Effect of Phytosynthesized Selenium and Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles on Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) against Stripe Rust Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Green Synthesis of SeNPs and CeONPs
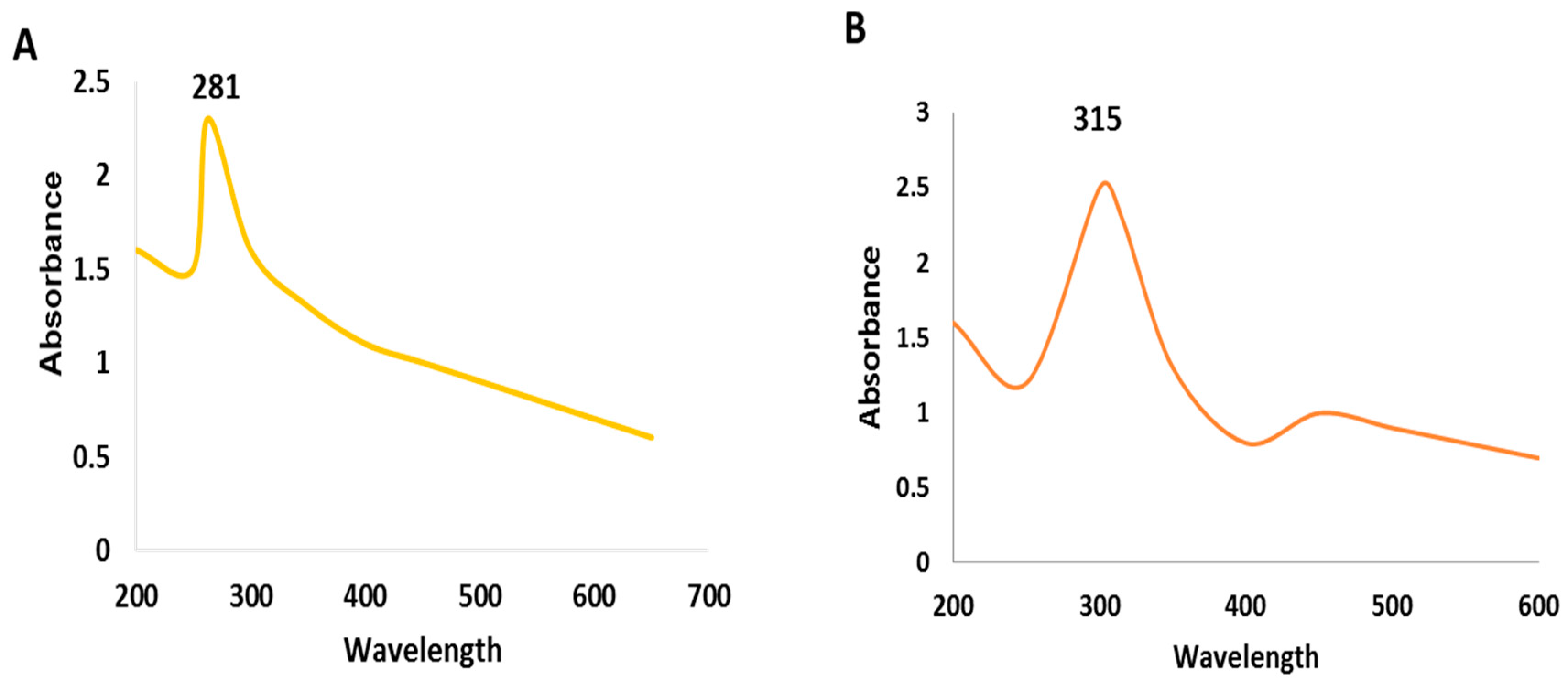
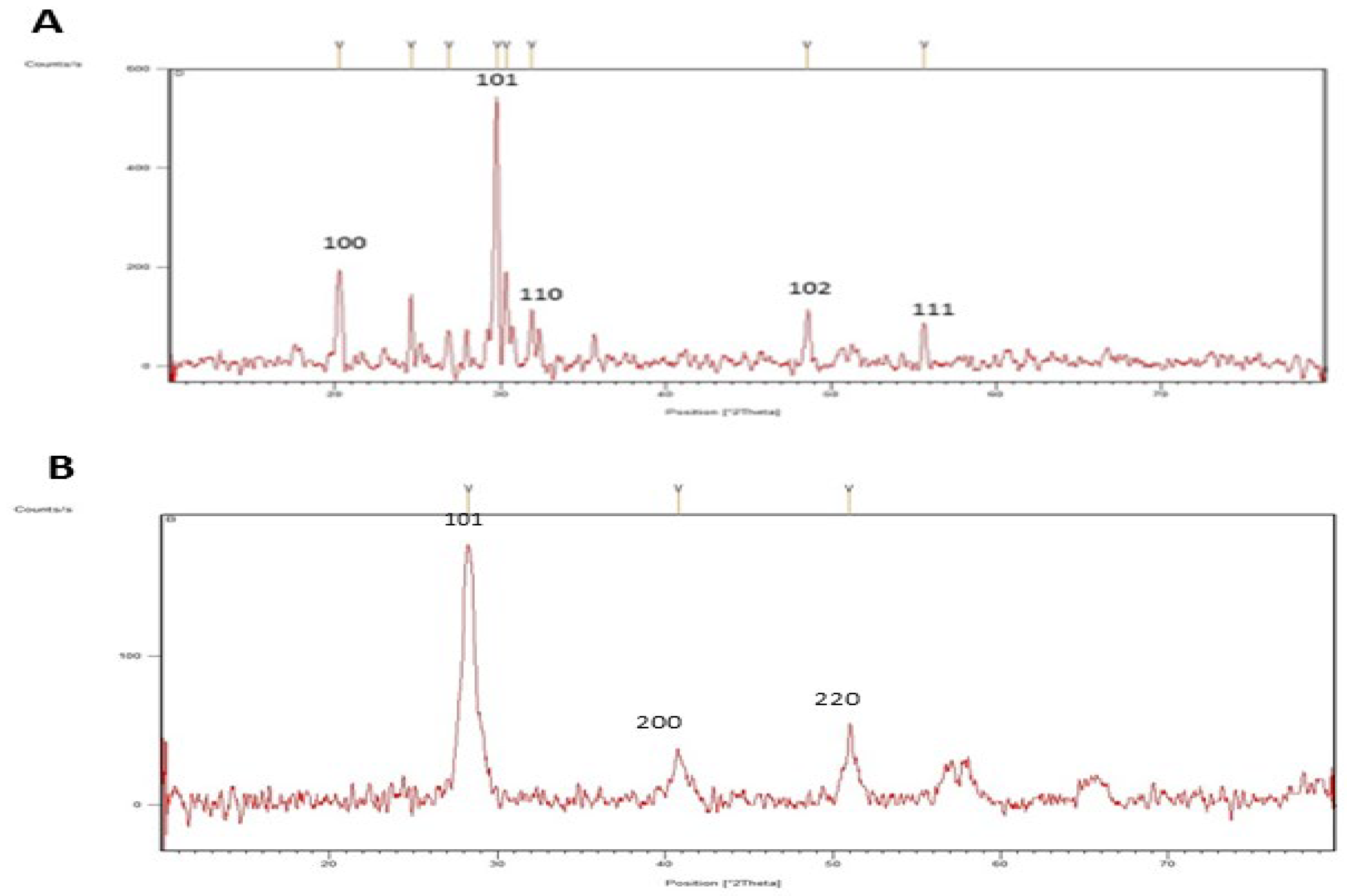
2.2. Characterization of SeNPs and CeONPs
2.3. Evaluation of Disease Severity
2.4. Effect of Exogenous Application of SeNPs and CeONPs on Morphological Profiles of Wheat
2.5. Effect of Exogenous Application of SeNPs and CeONPs on Physiological Profiles of Wheat
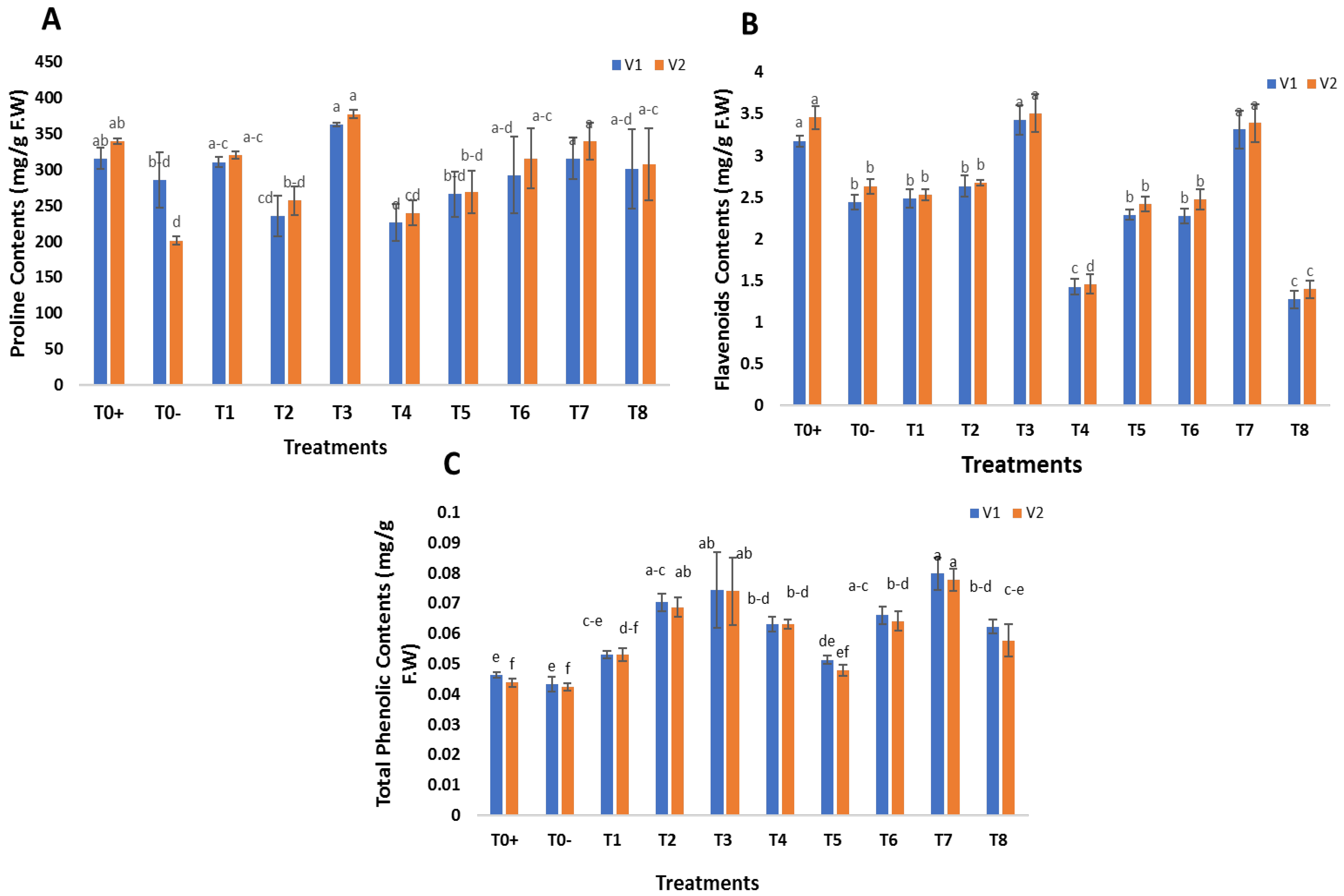
2.6. Exogenous Application of SeNPs and CeONPs on Biochemical Attributes of Wheat
2.7. Foliar Spray of Green Synthesized SeNPs and CeONPs on Antioxidant Defense System of Wheat
2.8. Antioxidant Activity of SeNPs and CeONPs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Phyto- Synthesis of SeNPs and CeONPs
3.2. Characterization of Nanoparticles
3.2.1. UV-Visible Analysis of SeNPs and CeONPs
3.2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy of SeNPs and CeONPs
3.2.3. Energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX)
3.2.4. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.3. Glass House Experiment
3.4. Inoculums Preparation
3.5. Inoculation of Fungus and Foliar Application of SeNPs and CeONPs on Wheat
3.6. Collection of Samples for Disease Severity
3.7. Evaluation of Plant Morphological Parameters
3.8. Evaluation of Plant Physiological Parameter
3.8.1. Chlorophyll Contents (mg/g F.W)
3.8.2. Membrane Stability Index (%)
3.9. Evaluation of Plant Biochemical Parameters
3.9.1. Proline Contents
3.9.2. Total Flavenoid Contents
3.9.3. Total Phenolic Contents
3.9.4. SOD Activity
3.9.5. POD Activity
3.10. Antioxidant Activity
3.10.1. DPPH Assay
3.10.2. ABTS Assay
3.10.3. Reducing Power Assay
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X. Pathogens which threaten food security: Puccinia striiformis, the wheat stripe rust pathogen. Food Secur. 2020, 12, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, U.; Mumtaz, R.; Shafaq, Z.; Zaidi, S.M.H.; Kaifi, M.O.; Mahmood, Z.; Zaidi, S.A.R. Wheat rust disease detection techniques: A technical perspective. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2022, 129, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, H.S.; Al Mutery, A.; Osman, N.H.; Reyad, N.E.H.A.; Abou-Zeid, M.A. Genetic diversity, antifungal evaluation and molecular docking studies of Cu-chitosan nanoparticles as prospective stem rust inhibitor candidates among some Egyptian wheat genotypes. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosegrant, M.W.; Agcaoili-Sombilla, P.N. Global Food Projects to 2020; Discussion Paper 5; IFPRI: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, H.; Ilyas, N.; Akhtar, N.; Raja, N.I.; Zainab, T.; Shah, T.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, P. Biosynthesis and characterization of titanium dioxide nanoparticles and its effects along with calcium phosphate on physicochemical attributes of wheat under drought stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 223, 112519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bux, H.; Ashraf, M.; Hussain, F.; Rattu, A.-U.-R.; Fayyaz, M. Characterization of wheat germplasm for stripe rust (‘Puccini striiformis’f. sp.’tritici’) resistance. Aust. J. Crop. Sci. 2012, 6, 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, C.K.; Thach, T.; Hovmøller, M.S. Evaluation of spray and point inoculation methods for the phenotyping of Puccinia striiformis on wheat. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wellings, C.; Chen, X.; Kang, Z.; Liu, T. Wheat stripe (yellow) rust caused by Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2014, 15, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, G.; Sharma, A.; Mackay, I.; Srivastava, P.; Kaur, S.; Kaur, J.; Bains, N.S. Identification of a novel stripe rust resistance gene from the European winter wheat cultivar ‘Acienda’: A step towards rust proofing wheat cultivation. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandy, S.; Mandal, N.; Bhowmik, P.; Khan, M.; Basu, S. Sustainable management of rice blast (Magnaporthe grisea (Hebert) Barr): 50 years of research progress in molecular biology. In Management of Fungal Plant Pathogens; Arya, A., Perello, A.E., Eds.; CAB International: Oxforshire, UK, 2010; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Satti, S.H.; Raja, N.I.; Javed, B.; Akram, A.; Mashwani, Z.-u.-R.; Ahmad, M.S.; Ikram, M. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles elicited agro-morphological and physicochemical modifications in wheat plants to control Bipolaris sorokiniana. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TaghavizadehYazdi, M.E.; Darroudi, M.; Amiri, M.S.; Zarrinfar, H.; Hosseini, H.A.; Mashreghi, M.; Mozafarri, H.; Ghorbani, A.; Mousavi, S.H. Antimycobacterial, Anticancer, Antioxidant and Photocatalytic Activity of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Berberis Integerrima. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Sci. 2022, 46, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Akbari, A.; Sabouri, Z.; Soleimanpour, S.; Zarrinfar, H.; Khatami, M.; Darroudi, M. Green synthesis of colloidal selenium nanoparticles in starch solutions and investigation of their photocatalytic, antimicrobial, and cytotoxicity effects. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fardsadegh, B.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H. Aloe vera leaf extract mediated green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles and assessment of their in vitro antimicrobial activity against spoilage fungi and pathogenic bacteria strains. Green Process Synth. 2019, 8, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafghi, M.H.; Nazari, R.; Darroudi, M.; Zargar, M.; Zarrinfar, H. The effect of biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles on the expression of CYP51A and HSP90 antifungal resistance genes in Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillus flavus. Biotechnol. Prog. 2022, 38, e3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Xun, W.; Yue, W.; Zhang, C.; Ren, Y.; Shi, L.; Wang, Q.; Yang, R.; Lei, F. Effect of sodium selenite, Se-yeast and nano-elemental selenium on growth performance, Se concentration and antioxidant status in growing male goats. Small Rumin. Res. 2011, 96, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghian, S.; Kojouri, G.A.; Mohebbi, A. Nanoparticles of selenium as species with stronger physiological effects in sheep in comparison with sodium selenite. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2012, 146, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, I.A.; Santos, C.C.; Xavier, A.L.; Batista, T.M.; Nascimento, Y.M.; Nunes, J.M.; de Freitas e Silva, P.M.; Menezes-Júnior, R.A.; Ferreira, J.M.; Lima, E.; et al. Synthesis, physicochemical characterization, antifungal activity and toxicological features of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 102888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korde, P.; Ghotekar, S.; Pagar, T.; Pansambal, S.; Oza, R.; Mane, D. Plant extract assisted eco-benevolent synthesis of selenium nanoparticles-a review on plant parts involved, characterization, and their recent applications. J. Chem. Rev. 2020, 2, 157–168. [Google Scholar]
