Production of Prosaikogenin F, Prosaikogenin G, Saikogenin F and Saikogenin G by the Recombinant Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Saikosaponin and their Anti-Cancer Effect
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Quantitative Analysis of Bupleurum falcatum L.
2.2. Purification of Saikosaponin A and Saikosaponin D with High Purity
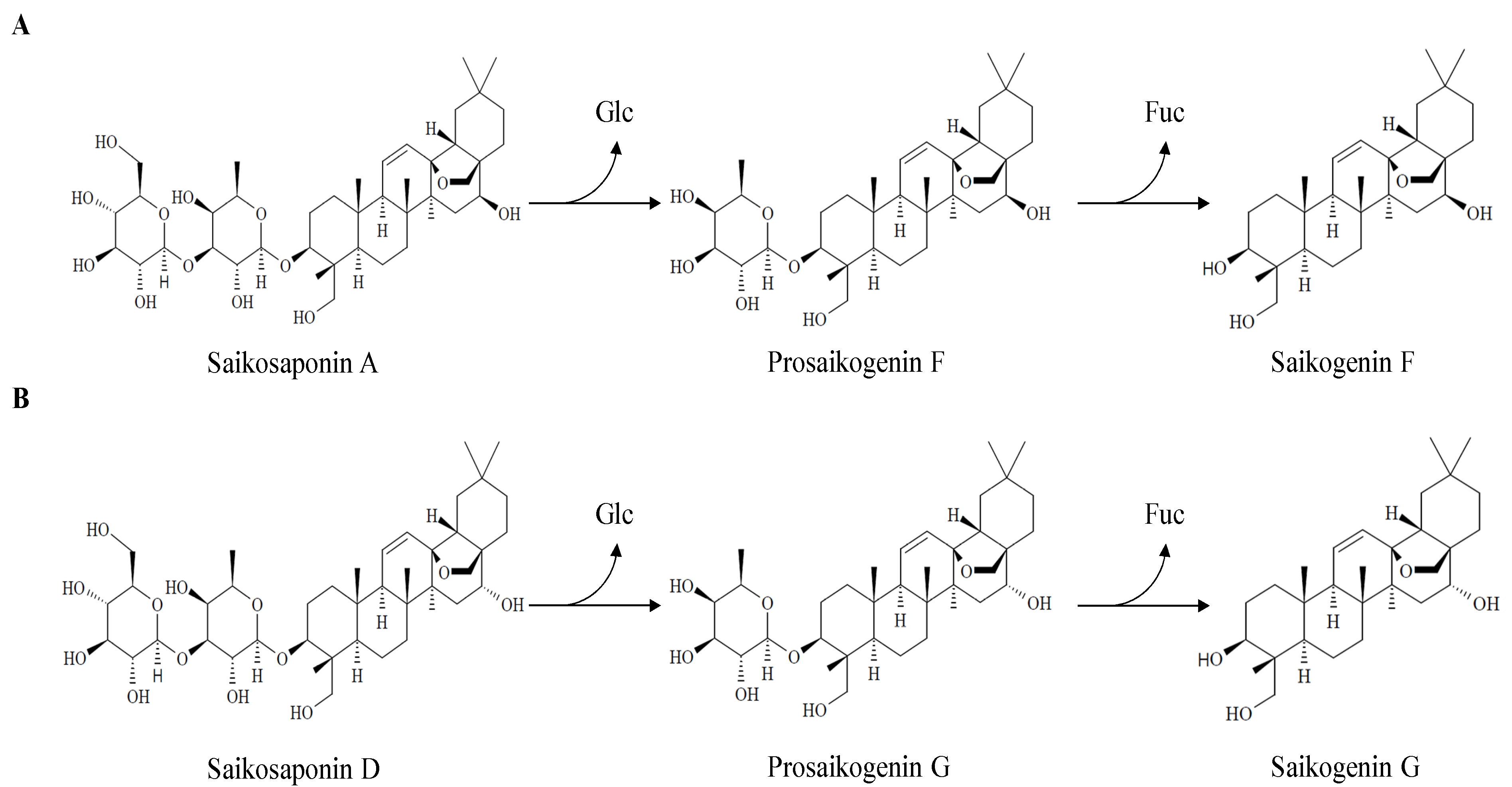
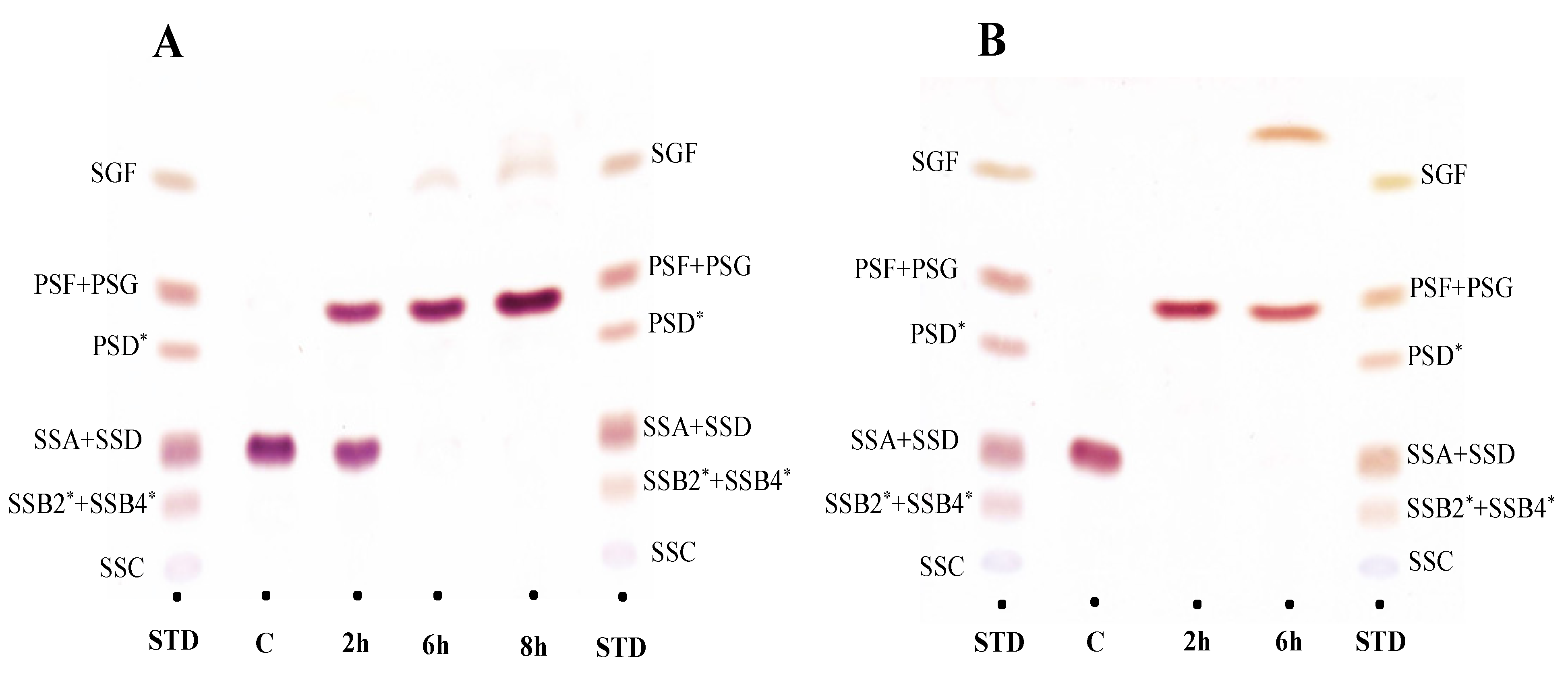
2.3. Biotransformation of Saikosaponin into Saikogenin via Prosaikogenin
