Zebrafish: A Pharmacological Model for Learning and Memory Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Types of Learning and Memory in Zebrafish
2.1. Non-Associative Learning
2.2. Associative Learning
2.2.1. Classical Conditioning
2.2.2. Operant Conditioning
2.3. Remarks on Leaning Conditionings in Zebrafish
2.4. Memory
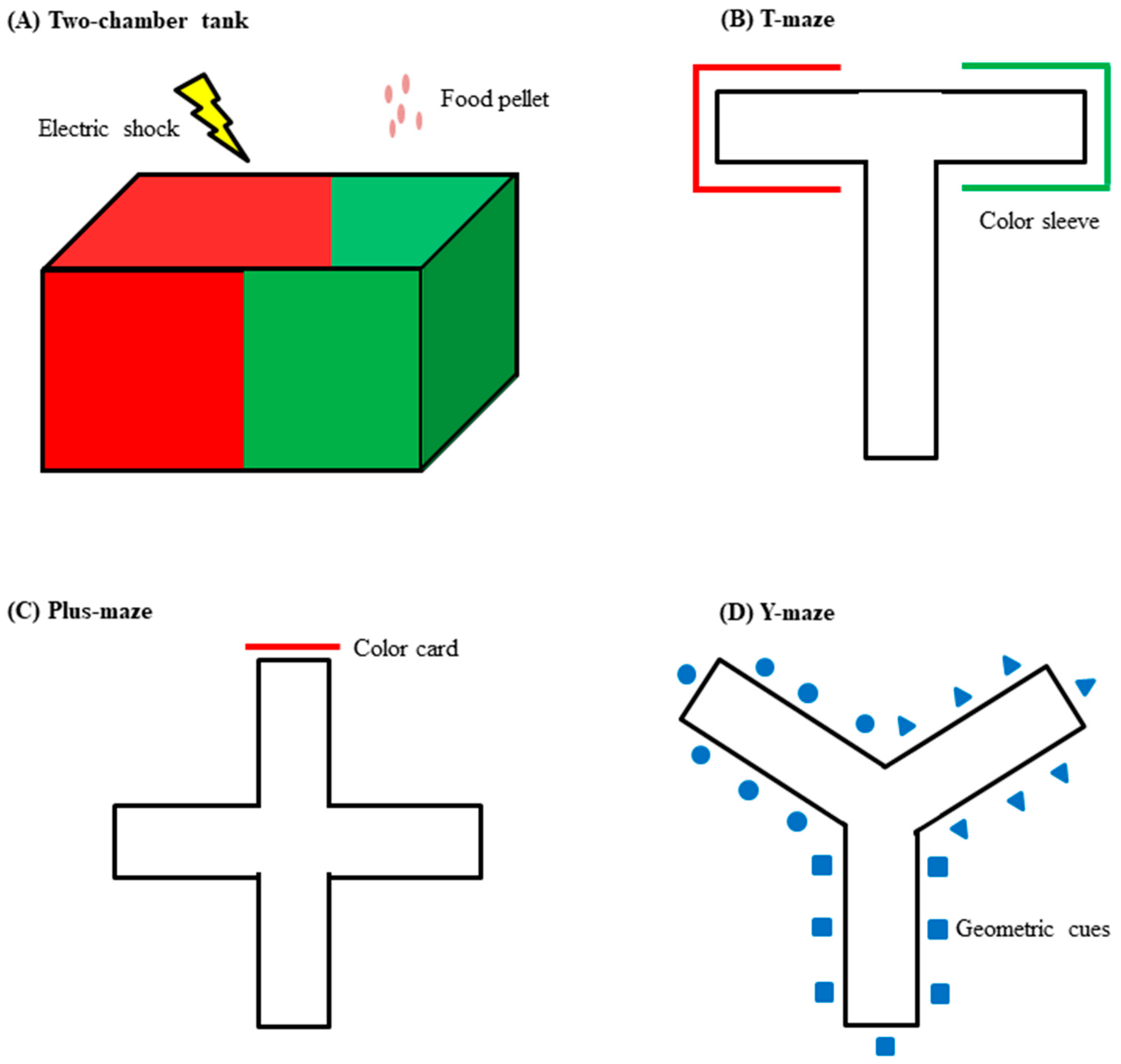
3. Behavioral Assessment Tests in Zebrafish
3.1. Locomotor Activity Test
3.2. Novel Tank Test
3.3. Inhibitory Avoidance Test
3.4. Appetitive Conditioning Test
3.5. Y-Maze Test
3.6. Novel Object Recognition Test
4. Zebrafish Models for Pharmacological Studies on Learning and Memory
4.1. Neuroprotective Screening
4.2. Neurotoxicity Screening
5. Limitations of Zebrafish as a Pharmacological Model for Learning and Memory Research
6. Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kenney, J.W. Chapter 12—Associative and Nonassociative Learning in Adult Zebrafish. In Behavioral and Neural Genetics of Zebrafish, 1st ed.; Gerlai, R., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 187–204. ISBN 978-0-12-817528-6. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, T.-Y.; Choi, T.-I.; Lee, Y.-R.; Choe, S.-K.; Kim, C.-H. Zebrafish as an animal model for biomedical research. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patton, E.E.; Zon, L.I.; Langenau, D.M. Zebrafish disease models in drug discovery: From preclinical modelling to clinical trials. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 611–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teoh, S.L.; Sapri, S.R.B.; Yusof, M.R.B.M.; Yahaya, M.F.; Das, S. Construction of an Affordable Open-Design Recirculating Zebrafish Housing System. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2020, 59, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najib, N.H.M.; Nies, Y.H.; Abd Halim, S.A.S.; Yahaya, M.F.; Das, S.; Lim, W.L.; Teoh, S.L. Modeling Parkinson’s Disease in Zebrafish. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 19, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad Najib, N.H.; Yahaya, M.F.; Das, S.; Teoh, S.L. The effects of metallothionein in paraquat-induced Parkinson disease model of zebrafish. Int. J. Neurosci. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, E.; Steinmetz, J.D.; Vollset, S.E.; Fukutaki, K.; Chalek, J.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdoli, A.; Abualhasan, A.; Abu-Gharbieh, E.; Akram, T.T.; et al. Estimation of the global prevalence of dementia in 2019 and forecasted prevalence in 2050: An analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Health 2022, 7, e105–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husna Ibrahim, N.; Yahaya, M.F.; Mohamed, W.; Teoh, S.L.; Hui, C.K.; Kumar, J. Pharmacotherapy of Alzheimer’s Disease: Seeking Clarity in a Time of Uncertainty. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woon, K.C.; Hui, K.W.; Abas, R.; Haron, H.M.; Das, S.; Lin, S.T. Natural Product-based Nanomedicine: Recent Advances and Issues for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2022, 20, 1498–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, S.; Kannan, R.R. Zebrafish: An emerging real-time model system to study Alzheimer’s disease and neurospecific drug discovery. Cell Death Discov. 2018, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.-B.; He, K.-J.; Wang, F.; Liu, C.-F. Advances of Zebrafish in Neurodegenerative Disease: From Models to Drug Discovery. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, F.E.; White, D.; Messer, W.S. A simple spatial alternation task for assessing memory function in zebrafish. Behav. Process. 2002, 58, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, M.; Volkmann, P.; Rossner, M.J. Assessing behavior and cognition in rodents, nonhuman primates, and humans: Where are the limits of translation? Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 21, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maximino, C.; Silva, R.X.D.C.; da Silva, S.D.N.S.; Rodrigues, L.D.S.D.S.; Barbosa, H.; De Carvalho, T.S.; Leão, L.K.D.R.; Lima, M.G.; Oliveira, K.R.M.; Herculano, A.M. Non-mammalian models in behavioral neuroscience: Consequences for biological psychiatry. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, P.D. Domains of cognition and their assessment. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 21, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlai, R. Learning and memory in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Methods Cell Biol. 2016, 134, 551–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindeyer, C.M.; Reader, S.M. Social learning of escape routes in zebrafish and the stability of behavioural traditions. Anim. Behav. 2010, 79, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, T.; Zwart, M.F.; Yang, C.-T.; Mensh, B.D.; Ahrens, M.B. The Serotonergic System Tracks the Outcomes of Actions to Mediate Short-Term Motor Learning. Cell 2016, 167, 933–946.