Vortex Fluidic Mediated Oxidative Sulfitolysis of Oxytocin
Abstract
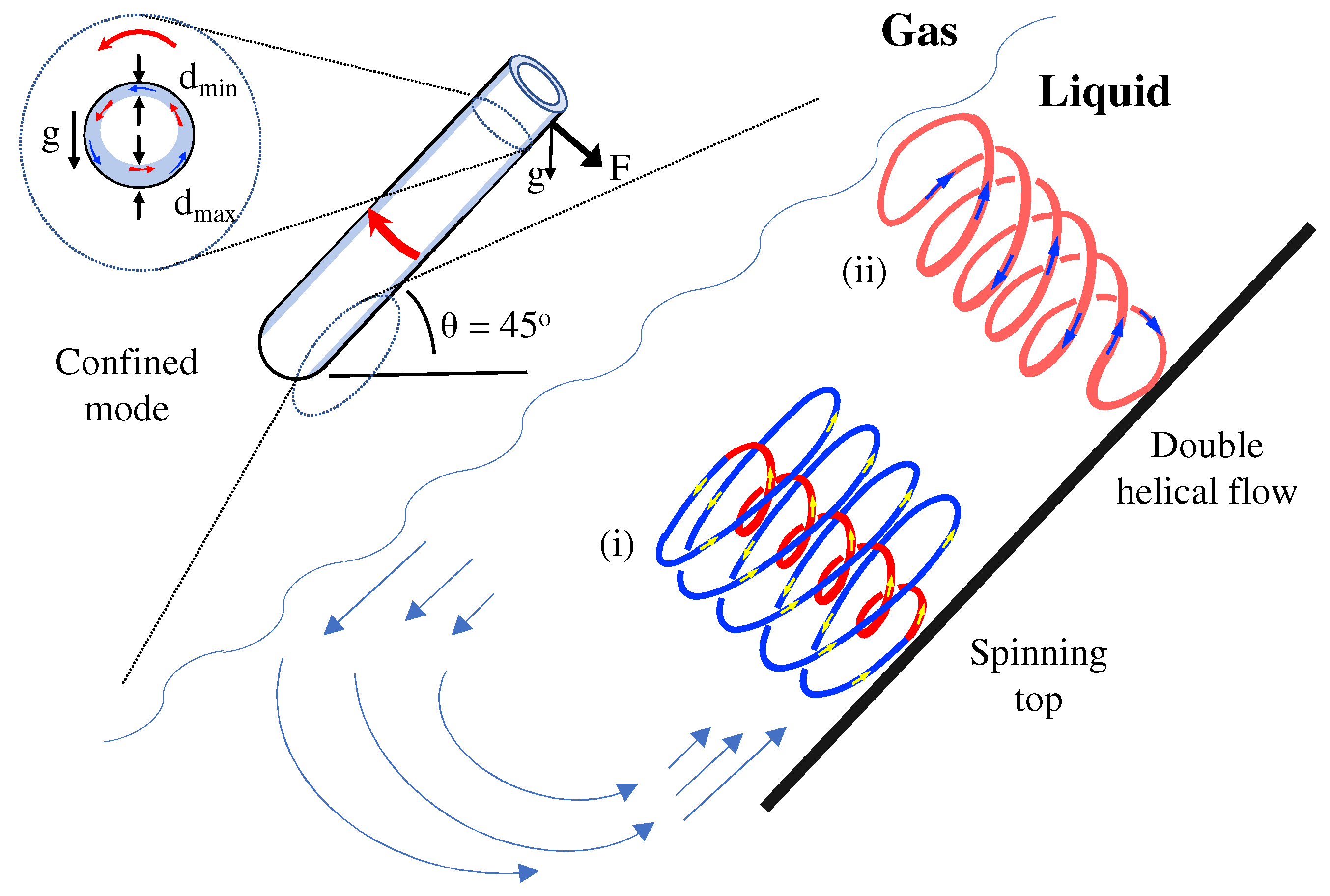
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
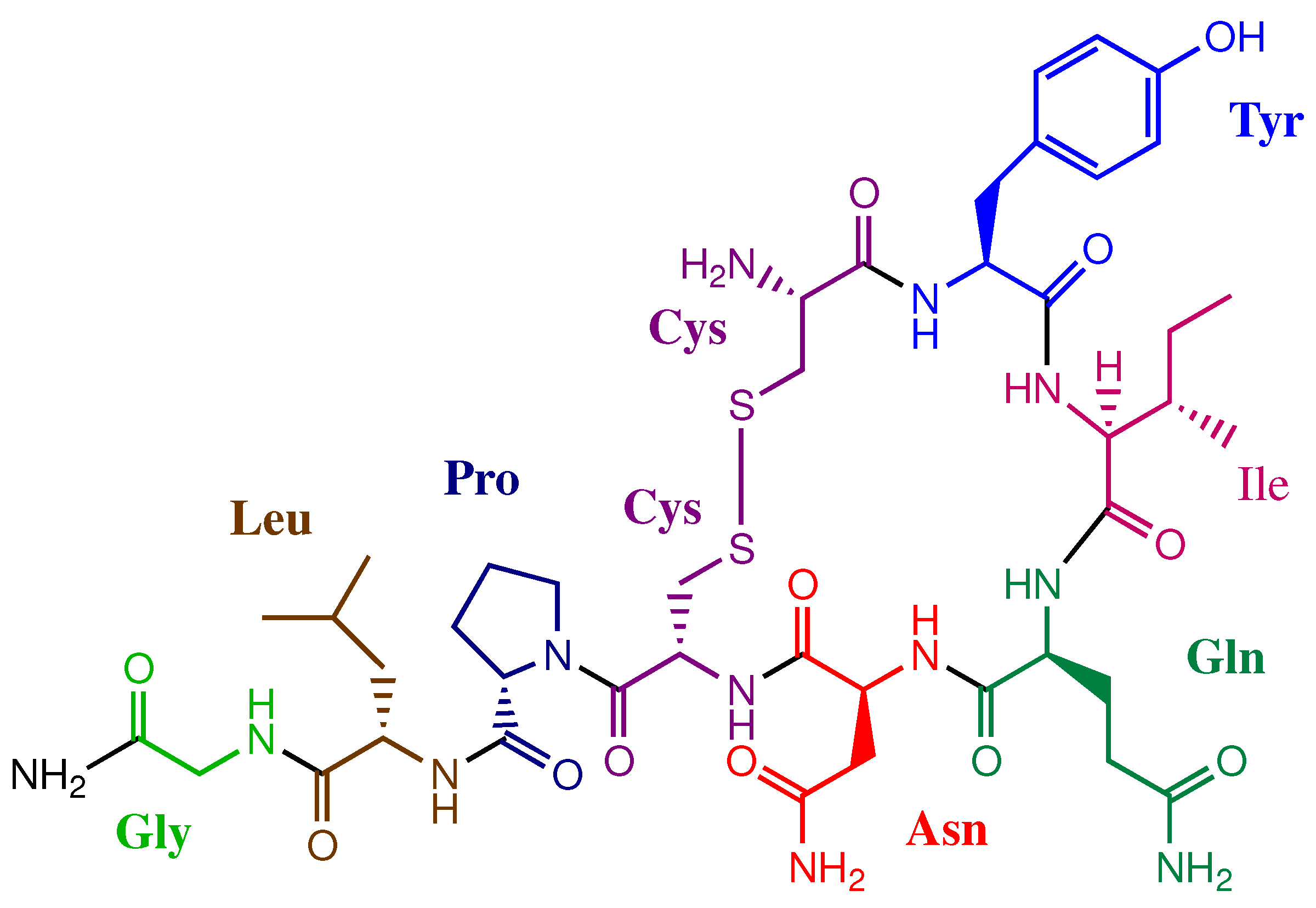
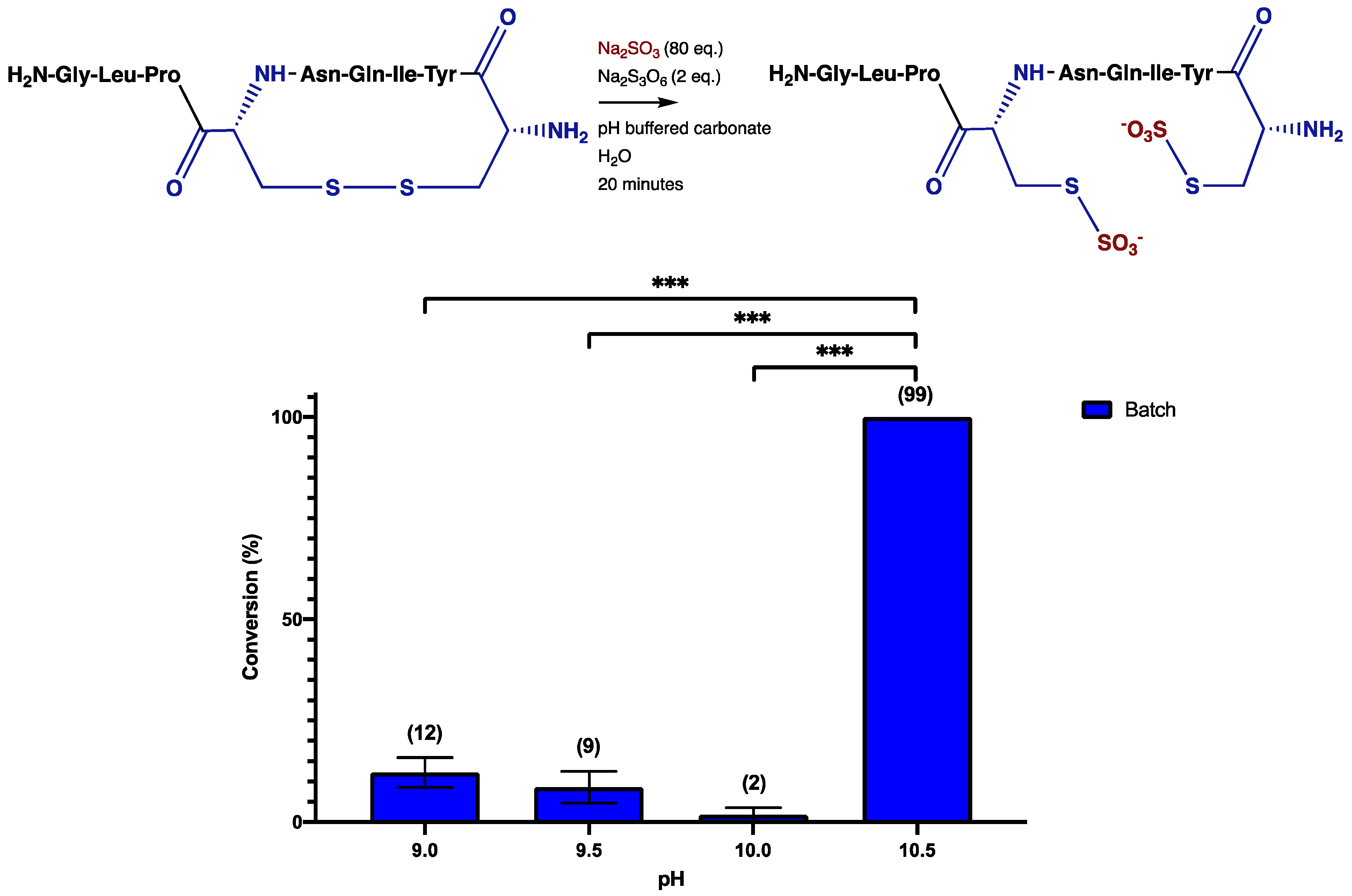
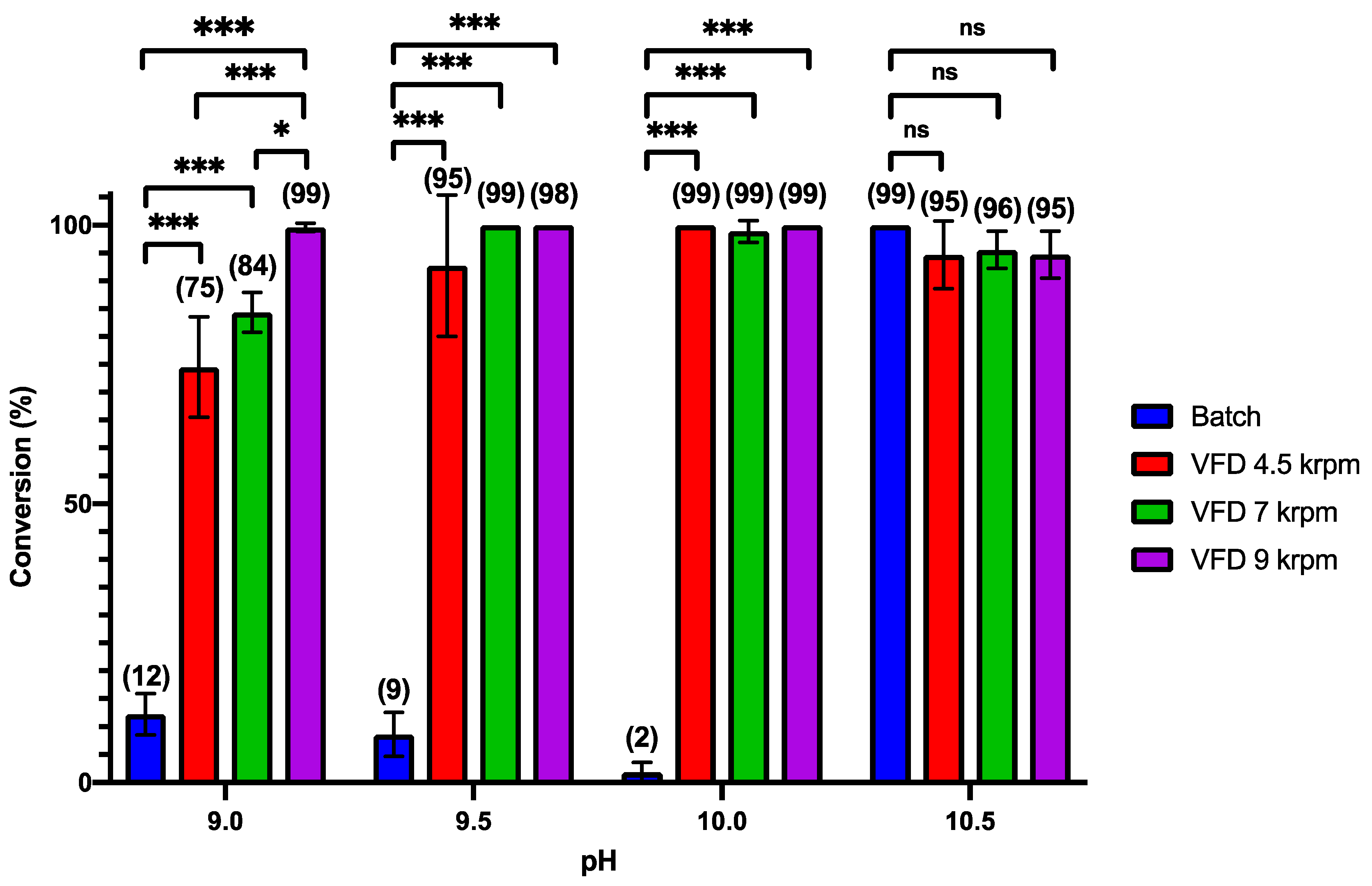
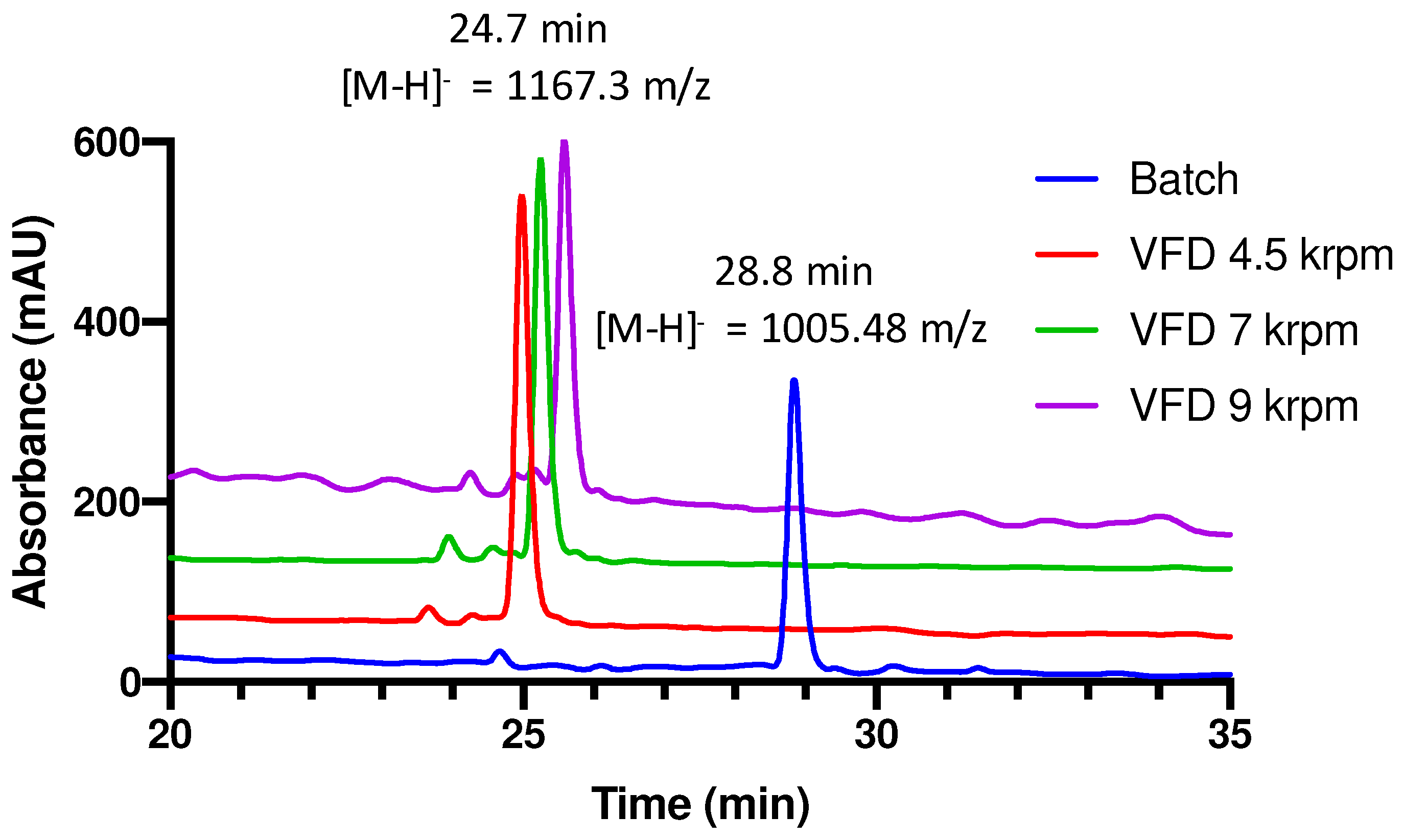
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cowley, D.J.; Mackin, R.B. Expression, purification and characterization of recombinant human proinsulin. FEBS Lett. 1997, 402, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, W.W.C. Complete S-sulfonation of cysteine residues in proteins. Biochemistry 1968, 7, 4247–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weil-Ktorza, O.; Rege, N.; Lansky, S.; Shalev, D.E.; Shoham, G.; Weiss, M.A.; Metanis, N. Substitution of an Internal Disulfide Bridge with a Diselenide Enhances both Foldability and Stability of Human Insulin. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 8513–8521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Jiang, Q.; Song, G.; Liu, Y.-L.; Xu, Z.-G.; Guo, Z.-Y. Efficient oxidative folding and site-specific labeling of human hepcidin to study its interaction with receptor ferroportin. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 3166–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Q.-x.; Chu, Y.-C.; Jia, W.; Phillips, N.F.; Wang, R.-y.; Katsoyannis, P.G.; Weiss, M.A. Mechanism of Insulin Chain Combination asymmetric roles of a-chain α-helices in disulfide pairing. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 43443–43453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, J.L.; Cole, R.D. Studies on the Reaction of Sulfite with Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1959, 234, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, J.M. Thiols, Disulphides and Thiosulphates: Some New Reactions and Possibilities in Peptide and Protein Chemistry. Nature 1957, 180, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kella, N.K.D.; Kinsella, J.E. A method for the controlled cleavage of disulfide bonds in proteins in the absence of denaturants. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 1985, 11, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhelj, R.; Dolinar, M.; Pungerčar, J.; Turk, V. The Preparation of Catalytically Active Human Cathepsin B from Its Precursor Expressed in Escherichia coli in the Form of Inclusion Bodies. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 229, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, R.V.; Pechenov, S.E.; Belacheu, I.A.; Yakimov, S.A.; Klyushnichenko, V.E.; Boldireva, E.F.; Korobko, V.G.; Tunes, H.; Thiemann, J.E.; Vilela, L.; et al. Recombinant Human Insulin: VIII. Isolation of Fusion Protein–S-Sulfonate, Biotechnological Precursor of Human Insulin, from the Biomass of Transformed Escherichia coli Cells. Protein Expr. Purif. 2001, 21, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBella, E.E.; Maurer, M.C.; Scheraga, H.A. Expression and Folding of Recombinant Bovine Prethrombin-2 and Its Activation to Thrombin. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Bernardez Clark, E. Refolding of recombinant proteins. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1998, 9, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobbitt, J.L.; Manetta, J. Purification and Refolding of Recombinant Proteins. U.S. Patent US4923967A, 8 May 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Patrick, J.S.; Lagu, A.L. Determination of recombinant human proinsulin fusion protein produced in Escherichia coli using oxidative sulfitolysis and two-dimensional HPLC. Anal. Chem. 1992, 64, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, G.H.; Wardlaw, A.C. Regeneration of Insulin Activity from the Separated and Inactive A and B Chains. Nature 1960, 188, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.S.; Lu, Z.; Tsou, C. Resynthesis of insulin from its glycyl and phenylalanyl chains. Sci. Sin. 1961, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.-K.; Kim, Y.-I.; Pheu, J.-N.; Shin, J.-W.; Oh, S.-J.; Hong, C.-I.; Kim, J.-W.; Lee, W.-S. Process for Preparing Human Proinsulin. U.S. Patent US5952461A, 14 September 1999. [Google Scholar]
- DiMarchi, R.D. Process for Purifying Proinsulin-Like Materials. U.S. Patent US4616078A, 14 September 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Z.-S.; Guo, Z.-Y.; Feng, Y.-M. Putative Disulfide-Forming Pathway of Porcine Insulin Precursor during Its Refolding in Vitro. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 2662–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kroot, J.J.C.; Kemna, E.H.J.M.; Bansal, S.S.; Busbridge, M.; Campostrini, N.; Girelli, D.; Hider, R.C.; Koliaraki, V.; Mamalaki, A.; Olbina, G.; et al. Results of the first international round robin for the quantification of urinary and plasma hepcidin assays: Need for standardization. Haematologica 2009, 94, 1748–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunter, H.N.; Fulton, D.B.; Ganz, T.; Vogel, H.J. The