CXCR4-Targeted Radiopharmaceuticals for the Imaging and Therapy of Malignant Tumors
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Chemokines
1.2. Chemokine Receptors
| Chemokine Receptor | Chemokine |
|---|---|
| CCR1 | CCL1, CCL3, CCL4, CCL5, CCL8, CCL14, CCL15, CCL16 |
| CCR2 | CCL2, CCL7, CCL8, CCL12, CCL13, CCL16 |
| CCR3 | CCL5, CCL7, CCL8, CCL11, CCL13, CCL15, CCL23, CCL24, CCL26, CCL28 |
| CCR4 | CCL17, CCL22 |
| CCR5 | CCL3, CCL4, CCL5, CCL7, CCL8, CCL13, CCL16 |
| CCR6 | CCL20, CCL21 |
| CCR7 | CCL19, CCL21 |
| CCR8 | CCL1, CCL8, CCL18 |
| CCR9 | CCL25 |
| CCR10 | CCL27, CCL28 |
| CXCR1 | CXCL6, CXCL8 |
| CXCR2 | CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, CXCL5, CXCL6, CXCL7, CXCL8 |
| CXCR3 | CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11 |
| CXCR4 | CXCL12 |
| CXCR5 | CXCL13 |
| CXCR6 | CXCL16 |
| CXCR7 | CXCL11, CXCL12 |
| CXCR9 | CXCL16 |
| CX3CR1 | CX3CL1, CCL26 |
| XCR1 | XCL1, XCL2 |
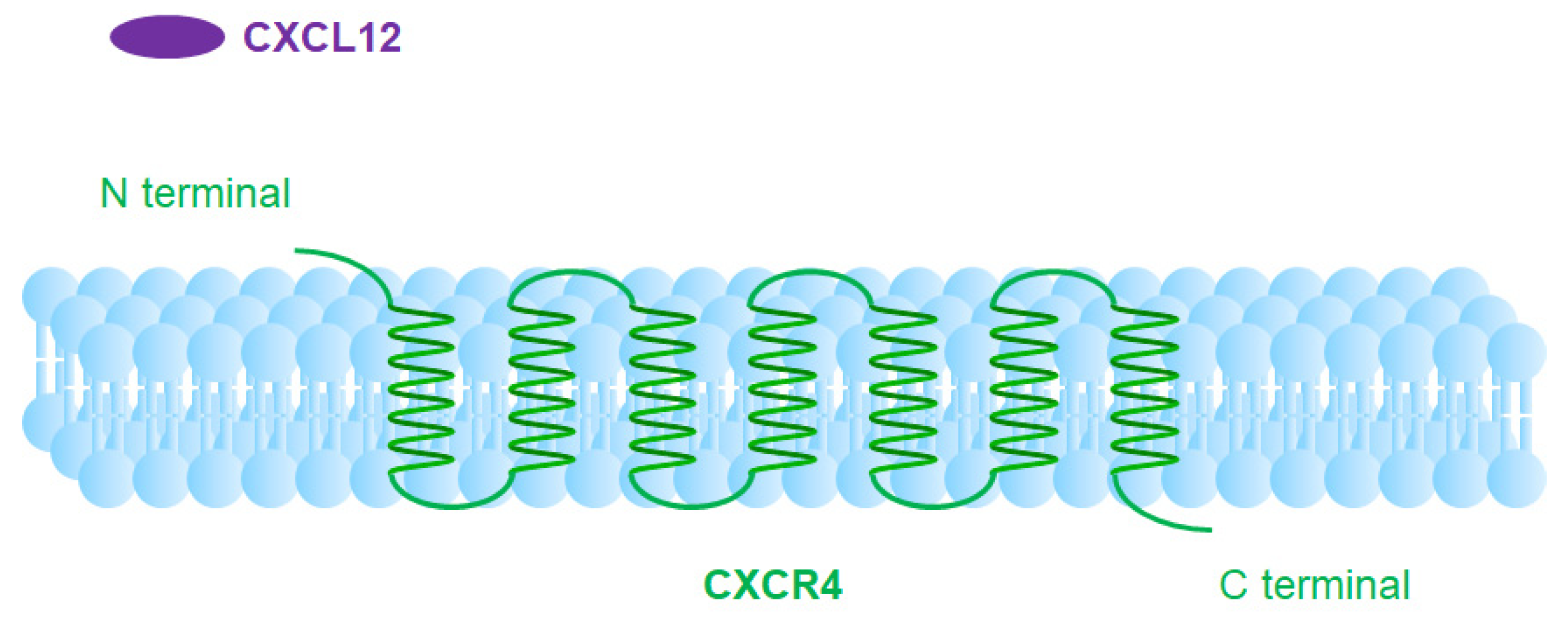
1.3. CXCR4
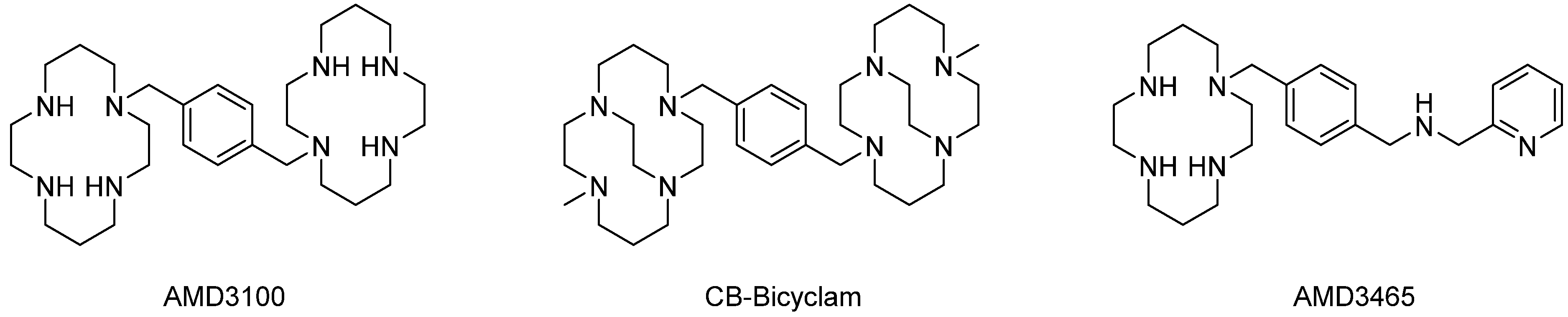
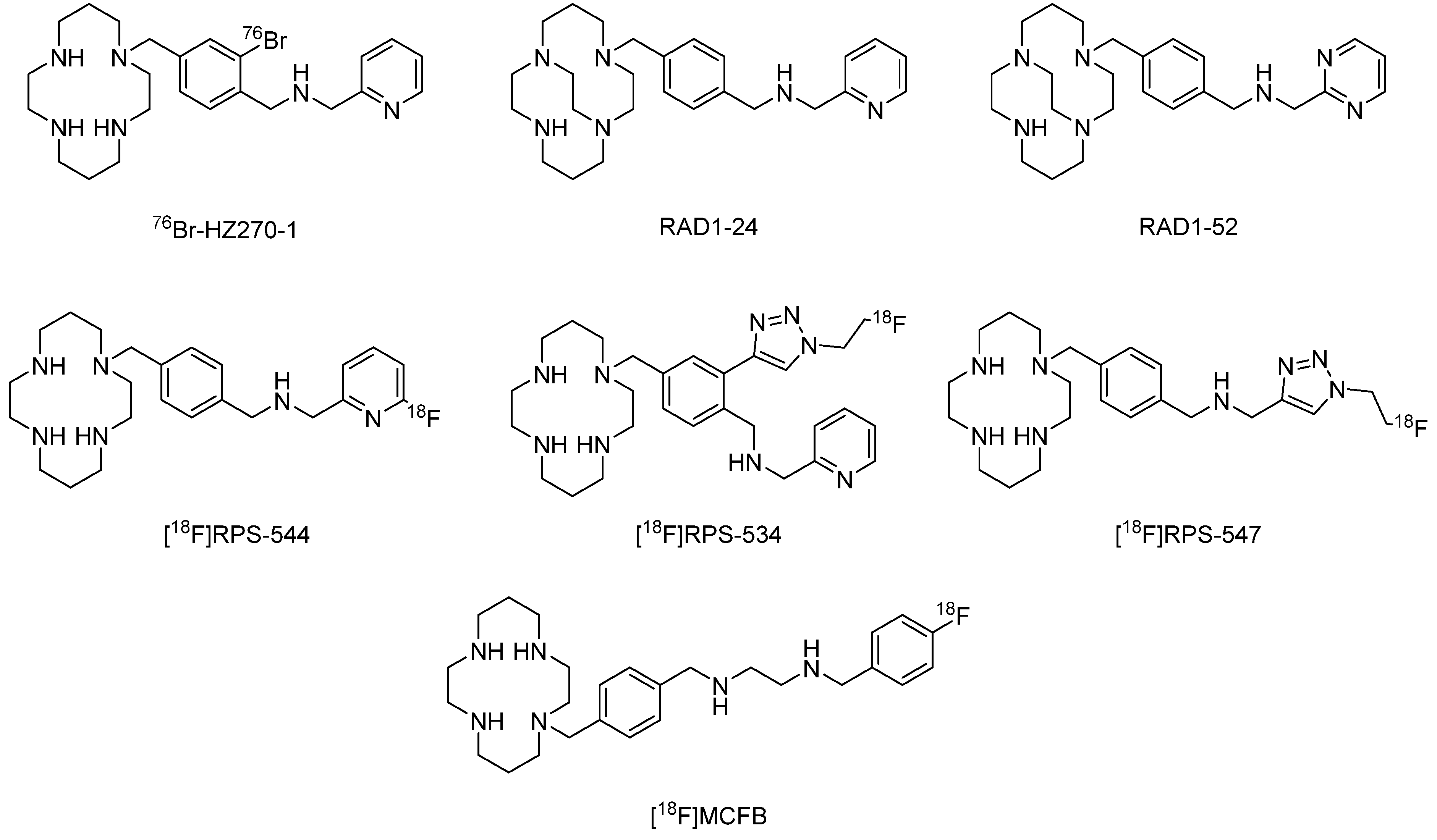
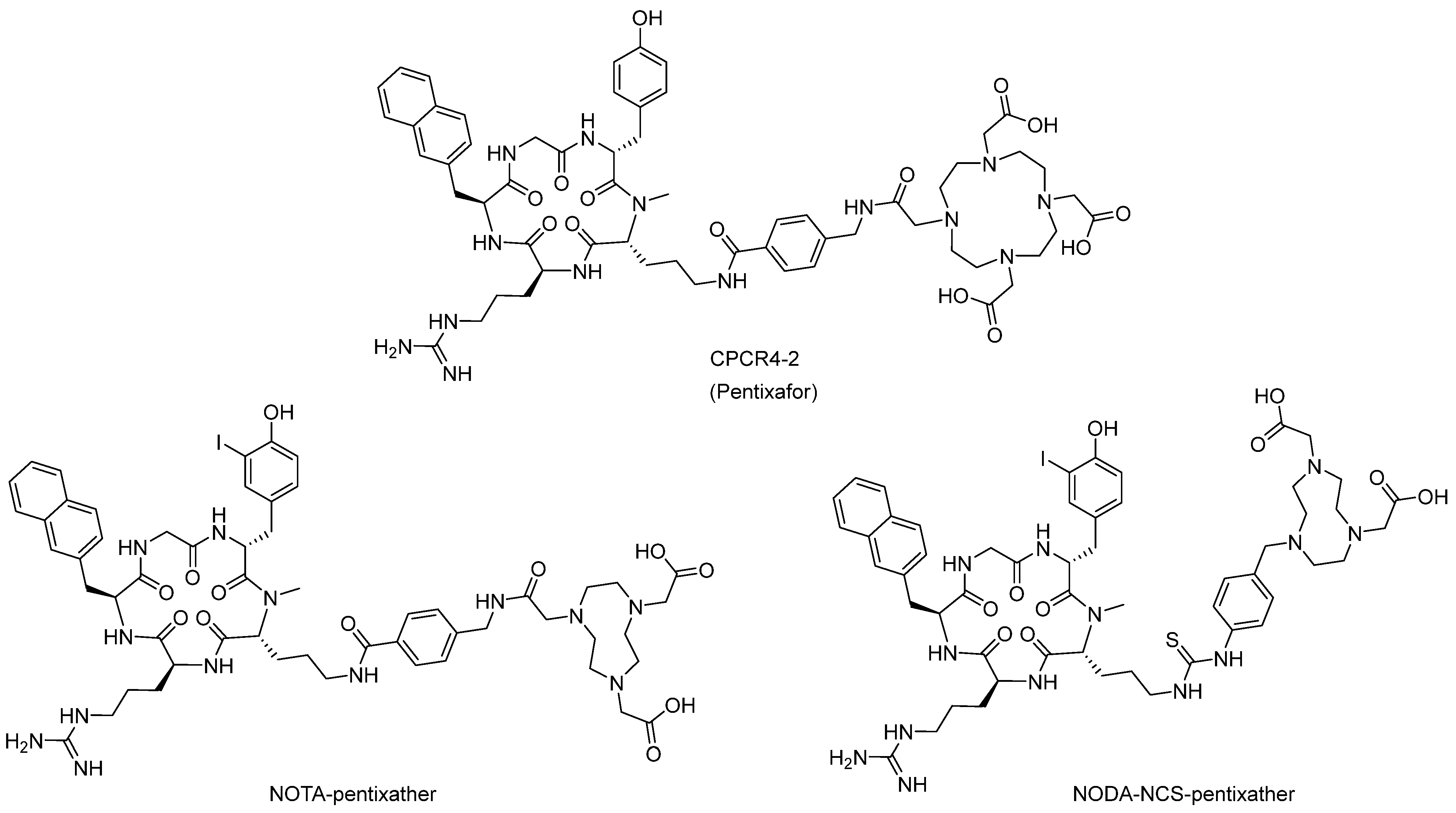
2. Radiopharmaceuticals Based on CXCR4
3. Current Clinical and Marketing Information [77]
4. Perspective Development
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Bianchi, M.E.; Mezzapelle, R. The chemokine receptor CXCR4 in cell proliferation and tissue regeneration. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.E.; Nibbs, R.J.B. A guide to chemokines and their receptors. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 2944–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horuk, R. Chemokine receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2001, 12, 313–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crijns, H.; Vanheule, V.; Proost, P. Targeting chemokine—Glycosaminoglycan interactions to inhibit inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhari, A.; Aghanejad, A.; Jalilian, A.R.; Gharepapagh, E. Recent developments in targeted imaging of CXCR4-chemokine receptor. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2018, 317, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alluri, S.R.; Higashi, Y.; Kil, K.-E. PET imaging radiotracers of chemokine receptors. Molecules 2021, 26, 5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, J.W.; Sokol, C.L.; Luster, A.D. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: Positioning cells for host defense and immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 659–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhatib, G. The biology of CCR5 and CXCR4. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2009, 4, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, G.P.C.; Pisaneschi, F.; Nguyen, Q.-D.; Aboagye, E.O. Positron emission tomographic imaging of CXCR4 in cancer: Challenges and promises. Mol. Imaging 2014, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.