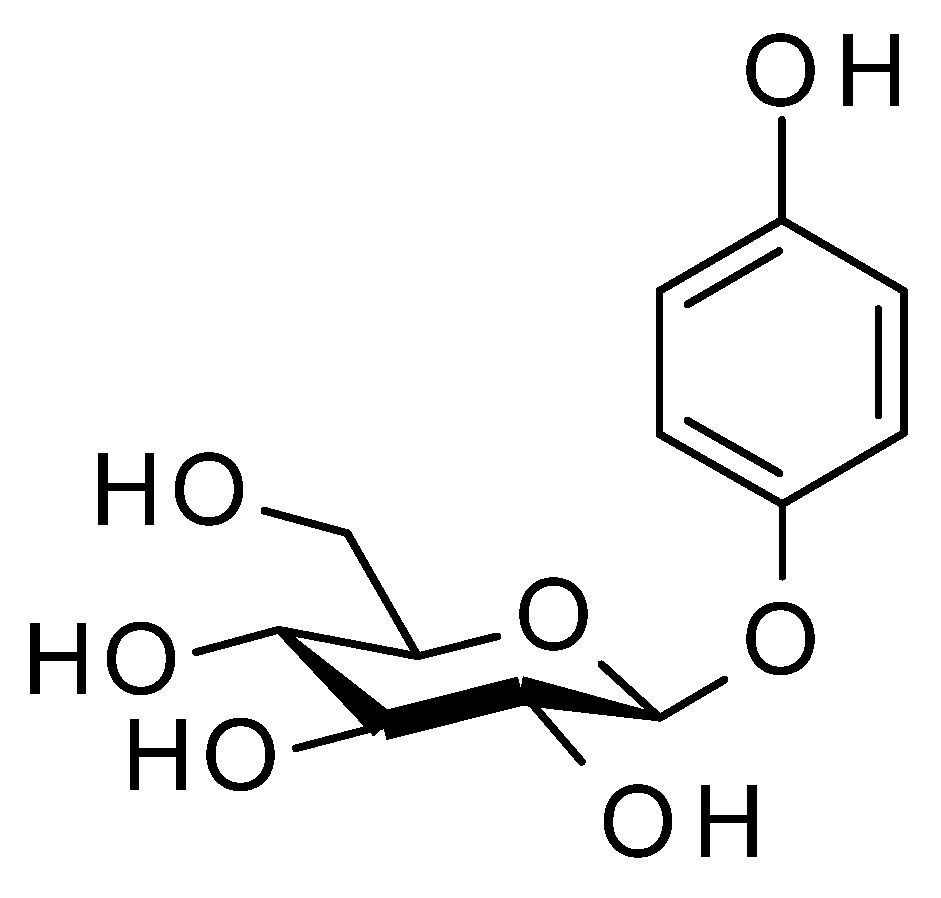
Arbutin: Occurrence in Plants, and Its Potential as an Anticancer Agent
Abstract
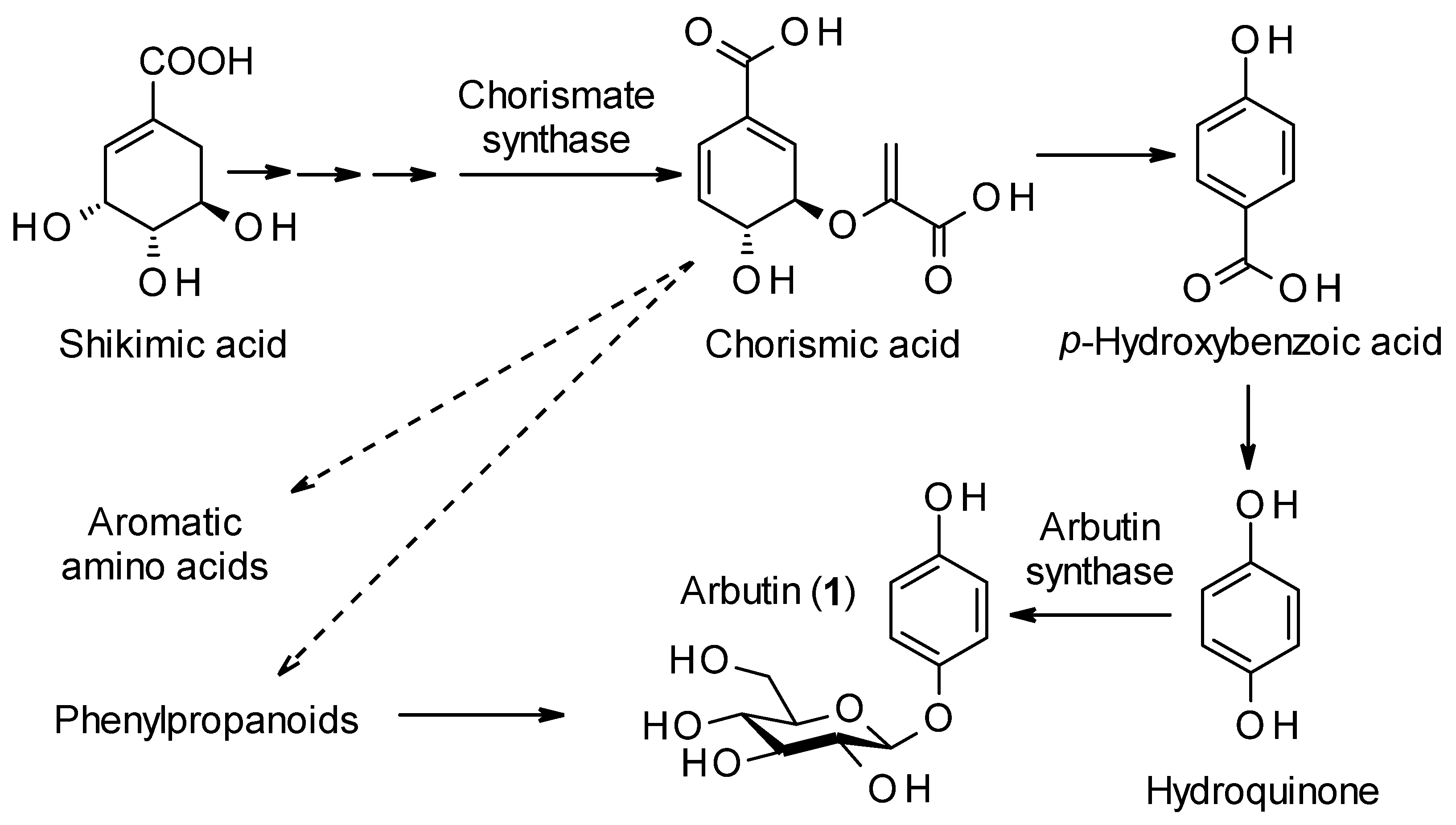
1. Introduction
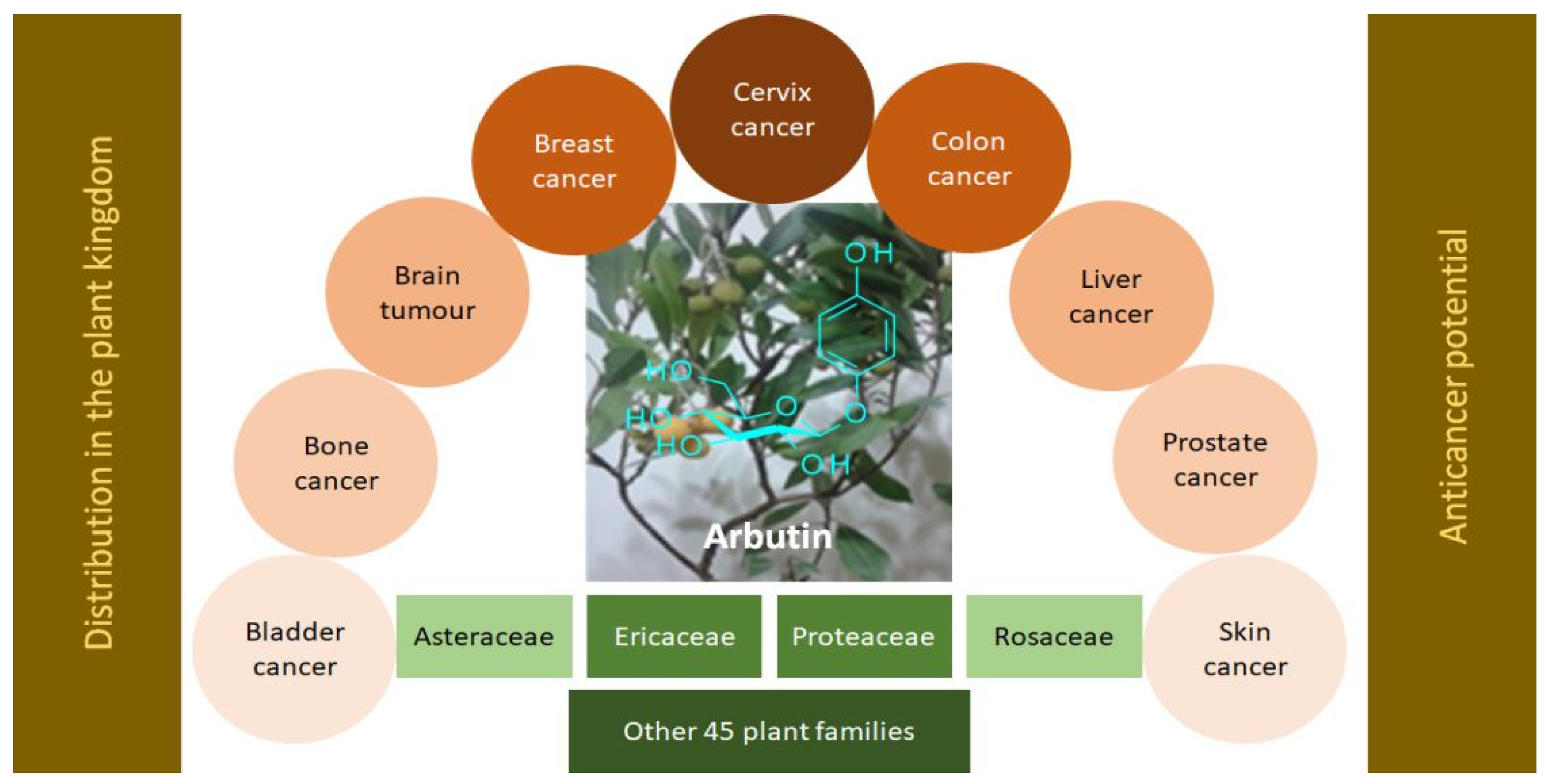
2. Distribution of Arbutin (1) in the Plant Kingdom
3. Anticancer Potential of Arbutin
3.1. Bladder Cancer
3.2. Brain Tumour
3.3. Breast Cancer
3.4. Cervical Cancer
3.5. Colon Cancer
3.6. Gastric Cancer
3.7. Liver Cancer
3.8. Melanoma or Skin Cancer
3.9. Osteosarcoma
3.10. Prostate Cancer
3.11. Miscellaneous
4. Toxicological Aspects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thies, H.; Sulc, D. Arbutus unedo L. I. Determination of arbutin in the leaves of the strawberry tree. Pharmazie 1950, 5, 553–555. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.F.; Liu, D.Z.; Xie, Z.M. Rapid and specific fluorescence method for the quantification of arbutin in cosmetics. Anal. Lett. 2022, 55, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boo, Y.C. Arbutin as a skin depigmenting agent with antimelanogenic and antioxidant properties. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, I.; Ying, B.P. Phenolic constituents of California buckeye fruit. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 3793–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suktap, C.; Lee, H.K.; Amnuaypol, S.; Suttisri, R.; Sukrong, S. Would healing effect of flavonoid glycosides from Afgekia mahidolae B L Burtt & Chermsir. leaves. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2018, 12, 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, J.C.; Shi, J.T.; Tan, Q.W.; Chen, Q.J. Phenylpropionamides, piperidine, and phenolic derivatives from the fruit of Ailanthus Altissima. Molecules 2017, 22, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.Y.; He, N.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Xia, D.D.; Wei, J.F.; Kang, W.Y. Antimicrobial mechanism of hydroquinone. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 189, 1291–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Ramachandraiah, K.; Jiang, G.H.; Eun, J.B. Effects of ultra-sonication and agitation on bioactive compounds and structure of Amaranth extract. Foods 2020, 9, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gins, M.S.; Gins, V.K.; Motyleva, S.M.; Kulikov, I.M.; Medvedev, S.M.; Pivovarov, V.F.; Mertvishcheva, M.E. Metabolites with antioxidant and protective functions from leaves of vegetable Amaranth (Amaranthus tricolor L.). Sel’skokhozyaistvennaya Biol. 2017, 52, 1030–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwanprasert, T. The analysis of arbutin in Mao (Antidesma thwaitesianum Muell. Arg.) extracts. Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 2018, 41, 621–636. [Google Scholar]
- Sakar, M.K.; Berkman, M.Z.; Calis, I.; Ruedi, P. Constituents of Arbutus Andrachne. Fitoterapia 1991, 62, 176–177. [Google Scholar]
- Al Groshi, A.; Nahar, L.; Ismail, F.M.D.; Evans, A.R.; Sarker, S.D. Dichloromethane extract of the leaves of Arbutus pavarii Pamp. exhibits cytotoxicity against the prostate cancer cell line PC3: A bioassay-guided isolation and identification of arbutin and betulinic acid methyl ester. J. Nat. Prod. Discovery. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karikas, G.A.; Giannitsaros, A. Phenolic glucosides from the leaves of Arbutus Unedo. Plantes Med. Et. Phytother. 1990, 24, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowska, A.M.; De Leo, M.; Braca, A. Phenolics of Arbutus unedo. (Ericaceae) fruits: Identification of anthocyanins and gallic acid derivatives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 10234–10238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panusa, A.; Petrucci, R.; Marrosu, G.; Multari, G.; Gallo, F.R. UHPLC-PDA-ESI-TOF/MS metabolic profiling of Arctostaphylos pungens and Arctostaphylos uva-ursi. A comparative study of phenolic compounds from leaf methanolic extracts. Phytochemistry 2015, 115, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamberg, T. Determination of arbutin in bearberry leaves under various conditions. Sven. Farm. Tidskr. 1952, 56, 401–407. [Google Scholar]
- Sticher, O.; Soldati, F.; Lehmann, D. High-performance liquid-chromatographic separation and quantitative-determination of arbutin, methylarbutin, hydroquinone and hydroquinonemonomethylether in Arctostaphylos, Bergenia, Calluna and Vaccinium species. Planta Med. 1979, 35, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreitmair, H. Arctostaphylos uva-ursi—Bearberry. Pharmazie 1953, 8, 347–349. [Google Scholar]
- Fursa, N.S.; Ermolaeva, O.M. Arctous alpina leaves: Arbutin content. Farmatsiya 2013, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Garai, S.; Garai, S.; Jaisankar, P.; Singh, J.K.; Elango, A. A comprehensive study on crude methanolic extract of Artemisia pallens (Asteraceae) and its active component as effective corrosion inhibitors of mild steel in acid solution. Corros. Sci. 2012, 60, 193–204. [Google Scholar]
- Noikotr, K.; Chaveerach, A.; Sudmoon, R.; Tanee, T.; Patarapadungkit, N. Phytochemicals, cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of three Artocarpus species reveal arbutin in A. Lacucha. Scienceasia 2018, 44, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajbhandari, M.; Lalk, M.; Mentel, R.; Lindequist, U. Antiviral activity and constituents of the Nepalese medicinal plant Astilbe Rivularis. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2011, 5, 138–142. [Google Scholar]
- Godevac, D.; Stankovic, J.; Novakovic, M.; Andelkovic, B.; Dajic-Stevanovic, Z.; Petrovic, M. Phenolic compounds from Atriplex littoralis and their radiation mitigating activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2198–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Cortazar, M.; Lopez-Gayou, V.; Tortoriello, J.; Dominguez-Mendoza, B.E.; Rios-Cortes, A.M.; Ble-Gonzalez, E.A.; Zamilpa, A. Antimicrobial gastrodin derivatives isolated from Bacopa procumbens. Phytochem. Lett. 2019, 31, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, B.J.; Kilah, N.L.; Jordan, G.J.; Bissember, A.C.; Smith, J.A. Arbutin derivatives isolated from ancient Proteaceae: Potential phytochemical markers present in Bellendena, Cenarrhenes and Pers. Genera. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.N.; Liu, C.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Xu, Q.M.; Li, X.R.; Yang, S.L. New triterpenes and other constituents from the fruits of Benincasa hispida (Thunb.) Cogn. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 61, 12692–12699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuji, M.; Miyaichi, Y.; Tomimori, T. Studies on Nepalese crude drugs: XXII. On the phenolic constituents of the rhizome of Bergenia ciliata (Haw.) Sternb. Nat. Med. 1996, 50, 404–407. [Google Scholar]
- Roselli, M.; Lentini, G.; Habtemariam, S. Phytochemical, antioxidant and anti-alpha-glucosidase activity evaluations of Bergenia Cordifolia. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuz’min, V.I.; Gontar’E, M.; Pushkarev, G.N. Productivity of Bergenia crassifolia raw material and the content of phenol compounds in it Western Baikal-Amur railway and Khakass autonomous Oblast Russian-SFSR USSR. Rastit. Resur. 1985, 21, 180–183. [Google Scholar]
- Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Ivanova, S.A.; Shikov, A.N.; Makarov, V.G.; Galamnosi, B. Separation and evaluation of free radical-scavenging activity of phenol components of green, brown, and black leaves of Bergenia crassifolia by using HPTLC-DPPH center dot method. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 2447–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, C.; Vlase, L.; Tamas, M. Natural resources containing arbutin. determination of arbutin in the leaves of Bergenia crassifolia (L.) Fritsch acclimated in Romania. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2009, 37, 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.X.; Zhang, C.N.; Liu, R.H.; Wu, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, N.; Nima, C.R.; Danpei, Q.Z.; Zhang, S.F.; Sun, Y.K. Rapid characterization the chemical constituents of Bergenia purpurascens and explore potential mechanism in treating osteoarthritis by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry combined with network pharmacology. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 3333–3348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, H. Studies on tanning principle of Bergenia species and its relation to arbutin. Pharmazie 1954, 9, 138–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frohne, D. Occurrence of arbutin in Saxafragaceae—D. Pharmazie 1969, 24, 701–702. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, H.; Wehnert, H.U. Distribution of arbutin and bergenine in Bergenia plants. Arch. Pharm. 1973, 306, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Ali, I.; Li, Z.; Sulaiman, A.; Aziz, S.; Chen, L.; Hussain, H.; Cui, L.; Wang, D.J.; Zheng, X. Separation of constituents from Bergenia stracheyi (Hook. F. & Thoms.) Engl. by high-speed countercurrent chromatography with elution mode and its antidiabetic and antioxidant in vitro evaluation. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 44, 202000999. [Google Scholar]