2.4. Purification of Biotransformed Prosaikogenins and Saikogenins
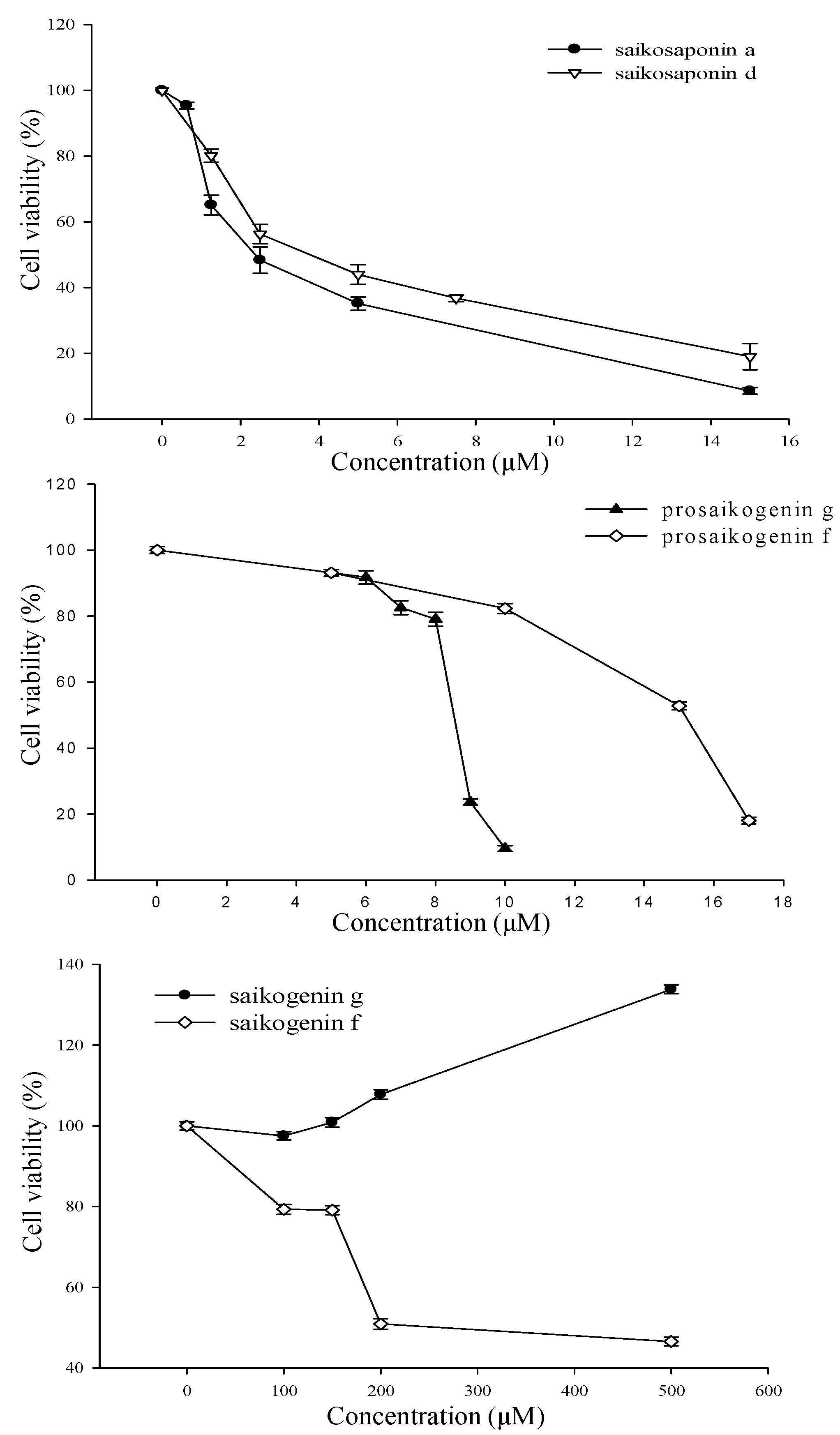
2.5. Anti-Cancer Effect of Saikosaponin, Prosaikogenin, and Saikogenin
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Quantitative Analysis of Bupleurum falcatum L.