-R.; Kottmann, A.H.; Kuroda, M.; Taniuchi, I.; Littman, D.R. Function of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in haematopoiesis and in cerebellar development. Nature 1998, 393, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, O.; Weiss, I.D. CXCR4 chemokine receptor overview: Biology, pathology and applications in imaging and therapy. Theranostics 2013, 3, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schottelius, M.; Herrmann, K.; Lapa, C. In vivo targeting of CXCR4—New horizons. Cancers 2021, 13, 5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, B.; Xu, S.; Grande, F.; Garofalo, A.; Neamati, N. Small molecule inhibitors of CXCR4. Theranostics 2013, 3, 47–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamamura, H.; Xu, Y.; Hattori, T.; Zhang, X.; Arakaki, R.; Kanbara, K.; Omagari, A.; Otaka, A.; Ibuka, T.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. A low-molecular-weight inhibitor against the chemokine receptor CXCR4: A strong anti-HIV peptide T140. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 253, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamamura, H.; Hiramatsu, K.; Ueda, S.; Wang, Z.; Kusano, S.; Terakubo, S.; Trent, J.O.; Peiper, S.C.; Yamamoto, N.; Nakashima, H.; et al. Stereoselective synthesis of [L-Arg-L/D-3-(2-naphthyl)alanine]-type (E)-alkene dipeptide isosteres and its application to the synthesis and biological evaluation of pseudopeptide analogues of the CXCR4 antagonist FC131. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooring, S.R.; Liu, J.; Liang, Z.; Ahn, J.; Hong, S.; Yoon, Y.; Snyder, J.P.; Shim, H. Benzenesulfonamides: A unique class of chemokine receptor type 4 inhibitors. Chem. Med. Chem. 2013, 8, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, O.; Weiss, I.D.; Szajek, L.; Farber, J.M.; Kiesewetter, D.O. 64Cu-AMD3100---A novel imaging agent for targeting chemokine receptor CXCR4. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 1486–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmagadda, S.; Pullambhatla, M.; Stone, K.; Green, G.; Bhujwalla, Z.M.; Pomper, M.G. Molecular imaging of CXCR4 receptor expression in human cancer xenografts with [64Cu]AMD3100 positron emission tomography. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3935–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, I.D.; Jacobson, O.; Kiesewetter, D.O.; Jacobus, J.P.; Szajek, L.P.; Chen, X.; Farber, J.M. Positron emission tomography imaging of tumors expressing the human chemokine receptor CXCR4 in mice with the use of 64Cu-AMD3100. Mol. Imaging. Biol. 2012, 14, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, L.O.; Skerlj, R.T.; Bridger, G.J.; Schwartz, T.W. Molecular interactions of cyclam and bicyclam non-peptide antagonists with the CXCR4 chemokine receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 14153–14160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trent, J.O.; Wang, Z.X.; Murray, J.L.; Shao, W.; Tamamura, H.; Fujii, N.; Peiper, S.C. Lipid bilayer simulations of CXCR4 with inverse agonists and weak partial agonists. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 47136–47144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkilde, M.M.; Gerlach, L.O.; Hatse, S.; Skerlj, R.T.; Schols, D.; Bridger, G.J.; Schwartz, T.W. Molecular mechanism of action of monocyclam versus bicyclam non-peptide antagonists in the CXCR4 chemokine receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 27354–27365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatse, S.; Princen, K.; Gerlach, L.O.; Bridger, G.; Henson, G.; De Clercq, E.; Schwartz, T.W.; Schols, D. Mutation of Asp171 and Asp262 of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 impairs its coreceptor function for human immunodeficiency virus-1 entry and abrogates the antagonistic activity of AMD3100. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 60, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.S.Y.; Bodart, V.; Metz, M.; Labrecque, J.; Bridger, G.; Fricker, S.P. Comparison of the potential multiple binding modes of bicyclam, monocylam, and noncyclam small-molecule CXC chemokine receptor 4 inhibitors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 74, 1485–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartimath, S.V.; Domanska, U.M.; Walenkamp, A.M.E.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; De Vries, E.F.J. [99mTc]O2-AMD3100 as a SPECT tracer for CXCR4 receptor imaging. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2013, 40, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghanejad, A.; Jalilian, A.R.; Fazaeli, Y.; Alirezapoor, B.; Pouladi, M.; Beiki, D.; Maus, S.; Khalaj, A. Synthesis and evaluation of [67Ga]-AMD3100; A novel imaging agent for targeting chemokine receptor CXCR4. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2014, 41, 640–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghanejad, A.; Jalilian, A.R.; Fazaeli, Y.; Beiki, D.; Fateh, B.; Khalaj, A. Radiosynthesis and biodistribution studies of [62Zn/62Cu]–plerixafor complex as a novel in vivo PET generator for chemokine receptor imaging. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2014, 299, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Nicholson, G.; Greenman, J.; Madden, L.; McRobbie, G.; Pannecouque, C.; De Clercq, E.; Ullom, R.; Maples, D.L.; Maples, R.D.; et al. Binding optimization through coordination chemistry: CXCR4 chemokine receptor antagonists from ultra-rigid metal complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3416–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maples, R.D.; Cain, A.N.; Burke, B.P.; Silversides, J.D.; Mewis, R.E.; D’huys, T.; Schols, D.; Linder, D.P.; Archibald, S.J.; Hubin, T.J. Aspartate-based CXCR4 chemokine receptor binding of cross-bridged tetraazamacrocyclic Copper(II) and Zinc(II) complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 12916–12930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, B.P.; Miranda, C.S.; Lee, R.E.; Renard, I.; Nigam, S.; Clemente, G.S.; D’Huys, T.; Ruest, T.; Domarkas, J.; Thompson, J.A.; et al. 64Cu PET imaging of the CXCR4 chemokine receptor using a cross-bridged cyclam bis-tetraazamacrocyclic antagonist. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodart, V.; Anastassov, V.; Darkes, M.C.; Idzan, S.R.; Labrecque, J.; Lau, G.; Mosi, R.M.; Neff, K.S.; Nelson, K.L.; Ruzek, M.C.; et al. Pharmacology of AMD3465: A small molecule antagonist of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Silva, R.A.; Peyre, K.; Pullambhatla, M.; Fox, J.J.; Pomper, M.G.; Nimmagadda, S. Imaging CXCR4 expression in human cancer xenografts: Evaluation of monocyclam 64Cu-AMD3465. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; You, L.; Chen, S.; Gao, M.; Guo, Z.; Du, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, X. Development of a novel 99mTc-labeled small molecular antagonist for CXCR4 positive tumor imaging. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2018, 61, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartimath, S.V.; Van Waarde, A.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; De Vries, E.F.J. Evaluation of N-[11C]methyl-AMD3465 as a PET tracer for imaging of CXCR4 receptor expression in a C6 glioma tumor model. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 3810–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Maeda, M.; Shindo, M.; Ko, M.; Mane, M.; Grommes, C.; Weber, W.; Blasberg, R. Imaging CXCR4 expression with iodinated and brominated cyclam derivatives. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2020, 22, 1184–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodard, L.E.; De Silva, R.A.; Azad, B.B.; Lisok, A.; Pullambhatla, M.; Lesniak, W.G.; Mease, R.C.; Pomper, M.G.; Nimmagadda, S. Bridged cyclams as imaging agents for chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4). Nucl. Med. Biol. 2014, 41, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor-Coarasa, A.; Kelly, J.; Ponnala, S.; Vedvyas, Y.; Nikolopoulou, A.; Williams, C.; Jin, M.M.; Warren, J.D.; Babich, J.W. [18F]RPS-544: A PET tracer for imaging the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Nucl. Med. Bio. 2018, 60, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor-Coarasa, A.; Kelly, J.M.; Singh, P.K.; Ponnala, S.; Nikolopoulou, A.; Williams Jr., C.; Vedvyas, Y.; Jin, M.M.; Warren, J.D.; Babich, J.W. [18F]Fluoroethyltriazolyl monocyclam derivatives as imaging probes for the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Molecules 2019, 24, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brickute, D.; Braga, M.; Kaliszczak, M.A.; Barnes, C.; Lau, D.; Carroll, L.; Stevens, E.; Trousil, S.; Alam, I.S.; Nguyen, Q.-D.; et al. Development and evaluation of an 18F-radiolabeled monocyclam derivative for imaging CXCR4 expression. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 2106–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmer, O.; Gourni, E.; Schumacher, U.; Kessler, H.; Wester, H.-J. PET imaging of CXCR4 receptors in cancer by a new optimized ligand. Chem. Med. Chem. 2011, 6, 1789–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourni, E.; Demmer, O.; Schottelius, M.; D’Alessandria, C.; Schulz, S.; Dijkgraaf, I.; Schumacher, U.; Schwaiger, M.; Kessler, H.; Wester, H.-J. PET of CXCR4 expression by a 68Ga-labeled highly specific targeted contrast agent. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 1803–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vag, T.; Gerngross, C.; Herhaus, P.; Eiber, M.; Philipp-Abbrederis, K.; Graner, F.-P.; Ettl, J.; Keller, U.; Wester, H.-J.; Schwaiger, M. First experience with chemokine receptor CXCR4–targeted PET imaging of patients with solid cancers. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Cao, X.; Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Feng, J.; Li, F. Chemokine receptor-4 targeted PET/CT with 68Ga-Pentixafor in assessment of newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: Comparison to 18F-FDG PET/CT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapa, C.; Herrmann, K.; Schirbel, A.; Hänscheid, H.; Lückerath, K.; Schottelius, M.; Kircher, M.; Werner, R.A.; Schreder, M.; Samnick, S.; et al. CXCR4-directed endoradiotherapy induces high response rates in extramedullary relapsed multiple myeloma. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, K.; Schottelius, M.; Lapa, C.; Osl, T.; Poschenrieder, A.; Hänscheid, H.; Lückerath, K.; Schreder, M.; Bluemel, C.; Knott, M.; et al. First-in-human experience of CXCR4-directed endoradiotherapy with 177Lu- and 90Y-labeled pentixather in advanced-stage multiple myeloma with extensive intra- and extramedullary disease. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapa, C.; Schreder, M.; Schirbel, A.; Samnick, S.; Kortüm, K.M.; Herrmann, K.; Kropf, S.; Einsele, H.; Buck, A.K.; Wester, H.-J.; et al. [68Ga]Pentixafor-PET/CT for imaging of chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression in multiple myeloma-Comparison to [18F]FDG and laboratory values. Theranostics 2017, 7, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp-Abbrederis, K.; Herrmann, K.; Knop, S.; Schottelius, M.; Eiber, M.; Lückerath, K.; Pietschmann, E.; Habringer, S.; Gerngroß, C.; Franke, K.; et al. In vivo molecular imaging of chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression in patients with advanced multiple myeloma. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Luo, Y.; Cao, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, F. Multiple myeloma presenting as a superscan on 68Ga-pentixafor PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2018, 43, 462–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herhaus, P.; Habringer, S.; Philipp-Abbrederis, K.; Vag, T.; Gerngross, C.; Schottelius, M.; Slotta-Huspenina, J.; Steiger, K.; Altmann, T.; Weißer, T.; et al. Targeted positron emission tomography imaging of CXCR4 expression in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2016, 101, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habringer, S.; Lapa, C.; Herhaus, P.; Schottelius, M.; Istvanffy, R.; Steiger, K.; Slotta-Huspenina, J.; Schirbel, A.; Hänscheid, H.; Kircher, S.; et al. Dual targeting of acute leukemia and supporting niche by CXCR4-directed theranostics. Theranostics 2018, 8, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluemel, C.; Hahner, S.; Heinze, B.; Fassnacht, M.; Kroiss, M.; Bley, T.A.; Wester, H.-J.; Kropf, S.; Lapa, C.; Schirbel, A.; et al. Investigating the chemokine receptor 4 as potential theranostic target in adrenocortical cancer patients. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2017, 42, e29–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapa, C.; Lückerath, K.; Kleinlein, I.; Monoranu, C.M.; Linsenmann, T.; Kessler, A.F.; Rudelius, M.; Kropf, S.; Buck, A.K.; Ernestus, R.