A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial to Determine the Effectiveness of a Polyphenolic Extract (Hibiscus sabdariffa and Lippia citriodora) for Reducing Blood Pressure in Prehypertensive and Type 1 Hypertensive Subjects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
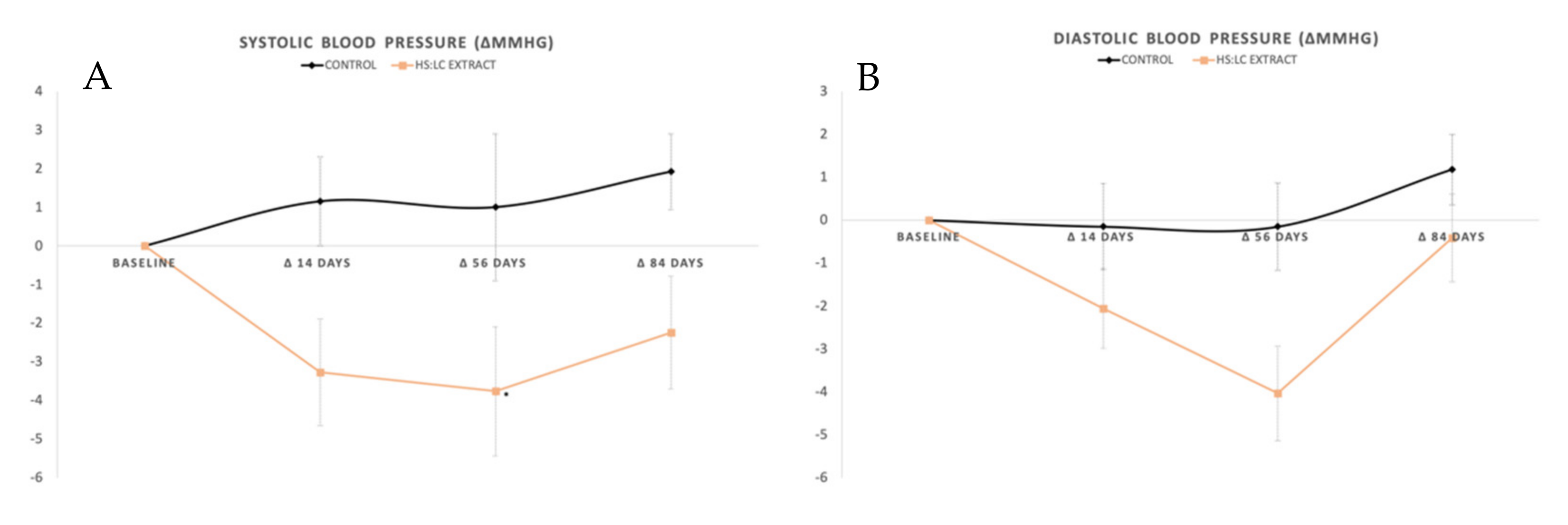
2.1. Blood Pressure Measured with Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring
General SBP, DBP, and Mean Blood Pressure (MBP)
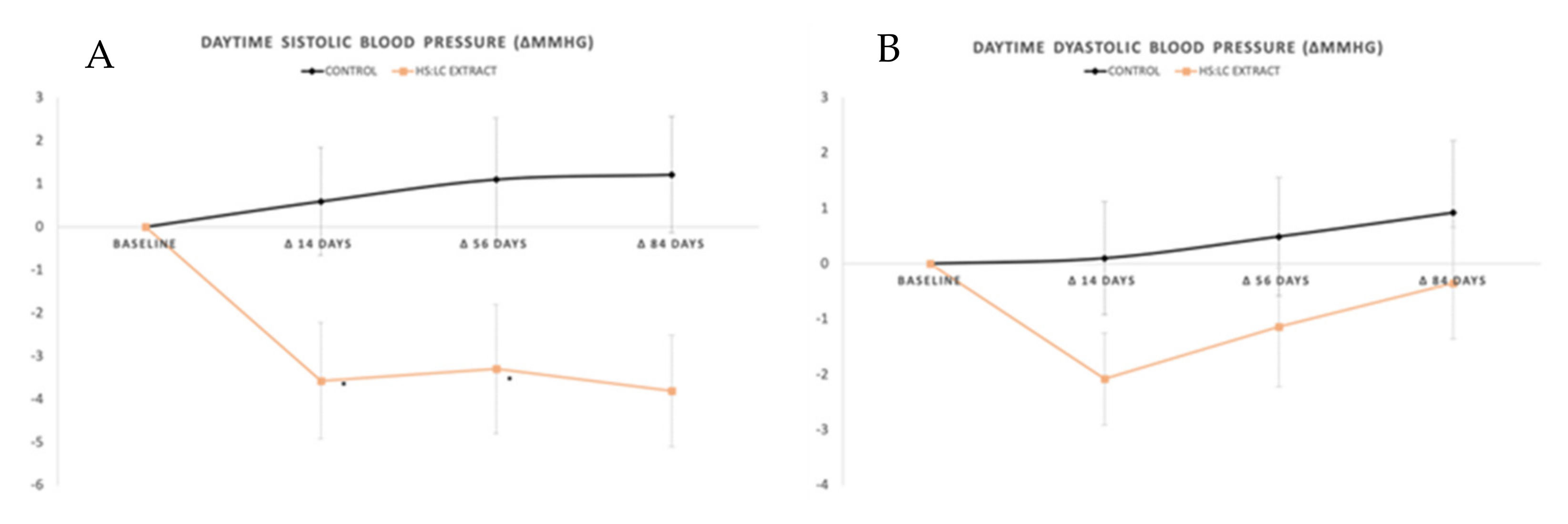
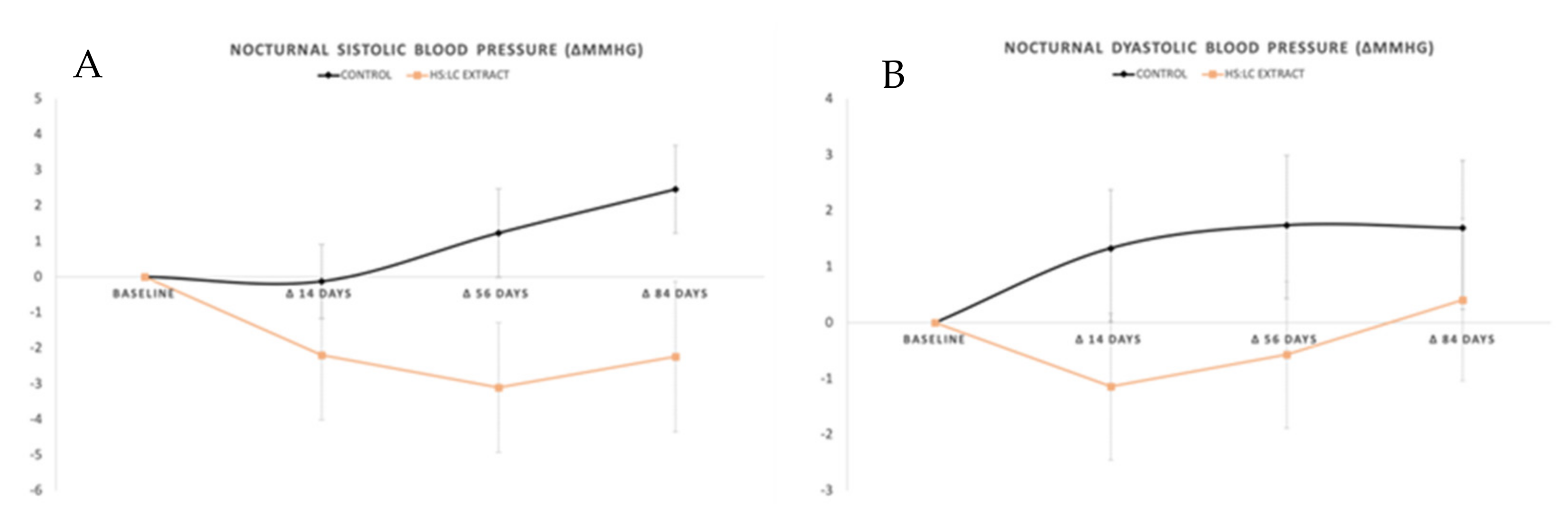
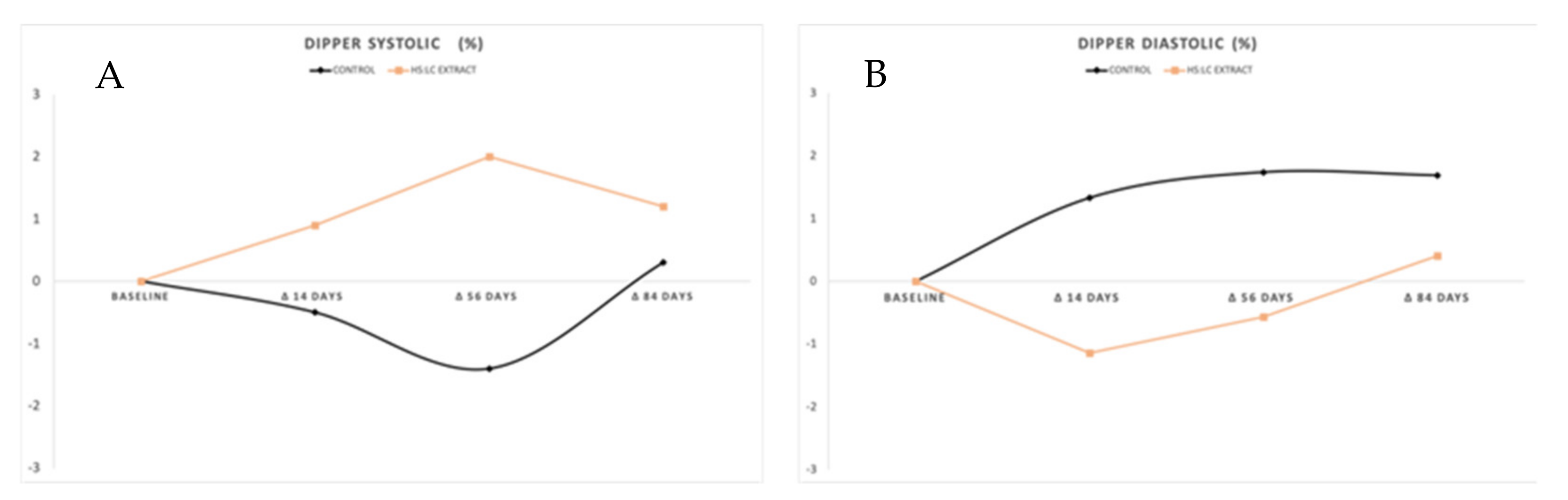
2.2. Daily Evolution of Blood Pressure Measured with ABPM
2.2.1. Daytime SBP and DBP
2.2.2. Nocturnal SBP and DBP
2.2.3. Dipper
2.3. Blood Parameters
2.4. Physical Activity
3. Discussion
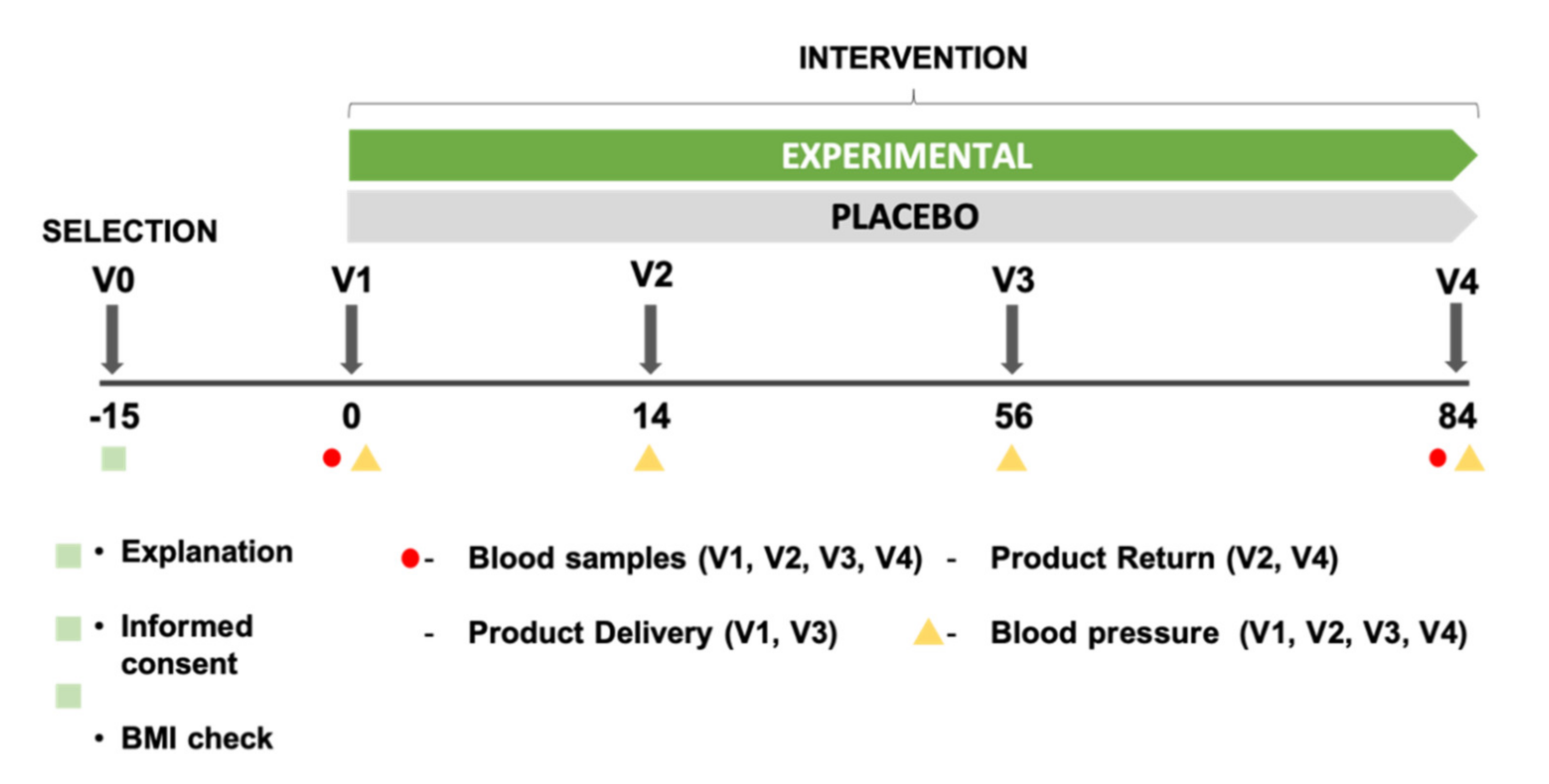
4. Materials and Methods
Statistic Determinations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Egan, B.M. Optimal Systolic Blood Pressure Target in Resistant Hypertension. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, e623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales Rigau, J.M.; Achiong Estupiñán, F.; Díaz Hernández, O.; Fuentes García, S. Pesquisa activa de hipertensión arterial: Un éxito de la atención primaria de salud. Rev. Cuba. Med. Gen. Integr. 2003, 19, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, K.T.; Stefanescu, A.; He, J. The global epidemiology of hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menéndez, E.; Delgado, E.; Fernández-Vega, F.; Prieto, M.A.; Bordiú, E.; Calle, A.; Carmena, R.; Castaño, L.; Catalá, M.; Franch, J. Prevalencia, diagnóstico, tratamiento y control de la hipertensión arterial en España. Resultados del estudio Diabet. es. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2016, 69, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 1953–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawes, C.M.M.; Vander Hoorn, S.; Rodgers, A. Global burden of blood-pressure-related disease, 2001. Lancet 2008, 371, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangen-Lønne, A.M.; Wilsgaard, T.; Johnsen, S.H.; Løchen, M.