Simultaneous Extraction and Determination of Characteristic Steroidal Saponins and Homoisoflavonoids in Zhejiang Ophiopogon japonicus
Abstract
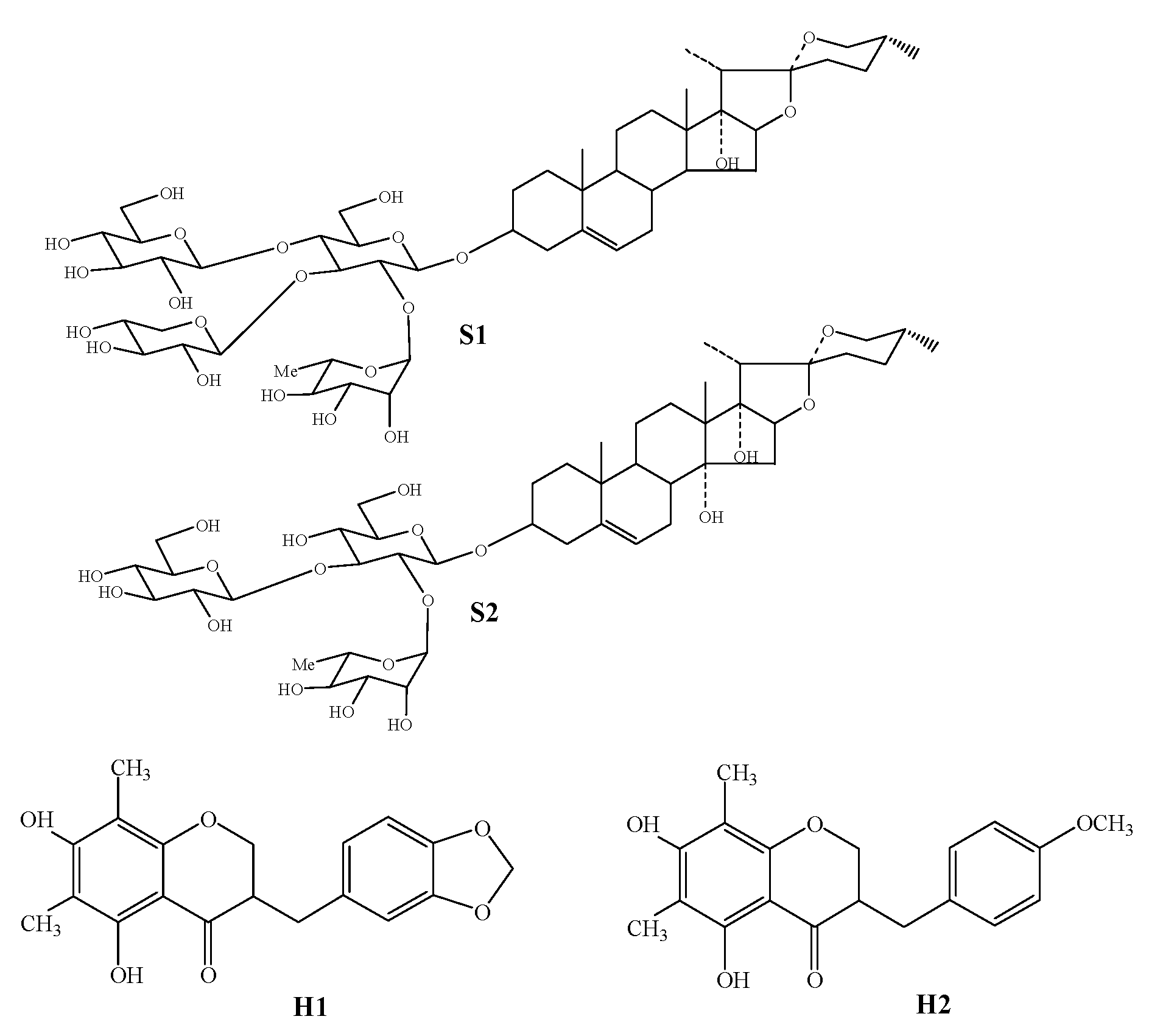
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
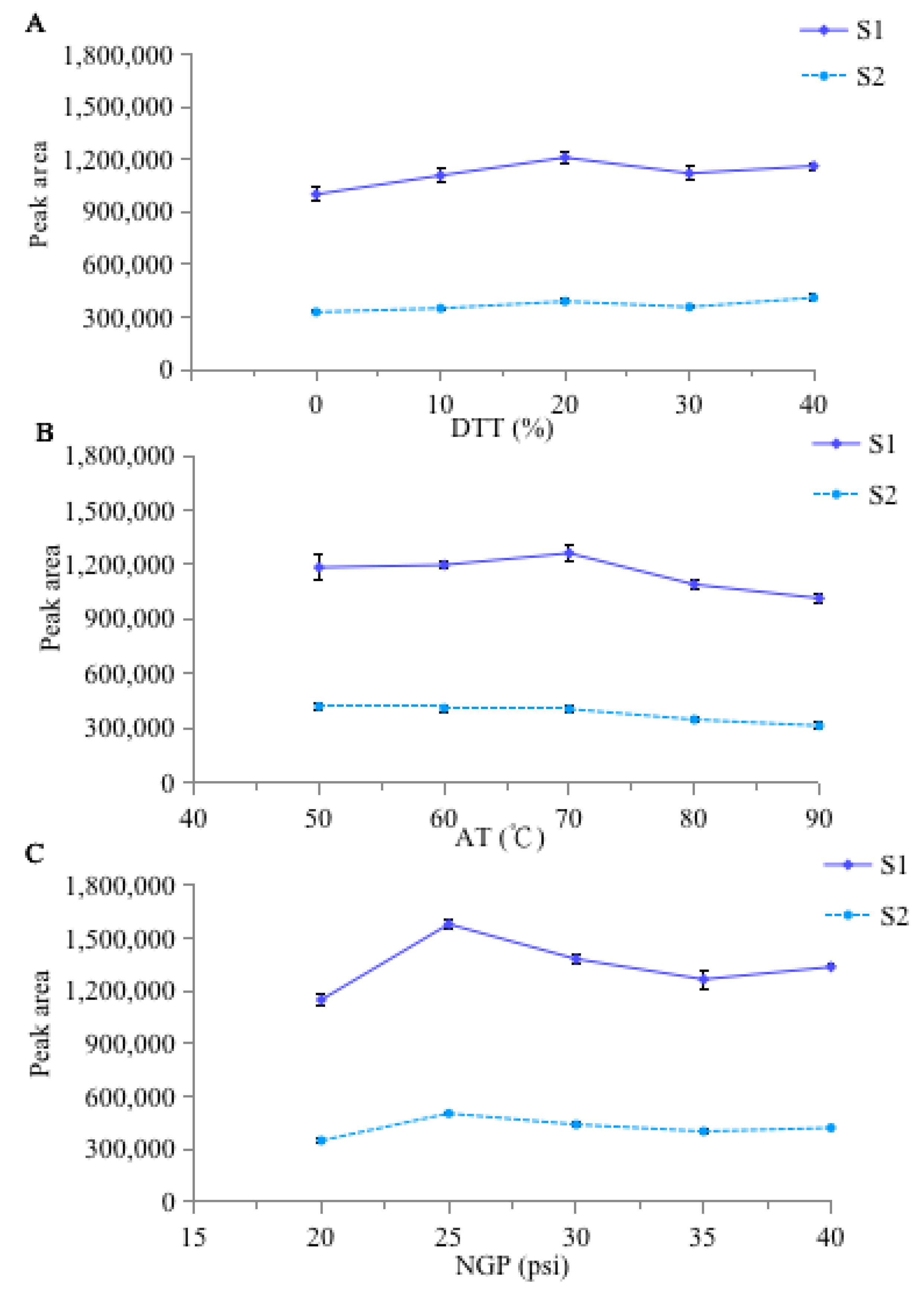
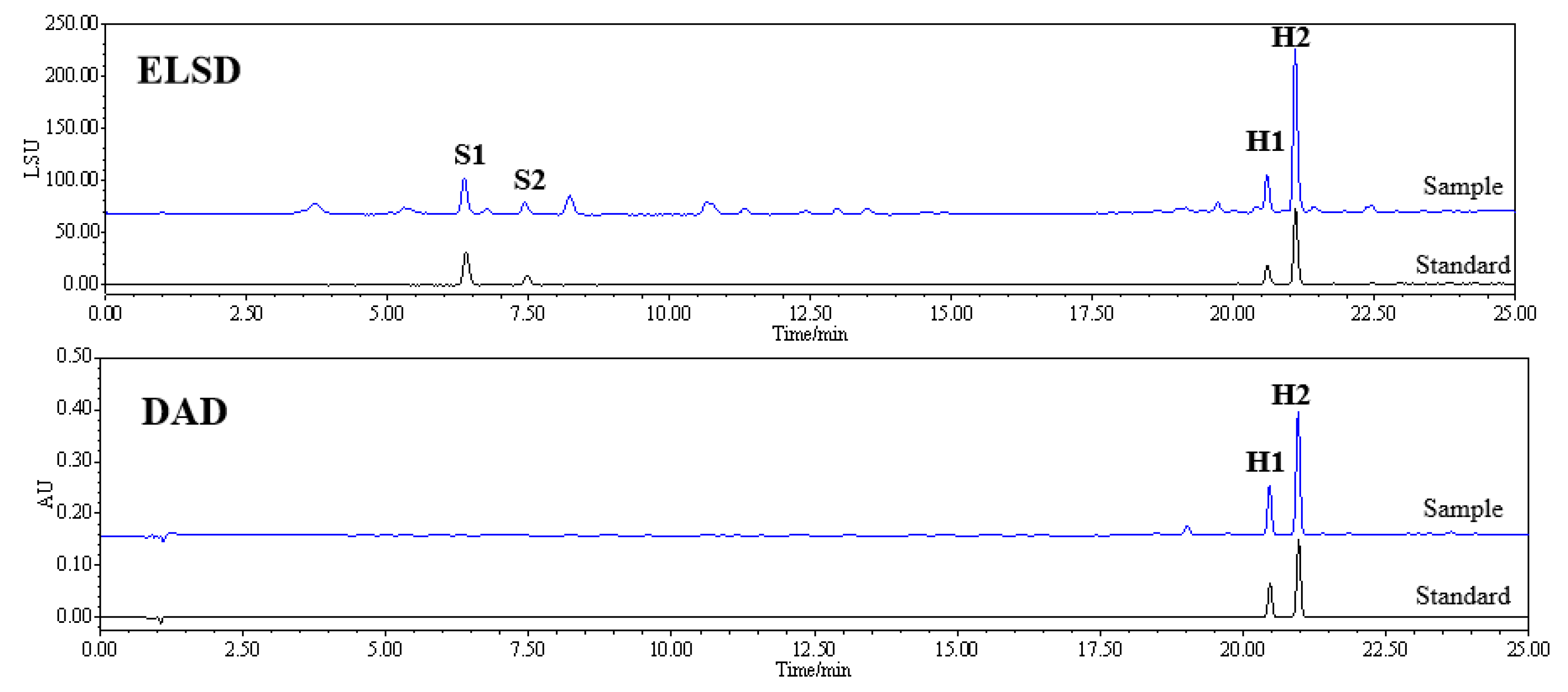
2.1. Optimization of HPLC Conditions
2.2. Optimization of IL Ultrasonic Extraction Conditions
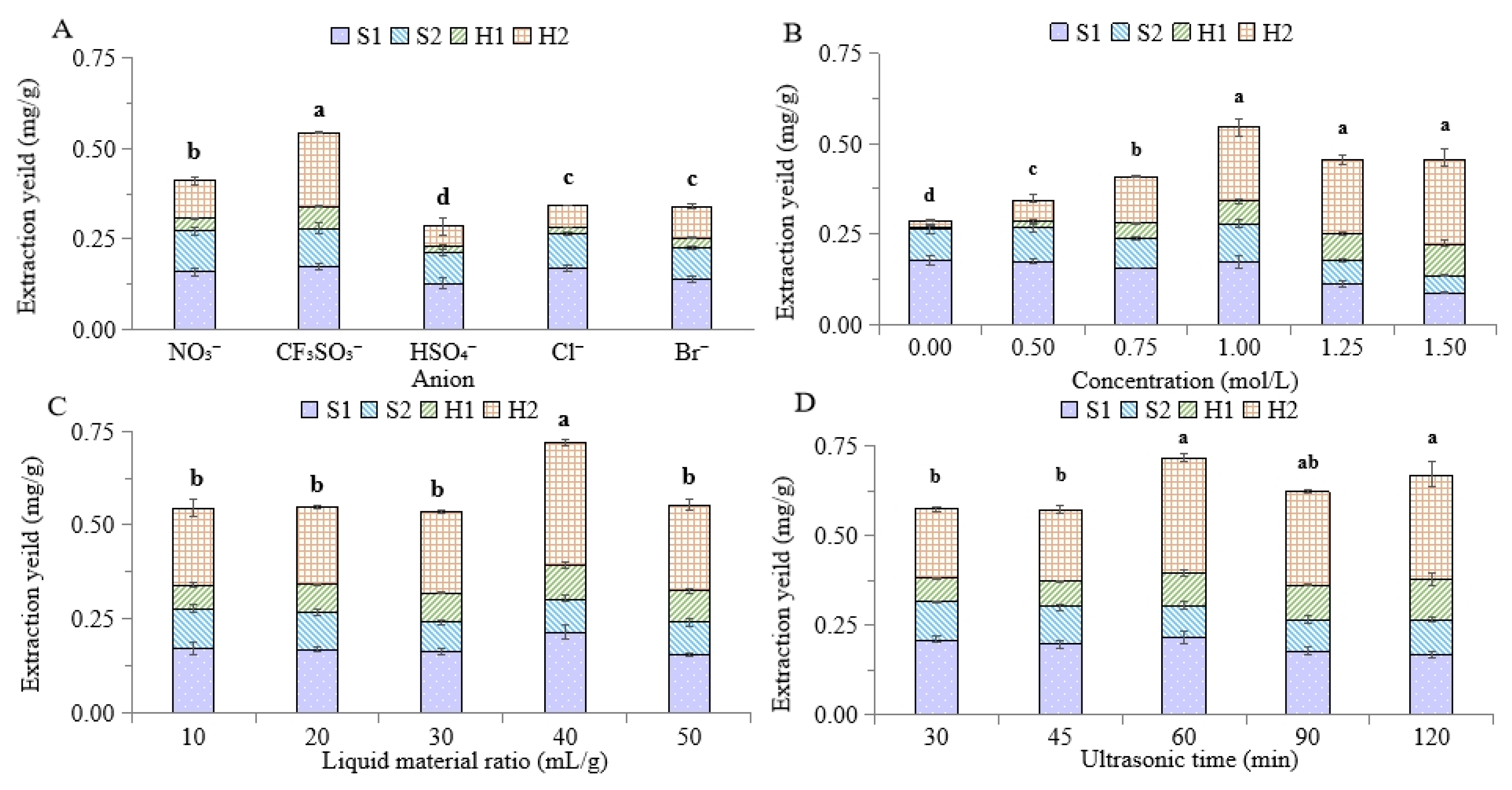
2.2.1. Type of IL
2.2.2. IL Concentration
2.2.3. Liquid–Material Ratio
2.2.4. Ultrasonic Time
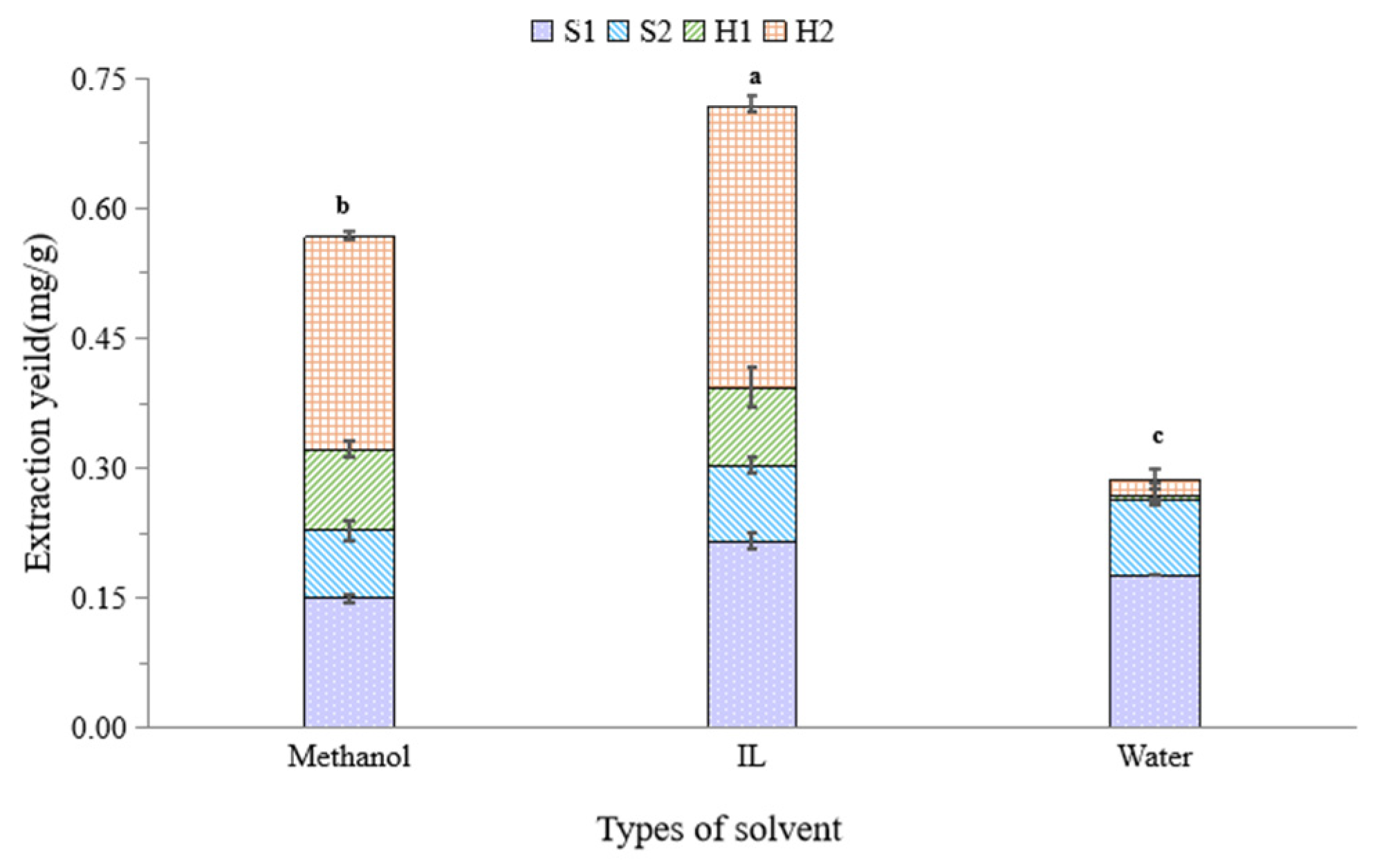
2.2.5. Comparison of Extraction Solvent
2.3. Method Validation
2.3.1. Linearity, LOD, and LOQ
2.3.2. Precision, Repeatability, and Stability
2.3.3. Accuracy
2.3.4. Analysis of Real Samples
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Chromatographic Conditions
3.3. Sample Preparation
3.4. Method Validation
3.4.1. Linearity, LOD, and LOQ
3.4.2. Precision
3.4.3. Repeatability and Stability
3.4.4. Accuracy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, M.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y. Ophiopogon japonicus—A phytochemical, ethnomedicinal and pharmacological review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 181, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, T.M.; Thu, C.V.; Dat, N.T.; Ryoo, S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.C.; Na, M.; Jung, H.; Bae, K.; Min, B.S. Homoisoflavonoid derivatives from the roots of Ophiopogon japonicus and their in vitro anti-inflammation activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 2412–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Miyamoto, A.; Zhao, S.; Liu, C.; Zheng, W.; Wang, H. Effects of steroidal saponins extract from Ophiopogon japonicus root ameliorates doxorubicin-induced chronic heart failure by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammatory response. Pharm. Biol. 2019, 57, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Kang, C.; Kang, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, S.; He, Y.; Deng, A.; Wang, H.; Huang, L.; Guo, L. Structural characterization and discrimination of Ophiopogon japonicas (Liliaceae) from different geographical origins based on metabolite profiling analysis. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2020, 185, 113212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Ye, L.; Li, J.; Huang, W.; Huo, Y.; Gao, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, W. Identification of Ophiopogonis Radix from different producing areas by headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry analysis. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e13850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Xu, W.; Shen, H.; Shen, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Yan, T.; Wang, L.; et al. Comparison of bioactive components and pharmacological activities of ophiopogon japonicas extracts from different geographical origins. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2017, 138, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Zhu, D.; Qi, J.; Qin, M.; Yu, B. Characterization of homoisoflavonoids in different cultivation regions of Ophiopogon japonicus and related antioxidant activity. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2010, 52, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Tu, P. Fingerprint analysis of Ophiopogonis Radix by HPLC-UV-ELSD coupled with chemometrics methods. J. Chin. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 22, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Liu, W.; Zhang, N.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, S.; Zuo, T.; Kang, S.; Wei, F.; Ma, S. A novel method to identify three quality grades of herbal medicine ophiopogonis radix by microscopic quantification. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 591310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Tong, W.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zheng, J.; Fan, X.; Liu, L. Comparison of the chemical consituents and immunomodulatory activity of ophiopogonis radix from two different producing areas. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2017, 134, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cui, Y.; Lu, J.; Liu, C.; Chen, S.; Ma, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Kang, W. Ionic Liquid-Based Ultrasonic-Assisted extraction coupled with HPLC and artificial neural network analysis for ganoderma lucidum. Molecules 2020, 25, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Liu, Q.; Li, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H. Microwave-assisted ionic liquid microextraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography for the determination of naphthoquinones from Arnebia euchroma (Royle) Johnst. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2019, 42, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Niu, Y.; Liu, J.; Shi, M.; Xu, R.; Kang, W. Efficient Extraction of Anti-Inflammatory Active Ingredients from Schefflera octophylla Leaves Using Ionic Liquid-Based Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction Coupled with HPLC. Molecules 2019, 24, 2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Cui, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Kang, W. Ionic Liquid-Based Ultrasonic-Assisted extraction to analyze seven compounds in psoralea fructus coupled with HPLC. Molecules 2019, 24, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, M.; Fernandes, A.P.M.; Torres-Acosta, M.A.; Collén, P.N.; Abreu, M.H.; Ventura, S.P.M. Extraction of chlorophyll from wild and farmed Ulva spp. Using aqueous solutions of ionic liquids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Gomes, H.M.D.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Valorization of spent coffee by caffeine extraction using aqueous solutions of Cholinium-Based ionic liquids. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, X.; Wu, F.; Wang, L.; Feng, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H. Ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction followed by dispersive solid phase extraction coupled with HPLC-DAD for the determination of sulfonylurea herbicides in soymilk samples. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2022, 44, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, X.; Fu, S. Simultaneous determination of three homoisoflavonoids in Ophiopogon japonicus by HPLC. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2012, 37, 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.-M.; Yang, R.-S.; Zhang, S.-D.; Bao, X.-H.; Li, M.; Zhou, J. Simultaneous determination of three flavone constituents in Ophiopogonis Radix by HPLC Method. Chin. Pharm. J. 2016, 51, 655–658. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, C.; Ye, Z.-L.; Jiang, X.-J.; Zhou, D.-Z.; Li, D.-K. Simultaneous determination of contents of three flavonoid ingredients in Radix Ophiopogonis by HPLC. Chin. Pharm. J. 2011, 46, 1209–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Liang, Z.; Peng, L.; Wang, B.; Yu, J.; Su, Y.; Ma, C. Homoisoflavonoids and the Antioxidant Activity of Ophiopogon japonicus Root. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 16, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, P.; Liao, D. Determination of saponin content in hang maidong and chuan maidong via HPLC-ELSD analysis. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2016, 2016, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-M.; Cai, X.-Y.; Wang, P.; Bao, X.-H.; Li, M.; Zhou, J. HPLC simultaneous determination of contents of 5 saponin constituents in Ophiopogonis radix. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2015, 40, 4022–4025. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Li, M.; Feng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yu, B.; Qi, J. Determination of ruscogenin in ophiopogonis radix by high-performance liquid chromatography-evaporative light scattering detector coupled with hierarchical clustering analysis. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2016, 12, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Qu, H. Determination of three steroidal saponins from Ophiopogon japonicus (Liliaceae) via high-performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Qu, H. Structure characterization and identification steroidal saponins from Ophiopogon japonicus Ker-Gawler (Liliaceae) by High-Performance liquid chromatography with ion trap mass spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. 2011, 22, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Cheng, T.; Dong, X.; Li, P.; Yang, H. Global analysis of chemical constituents in Shengmai injection using high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2016, 117, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Lu, Y.; Shao, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Qu, H. Binary chromatographic fingerprinting for quality evaluation of Radix Ophiopogonis by high- performance liquid chromatography coupled with ultraviolet and evaporative light-scattering detectors. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 2628–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Liang, Y.; Hao, H.; Jiye, A.; Xie, L.; Gong, P.; Dai, C.; Liu, L.; Kang, A.; Zheng, X.; et al. Rapid identification of ophiopogonins and ophiopogonones in Ophiopogon japonicus extract with a practical technique of mass defect filtering based on high resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1227, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, P.W.; Stoll, D.R.; Wang, X. Perspectives on recent advances in the speed of high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1890–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qu, H. Development and optimization of SPE-HPLC-UV/ELSD for simultaneous determination of nine bioactive components in Shenqi Fuzheng Injection based on Quality by Design principles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 2133–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yang, F.; Feng, K.; Li, D.; Zhao, J.; Li, S. Simultaneous determination of nucleosides, myriocin, and carbohydrates in Cordyceps by HPLC coupled with diode array detection and evaporative light scattering detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 4069–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.; Jiménez, A.; Garrigós, M.C. Il-based advanced techniques for the extraction of value-added compounds from natural sources and food by-products. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Wilfred, C.D.; Shaharun, M.S. Ionic liquid-based extraction and separation trends of bioactive compounds from plant biomass. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 559–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, M.G. Ionic liquids as alternative solvents for extraction of natural products. In Alternative Solvents for Natural Products Extraction; Chemat, F., Vian, M.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 127–166. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Sui, X.; Li, J.; Liu, T.; Yang, L. Development of a novel functionality for a highly efficient imidazole-based ionic liquid non-aqueous solvent system for the complete extraction of target alkaloids from Phellodendron amurense Rupr. Under ultrasound-assisted conditions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 168, 113596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarata, L.; Kazarian, S.G.; Salter, P.A.; Welton, T. Molecular states of water in room temperature ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2001, 3, 5192–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cláudio, A.F.M.; Swift, L.; Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T.; Coutinhoa, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Extended scale for the Hydrogen-Bond basicity of ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 6593–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemin, J.; Husson, P.; Padua, A.A.H.; Majer, V. Density and viscosity of several pure and water-saturated ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, L.; Liu, T.; Zu, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z. Development of sample preparation method for isoliquiritigenin, liquiritin, and glycyrrhizic acid analysis in licorice by ionic liquids-ultrasound based extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography detection. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Wang, Y.; Su, Z.; He, D.; Du, Y.; Guo, M.; Yang, D.; Tang, D. Ionic liquids-ultrasound based efficient extraction of flavonoid glycosides and triterpenoid saponins from licorice. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 13989–13996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Feng, C.; Tian, M.; Meng, X.; Zhao, C. A novel approach for echinacoside and acteoside extraction from Cistanche deserticola Y. C. Ma using an aqueous system containing ionic liquid surfactants. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 26, 100644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Yi, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C. Extraction, preconcentration and isolation of flavonoids from apocynum venetum l. Leaves using ionic Liquid-Based Ultrasonic-Assisted extraction coupled with an aqueous biphasic system. Molecules 2016, 21, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Cao, P.; Wang, J.; Kang, W. Analysis