-I.; et al. 68Ga-Pentixafor-PET/CT for imaging of chemokine receptor 4 expression in glioblastoma. Theranostics 2016, 6, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapa, C.; Lückerath, K.; Rudelius, M.; Schmid, J.-S.; Schoene, A.; Schirbel, A.; Samnick, S.; Pelzer, T.; Buck, A.K.; Kropf, S.; et al. [68Ga]Pentixafor-PET/CT for imaging of chemokine receptor 4 expression in small cell lung cancer-Initial experience. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 9288–9295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Watts, A.; Basher, R.; Singh, H.; Bal, A.; Kapoor, R.; Arora, S.K.; Wester, H.J.; Mittal, B.R.; Behera, D. 68Ga-Pentixafor PET/CT demonstrating higher CXCR4 density in small cell lung carcinoma than in non-small cell variant. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2017, 44, 909–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derlin, T.; Jonigk, D.; Bauersachs, J.; Bengel, F.M. Molecular imaging of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in non-small cell lung cancer using 68Ga-pentixafor PET/CT comparison with 18F-FDG. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2016, 41, e204–e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wester, H.J.; Keller, U.; Schottelius, M.; Beer, A.; Philipp-Abbrederis, K.; Hoffmann, F.; Šimeček, J.; Gerngross, C.; Lassmann, M.; Herrmann, K.; et al. Disclosing the CXCR4 expression in lymphoproliferative diseases by targeted molecular imaging. Theranostics 2015, 5, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, R.A.; Weich, A.; Schirbel, A.; Samnick, S.; Buck, A.K.; Higuchi, T.; Wester, H.-J.; Lapa, C. Intraindividual tumor heterogeneity in NET—Further insight by C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4-directed imaging. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2017, 44, 553–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, R.A.; Weich, A.; Higuchi, T.; Schmid, J.S.; Schirbel, A.; Lassmann, M.; Wild, V.; Rudelius, M.; Kudlich, T.; Herrmann, K.; et al. Imaging of chemokine receptor 4 expression in neuroendocrine tumors-A triple tracer comparative approach. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herhaus, P.; Habringer, S.; Vag, T.; Steiger, K.; Slotta-Huspenina, J.; Gerngroß, C.; Wiestler, B.; Wester, H.-J.; Schwaiger, M.; Keller, U. Response assessment with the CXCR4-directed positron emission tomography tracer [68Ga]pentixafor in a patient with extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of the orbital cavities. EJNMMI Res. 2017, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.-Y.; Münch, N.S.; Schottelius, M.; Ingermann, J.; Liu, H.; Schauer, M.; Stangl, S.; Multhoff, G.; Steiger, K.; Gerngroß, C.; et al. CXCR4 is a potential target for diagnostic PET/CT imaging in barrett’s dysplasia and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1048–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poschenrieder, A.; Osl, T.; Schottelius, M.; Hoffmann, F.; Wirtz, M.; Schwaiger, M.; Wester, H.-J. First 18F-labeled pentixafor-based imaging agent for PET imaging of CXCR4 expression in vivo. Tomography 2016, 2, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schottelius, M.; Ludescher, M.; Richter, F.; Kapp, T.G.; Kessler, H.; Wester, H.