3.3. Purification and Separation of Saikosaponin Mixture as Saikosaponin A and Saikosaponin D
3.4. Transformation of the Saikosaponin A and D Using Recombinant Enzymes BglPm and BglLk
3.5. Purification of Prosaikogenins and Saikogenins
3.6. Cell Culture
3.7. Cell Viability Assay
3.8. Analytic Methods
3.8.1. Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) Analysis
3.8.2. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and LC/MS Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Xie, J.Y.; Di, H.Y.; Li, H.; Cheng, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Chen, D.F. Bupleurum chinense DC polysaccharides attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.Y.; Li, J.P. Saikosaponin-d inhibits proliferation of human undifferentiated thyroid carcinoma cells through induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 2435–2443. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhao, J. Mechanisms underlying the beneficial effects of Kaiyu Granule for depression. Neural Regen. Res. 2013, 8, 3241–3248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chiang, L.C.; Ng, L.T.; Liu, L.T.; Shieh, D.E.; Lin, C.C. Cytotoxicity and antihepatitis B virus activities of saikosaponins from Bupleurum species. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, T.; Cui, X.; Li, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhong, X. Hepatoprotective effects of a Chinese herbal formula, longyin decoction, on carbon-tetrachloride-induced liver injury in chickens. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 392743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, Z.L.; Li, X.J.; Dang, H.; Wang, F.; Xu, X.Y. Saikosaponin-d affects the differentiation, maturation and function of monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 7, 1354–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Cheng, H.; Xu, D.; Yin, Q.; Cheng, L.; Wang, L.; Song, S.; Zhang, M. Attenuation of neuropathic pain by saikosaponin A in a rat model of chronic constriction injury. Neurochem. Res. 2014, 39, 2136–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.Y.; Chiou, C.Y.; Chiou, S.J. Putative genes involved in saikosaponin biosynthesis in Bupleurum species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 12806–12826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Huang, N.; Liu, R.; Sun, R. A comprehensive review and perspectives on pharmacology and toxicology of saikosaponins. Phytomedicine 2018, 50, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, B.; Rui, Y.; Yongsheng, M.; Shan, Z.; Xiaodong, Z.; Ying, L. A systematic review of the active saikosaponins and extracts isolated from Radix Bupleuri and their applications. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 620–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Zheng, X.; Yang, L.; Shi, F.; Gao, L.; Zhong, Y.; Sun, H.; He, F.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X. Reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis contributes to chemosensitization effect of saikosaponins on cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Chang, N.; Chung, J.; Chen, K. Saikosaponin-A Induces Apoptotic Mechanism in Human Breast MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 Cancer Cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2003, 31, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.; Kuo, P.; Chiang, L.; Lin, C. Involvement of p53, nuclear factor kappaB and Fas/Fas ligand in induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by saikosaponin d in human hepatoma cell lines. Cancer Lett. 2004, 213, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.; Sierra, M.S.