of tilianin and acacetin in Agastache rugosa by high-performance liquid chromatography with ionic liquids-ultrasound based extraction. Chem. Cent. J. 2016, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Han, M.; Yang, L. Aqueous ionic liquid based ultrasonic assisted extraction of eight ginsenosides from ginseng root. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ağar, O.T.; Demirezer, L.Ö. Development of a new validated HPLC method for the chemical specification of Rosa damascena petals. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2021, 44, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-M.; Zhang, S.-D.; Zeng, J.; Yang, R.-S.; Li, M.; Bao, X.-H.; Zhou, J. Determination of the 4 representative components in Maidong from different producing areas by HPLC-ELSD method*. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 36, 1370–1376. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, T.; Sha, R.; Mao, J. Enrichment and separation of steroidal saponins from the fibrous roots of Ophiopogon japonicus using macroporous adsorption resins. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 6689–6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, T.; Mao, Z.; Ge, Q.; Mao, J. Isolation of homoisoflavonoids from the fibrous roots of Ophiopogon japonicus by recycling high-speed counter-current chromatography and online antioxidant activity assay. Acta Chromatogr. 2019, 31, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, C.; Shin, H. Simultaneous analysis of 19 marker components for quality control of Oncheong-Eum using HPLC-DAD. Molecules 2022, 27, 2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Analyte | Regression Equation | R2 | Linear Range (μg/mL) | LOD (μg/mL) | LOQ (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | logY = 1.2603 logX + 3.861 | 0.9992 | 15.00 – 75.00 | 1.80 | 4.80 |
| S2 | logY = 1.2236 logX + 3.831 | 0.9978 | 6.76 – 33.80 | 2.16 | 5.41 |
| H1 | Y = 42276X + 10292 | 0.9999 | 6.90 – 34.50 | 0.07 | 0.28 |
| H2 | Y = 38451X + 28209 | 0.9999 | 17.16 – 85.80 | 0.10 | 0.34 |
| Analyte | Precision | Repeatability (n = 9) | Stability (n = 9, 3 Days) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level | Inter-Day (n = 4) | Intra-Day (n = 9) | |||
