Nematicidal Coumarins from Cnidium monnieri Fruits and Angelica dahurica Roots and Their Physiological Effect on Pine Wood Nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Nematicidal Activity of Extracts
2.2. Identification of Nematicidal Compounds
2.3. Nematicidal Activity of Compounds
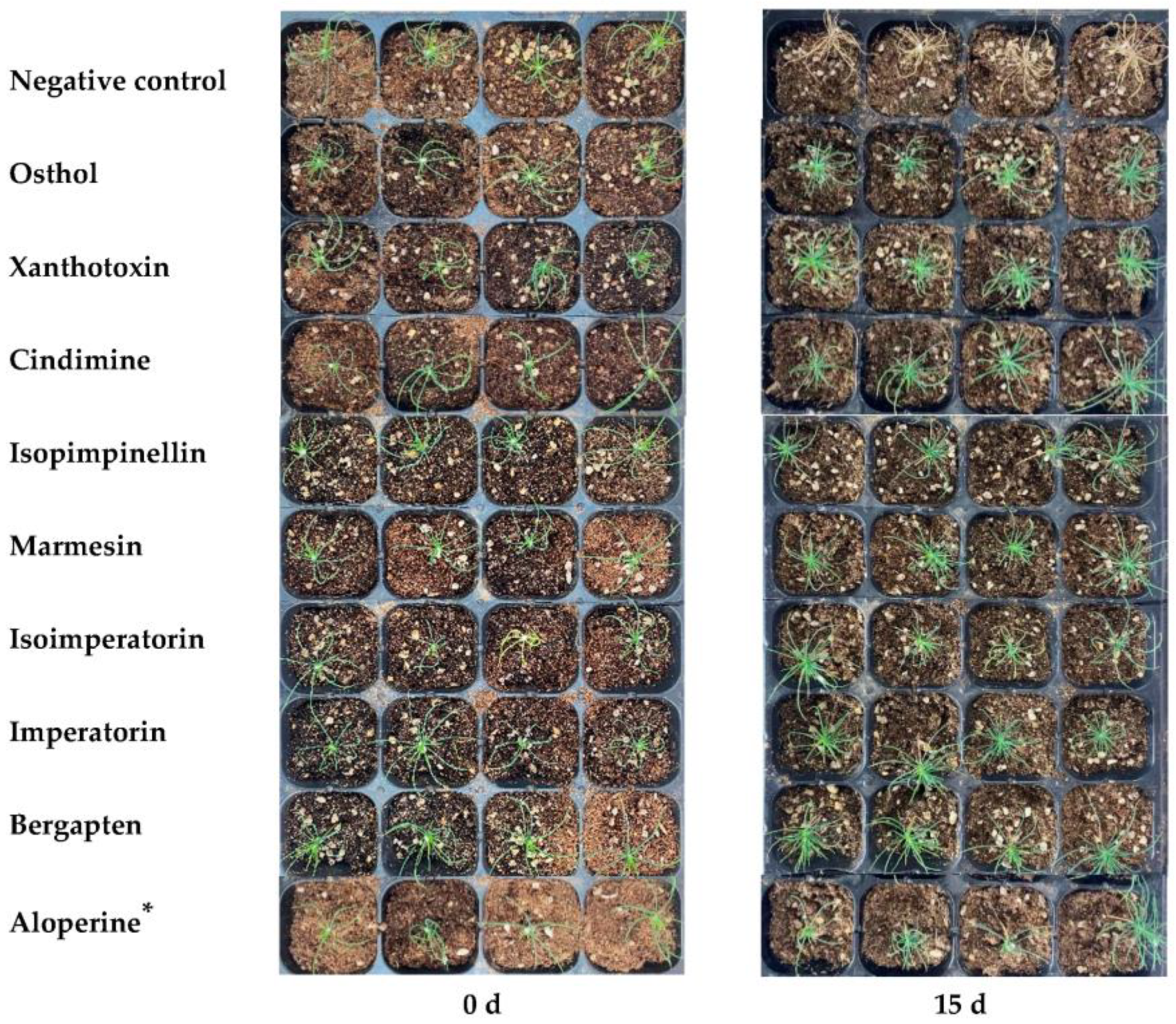
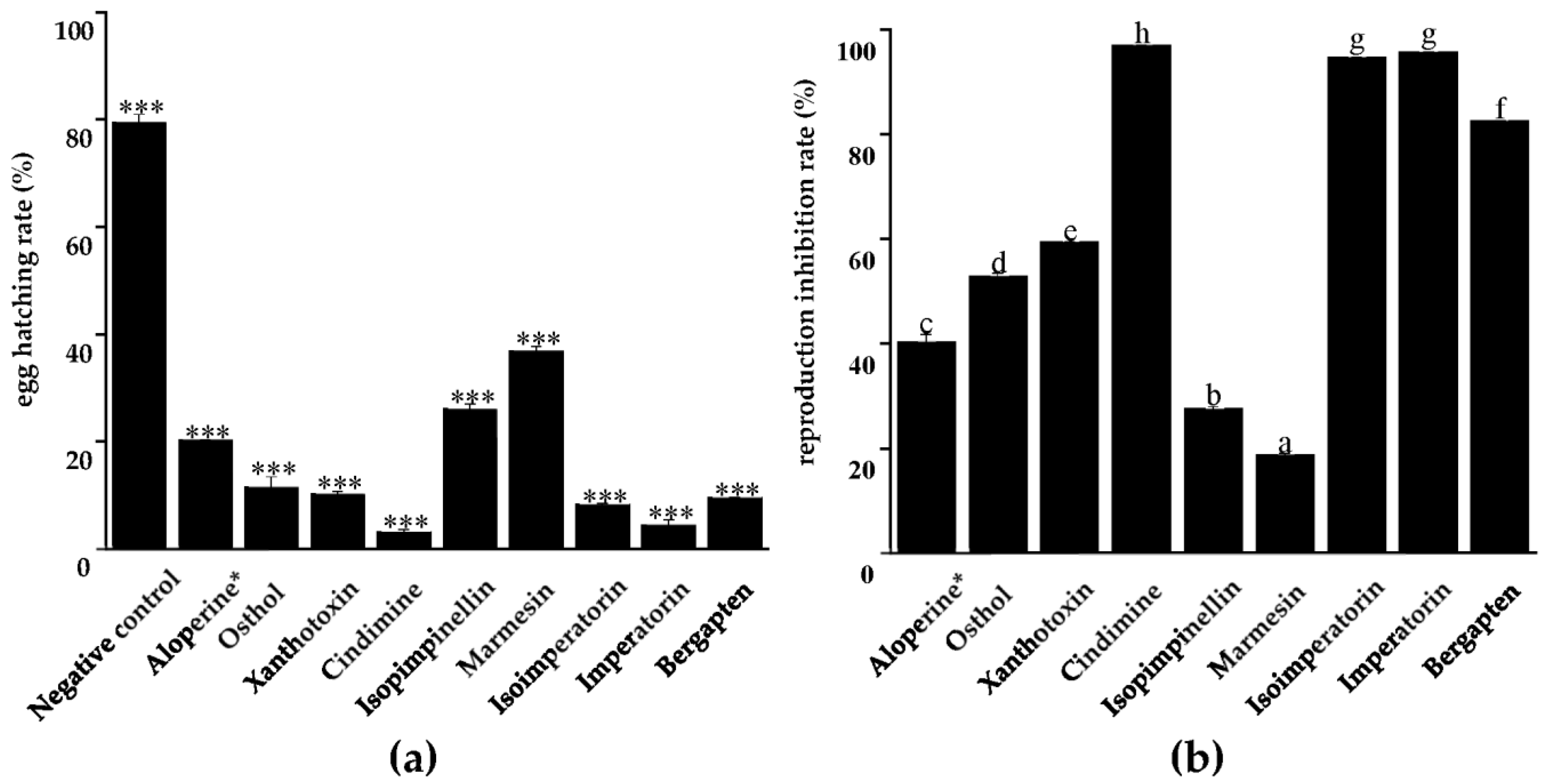
2.4. Effect of Compounds on Egg Hatching and Reproduction
2.5. Effect of compounds on Feeding Inhibition
2.6. Effect of Compounds on AChE and Ca2+ ATPase
2.7. Influence on PWN Pathogenicity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Instruments
3.2. Isolation and Identification of Compounds
3.3. Nematicidal Assay
control)/(1 − Mortality% in negative control)
3.4. Egg Hatching Inhibition Assay
3.5. Reproduction Inhibition Assay
group/Final PWN population in negative control) × 100%
3.6. Feeding Inhibition Assay
3.7. Effects of the Compounds on the Enzymes of PWNs
3.7.1. Preparation of Enzyme Solution
3.7.2. Effect on AChE
3.7.3. Effect on Ca2+ ATPase
3.8. Influence of the Compounds on Pathogenicity to Pine Seedlings
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Vicente, C.; Espada, M.; Vieira, P.; Mota, M. Pine Wilt Disease: A threat to European forestry. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 133, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.N.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, J.Y.; Kim, S.C.; Cho, B.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Min, J. A short review of the pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2020, 12, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, J.M.S.; Barbosa, P.; Vieira, P.; Vicente, C.S.L.; Figueiredo, A.C.; Mota, M. Phytochemicals as biopesticides against the pinewood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus: A review on essential oils and their volatiles. Plants 2021, 10, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamiya, Y. Pathology of the Pine Wilt Disease Caused by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 1983, 21, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.T.; Haegeman, A.; Danchin, E.G.; Gaur, H.S.; Helder, J.; Jones, M.G.; Kikuchi, T.; Manzanilla-Lopez, R.; Palomares-Rius, J.E.; Wesemael, W.M.; et al. Top 10 plant-parasitic nematodes in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 946–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takai, K.; Soejima, T.; Suzuki, T.; Kawazu, K. Development of a water-soluble preparation of emamectin benzoate and its preventative effect against the wilting of pot-grown pine trees inoculated with the pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Pest Manag. Sci. 2001, 57, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, E.; Naves, P.; Vieira, M. Prevention of pine wilt disease induced by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and Monochamus galloprovincialis by trunk injection of emamectin benzoate. Phytoparasitica 2013, 41, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zasada, I.A.; Halbrendt, J.M.; Kokalis-Burelle, N.; Lamondia, J.; Mckenry, M.V.; Noling, J.W. Managing nematodes without methyl bromide. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2010, 48, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.P.; Lin, Q.X.; Qian, X.L.; Zheng, Y.; Yao, J.M.; Wu, H.C.; Li, M.M.; Jin, X.; Pan, X.H.; Zhang, L.L.; et al. Nematicidal Activity of Cry1Ea11 from Bacillus thuringiensis BRC-XQ12 against the Pine Wood Nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus). Phytopathology 2018, 108, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Song, B.A. Natural nematicidal active compounds: Recent research progress and outlook. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 2015–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.X.; Wang, C.; Du, G.C.; Deng, W.J.; Yang, H.; Li, R.G.; Xu, Q.; Guo, Q.Q. Two Nematicidal Compounds from Lysinimonas M4 against the Pine Wood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Forests 2022, 13, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isman, M.B. Botanical insecticides, deterrents, and repellents in modern agriculture and an increasingly regulated world. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 51, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isman, M.B. Botanical Insecticides in the Twenty-First Century—Fulfilling Their Promise? Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2020, 65, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitwood, D.J. Phytochemical based strategies for nematode control. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2002, 40, 221–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntalli, N.G.; Caboni, P. Botanical nematicides: A review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9929–9940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Tariq, M.; Ahmad, F.; Mennan, S.; Khan, F.; Asif, M.; Nadeem, H.; Ansari, T.; Shariq, M.; Siddiqui, M.A. Assessment of nematicidal efficacy of chitosan in combination with botanicals against Meloidogyne incognita on carrot. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2021, 71, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.L.; Li, R.G.; Wang, C.; Yang, H.; Deng, W.J.; Du, G.C.; Guo, Q.Q. Nematicidal phytochemicals against pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (nematoda: Aphelenchoididae). J. Plant Dis. Protect. 