A Dual-Mode Method Based on Aptamer Recognition and Time-Resolved Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer for Histamine Detection in Fish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
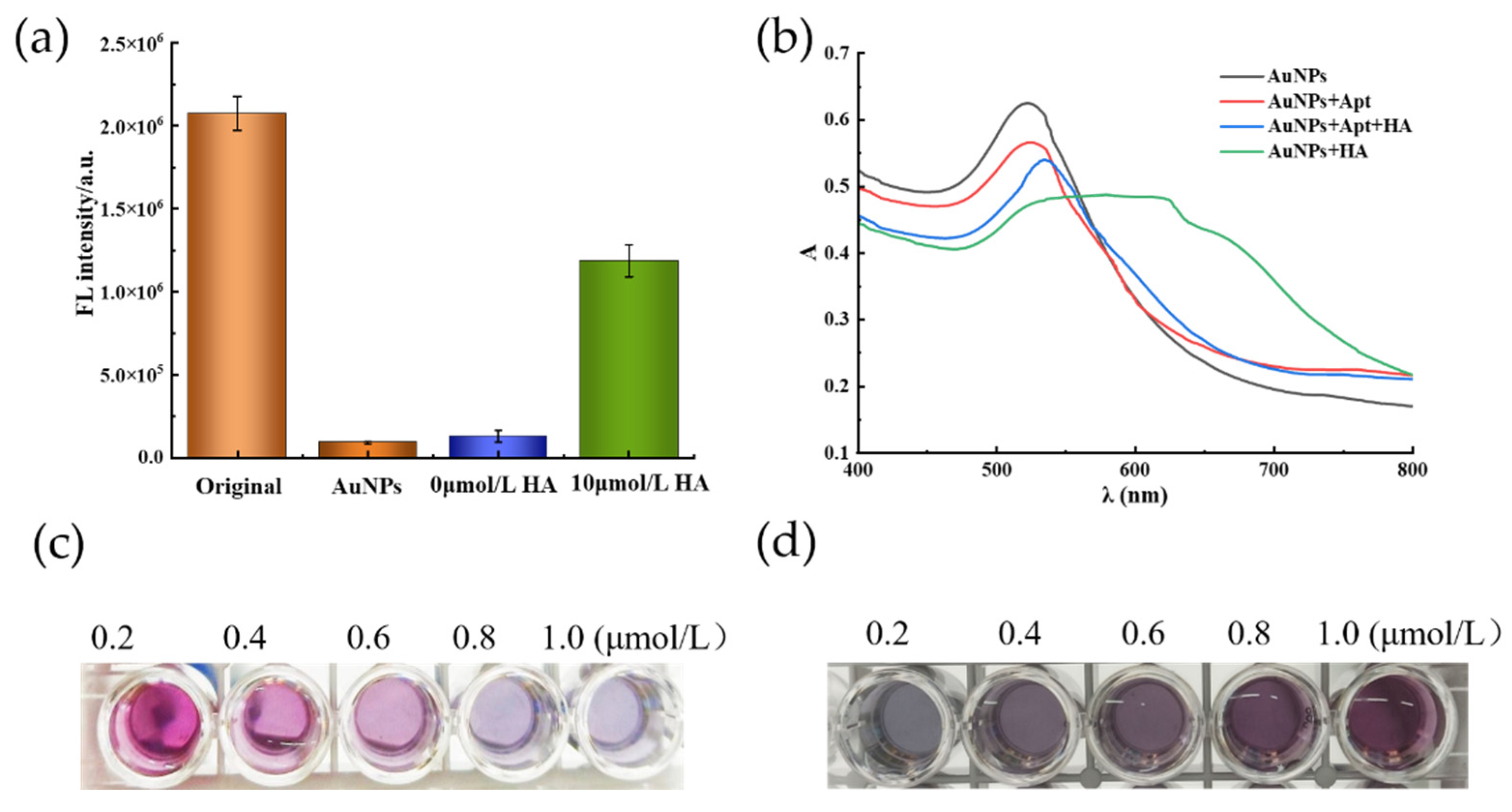
2.1. Feasibility of Fluorometric and Colorimetric Dual-Mode Detection of Histamine
2.2. Optimization of Dual-Mode Sensing System
2.2.1. Optimization of Aptamer Concentration
2.2.2. Optimization of Reaction Time
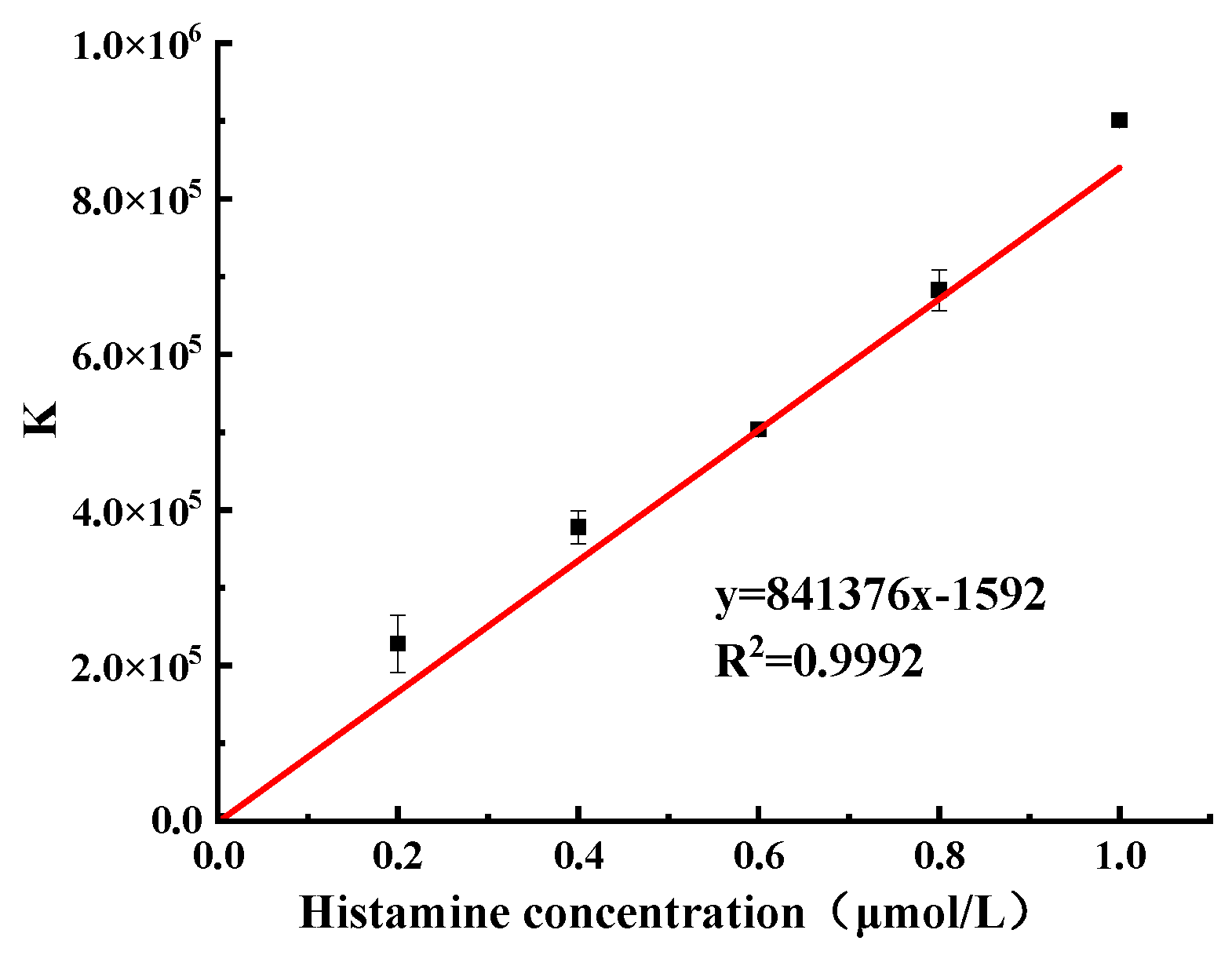
2.3. Establishment of Fluorometric/Colorimetric Dual-Mode Method for Detection of Histamine
2.4. Precision Analysis of the Measurement Results
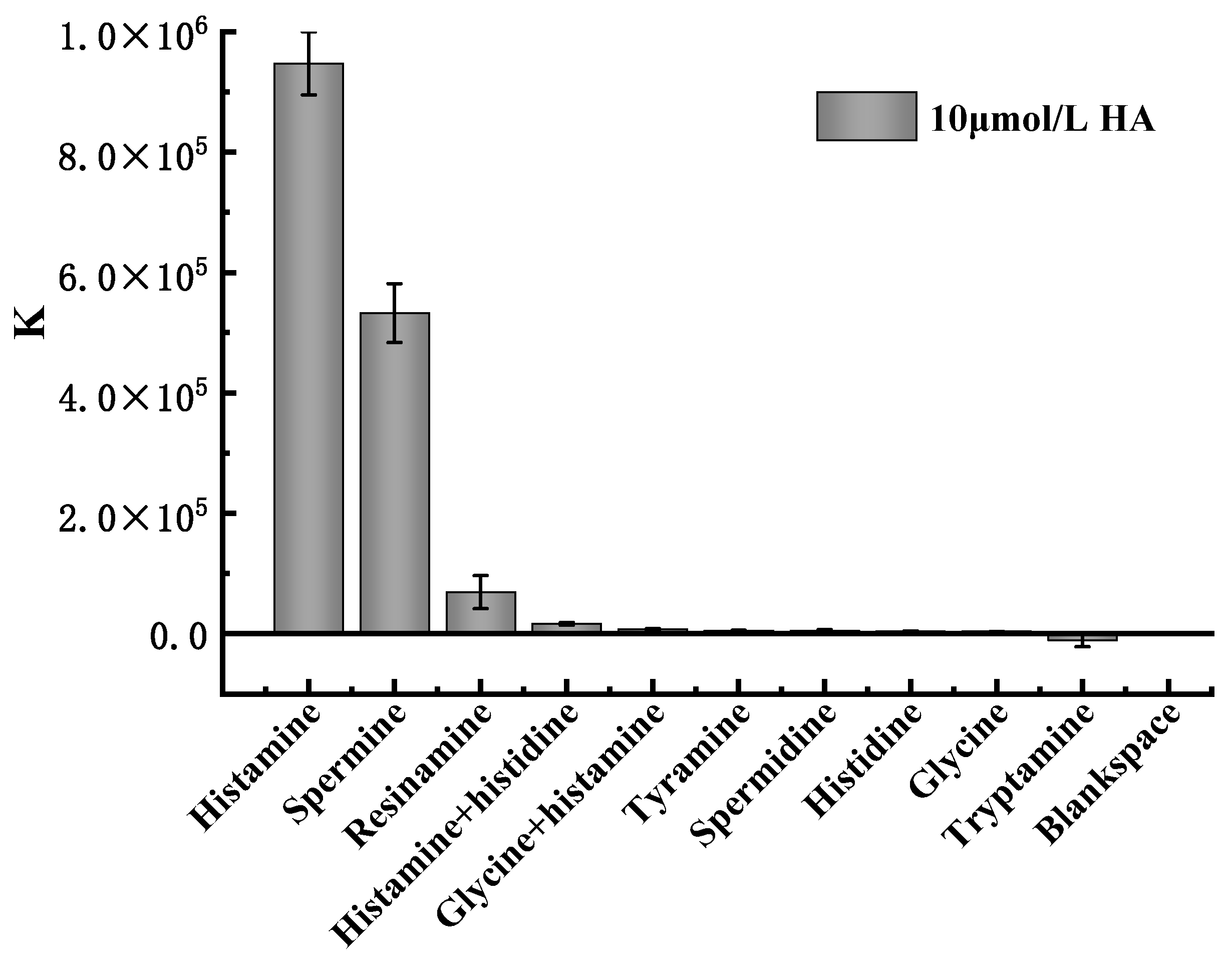
2.5. Analysis of Specificity
2.6. Comparison with Other Methods
2.7. Sample Detection Analysis and Recovery Experiment
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Instruments and Equipment
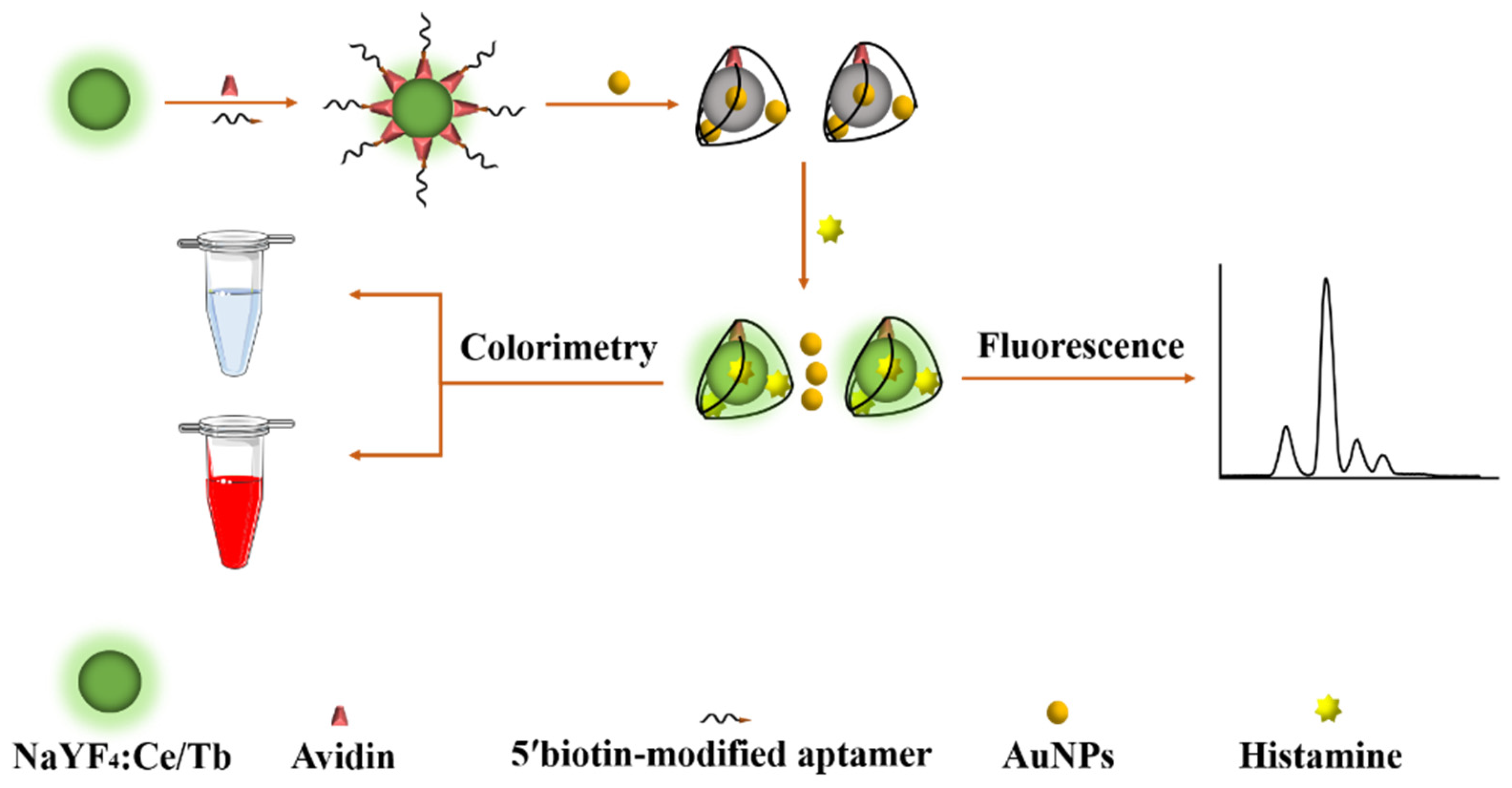
3.3. Detection Principle
3.4. Experimental Methods
3.4.1. Preparation of AuNPs
3.4.2. Preparation of NaYF4:Ce/Tb Nanoparticles
3.4.3. Preparation of NaYF4:Ce/Tb Nanoparticles Modified with Avidin
3.4.4. Assembly of Aptamer@NaYF4:Ce/Tb Nanoparticles
3.4.5. Construction of a Fluorescent Colorimetric Dual-Mode Based Method for the Detection of Histamine
3.4.6. Spiked Recoveries of Actual Samples with Detection Applications
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Karovicova, J.; Kohajdova, Z. Biogenic amines in food. Chem. Pap. 2005, 59, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emborg, J.; Dalgaard, P. Formation of histamine and biogenic amines in cold-smoked tuna: An investigation of psychrotolerant bacteria from samples implicated in cases of histamine fish poisoning. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanki, M.; Yoda, T.; Ishibashi, M.; Tsukamoto, T. Photobacterium phosphoreum caused a histamine fish poisoning incident. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 92, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, M.; Lambropoulou, D.; Morrison, C.; Modzinska, E.; Namiesnik, J.; Plotka-Wasylka, J. Literature update of analytical methods for biogenic amines determination in food and beverages. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerga, T.M.; Skouridou, V.; Bermudo, M.C.; Bashammakh, A.S.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Alyoubi, A.O.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Gold nanoparticle aptamer assay for the determination of histamine in foodstuffs. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, B.S.; Wang, J.T.; Choong, Y.M. A rapid gas chromatographic method for the determination of histamine in fish and fish products. Food Chem. 2003, 82, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Sato, M.; Han, Y.; Tan, Z.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nakano, T. A simple and rapid method for histamine analysis in fish and fishery products by TLC determination. Food Control 2011, 22, 1154–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiwaki, F.; Kuroda, K.; Inoue, Y.; Endo, G. Determination of histamine, 1-methylhistamine and N-methylhistamine by capillary electrophoresis with micelles. Biomed. Chromatogr. BMC 2000, 14, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spichiger, U.E.; Fakler, A. Potentiometric microelectrodes as sensor and detectors. Magnesium-selective electrodes as sensors, and hofmeister electrodes as detectors for histamine in capillary electrophoresis. Electrochim. Acta 1997, 42, 3137–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veseli, A.; Vasjari, M.; Arbneshi, T.; Hajrizi, A.; Svorc, L.; Samphao, A.; Kalcher, K. Electrochemical determination of histamine in fish sauce using heterogeneous carbon electrodes modified with rhenium(IV) oxide. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2016, 228, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, f.; Huang, y.; Yuan, y. Non-destructive identification of adulterated honey based on electronic nose. J. Xihua Univ. 2018, 37, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. Nanozyme and aptamer- based immunosorbent assay for aflatoxin B1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 123154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Yang, Z.; Khan, I.M.; Niazi, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H. Split aptamer acquisition mechanisms and current application in antibiotics detection: A short review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Catanante, G.; Hayat, A.; Istamboulie, G.; Ben Rejeb, I.; Bhand, S.; Marty, J.L. Development of structure switching aptamer assay for detection of aflatoxin M1 in milk sample. Talanta 2016, 158, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Duan, N.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Z.; Che, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Chen, X. Selection and characterization, application of a DNA aptamer targeted to Streptococcus pyogenes in cooked chicken. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 551, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairal Lerga, T.; Jauset-Rubio, M.; Skouridou, V.; Bashammakh, A.S.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Alyoubi, A.O.; O’Sullivan, C.K. High Affinity Aptamer for the Detection of the Biogenic Amine Histamine. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 7104–7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, S.; Sun, H.B.; Kawata, S. Photofabrication of wood-pile three-dimensional photonic crystals using four-beam laser interference. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 608–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. Study of a Nucleic Acid Aptamer Recognition-Based Time-Resolved Fluorescent Nanoprobe for Biotoxin Detection; Jiangnan University: Wuxi, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Brandao, M.P.; dos Anjos, V.d.C.; Bell, M.J.V. Time resolved fluorescence of cow and goat milk powder. Spectrochim. Acta Part A-Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 171, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulpakko, J.; Kopra, K.; Hanninen, P. Time-resolved fluorescence-based assay for rapid detection of Escherichia coli. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 470, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, T.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Guo, P. Characterization of edible oils using time-resolved fluorescence. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, C.; Huo, Q.; Song, Y.; Du, G.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Chen, X. A time-resolved luminescence aptasensor of ofloxacin based on rolling circle amplification and magnetic separation. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 4555–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, J.; Qi, Q.; Fu, L. A colorimetric and fluorescent gold nanoparticle-based dual-mode aptasensor for parvalbumin detection. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Shi, J.; Shi, Y.; Zou, X.; Tahir, H.E.; Holmes, M.; Zhang, W.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y. A dual-mode sensor for colorimetric and fluorescent detection of nitrite in hams based on carbon dots-neutral red system. Meat Sci. 2019, 147, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, B.; Ma, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, L. A SPR aptamer sensor for mercury based on AuNPs@NaYF4: Yb, Tm, Gd upconversion luminescent nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 6032–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tang, P.; Xing, X.; Cheng, W.; Liu, S.; Lu, X.; Zhong, L. Colorimetry/SERS dual-sensor of H2O2 constructed via TMB-Fe3O4@ AuNPs. Talanta 2022, 240, 