Reaction Mechanism for the Removal of NOx by Wet Scrubbing Using Urea Solution: Determination of Main and Side Reaction Paths
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Determination of the Boundary Conditions for the Formation of Urea Nitrate
2.2. Reaction Mechanism for NOx Removal
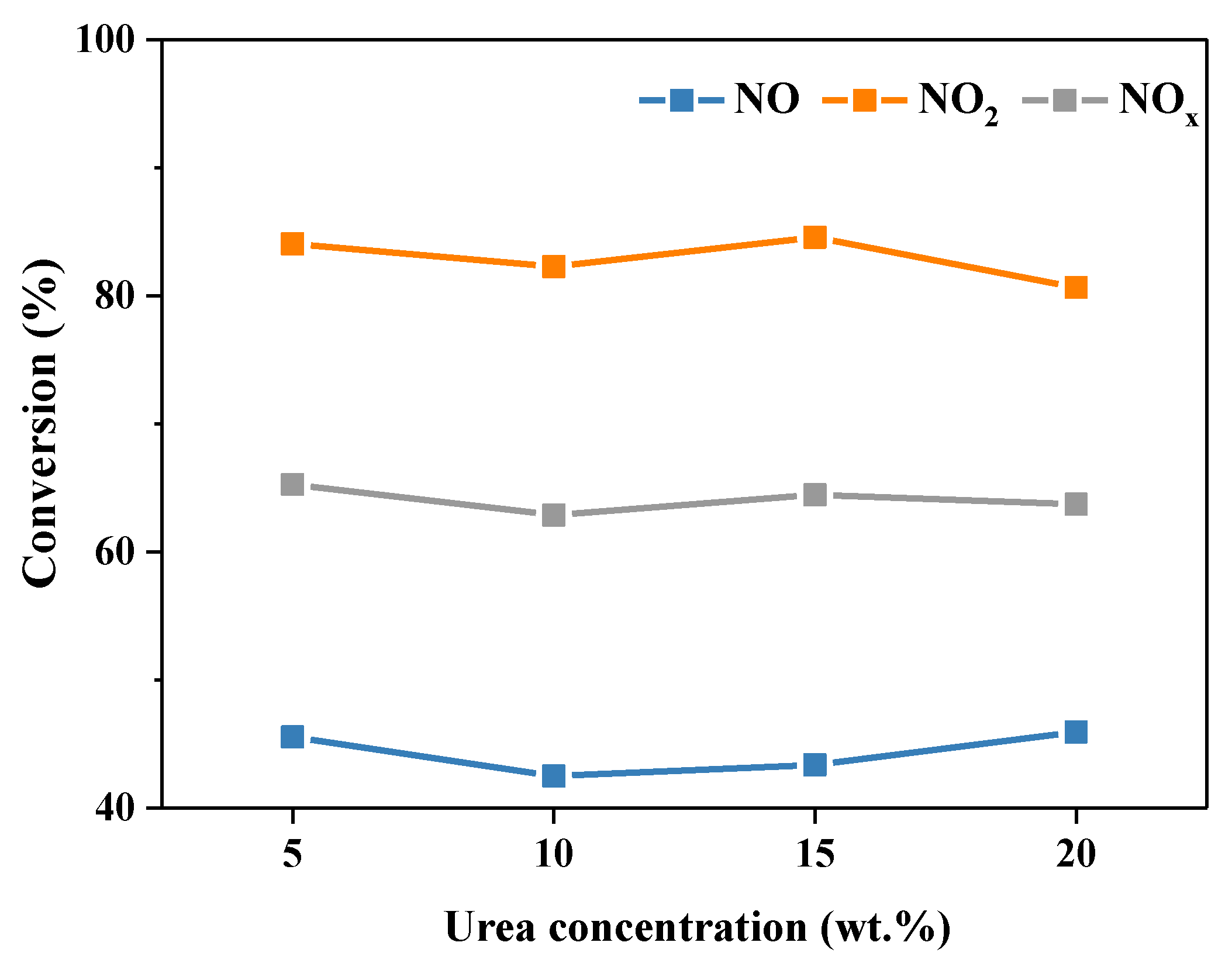
2.2.1. Concentration of Urea Solution
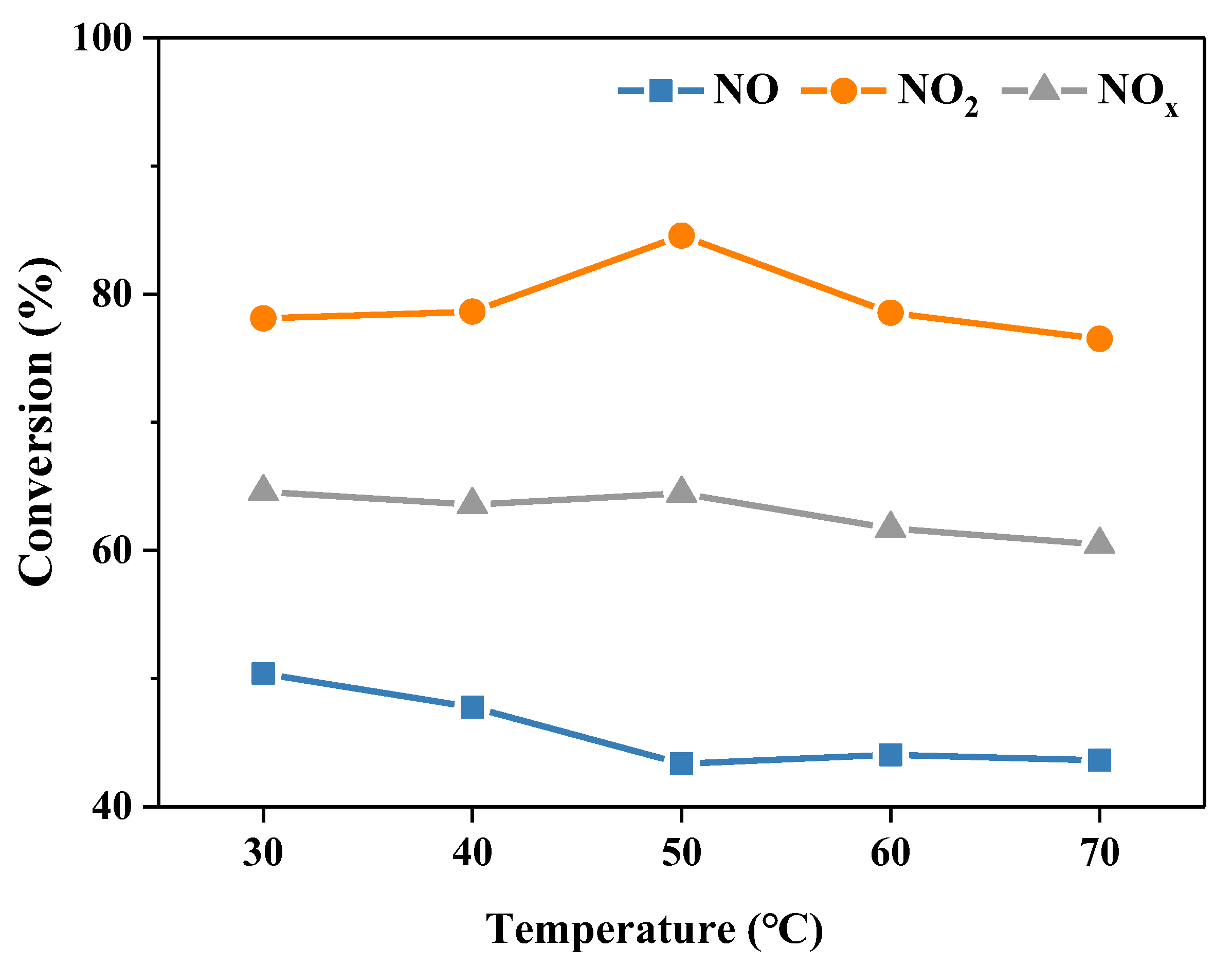
2.2.2. Reaction Temperature
2.2.3. Oxidation Degree of NOx
2.2.4. Initial pH of Urea Solution
2.3. Simultaneous Removal of NOx and SO2
3. Experimental
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forzatti, P. Present status and perspectives in de-NOx SCR catalysis. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 222, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.M.; Woo, S.I. Recent advances in catalytic DeNOx science and technology. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 2006, 48, 43–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chang, H.; Ma, L.; Hao, J.; Yang, R.T. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOxwith NH3 over metal oxide and zeolite catalysts-A review. Catal. Today 2011, 175, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Guo, F.; Yu, J.; Xu, G. Improved low-temperature activity of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 for denitration using different vanadium precursors. Catalysts 2016, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, H.; Hu, C.; Zhao, J. The abatement of major pollutants in air and water by environmental catalysis. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2013, 7, 302–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, L.; Li, K.; Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, J. Core-shell-like structured α-MnO2@CeO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO: Promoted activity and SO2 tolerance. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Shi, W.; Li, K.; Chen, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, J. Synergistic promotion effect between NOxand chlorobenzene removal on MnOx–CeO2 catalyst. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 30426–30432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Deng, X.; Chen, M. Nitric oxide removal by combined urea and FeII EDTA reaction systems. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Luo, Y.; Yu, P.; Cai, B.; Tan, H. Removal of NO from flue gas by wet scrubbing with NaClO2/(NH2)2CO solutions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2009, 15, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Yang, F. Combination of complex adsorption and anammox for nitric oxide removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 312, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Cen, C.; Tang, Z.; Zhong, P.; Chen, D.; Chen, Z. Simultaneous removal of SO2 and NOx by wet scrubbing using urea solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Shen, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Cen, K. Experimental Study on the NOx Removal by Scrubbing with Urea-H2O2 Solution after NO Partial Preoxidation. Energy Fuel 2019, 33, 6600–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Cen, C.-p.; Wang, X.-m.; Tang, Z.-j.; Tang, Z.-x.; Chen, D.-s. Simultaneous removal of SO2, NO and Hg0 by wet scrubbing using urea+KMnO4 solution. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 106, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Ma, X.; Yin, J.a.; Gao, X. A study on simultaneous removal of NO and SO2 by using sodium persulfate aqueous scrubbing. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 1536–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, T.-x.; Chen, Z.-y.; Du, Y.-r. Simultaneous removal of SO2 and NO using M/NaClO2 complex absorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 160, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Luo, S.; He, Z.; Liu, Y. Applications of high gravity technologies for wastewater treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 912–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, F.; Wang, D.; Pu, Y.; Zeng, X.-F.; Wang, J.-X.; Chen, J.-F. Efficient preparation of monodisperse CaCO3 nanoparticles as overbased nanodetergents in a high-gravity rotating packed bed reactor. Powder Technol. 2018, 325, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-F.; Lee, S.-C. Adsorption behavior of pesticide methomyl on activated carbon in a high gravity rotating packed bed reactor. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2869–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasalle, A.; Roizard, C.; Midoux, N.; Bourret, P.; Dyens, P.J. Removal of nitrogen oxides (NOx) from flue gases using the urea acidic process: Kinetics of the chemical reaction of nitrous acid with urea. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1992, 31, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almog, J.; Klein, A.; Tamiri, T.; Shloosh, Y. A field diagnostic test for the improvised explosive urea nitrate. J. Forensic Sci. 2005, 50, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Désilets, S.; Brousseau, P.; Chamberland, D.; Singh, S.; Feng, H.; Turcotte, R.; Armstrong, K.; Anderson, J. Analyses of the thermal decomposition of urea nitrate at high temperature. Thermochim. Acta 2011, 521, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokmakov, I.V.; Alavi, S.; Thompson, D.L. Urea and Urea Nitrate Decomposition Pathways: A Quantum Chemistry Study. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 2759–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worsham, J.E., Jnr; Busing, W.R. The crystal structure of uronium nitrate (urea nitrate) by neutron diffraction. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B 1969, 25, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayan, G.Ö.; Kayan, A. Composite of Natural Polymers and Their Adsorbent Properties on the Dyes and Heavy Metal Ions. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 3477–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, X.; Luo, Z.; Cen, K. Nitrogen oxide absorption and nitrite/nitrate formation in limestone slurry for WFGD system. Appl. Energy 2014, 129, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Vanderschuren, J. Analysis and prediction of the liquid phase composition for the absorption of nitrogen oxides into aqueous solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 1999, 18, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
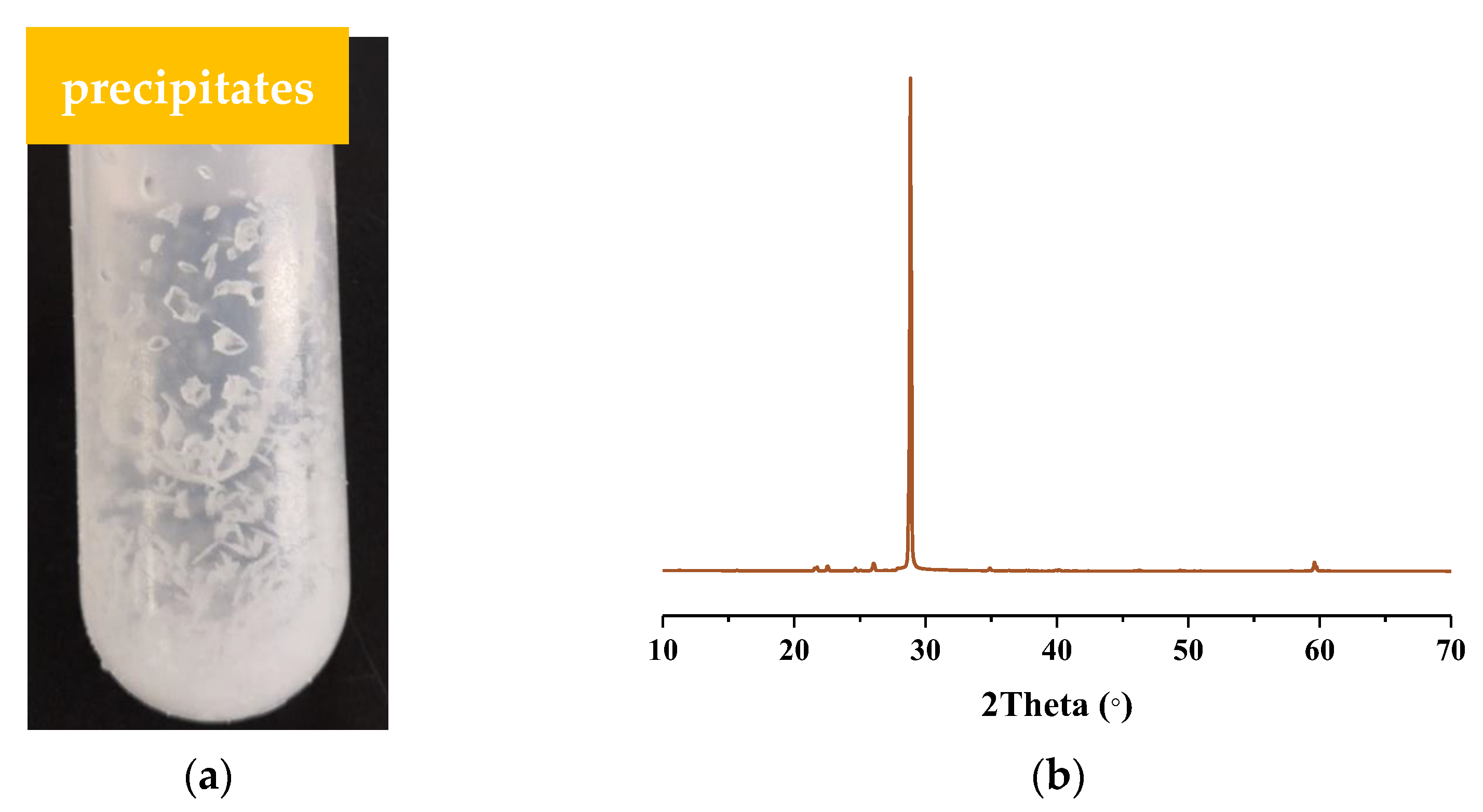

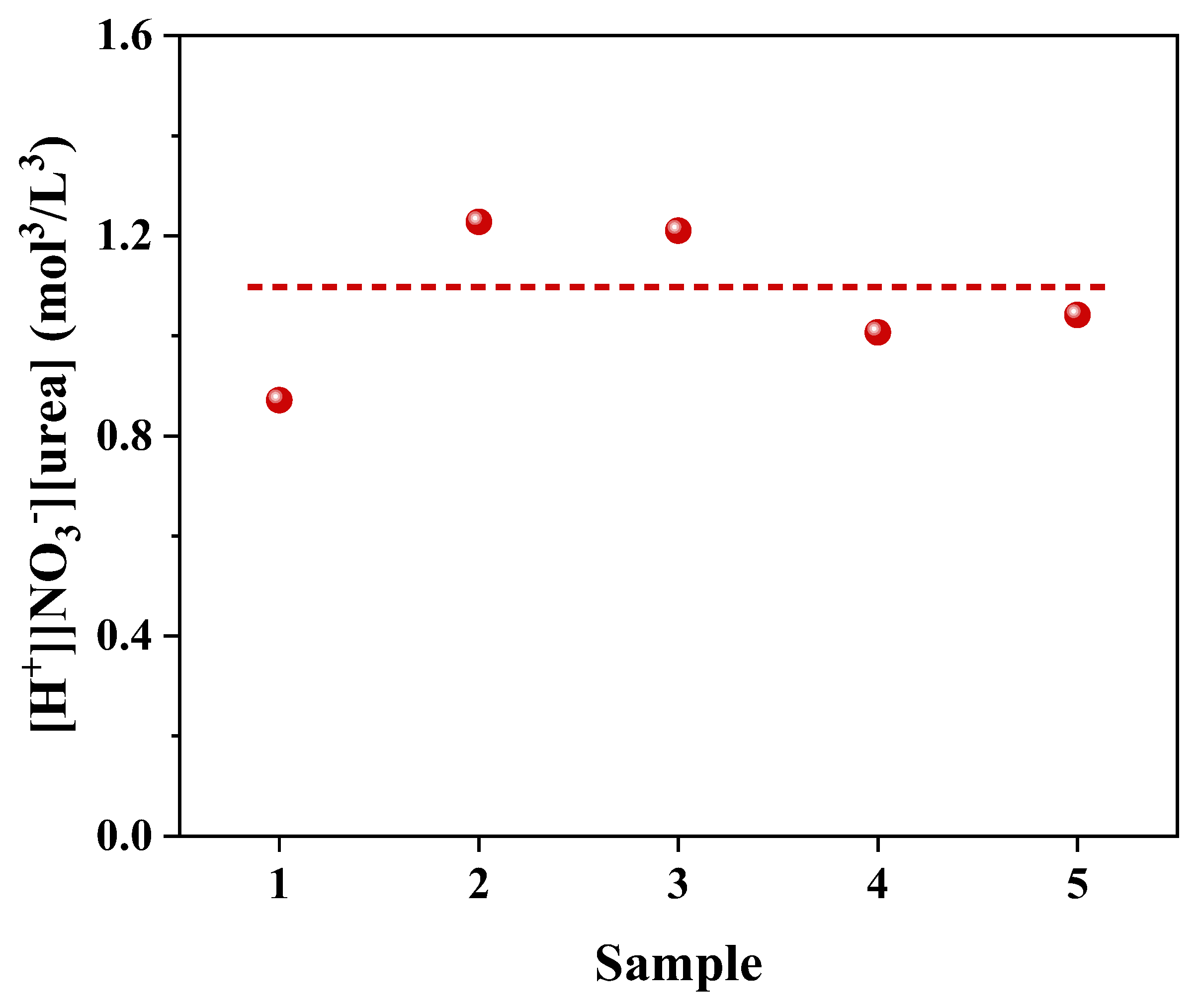
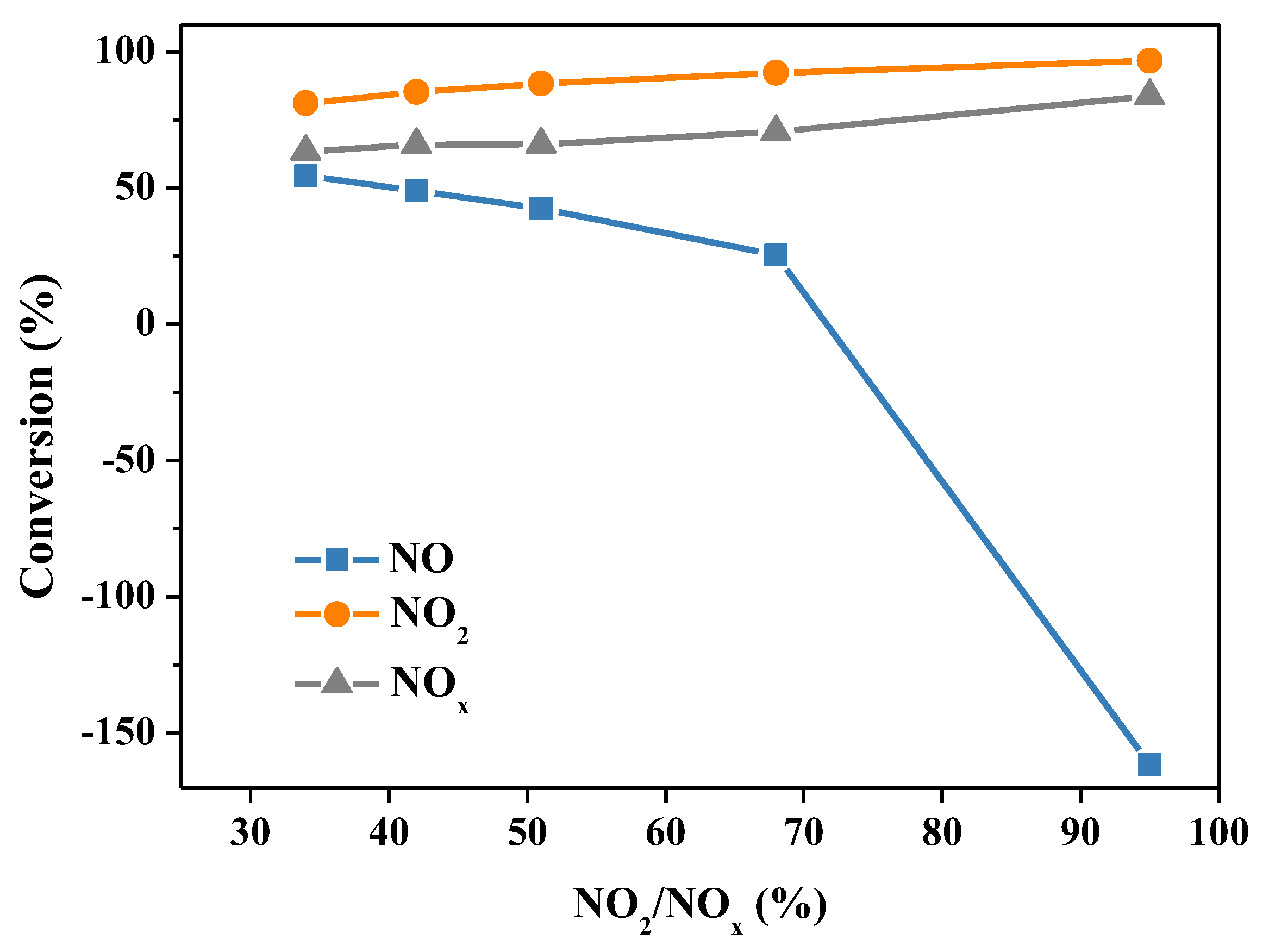
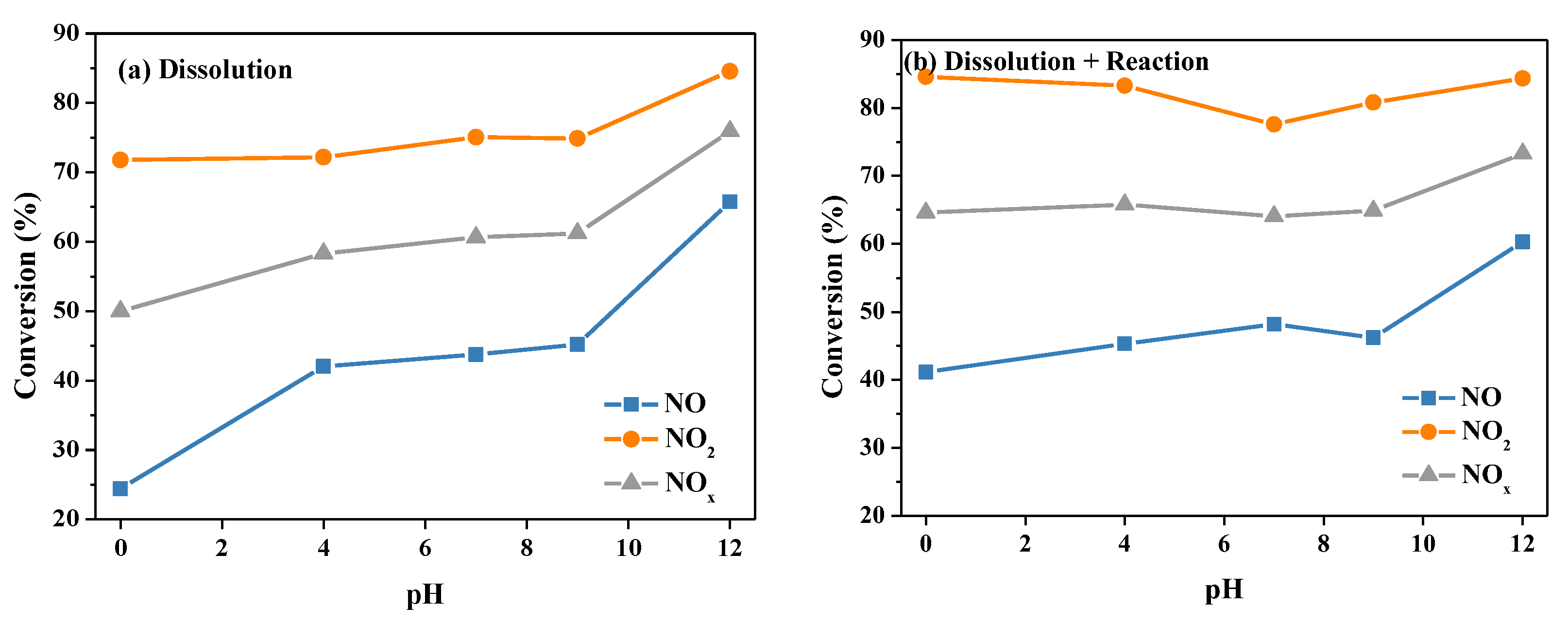
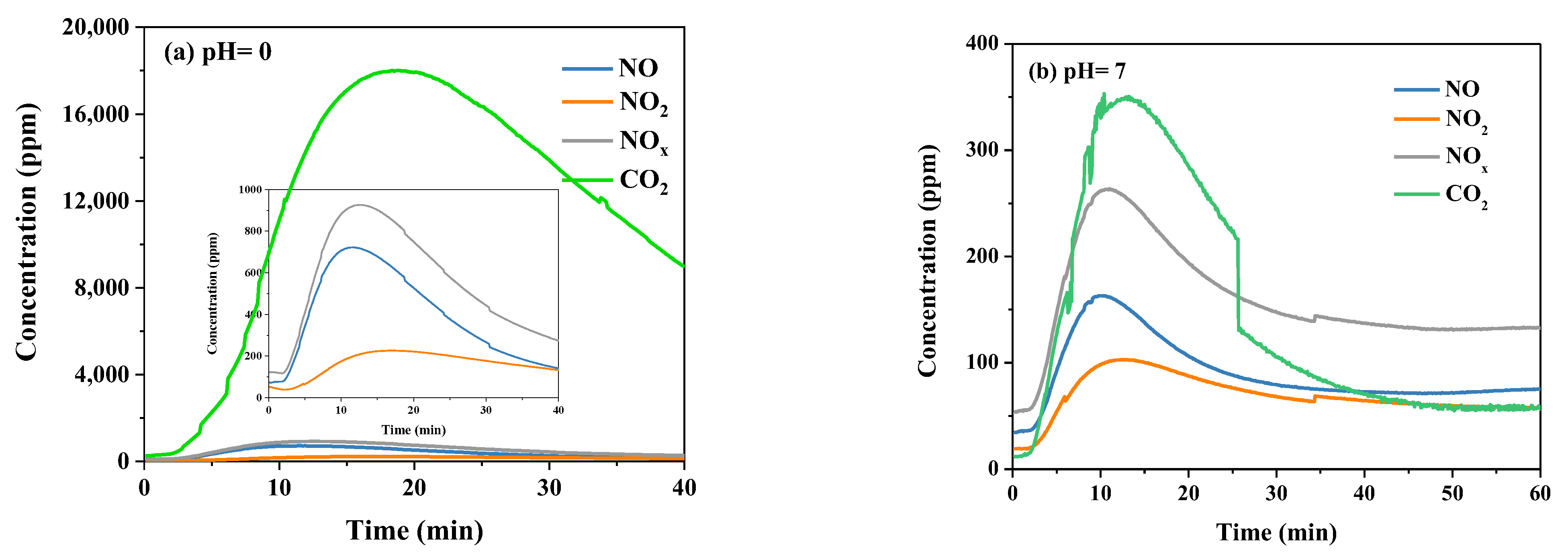

| Sample | NH4+ (mg/L) | NO2− (mg/L) | NO3− (mg/L) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34% | 5.80 | 12.35 | 1.13 | 6.29 |
