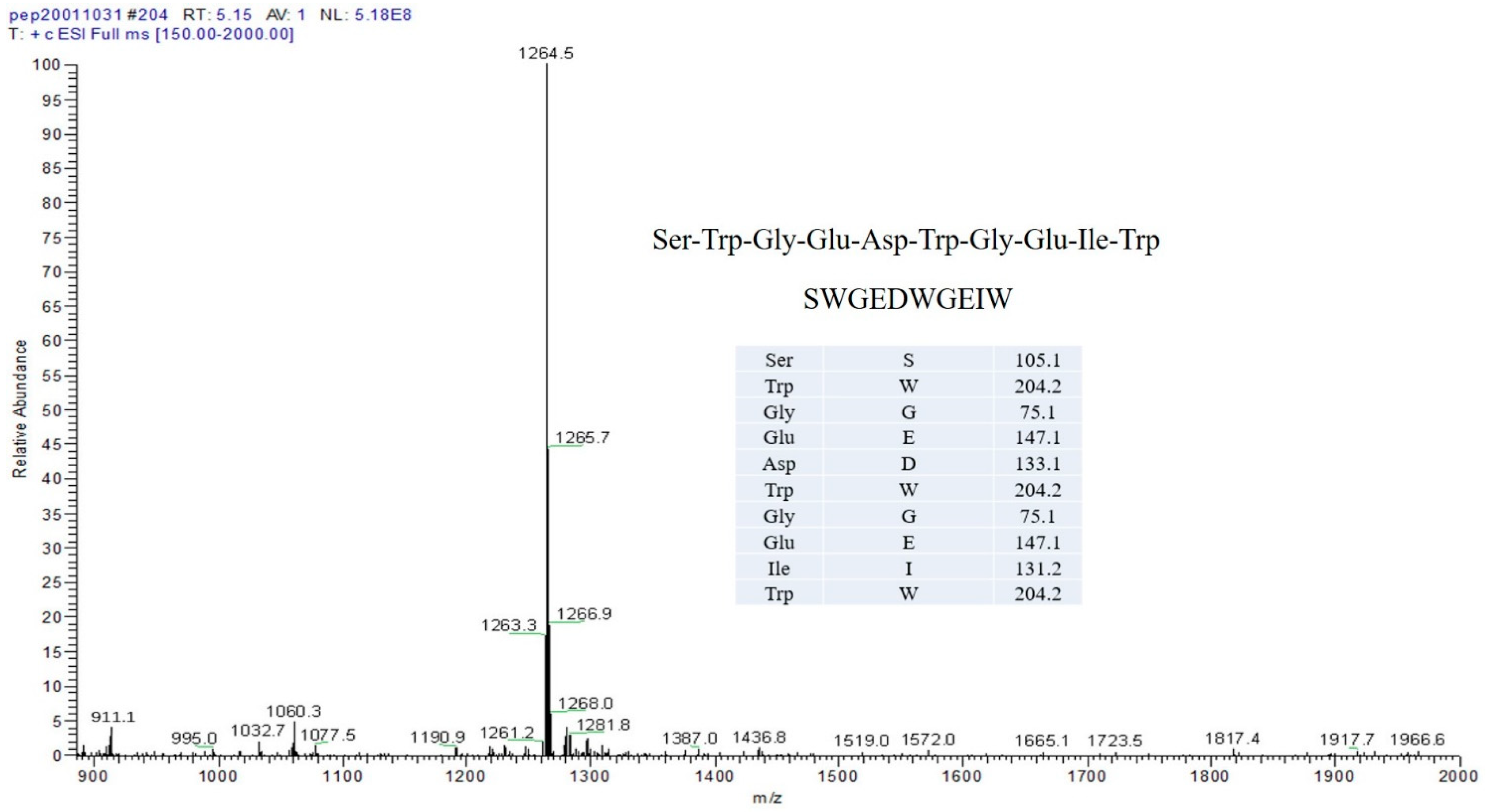
The SWGEDWGEIW from Soybean Peptides Reduce Oxidative Damage-Mediated Apoptosis in PC-12 Cells by Activating SIRT3/FOXO3a Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
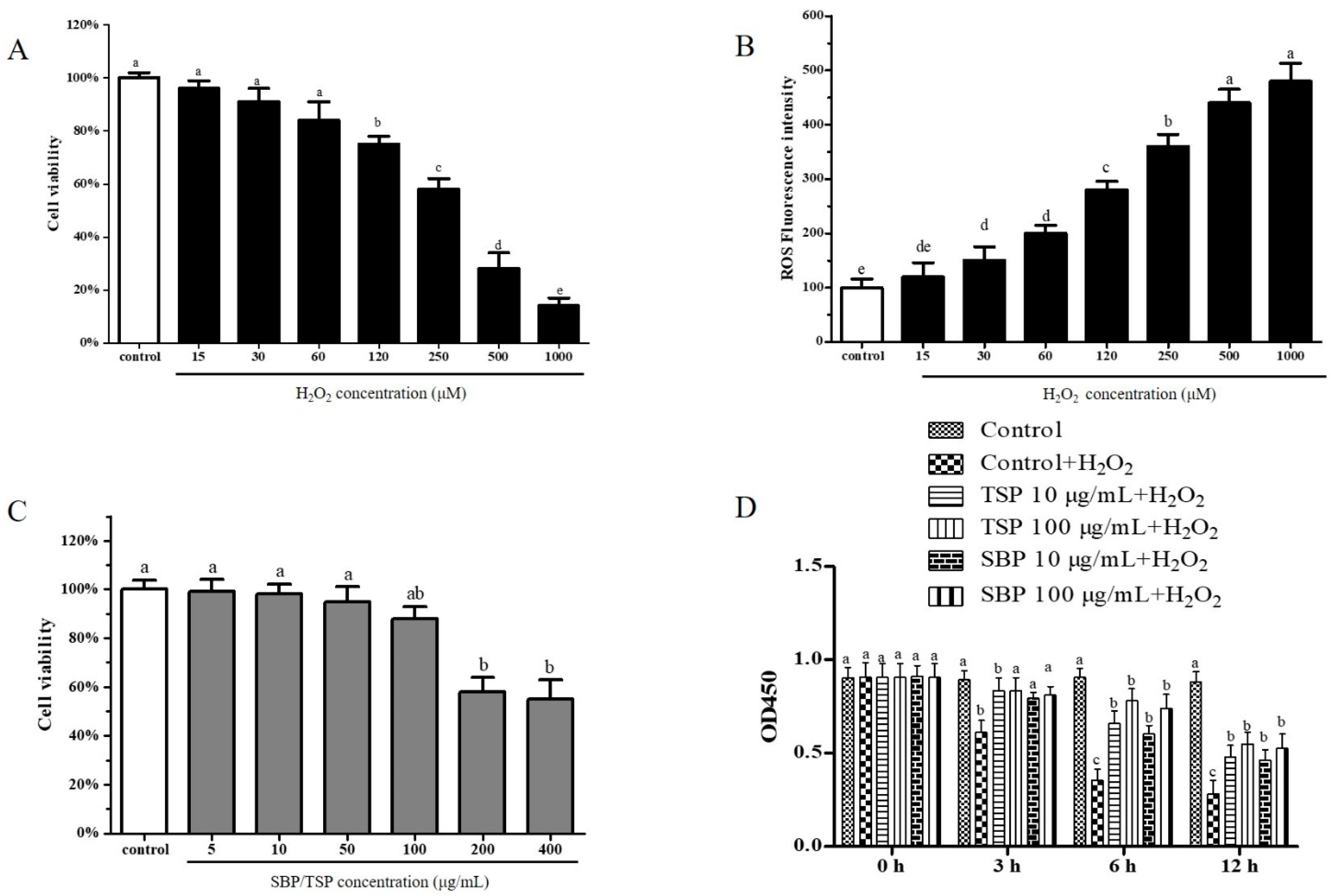
2.1. Protective Effects on PC-12 Cells Oxidative Damage Induced by H2O2
2.2. TSP and SBP’s Inhibition on PC-12 Cells’ Oxidative Stress-Induced Mitochondria-Dependent Apoptosis
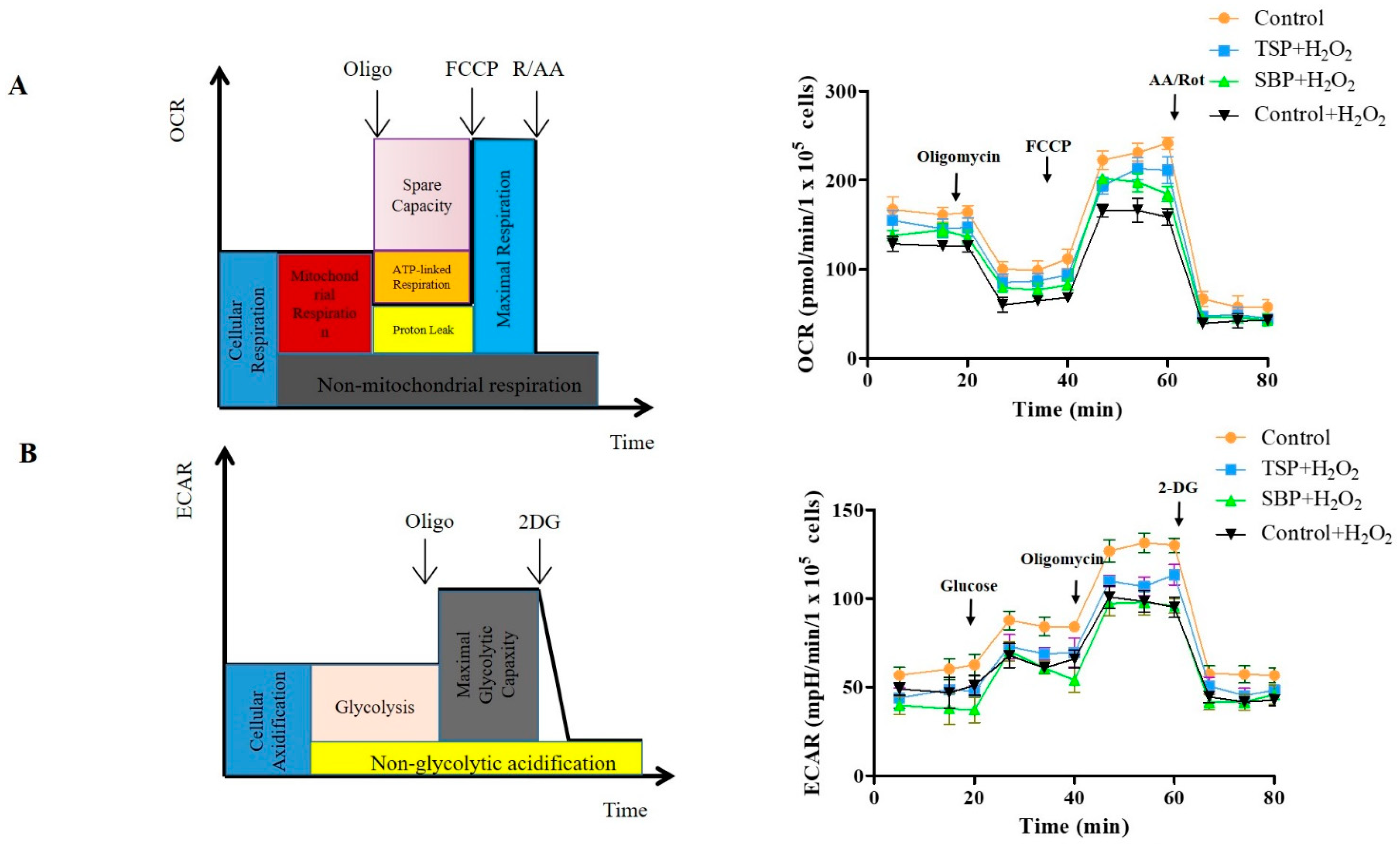
2.3. SBP and TSP’s Protection against the Mitochondrial Respiratory Dysfunction Caused by Oxidative Stress
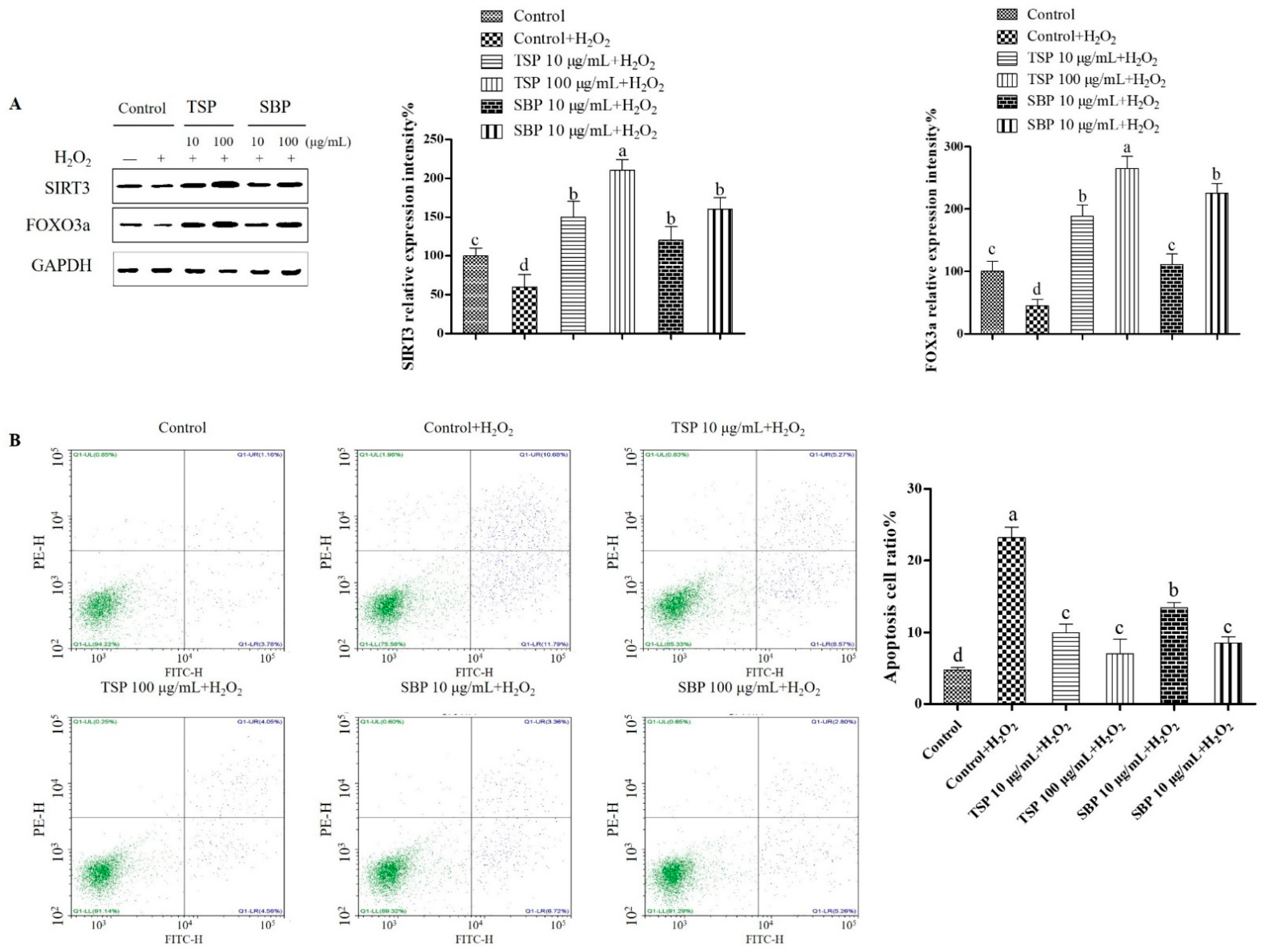
2.4. SBP and TSP’s Prevention of Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis and Oxidative Damage through the Signaling Pathway of SIRT3-FOXO3a
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Samples
3.2. Rat Pheochromocytoma (PC-12) Culture
3.3. Cell Viability Treatments Assessment
3.4. Intracellular Apoptosis and ROS Detection
3.5. Oxygen Consumption Rate (OCR) Determination
3.6. Western Blot Assay
3.7. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| SBP | Soybean peptide |
| TSP | The Single peptide (SWGEDWGEIW) |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| Bcl-2 | B-cell lymphoma-2 |
| Bax | BCL2-associated X protein |
| SIRT3 | Sirtuin 3 |
| FOXO3a | Forkhead box O3 |
| ECAR | Extracellular acidification rate |
| OCR | Oxygen consumption rate |
| PC-12 | PC-12 Rat pheochromocytoma cell line |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| HS | Horse Serum |
| HBSS | Hank’s balanced salt solution |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modification of Eagle’s medium Dulbecco |
References
- Kennedy, D.P.; Adolphs, R. The social brain in psychiatric and neurological disorders. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2012, 16, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pape, K.; Tamouza, R.; Leboyer, M.; Zipp, F. Immunoneuropsychiatry—Novel perspectives on brain disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.; Sharma, M. Prevalence and Diagnosis of Neurological Disorders Using Different Deep Learning Techniques: A Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Syst. 2020, 44, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajares, M.; Rojo, A.I.; Manda, G.; Bosca, L.; Cuadrado, A. Inflammation in Parkinson’s Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2020, 9, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfrich, R.F.; Mander, B.A.; Jagust, W.J.; Knight, R.T.; Walker, M.P. Old Brains Come Uncoupled in Sleep: Slow Wave-Spindle Synchrony, Brain Atrophy, and Forgetting. Neuron 2018, 97, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mander, B.A.; Winer, J.R.; Jagust, W.J.; Walker, M.P. Sleep: A Novel Mechanistic Pathway, Biomarker, and Treatment Target in the Pathology of Alzheimer’s Disease? Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 552–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, M.R.; Vitiello, M.V. Implications of sleep disturbance and inflammation for Alzheimer’s disease dementia. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J. The Prospect of Treating Alzheimer Disease through Sleep. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2020, 32, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solfrizzi, V.; Custodero, C.; Lozupone, M.; Imbimbo, B.P.; Valiani, V.; Agosti, P.; Schilardi, A.; D’Introno, A.; La Montagna, M.; Calvani, M.; et al. Relationships of Dietary Patterns, Foods, and Micro- and Macronutrients with Alzheimer’s Disease and Late-Life Cognitive Disorders: A Systematic Review. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 59, 815–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.C.L.; Deprez, L.M.; Mortimer, G.M.N.; Murtagh, D.K.J.; McCoy, S.; Mylchreest, R.; Gilbertson, L.J.; Clark, K.M.; Simpson, P.V.; McManus, E.J.; et al. Randomized crossover trial of a modified ketogenic diet in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 1422–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, W. How Western Diet And Lifestyle Drive The Pandemic Of Obesity And Civilization Diseases. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes.-Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 2221–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor, A.; Tankiewicz-Kwedlo, A.; Krupa, A.; Pawlak, D. Role of Kynurenine Pathway in Oxidative Stress during Neurodegenerative Disorders. Cells 2021, 10, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, G.; Din, J.U.; Zhao, F.; Liu, X. Effect of soybean peptides against hydrogen peroxide induced oxidative stress in HepG2 cells via Nrf2 signaling. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 2725–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, G.; Safdar, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. A study of the mechanism of small-molecule soybean-protein-derived peptide supplement to promote sleep in a mouse model. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 11264–11273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beermann, C.; Euler, M.; Herzberg, J.; Stahl, B. Anti-oxidative capacity of enzymatically released peptides from soybean protein isolate. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 229, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjukta, S.; Padhi, S.; Sarkar, P.; Singh, S.P.; Sahoo, D.; Rai, A.K. Production, characterization and molecular docking of antioxidant peptides from peptidome of kinema fermented with proteolytic Bacillus spp. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangsopha, J.; Johns, N.P.; Johns, J.; Moongngarm, A. Dietary sources of melatonin and benefits from production of high melatonin pasteurized milk. J. Food Sci. Technol.-Mysore 2020, 57, 2026–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guofu, Y.; Jian, Z.; He, L.; Xinqi, L.; Liduan, Y. Effects of soybean peptide on sleep in Drosophila. J. Food Sci. Technol. China 2020, 38, 63–78. [Google Scholar]