2022, 130, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Huang, W.; Yang, Y. Cytochrome P450 isoenzymes in rat and human liver microsomes associate with the metabolism of total coumarins in Fructus Cnidii. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2015, 40, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Luo, M.; Wang, Y.; LI, Y.Q. Progress in Plant Biology Research of Fructus Cnidii. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2020, 28, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Li, G.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Chang, H.W.; Jahng, Y.; Woo, M.H.; Song, D.K.; Son, J.K. Two new furanocoumarins from the roots of Angelica dahurica. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2003, 24, 1699–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.H.; Lim, H.H.; Song, Y.K.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Ko, I.G.; Kim, K.J.; Shin, M.S.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, C.J. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect of the aqueous extract of root of Angelica Dahurica. Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 2008, 7, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, H.; Tomohiro, N.; Ido, Y.; Kubo, M. Anti-allergic effects of Cnidii Monnieri Fructus (Dried fruits of Cnidium monnieri) and its major component, osthol. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 25, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Z.; Feng, X.; Jia, X.D.; Wang, M.; Shan, Y.; Dong, Y.F. New coumarin glucoside from Angelica dahurica. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2007, 43, 399–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Guo, D.S.; Lu, M.H.; Yue, J.Y.; Liu, Y.; Shang, C.M.; An, D.R.; Zhao, M.M. Inhibitory Effect of Osthole from Cnidium monnieri on Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) Infection in Nicotiana glutinosa. Molecules 2019, 25, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Takaishi, Y.; Duan, H.Q.; Chen, B.; Honda, G.; Itoh, M.; Takeda, Y.; Kodzhimatov, O.K.; Lee, K.H. Coumarins and bicoumarin from Ferula sumbul: Anti-HIV activity and inhibition of cytokine release. Phytochemistry 2000, 53, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marumoto, S.; Miyazawa, M. Biotransformation of Bergapten and Xanthotoxin by Glomerella cingulata. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7777–7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.S.; Xie, F.Z.; Liu, Q.H.; Wu, X. Studies on Coumarins of Saussurea involucrate Kar. et Kir. Chinese Pharm. J. 2006, 41, 1774–1776. [Google Scholar]