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut 2017, 66, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurunathan, S.; Muhammad, Q.; Park, C.; Yoo, H.; Kim, J.; Hong, K. Cytotoxic Potential and Molecular Pathway Analysis of Silver Nanoparticles in Human Colon Cancer Cells HCT116. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Shin, S.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Moon, J.S.; Im, W.T.; Han, N.S. Production of Ginsenoside F2 by Using Lactococcus lactis with Enhanced Expression of beta-Glucosidase Gene from Paenibacillus mucilaginosus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2506–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H. Characterization of Ginsenoside Conversion Ability of BglLk Cloned from Lactobacillus Koreensis and the Enhanced Production of Ginsenoside C-K from PPD Mix Using Four Glycosidases in Series. Master’s Thesis, Hankyong National University, Anseong, Korea, July 2020. [Google Scholar]
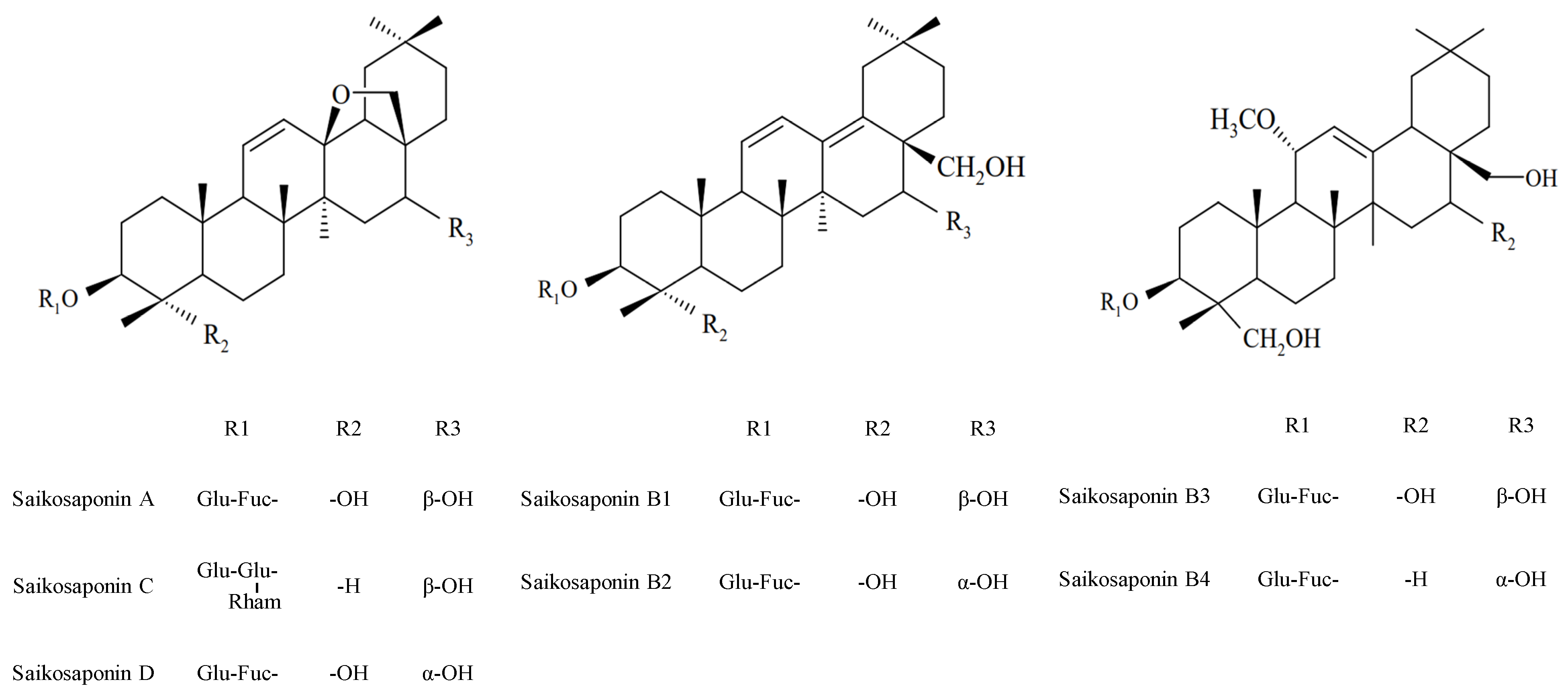

| Saikosaponins | Calibration Curves | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| SSC * | y = 0.0835x − 3.1814 | 0.9999 |
| SSA * | y = 0.1354x + 0.4894 | 0.9999 |
| PSF * | y = 0.1058x + 0.8263 | 0.9998 |
| SSD * | y = 0.1589x + 1.3423 | 0.9999 |
| SGF * | y = 0.0772x − 2.8478 | 0.9997 |
| PSG * | y = 0.1245x − 0.3113 | 0.9999 |
| Samples | SSC | SSA | PSF | SSD | SGF | PSG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bupleurum falcatum (Korea) | 0.47 ± 0.08 | 2.01 ± 0.08 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.76 ± 0.08 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.12 ± 0.01 |
| Bupleurum falcatum (China) | 0.54 ± 0.07 | 3.77 ± 0.09 | 0.25 ± 0.05 | 1.76 ± 0.1 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 0.43 ± 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.-E.; Song, B.-K.; Kim, J.-H.; Siddiqi, M.-Z.; Im, W.-T. Production of Prosaikogenin F, Prosaikogenin G, Saikogenin F and Saikogenin G by the Recombinant Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Saikosaponin and their Anti-Cancer Effect. Molecules 2022, 27, 3255. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103255
Lee J-E, Song B-K, Kim J-H, Siddiqi M-Z, Im W-T. Production of Prosaikogenin F, Prosaikogenin G, Saikogenin F and Saikogenin G by the Recombinant Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Saikosaponin and their Anti-Cancer Effect. Molecules. 2022; 27(10):3255. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103255
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ji-Eun, Bong-Kyu Song, Ju-Hyeon Kim, Muhammad-Zubair Siddiqi, and Wan-Taek Im. 2022. "Production of Prosaikogenin F, Prosaikogenin G, Saikogenin F and Saikogenin G by the Recombinant Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Saikosaponin and their Anti-Cancer Effect" Molecules 27, no. 10: 3255. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103255
APA StyleLee, J.-E., Song, B.-K., Kim, J.-H., Siddiqi, M.-Z., & Im, W.-T. (2022). Production of Prosaikogenin F, Prosaikogenin G, Saikogenin F and Saikogenin G by the Recombinant Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Saikosaponin and their Anti-Cancer Effect. Molecules, 27(10), 3255. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103255