- Koltunov, Y. The effect of the stem rot at composition and content of phenolic compounds in leaves of Birch (Betula pendula Roth.). Khimia Rastit. Syr’ja 2019, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.B.; Kojima, Y.; Terazawa, M. Four glucosides of p-hydroxyphenyl derivatives from birch leaves. J. Wood Sci. 1999, 45, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-H.; Sook, C.H. Identification of antioxidant and anti-tyrosinase activity of phenolic components isolated from Betula Schmidtii. Korean J. Food Nutr. 2021, 34, 553–559. [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa, H.; Kasai, R.; Otsuka, H.; Hirata, E.; Shinzato, T.; Aramoto, M.; Takeda, Y. Terpenic and phenolic glycosides form leaves of Breynia officinalis Hemsl. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-H.; Yang, X.-D.; Zhao, J.-F.; Li, L. The chemical constituents of Breynia Rostrata. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2006, 41, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leifertova, I.; Lisa, M.; Pechova, Z.; Prokes, J. Evaluation of the composition of Calluna vulgaris L. Hull. Farm. Obz. 1989, 58, 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Fursa, N.S.; Onegin, S.V. Arbutin levels in the ling (Calluna Vulgaris). Farmatsiya 2007, 2007, 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.; Patil, D.; Patil, A. Qualitative HPTLC phytochemical profiling of Careya arborea Roxb. bark, leaves and seeds. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosaddik, M.A.; Flowers, A.; Karagianis, G.; Waterman, P.G. New phenolic glycosides from the stems and leaves of Casearia Multinervosa. Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 20, 641–647. [Google Scholar]
- Gulcemal, D.; Alankus-Caliskan, O.; Karaalp, C.; Ors, A.U.; Ballar, P.; Bedird, E. Phenolic glycosides with antiproteasomal activity from Centaurea urvillei DC. subsp. urvillei. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 2529–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavand, E.; Charkhabi, N.F.; Khodaygan, P.; Rahimian, H. Agrobacterium pusense, a new plant tumour-inducing pathogen isolated from Lawson cypress. For. Pathol. 2020, 51, e12655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.M.; He, R.P.; Li, Z.H.; Wang, L. LC-Q-Orbitrap-MS/MS characterization, antioxidant activity, and alpha-glucosidase-inhibiting activity with in silico analysis of extract from Clausena Indica (Datz.) Oliv fruit pericarps. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 727087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anesyan, E.T.; Nersesyan, Z.M.; Parkhomenko, A.Y. Chemical composition of the above-ground part of Coriandrum sativum. Khimiko-Farnatsevticheskii Zhurnal 2007, 41, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Palme, E.; Bilia, A.R.; Morelli, I. Flavonols and isoflavonols from Cotoneaster simonsii. Phytochemistry 1996, 42, 903–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahara, S.; Domoto, H.; Sugimura, C.; Nohara, T.; Niho, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Ito, H. An alkaloid and two lignans from Cuscuta Sinensis. Phytochemistry 1994, 37, 1755–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.-S.; Cao, X.-W.; Kuang, H.-X.; Zheng, X.-K. Flavanone O-glycosides from the rhizomes of Dryopteris Sublaeta. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2007, 42, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.P.; Qiao, Y.C.; Lin, S.Q.; Jiang, Y.M.; Chen, F. Characterization of antioxidant compounds in Eriobotrya fragrans Champ. Leaf. Sci. Hortic. 2008, 118, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadiz-Gurrea, M.D.; Fernandez-Arroyo, S.; Joven, J.; Segura-Carretero, A. Comprehensive characterization by UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS from an Eryngium bourgatii extract and their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokesch, H.R.; Wamiru, A.; Le Grice, S.F.J.; Beutler, J.A.; Mckee, T.C.; McMahon, J.B. HIV-1 ribonuclease H inhibitory phenolic glycosides from Eugenia Hyemalis. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1634–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.H.; Wang, D.; Yu, J.; Ma, G.X.; Pei, F.; Yang, W.J. Neuroprotective effects of six components from Flammulina velutipes on H2O2-induced oxidative damage in PC12 cells. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 37, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemec, S. Phenolics in strawberry root. Ann. Bot. 1973, 37, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.; Mpondo, E.M.; Kaouadji, M.; Mariotte, A.M. Arbutin derivatives in Gentiana Pyrenaica. J. Nat. Prod. 1989, 52, 858–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Leach, D.; Thomas, M.C.; Blanksby, S.J.; Forster, P.I.; Waterman, P.G. Bisresorcinols and arbutin derivatives from Grevillea banksii R. Br. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2008, 3, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manju, M.; Varma, R.S.; Parthasarathy, M.R. New arbutin derivatives from leaves of Grevillea robusta and Hakea Saligna. Phytochemistry 1977, 16, 793–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.S. Phytochemical and biological study of Grevillea robusta A. Cunn, cultivated in Egypt. Bull. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 29, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Perry, N.B.; Benn, M.H.; Foster, L.M.; Routledge, A.; Weavers, R.T. The glycosidic precursor of (Z)-5-ethylidene-1(5H)-furanone in Halocarpus biformisjuvenile foliage. Phytochemistry 1996, 42, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.Y.; Ou, N.; Wu, X.D.; Xu, H.M. New arbutin derivatives from the leaves of Heliciopsis lobata with cytotoxicity. Chin. J. Nat. Remedies 2016, 14, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Yamg, P.-P.; Wang, P.-L.; Ling, H.-L.; Chen, M. Study on the constituents of Herpetospermum Caudigerum. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2012, 35, 1080–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Rout, D.; Dash, U.C.; Kanhar, S.; Swain, S.K.; Sahoo, A.K. Homalium zeylanicum attenuates streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia and cellular stress in experimental rats via attenuation of oxidative stress imparts inflammation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 283, 114649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.Y.; Wang, B.D.; Li, Y.M.; Jiang, S.H.; Zhu, D.Y. A new alkaloid and arbutin from the whole plant Huperzia serrata. Chin. J. Chem. 2000, 18, 614–616. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.C. Whitening efficacy of water-soluble extracts from Prunophora salicina’s (Daeseokjosaeng, Purplekin, Formosa) peel. J. Investig. Cosmetol. 2013, 9, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, H.; Inoue, E.; Kitamura, Y.; Sugii, M. Examination and determination of arbutin in the leaves of Viburnum spp. and Ilex Spp. Shoyakugaku Zasshi 1985, 39, 181–184. [Google Scholar]
- Gousiadou, C.; Li, H.Q.; Gotfredsen, C.; Jensen, S.R. Iridoids in Hydrangeaceae. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2016, 64, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fuentealba, C.; Hernandez, I.; Saa, S.; Toledo, L.; Burdiles, P.; Chirinos, R.; Campos, D.; Brown, P.; Pedreschi, R. Colour and in vitro quality attributes of walnuts from different growing conditions correlate with key precursors of primary and secondary metabolism. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, G.J. Phenolics from Larix needles.5. Phenolic glucosides from needles of Larix leptolepis. Phytochemistry 1973, 12, 723–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsopmo, A.; Muir, A.D. Chemical profiling of lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) cultivars and isolation of compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8715–8721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glennie, C.W. Flavonoid glycosides of Leucadendron and their chemotaxonomic significance. J. South Afr. Bot. 1980, 46, 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Bolio, G.I.; Kutzner, E.; Eisenreich, W.; Torres-Acosta, J.F.D.; Pena-Rodriguez, L.M. The use of H-1-NMR metabolomics to optimise the extraction and preliminary identification of anthelmintic products from the leaves of Lysiloma Latisiliquum. Phytochem. Anal. 2018, 29, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Kardar, M.N.; Siddiqui, B.S. Arbutin derivatives from the seeds of Madhuca latifolia. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 1661–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Banerjee, A.; De, B. Antioxidant and enzyme inhibitory properties of Magnifera indica leaf extract. Nat. Prod. J. 2020, 10, 384–394. [Google Scholar]