- Benahmed, M.; Akkal, S.; Elomri, A.; Laouer, H.; Verite, P.; Seguin, E. Secondary Constituents from Carum montanum. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2008, 44, 510–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schun, Y.; Cordell, G.A. Studies on the NMR spectroscopic properties of gelsemine—Revisions and refinements. J. Nat. Prod. 1985, 48, 969–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.W.; Shi, J.M.; Wang, J.Z.; Chen, D.L. Study on the chemical constituents of Notopterygium incisum Radix. West China J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 35, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, H.; Abbas, Q.; Hassan, M.; Eo, S.H.; Ashraf, Z.; Kim, D.; Phull, A.R.; Kim, S.J.; Kang, S.K.; Seo, S.Y. Isolation, characterization, and in silico, in vitro and in vivo antiulcer studies of isoimperatorin crystallized from Ostericum koreanum. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, L.; Liu, H.Y.; Meng, F.H. Chemical constituents of Gelsemium elegans. Zhong Cao Yao 2017, 48, 2028–2032. [Google Scholar]
- Beane, R.D.; Hobbs, N.T. The Baermann technique for estimating Protostrongylus infection in bighorn sheep: Effect of laboratory procedures. J. Wildl. Dis. 1983, 19, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.G. Nematicidal Activity of Quinolizidine Alkaloids and the Functional Group Pairs in Their Molecular Structure. J. Chem. Ecol. 1999, 25, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.G.; Liu, X.H. Method of Controlling Pine Wood Nematode Disease with Aloperine. Patent CN94111492.9, 21 June 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, S.M.; Kim, J.; Kim, E.; Park, H.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, I.K. Structure-Activity Relationship of Aliphatic Compounds for Nematicidal Activity against Pine Wood Nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1823–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.M.; Wang, G.L.; Bai, C.Q.; Liu, P.; Liu, Z.M.; Liu, Q.Z.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, Z.L.; Du, S.S.; Deng, Z.W. A New Eudesmane Sesquiterpene Glucoside from Liriope muscari Fibrous Roots. Molecules 2011, 16, 9017–9024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.Q.; Du, G.C.; Qi, H.T.; Zhang, Y.A.; Yue, T.Q.; Wang, J.C.; Li, R.G. A nematicidal tannin from Punica granatum L. rind and its physiological effect on pine wood nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 135, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.J.; Hwang, B.S.; Jin, C.Z.; Li, W.J.; Park, D.J.; Seo, S.T.; Kim, C.J. Screening, isolation and evaluation of a nematicidal compound from actinomycetes against the pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.J.; Feather-Stone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, Z.B.; Zhu, S.W.; Weng, Q.F. (60)Co-γ irradiation affects the enzymatic antioxidant system of the citrus red mite Panonychus citri (Acari: Tetranychidae). Molecules 2014, 19, 6382–6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Qi, Y.M.; Yu, X.H.; Wang, B.F.; Cao, R.H.; Jiang, D.X. Nematicidal effect against Bursaphelenchus xylophilus of harmine quaternary ammonium derivatives, inhibitory activity and molecular docking studies on acetylcholinesterase. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 153, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogenauer, K.; Baumann, K.; Enz, A.; Mulzer, J. Synthesis and acetylcholinesterase inhibition of 5-desamino huperzine A derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 2627–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, B.; Chompoo, J.; Tawata, S. Insecticidal and Nematicidal Activities of Novel Mimosine Derivatives. Molecules 2015, 20, 16741–16756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oku, H.; Shiraishi, T.; Ouchi, S.; Kurozumi, S.; Ohta, H. Pine Wilt Toxin, the Metabolite of a Bacterium Associated with a Nematode. Naturwissenschaften 1980, 67, 198–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.Q.; Du, G.C.; He, H.W.; Xu, H.K.; Guo, D.S.; Li, R.G. Two nematicidal furocoumarins from Ficus carica L. leaves and their physiological effects on pine wood nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus). Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.Q.; Du, G.C.; Li, Y.X.; Liang, C.Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.N. Nematotoxic coumarins from Angelica pubescens Maxim. f. biserrata Shan et Yuan roots and their physiological effects on Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J. Nematol. 2018, 50, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Z.Z.; Gong, Y.T.; Huang, X.J.; Yu, H.S.; Hu, J.F. Efficacy of Four Nematicides Against the Reproduction and Development of Pinewood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J. Nematol. 2015, 47, 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- Massoulié, J.; Pezzementi, L.; Bon, S.; Krejci, E.; Vallette, F.-M. Molecular and cellular biology of cholinesterases. Prog. Neurobiol. 1993, 41, 31–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S.; Kim, E.; Lee, S.H.; Park, I.K. Inhibition of acetylcholinesterases of the pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, by phytochemicals from plant essential oils. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2013, 105, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S.; Moon, Y.S.; Lee, S.H.; Park, I.K. Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase and glutathione S-transferase of the pinewood nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus) by aliphatic compounds. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2013, 105, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brini, M.; Carafoli, E. Calcium Pumps in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 1341–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerek, F.; Stimac, R.; Apell, H.J.; Freudenmann, F.; Moroder, L. Characterization of the macrocyclic carbon suboxide factors as potent Na,K+-ATPase and SR Ca2+ATPase inhibitors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1567, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]




| Samples (1 mg/mL) | Corrected Mortality (%, Mean ± SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |
| Ethanol extract | 43.14 ± 0.20 | 62.08 ± 0.41 | 77.93 ± 0.82 b |
| Ethyl acetate extract | 78.30 ± 2.49 | 82.33 ± 2.49 | 96.00 ± 0.81 c |
| Aqueous fraction | 5.23 ± 0.33 | 12.3 ± 0.81 | 14.01 ± 2.49 a |
| Samples (1 mg/mL) | Corrected Mortality (%, Mean ± SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |
| Ethanol extract | 32.28 ± 0.99 | 65.60 ± 0.50 | 84.64 ± 0.55 b |
| Ethyl acetate extract | 29.53 ± 1.68 | 66.81 ± 1.31 | 86.15 ± 0.92 c |
| Aqueous fraction | 7.38 ± 1.22 | 16.2 ± 0.83 | 20.27 ± 0.83 a |
| Sample (500 µg/mL) | Corrected Mortality (%, Mean ± SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |
| Fr.1 | 71.14 ± 1.24 | 85.86 ± 0.82 | 93.92 ± 0.85 n |
| Fr.2 | 76.51 ± 1.29 | 83.84 ± 0.82 | 91.22 ± 1.23 m |
| Fr.3 | 53.69 ± 0.85 | 61.28 ± 0.48 | 69.60 ± 0.71 l |
| Fr.4 | 12.08 ± 0.06 | 24.58 ± 0.48 | 30.41 ± 0.84 h |
| Fr.5 | 1.68 ± 0.47 | 9.43 ± 0.48 | 13.51 ± 0.45 de |
| Fr.6 | 0.67 ± 0.47 | 2.36 ± 0.48 | 3.04 ± 0.01 a |
| Fr.7 | 13.76 ± 0.45 | 27.61 ± 0.48 | 40.20 ± 0.87 i |
| Fr.8 | 19.80 ± 0.44 | 23.91 ± 0.48 | 41.55 ± 0.66 j |
| Fr.9 | 5.70 ± 0.46 | 14.81 ± 0.95 | 29.39 ± 0.14 h |
| Fr.10 | 3.68 ± 0.92 | 6.10 ± 0.82 | 49.33 ± 0.63 k |
| Fr.11 | 1.67 ± 0.94 | 3.37 ± 0.48 | 5.40 ± 0.46 b |
| Fr.12 | 2.01 ± 0.01 | 6.06 ± 0.82 | 29.73 ± 0.42 h |
| Fr.13 | 4.70 ± 0.46 | 9.43 ± 0.48 | 14.53 ± 0.45 g |
| Fr.14 | 0.67 ± 0.47 | 5.38 ± 0.95 | 12.50 ± 0.90 d |
| Fr.15 | 1.34 ± 0.48 | 11.45 ± 0.48 | 13.50 ± 0.89 ef |
| Fr.16 | 4.70 ± 0.46 | 6.73 ± 0.95 | 14.18 ± 1.60 fg |
| Fr.17 | 0.67 ± 0.47 | 1.34 ± 0.48 | 2.70 ± 0.95 a |
| Fr.18 | 1.68 ± 0.47 | 2.69 ± 0.48 | 7.43 ± 0.46 c |
| Sample (500 µg/mL) | Corrected Mortality (%, Mean ± SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |
| Fr.1 | 6.67 ± 0.58 | 39.24 ± 1.30 | 59.65 ± 1.31 i |
| Fr.2 | 3.34 ± 0.58 | 9.72 ± 1.30 | 21.75 ± 0.99 c |
| Fr.3 | 2.67 ± 1.15 | 17.01 ± 0.49 | 28.42 ± 1.72 e |
| Fr.4 | 2.33 ± 0.58 | 17.36 ± 0.49 | 26.32 ± 2.27 d |
| Fr.5 | 2.33 ± 0.58 | 32.64 ± 0.49 | 70.87 ± 0.50 j |
| Fr.6 | 2.33 ± 0.58 | 17.36 ± 0.98 | 74.74 ± 1.49 k |
