Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel 4-(4-Formamidophenylamino)-N-methylpicolinamide Derivatives as Potential Antitumor Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
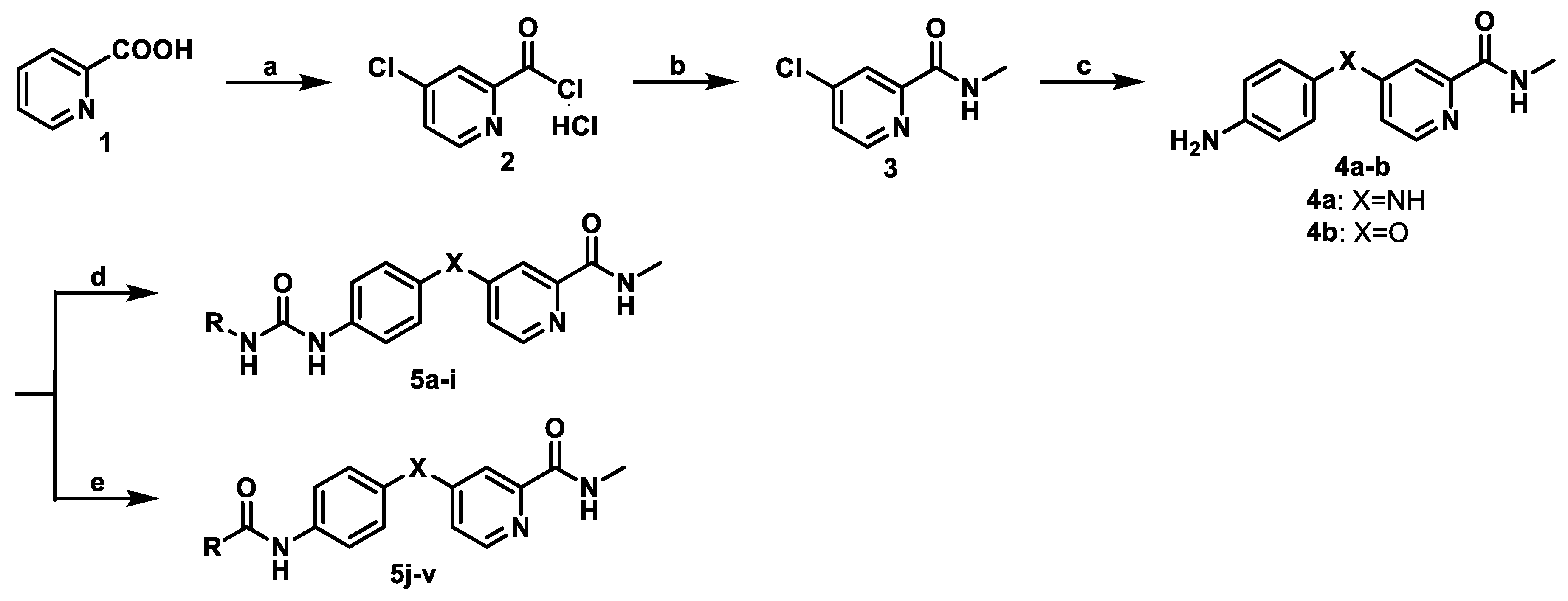
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Pharmacology
2.2.1. In Vitro Anticancer Activities
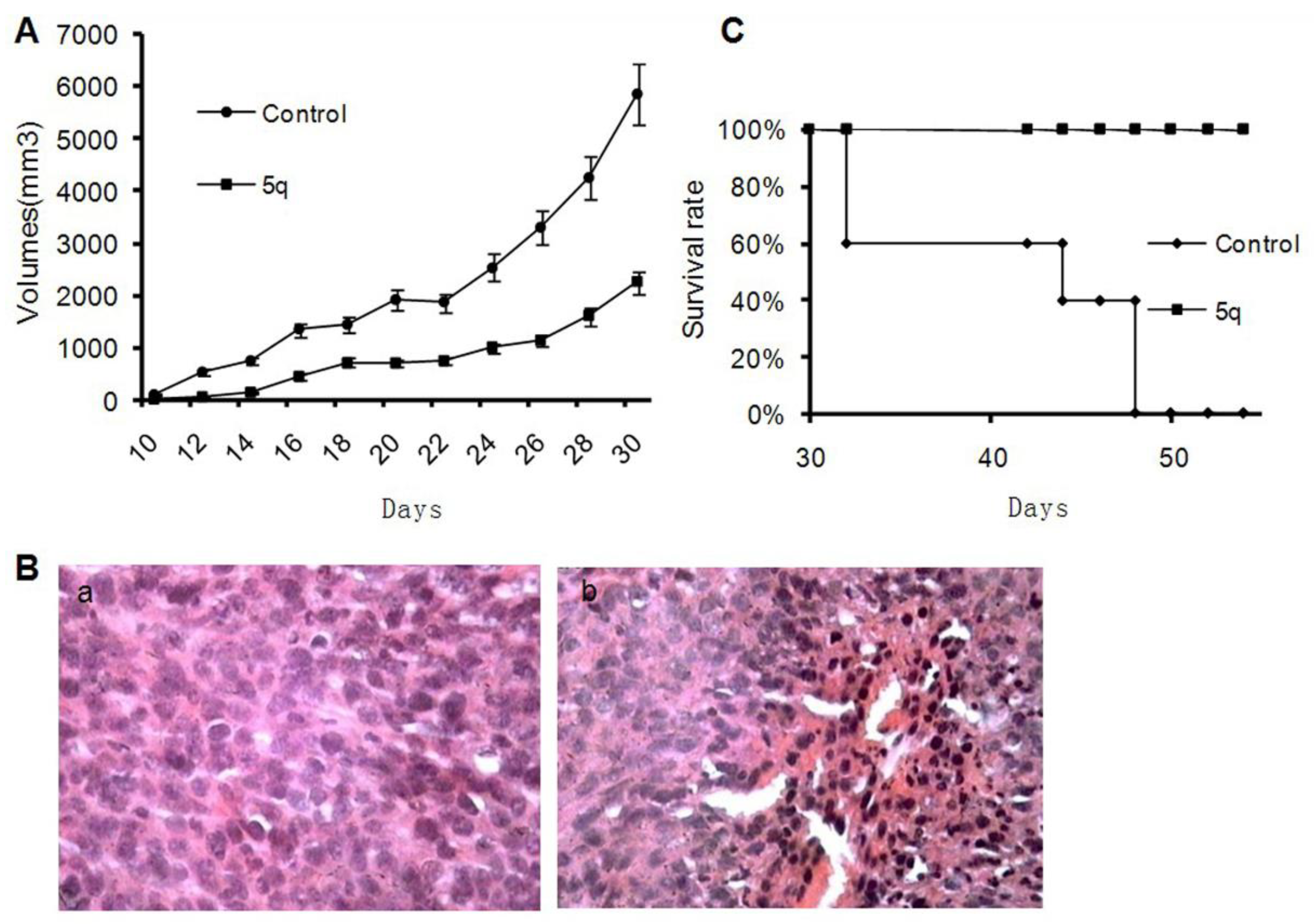
2.2.2. In Vivo Antitumor Effects
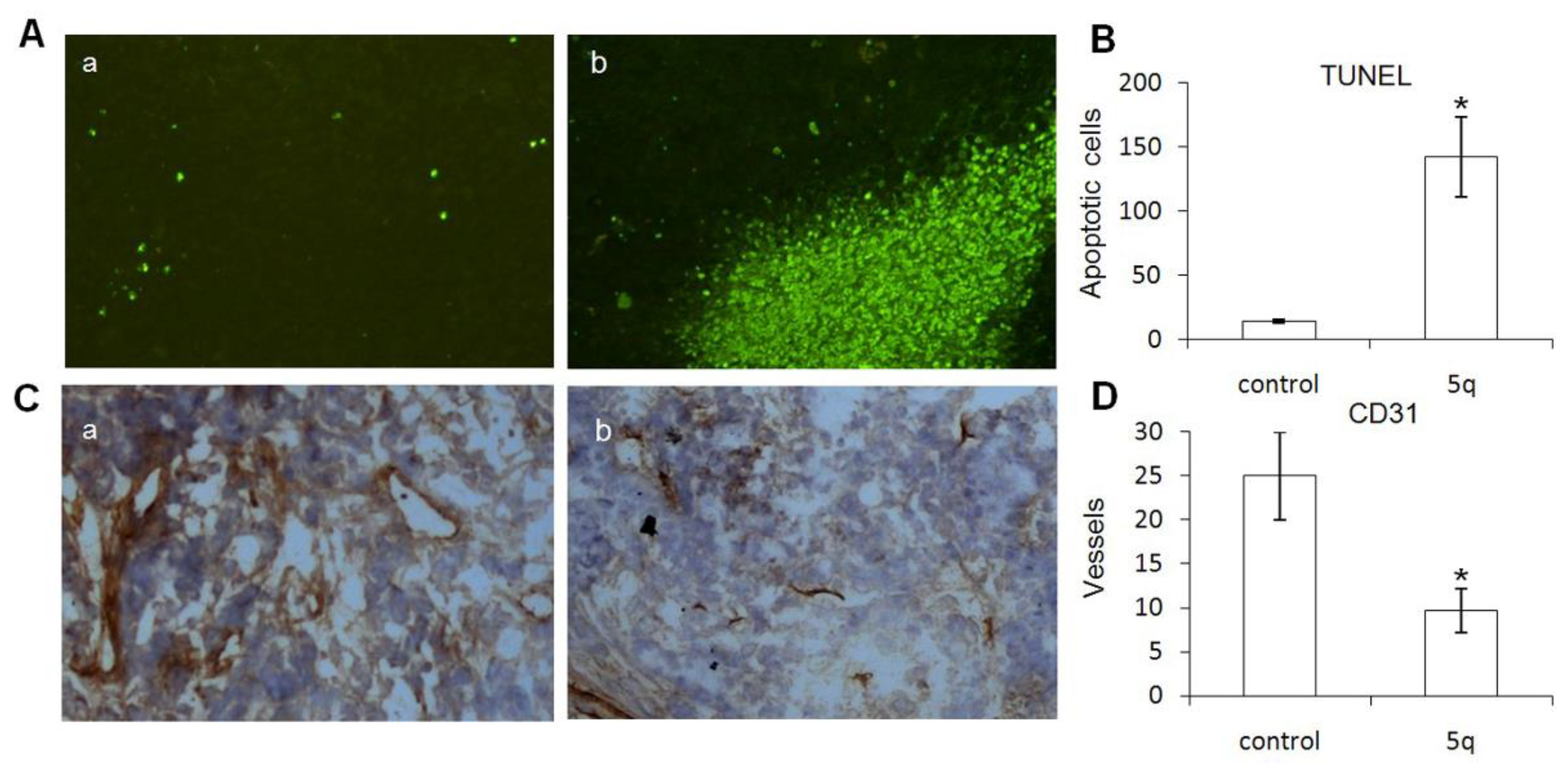
2.2.3. Apoptosis and Anti-Angiogenesis Effect
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Synthesis of 4-Chloro-N-methylpicolinamide (3)
3.1.2. Synthesis of 4-(4-Aminophenylamino)-N-methylpicolinamide (4a)
3.1.3. Synthesis of 4-(4-Aminophenoxy)-N-methylpicolinamide (4b)
3.1.4. General Procedure for Synthesizing of 5a–i
3.1.5. General Procedure for Synthesizing of 5j–n
3.1.6. General Procedure for Synthesizing of 5o–v
3.2. Pharmacology
3.2.1. Cell Culture
3.2.2. MTT
3.2.3. Mice Tumor Models and Treatment
3.2.4. Histological Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Torre, L.A.; Siegel, R.L.; Ward, E.M.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Incidence and Mortality Rates and Trends-An Update. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2016, 25, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evan, G.I.; Vousden, K.H. Proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature 2001, 411, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viallard, C.; Larrivee, B. Tumor angiogenesis and vascular normalization: Alternative therapeutic targets. Angiogenesis 2017, 20, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajib, S.; Zahra, F.T.; Lionakis, M.S.; German, N.A.; Mikelis, C.M. Mechanisms of angiogenesis in microbe-regulated inflammatory and neoplastic conditions. Angiogenesis 2018, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, F.M.; Gray, N.S. Kinase inhibitors: The road ahead. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Lovly, C.M. Mechanisms of receptor tyrosine kinase activation in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkman, J.; Long, D.M., Jr.; Becker, F.F. Growth and metastasis of tumor in organ culture. Cancer 1963, 16, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N.; Kerbel, R.S. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature 2005, 438, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Hartandi, K.; Ji, Z.; Ahmed, A.A.; Albert, D.H.; Bauch, J.L.; Bouska, J.J.; Bousquet, P.F.; Cunha, G.A.; Glaser, K.B.; et al. Discovery of N-(4-(3-amino-1H-indazol-4-yl)phenyl)-N’-(2-fluoro-5-methylphenyl)urea (ABT-869), a 3-aminoindazole-based orally active multitargeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 1584–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liang, C.; Shirazian, S.; Zhou, Y.; Miller, T.; Cui, J.; Fukuda, J.Y.; Chu, J.Y.; Nematalla, A.; Wang, X.; et al. Discovery of 5-[5-fluoro-2-oxo-1,2- dihydroindol-(3Z)-ylidenemethyl]-2,4- dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylic acid (2-diethylaminoethyl)amide, a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial and platelet-derived growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 1116–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietras, K.; Rubin, K.; Sjoblom, T.; Buchdunger, E.; Sjoquist, M.; Heldin, C.H.; Ostman, A. Inhibition of PDGF receptor signaling in tumor stroma enhances antitumor effect of chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 5476–5484. [Google Scholar]
- Potashman, M.H.; Bready, J.; Coxon, A.; DeMelfi, T.M., Jr.; DiPietro, L.; Doerr, N.; Elbaum, D.; Estrada, J.; Gallant, P.; Germain, J.; et al. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of orally active benzimidazoles and benzoxazoles as vascular endothelial growth factor-2 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 4351–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, P.; Johansson, B.R.; Leveen, P.; Betsholtz, C. Pericyte loss and microaneurysm formation in PDGF-B-deficient mice. Science 1997, 277, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.; Carter, C.; Lynch, M.; Lowinger, T.; Dumas, J.; Smith, R.A.; Schwartz, B.; Simantov, R.; Kelley, S. Discovery and development of sorafenib: A multikinase inhibitor for treating cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2006, 5, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spano, J.P.; Chodkiewicz, C.; Maurel, J.; Wong, R.; Wasan, H.; Barone, C.; Letourneau, R.; Bajetta, E.; Pithavala, Y.; Bycott, P.; et al. Efficacy of gemcitabine plus axitinib compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: An open-label randomised phase II study. Lancet 2008, 371, 2101–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Herbst, R.S.; Burris, H.; Cleverly, A.; Musib, L.; Lahn, M.; Bepler, G. Enzastaurin, an oral serine/threonine kinase inhibitor, as second- or third-line therapy of non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetri, G.D.; van Oosterom, A.T.; Garrett, C.R.; Blackstein, M.E.; Shah, M.H.; Verweij, J.; McArthur, G.; Judson, I.R.; Heinrich, M.C.; Morgan, J.A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sunitinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumour after failure of imatinib: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2006, 368, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deremer, D.L.; Ustun, C.; Natarajan, K. Nilotinib: A second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Clin. Ther. 2008, 30, 1956–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, P.J.; Goodin, S. Lapatinib: A dual inhibitor of human epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Clin. Ther. 2008, 30, 1426–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.X.; Zheng, R.L.; Zhou, T.; He, H.Y.; Liu, J.