-J. Validation of [125I]CPCR4.3 as an investigative tool for the sensitive and specific detection of hCXCR4 and mCXCR4 expression in vitro and in vivo. EJNMMI Res. 2019, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osl, T.; Schmidt, A.; Schwaiger, M.; Schottelius, M.; Wester, H.-J. A new class of PentixaFor- and PentixaTher-based theranostic agents with enhanced CXCR4-targeting efficiency. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8264–8280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ávila-Sánchez, M.; Ferro-Flores, G.; Jiménez-Mancilla, N.; Ocampo-García, B.; Bravo-Villegas, G.; Luna-Gutiérrez, M.; Santos-Cuevas, C.; Azorín-Vega, E.; Aranda-Lara, L.; Isaac-Olivé, K.; et al. Synthesis and preclinical evaluation of the 99mTc-/177Lu-CXCR4-L theranostic pair for in vivo chemokine-4 receptor-specific targeting. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2020, 324, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo-Armenta, P.; Santos-Cuevas, C.; Soto-Andonaegui, J.; Villanueva-Pérez, R.M.; González-Díaz, J.I.; García-Pérez, F.O.; Arrellano-Zarate, A.; Luna-Gutiérrez, M.; Azorín-Vega, E.; Ocampo-García, B.; et al. 99mTc-CXCR4-L for imaging of the chemokine-4 receptor associated with brain tumor invasiveness: Biokinetics, radiation dosimetry, and proof of concept in humans. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2020, 2020, 2525037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcazzan, S.; Carvalho, M.J.B.; Konrad, M.; Strangmann, J.; Tenditnaya, A.; Baumeister, T.; Schmid, R.M.; Wester, H.-J.; Ntziachristos, V.; Gorpas, D.; et al. CXCR4 peptide-based fluorescence endoscopy in a mouse model of Barrett’s esophagus. EJNMMI Res. 2022, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotta, A.M.; Aurilio, M.; D’Alterio, C.; Ieranoò, C.; Martino, D.D.; Barbieri, A.; Luciano, A.; Gaballo, P.; Santagata, S.; Portella, L.; et al. Novel peptide-based PET probe for non-invasive imaging of C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) in tumors. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 3449–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.-B.; Zhang, X.; Paul, D.; Kays, L.M.; Gough, W.; Stewart, J.; Uhlik, M.T.; Chen, Q.; Hui, Y.-H.; Zamek-Gliszczynski, M.J.; et al. Identification of LY2510924, a novel cyclic peptide CXCR4 antagonist that exhibits antitumor activities in solid tumor and breast cancer metastatic models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Ui, T.; Nagano, A.; Hino, A.; Arano, Y. C-terminal-modified LY2510924: A versatile scaffold for targeting C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, J.; Kwon, D.; Rousseau, E.; Zhang, Z.; Zeisler, J.; Uribe, C.F.; Kuo, H.-T.; Zhang, C.; Lin, K.-S.; Bénard, F. [68Ga]Ga/[177Lu]Lu-BL01, a novel theranostic pair for targeting C-X-C chemokine receptor 4. Mol. Pharmaceut. 2019, 16, 4688–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.; Lozada, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zeisler, J.; Poon, R.; Zhang, C.; Roxin, Á.; Lin, K.-S.; Perrin, D.; Benard, F. High-contrast CXCR4-targeted 18F-PET imaging using a potent and selective antagonist. Mol. Pharmaceut. 2021, 18, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Bi, L.; Gao, J.; Yang, M.; Wang, Y.; Yao, X.; Shan, H.; Jin, H. Preclinical evaluation of [64Cu]NOTA-CP01 as a PET imaging agent for metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Pharmaceut. 2021, 18, 3638–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