| S1 | Low | 3.57 | 3.35 | 3.84 | 3.73 |
| Medium | 2.54 | 1.83 | |||
| High | 2.69 | 4.71 | |||
| S2 | Low | 4.63 | 4.05 | 4.97 | 4.62 |
| Medium | 4.46 | 1.28 | |||
| High | 3.75 | 3.05 | |||
| H1 | Low | 4.38 | 1.27 | 3.07 | 3.72 |
| Medium | 2.57 | 2.21 | |||
| High | 2.13 | 2.62 | |||
| H2 | Low | 4.45 | 1.29 | 1.82 | 2.85 |
| Medium | 2.62 | 3.48 | |||
| High | 2.13 | 2.60 | |||
| Samples | Parts | Origin * | S1 | S2 | H1 | H2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tuber roots | Chongshou | 0.1742 ± 0.0085 | 0.0709 ± 0.0083 | 0.1350 ± 0.0030 | 0.3251 ± 0.0051 |
| 2 | Kandun | 0.2174 ± 0.0058 | 0.0857 ± 0.0101 | 0.1409 ± 0.0057 | 0.3407 ± 0.0099 | |
| 3 | Shengshan | 0.2250 ± 0.0100 | 0.1015 ± 0.0107 | 0.1442 ± 0.0029 | 0.3242 ± 0.0037 | |
| 4 | Fibrous roots | Chongshou | 0.4693 ± 0.0184 | 0.3518 ± 0.0211 | 0.3099 ± 0.0086 | 0.5278 ± 0.0145 |
| 5 | Kandun | 0.4941 ± 0.0026 | 0.2933 ± 0.0027 | 0.2602 ± 0.0077 | 0.4141 ± 0.0089 | |
| 6 | Shengshan | 0.5313 ± 0.0298 | 0.3354 ± 0.0278 | 0.2784 ± 0.0059 | 0.4919 ± 0.0088 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, J. Simultaneous Extraction and Determination of Characteristic Steroidal Saponins and Homoisoflavonoids in Zhejiang Ophiopogon japonicus. Molecules 2022, 27, 7380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217380
Zhu Y, Wang L, Chen M, Zhou Y, Huang J. Simultaneous Extraction and Determination of Characteristic Steroidal Saponins and Homoisoflavonoids in Zhejiang Ophiopogon japonicus. Molecules. 2022; 27(21):7380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217380
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yaoyao, Liling Wang, Meixu Chen, Yifeng Zhou, and Jun Huang. 2022. "Simultaneous Extraction and Determination of Characteristic Steroidal Saponins and Homoisoflavonoids in Zhejiang Ophiopogon japonicus" Molecules 27, no. 21: 7380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217380
APA StyleZhu, Y., Wang, L., Chen, M., Zhou, Y., & Huang, J. (2022). Simultaneous Extraction and Determination of Characteristic Steroidal Saponins and Homoisoflavonoids in Zhejiang Ophiopogon japonicus. Molecules, 27(21), 7380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217380