- Nesterova, N.V.; Kuzmenko, A.N.; Kuzmenko, I.A.; Krasnyk, I.I., Jr.; Evgrafov, A.A. Quantitative determination of arbutin in leaves of Malus sylvestris by method of high-efficient liquid chromatography. Mosc. Univ. Chem. Bull. 2019, 74, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterova, N.V.; Samylina, I.A. Impact of a preservation method on the content of biologically active substances in apples. Farmatsiya 2017, 66, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Gug, K. Physiological and whitening effects of Morus alba extracts. J. Chosun Nat. Sci. 2012, 5, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Catalano, S.; Cioni, P.L.; Flamini, G.; Defeo, V.; Morelli, I. Chemical investigation of the aerial parts of Mutisia acuminata. Int. J. Pharmacogn. 1995, 33, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, A.; Seligmann, O.; Nonnenmacher, G.; Fessler, B.; Wong, S.M.; Wagner, H. New chromone, coumarin and coumestan derivatives from Mutisia Acuminata Var Hirsute. Planta Med. 1988, 54, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.N.; Otsuka, H.; Ide, T.; Hirata, E.; Takushi, A.; Takeda, Y. Hydroquinone glycosides from leaves of Myrsine Seguinii. Phytochemistry 1998, 49, 2149–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suau, R.; Cuevas, A.; Valpuest, V.; Reid, M.S. Arbutin and sucrose in the leaves of the resurrection plant Myrothamnus flabellifolia. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 2555–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, C.; Petereit, F.; Anke, J.; Hensel, A. A new arbutin derivative from the herb of Myrothamnus flabellifolia Welw. Pharmazie 2007, 62, 558–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniava, I.I. Arbutin from Onobrychis kachetica. Chem. Nat. Compd. 1970, 6, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regos, I.; Urbanella, A.; Treutter, D. Identification and quantification of phenolic compounds from the forage legume Sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 5843–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karioti, A.; Milosevic-Ifantis, T.; Pachopos, N.; Niryiannaki, N.; Hadjipavlou-Latina, D.; Skaltsa, H. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory potential and chemical constituents of Origanum dubium Boiss., growing in Cyprus. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2015, 30, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, M.H.; Ali, A.A.; Makboul, M.A.; Beck, J.P.; Anton, R. Preliminary study of phenolic glycosides from Origanum majorana–quantitative estimation of arbutin–cytotoxic activity of hydroquinone. Planta Med. 1987, 53, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghrovyan, A.; Sahakyan, N.; Babayan, A.; Chichoyan, N.; Petrosyan, M.; Trchounian, A. Essential oil and ethanol extract of Oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) from Armenian flora as a natural source of terpenes, flavonoids and other phytochemicals with antiradical, antioxidant, metal chelating, tyrosinase inhibitory and antibacterial activity. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.G.; Zhang, K.; Mo, J.Y.; Pan, A.H.; Zhou, Q. The determination of arbutin in Paederia scandens (Lour) Merr by capillary electrophoresis with amperometric detection. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2002, 30, 886. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.-Q.; Zhang, P.-F.; Duan, W.-D.; Zhang, D.-L.; Li, C. Studies on the chemical constituents from flowers of Paulownia Fortunei. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2009, 32, 1227–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, F.; Zeng, P.; Jia, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhu, W.; Chen, K. Phenolic components from Petasites Tricholobus. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2012, 37, 1782–1787. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H. Peroxynitrite scavengers from Phellinus linteus. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2008, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.; Wang, Y.; Hao, X. Water-soluble chemical constituents from fruits of Phellodendron chinense var. glabriusculum. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2009, 34, 2895–2897. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura, M.; Ochi, K.; Sekiya, H.; Tamai, E.; Maki, J.; Tada, A.; Sugimoto, N.; Akiyama, H.; Amakura, Y. Identification of characteristic phenolic constituents in Mousouchiku extract used as food additives. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 65, 878–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.Z.; Ouyang, P.; Xu, X.; Zhou, L.G.; Wang, D.C.; Deng, X.M. Isolation and identification of a new compounds from the roots of Picrorhiza Scrophulariiflora. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. Chin. 2010, 31, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.T.; Shao, S.; Xiao, F.Q.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, R.R.; Wang, M.; Li, G.Z.; Yan, M.M. Platycodon grandiflorum extract: Chemical composition and whitening, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 10814–10826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acikara, O.B.; Ilhan, M.; Kurtul, E.; Smejkal, K.; Akkol, E.K. Inhibitory activity of Podospermum canum and its active components on collagenase, elastase and hyaluronidase enzymes. Bioorganic Chem. 2019, 93, 103330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.R.K.; Lakshmi, N.V. Preliminary phytochemical and GC-MS analysis of different extracts of Psophocarpus tetragonolobus leaves. Indo Am. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 5, 1649–1656. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.-K. Quantitative determination of arbutin and gallotannin in Pyrola calliantha. Bull. Chin. Mater. Med. 1987, 12, 45–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Yao, X.H.; Duan, M.H.; Luo, M.; Zhao, C.J.; Zu, Y.G.; Fu, Y.J. An effective homogenate-assisted negative pressure cavitation extraction for the determination of phenolic compounds in Pyrola by LC-MS/MS and the evaluation of its antioxidant activity. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3323–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulduk, I.; Sahin, M.D.; Sanli, S. Arbutin analysis in leaves, fruits and branches of Pyrus anatolica, method optimization. Eurasian J. Anal. Chem. 2016, 11, 233–244. [Google Scholar]
- Mir, H.; Komi, D.E.A.; Pouramir, M.; Parsian, H.; Moghadamnia, A.A.; Seyfizadeh, N.; Lakzaei, M. The hepatoprotective effects of Pyrus biossieriana Buhse. leaf extract on tert-butyl hydroperoxide toxicity in HepG2 cell line. BMC Res. Notes 2021, 14, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.G.; Zheng, Y.; Cao, Y.F.; Tian, L.M.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, D.; Huo, H.L.; Wang, D.J. Evaluation of phenolic composition and content of pear varieties in leaves from China. Erwerbs Obstbau 2018, 60, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilia, A.R.; Rubio, M.D.E.; Alvarez, M.L.; Morelli, I.; Gonzalez, J.M. New benzyl alcohol glycosides from Pyrus bourgaeana. Planta Med. 1994, 60, 569–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, H. Studies on phenolic components of Pyrus communis. II. Arbutin content of pear leaves. Pharmazie 1957, 12, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salta, J.; Martins, A.; Santos, R.G.; Neng, N.R.; Nogueira, J.M.P.; Justino, J.; Rauter, A.P. Phenolic composition and antioxidant activity of Rocha pear and other pear cultivars—A comparative study. J. Funct. Foods 2010, 2, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, H. Studies on phenolic constituents of Pyrus communis. IV. Content of arbutin in germinating pear seeds and distribution in young plants. Pharmazie 1958, 13, 153–155. [Google Scholar]
- Rychlinska, I.; Gudej, J. Qualitative and quantitative chromatographic investigation of hydroquinone derivatives in Pyrus communis L. flowers. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2003, 60, 309–312. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.-K.; Zuo, C.-X. Studies of the chemical constituents of Pyrus Communis. Acta Bot. Sin. 1987, 29, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Feng, Y.X.; Zhao, Z.; Cheng, Y.D.; Guan, J.F. The involvement of phenolic metabolism in superficial scald development in ‘Wujiuxiang’ pear. J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual. 2020, 93, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kavac, D.D.; Kececi, S. Extraction of phenolic antioxidants from Pyrus elaeagrifolia Pallas: Process optimization, investigation of the bioactivity and beta-glucuronidase inhibitory potential. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 2894–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Om, P.; Gopinath, M.S.; Kumar, P.M.; Kumar, S.P.M.; Kudachikar, V.B. Ethanolic extract of Pyrus pashia Buch ham ex Don (Kainth): A bioaccessible source of polyphenolics with anti-inflammatory activity in vitro and in vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 2982, 114628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes-Lasala, E.; Fernandez, M.; Martinez, L.; Garcia-Mina, M.C.; Vega, F.A. Phenolic compounds in Pyrus Pyraster. An. Inst. Bot. A. J. Cavinilles 1975, 32, 245–267. [Google Scholar]