- Nanau, R.M.; Neuman, M.G. Adverse drug reactions induced by valproic acid. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 1323–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neininger, M.P.; Woltermann, S.; Jeschke, S.; Herziger, B.; Mueller, R.M.; Kiess, W.; Bertsche, T.; Bertsche, A. How do pediatric patients perceive adverse drug events of anticonvulsant drugs? A survey. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2020, 179, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amakye, W.K.; Hou, C.; Xie, L.; Lin, X.; Gou, N.; Yuan, E.; Ren, J. Bioactive anti-aging agents and the identification of new anti-oxidant soybean peptides. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Yu, W.; Yiming, H.; Ziyuan, W.; Jie, L.; Jing, W. Piceatannol alleviate ROS-mediated PC-12 cells damage and mitochondrial dysfunction through SIRT3/FOXO3a signaling pathway. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e13820. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Deng, Y.N.; Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.B.; Su, H.; Qu, Q.M. SIRT3 Protects Rotenone-induced Injury in SH-SY5Y Cells by Promoting Autophagy through the LKB1-AMPK-mTOR Pathway. Aging Dis. 2018, 9, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Liu, T.; Hwang, Y.J.; Hyeon, S.J.; Im, H.; Lee, K.; Alvarez, V.E.; McKee, A.C.; Um, S.-J.; et al. SIRT3 deregulation is linked to mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Cell 2018, 17, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.X.; Nielsen, M.; Li, S.P.; Shi, J. Ketones improves Apolipoprotein E4-related memory deficiency via sirtuin 3. Aging Albany NY 2019, 11, 4579–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingchuan, L.; Shengjie, Y.; Jinping, Y.; Yita, L.; Junping, K.; Chaojih, W. Neuroprotective and memory-enhancing effects of antioxidant peptide from walnut (Juglans regia L.) protein hydrolysates. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1934578X1986583. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.-L.; Wang, H.