-L.; Njølstad, I.; Mathiesen, E.B. Declining Incidence of Ischemic Stroke: What Is the Impact of Changing Risk Factors? The Tromsø Study 1995 to 2012. Stroke 2017, 48, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveria, S.A.; Lapuerta, P.; McCarthy, B.D.; L’Italien, G.J.; Berlowitz, D.R.; Asch, S.M. Physician-related barriers to the effective management of uncontrolled hypertension. Arch. Intern. Med. 2002, 162, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, P.M.; Magid, D.J.; Shetterly, S.M.; Olson, K.L.; Peterson, P.N.; Masoudi, F.A.; Rumsfeld, J.S. Importance of therapy intensification and medication nonadherence for blood pressure control in patients with coronary disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 168, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serban, C.; Sahebkar, A.; Ursoniu, S.; Andrica, F.; Banach, M. Effect of sour tea (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) on arterial hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhuenda, J.; Medina, S.; Martínez-Hernández, P.; Arina, S.; Zafrilla, P.; Mulero, J.; Oger, C.; Galano, J.-M.; Durand, T.; Ferreres, F.; et al. Melatonin and hydroxytyrosol protect against oxidative stress related to the central nervous system after the ingestion of three types of wine by healthy volunteers. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhuenda, J.; Medina, S.; Martínez-Hernández, P.; Arina, S.; Zafrilla, P.; Mulero, J.; Oger, C.; Galano, J.-M.; Durand, T.; Solana, A.; et al. Effect of the dietary intake of melatonin- and hydroxytyrosol-rich wines by healthy female volunteers on the systemic lipidomic-related oxylipins. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3745–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, M.E.; El-Bassyouni, H.T.; El-Gammal, M.; Kamal, S. Indicators of the metabolic syndrome in obese adolescents. Arch. Med. Sci. 2015, 11, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walton, R.J.; Whitten, D.L.; Hawrelak, J.A. The efficacy of Hibiscus sabdariffa (rosella) in essential hypertension: A systematic review of clinical trials. Aust. J. Herb. Med. 2016, 28, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Eddouks, M.; Maghrani, M.; Lemhadri, A.; Ouahidi, M.-L.; Jouad, H. Ethnopharmacological survey of medicinal plants used for the treatment of diabetes mellitus, hypertension and cardiac diseases in the south-east region of Morocco (Tafilalet). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 82, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boix-Castejón, M.; Herranz-López, M.; Pérez Gago, A.; Olivares-Vicente, M.; Caturla, N.; Roche, E.; Micol, V. Hibiscus and Lemon verbena polyphenols modulate appetite-related biomarkers in overweight subjects: A randomized controlled trial. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 3173–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herranz-lópez, M.; Olivares-vicente, M.; Boix-castejón, M.; Caturla, N. Differential effects of a combination of Hibiscus sabdariffa and Lippia citriodora polyphenols in overweight/obese subjects: A randomized controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandes Fernandes, E.; Coelho, D.; Missel Correa, J.R.; Kumpinski, D. [Circadian alterations of the cardiovascular system]. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2000, 53, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, J.M.M.; Otegui, A.U.; Ayuso, J.M. Necesidades energéticas, hídricas y nutricionales en el deporte. Eur. J. Hum. Mov. 2013, 30, 37–52. [Google Scholar]
- Joven, J.; March, I.; Espinel, E.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Rodríguez-Gallego, E.; Aragonès, G.; Beltrán-Debón, R.; Alonso-Villaverde, C.; Rios, L.; Martin-Paredero, V.; et al. Hibiscus sabdariffa extract lowers blood pressure and improves endothelial function. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1374–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, A.L.; Lamm, M.G.; Funk, J.L.; Ritenbaugh, C. Hibiscus sabdariffa L. in the treatment of hypertension and hyperlipidemia: A comprehensive review of animal and human studies. Fitoterapia 2013, 85, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji Faraji, M.; Haji Tarkhani, A. The effect of sour tea (Hibiscus sabdariffa) on essential hypertension. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1999, 65, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Arellano, A.; Flores-Romero, S.; Chávez-Soto, M.A.; Tortoriello, J. Effectiveness and tolerability of a standardized extract from Hibiscus sabdariffa in patients with mild to moderate hypertension: A controlled and randomized clinical trial. Phytomedicine 2004, 11, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Arellano, A.; Miranda-Sánchez, J.; Avila-Castro, P.; Herrera-Alvarez, S.; Jiménez-Ferrer, J.E.; Zamilpa, A.; Román-Ramos, R.; Ponce-Monter, H.; Tortoriello, J. Clinical effects produced by a standardized herbal medicinal product of Hibiscus sabdariffa on patients with hypertension. A randomized, double-blind, lisinopril-controlled clinical trial. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares-vicente, M.; Barrajón-catalán, E.; Herranz-lópez, M.; Segura-carretero, A.; Joven, J.; Encinar, J.A.; Micol, V. Plant-Derived Polyphenols in Human Health: Biological Activity, Metabolites and Putative Molecular Targets. Curr. Drug Metab. 2018, 19, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendrame, S.; Klimis-zacas, D. Anti-inflammatory effect of anthocyanins via modulation of nuclear factor- j B and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascades. Nutr Rev. 2015, 73, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-debón, R.; Rull, A.; Rodríguez-sanabria, F.; Iswaldi, I.; Herranz-lópez, M.; Aragonès, G. Phytomedicine Continuous administration of polyphenols from aqueous rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) extract ameliorates dietary-induced metabolic disturbances in hyperlipidemic mice. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardiola, S.; Mach, N. Therapeutic potential of Hibiscus sabdariffa: A review of the scientific evidence. Endocrinol. Nutr. Organo Soc. Esp. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2014, 61, 274–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hügel, H.M.; Jackson, N.; May, B.; Zhang, A.L.; Xue, C.C. Polyphenol protection and treatment of hypertension. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassidy, A.; O’Reilly, É.J.; Kay, C.; Sampson, L.; Franz, M.; Forman, J.P.; Curhan, G.; Rimm, E.B. Habitual intake of flavonoid subclasses and incident hypertension in adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourová, J.; Najmanová, I.; Vopršalová, M.; Migkos, T.; Pilařová, V.; Applová, L.; Nováková, L.; Mladěnka, P. Two flavonoid metabolites, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and 4-methylcatechol, relax arteries ex vivo and decrease blood pressure in vivo. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2018, 111, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najmanová, I.; Pourová, J.; Vopršalová, M.; Pilařová, V.; Semecký, V.; Nováková, L.; Mladěnka, P. Flavonoid metabolite 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid formed by human microflora decreases arterial blood pressure in rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najmanová, I.; Pourová, J.; Mladěnka, P. A Mixture of Phenolic Metabolites of Quercetin Can Decrease Elevated Blood Pressure of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Even in Low Doses. Nutrients 2020, 12, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Räthel, T.R.; Samtleben, R.; Vollmar, A.M.; Dirsch, V.M. Activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by red wine polyphenols: Impact of grape cultivars, growing area and the vinification process. J. Hypertens. 