- Murugesan, G.; Nagaraj, K.; Sunmathi, D.; Subramani, K. Methods involved in the synthesis of selenium nanoparticles and their different applications-a review. Eur. J. Biomed. 2019, 6, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.D.; Datta, S. Antioxidant enzyme activities during in vitro morphogenesis of gladiolus and the effect of application of antioxidants on plant regeneration. Biol. Plant. 2003, 47, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Raja, N.I.; Naz, F.; Iqbal, M.; Aslam, S. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles and their effects on antimicrobial efficacy and biochemical profiling in Citrus reticulata. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 12, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauwel, P.; Kuunal, S.; Ferdov, S.; Rauwel, E. A review on the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their morphologies studied via TEM. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015, 682749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.S.; Rai, A.; Ahmad, A.; Sastry, M. Rapid synthesis of Au, Ag, and bimetallic Au core–Ag shell nanoparticles using Neem (Azadirachtaindica) leaf broth. J. Colloid Interface sci. 2004, 275, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.S.; Abbas, K.; Qadir, M.I. Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of biological properties of selenium nanoparticles from Solanum lycopersicum. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103901. [Google Scholar]
- Satgurunathan, T.; Bhavan, P.S.; Komachi, S. Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles from sodium selenite using garlic extract and its enrichment on Artemianauplii to feed the freshwater prawn Macrobrachiumrosenbergii post–larvae. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2017, 21, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Hussain, I.; Singh, N.; Singh, H. Uptake, translocation and impact of green synthesized nanoceria on growth and antioxidant enzymes activity of Solanum lycopersicum L. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan Irshad, M.; Aziz, M.H.; Fatima, M.; Rehman, S.U.; Idrees, M.; Rana, S.; Shaheen, F.; Ahmed, A.; Javed, M.Q.; Huang, Q. Green synthesis, cytotoxicity, antioxidant and photocatalytic activity of CeO2 nanoparticles mediated via orange peel extract (OPE). Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 0950a4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiling, W.; Murakonda, G.K.; Jarubula, R. Application of green-synthesized cerium oxide nanoparticles to treat spinal cord injury and cytotoxicity evaluation on paediatricleukaemia cells. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 07500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fesharaki, P.J.; Nazari, P.; Shakibaie, M.; Rezaie, S.; Banoee, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Shahverdi, A.R. Biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles using Klebsiellapneumoniae and their recovery by a simple sterilization process. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2010, 41, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokila, K.; Elavarasan, N.; Sujatha, V. Diospyrosmontana leaf extract-mediated synthesis of selenium nanoparticles and their biological applications. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 7481–7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, Q.; Nazar, M.; Naz, S.; Hussain, T.; Jabeen, N.; Kausar, R.; Jan, T. Antimicrobial potential of green synthesized CeO2 nanoparticles from Oleaeuropaea leaf extract. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, P.; Maheshwari, S.K. Preparation of sliver and selenium nanoparticles and its characterization by dynamic light scattering and scanning electron microscopy. J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 2018, 6, 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- Matai, I.; Pandey, S.K.; Garg, D.; Rani, K.; Sachdev, A. Phytogreen synthesis of multifunctional nano selenium with antibacterial and antioxidant implications. Nano Express 2020, 1, 010031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, M.; Manoharadas, S.; Zeyad, M.T. Green synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles using Acoruscalamus extract and their antibiofilm activity against bacterial pathogens. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2021, 84, 1638–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Du, Y.; Liu, T.; Wong, K.H.; Chen, T. Systematic acute and subchronic toxicity evaluation of polysaccharide–protein complex-functionalized selenium nanoparticles with anticancer potency. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 5112–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gougis, M.; Pereira, A.; Ma, D.; Mohamedi, M. Simultaneous deposition of cerium oxide and gold nanostructures-characterization and analytical properties toward glucose electro-oxidation and sensing. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 39955–39961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresneda, M.A.; Martin, J.D.; Bolivar, J.G.; Cantos, M.V.; Bosch-Estevez, G.; Moreno, M.F.; Merroun, M.L. Green synthesis and biotransformation of amorphous Se nanospheres to trigonal 1D Se nanostructures: Impact on Se mobility within the concept of radioactive waste disposal. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 2103–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Khan, S.B.; Khan, L.U.; Farooq, A.; Akhtar, K.; Asiri, A.M. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy: Fundamentals and application in functional groups and nanomaterials characterization. In Handbook of Materials Characterization; Sharma, S.K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 317–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Mukherjee, R.; Patra, M.; Banik, M.; Dasgupta, R.; Mukherjee, M.; Basu, T. Green synthesized cerium oxide nanoparticle: A prospective drug against oxidative harm. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 147, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Rajan, A.R.; Rajan, A.; John, A.; Philip, D. Green synthesis of CeO2 nanostructures by using Morus nigra fruit extract and its antidiabetic activity. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2105, p. 020008. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, H.; Khatoon, N.; Raza, M.; Ghosh, P.C.; Sardar, M. Synthesis and characterization of nano selenium using plant biomolecules and their potential applications. Bionanoscience 2019, 9, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, K.; Hong, B.; He, J.; Hong, Z.; Tan, R. Preparation and antioxidant properties of selenium nanoparticles-loaded chitosan microspheres. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 4527. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, M.J.; Ahmad, I.; Khanzada, K.A.; Ahmad, N.; Rattu, U.R.; Fayyaz, M.; Ahmad, Y.; Hakro, A.A.; Kazi, A.M. Local stem rust virulence in Pakistan and future breeding strategy. Pak. J. Bot. 2010, 42, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Blinov, A.V.; Serov, A.V.; Gvozdenko, A.A.; Kravtsov, A.A.; Nagdalian, A.A.; Ibrahim, S.A. Effect of selenium nanoparticles on germination of Hordéum Vulgáre barley seeds. Coatings 2021, 11, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desoky, E.S.M.; Merwad, A.R.M.; Abo El-Maati, M.F.; Mansour, E.; Arnaout, S.M.; Awad, M.F.; Ramadan, M.; Ibrahim, S.A. Physiological and biochemical mechanisms of exogenously applied selenium for alleviating destructive impacts induced by salinity stress in bread wheat. Agronomy 2021, 11, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, S.; Asad, S.; Munir, A.; Ahmad, I.; Sultan, A. Prevalence and distribution of foliar blight pathogens of wheat in different agro ecological zones of Pakistan with special reference to Bipolarissorokiniana. Pak. J. Bot. 2006, 38, 205–218. [Google Scholar]
- Rico, C.M.; Barrios, A.C.; Tan, W.; Rubenecia, R.; Lee, S.C.; Varela-Ramirez, A.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Physiological and biochemical response of soil-grown barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) to cerium oxide nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10551–10558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.P.; Capen, J.D.; Zhang, W.; Ma, X.; Rossi, L. Effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles and cadmium on corn (Zea mays L.) seedlings physiology and root anatomy. NanoImpact 2020, 20, 100264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allakhverdiev, S.I.; Nishiyama, Y.; Miyairi, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Inagaki, N.; Kanesaki, Y.; Murata, N. Salt stress inhibits the repair of photodamaged photosystem II by suppressing the transcription and translation of psbA genes in Synechocystis. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Raza, M.A.; Awan, S.A.; Shah, G.A.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, B.; Huang, L. Amelioration of salt induced toxicity in pearl millet by seed priming with silver nanoparticles (AgNPs): The oxidative damage, antioxidant enzymes and ions uptake are major determinants of salt tolerant capacity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 156, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, F.; Majd, A.; Jonoubi, P.; Najafi, F. Effects of silicon nanoparticles on molecular, chemical, structural and ultrastructural characteristics of oat (Avena sativa L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 127, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrees, M.; Khan, Z.S.; Ali, S.; Hafeez, M.; Khalid, S.; ur Rehman, M.Z.; Hussain, A.; Hussain, K.; Chatha, S.A.S.; Rizwan, M.; et al. Simultaneous mitigation of cadmium and drought stress in wheat by soil application of iron nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.; Ji, R.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, J.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Guo, H. Physiological and biochemical changes imposed by CeO2 nanoparticles on wheat: A life cycle field study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11884–11893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djanaguiraman, M.; Nair, R.; Giraldo, J.P.; Prasad, P.V.V. Cerium oxide nanoparticles decrease drought-induced oxidative damage in sorghum leading to higher photosynthesis and grain yield. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 14406–14416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiterio-Gutierrez, T.; Ortega-Ortiz, H.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Hernandez-Fuentes, A.D.; Sandoval-Rangel, A.; Benavides-Mendoza, A.; Cabrera-de la Fuente, M.; Juarez-Maldonado, A. The application of selenium and copper nanoparticles modifies the biochemicalresponses of tomato plants under stress by Alternaria Solani. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, S.M.; Abdelrahman, M.; Hosseini, M.S.; Hoveizeh, N.F.; Tran, L.P. Alleviation of the effect of salinity on growth andyield of strawberry by foliar spray of selenium-nanoparticles. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.H.; Yin, L.P.; Xu, G.J.; Zheng, C.; Lei, C.; Zhang, M.Z. Selenium increases chlorogenic acid, chlorophyll and carotenoids of Lyciumchinense leaves. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rady, M.M.; Desoky, E.S.; Ahmed, S.M.; Majrashi, A.; Ali, E.F.; Arnaout, S.M.; Selem, E. Foliar nourishment with nano-selenium dioxide promotes physiology, biochemistry, antioxidant defenses, and salt tolerance in phaseolus vulgaris. Plants 2021, 10, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi-Cheraghabadi, M.; Modarres-Sanavy, S.A.M.; Sefidkon, F.; Rashidi-Monfared, S.; Mokhtassi-Bidgoli, A. Improving water deficit tolerance of Salvia officinalis L. using putrescine. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil-Kumar, M.; Mysore, K.S. Ornithine-delta-aminotransferase and proline dehydrogenase genes play a role in non-host disease resistance by regulating pyrroline-5-carboxylate metabolism-induced hypersensitive response. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 1329–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, A.; Gelani, S.; Ashraf, M.; Foolad, M.R. Heat tolerance in plants: An overview. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 61, 199–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemian, S.; Masoudian, N.; SaeidNematpour, F.; SafipourAfshar, A. Selenium nanoparticles stimulate growth, physiology, and gene expression to alleviate salt stress in Melissa officinalis. Biologia 2021, 76, 2879–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, R.; Ahmed, S.; Shah, A.A.; Yasin, N.A. Selenium nanoparticles reduced cadmium uptake, regulated nutritional homeostasis and antioxidative system in Coriandrum sativum grown in cadmium toxic conditions. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hoseiny, H.; Helaly, M.N.; Elsheery, N.I.; Alam-Eldein, S.M. Humic acid and boron to minimize the incidence of alternate bearing and improve the productivity and fruit quality of mango trees. Hortscience 2020, 55, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahani, S.; Saadatmand, S.; Mahmoodzadeh, H.; Khavari-Nejad, R.A. Effect of foliar application of cerium oxide nanoparticles on growth, photosynthetic pigments, electrolyte leakage, compatible osmolytes and antioxidant enzymes activities of Calendula officinalis L. Biologia 2019, 74, 1063–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raigond, P.; Raigond, B.; Kaundal, B.; Singh, B.; Joshi, A.; Dutt, S. Effect of zinc nanoparticles on antioxidativesystem of potato plants. J. Environ. Biol. 2017, 38, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Vargas, E.R.; Ortega-Ortiz, H.