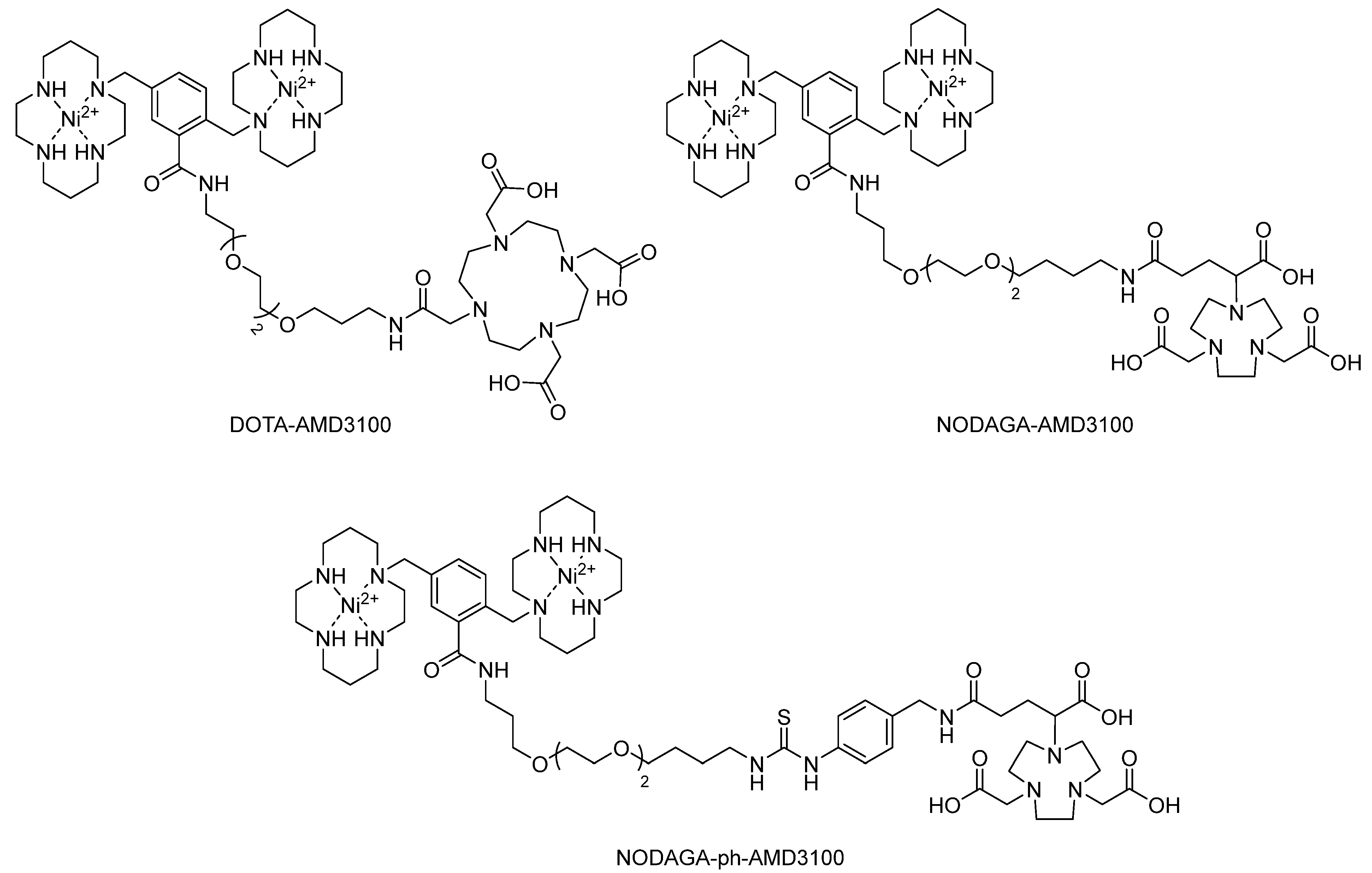
- Poty, S.; Gourni, E.; Désogère, P.; Boschetti, F.; Goze, C.; Maecke, H.R.; Denat, F. AMD3100: A versatile platform for CXCR4 targeting 68Ga-based radiopharmaceuticals. Bioconjugate Chem. 2016, 27, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
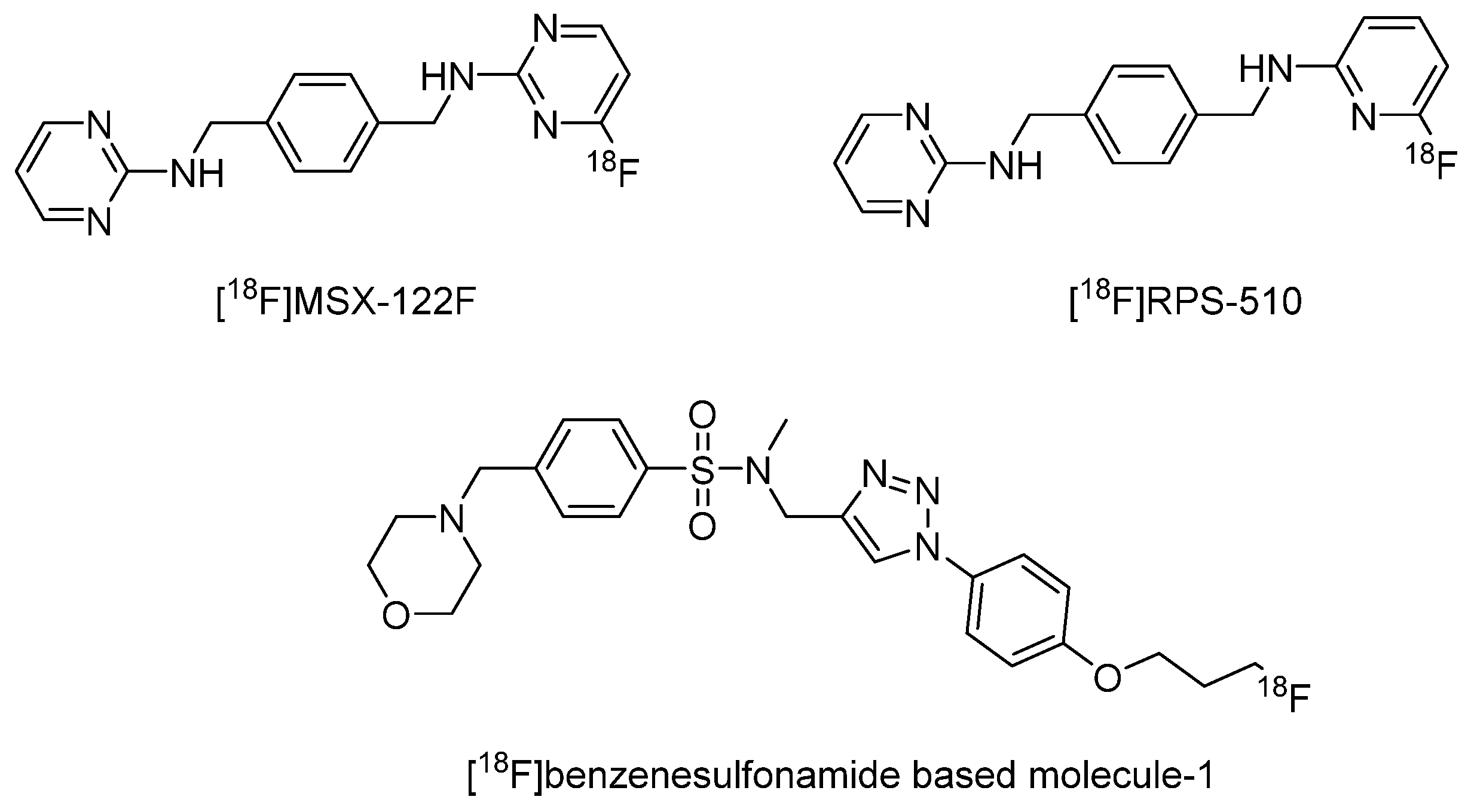
- Demoin, D.W.; Shindo, M.; Zhang, H.; Edwards, K.J.; Serganova, I.; Pillarsetty, N.V.K.; Lewis, J.S.; Blasberg, R.G. Synthesis and evaluation of an 18F-labeled pyrimidine-pyridine amine for targeting CXCR4 receptors in gliomas. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2016, 43, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Zhan, W.; Zhu, A.; Yoon, Y.; Lin, S.; Sasaki, M.; Klapproth, J.-M.A.; Yang, H.; Grossniklaus, H.E.; Xu, J.; et al. Development of a unique small molecule modulator of CXCR4. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oum, Y.H.; Shetty, D.; Yoon, Y.; Liang, Z.; Voll, R.J.; Goodman, M.M.; Shim, H. A benzenesulfonamide derivative as a novel PET radioligand for CXCR4. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.yaozh.com/login (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Shi, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; Pei, H.; Wang, G.; Zhou, H.; Fan, L.; Yang, K.; Jiang, B.; Wang, F.; et al. Semiconducting polymer nano-radiopharmaceutical for combined radio-photothermal therapy of pancreatic tumor. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, R.; Maiti, D.; Zhong, J.; Xiong, S.S.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, R.; Wan, J.; Yang, K. T1/T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and SPECT imaging guided combined radioisotope therapy and chemotherapy using functionalized reduced graphene oxide-manganese ferrite nanocomposites. Carbon 2019, 149, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, J.; Zhou, X.; Shen, L. CXCR4-Targeted Radiopharmaceuticals for the Imaging and Therapy of Malignant Tumors. Molecules 2023, 28, 4707. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124707
Yu J, Zhou X, Shen L. CXCR4-Targeted Radiopharmaceuticals for the Imaging and Therapy of Malignant Tumors. Molecules. 2023; 28(12):4707. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124707
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Jingjing, Xu Zhou, and Langtao Shen. 2023. "CXCR4-Targeted Radiopharmaceuticals for the Imaging and Therapy of Malignant Tumors" Molecules 28, no. 12: 4707. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124707
APA StyleYu, J., Zhou, X., & Shen, L. (2023). CXCR4-Targeted Radiopharmaceuticals for the Imaging and Therapy of Malignant Tumors. Molecules, 28(12), 4707. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124707