- Usjak, L.J.; Milutinovic, V.M.; Crnogorac, M.J.D.; Stanojkovic, T.P.; Niketic, M.S.; Kukic-Markovic, J.M.; Petrovic, S.D. Barks of three wild Pyrus taxa: Phenolic constituents, antioxidant activity and in vitro and in silico investigations of alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase inhibition. Chem. Biodivers. 2021, 18, e2100446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.H.; Lee, K.C.; Ameer, K.; Eun, J.B. Comparison of freeze-drying and hot air-drying on Asian pear (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai Niitaka) powder: Changes in bioaccessibility, antioxidant activity, and bioactive and volatile compounds. J. Food Sci. Technol. Mysore 2019, 56, 2836–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, J.-B. Changes in phenolic substances and pectin according to the growth period of the pear. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 39, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.H.; Cho, J.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Park, K.Y.; Ma, Y.K.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, J.A.; Kim, W.S.; Park, K.H.; Moon, J.H. Isolation and identification of phenolic compounds from an Asian pear (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai) fruit peel. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, C.; Ichitani, M.; Kunimoto, K.K.; Asada, C.; Nakamura, Y. Extraction of arbutin and its comparative content in branches, leaves, stems and fruits of Japanese pear Pyrys cv. Kousui. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 874–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, T.; Igarashi, K. Variation in polyphenol components and radical scavenging activity of Japanese pear (Pyrus serotina Rehder var. culta Rehder) during fruit maturation. J. Jpn. Soc. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 60, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challice, J.S. Phenolic compounds of genus Pyrus. 6. Distribution of phenols among various tissues of Pyrus stem. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1973, 24, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoruzhaya, T.G.; Krasnov, E.A. Phenol compounds of Rhodiola Coccinea. Khimiya Prir. Soedin. 1972, 677–678. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.S.; Zhou, S.S.; Shen, C.Y.; Jiang, J.G. Isolation and identification of four antioxidants from Rhodiola crenulata and evaluation of their UV photoprotection capacity in vitro. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 66, 103825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Chen, K.; Liu, Q.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhuo, Z.; Guo, K.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; et al. The protective effect of Rhodiola rosea on radiation induced intestinal injury. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e2000652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhavoronkova, M.E.; Belousov, M.V.; Fursa, N.S. Arbutin levels in the leaves of several species of the genus Rhododendron. I.P. Pavlov. Russ. Med. Biol. Her. 2008, 16, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.M.; He, R.P.; Li, Z.H.; Lin, X.; Wang, L. HPLC-Q-Orbitrap-MS/MS phenolic profiles and biological activities of extracts from roxburgh rose (Rosa roxburghii Tratt.) leaves. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, K.; Malik, A.; Mehmood, A.; Mukhtar, N.; Tareen, R.B. Phytochemical studies of Salix acmophylla Boiss. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2004, 26, 392–394. [Google Scholar]
- De Falco, B.; Grauso, L.; Fiore, A.; Bochicchio, R.; Amato, M.; Lanzotti, V. Metabolomic analysis and antioxidant activity of wild type and mutant chia (Salvia hispanica L.) stem and flower grown under different irrigation regimes. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 6010–6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontana-Uribe, B.A.; Escarcega-Bobadilla, M.V.; Estrada-Reyes, R.; Morales-Serna, J.A.; Salmon, M.; Cardenas, J. A new languidulane diterpenenoid from Salvia mexicana var. Mexicana. Mol. 2011, 16, 8866–8873. [Google Scholar]
- Natic, M.; Pavlovic, A.; Lo Bosco, F.; Stanisavljevic, N.; Zagorac, D.D.; Aksic, M.F.; Papetti, A. Nutraceutical properties and phytochemical characterization of wild Serbian fruits. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneyama, M.; Yoshida, S. Studies on C-glycosides in higher plants. 2. Incorporation of glucose C-14 into bergenin and arbutin in Saxifraga stolonifera. Bot. Mag. Tokyo 1979, 92, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.-H.; Shen, G.-M.; Tian, X. Chemical components of Scrofella chinensis (I). Xibei Zhiwu Xue Bao 2006, 26, 412–415. [Google Scholar]
- Pokotylo, I.V.; Gumenyuk, L.A.; Dykhavov, N.N. Phenol compounds from Sedum Purpureum. Khimiya Prir. Soedin. 1974, 2, 252–253. [Google Scholar]
- Krasnov, E.A.; Petrova, L.V. Arbutin in certain plants of Sedum genus. Khimiya Prir. Soedin. 1970, 4, 476. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.-K.; Bi, Y.-F.; Feng, W.-S.; Shi, S.-P.; Wang, J.-F.; Niu, J.-Z. Study on the chemical constituents of Selaginella tamariscina (Beauv.) Spring. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2004, 39, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Myagchilov, A.V.; Mineev, S.A.; Sokolova, L.I.; Gardasova, E.D.; Gorovoi, P.G. Arbutin content in the far-eastern species Serratula Komaroviilljin. Pharm. Chem. J. 2020, 54, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nycz, J.E.; Malecki, G.; Morag, M.; Nowak, G.; Ponikiewski, L.; Kusz, J.; Switlicka, A. Arbutin: Isolation, X-ray structure and computational studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2010, 980, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatsny, I.L.; Gorovits, M.B.; Abubakir, N.K. Arbutin from Serratula Sogdiana. Chem. Nat. Compd. 1973, 9, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsutani, K.; Sugimoto, S.; Yamano, Y.; Otsuka, H.; Matsunami, K.; Mizuta, T. Eudesmane-type sesquiterpene glycosides: Sonneratiosides A-E and eudesmol beta-D-glucopyranoside from the leaves of Sonneratia alba. J. Nat. Med. 2020, 74, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Y.-M.; Yan, M.-R.; Xu, Q.; Qu, Z.-R.; Miao, Z. Chemical composition of stems and branches of Sorboria arborea. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2015, 38, 2098–2101. [Google Scholar]
- Venditti, A.; Frezza, C.; Lorenzetti, L.M.; Maggi, F.; Serafini, M.; Bianco, A. Reassessment of the polar fraction of Stachys alopecuros (L.) Benth. subsp. divulsa (Ten.) Grande (Lamiaceae) from the Monti Sibillini National Park: A potential source of bioactive compounds. J. Intercult. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 6, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venditti, A.; Serrilli, A.M.; Di Cecco, M.; Ciaschetti, G.; Andrisano, T.; Bianca, A. Phytochemical composition of polar fraction of Stachys gemanica L. subsp. Salviifolia (Ten.) Gams., a typical plant of Majella National Park. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tundis, R.; Bonesi, M.; Pugliese, A.; Nadjafi, F.; Menchini, F.; Loizzo, M.R. Tyrosinase, acetyl- and butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitory activity of Stachys lavandulifolia Vahl (Lamiaceae) and its major constituents. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2015, 9, 81–93. [Google Scholar]