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; de Alba Romenus, K.; Cabrera de la Fuente, M.; Benavides-Mendoza, A.; Juarez-Maldonado, A. Foliar application of copper nanoparticles increases the fruit quality and the content of bioactive compounds in tomatoes. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Wei, T.; Che, S.; Yan, G. Identification of MsHsp20 gene family in Malussieversii and functional characterization of MsHsp16. 9 in heat tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zu, C.; Lu, D.; Zheng, Q.; Shen, J.; Wang, H.; Li, D. Effect of exogenous selenium supply on photosynthesis, Na+ accumulation and antioxidative capacity of maize (Zea mays L.) under salinity stress. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali-Andani, N.; Fallah, S.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Golkar, P. A comprehensive study of selenium and cerium oxide nanoparticles on mung bean: Individual and synergistic effect on photosynthesis pigments, antioxidants, and dry matter accumulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Stowers, C.; Rossi, L.; Zhang, W.; Lombardini, L.; Ma, X. Physiological effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles on the photosynthesis and water use efficiency of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.). Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khai, H.D.; Mai, N.T.N.; Tung, H.T.; Luan, V.Q.; Cuong, D.M.; Ngan, H.T.M.; Chau, N.H.; Buu, N.Q.; Vinh, N.Q.; Dung, D.M.; et al. Selenium nanoparticles as in vitro rooting agent, regulates stomata closure and antioxidant activity of gerbera to tolerate acclimatization stress. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2022, 150, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardsadegh, B.; Vaghari, H.; Mohammad-Jafari, R.; Najarian, Y.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H. Biosynthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activities assessment of fabricated selenium nanoparticles using Pelargonium zonale leaf extract. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, S.N.H.; Al-Jassasi, B.M.H.; Al-Sawafi, H.M.S.; Al-Shukaili, S.H.G.; Rahman, N.; Nasir, M. Optimization for synthesis of silver nanoparticles through response surface methodology using leaf extract of Boswellia sacra and its application in antimicrobial activity. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.; Shahat, A.; El-Didamony, A.; El-Desouky, M.G.; El-Bindary, A.A. Mesoporous iron oxide nano spheres for capturing organic dyes from water sources. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1217, 128361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiwaan, H.; Mohamd, F.; El-Bindary, A.; El-Ghamaz, N.; Abo-Yassin, H.; El-Bindary, M. Synthesis, identification and application of metal organic framework for removal of industrial cationic dyes. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 342, 117435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruinsma, J. Investigation of the chlorophyll contents in the leaves extracts. Photochem. Photobiol. 1963, 2, 241–244. [Google Scholar]