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J.D.; Berghmans, S.; Hunt, J.J.F.G.; Clarke, S.C.; Fleming, A.; Goldsmith, P.; Roach, A.G. Non-associative learning in larval zebrafish. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisera-Fuster, A.; Rocco, L.; Faillace, M.P.; Bernabeu, R. Sensitization-dependent nicotine place preference in the adult zebrafish. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 92, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, J.W.; Scott, I.C.; Josselyn, S.A.; Frankland, P.W. Contextual fear conditioning in zebrafish. Learn. Mem. 2017, 24, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.R.; Wong, R.Y. Contextual fear learning and memory differ between stress coping styles in zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manabe, K.; Dooling, R.J.; Takaku, S. An automated device for appetitive conditioning in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Zebrafish 2013, 10, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Scott-Scheiern, T.; Kempker, L.; Simons, K. Active avoidance conditioning in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2007, 87, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, M.; Guerim, L.D.; Cordeiro, R.F.; Vianna, M.R.M. A one-trial inhibitory avoidance task to zebrafish: Rapid acquisition of an NMDA-dependent long-term memory. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2009, 92, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randlett, O.; Haesemeyer, M.; Forkin, G.; Shoenhard, H.; Schier, A.F.; Engert, F.; Granato, M. Distributed Plasticity Drives Visual Habituation Learning in Larval Zebrafish. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 1337–1345.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchett, D.; Brennan, C.H. Chapter 7—Classical and Operant Conditioning in Larval Zebrafish. In Behavioral and Neural Genetics of Zebrafish, 1st ed.; Gerlai, R., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 107–122. ISBN 978-0-12-817528-6. [Google Scholar]
- Staddon, J.E.R.; Cerutti, D.T. Operant conditioning. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2003, 54, 115–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, B.F. Two Types of Conditioned Reflex: A Reply to Konorski and Miller. J. Gen. Psychol. 1937, 16, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sison, M.; Gerlai, R. Associative learning in zebrafish (Danio rerio) in the plus maze. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 207, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, A.; Huang, K.H.; Portugues, R.; Engert, F. Ontogeny of classical and operant learning behaviors in zebrafish. Learn. Mem. 2012, 19, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlai, R.T. Chapter 10—Fear Responses and Antipredatory Behavior of Zebrafish: A Translational Perspective. In Behavioral and Neural Genetics of Zebrafish, 1st ed.; Gerlai, R., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 155–171. ISBN 978-0-12-817528-6. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, R.Y.; Lamm, M.S.; Godwin, J. Characterizing the neurotranscriptomic states in alternative stress coping styles. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximino, C.; Lima, M.G.; Costa, C.C.; Guedes, I.M.L.; Herculano, A.M. Fluoxetine and WAY 100,635 dissociate increases in scototaxis and analgesia induced by conspecific alarm substance in zebrafish (Danio rerio Hamilton 1822). Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 124, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manuel, R.; Gorissen, M.; Piza Roca, C.; Zethof, J.; Van De Vis, H.; Flik, G.; Van Den Bos, R. Inhibitory avoidance learning in zebrafish (Danio Rerio): Effects of shock intensity and unraveling differences in task performance. Zebrafish 2014, 11, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camina, E.; Güell, F. The Neuroanatomical, Neurophysiological and Psychological Basis of Memory: Current Models and Their Origins. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandel, E.R.; Dudai, Y.; Mayford, M.R. The Molecular and Systems Biology of Memory. Cell 2014, 157, 163–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cognato, G.D.P.; Bortolotto, J.W.; Blazina, A.R.; Christoff, R.R.; Lara, D.R.; Vianna, M.R.; Bonan, C.D. Y-Maze memory task in zebrafish (Danio rerio): The role of glutamatergic and cholinergic systems on the acquisition and consolidation periods. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2012, 98, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braida, D.; Ponzoni, L.; Martucci, R.; Sala, M. A new model to study visual attention in zebrafish. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 55, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, N.; Oliveira, R.F. Long-Term Social Recognition Memory in Zebrafish. Zebrafish 2017, 14, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Imari, L.; Gerlai, R. Sight of conspecifics as reward in associative learning in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 189, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleal, M.; Parker, M.O. Moderate developmental alcohol exposure reduces repetitive alternation in a zebrafish model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2018, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, S.; Froc, C.; Pontiggia, A.; Yamamoto, K. Existence of working memory in teleosts: Establishment of the delayed matching-to-sample task in adult zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 370, 111924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, T.J.; Myggland, A.; Duperreault, E.; May, Z.; Gallup, J.; Powell, R.A.; Schalomon, M.; Digweed, S.M. Episodic-like memory in zebrafish. Anim. Cogn. 2016, 19, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco-Restrepo, J.E.; Forero, D.A.; Vargas, R.A. A Review of Freely Available, Open-Source Software for the Automated Analysis of the Behavior of Adult Zebrafish. Zebrafish 2019, 16, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braida, D.; Ponzoni, L.; Moretti, M.; Viani, P.; Pallavicini, M.; Bolchi, C.; Appiani, R.; Bavo, F.; Gotti, C.; Sala, M. Behavioural and pharmacological profiles of zebrafish administrated pyrrolidinyl benzodioxanes and prolinol aryl ethers with high affinity for heteromeric nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Psychopharmacology 2020, 237, 2317–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devidas, S.B.; Rahmatkar, S.N.; Singh, R.; Sendri, N.; Purohit, R.; Singh, D.; Bhandari, P. Amelioration of cognitive deficit in zebrafish by an undescribed anthraquinone from Juglans regia L.: An in-silico, in-vitro and in-vivo approach. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 906, 174234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fan, R.; Wang, Y.; Huang, T.; Shang, N.; He, K.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.; Niu, Q.; Zhang, Q. Progressive impairment of learning and memory in adult zebrafish treated by Al2O3 nanoparticles when in embryos. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Fukushima, N.; Hasumi, A. Standardized Method for the Assessment of Behavioral Responses of Zebrafish Larvae. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audira, G.; Sampurna, B.P.; Juniardi, S.; Liang, S.-T.; Lai, Y.-H.; Hsiao, C.-D. A Simple Setup to Perform 3D Locomotion Tracking in Zebrafish by Using a Single Camera. Inventions 2018, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogi, A.; Licitra, R.; Naef, V.; Marchese, M.; Fronte, B.; Gazzano, A.; Santorelli, F.M. Social Preference Tests in Zebrafish: A Systematic Review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 590057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasamma, S.; Audira, G.; Juniardi, S.; Sampurna, B.P.; Liang, S.-T.; Hao, E.; Lai, Y.-H.; Hsiao, C.-D. Zinc Chloride Exposure Inhibits Brain Acetylcholine Levels, Produces Neurotoxic Signatures, and Diminishes Memory and Motor Activities in Adult Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, Y.; Kim, D.; Jung, M.W.; Lee, C.-J. Scopolamine-induced learning impairment reversed by physostigmine in zebrafish. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 67, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, V.; Mridhulmohan, M.; Jayaseelan, S.; Sivakumar, P.; Ganesan, V. Mefenamic Acid Attenuates Chronic Alcohol Induced Cognitive Impairment in Zebrafish: Possible Role of Cholinergic Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 1392–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capatina, L.; Napoli, E.M.; Ruberto, G.; Hritcu, L. Origanum vulgare ssp. hirtum (Lamiaceae) Essential Oil Prevents Behavioral and Oxidative Stress Changes in the Scopolamine Zebrafish Model. Molecules 2021, 26, 7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nery, L.R.; Eltz, N.S.; Hackman, C.; Fonseca, R.; Altenhofen, S.; Guerra, H.N.; Freitas, V.M.; Bonan, C.D.; Vianna, M.R.M.R. Brain Intraventricular Injection of Amyloid-β in Zebrafish Embryo Impairs Cognition and Increases Tau Phosphorylation, Effects Reversed by Lithium. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanandrea, R.; Abreu, M.S.; Piato, A.; Barcellos, L.J.G.; Giacomini, A.C.V. V Lithium prevents scopolamine-induced memory impairment in zebrafish. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 664, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, C.-J.; Kim, Y.-H. MK-801-induced learning impairments reversed by physostigmine and nicotine in zebrafish. Anim. Cells Syst. 2011, 15, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franscescon, F.; Müller, T.E.; Bertoncello, K.T.; Rosemberg, D.B. Neuroprotective role of taurine on MK-801-induced memory impairment and hyperlocomotion in zebrafish. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 135, 104710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boiangiu, R.S.; Mihasan, M.; Gorgan, D.L.; Stache, B.A.; Hritcu, L. Anxiolytic, Promnesic, Anti-Acetylcholinesterase and Antioxidant Effects of Cotinine and 6-Hydroxy-L-Nicotine in Scopolamine-Induced Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitru, G.; El-Nashar, H.A.S.; Mostafa, N.M.; Eldahshan, O.A.; Boiangiu, R.S.; Todirascu-Ciornea, E.; Hritcu, L.; Singab, A.N.B. Agathisflavone isolated from Schinus polygamus (Cav.) Cabrera leaves prevents scopolamine-induced memory impairment and brain oxidative stress in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Phytomedicine 2019, 58, 152889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinza, I.; Abd-Alkhalek, A.M.; El-Raey, M.A.; Boiangiu, R.S.; Eldahshan, O.A.; Hritcu, L. Ameliorative Effects of Rhoifolin in Scopolamine-Induced Amnesic Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Model. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todirascu-Ciornea, E.; El-Nashar, H.A.S.; Mostafa, N.M.; Eldahshan, O.A.; Boiangiu, R.S.; Dumitru, G.; Hritcu, L.; Singab, A.N.B. Schinus terebinthifolius Essential Oil Attenuates Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficits via Cholinergic Modulation and Antioxidant Properties in a Zebrafish Model. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 5256781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Won, Y.J.; Lim, B.G.; Min, T.J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, I.O. Neuroprotective effects of magnesium l-threonate in a hypoxic zebrafish model. BMC Neurosci. 2020, 21, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Sohn, S.-H.; Min, T.J. Protective Effect of Ulinastatin on Cognitive Function After Hypoxia. NeuroMolecular Med. 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibt, K.J.; Piato, A.L.; da Luz Oliveira, R.; Capiotti, K.M.; Vianna, M.R.; Bonan, C.D. Antipsychotic drugs reverse MK-801-induced cognitive and social interaction deficits in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 224, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundap, U.P.; Choo, B.K.M.; Kumari, Y.; Ahmed, N.; Othman, I.B.; Shaikh, M.F. Embelin Protects Against Acute Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Seizures and Positively Modulates Cognitive Function in Adult Zebrafish. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundap, U.P.; Paudel, Y.N.; Kumari, Y.; Othman, I.; Shaikh, M.F. Embelin Prevents Seizure and Associated Cognitive Impairments in a Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Kindling Zebrafish Model. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishitha, N.; Muthuraman, A. Therapeutic evaluation of solid lipid nanoparticle of quercetin in pentylenetetrazole induced cognitive impairment of zebrafish. Life Sci. 2018, 199, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolotto, J.W.; de Melo, G.M.; Cognato, G.D.P.; Vianna, M.R.M.; Bonan, C.D. Modulation of adenosine signaling prevents scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment in zebrafish. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2015, 118, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richetti, S.K.; Blank, M.; Capiotti, K.M.; Piato, A.L.; Bogo, M.R.; Vianna, M.R.; Bonan, C.D. Quercetin and rutin prevent scopolamine-induced memory impairment in zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 217, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, V.; Ilanthalir, S. Cognition Enhancing Activity of Sulforaphane Against Scopolamine Induced Cognitive Impairment in Zebra Fish (Danio rerio). Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 2538–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Su, G.; Zhang, X.; Song, G.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, L.; Zhao, M. Characterization and Exploration of Potential Neuroprotective Peptides in Walnut (Juglans regia) Protein Hydrolysate against Cholinergic System Damage and Oxidative Stress in Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive and Memory Impairment Mice and Zebrafish. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 2773–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Ma, Y.; Huang, W.; Ling, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Zeng, A.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Wang, C.; Wang, H. Dietary Lactobacillus plantarum ST-III alleviates the toxic effects of triclosan on zebrafish (Danio rerio) via gut microbiota modulation. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, F.T.; Lim, S.M.; Ramasamy, K. Cholesterol lowering by Pediococcus acidilactici LAB4 and Lactobacillus plantarum LAB12 in adult zebrafish is associated with improved memory and involves an interplay between npc1l1 and abca1. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 2817–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoncello, K.T.; Müller, T.E.; Fontana, B.D.; Franscescon, F.; Filho, G.L.B.; Rosemberg, D.B. Taurine prevents memory consolidation deficits in a novel alcohol-induced blackout model in zebrafish. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 93, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanello, F.V.; Müller, T.E.; Franscescon, F.; Quadros, V.A.; Souza, T.P.; Canzian, J.; Leitemperger, J.; Loro, V.L.; Rosemberg, D.B. Taurine modulates behavioral effects of intermittent ethanol exposure without changing brain monoamine oxidase activity in zebrafish: Attenuation of shoal- and anxiety-like responses, and abolishment of memory acquisition deficit. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2021, 209, 173256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, P.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Shang, N.; Chen, J.; Fan, R.; Wang, Y.; Huang, T.; Niu, Q.; et al. Necrostatin-1 Relieves Learning and Memory Deficits in a Zebrafish Model of Alzheimer’s Disease Induced by Aluminum. Neurotox. Res. 2022, 40, 198–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomini, A.C.V.V.; Teixeira, K.H.; Marcon, L.; Scolari, N.; Bueno, B.W.; Genario, R.; de Abreu, N.S.; Demin, K.A.; Galstyan, D.S.; Kalueff, A.V.; et al. Melatonin treatment reverses cognitive and endocrine deficits evoked by a 24-h light exposure in adult zebrafish. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 733, 135073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundap, U.P.; Kumari, Y.; Othman, I.; Shaikh, M.F. Zebrafish as a Model for Epilepsy-Induced Cognitive Dysfunction: A Pharmacological, Biochemical and Behavioral Approach. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, H.A.; Sigstad, C.; Scalzo, F.M. Effects of dizocilpine (MK-801) on circling behavior, swimming activity, and place preference in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2004, 26, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.-C.; Hsu, C.-P.; Wu, Y.-J.; Wu, S.-Y.; Yang, Y.-L.; Lu, K.-T. Effect of MK-801-induced impairment of inhibitory avoidance learning in zebrafish via inactivation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) in telencephalon. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sison, M.; Gerlai, R. Associative learning performance is impaired in zebrafish (Danio rerio) by the NMDA-R antagonist MK-801. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2011, 96, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesnikova, T.O.; Galstyan, D.S.; Demin, K.A.; Barabanov, M.A.; Pestov, A.V.S.; de Abreu, M.; Strekalova, T.; Kalueff, A.V. Pharmacological characterization of a novel putative nootropic beta-alanine derivative, MB-005, in adult zebrafish. J. Psychopharmacol. 2022, 36, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echevarria, D.J.; Caramillo, E.M.; Gonzalez-Lima, F. Methylene blue facilitates memory retention in Zebrafish in a dose-dependent manner. Zebrafish 2016, 13, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, M.M.; Hernandez-Baixauli, J.; Puiggrós, F.; Arola, L.; Caimari, A.; Del Bas, J.M.; Baselga, L. Mediterranean natural extracts improved cognitive behavior in zebrafish and healthy rats and ameliorated lps-induced cognitive impairment in a sex dependent manner. Behav. Brain Funct. 2022, 18, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.D.; Limpuangthip, J.; Rachakonda, T.; Peterson, M. Timing of nicotine effects on learning in zebrafish. Psychopharmacology 2006, 184, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, E.D.; Chen, E. Nicotinic involvement in memory function in zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2004, 26, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, L.; Stewart, A.; Gaikwad, S.; Utterback, E.; Wu, N.; DiLeo, J.; Frank, K.; Hart, P.; Howard, H.; Kalueff, A.V. Effects of piracetam on behavior and memory in adult zebrafish. Brain Res. Bull. 2011, 85, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.W.; Sohn, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Min, T.J. The Effect of Ulinastatin to the Learning and Memory in Zebrafish. NeuroMolecular Med. 2021, 23, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Narang, R.K.; Singh, S. AlCl3 induced learning and memory deficit in zebrafish. Neurotoxicology 2022, 92, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, N.; Zhang, P.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Fan, R.; Chen, J.; Huang, T.; Wang, Y.; Duncan, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. Aluminum-Induced Cognitive Impairment and PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway Involvement in Occupational Aluminum Workers. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 38, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.-W.; Horng, J.-L.; Tong, S.-K.; Cherng, B.-W.; Liao, B.-K.; Lin, L.-Y.; Chou, M.-Y. Exposure to silver impairs learning and social behaviors in adult zebrafish. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 124031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipp, V.R.; Valles, S.; Ortiz-Kerbertt, H.; Suarez, J.V.; Bardullas, U. Neurobehavioral Alterations in Zebrafish Due to Long-Term Exposure to Low Doses of Inorganic Arsenic. Zebrafish 2018, 15, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Castro, M.R.; Lima, J.V.; Salomão de Freitas, D.P.; de Souza Valente, R.; Dummer, N.S.; de Aguiar, R.B.; dos Santos, L.C.; Marins, L.F.; Geracitano, L.A.; Monserrat, J.M.; et al. Behavioral and neurotoxic effects of arsenic exposure in zebrafish (Danio rerio, Teleostei: Cyprinidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 150, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilehvar, A.; Town, R.M.; Blust, R. The effect of copper on behaviour, memory, and associative learning ability of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 188, 109900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, D.D.S.; Danielle, N.M.; Altenhofen, S.; Luzardo, M.D.; Costa, P.G.; Bianchini, A.; Bonan, C.D.; da Silva, R.S.; Dafre, A.L. Copper at low levels impairs memory of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) and affects swimming performance of larvae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 185–186, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strungaru, S.-A.; Robea, M.A.; Plavan, G.; Todirascu-Ciornea, E.; Ciobica, A.; Nicoara, M. Acute exposure to methylmercury chloride induces fast changes in swimming performance, cognitive processes and oxidative stress of zebrafish (Danio rerio) as reference model for fish community. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 47, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenhofen, S.; Wiprich, M.T.; Nery, L.R.; Leite, C.E.; Vianna, M.R.M.R.; Bonan, C.D. Manganese(II) chloride alters behavioral and neurochemical parameters in larvae and adult zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 182, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Bai, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, K.; Li, R.; Zhu, J.-H.; Huang, C. Developmental lead acetate exposure induces embryonic toxicity and memory deficit in adult zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2012, 34, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui Thi, N.H.; Nguyen Thi, N.A.; Audira, G.; Siregar, P.; Liang, S.-T.; Huang, J.-C.; Hsiao, C.-D. Chronic Exposure to Low Concentration Lead Chloride-Induced Anxiety and Loss of Aggression and Memory in Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Li, X.; Han, G.; Du, L.; Li, M. Zebrafish neuro-behavioral profiles altered by acesulfame (ACE) within the range of “no observed effect concentrations (NOECs)”. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knecht, A.L.; Truong, L.; Simonich, M.T.; Tanguay, R.L. Developmental benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) exposure impacts larval behavior and impairs adult learning in zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2017, 59, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Liu, C.; Huang, Y.; Bao, M.; Huang, Y.; Wu, K. Effects of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether on neurobehavior and memory change and bcl-2, c-fos, grin1b and lingo1b gene expression in male zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 333, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Liu, S.; Jiang, X.; Ren, Q.; Deng, H.; Paudel, Y.N.; Wang, B.; Liu, K.; Jin, M. Benzoresorcinol induces developmental neurotoxicity and injures exploratory, learning and memorizing abilities in zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 834, 155268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.; Kim, J.L.; Hwang, K.-S.; Park, H.-C.; Bae, M.A.; Kim, K.-T.; Cho, S.-H. Mechanism of action and neurotoxic effects of chronic exposure to bisphenol F in adult zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.L.; Kim, S.S.; Hwang, K.-S.; Park, H.-C.; Cho, S.-H.; Bae, M.A.; Kim, K.-T. Chronic exposure to butyl-paraben causes photosensitivity disruption and memory impairment in adult zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 251, 106279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobao-Soares, B.; Eduardo-da-Silva, P.; Amarilha, H.; Pinheiro-da-Silva, J.; Silva, P.F.; Luchiari, A.C. It’s Tea Time: Interference of Ayahuasca Brew on Discriminative Learning in Zebrafish. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazario, L.R.; Antonioli, R.; Capiotti, K.M.; Hallak, J.E.C.; Zuardi, A.W.; Crippa, J.A.S.; Bonan, C.D.; da Silva, R.S. Caffeine protects against memory loss induced by high and non-anxiolytic dose of cannabidiol in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 135, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freddo, N.; Soares, S.M.; Fortuna, M.; Pompermaier, A.; Varela, A.C.C.; Maffi, V.C.; Mozzato, M.T.; de Alcantara Barcellos, H.H.; Koakoski, G.; Barcellos, L.J.G.; et al. Stimulants cocktail: Methylphenidate plus caffeine impairs memory and cognition and alters mitochondrial and oxidative status. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 106, 110069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.D.; Sledge, D.; Roach, S.; Petro, A.; Donerly, S.; Linney, E. Persistent behavioral impairment caused by embryonic methylphenidate exposure in zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2011, 33, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhl, T.; Prinz, N.; Oellers, N.; Seidel, N.I.; Jonas, A.; Albayram, Ö.; Bilkei-Gorzo, A.; von der Emde, G. Acute administration of THC impairs spatial but not associative memory function in zebrafish. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 3829–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon, D.M.; Luchiari, A.C. A dose for the wiser is enough: The alcohol benefits for associative learning in zebrafish. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 53, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, Y.; Tran, S.; Abraham, E.; Gerlai, R. Embryonic alcohol exposure impairs associative learning performance in adult zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 265, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuaden, F.C.; Savio, L.E.B.; Piato, A.L.; Pereira, T.C.; Vianna, M.R.; Bogo, M.R.; Bonan, C.D.; Wyse, A.T.S. Long-Term Methionine Exposure Induces Memory Impairment on Inhibitory Avoidance Task and Alters Acetylcholinesterase Activity and Expression in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Neurochem. Res. 2012, 37, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sison, M.; Gerlai, R. Behavioral performance altering effects of MK-801 in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 220, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelotti, P.; Franscescon, F.; Müller, T.E.; Rosemberg, D.B.; Pereira, M.E. Ketamine acutely impairs memory consolidation and repeated exposure promotes stereotyped behavior without changing anxiety- and aggression-like parameters in adult zebrafish. Physiol. Behav. 2022, 247, 113708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, X.; Zheng, S. Effects of embryonic propofol exposure on axonal growth and locomotor activity in zebrafish. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2020, 40, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Chen, R.; Zhang, L.; Yan, L.; Xin, J.; Li, J.; Zha, J. Long-Term Exposure to SSRI Citalopram Induces Neurotoxic Effects in Zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 12380–12390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patta, P.C.; de Oliveira, E.M.N.; Goulart, A.C.F.; Zaluski, A.B.; Papaléo, R.M.; Vianna, M.R.M. Nanoscale Structural Characterization and Impact on Long-term memory of Amyloid-β42 Oligomeric forms in Zebrafish. Neuroscience 2022, 497, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Qiu, J.; Zhao, M.; Li, F.; Yu, R.; Li, A. Accumulation and distribution of neurotoxin BMAA in aquatic animals and effect on the behavior of zebrafish in a T-maze test. Toxicon 2020, 173, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotto, J.W.; Cognato, G.P.; Christoff, R.R.; Roesler, L.N.; Leite, C.E.; Kist, L.W.; Bogo, M.R.; Vianna, M.R.; Bonan, C.D. Long-Term Exposure to Paraquat Alters Behavioral Parameters and Dopamine Levels in Adult Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Zebrafish 2014, 11, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, W.; Gao, Y.; Tian, Y. Changes of embryonic development, locomotor activity, and metabolomics in zebrafish co-exposed to chlorpyrifos and deltamethrin. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, S.; Sharma, P.K. Study of learning and memory in type 2 diabetic model of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Endocr. Metab. Sci. 2020, 1, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audira, G.; Ngoc Anh, N.T.; Ngoc Hieu, B.T.; Malhotra, N.; Siregar, P.; Villalobos, O.; Villaflores, O.B.; Ger, T.-R.; Huang, J.-C.; Chen, K.H.-C.; et al. Evaluation of the Adverse Effects of Chronic Exposure to Donepezil (An Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor) in Adult Zebrafish by Behavioral and Biochemical Assessments. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Escudero, A.; Vicente-Page, J.; Hinz, R.C.; Arganda, S.; de Polavieja, G.G. idTracker: Tracking individuals in a group by automatic identification of unmarked animals. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itskovits, E.; Levine, A.; Cohen, E.; Zaslaver, A. A multi-animal tracker for studying complex behaviors. BMC Biol. 2017, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Zhang, H.; Klaminder, J.; Brodin, T.; Andersson, P.L.; Andersson, M. ToxTrac: A fast and robust software for tracking organisms. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Zhang, H.; Klaminder, J.; Brodin, T.; Andersson, M. ToxId: An efficient algorithm to solve occlusions when tracking multiple animals. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Category | Subcategory | Paradigm | Further Subcategory | Behavioral Response | Example | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-associative learning | ||||||