2007, 25, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xu, X.; Liang, Y.; Head, R.; Bennett, L. Inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) activity by polyphenols from tea (Camellia sinensis) and links to processing method. Food Funct. 2011, 2, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón-alonso, J.; Zamilpa, A.; Alarcón, F.; Herrera-ruiz, M.; Tortoriello, J.; Jimenez-ferrer, E. Pharmacological characterization of the diuretic effect of Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn (Malvaceae) extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalalyazdi, M.; Ramezani, J.; Izadi-Moud, A.; Madani-Sani, F.; Shahlaei, S.; Ghiasi, S.S. Effect of hibiscus sabdariffa on blood pressure in patients with stage 1 hypertension. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2019, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Dusting, G.J. NADPH oxidase-mediated redox signaling: Roles in cellular stress response, stress tolerance, and tissue repair. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 218–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herranz-lópez, M.; Barrajón-catalán, E.; Segura-carretero, A.; Menéndez, J.A.; Joven, J.; Micol, V. Lemon verbena (Lippia citriodora) polyphenols alleviate obesity-related disturbances in hypertrophic adipocytes through AMPK-dependent mechanisms. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijón-Conde, T.; Gorostidi, M.; Banegas, J.R.; de la Sierra, A.; Segura, J.; Vinyoles, E.; Divisón-Garrote, J.A.; Ruilope, L.M. Position statement on ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) by the Spanish Society of Hypertension. Hipertens. Riesgo Vasc. 2019, 36, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, W.B. Relevance of blood pressure variation in the circadian onset of cardiovascular events. J. Hypertens Suppl. 2003, 21, S9–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2019, 72, 160. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Yang, W.-K.; Kim, H.Y.; Min, B.; Caturla, N.; Jones, J.; Park, Y.-C.; Lee, Y.-C.; Kim, S.