- Sairam, R.K.; Deshmukh, P.S.; Shukla, D.S. Tolerance of drought and temperature stress in relation to increased antioxidant enzyme activity in wheat. J. Agron. Crop. Sci. 1997, 178, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.S.; Rizwan, M.; Hafeez, M.; Ali, S.; Adrees, M.; Qayyum, M.F.; Khalid, S.; ur Rehman, M.Z.; Sarwar, M.A. Effects of silicon nanoparticles on growth and physiology of wheat in cadmium contaminated soil under different soil moisture levels. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 4958–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, H.; Anjum, T.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Microwave-assisted green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Melia azedarach for the management of Fusarium wilt in tomato. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.M.; De Britto, S.; Jogaiah, S.; Ito, S.I. Mycogenic selenium nanoparticles as potential new generation broad spectrum antifungal molecules. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunti, L.; Dass, R.S.; Kalagatur, N.K. Phytofabrication of selenium nanoparticles from Emblicaofficinalis fruit extract and exploringitsbiopotential applications: Antioxidant, antimicrobial, and biocompatibility. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Treatments | Concentrations (mg/L) |
|---|---|
| To (Positive) | Control (healthy wheat plants) |
| To (Negative) | Pathogen (P. striiformis) |
| T1 | 10 mg/L of SeNPs + Pathogen |
| T2 | 20 mg/L of SeNPs + Pathogen |
| T3 | 30 mg/L of SeNPs + Pathogen |
| T4 | 40 mg/L of SeNPs + Pathogen |
| T5 | 10 mg/L of CeONPs + Pathogen |
| T6 | 20 mg/L of CeONPs + Pathogen |
| T7 | 30 mg/L of CeONPs + Pathogen |
| T8 | 40 mg/L of CeONPs + Pathogen |
| 0 | No Symptoms | Resistant |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1–5% stripes on the leaves | Moderately resistant |
| 2 | 6–20% stripes on the leave | Moderately resistant |
| 3 | 21–40% stripes on the leaves | Moderately susceptible |
| 4 | 41–60% stripes on the leaves | Moderately susceptible |
| 5 | >61% stripes on the leaves | Susceptible |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahbaz, M.; Fatima, N.; Mashwani, Z.-u.-R.; Akram, A.; Haq, E.u.; Mehak, A.; Abasi, F.; Ajmal, M.; Yousaf, T.; Raja, N.I.; et al. Effect of Phytosynthesized Selenium and Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles on Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) against Stripe Rust Disease. Molecules 2022, 27, 8149. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238149
Shahbaz M, Fatima N, Mashwani Z-u-R, Akram A, Haq Eu, Mehak A, Abasi F, Ajmal M, Yousaf T, Raja NI, et al. Effect of Phytosynthesized Selenium and Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles on Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) against Stripe Rust Disease. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8149. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238149
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahbaz, Muhammad, Noor Fatima, Zia-ur-Rehman Mashwani, Abida Akram, Ehsan ul Haq, Asma Mehak, Fozia Abasi, Maryam Ajmal, Tayyaba Yousaf, Naveed Iqbal Raja, and et al. 2022. "Effect of Phytosynthesized Selenium and Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles on Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) against Stripe Rust Disease" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8149. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238149
APA StyleShahbaz, M., Fatima, N., Mashwani, Z.-u.-R., Akram, A., Haq, E. u., Mehak, A., Abasi, F., Ajmal, M., Yousaf, T., Raja, N. I., UlHassan, H., & Pérez de la Lastra, J. M. (2022). Effect of Phytosynthesized Selenium and Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles on Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) against Stripe Rust Disease. Molecules, 27(23), 8149. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238149