Solution Structure of Human Hepcidin, a Peptide Hormone with Antimicrobial Activity That Is Involved in Iron Uptake and Hereditary Hemochromatosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 37597–37603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esipov, R.S.; Chupova, L.A.; Shvets, S.V.; Chuvikovsky, D.V.; Gurevich, A.I.; Muravyova, T.I.; Miroshnikov, A.I. Production And Purification Of Recombinant Human Oxytocin Overexpressed As A Hybrid Protein In Escherichia Coli. Protein Pept. Lett. 2003, 10, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Macbeth, A.H.; Pagani, J.H.; Scott Young, W. Oxytocin: The great facilitator of life. Prog. Neurobiol. 2009, 88, 127–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- du Vigneaud, V.; Ressler, C.; Trippett, S. The sequence of amino acids in oxytocin, with a proposal for the structure of oxytocin. J. Biol. Chem. 1953, 205, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuppy, H. The amino-acid sequence in oxytocin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1953, 11, 449–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, S.J.; Dalgarno, S.J.; Chalker, J.M.; Raston, C.L. Organic oxidations promoted in vortex driven thin films under continuous flow. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Britton, J.; Chalker, J.M.; Raston, C.L. Rapid Vortex Fluidics: Continuous Flow Synthesis of Amides and Local Anesthetic Lidocaine. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 10660–10665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.Z.; Ormonde, C.F.G.; Kudlacek, S.T.; Kunche, S.; Smith, J.N.; Brown, W.A.; Pugliese, K.M.; Olsen, T.J.; Iftikhar, M.; Raston, C.L.; et al. Shear stress-mediated refolding of proteins from aggregates and inclusion bodies. ChemBioChem 2015, 16, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, J.; Meneghini, L.M.; Raston, C.L.; Weiss, G.A. Accelerating Enzymatic Catalysis Using Vortex Fluidics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 11387–11391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vimalanathan, K.; Gascooke, J.R.; Suarez-Martinez, I.; Marks, N.A.; Kumari, H.; Garvey, C.J.; Atwood, J.L.; Lawrance, W.D.; Raston, C.L. Fluid dynamic lateral slicing of high tensile strength carbon nanotubes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alharbi, T.M.D.; Jellicoe, M.; Luo, X.; Vimalanathan, K.; Alsulami, I.K.; Al Harbi, B.S.; Igder, A.; Alrashaidi, F.A.J.; Chen, X.; Stubbs, K.A.; et al. Sub-micron moulding topological mass transport regimes in angled vortex fluidic flow. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 3064–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerletti, N.; McMaster, G.K.; Cox, D.; Schmitz, A.; Meyhack, B. Process for Refolding Recombinantly Produced TGF-β-Like Proteins. U.S. Patent 5,650,494, 22 July 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Strauss, C.R. A Strategic, Green Approach to Organic Chemistry with Microwave Assistance and Predictive Yield Optimization as Core, Enabling Technologies. Aust. J. Chem. 2009, 62, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vimalanathan, K.; Shrestha, R.G.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, J.; Nakayama, T.; Raston, C.L. Surfactant-free Fabrication of Fullerene C60 Nanotubules Under Shear. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 8398–8401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vimalanathan, K.; Suarez-Martinez, I.; Peiris, M.C.R.; Antonio, J.; de Tomas, C.; Zou, Y.; Zou, J.; Duan, X.; Lamb, R.N.; Harvey, D.P.; et al. Vortex fluidic mediated transformation of graphite into highly conducting graphene scrolls. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 2495–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sitepu, E.K.; Corbin, K.; Luo, X.; Pye, S.J.; Tang, Y.; Leterme, S.C.; Heimann, K.; Raston, C.L.; Zhang, W. Vortex fluidic mediated direct transesterification of wet microalgae biomass to biodiesel. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Al-Antaki, A.H.M.; Harvey, D.P.; Ruan, Y.; He, S.; Zhang, W.; Raston, C.L. Vortex Fluidic Mediated Synthesis of Macroporous Bovine Serum Albumin-Based Microspheres. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 27224–27232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britton, J.; Dalziel, S.B.; Raston, C.L. The synthesis of di-carboxylate esters using continuous flow vortex fluidics. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 2193–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.K.; Lee, S.-B.; Son, Y.-J. Large-Scale Refolding and Enzyme Reaction of Human Preproinsulin for Production of Human Insulin. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 1742–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esipov, R.S.; Stepanenko, V.N.; Chupova, L.A.; Miroshnikov, A.I. Production of Recombinant Oxytocin Through Sulfitolysis of Inteincontaining Fusion Protein. Protein Pept. Lett. 2012, 19, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, T.C.; Epp, J.; Hsiung, H.M.; Hoskins, J.; Long, G.L.; Mendelsohn, L.G.; Schoner, B.; Smith, D.P.; Smith, M.C. Recombinant Human Insulin-Like Growth Factor II Expressed in Escherichia coli. Nat. Biotechnol. 