-H. Metabolaid(®) Combination of Lemon Verbena and Hibiscus Flower Extract Prevents High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity through AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Activation. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grupo de Trabajo de la Sociedad Europea de Cardiología. Guía ESC/ESH 2018 sobre el diagnóstico y tratamiento de la hipertensión arterial. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2019, 72, 160. [Google Scholar]
- McCormack, T.; Krause, T.; O’Flynn, N. Management of hypertension in adults in primary care: NICE guideline. Br. J. Gen. Pract. J. R. Coll. Gen. Pract. 2012, 62, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, E.; Parati, G.; Stergiou, G.; Asmar, R.; Beilin, L.; Bilo, G.; Clement, D.; de la Sierra, A.; de Leeuw, P.; Dolan, E.; et al. European Society of Hypertension position paper on ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 1731–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellén-Sanchén, E. Monitorización ambulatoria de presión arterial, acercamiento al verdadero valor de una variable biológica. Rev. Arch. Médico Camagüey 2018, 22, 699–702. [Google Scholar]
- Berenguer Guarnaluses, L.J. Algunas consideraciones sobre la hipertensión arterial. Medisan 2016, 20, 2434–2438. [Google Scholar]
- Ainsworth, B.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Herrmann, S.D.; Meckes, N.; Bassett, D.R.J.; Tudor-Locke, C.; Greer, J.L.; Vezina, J.; Whitt-Glover, M.C.; Leon, A.S. Compendium of Physical Activities: A second update of codes and MET values. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1575–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Control | Hs-Lc Extract | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (number: % men) | 33: 84.62% | 25: 67.57% | 0.107 |
| Age (years) | 31.51 ± 11.80 | 38.30 ± 12.02 | 0.015 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.95 ± 5.98 | 28.86 ± 3.81 | 0.431 |
| Physical activity (METs · min/week) | 711.19 ± 111.81 | 745.69 ± 189.07 | 0.333 |
| SBP Sphygmomanometer (mmHg) | 133.64 ± 12.42 | 135.43 ± 11.44 | 0.516 |
| DBP Sphygmomanometer (mmHg) | 86.13 ± 7.60 | 90.27 ± 8.05 | 0.150 |
| Baseline | Final | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | Control | 228.2 ± 6.2 | 232.8 ± 9.5 |
| Extract | 234.9 ± 6 | 223.2 ± 9 | |
| HDL Cholesterol(mg/dL) | Control | 56.5 ± 2.5 | 58.9 ± 2.4 |
| Extract | 58.5 ± 2.1 | 60,6 ± 2.2 | |
| LDL Cholesterol (mg/dL) | Control | 144.1 ± 6.3 | 144.1 ± 7.6 |
