Technetium-99m Radiopharmaceuticals for Ideal Myocardial Perfusion Imaging: Lost and Found Opportunities
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (a)
- High myocardial uptake with minimal or absent myocardial redistribution;
- (b)
- High and stable target-to-background ratio with low uptake in the lungs, liver, stomach, and gut during the image acquisition period. In particular, absorption into the liver and lungs should be minimal, so that diagnostic useful images can be obtained within 30 min after injection. The intense absorption of the liver and the subsequent visualization, through radioactive bile, of the gut and stomach makes it difficult to interpret cardiac activity in the lower and left ventricular walls;
- (c)
- High first-pass myocardial extraction fraction and very rapid blood clearance. These are both fundamental characteristics for evaluating the kinetics of entry of the radiopharmaceutical into the myocyte and the relative removal from the bloodstream. A low extraction fraction of the first passage often leads to an inaccurate determination of blood flow characteristics;
- (d)
- A linear relationship between radiotracer myocardial uptake and coronary blood flow.
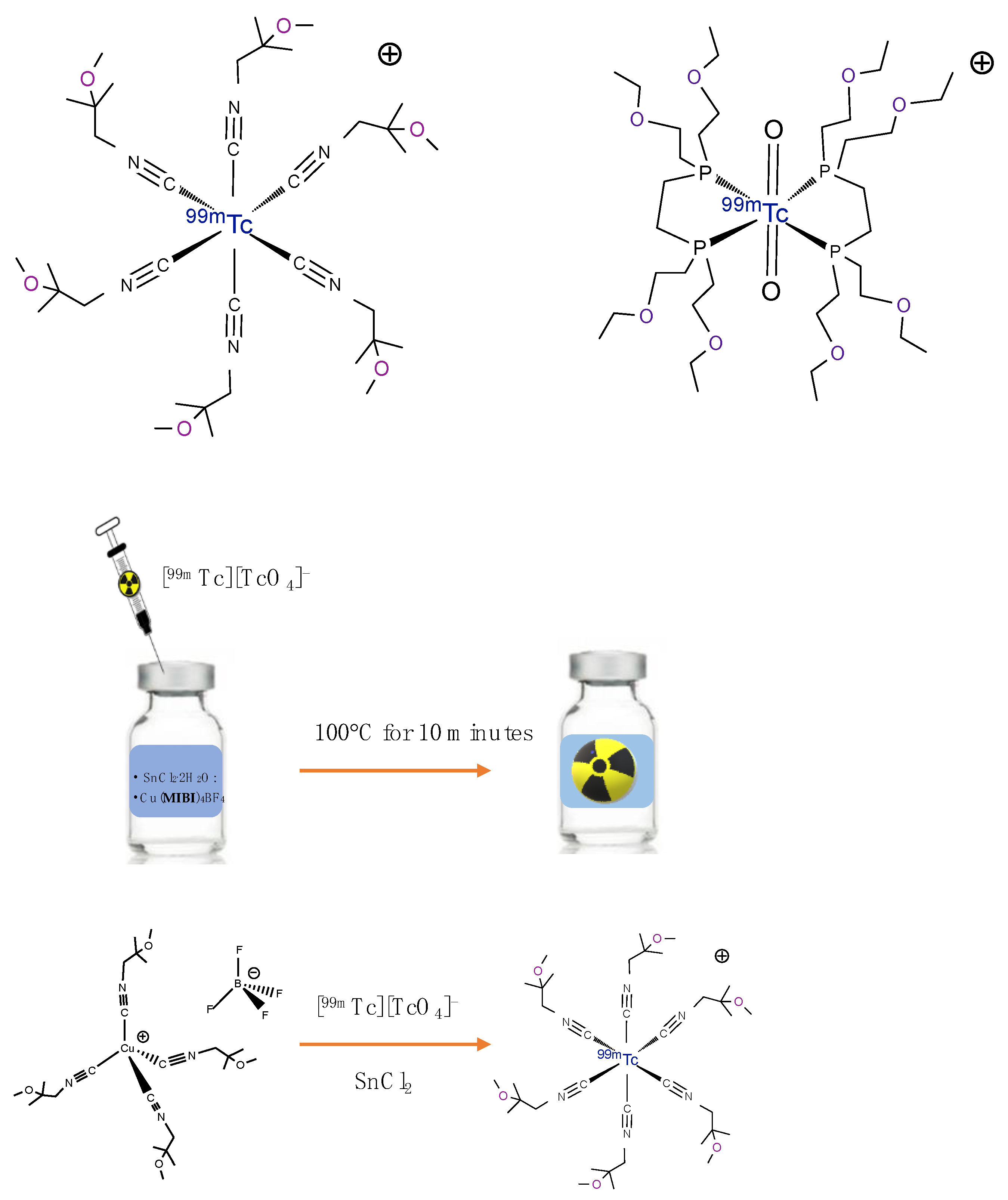
2. Technetium-99m Radiopharmaceuticals for MPI in Clinical Use
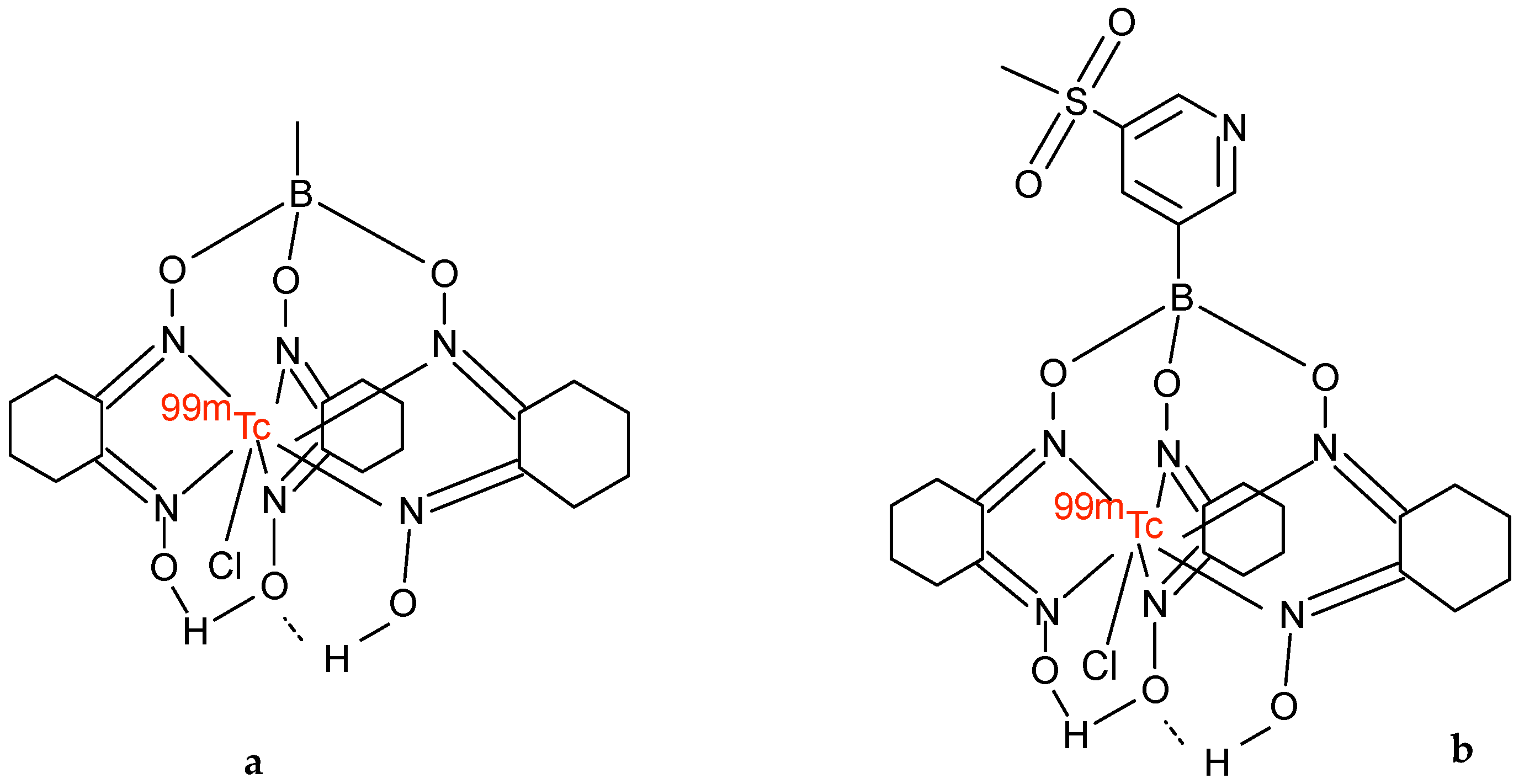
3. Technetium-99m Teboroxime
4. Technetium-99m Radiopharmaceuticals for MPI Based on the Nitride Core
4.1. [99mTc][TcN(NOEt)2]
4.2. [99mTc]TcN-PNP Monocationic Compounds
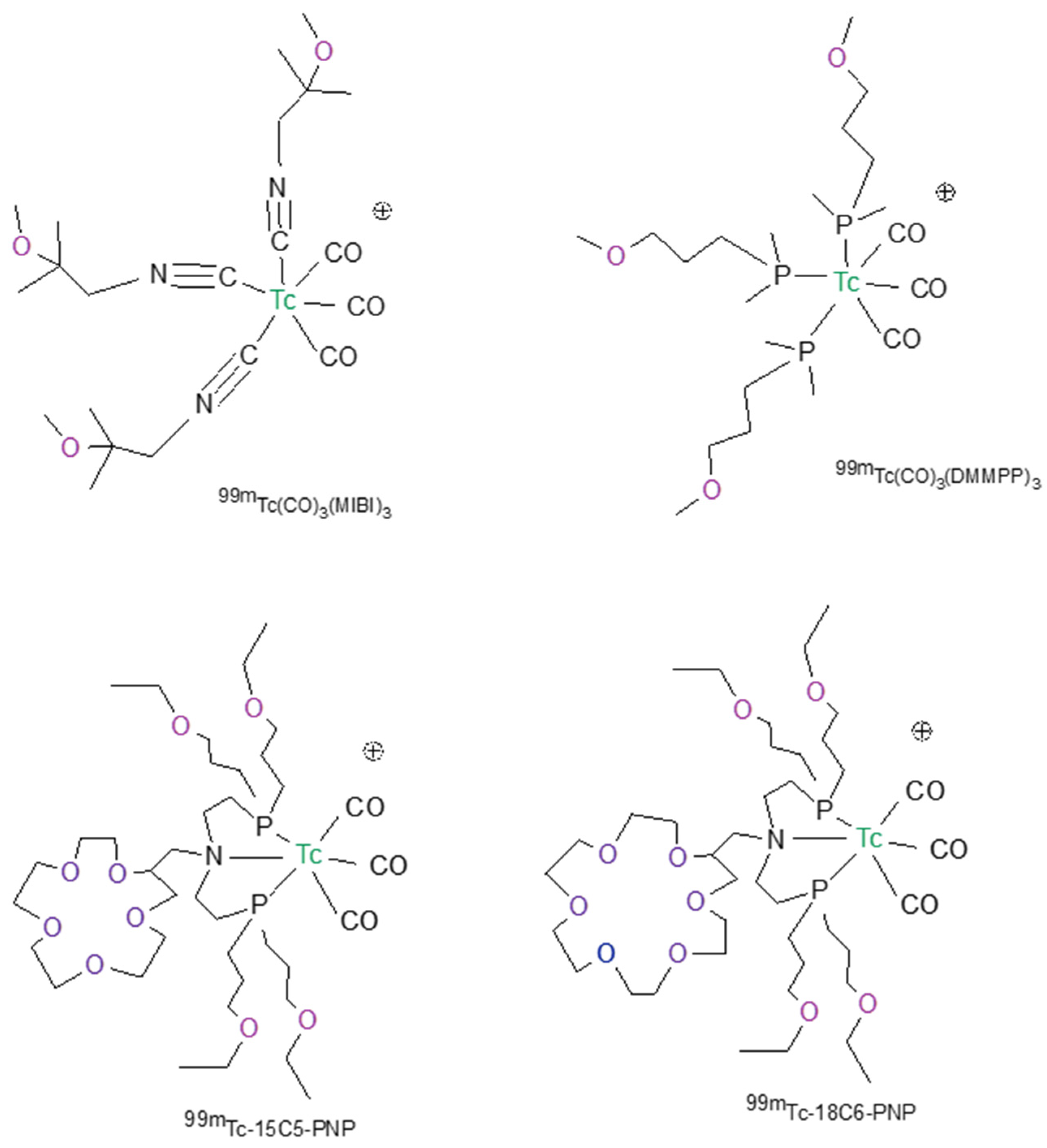
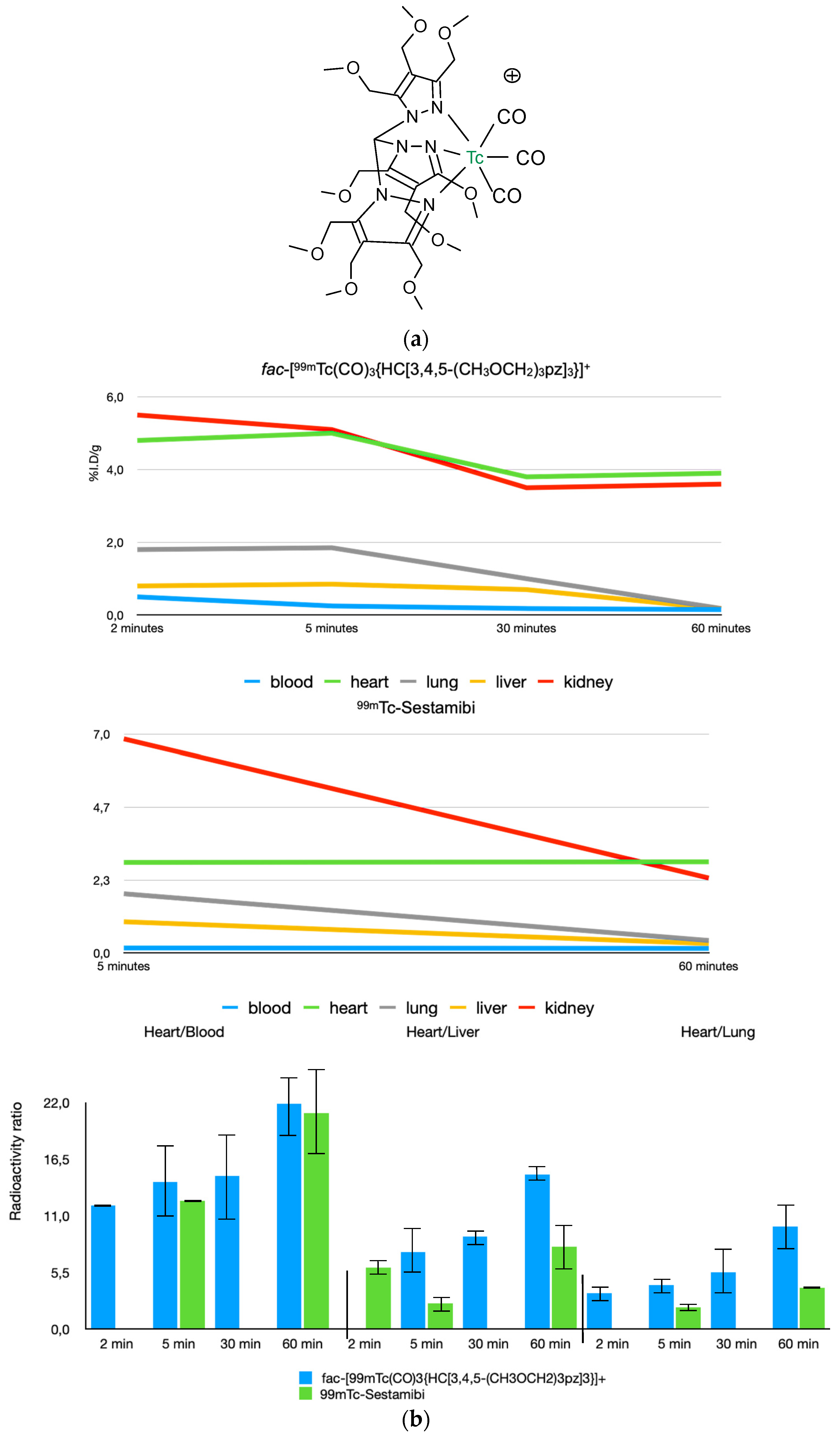
5. Technetium-99m Radiopharmaceutical for MPI Based on the Tris-Carbonyl Core
6. Development and Application of High-Resolution CZT Cameras
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nunn, A.D. Radiopharmaceuticals for Imaging Myocardial Perfusion. Semin. Nucl. Med. 1990, 20, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, G.B.; Go, R.T.; MacIntyre, W.J. Radiopharmaceucticals for Cardiovascular Imaging. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part B Nucl. Med. Biol. 1992, 19, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opie, L.H.; Hesse, B. Radionuclide Tracers in the Evaluation of Resting Myocardial Ischaemia and Viability. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 1997, 24, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, D.S.; Germano, G.; Shaw, L.J. The Role of Nuclear Cardiology in Clinical Decision Making. Semin. Nucl. Med. 1999, 29, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, D. Technetium-99m Labeled Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Agents. Semin. Nucl. Med. 1999, 29, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acampa, W.; Di Benedetto, C.; Cuocolo, A. An Overview of Radiotracers in Nuclear Cardiology. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2000, 335, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilsizian, V. The Role of Myocardial Perfusion Imaging in Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2000, 7, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.A. Cardiac Nuclear Medicine in Monitoring Patients with Coronary Heart Disease. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2001, 31, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanoudy, H.; Raggi, P.; Beller, G.A.; Soliman, A.; Ammermann, E.G.; Kastner, R.J.; Watson, D.D. Comparison of Technetium-99m Tetrofosmin and Thallium-201 Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomographic Imaging for Detection of Myocardial Perfusion Defects in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1998, 31, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, A.; Latus, K.A.; Davies, G.; Dhawan, R.T.; Eastick, S.; Jarritt, P.H.; Roussakis, G.; Young, M.C.; Anagnostopoulos, C.; Bomanji, J.; et al. A Comparison of Three Radionuclide Myocardial Perfusion Tracers in Clinical Practice: The ROBUST Study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2002, 29, 1608–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackers, F.J.T.; Sokole, E.B.; Samson, G.; Schoot, J.B.V.D.; Lie, K.I.; Liem, K.L.; Wellens, H.J.J. Value and Limitations of Thallium-201 Scintigraphy in the Acute Phase of Myocardial Infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 1976, 295, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, E.; Glavan, K.A.; Sodd, V.J.; Nishiyama, H.; Ferguson, D.L.; Lukes, S.J. Cationic Tc-99m Complexes as Potential Myocardial Imaging Agents. J. Nucl. Med. 1981, 22, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, E.; Bushong, W.; Glavan, K.A.; Elder, R.C.; Sodd, V.J.; Scholz, K.L.; Fortman, D.L.; Lukes, S.J. Heart Imaging with Cationic Complexes of Technetium. Science 1981, 214, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschi, A.; Uccelli, L.; Martini, P. A Picture of Modern Tc-99m Radiopharmaceuticals: Production, Chemistry, and Applications in Molecular Imaging. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Ambikalmajan Pillai, M.R.; Ramamoorthy, N. Evolution of Tc-99m in Diagnostic Radiopharmaceuticals. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2001, 31, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuocolo, A.; Cittanti, C.; Acampa, W.; Larobina, M.; Petretta, M. Current and Future Status of Blood Flow Tracers. Curr. Cardiovasc. Imaging Rep. 2011, 4, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadafora, M.; Cuocolo, A.; Golia, R.; de RiminI, M.L.; Rosato, G.; Rizzo, V.; Sullo, P.; Florimonte, L.; Mansi, L.; Miletto, P. Effect of Trimetazidine on 99Tcm-Tetrofosmin Uptake in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2000, 21, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackers, F.J.T.; Berman, D.S.; Maddahi, J.; Watson, D.D.; Beller, G.A.; Strauss, H.W.; Boucher, C.A.; Picard, M.; Holman, B.L.; Fridrich, R.; et al. Technetium-99m Hexakis 2-Methoxyisobutyl Isonitrile: Human Biodistribution, Dosimetry, Safety, and Preliminary Comparison to Thallium-201 for Myocardial Perfusion Imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 1989, 30, 301–311. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, D.; Wackers, F.J.T.; Mattera, J.; McMahon, M.; Sinusas, A.J.; Zaret, B.L. Biokinetics of Technetium-99m-Tetrofosmin: Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Agent: Implications for a One-Day Imaging Protocol. J. Nucl. Med. 1993, 34, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar]
- Higley, B.; Smith, F.W.; Smith, T.; Gemmell, H.G.; Gupta, P.D.; Gvozdanovic, D.V.; Graham, D.; Hinge, D.; Davidson, J.; Lahiri, A. Technetium-99m-1, 2-Bis [Bis (2-Ethoxyethyl) Phosphino] Ethane: Human Biodistribution, Dosimetry and Safety of a New Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Agent. J. Nucl. Med. 1993, 34, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S.; Hendel, R.C. Technetium-99m Tetrofosmin: A New Myocardial Perfusion Agent. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 1993, 21, 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Narra, R.K.; Feld, T.; Nunn, A.D. Absorbed Radiation Dose to Humans from Technetium-99m-Teboroxime. J. Nucl. Med. 1992, 33, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pieri, P.L.; Strauss, H.W. Advances in Myocardial Perfusion Imaging: 99mTc-Teboroxime. J. Nucl. Biol. Med. 1992, 36, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taillefer, R.; Lambert, R.; Essiambre, R.; Phaneuf, D.C.; Léveillé, J. Comparison between Thallium-201, Technetium-99m-Sestamibi and Technetium-99m-Teboroxime Planar Myocardial Perfusion Imaging in Detection of Coronary Artery Disease. J. Nucl. Med. 1992, 33, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, H.; Dahlberg, S.T.; McSherry, B.A.; Hendel, R.C.; Leppo, J.A. Rapid Redistribution of Teboroxime. Am. J. Cardiol. 1993, 71, 848–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlberg, S.T.; Gilmore, M.P.; Leppo, J.A. Interaction of Technetium 99m-Labeled Teboroxime with Red Blood Cells Reduces the Compound’s Extraction and Increases Apparent Cardiac Washout. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 1994, 1, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narra, R.K.; Nunn, A.D.; Kuczynski, B.L.; Feld, T.; Wedeking, P.; Eckelman, W.C. A Neutral Technetium-99m Complex for Myocardial Imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 1989, 30, 1830–1837. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, X.-Y.; Wang, L.; Hsu, B.; Zhao, Z.-Q.; Liu, S.; Fang, W. 99mTc-3SPboroxime: A Neutral 99mTc(III) Radiotracer with High Heart Uptake and Long Myocardial Retention. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2021, 28, 2687–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-Q.; Liu, M.; Fang, W.; Liu, S. Sulfonyl-Containing Boronate Caps for Optimization of Biological Properties of 99m Tc(III) Radiotracers [99m TcCl(CDO)(CDOH) 2 B-R] (CDOH 2 = Cyclohexanedione Dioxime). J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, S. 99m Tc-3Cboroxime: A Novel 99m Tc(iii) Complex [99m TcCl(CDO)(CDOH) 2 B-3C] (CDOH 2 = Cyclohexanedione Dioxime; 3C-B(OH) 2 = 3-(Carbamoylphenyl)Boronic Acid) with High Heart Uptake and Long Myocardial Retention. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 14509–14518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualini, R.; Duatti, A.; Bellande, E.; Comazzi, V.; Brucato, V.; Hoffschir, D.; Fagret, D.; Comet, M. Bis (Dithiocarbamato) Nitrido Technetium-99m Radiopharmaceuticals: A Class of Neutral Myocardial Imaging Agents. J. Nucl. Med. 1994, 35, 334–341. [Google Scholar]
- Duatti, A.; Boschi, A.; Uccelli, L. Technetium-99m Nitrido Radiopharmaceuticals with Unprecedented Biological Properties. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2002, 45, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vanzetto, G.; Fagret, D.; Pasqualini, R.; Mathieu, J.P.; Chossat, F.; Machecourt, J. Biodistribution, Dosimetry, and Safety of Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Agent 99mTcN-NOET in Healthy Volunteers. J. Nucl. Med. 2000, 41, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calnon, D.A.; Ruiz, M.; Vanzetto, G.; Watson, D.D.; Beller, G.A.; Glover, D.K. Myocardial Uptake of 99m Tc-N-NOET and 201 Tl During Dobutamine Infusion. Circulation 1999, 100, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi, C.; Fagret, D.; Arvieux, C.C.; Mathieu, J.-P.; Bontron, R.; Pasqualini, R.; de Leiris, J.; Comet, M. Myocardial Kinetics of TcN-NOET: A Neutral Lipophilic Complex Tracer of Regional Myocardial Blood Flow. J. Nucl. Med. 1995, 36, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Riou, L.; Ghezzi, C.; Pasqualini, R.; Fagret, D. Influence of Calcium Channel Inhibitors on the Myocardial Uptake and Retention of Technetium 99m N-NOET, a New Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Agent: A Study on Isolated Perfused Rat Hearts. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2000, 7, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagret, D.; Ghezzi, C.; Vanzetto, G. 99mTc-N-NOET Imaging for Myocardial Perfusion: Can It Offer More Than We Already Have? J. Nucl. Med. 2001, 42, 1395–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Bolzati, C.; Refosco, F.; Cagnolini, A.; Tisato, F.; Boschi, A.; Duatti, A.; Uccelli, L.; Dolmella, A.; Marotta, E.; Tubaro, M. Synthesis, Solution-State and Solid-State Structural Characterization of Monocationic Nitrido Heterocomplexes [M(N)(DTC)(PNP)] + (M = 99 Tc, Re; DTC = Dithiocarbamate; PNP = Heterodiphosphane). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 2004, 1902–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzati, C.; Boschi, A.; Uccelli, L.; Tisato, F.; Refosco, F.; Cagnolini, A.; Duatti, A.; Prakash, S.; Bandoli, G.; Vittadini, A. Chemistry of the Strong Electrophilic Metal Fragment [99 Tc(N)(PXP)] 2+ (PXP = Diphosphine Ligand). A Novel Tool for the Selective Labeling of Small Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 11468–11479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boschi, A.; Bolzati, C.; Uccelli, L.; Duatti, A.; Benini, E.; Refosco, F.; Tisato, F.; Piffanelli, A. A Class of Asymmetrical Nitrido 99mTc Heterocomplexes as Heart Imaging Agents with Improved Biological Properties. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2002, 23, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boschi, A.; Uccelli, L.; Bolzati, C.; Duatti, A.; Sabba, N.; Moretti, E.; di Domenico, G.; Zavattini, G.; Refosco, F.; Giganti, M. Synthesis and Biologic Evaluation of Monocationic Asymmetric 99mTc-Nitride Heterocomplexes Showing High Heart Uptake and Improved Imaging Properties. J. Nucl. Med. 2003, 44, 806–814. [Google Scholar]
- Hatada, K.; Ruiz, M.; Riou, L.; Lima, R.; Goode, A.; Watson, D.; Beller, G.; Glover, D. Organ Biodistribution and Myocardial Uptake, Washout, and Redistribution Kinetics of Tc-99m N-DBODC5 When Injected during Vasodilator Stress in Canine Models of Coronary Stenoses. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2006, 13, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolzati, C.; Cavazza-Ceccato, M.; Agostini, S.; Refosco, F.; Yamamichi, Y.; Tokunaga, S.; Carta, D.; Salvarese, N.; Bernardini, D.; Bandoli, G. Biological in Vitro and in Vivo Studies of a Series of New Asymmetrical Cationic [99m Tc(N)(DTC-Ln)(PNP)] + Complex (DTC-Ln = Alicyclic Dithiocarbamate and PNP = Diphosphinoamine). Bioconjugate Chem. 2010, 21, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvarese, N.; Carta, D.; Marzano, C.; Gerardi, G.; Melendez-Alafort, L.; Bolzati, C. [99m Tc][Tc(N)(DASD)(PNP n)] + (DASD = 1,4-Dioxa-8-Azaspiro[4,5]Decandithiocarbamate, PNP n = Bisphosphinoamine) for Myocardial Imaging: Synthesis, Pharmacological and Pharmacokinetic Studies. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 11114–11126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. Ether and Crown Ether-Containing Cationic 99mTc Complexes Useful as Radiopharmaceuticals for Heart Imaging. Dalton Trans. 2007, 12, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; He, Z.; Hsieh, W.-Y.; Kim, Y.-S. Evaluation of Novel Cationic 99mTc-Nitrido Complexes as Radiopharmaceuticals for Heart Imaging: Improving Liver Clearance with Crown Ether Groups. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2006, 33, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Kim, Y.-S.; Liu, S.; He, Z.-X. Evaluation of 99mTcN-15C5 as a New Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Agent in Normal Dogs and Canines with Coronary Stenosis. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2008, 29, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Wang, J.; Broisat, A.; Glover, D.; Liu, S. Tc-99m-N-MPO: Novel Cationic Tc-99m Radiotracer for Myocardial Perfusion Imaging. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2008, 15, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beller, G. Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Agents: SPECT and PET. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2004, 11, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzati, C.; Carta, D.; Gandin, V.; Marzano, C.; Morellato, N.; Salvarese, N.; Cantore, M.; Colabufo, N.A. 99mTc(N)-DBODC(5), a Potential Radiolabeled Probe for SPECT of Multidrug Resistance: In Vitro Study. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 18, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzati, C.; Cavazza-Ceccato, M.; Agostini, S.; Tokunaga, S.; Casara, D.; Bandoli, G. Subcellular Distribution and Metabolism Studies of the Potential Myocardial Imaging Agent [99m Tc(N)(DBODC)(PNP5)]+. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanzetto, G.; Glover, D.K.; Ruiz, M.; Calnon, D.A.; Pasqualini, R.; Watson, D.D.; Beller, G.A. 99m Tc-N-NOET Myocardial Uptake Reflects Myocardial Blood Flow and Not Viability in Dogs with Reperfused Acute Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 2000, 101, 2424–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cittanti, C.; Uccelli, L.; Pasquali, M.; Boschi, A.; Flammia, C.; Bagatin, E.; Casali, M.; Stabin, M.G.; Feggi, L.; Giganti, M.; et al. Whole-Body Biodistribution and Radiation Dosimetry of the New Cardiac Tracer 99m Tc-N-DBODC. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubiger, P.A.; Grünberg, J.; Ametamey, S.M.; Honer, M.; Garcia-Garayoa, E.; Bläuenstein, P.; Waibel, R.; Novak-Hofer, I.; Schibli, R. Radiopharmaceuticals: From Molecular Imaging to Targeted Radionuclide Therapy. CHIMIA Int. J. Chem. 2004, 58, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schibli, R.; Schubiger, A. Current Use and Future Potential of Organometallic Radiopharmaceuticals. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2002, 29, 1529–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schibli, R.; la Bella, R.; Alberto, R.; Garcia-Garayoa, E.; Ortner, K.; Abram, U.; Schubiger, P.A. Influence of the Denticity of Ligand Systems on the In Vitro and In Vivo Behavior of 99m Tc(I)−Tricarbonyl Complexes: A Hint for the Future Functionalization of Biomolecules. Bioconjug. Chem. 2000, 11, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Wang, F.; Liu, S. Minimizing Liver Uptake of Cationic 99mTc Radiotracers with Ether and Crown Ether Functional Groups. World J. Hepatol. 2010, 2, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Hsieh, W.-Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; Liu, S. Evaluation of Novel Cationic 99mTc(I)–Tricarbonyl Complexes as Potential Radiotracers for Myocardial Perfusion Imaging. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2006, 33, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, L.; Fernandes, C.; Garcia, R.; Gano, L.; Paulo, A.; Santos, I.C.; Santos, I. Tris(Pyrazolyl)Methane 99m Tc Tricarbonyl Complexes for Myocardial Imaging. Dalton Trans. 2009, 4, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharir, T.; Slomka, P.J.; Berman, D.S. Solid-State SPECT Technology: Fast and Furious. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2010, 17, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenaar, D.J.; Parnham, K.; Sundal, B.; Maehlum, G.; Chowdhury, S.; Meier, D.; Vandehei, T.; Szawlowski, M.; Patt, B.E. Advantages of Semiconductor CZT for Medical Imaging. In Proceedings of the Penetrating Radiation Systems and Applications VIII, San Diego, CA, USA, 29–30 August 2007; Volume 6707, p. 67070I. [Google Scholar]
- Zavadovsky, K.V.; Mochula, A.V.; Maltseva, A.N.; Shipulin, V.V.; Sazonova, S.I.; Gulya, M.O.; Liga, R.; Gimelli, A. The Current Status of CZT SPECT Myocardial Blood Flow and Reserve Assessment: Tips and Tricks. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slomka, P.J.; Miller, R.J.H.; Hu, L.-H.; Germano, G.; Berman, D.S. Solid-State Detector SPECT Myocardial Perfusion Imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1194–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon DePuey, E. Advances in Cardiac Processing Software. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2014, 44, 252–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorbala, S.; Ananthasubramaniam, K.; Armstrong, I.S.; Chareonthaitawee, P.; De Puey, E.G.; Einstein, A.J.; Gropler, R.J.; Holly, T.A.; Mahmarian, J.J.; Park, M.