- Frezza, C.; Venditti, A.; Matrone, G.; Serafini, I.; Foddai, S.; Bianco, A.; Serafini, M. Iridoid glycosides and polyphenolic compounds from Teucrium chamaedrys L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avelino-Flores, M.D.; Cruz-Lopez, M.D.; Jimenez-Montejo, F.E.; Reyes-Leyva, J. Cytotoxic activity of the methanolic extract of Turnea diffusa Willd. on breast cancer cells. J. Med. Food. 2015, 18, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mzhavanadze, V.V.; Targamadze, I.L.; Dranik, L.I. Phenol compounds from the leaves of Vaccinium Arctostaphylos. Khim. Prir. Soedin. 1972, 8, 124. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.H.; Zhao, T.R.; Liu, Y.P.; Wang, Y.F.; Cheng, G.G.; Cao, J.X. Phenolic constituents, antioxidant activity and neuroprotective effects of ethanol extracts of fruits, leaves and flower buds from Vaccinium dunalianum Wight. Food Chem. 2021, 374, 131752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, H.; Schonert, J. Phytochemical investigation of leaves and fruits of Vaccinium Myrtillus. Planta Med. 1973, 24, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocik, H.; Wojciechowska, B.; Filec, J. Analysis of flavonoids and phenol compounds of Vaccinium Myrtillus. Prod. Nauk. Uniw. Slaskiego W. Katowicach 1980, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Askari, A.; Worthen, L.R. Isolation of isopyroside from Vaccinium Vacillans. Phytochemistry 1971, 11, 1509–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandzaitene, Z.Y.U.; Butkus, V.F. Biological and biochemical characteristics of cowberry. Part 4. Content of some organic substances in the leaves and berries. Liet. TSR Moksl. Akad. Darb. Ser. C Biol. Moksl. 1975, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Pyka, A.; Bober, K.; Strolarczyk, A. Densitometric determination of arbutin in cowberry leaves (Vaccinium vitis idaeae). Acta Pol. Pharm. 2007, 64, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Huang, R.; Yuan, C. Determination of arbutin in the herbs of Vaccinium vitis-idaea L. by RP-HPLC. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi 1997, 22, 555–577. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dimitrova, P.A.; Alipieva, K.; Grozdanova, T.; Leseva, M.; Gerginova, D.; Simova, S.; Marchev, A.S.; Bankova, V.; Georgiev, M.I.; Popova, M.P. Veronica austriaca L. extract and arbutin mature double TNF-alpha/IFN-gamma neutrophils in murine bone marrow pool. Molecules 2020, 25, 3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostadinova, E.P.; Alipieva, K.I.; Kokubun, T.; Taskova, R.M.; Handjieva, N.V. Phenylethanoids, iridoids and a spirostanol saponin from Veronica turrilliana. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.H.; Chen, J.; Zhao, C.C.; Shen, J.; Liu, W.Y.; Gu, W.Y.; Li, K.H. Insecticidal and alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activities of chemical constituents from Viburnum fordiae Hance. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 2662–2667. [Google Scholar]
- Petricic, J.; Stanic, G.; Holic, L. Flavonoids saponins tannins and arbutin as constituents of leaves of Viburnum tinus, Viburnum opulus and Viburnum lanata. Acta Pharm. Jugosl. 1980, 30, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Takido, M.; Fukuhara, K.; Yamanouchi, S.; Takahashi, S. Phlebotrichin, a phenolic compound from the fresh leaves of Viburnum phlebotrichum. Phytochemistry 1983, 22, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubenchicov, R.A.; Goncharov, N.F. The study of the composition of the phenolic compounds of Viola Arvensis. Khimiko-Farmatsevticheskii Zhurnal 2005, 39, 31–32. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, S.R.; Gotfredsen, C.H.; Zidorn, C. Iridoids and phenylethanoids in Lagotis integrifolia and Wulfeniopsis amherstiana (Plantaginaceae). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2009, 37, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisatomi, E.; Matsui, M.; Kobayashi, A.; Kubota, K. Antioxidative activity in the pericarp and sees of Japanese pepper (Xanthoxylum piperitum DC). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 4924–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Q.B.; Shi, D.W.; Mizuno, M. Flavonol glucosides in pericarps of Zanthoxylum Bungeanum. Phytochem. 1995, 39, 723–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisdale, S.K.; Towers, G.H.N. Biosynthesis of arbutin from some phenylpropanoid compounds in Pyrus Communis. Nat. 1960, 188, 1130–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.-X.; Xue, M.-G.; Li, Z.; Ye, B.-C.; Zhang, B. Recent progress on feasible strategies for arbutin production. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 914280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Yan, Y. High-level de novo biosynthesis of arbutin in engineered Escherichia coli. Metab. Eng. 2017, 42, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jeong, Y.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, D.S. Arbutin inhibits TCCSUP human bladder cancer cell proliferation via up-regulation of p21. Pharmazie 2011, 66, 306–309. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.K.; Shi, H.Y.; Chinnathambi, A.; Salmen, S.H.; Alharbi, S.A.; Veeraraghavan, V.P.; Surapaneni, K.M.; Arulselvan, P. Arbutin exerts anticancer activity against rat C6 glioma cells by inducing apoptosis and inhibiting the inflammatory markers and P13/Akt/mTOR cascade. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22857. [Google Scholar]
- Erenler, R.; Sen, O.; Aksit, H.; Demirtas, I.; Yaglioglu, A.S.; Elmastas, M.; Telci, I. Isolation and identification of chemical constituents from origanum majorana and investigation of antiproliferative and antioxidant activities. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 822–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazman, O.; Sariova, A.; Bozkurt, M.F.; Cigerci, I.H. The anticarcinogen activity of beta-arbutin on MSC-7 cells: Stimulation of apoptosis through estrogen receptors-alpha signal pathway, inflammation and genotoxicity. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdowska, I.; Zielinski, B.; Fecka, I.; Kulbacka, J.; Saczko, J.; Gamian, A. Cytotoxic impact of phenolics from Lamiaceae species on human breast cancer cells. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, H.; Kojima, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Hasegawa, M. Inhibition of cells growth in culture by quinones. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 1998, 13, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.T.; Liu, H.P.; Huang, Z.P.; Dong, P.; Chen, X. Anticancer effect of arbutin on diethylnitrosamine-induced liver carcinoma in rats via the GRP and GADD pathway. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2022, 41, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, G.M.; Latropoulos, M.; Jeffrey, A.M.; Duan, J.D. Inhibition by dietary hydroquinone of acetylaminofluorene induction of initiation of rat carcinogenesis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazman, O.; Evin, H.; Bozkurt, M.F.; Cigerci, I.H. Two faces of arbutin in hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells: Anticarcinogenic effect in high concentration and protective effect against cisplatin toxicity through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity in low concentration. Biologia 2022, 77, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Ha, H.W.; Kim, H.G.; Lee, D.H.; Kong, M.; Ahn, Y.T.; Kim, D.H.; Shin, B.S.; Kang, W.; Jeong, H.G. Role of metabolism by intestinal bacteria in arbutin-induced toxicity in vitro. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2011, 34, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.F.; Li, J.Y.; Wu, Z.P.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D. Investigation of the pro-apoptotic effects of arbutin and its acylated derivatives on murine melanoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 41, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.B.; Sun, X.W.; Wu, R.X.; Zhang, X.; Tu, Y.Z. Molecular spectroscopic behaviors of beta-arbutin in anti-skin cancer. Spectrosc. Lett. 2020, 53, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Q.; Wang, X.M.; Li, B.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Wang, L. Arbutin suppresses osteosarcoma progression via miR-338-3p/MTHFD1L and inactivation of the AKT/mTOR pathway. FEBS Open Bio 2021, 11, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, H.; Zabihi, E.; Pouramir, M.; Morakabati, P.; Abedian, Z.; Karkhah, A.; Nouri, H.R. Decrease of intracellular ROS by arbutin is associated with apoptosis induction and downregulation of IL-1 beat and TNF-alpha in LNCaP; prostate cancer. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadollahi, S.H.; Pouramir, M.; Zabihi, E.; Golpour, M.; Aghajanpour-Mir, M. The effect of arbutin on the expression of tumor suppressor P53, BAX/BCL-2 ratio and oxidative stress induced by tert-butyl hydroperoxide in fibroblast and LNCap cell lines. Cell J. 2021, 22, 532–541. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaei, S.; Zarrabi, A.; Asnaf, S.E.; Hashemi, F.; Zabolian, A.; Hushmandi, K.; Raej, M.; Goharrizi, M.A.S.B.; Makyandi, P.; Samarghandian, S.; et al. The role of microRNA-338-3p in cancer: Growth, invasion, chemoresistance, and mediators. Life Sci. 2021, 268, 119005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health Service (NHS). Overview—Bladder Cancer. Available online: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/bladder-cancer/ (accessed on 8 October 2022).