| Extract | 134.1 ± 7.2 | 133.8± 7.5 | |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | Control | 138.8 ± 12.1 | 134.1 ± 612.4 |
| Extract | 136 ± 612.4 | 133.1 ± 12.4 | |
| Blood Glucose (mg/dL) | Control | 97 ± 3.5 | 94.4 ± 2.8 |
| Extract | 94.8 ± 2.9 | 93.2 ± 2.3 | |
| Glycated Hemoglobin (%) | Control | 5.4 ± 0.2 | 5.2 ± 0.1 |
| Extract | 5 ± 0.2 | 4.8 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marhuenda, J.; Pérez-Piñero, S.; Arcusa, R.; Victoria-Montesinos, D.; Cánovas, F.; Sánchez-Macarro, M.; García-Muñoz, A.M.; Querol-Calderón, M.; López-Román, F.J. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial to Determine the Effectiveness of a Polyphenolic Extract (Hibiscus sabdariffa and Lippia citriodora) for Reducing Blood Pressure in Prehypertensive and Type 1 Hypertensive Subjects. Molecules 2021, 26, 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061783
Marhuenda J, Pérez-Piñero S, Arcusa R, Victoria-Montesinos D, Cánovas F, Sánchez-Macarro M, García-Muñoz AM, Querol-Calderón M, López-Román FJ. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial to Determine the Effectiveness of a Polyphenolic Extract (Hibiscus sabdariffa and Lippia citriodora) for Reducing Blood Pressure in Prehypertensive and Type 1 Hypertensive Subjects. Molecules. 2021; 26(6):1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061783
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarhuenda, Javier, Silvia Pérez-Piñero, Raúl Arcusa, Desirée Victoria-Montesinos, Fernando Cánovas, Maravillas Sánchez-Macarro, Ana María García-Muñoz, María Querol-Calderón, and Francisco Javier López-Román. 2021. "A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial to Determine the Effectiveness of a Polyphenolic Extract (Hibiscus sabdariffa and Lippia citriodora) for Reducing Blood Pressure in Prehypertensive and Type 1 Hypertensive Subjects" Molecules 26, no. 6: 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061783
APA StyleMarhuenda, J., Pérez-Piñero, S., Arcusa, R., Victoria-Montesinos, D., Cánovas, F., Sánchez-Macarro, M., García-Muñoz, A. M., Querol-Calderón, M., & López-Román, F. J. (2021). A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial to Determine the Effectiveness of a Polyphenolic Extract (Hibiscus sabdariffa and Lippia citriodora) for Reducing Blood Pressure in Prehypertensive and Type 1 Hypertensive Subjects. Molecules, 26(6), 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061783