| 42% | 13.74 | 20.10 | 7.10 | 5.65 |
| 50% | 11.10 | 4.14 | -- | 5.82 |
| 70% | 8.04 | 13.94 | 6.85 | 5.49 |
| 95% | 10.38 | 10.92 | 6.25 | 6.09 |
| Sample | Dissolution | Dissolution + Reaction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh Solution | Used Solution | Fresh Solution | Used Solution | |
| 0 | −0.38 | −0.33 | 0.10 | 0.11 |
| 4 | 2.06 | 1.99 | 3.09 | 2.98 |
| 7 | 5.24 | 2.87 | 7.43 | 6.66 |
| 9 | 10.08 | 2.97 | 8.20 | 7.25 |
| 12 | 12.79 | 12.09 | 12.93 | 12.68 |
| Sample | Dissolution | Dissolution + Reaction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO2− | NO3− | NO2− | NO3− | NH4+ | |
| 4 | 3.44 | 43.24 | 2.58 | 8.28 | 43.8 |
| 7 | 3.70 | 24.01 | 14.81 | 8.42 | 22.6 |
| 9 | 6.72 | 46.65 | 18.36 | 10.24 | 13.2 |
| 12 | 69.34 | 10.66 | 23.92 | 4.13 | 1.2 |
| Sample | NH4+ (mg/L) | NO2− (mg/L) | NO3− (mg/L) | SO42− (mg/L) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SO2 0 | 22.6 | 14.81 | 8.42 | -- | 6.66 |
| SO2 250 ppm | 32.2 | 18.13 | 22.28 | 16.76 | 5.49 |
| SO2 600 ppm | 31.3 | 15.32 | 26.85 | 33.82 | 5.29 |
| SO2 1000 ppm | 38.3 | -- | 46.02 | 53.47 | 3.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gan, L.; Liu, Y.; Ye, P.; Niu, H.; Li, K. Reaction Mechanism for the Removal of NOx by Wet Scrubbing Using Urea Solution: Determination of Main and Side Reaction Paths. Molecules 2023, 28, 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010162
Gan L, Liu Y, Ye P, Niu H, Li K. Reaction Mechanism for the Removal of NOx by Wet Scrubbing Using Urea Solution: Determination of Main and Side Reaction Paths. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010162
Chicago/Turabian StyleGan, Lina, Yang Liu, Peng Ye, Hejingying Niu, and Kezhi Li. 2023. "Reaction Mechanism for the Removal of NOx by Wet Scrubbing Using Urea Solution: Determination of Main and Side Reaction Paths" Molecules 28, no. 1: 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010162
APA StyleGan, L., Liu, Y., Ye, P., Niu, H., & Li, K. (2023). Reaction Mechanism for the Removal of NOx by Wet Scrubbing Using Urea Solution: Determination of Main and Side Reaction Paths. Molecules, 28(1), 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010162