- Gartel, A. p21(WAF1/CIP1) and cancer: A shifting paradigm? Biofactors 2009, 35, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. Astaxanthin inhibits matrix metalloproteinase expression by suppressing PI3K/AKT/mTOR activation in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chicoine, M.R.; Silbergeld, D.L. Invading C6 glioma cells maintaining tumorigenicity. J. Neurosurg. 1995, 83, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Service (NHS). Overview—Brain Tumour. Available online: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/brain-tumours/ (accessed on 7 October 2022).
- National Health Service (NHS). Overview—Breast Cancer. Available online: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/breast-cancer/ (accessed on 7 October 2022).
- Yu, S.; Kim, T.; Yoo, K.H.; Kang, K. The T47D cell line is an ideal experimental model to elucidate the progesterone-specific effect of a luminal A subtype of breast cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 486, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health Service (NHS). Overview—Cervical Cancer. Available online: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/cervical-cancer/ (accessed on 9 October 2022).
- National Health Service (NHS). Overview—Bowel Cancer. Available online: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/bowel-cancer/ (accessed on 9 October 2022).
- National Health Service (NHS). Overview—Stomach Cancer. Available online: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/stomach-cancer/ (accessed on 9 October 2022).
- World Cancer Research Fund International. Liver Cancer Statistics. Available online: https://www.wcrf.org/cancer-trends/liver-cancer-statistics/ (accessed on 9 October 2022).
- National Health Service (NHS). Overview—Skin Cancer (Melanoma). Available online: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/melanoma-skin-cancer/ (accessed on 13 October 2022).
- American Cancer Society. About Osteosarcoma. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/osteosarcoma/about/what-is-osteosarcoma.html (accessed on 13 October 2022).
- National Health Service (NHS). Overview—Bone Cancer (Melanoma). Available online: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/bone-cancer/ (accessed on 13 October 2022).
- Prostate Cancer UK. Available online: https://prostatecanceruk.org/prostate-information/about-prostate-cancer (accessed on 14 October 2022).
- Novak, J. Arbutin—A risk substance in herbs? J. Med. Spice Plants 2010, 15, 170–173. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.L.; Liu, R.H.; Sheu, J.N.; Chen, S.T.; Sinchaikul, S.; Tsay, G.T. Toxicogenomics of A375 human malignant melanoma cells treated with arbutin. J. Biomed. Sci. 2007, 14, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donoghue, J.L. Hydroquinone and its analogues in dermatology—A risk-benefit viewpoint. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2006, 5, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Arriba, S.G.; Naser, B.; Nolte, K.-U. Risk assessment of free hydroquinone derived from Arctostaphylos Uva-ursi folium herbal preparations. Int. J. Toxicol. 2013, 32, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drug Bank Online. Arbutin. Available online: https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB11217 (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Seyfizadeh, N.; Mahjoub, S.; Zabihi, E.; Moghadamnia, A.; Pouramir, A.; Mir, H.; Khosravifarsani, M.; Elahimanesh, F. Cytoprotective effects of arbutin against tert-butyl hydroperoxide induced toxicity in Hep-G2 cell line. World Appl. Sci. J. 2012, 19, 163–167. [Google Scholar]
- Pecivova, J.; Nosal, R.; Svitekova, K. Arbutin and decrease of potentially toxic substances generated in human blood neutrophils. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadir, F.; Pouramir, M.; Joorsaraie, G.; Feizi, F.; Sorkhi, H.; Yousefi, F. A study of arbutin protective effect on cyclosporin A induced oxidative damage. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 6, 196–200. [Google Scholar]
| Species | Family | Common Name | Plant Part | Geographical Source | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aesculus californica Nutt. | Hippocastanaceae | California buckeye | Fruit endosperm | USA | [4] |
| Afgekia mahidolae B.L. Burtt & Chermsir. | Fabaceae | Kan Pai Mahidol | Leaves | Thailand | [5] |
| Ailanthus altissima (Mill.) Swingle | Simaroubaceae | Varnish tree | Fruits | China | [6] |
| Ainsliaea bonatii Beauverd | Asteraceae | Chinese daisy | Leaves | China | [7] |
| Amaranthus spp. | Amaranthaceae | Amaranth | Leaves | Bangladesh | [8] |
| Amaranthus tricolor L. | Amaranthaceae | Amaranth | Leaves | Russia | [9] |
| Antidesma thwaitesianum Muell. Arg. | Phyllanthaceae | Mao tree | Fruits and leaves | Thailand | [10] |
| Arbutus andrachne L. | Ericaceae | Greek strawberry tree | Leaves | Greece and Turkey | [11] |
| Arbutus pavarii Pamp. | Ericaceae | Libyan strawberry tree | Leaves | Libya | [12] |
| Arbutus unedo L. | Ericaceae | Strawberry tree | Leaves | Mediterranean region and western Europe | [1,13] |
| Fruits | [14] | ||||
| Arctostaphylos pungens Kunth. | Ericaceae | Point leaf manzanita | Leaves | Italy, Mexico and USA | [15] |
| Arctostaphylos spp. | Ericaceae | Bearberry | Leaves | Scotland and Scandinavia | [16,17] |
| Arctostaphylos uva-ursi (L.) Spreng. | Ericaceae | Bearberry | Leaves | Bulgaria, Turkey | [18] |
| Arctous alpina (L.) Nied. | Ericaceae | Alpine bearberry | Leaves | Russia | [19] |
| Artemisia pallens Wall. Ex. DC. | Asteraceae | Damanaka | Leaves | India | [20] |
| Artocarpus lacucha L. | Moraceae | Monkey fruit | Leaves | South-east Asia | [21] |
| Astilbe rivularis L. | Saxifragaceae | False spirea | Leaves | Nepal and UK | [22] |
| Atriplex littoralis L. | Amaranthaceae | Grass leaf orache | Aerial parts | Serbia | [23] |
| Bacopa procumbens (Mill.) Greenm. | Plantaginaceae | Baby jump-up | Aerial parts | Tropical and subtropical areas of North and South America | [24] |
| Bellendena montana R. Br. | Proteaceae | Mountain rocket | Leaves | Tasmania | [25] |
| Benincasa hispida (Thunb.) Cogn. | Cucurbitaceae | Wax gourd | Fruits | China | [26] |
| Bergenia ciliata (Haw.) Sternb. | Saxifragaceae | Fringed elephant’s ears | Rhizome | Nepal | [27] |
| Bergenia cordifolia L. | Saxifragaceae | Heartleaf Bergenia | Leaves | Russia | [28] |
| Bergenia crassifolia (L.) Fritsch. | Saxifragaceae | Heart-leaved Bergenia | Aerial parts | Russia | [29] |
| Leaves | Russia | [30] | |||
| Leaves | Romania | [31] | |||
| Bergenia purpurascens (Hook. f. & Thomson) Engl. | Saxifragaceae | Purple Bergenia | Leaves | China | [32] |
| Bergenia spp. | Saxifragaceae | Elephant’s ears | Aerial parts | Afghanistan to China and the Himalayan region | [17,33,34,35] |
| Bergenia stracheyi (Hook. F. & Thoms.) Engl. | Saxifragaceae | Elephant’s ears | Aerial parts | The Himalayas | [36] |
| Betula pendula Roth. | Betulaceae | Silver birch | Leaves | Europe and Asia | [37] |
| Betula platyphylla Sukatchev var. japonica Hara | Betulaceae | Shirakamba | Leaves | China | [38] |
| Betula schmidtii Regel. | Betulaceae | Schmidt’s birch | Bark | China, Japan, Korea and Russia | [39] |
| Breynia officinalis Hemsl. | Phyllanthaceae | Chi R Yun | Leaves | China and Japan | [40] |
| Breynia rostrata Merr. | Phyllanthaceae | Hui Guo Hei Mian Shen | Aerial parts | China and Vietnam | [41] |
| Calluna spp. | Ericaceae | Heather | Leaves | Europe and Asia Minor | [17] |
| Calluna vulgaris L. Hull. | Ericaceae | Heather | Aerial parts | Asia Minor | [42] |
| Leaves | Russia | [43] | |||
| Careya arborea Roxb. | Lecythidaceae | Slow match tree | Bark, leaves and seeds | India | [44] |