123118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Wang, M.; Zheng, Y.; Cao, H.; Xu, F.; Ye, T.; Yu, J. Dual-mode fluorescent colorimetric detection of As(III) based on aptamer and gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2021, 49, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-F.; Lin, Z.-Z.; Hong, C.-Y.; Huang, Z.-Y. Histamine detection in fish samples based on indirect competitive ELISA method using iron-cobalt co-doped carbon dots labeled histamine antibody. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakthong, P.; Kondo, T.; Chailapakul, O.; Siangproh, W. Development of an unmodified screen-printed graphene electrode for nonenzymatic histamine detection. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 5407–5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Ashley, J.; Zhou, T.; Halder, A.; Sun, Y. A facile molecularly imprinted polymer-based fluorometric assay for detection of histamine. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 2365–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, G.; Dong, S. Electrochemiluminescence of tris(2,2′-bipyridine)ruthenium(II) immobilized in poly(p-styrenesulfonate)-silica-Triton X-100 composite thin-films. Analyst 2001, 126, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Song, Y.; Chen, F. Analysis of 8 biogenic amines in traditional Pixian douban based on response surface methodology optimized by precolumn derivatization-high performance liquid chromatography. J. Xihua Univ. 2020, 39, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Hu, C. Detection of pefloxacin veterinary drug residues in milk based on nucleic acid aptamer recognition with time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Food Ferment. Ind. 2021, 47, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Wu, S.; Duan, N.; Xu, B.; Wang, Z. Simultaneous detection of Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella typhimurium using multicolor time-resolved fluorescence nanoparticles as labels. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 237, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Histamine Concentration (μmol) | Measurement Results (n = 3) (105) | (105) | S (105) | RSD/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.2 | 2.0 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 7.5 | 3.4 |
| 0.4 | 3.3 | 3.4 | 3.6 | 3.5 | 9.7 | 2.7 |
| 0.6 | 5.1 | 5.0 | 5.3 | 5.2 | 2.0 | 3.8 |
| 0.8 | 6.5 | 6.7 | 6.6 | 6.7 | 9.1 | 1.4 |
| 1.0 | 8.3 | 8.1 | 8.4 | 8.2 | 2.1 | 2.6 |
| Histamine Concentration (μmol) | Measurement Results (n = 3) | S (10−3) | RSD/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 9.1 | 1.8 |
| 0.2 | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.58 | 16.4 | 2.8 |
| 0.4 | 0.64 | 0.65 | 0.66 | 0.65 | 0.4 | 0.1 |
| 0.6 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.74 | 16.8 | 2.2 |
| 0.8 | 0.81 | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 14.1 | 1.6 |
| 1.0 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 7.8 | 0.8 |
| Methods | Linear Range | Detection Limit | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indirect competitive ELISA method | 20~1350 μmol/L | 4500 nmol/L | [28] |
| Non-enzymatic unmodified graphene electrode based method | 40~900 μmol/L | 5580 nmol/L | [29] |
| Molecularly imprinted polymer-based fluorescence assay | 1.8~44.98 μmol/L | 1800 nmol/L | [30] |
| Plasmonic nanoparticle-based surface plasmon resonance electrochemiluminescence of polyacid-bipyridyl ruthenium | 1~1000 μmol/L | 100 nmol/L | [31] |
| Colorimetric | 0.2~1.0 μmol/L | 69.37 nmol/L | This work |
| Fluorescence | 0.2~1.0 μmol/L | 9.21 nmol/L | This work |
| Dual mode (K-value) | 0.2~1.0 μmol/L | 4.57 nmol/L | This work |
| Samples | Amount Added (μmol) | Detection Amount | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trichiurus haumela | 0 | - | 0 |
| 0.2 | 0.166 ± 0.003 | 83.41 ± 0.016 | |