| Habituation | - | Continuous exposure of stimulus | - | Decrease | Reduced zebrafish startle response to repeated sound stimulus | [19] |
| Sensitization | - | - | Increase | Repeated nicotine exposure increased locomotor activity and sensitivity of zebrafish | [20] | |
| Associative learning | ||||||
| Classical (Pavlovian) | Appetitive conditioning | Association of favorable stimulus with cue | - | Increase/Decrease (involuntary response) | Increased dog salivation upon hearing sound of bell that was previously paired with food | - |
| Aversive conditioning | Association of unfavorable stimulus with cue | - | Increase/Decrease (involuntary response) | Decreased zebrafish distance traveled in tank that was previously paired with electric shock (Increased contextual fear response) | [21] | |
| Increased zebrafish freezing time and erratic movement in tank that was previously paired with electric shock (Increased contextual fear response) | [22] | |||||
| Operant (Instrumental) | Positive reinforcement | Association of behavioral response with administration of appetitive stimulus | - | Increase | Increased zebrafish approach to a response key that was equipped with a sensor to dispense brine shrimp eggs | [23] |
| Negative reinforcement | Association of behavioral response with removal of aversive stimulus | Escape learning (Engage a behavior to remove the existing aversive stimulus) | Increase | Increased rodent crossing response from a compartment with existing foot shock to the opposite compartment in a shuttle box | - | |
| Active avoidance (Engage a behavior to prevent the occurrence of aversive stimulus) | Increased zebrafish crossing response to a compartment without electric shock upon the presentation of light signal that was previously paired with administration of the shock | [24] | ||||
| Passive (inhibitory) avoidance (Suppress an innate behavior to prevent the occurrence of aversive stimulus) | Increased zebrafish latency to enter dark (preferred) compartment that was previously paired with electric shock | [25] | ||||
| Positive punishment | Association of behavioral response with administration of aversive stimulus | - | Decrease | Refrained from pressing a lever that will lead to foot shock for a rodent | - | |
| Negative punishment | Association of behavioral response with removal of appetitive stimulus | - | Decrease | Decreased the undesired behavior by taking away the reward in a dog training | - | |
| Behavioral Test | Behavioral Domain | Procedure | Parameters Tested (unit) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Locomotor activity test | Locomotor activity | Zebrafish is allowed to swim for a certain period of time. |
|
| Novel tank test | Anxiety-like behavior And locomotor activity | Zebrafish is allowed to swim for a certain period of time. Tank is divided horizontally (virtually) into 2 segments. |
|
| Inhibitory avoidance test | Learning and memory retention | Can be consisted of habituation, training and probe phases. A form of operant conditioning with negative reinforcement. |
|
| Appetitive conditioning test | Learning and memory retention | Can be consisted of habituation, training and probe phases. A form of associative learning with appetitive stimulus. |
|
| Y-maze test | Spatial recognition and memory | Zebrafish is allowed to explore the maze for a certain period of time. |
|
| Novel object recognition test | Object recognition and memory | Zebrafish is allowed to explore the objects for a certain period of time. |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, J.K.; Nazar, F.H.; Makpol, S.; Teoh, S.L. Zebrafish: A Pharmacological Model for Learning and Memory Research. Molecules 2022, 27, 7374. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217374
Tan JK, Nazar FH, Makpol S, Teoh SL. Zebrafish: A Pharmacological Model for Learning and Memory Research. Molecules. 2022; 27(21):7374. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217374
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Jen Kit, Faris Hazwan Nazar, Suzana Makpol, and Seong Lin Teoh. 2022. "Zebrafish: A Pharmacological Model for Learning and Memory Research" Molecules 27, no. 21: 7374. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217374
APA StyleTan, J. K., Nazar, F. H., Makpol, S., & Teoh, S. L. (2022). Zebrafish: A Pharmacological Model for Learning and Memory Research. Molecules, 27(21), 7374. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217374