| Casearia multinervosa C.T.White & Sleumer | Salicaceae | Casearia | Stem | Australia | [45] |
| Cenarrhenes nitida R. Br. | Proteaceae | Port Arthur plum | Leaves | Tasmania | [25] |
| Centaurea urvillei DC. subsp. urvillei | Asteraceae | Star thistle | Leaves | Turkey | [46] |
| Chamaecyparis lawsoniana | Cupressaceae | Lawson cypress | Galls | Iran | [47] |
| Clausena indica (Datz.) Oliver | Rutaceae | Indian wampi | Fruit pericarp | India and Sri Lanka | [48] |
| Coriandrum sativum L. | Apiaceae | Coriander | Aerial parts | Western Asia, Southern Europe and Russia | [49] |
| Cotoneaster simonsii Baker | Rosaceae | Himalayan cotoneaster | Aerial parts | The Himalayas | [50] |
| Cuscuta sinensis Lam. | Convolvulaceae | Chinese cuscuta | Semen | China, Japan and Korea | [51] |
| Dryopteris sublaeta Ching & Y. P. Hsu | Dryopteridaceae | Chinese male fern | Rhizome | China | [52] |
| Eriobotrya fragrans Champ. Ex. Benth. | Rosaceae | Xiang hua pi ba | Leaves | China and Vietnam | [53] |
| Eryngium bourgatii Gouan. | Apiaceae | Sea holly | Flowers and leaves | Spain | [54] |
| Eugenia hyemalis L. Cambess | Myrtaceae | Hyemalis | Aerial parts | Argentina, Bolivia and USA | [55] |
| Flammulina velutipes (Curtis) Singer | Physalacriaceae | Velvet shank | Leaves | China | [56] |
| Fragaria spp. | Rosaceae | Strawberry | Roots | Europe, North America and China | [57] |
| Gentiana pyrenaica L. | Gentianaceae | Pyrenian gentian | Leaves | United Kingdom | [58] |
| Grevillea banksii R. Br. | Proteaceae | Dwarf silky oak | Leaves | Australia | [59] |
| Grevillea robusta A. Cunn. Ex R. Br. | Proteaceae | Silk oak | Leaves | Australia and India | [60] |
| Bark and leaves | [61] | ||||
| Hakea saligna L. | Proteaceae | Hakea | Leaves | Australia and India | [60] |
| Halocarpus biformis (Hook.) C.J. Quinn | Podocarpaceae | Yellow pine | Leaves | New Zealand | [62] |
| Heliciopsis lobata (Merr.) Sleumer | Proteaceae | Helicia | Leaves | China and Vietnam | [63] |
| Herpetospermum caudigerum Wall. | Cucurbitaceae | Herpetospermum | Leaves | China, India and Tibet | [64] |
| Homalium zeylanicum (Gardner) Benth. | Flacourtiaceae | Kalavaram | Leaves | India | [65] |
| Huperzia serrata | Lycopodiaceae | Toothed clubmoss | Whole plant | China, Japan, Korea, Russia and Tibet | [66] |
| Ilex brasiliensis (Spreng.) Loes. | Aquifoliaceae | Brazilian holly | Leaves | Brazil | [67] |
| Ilex integerrima Reiss. | Aquifoliaceae | Holly | Leaves | Brazil | [67] |
| Ilex latifolia Thunb. | Aquifoliaceae | Tarajo holly | Leaves | Japan | [68] |
| Ilex pseudobuxus Reiss. | Aquifoliaceae | Brazilian holly | Leaves | Brazil | [67] |
| Ilex theezans Mart. | Aquifoliaceae | Congonha | Leaves | Brazil | [67] |
| Jamesia americana Torr. & A. Gray | Hydrangeaceae | Cliffbush | Aerial parts | USA | [69] |
| Juglans regia L. | Juglandaceae | Walnuts | Nuts | The Balkans, the Himalayans and China | [70] |
| Larix leptolepis | Pinaceae | Japanese Larch | Needles | Japan | [71] |
| Lens culinaris Medik. | Fabaceae | Lentil | Seeds | India | [72] |
| Leucadendron spp. | Proteaceae | Conebushes | Leaves | South Africa | [73] |
| Lysiloma latisiliquum (L.) Benth. | Fabaceae | Wild tamarind | Leaves | USA | [74] |
| Madhuca latifolia (J. Konig) J.F. Macbr. | Sapotaceae | Mahua | Seeds | India, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka | [75] |
| Magnifera indica L. | Anacardiaceae | Mango | Leaves | India | [76] |
| Malus sylvestris (L.) Mill. | Rosaceae | Crab apple | Leaves | United Kingdom & Russia | [77] |
| Crab apple | Fruits | Russia | [78] | ||
| Morus alba L. | Moraceae | Mulberry | Leaves | China and India | [79] |
| Mutisia acuminata var. acuminata Ruiz & Pav. | Asteraceae | Bolivian Mutisia | Aerial parts | Peru and Bolivia | [80] |
| Mutisia acuminata var. hirsuta (Meyen) Cabrera | Asteraceae | Mutisia | Leaves | Peru | [81] |
| Myrsine seguinii H. Lev. | Myrsinaceae alt. Primulaceae | Myrsine | Leaves | China, Japan and New Zealand | [82] |
| Myrothamnus flabellifolia Welw. | Myrothamnaceae | Resurrection plant | Leaves | South Africa | [83] |
| Aerial parts | Germany | [84] | |||
| Onobrychis kachetica Boiss. & Buhse | Fabaceae | Espartzet Kakhetinski | Leaves | Trans-caucasus, and Russia | [85] |
| Onobrychis viciifolia Scop. | Fabaceae | Sainfoin | Petals | Euro Siberian temperate region | [86] |
| Origanum dubium Boiss. | Lamiaceae | Rouvanos | Aerial parts | Cyprus | [87] |
| Origanum majorana L. | Lamiaceae | Sweet majoram | Leaves | Egypt | [88] |
| Origanum vulgare L. | Lamiaceae | Oregano or wild majoram | Aerial parts | Mediterranean region | [89] |
| Paederia scandens (Loir.) Merr. | Rubiaceae | Gandheli | Aerial parts | China and India | [90] |
| Paulownia fortune (Seem.) Hemsl. | Paulowniaceae | Dragon tree | Flowers | China | [91] |
| Persoonia gunnii Hook. f. | Proteaceae | Persoonia | Leaves | Tasmania | [25] |
| Petasites tricholobus Franch. | Asteraceae | Butterburs | Aerial parts | China, Nepal, Pakistan and Vietnam | [92] |
| Phellinus linteus (Berk. & M.A. Curtis) Teng | Hymenochaetaceae | Meshimakobu | Aerial parts | China, Korea and Japan | [93] |
| Phellodendron chinense var. glabriusculum C.K. Schenid. | Rutaceae | Cork tree | Aerial parts | China | [94] |
| Phyllostachys heterocycla Mitf. | Poaceae | Mousouchiku or tortoise shell bamboo | Bamboo-sheath | Japan | [95] |
| Picrorhiza scrophulariiflora Pennell. | Scrophulariaceae | Xizang Huhuanglian | Roots | China, India and Tibet | [96] |
| Platycodon grandiflorum L. | Campanulaceae | Balloon flower | Leaves | China | [97] |
| Podospermum canum C. A. Mey | Asteraceae | Karakok | Aerial parts | Caucasia, Iran, Iraq, Syria and Turkey | [98] |
| Prunophora salicina Linn. | Rosaceae | Chinese Plum | Fruit peels | China and Korea | [67] |
| Psophocarpus tetragonolobus (L.) DC | Fabaceae | Winged bean | Leaves | India | [99] |
| Pyrola calliantha Andres | Ericaceae | Wintergreen | Leaves | Eastern Himalaya to China | [100] |
| Pyrola incarnata Fisch. | Ericaceae | Lu Shou Cha | Leaves | China | [101] |
| Pyrus anatolica Browicz | Rosaceae | Turkish pear | Fruits, leaves and stem | Turkey | [102] |
| Pyrus biossieriana Buhse | Rosaceae | Wild pear | Leaves | Iran | [103] |
| Pyrus bretschneideri Rehder | Rosaceae | Ya pear | Leaves | China | [104] |
| Pyrus bourgaeana Decne. | Rosaceae | Iberian pear | Aerial parts | Iberian Peninsula and Morocco | [105] |
| Pyrus communis L. | Rosaceae | Pear or Rocha pear | Leaves | Central and eastern Europe and western Asia | [106,107] |
| Aerial parts and seeds | [108] | ||||
| Flowers | Poland | [109] | |||
| Pyrus communis L. var. sativa (DC.) | Rosaceae | Pear | Twigs | China | [110] |
| Pyrus communis L. cv. Wujiuxiang | Rosaceae | Wujiuxiang pear | Fruit peels | China | [111] |
| Pyrus elaeagrifolia Pall. | Rosaceae | Wild pear | Leaves | Albania, Bulgaria, Romania and Turkey | [112] |
| Pyrus pashia Buch ham ex D. Don | Rosaceae | Kainth | Fruits | The Himalayas | [113] |
| Pyrus pyraster (L.) Burgsd. | Rosaceae | European wild pear | Fruit peels | Western Europe to the Caucasus | [114,115] |
| Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai | Rosaceae | Niitaka or Asian pear | Fruits | Japan | [104,116] |
| Fruits | Korea | [117] | |||
| Asian pear | Fruit peels | China | [118] | ||
| Pyrus pyrifolia cv. Kousui Nakai | Rosaceae | Japanese pear | Branches, fruits, leaves and stem | Japan | [119] |
| Pyrus serotina Rehder. var. culta Rehdar. | Rosaceae | Japanese pear | Leaves | Japan | [120] |
| Pyrus spinosa | Rosaceae | Almond-leaved pear | Twigs | Siberia | [115] |
| Pyrus spp. | Rosaceae | Pear | Stem | Central and eastern Europe and western Asia | [121] |