-A.; et al. Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Guidelines: Instrumentation, Acquisition, Processing, and Interpretation. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2018, 25, 1784–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.W. Recent Advances in Nuclear Cardiology. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 50, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kovalski, G.; Sharir, T.; Lee, D.S. Advances in Imaging Instrumentation for Nuclear Cardiology. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomka, P.J.; Berman, D.S.; Germano, G. New Cardiac Cameras: Single-Photon Emission CT and PET. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2014, 44, 232–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| [99mTc]Tc-Sestamibi | [99mTc]Tc-Tetrofosmin | [99mTc]Tc-Teboroxime | [99mTc]Tc-3SPboroxime | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical characteristics | cationic | cationic | neutral | neutral |
| Kit formulation | available | available | available | available |
| Myocardial uptake at rest (%) | 1 | 1.2 | 3–4 * | 4–5 |
| Heart/to liver ratio 15–20 min post-injection at rest | 0.5 | 0.8 | negligible | 0.8 |
| First pass extraction (%) | 65 | 54 | 88 | - |
| Redistribution | negligible | none | significant | - |
| Excretion | hepatobiliary | renal and hepatobiliary | hepatobiliary and renal |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boschi, A.; Uccelli, L.; Marvelli, L.; Cittanti, C.; Giganti, M.; Martini, P. Technetium-99m Radiopharmaceuticals for Ideal Myocardial Perfusion Imaging: Lost and Found Opportunities. Molecules 2022, 27, 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041188
Boschi A, Uccelli L, Marvelli L, Cittanti C, Giganti M, Martini P. Technetium-99m Radiopharmaceuticals for Ideal Myocardial Perfusion Imaging: Lost and Found Opportunities. Molecules. 2022; 27(4):1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041188
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoschi, Alessandra, Licia Uccelli, Lorenza Marvelli, Corrado Cittanti, Melchiore Giganti, and Petra Martini. 2022. "Technetium-99m Radiopharmaceuticals for Ideal Myocardial Perfusion Imaging: Lost and Found Opportunities" Molecules 27, no. 4: 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041188
APA StyleBoschi, A., Uccelli, L., Marvelli, L., Cittanti, C., Giganti, M., & Martini, P. (2022). Technetium-99m Radiopharmaceuticals for Ideal Myocardial Perfusion Imaging: Lost and Found Opportunities. Molecules, 27(4), 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041188