1987, 5, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Protein | Incubation | pH | Time (h) | Temp (°C) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human IGF-II | 7 M Urea 0.1 M Na2SO3 10 mM Na2S4O6 | 8.2 | 3 | RT | [41] |
| Hepcidin | 6 M GuHCl 0.1 M Na2SO3 80 mM Na2S4O6 | 8.5 | O/N | RT | [4] |
| Oxytocin | 8 M Urea 0.4 M Na2SO3 93 mM Na2S4O6 | 9.0 | 4 | 20 | [22,40] |
| Proinsulin | 7 M Urea 0.1 M Na2SO3 10 mM Na2S4O6 | 8.2 | 3 | RT | [1] |
| Proinsulin | 8 M Urea 0.2 M Na2SO3 20 mM Na2S4O6 | 9.5 | 4 | RT | [39] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crawley, E.M.; Pye, S.; Forbes, B.E.; Raston, C.L. Vortex Fluidic Mediated Oxidative Sulfitolysis of Oxytocin. Molecules 2022, 27, 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27031109
Crawley EM, Pye S, Forbes BE, Raston CL. Vortex Fluidic Mediated Oxidative Sulfitolysis of Oxytocin. Molecules. 2022; 27(3):1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27031109
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrawley, Emily M., Scott Pye, Briony E. Forbes, and Colin L. Raston. 2022. "Vortex Fluidic Mediated Oxidative Sulfitolysis of Oxytocin" Molecules 27, no. 3: 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27031109
APA StyleCrawley, E. M., Pye, S., Forbes, B. E., & Raston, C. L. (2022). Vortex Fluidic Mediated Oxidative Sulfitolysis of Oxytocin. Molecules, 27(3), 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27031109