| 0.4 | 0.371 ± 0.021 | 92.87 ± 0.051 | |
| 0.6 | 0.564 ± 0.044 | 94.02 ± 0.072 | |
| 0.8 | 0.816 ± 0.070 | 101.94 ± 0.087 | |
| 1.0 | 0.949 ± 0.069 | 94.98 ± 0.068 | |
| Thamnaconus septentrionalis | 0 | 0.075 ± 0.0138 | - |
| 0.2 | 0.164 ± 0.010 | 82.24 ± 0.047 | |
| 0.4 | 0.389 ± 0.005 | 97.41 ± 0.012 | |
| 0.6 | 0.636 ± 0.010 | 105.92 ± 0.017 | |
| 0.8 | 0.759 ± 0.30 | 94.97 ± 0.036 | |
| 1.0 | 0.919 ± 0.04 | 91.88 ± 0.040 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Yang, F.; Deng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Ye, H.; Zhong, J.; Wang, Z. A Dual-Mode Method Based on Aptamer Recognition and Time-Resolved Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer for Histamine Detection in Fish. Molecules 2022, 27, 8711. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248711
Wang X, Yang F, Deng C, Zhang Y, Yang X, Chen X, Huang Y, Ye H, Zhong J, Wang Z. A Dual-Mode Method Based on Aptamer Recognition and Time-Resolved Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer for Histamine Detection in Fish. Molecules. 2022; 27(24):8711. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248711
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xin, Fu Yang, Chengfang Deng, Yujie Zhang, Xiao Yang, Xianggui Chen, Yukun Huang, Hua Ye, Jianjun Zhong, and Zhouping Wang. 2022. "A Dual-Mode Method Based on Aptamer Recognition and Time-Resolved Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer for Histamine Detection in Fish" Molecules 27, no. 24: 8711. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248711
APA StyleWang, X., Yang, F., Deng, C., Zhang, Y., Yang, X., Chen, X., Huang, Y., Ye, H., Zhong, J., & Wang, Z. (2022). A Dual-Mode Method Based on Aptamer Recognition and Time-Resolved Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer for Histamine Detection in Fish. Molecules, 27(24), 8711. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248711





