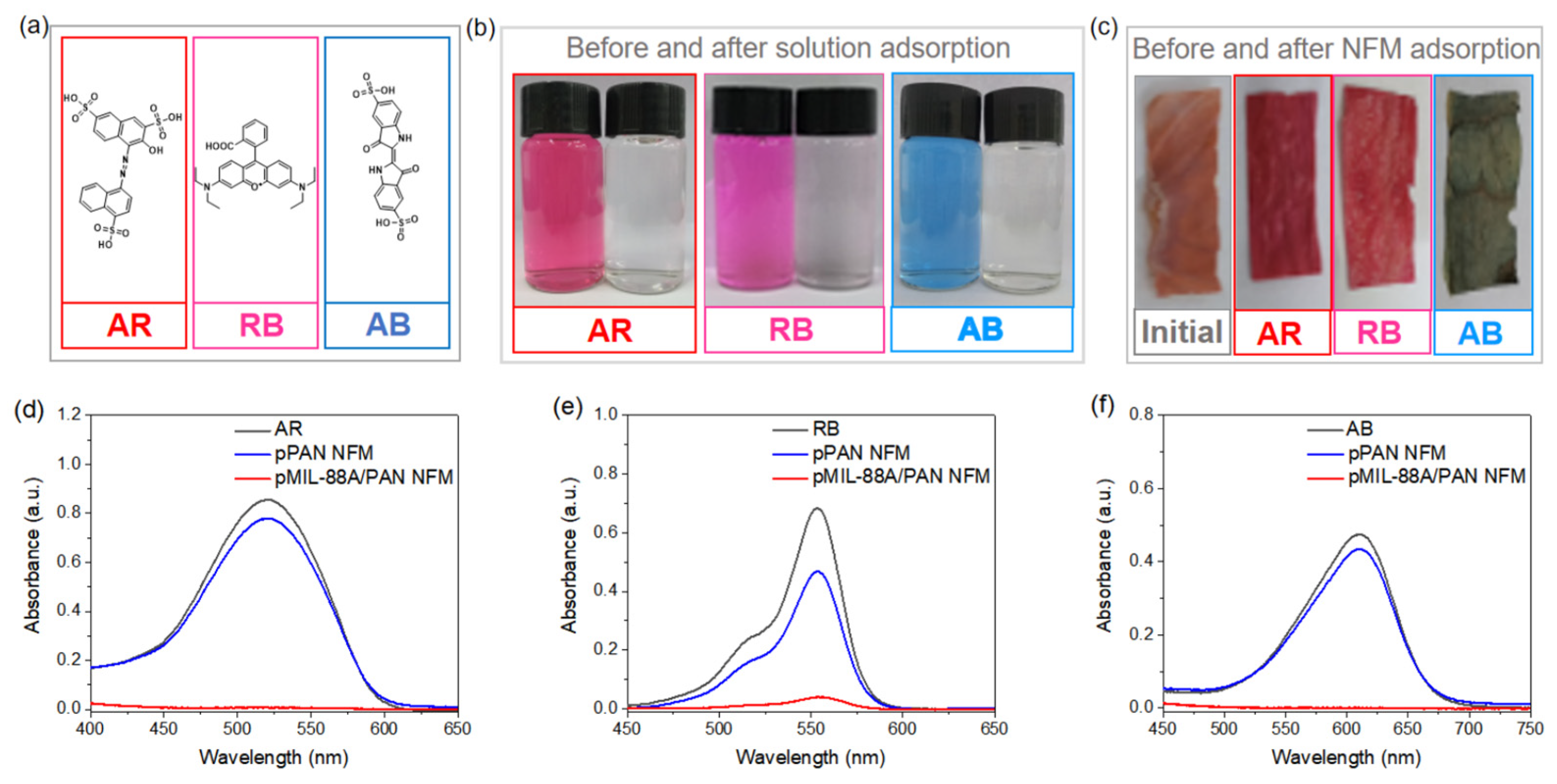
2.2. Adsorption Performance of the NFMs
2.2.1. Dye Removal Efficiencies
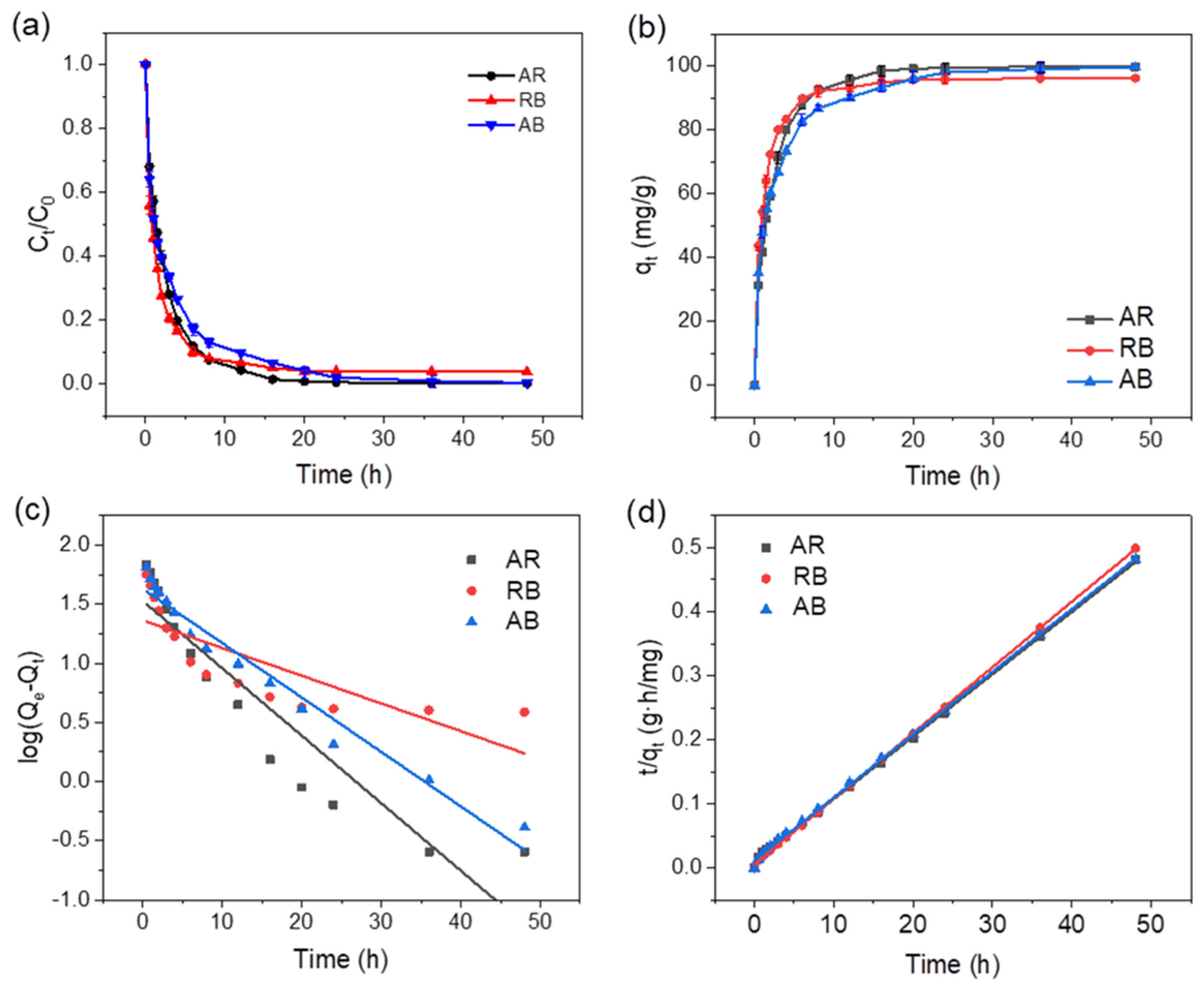
2.2.2. Adsorption Kinetics of pMIL-88A/PAN NFM
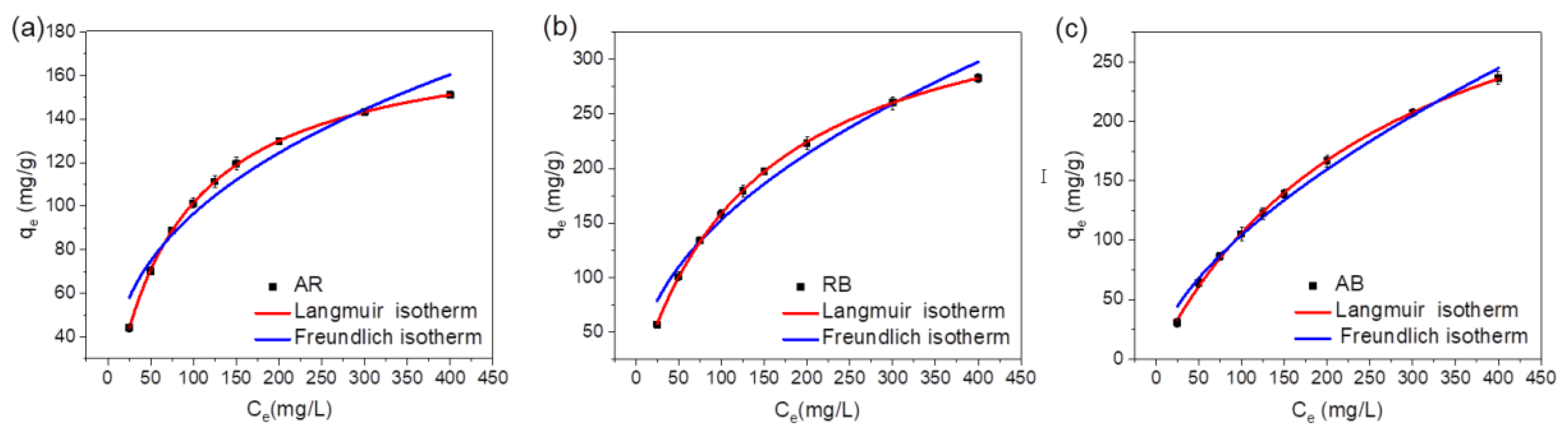
2.2.3. Adsorption Isotherms of pMIL-88A/PAN NFM
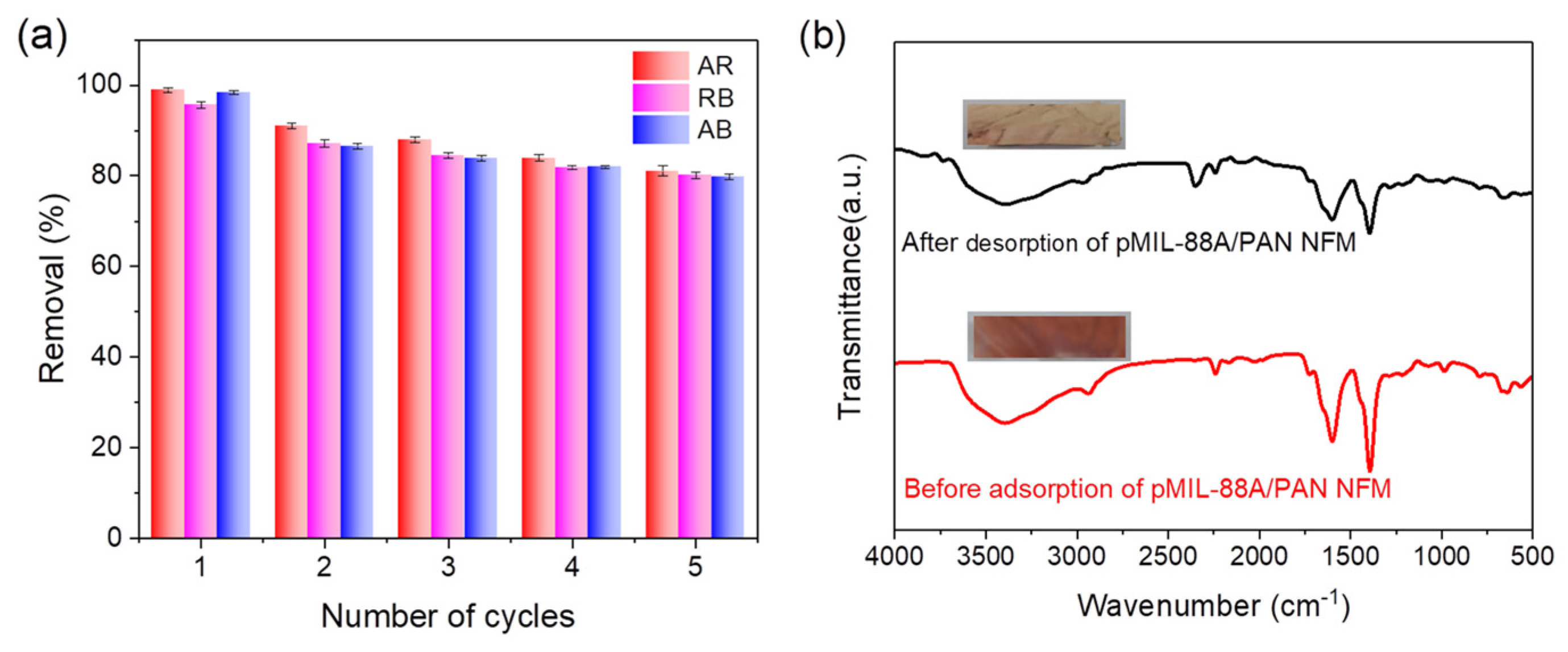
2.2.4. Recyclability of the pMIL-88A/PAN NFM
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of NFMs
3.3. Characterization
3.4. Adsorption and Desorption Experiments
3.4.1. Adsorption Experiments
3.4.2. Desorption Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rojas, S.; Horcajada, P. Metal–organic frameworks for the removal of emerging organic contaminants in water. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 8378–8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.H.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Ong, S.L. Suitability of artificial sweeteners as indicators of raw wastewater contamination in surface water and groundwater. Water Res. 2014, 48, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buerge, I.J.; Keller, M.; Buser, H.R.; Muller, M.D.; Poiger, T. Saccharin and other artificial sweeteners in soils: Estimated inputs from agriculture and households, degradation, and leaching to groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Yue, M.; Huang, X.; Duan, G.; Yang, Z.; Huang, W.; Shen, W.; Yin, X. Preparation, application and enhancement dyeing properties of ZnO nanoparticles in silk fabrics dyed with natural dyes. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Huang, M.; Liu, Y.; Meng, L.; Ma, M. Functionalized electrospun nanofiber membranes for water treatment: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 739, 139944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baigorria, E.; Galhardi, J.A.; Fraceto, L.F. Trends in polymers networks applied to the removal of aqueous pollutants: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.H.; Fan, H.X.; Yi, C.Y.; Dong, B.; Yuan, S.J. Solvent-free synthesis of a 2D biochar stabilized nanoscale zerovalent iron composite for the oxidative degradation of organic pollutants. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 6849–6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, J.; Abedini, H. MOF-based polymeric nanocomposite beads as an efficient adsorbent for wastewater treatment in batch and continuous systems: Modelling and experiment. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Rehman, S.; Zhang, P. Room temperature synthesis of monolithic MIL-100(Fe) in aqueous solution for energy-efficient removal and recovery of aromatic volatile organic compounds. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 129998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Shi, F.; Jiang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, K.; Jian, S.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, C.; Hu, J. Outstanding fluoride removal from aqueous solution by a La-based adsorbent. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 30522–30528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, J.; Duan, G.; Xu, W.; Jian, S. Magnetically separable and recyclable Fe3O4@ PDA covalent grafted by l-cysteine core-shell nanoparticles toward efficient removal of Pb2+. Vacuum 2021, 189, 110229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotore, O.; Osamu, N.; Rameshprabu, R.; Arthi, M.; Unpaprom, Y.; Itayama, T. Biochar derived from non-customized matamba fruit shell as an adsorbent for wastewater treatment. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2022, 7, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jjagwe, J.; Olupot, P.W.; Menya, E.; Kalibbala, H.M. Synthesis and application of Granular activated carbon from biomass waste materials for water treatment: A review. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 292–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintor, A.M.A.; Vilar, V.J.P.; Botelho, C.M.S.; Boaventura, R.A.R. Oil and grease removal from wastewaters: Sorption treatment as an alternative to state-of-the-art technologies. A critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 297, 229–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzisymeon, E.; Stypas, E.; Bousios, S.; Xekoukoulotakis, N.P. Photocatalytic treatment of black table olive processing wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotto, G.L.; McKay, G. Current scenario and challenges in adsorption for water treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhao, S.; Tian, Z.; Duan, G.; Pan, H.; Yue, Y.; Li, S.; Jian, S.; Yang, W.; Liu, K.; et al. MOFs meet wood: Reusable magnetic hydrophilic composites toward efficient water treatment with super-high dye adsorption capacity at high dye concentration. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 136851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Mei, C.; Zheng, J.; E, S.; Duan, G.; Liu, K.; Jiang, S. Liquid transport and real-time dye purification via lotus petiole-inspired long-range-ordered anisotropic cellulose nanofibril aerogels. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 20666–20677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hanshe, M.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Mei, C.; Duan, G.; Zheng, J.; E, S.; Jiang, S. Lightweight and anisotropic cellulose nanofibril/rectorite composite sponges for efficient dye adsorption and selective separation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 207, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadijokani, F.; Molavi, H.; Bahi, A.; Fernandez, R.; Alaee, P.; Wu, S.; Wuttke, S.; Ko, F.; Arjmand, M. Metal-Organic Frameworks and Electrospinning: A Happy Marriage for Wastewater Treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 25, 2207723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Tao, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C.; He, H.; Long, L.; Lee, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.B. Robust metal–triazolate frameworks for CO2 capture from flue gas. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 142, 2750–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Chou, L.Y.; Long, L.; Si, X.; Lo, W.S.; Tsung, C.K.; Li, T. Structural control of uniform MOF-74 microcrystals for the study of adsorption kinetics. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 35820–35826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Li, B.; He, H.; Zhou, W.; Chen, B.; Qian, G. Metal–organic frameworks as platforms for functional materials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, G.; Zheng, X.; Dai, M.; Peng, C. Metal-organic framework membranes: Recent development in the synthesis strategies and their application in oil-water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 127004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Yu, Q.; Chen, J.; Khan, U.; Wang, X.; Gao, J. Achievements and Perspectives in Metal–Organic Framework-Based Materials for Photocatalytic Nitrogen Reduction. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, C.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Cao, R. Graphene Quantum Dots Supported on Fe-based Metal-Organic Frameworks for Efficient Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction. Acta. Chim. Sin. 2022, 80, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Han, Z. Preparation of nanofibrous metal-organic framework filter for rapid adsorption and selective separation of cationic dye from aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 237, 116360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, P.W.; Khan, N.A.; Jhung, S.H. Removal of nitroimidazole antibiotics from water by adsorption over metal–organic frameworks modified with urea or melamine. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 315, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaj, M.; Bentz, K.C.; Ayala, S., Jr.; Palomba, J.M.; Barcus, K.S.; Katayama, Y.; Cohen, S.M. MOF-polymer hybrid materials: From simple composites to tailored architectures. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 8267–8302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: Methods, materials, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, S.; Chen, Y.; Shi, F.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Hu, J.; Han, X.; Jiang, S.; Yang, W. Template-Free Synthesis of Magnetic La-Mn-Fe Tri-Metal Oxide Nanofibers for Efficient Fluoride Remediation: Kinetics, Isotherms, Thermodynamics and Reusability. Polymers 2022, 14, 5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, M.; Veeramuthu, L.; Liang, F.C.; Chen, W.C.; Cho, C.J.; Chen, C.W.; Chen, J.Y.; Yan, Y.; Chang, S.H.; Kuo, C.K. Evolution of electrospun nanofibers fluorescent and colorimetric sensors for environmental toxicants, pH, temperature, and cancer cells–A review with insights on applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397, 125431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Shi, X.; Ma, T.; Rong, H.; Wang, Z.; Cui, F.; Zhu, G.; Wang, C. Constructing mesoporous adsorption channels and MOF–polymer interfaces in electrospun composite fibers for effective removal of emerging organic contaminants. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2020, 13, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Tian, Y.; Li, S.; Ma, T.; Lei, H.; Zhu, G. An electrospun fiber based metal–organic framework composite membrane for fast, continuous, and simultaneous removal of insoluble and soluble contaminants from water. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 22559–22570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, S.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, X.; Guo, H.; Hu, J.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, S.; Yang, W.; Duan, G. Excellent fluoride removal performance by electrospun La–Mn bimetal oxide nanofibers. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, S.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, K.; Duan, G.; Yang, W.; Jiang, S. Hydrothermal synthesis of Ce-doped ZnO heterojunction supported on carbon nanofibers with high visible light photocatalytic activity. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2021, 37, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Oveisi, W.; Taghizadeh, A.; Taghizadeh, M. Synthesis of pearl necklace-like ZIF-8@chitosan/PVA nanofiber with synergistic effect for recycling aqueous dye removal. Carbohyd. Polym. 2020, 227, 115364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Kaiser, A. Electrospinning of metal–organic frameworks for energy and environmental applications. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.X.; McEntee, M.; Browe, M.A.; Hall, M.G.; DeCoste, J.B.; Peterson, G.W. MOFabric: Electrospun nanofiber mats from PVDF/UiO-66-NH2 for chemical protection and decontamination. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2017, 9, 13632–13636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Cui, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Lang, J.; Li, C.; Yan, Y.; Dai, J. Graphene oxide/Fe (III)-based metal-organic framework membrane for enhanced water purification based on synergistic separation and photo-Fenton processes. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2020, 264, 118548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leus, K.; Krishnaraj, C.; Verhoeven, L.; Cremers, V.; Dendooven, J.; Ramachandran, R.K.; Dubruel, P.; Van der Voort, P. Catalytic carpets: Pt@ MIL-101@ electrospun PCL, a surprisingly active and robust hydrogenation catalyst. J. Catal. 2018, 360, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, H.; Li, B.G.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, S. Fabrication of metal-organic framework-based nanofibrous separator via one-pot electrospinning strategy. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Du, L.; Jin, J.; Meng, H.; Mi, J. In situ growth of MIL-88A into polyacrylate and its application in highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 564, 150404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, V.P.; Mathew, S.V.; Dubal, D.P.; Adarsh, N.N.; Mathew, S. Exploring the Effect of Morphologies of Fe (III) Metal-Organic Framework MIL-88A (Fe) on the Photocatalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 7534–7542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Xie, Y.; He, J.; Yu, J.; Song, Y. The MIL-88A-derived Fe3O4-carbon hierarchical nanocomposites for electrochemical sensing. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, J.; Ding, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, T. MIL-88/PVB nanofiber as recyclable heterogeneous catalyst for photocatalytic and Fenton process under visible light irradiation. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 749, 137431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, W.; Sun, F.; Shi, W.; Qi, D.; Wang, K.; Shi, R.; Cui, F.; Wang, C.; Chen, X. Highly efficient phosphate scavenger based on well-dispersed La (OH)3 nanorods in polyacrylonitrile nanofibers for nutrient-starvation antibacteria. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9292–9302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninwiwek, N.; Hongsawat, P.; Punyapalakul, P.; Prarat, P. Removal of the antibiotic sulfamethoxazole from environmental water by mesoporous silica-magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite technology: Adsorption characteristics, coadsorption and uptake mechanism. Coll. Surf. A 2019, 580, 123716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Dye | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg g−1) | k1 (h−1) | R2 | qe (mg g−1) | k2 (g (mg h)−1) | R2 | |
| AR | 33.81 | 0.1329 | 0.8646 | 102.56 | 0.009564 | 0.9992 |
| RB | 23.14 | 0.0546 | 0.6184 | 97.56 | 0.01846 | 0.9998 |
| AB | 42.88 | 0.1073 | 0.9626 | 101.94 | 0.008094 | 0.9992 |
| Dye | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax (mg g−1) | b (L mg−1) | R2 | KF | n | R2 | |
| AR | 180.41 | 0.0129 | 0.99989 | 17.8564 | 2.729 | 0.94561 |
| RB | 382.75 | 0.0071 | 0.99988 | 16.6871 | 2.079 | 0.97013 |
| AB | 399.35 | 0.0036 | 0.99950 | 6.10945 | 1.711 | 0.98950 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, H.; Xu, L.; Jia, J.; Dong, F.; Jia, Y.; Liu, X. In Situ Electrospun Porous MIL-88A/PAN Nanofibrous Membranes for Efficient Removal of Organic Dyes. Molecules 2023, 28, 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020760
Wu H, Xu L, Jia J, Dong F, Jia Y, Liu X. In Situ Electrospun Porous MIL-88A/PAN Nanofibrous Membranes for Efficient Removal of Organic Dyes. Molecules. 2023; 28(2):760. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020760
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Hao, Le Xu, Jiao Jia, Fengchun Dong, Yongtang Jia, and Xi Liu. 2023. "In Situ Electrospun Porous MIL-88A/PAN Nanofibrous Membranes for Efficient Removal of Organic Dyes" Molecules 28, no. 2: 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020760
APA StyleWu, H., Xu, L., Jia, J., Dong, F., Jia, Y., & Liu, X. (2023). In Situ Electrospun Porous MIL-88A/PAN Nanofibrous Membranes for Efficient Removal of Organic Dyes. Molecules, 28(2), 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020760