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-L.; Du, C.; Qian, H. Neuroprotective effects of torularhodin against H2O2-induced oxidative injury and apoptosis in PC12 cells. Pharmazie 2015, 70, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, T.Y.; Li, W.; Gao, N.; Zhang, T. Resveratrol attenuates oxidative damage through activating mitophagy in an in vitro model of Alzheimer’s disease. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 282, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, K.; Das, J.; Pal, P.B.; Sil, P.C. Oxidative stress: The mitochondria-dependent and mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1157–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Chen, M.F.; Huang, S.J.; Huang, C.Y.; Wang, H.K.; Hsieh, W.C.; Huang, C.H.; Liu, L.F.; Shiu, L.Y. Saikosaponin a Induces Apoptosis through Mitochondria-Dependent Pathway in Hepatic Stellate Cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2017, 45, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Deng, Y.N.; Zhang, M.; Su, H.; Qu, Q.M. SIRT3 Acts as a Neuroprotective Agent in Rotenone-Induced Parkinson Cell Model. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 1761–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jesko, H.; Wencel, P.; Strosznajder, R.P.; Strosznajder, J.B. Sirtuins and Their Roles in Brain Aging and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kincaid, B.; Bossy-Wetzel, E. Forever young: SIRT3 a shield against mitochondrial meltdown, aging, and neurodegeneration. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2013, 5, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.-D.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Li, G.-R.; Liu, X.-L. Damage to dopaminergic neurons by oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.W.; Shi, L.G.; Liang, F.; Xu, W.L.; Li, T.; Gao, L.S.; Sun, Z.Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.M. Sirt3 Ameliorates Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction After Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Diabetic Rats. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 162–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Yamagata, K.; Fujiyama, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Koshida, I.; Yoshimura, K.; Mihara, M.; Naitou, M.; Endoh, H.; Nakamura, T.; et al. DEAD-box RNA helicase subunits of the Drosha complex are required for processing of rRNA and a subset of microRNAs. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Sun, B.; Luo, X.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, F.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Sun, X.; Huang, M. Cytoprotective effects of a tripeptide from Chinese Baijiu against AAPH-induced oxidative stress in HepG2 cells via Nrf2 signaling. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 10898–10906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, G.; Zhou, M.; Du, Q.; Yang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. The SWGEDWGEIW from Soybean Peptides Reduce Oxidative Damage-Mediated Apoptosis in PC-12 Cells by Activating SIRT3/FOXO3a Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2022, 27, 7610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217610
Yi G, Zhou M, Du Q, Yang S, Zhu Y, Dong Y, Liu Y, Li H, Li Y, Liu X. The SWGEDWGEIW from Soybean Peptides Reduce Oxidative Damage-Mediated Apoptosis in PC-12 Cells by Activating SIRT3/FOXO3a Signaling Pathway. Molecules. 2022; 27(21):7610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217610
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Guofu, Mengyue Zhou, Qingfei Du, Shuibing Yang, Yuxia Zhu, Yining Dong, Yang Liu, He Li, You Li, and Xinqi Liu. 2022. "The SWGEDWGEIW from Soybean Peptides Reduce Oxidative Damage-Mediated Apoptosis in PC-12 Cells by Activating SIRT3/FOXO3a Signaling Pathway" Molecules 27, no. 21: 7610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217610
APA StyleYi, G., Zhou, M., Du, Q., Yang, S., Zhu, Y., Dong, Y., Liu, Y., Li, H., Li, Y., & Liu, X. (2022). The SWGEDWGEIW from Soybean Peptides Reduce Oxidative Damage-Mediated Apoptosis in PC-12 Cells by Activating SIRT3/FOXO3a Signaling Pathway. Molecules, 27(21), 7610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217610