| Fr.7 | 9.67 ± 0.58 | 44.79 ± 0.85 | 79.65 ± 3.47 l |
| Fr.8 | 9.67 ± 0.58 | 39.58 ± 1.70 | 49.82 ± 2.16 g |
| Fr.9 | 10.33 ± 0.65 | 45.14 ± 0.49 | 53.68 ± 3.10 h |
| Fr.10 | 9.33 ± 0.58 | 18.75 ± 1.47 | 28.77 ± 0.49 e |
| Fr.11 | 2.33 ± 0.58 | 13.19 ± 0.49 | 17.89 ± 1.72 b |
| Fr.12 | 4.33 ± 0.58 | 13.89 ± 0.49 | 20.00 ± 0.86 c |
| Fr.13 | 6.33 ± 0.58 | 18.75 ± 0.85 | 31.92 ± 0.50 f |
| Fr.14 | 6.33 ± 0.58 | 18.40 ± 1.30 | 29.82 ± 2.48 e |
| Fr.15 | 3.67 ± 0.58 | 12.15 ± 0.98 | 14.39 ± 1.31 a |
| Fr.16 | 2.33 ± 0.58 | 33.68 ± 0.49 | 48.07 ± 0.99 g |
| LC50 (μg/mL) | LC50 (μM) | 95% Confidence Intervals (μg/mL) | Χ2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aloperine * | 89.90 | 387 | 78.01–104.99 | 4.34 |
| Osthol (Compound 1) | 64.93 | 266 | 56.10–74.08 | 4.95 |
| Xanthotoxin (Compound 2) | 54.68 | 253 | 46.55–63.08 | 1.76 |
| Cindimine (Compound 3) | 24.73 | 64 | 11.15–36.01 | 0.98 |
| Isopimpinellin (Compound 4) | 92.16 | 375 | 80.44–111.24 | 2.85 |
| Marmesin (Compound 5) | 122.96 | 500 | 111.03–136.69 | 0.65 |
| Isoimperatorin (Compound 6) | 43.08 | 160 | 31.44–53.91 | 0.64 |
| Imperatorin (Compound 7) | 35.72 | 132 | 26.62–44.13 | 3.07 |
| Bergapten (Compound 8) | 52.07 | 241 | 45.59–62.16 | 2.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, J.; Qin, C.; Liu, X.; Li, R.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Du, G.; Guo, Q. Nematicidal Coumarins from Cnidium monnieri Fruits and Angelica dahurica Roots and Their Physiological Effect on Pine Wood Nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus). Molecules 2023, 28, 4109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104109
Feng J, Qin C, Liu X, Li R, Wang C, Li C, Du G, Guo Q. Nematicidal Coumarins from Cnidium monnieri Fruits and Angelica dahurica Roots and Their Physiological Effect on Pine Wood Nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus). Molecules. 2023; 28(10):4109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104109
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Jiale, Chenglei Qin, Xiaohong Liu, Ronggui Li, Chao Wang, Chunhan Li, Guicai Du, and Qunqun Guo. 2023. "Nematicidal Coumarins from Cnidium monnieri Fruits and Angelica dahurica Roots and Their Physiological Effect on Pine Wood Nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus)" Molecules 28, no. 10: 4109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104109
APA StyleFeng, J., Qin, C., Liu, X., Li, R., Wang, C., Li, C., Du, G., & Guo, Q. (2023). Nematicidal Coumarins from Cnidium monnieri Fruits and Angelica dahurica Roots and Their Physiological Effect on Pine Wood Nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus). Molecules, 28(10), 4109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104109