| Pyrus ussuriensis Maxim. | Rosaceae | Ussurian pear | Leaves | China | [104] |
| Rhodiola coccinea (Royle) Boriss. | Crassulaceae | Rhodiola | Aerial parts | Central Asia, south-western Siberia and central China | [122] |
| Rhodiola crenulata LLL | Crassulaceae | Arctic root | Aerial parts | China | [123] |
| Rhodiola rosea L. | Crassulaceae | Golden root | Aerial parts | China | [124] |
| Rhododendron adamsii Rehder | Ericaceae | Sagaan dali | Leaves | Russia | [125] |
| Rhododendron dauricum L. | Ericaceae | Dauria | Leaves | China, Mongolia and Russia | [125] |
| Rhododendron fauriei Franch. var. brachycarpum | Ericaceae | Japanese Rhododendron | Leaves | Japan, Korea and Russia | [125] |
| Rhododendron luteum Sweet | Ericaceae | Yellow azalea | Leaves | Poland and Russia | [125] |
| Rhododendron ponticum L. | Ericaceae | Common rhododendron | Leaves | Iberian Peninsula and Russia | [125] |
| Rosa roxburghii Tratt. | Rosaceae | Roxburgh rose | Leaves | China | [126] |
| Salix acmophylla Boiss. | Salicaceae | Brook willow | Aerial parts | Pakistan and central Asia | [127] |
| Salvia hispanica L. | Lamiaceae | Chia | Flowers and stem | Central America | [128] |
| Salvia mexicana var. Mexicana L. | Lamiaceae | Mexican sage | Aerial parts | Mexico | [129] |
| Sambucus nigra L. | Adoxaceae | Elderberry or black elder | Fruits | Serbia | [130] |
| Saxifraga stolonifera Curtis | Saxifragaceae | Creeping sailor | Leaves | China, Japan and Korea | [131] |
| Scrofella chinensis Maxim. | Plantaginaceae | Scrofella | Whole plant | China | [132] |
| Sedum purpureum L. | Crassulaceae | Purple spoon-leaved stonecrop | Leaves | United Kingdom | [133] |
| Sedum spp. | Crassulaceae | Stonecrops | Leaves | Northern hemisphere | [134] |
| Selaginella tamariscina (Beauv.) Spring | Selaginellaceae | Selaginella | Aerial parts | China, India, Japan, Korea, Russia and Thailand | [135] |
| Serratula komaroviilljin L. | Asteraceae | Saw-wort | Leaves | Russia | [136] |
| Serratula quinquefolia M. Bieb. ex. Willd. | Asteraceae | Five-leaved saw-wort | Leaves | Poland | [137] |
| Serratula sogdiana (Bunge) L. Martins | Asteraceae | Plumeless saw-wort | Leaves | Eurasia | [138] |
| Sonneratia alba Sm. | Lythraceae | Perepat | Leaves | East Africa and south-east/far east Asia | [139] |
| Sorbaria arborea Schneid. | Rosaceae | False spirea | Stem | China | [140] |
| Stachys alopecuros (L.) Benth. Subsp. divulsa (Ten.) Grande | Lamiaceae | Yellow betony | Aerial parts | Italy | [141] |
| Stachys germanica L subsp. Salviifolia (Ten.) Gams. | Lamiaceae | Downy woundwort | Aerial parts | Italy and Germany | [142] |
| Stachys lavandulifolia Vahl. | Lamiaceae | Wood betony | Aerial parts | Iran | [143] |
| Teucrium chamaedrys L. | Lamiaceae | Wall germander | Leaves | Mediterranean region | [144] |
| Turnera diffusa Willd. | Passifloraceae | Damiana | Leaves and stem | Mexico and USA | [145] |
| Vaccinium arctostaphylos L. | Ericaceae | Caucasian whortleberry | Leaves | Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bulgaria, Georgia, Iran, Russia and Turkey | [146] |
| Vaccinium dunalianum Wight | Ericaceae | Chinese blueberry | Flower buds, fruits and leaves | Assam, China South-Central, China Southeast, East Himalaya, Myanmar, Nepal, Taiwan, Tibet and Vietnam | [147] |
| Vaccinium myrtillus L. | Ericaceae | European blueberry | Leaves and fruits | Europe | [148] |
| Leaves and stem | Europe | [149] | |||
| Vaccinium vacillans Torr. | Ericaceae | Blueberry | Leaves | Rhode Island | [150] |
| Vaccinium vitis-idaea L. | Ericaceae | Cowberry | Leaves and berries | Alaska, Canada, Poland, Russia and Eurasia | [151,152] |
| Aerial parts | China | [153] | |||
| Veronica austriaca L. | Plantaginaceae | Broadleaf speedwell | Leaves | Bulgaria | [154] |
| Veronica turrilliana Stoj. & Stef. | Plantaginaceae | Speedwell | Aerial parts | Bulgaria | [155] |
| Viburnum fordiae Hance | Viburnaceae | Bright red berry | Stem | China | [156] |
| Viburnum opulus L. | Viburnaceae | Guelder rose | Leaves | Europe, northern Africa and central Asia | [68,157] |
| Viburnum phlebotrichum Siebold & Zucc. | Viburnaceae | Japanese viburnum | Leaves | Japan | [68,158] |
| Viola arvensis L. | Violaceae | Field Pansy | Aerial parts | Russia | [159] |
| Wulfeniopsis amherstiana (Benth.) D.Y. Hong | Plantaginaceae | Himalyan Wulfenia | Leaves | The Himalayas | [160] |
| Xanthoxylum piperitum DC | Rutaceae | Sichuan pepper or Japanese pepper | Pericarp and seeds | Japan | [161] |
| Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim. | Rutaceae | Japanese pepper tree | Pericarps | China and Japan | [162] |
| Type of Cancer/Tumour | Brief Description of Anticancer Activity of Arbutin (1) | In Vivo/In Vitro | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bladder cancer | Inhibition of TCCSUP (anaplastic transitional cell carcinoma in the neck of the urinary bladder) bladder cancer cell proliferation. | In vitro | [166] |
| Brain tumour | Activity against rat C6 glioma cells. | In vitro | [167,168] |
| Breast cancer | Cytotoxicity of arbutin containing methanolic extract against MDA-MB-231 and T-47D breast cancer cells. | In vitro | [145] |
| Cytotoxicity towards the MCF-7 (breast cancer) cell line. | In vitro | [169] | |
| Cytotoxicity against adriamycin-resistant MCF-7 and wild-type MCF-7. | In vitro | [170] | |
| Cervical cancer | Antiproliferative activity against HeLa cells. | In vitro | [168] |
| Activity against human cervical carcinoma HPV-16 positive (SiHa) and HPV negative (C-33) cell lines. | [145] | ||
| Colon cancer | Assessed for cytotoxicity against HCT-15 cells derived from human colon carcinoma. | In vitro | [171] |
| Gastric cancer | Inhibition of gastric carcinoma MGC-803 cells invasion. | In vitro | [63] |
| Liver cancer | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities against diethylnitrosamine-induced liver carcinoma in rats. | In vivo | [172] |
| Inhibition of DNA-reactive carcinogen acetylaminofluorene induction of initiation of rat liver carcinogenesis. | In vivo | [173] | |
| Anticarcinogenic activity against hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HepG2). | In vitro | [169,174] | |
| Cytotoxicity against HepG2 cells. | In vitro | [175] | |
| Skin cancer | Pro-apoptotic activity on B16 murine melanoma cells. | In vitro | [176] |
| Action on the toxic trans-crotonaldehyde. | In vitro | [177] | |
| Osteosarcoma | Suppression of osteosarcoma progression. | In vitro | [178] |
| Prostate cancer | Induction of apoptosis in human prostrate adenocarcinoma (LNCaP) cells. | In vitro | [179,180] |
| Cytotoxicity against the prostate cancer cell line PC3. | [12] | ||
| Miscellaneous | Promotion of expression of miRNA-338-3p in suppressing cancer progression. | In vitro | [181] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nahar, L.; Al-Groshi, A.; Kumar, A.; Sarker, S.D. Arbutin: Occurrence in Plants, and Its Potential as an Anticancer Agent. Molecules 2022, 27, 8786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248786
Nahar L, Al-Groshi A, Kumar A, Sarker SD. Arbutin: Occurrence in Plants, and Its Potential as an Anticancer Agent. Molecules. 2022; 27(24):8786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248786
Chicago/Turabian StyleNahar, Lutfun, Afaf Al-Groshi, Anil Kumar, and Satyajit D. Sarker. 2022. "Arbutin: Occurrence in Plants, and Its Potential as an Anticancer Agent" Molecules 27, no. 24: 8786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248786
APA StyleNahar, L., Al-Groshi, A., Kumar, A., & Sarker, S. D. (2022). Arbutin: Occurrence in Plants, and Its Potential as an Anticancer Agent. Molecules, 27(24), 8786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248786