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Tong, A.P.; Xiang, M.L.; Song, X.R.; Yang, S.Y.; et al. Novel thienopyridine derivatives as specific anti-hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) agents: Synthesis, preliminary structure-activity relationships, and in vitro biological evaluation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 6282–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Fu, A.F.; Chen, L.J.; Xie, X.J.; Yang, G.L.; Chen, X.C.; Wang, Y.S.; Li, J.; Chen, P.; Tang, M.H.; et al. Liposomal honokiol inhibits VEGF-D-induced lymphangiogenesis and metastasis in xenograft tumor model. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 2709–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L.; Hu, J.; Peng, C.; Xie, D.; Shi, J.; Huang, W.; Xu, G.; Peng, M.; et al. Semi-synthesis and anti-proliferative activity evaluation of novel analogues of Honokiol. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 4702–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Yang, S.; Yang, L. 4-(4-aminoanilino)-2-(methylcarbamoyl) Pyridine and Its Derivatives, and Their Preparation Method and Application. CN 101362717A, 2 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Yang, S.; Yang, L. 4-(4-benzoylaminophenoxy)-2-(methylcarbamoyl) Pyridine and Its Derivatives, and Their Preparation Method and Application. CN 101362718A, 2 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Anchoori, R.K.; Kortenhorst, M.S.; Hidalgo, M.; Sarkar, T.; Hallur, G.; Bai, R.; Diest, P.J.; Hamel, E.; Khan, S.R. Novel microtubule-interacting phenoxy pyridine and phenyl sulfanyl pyridine analogues for cancer therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 5953–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, L.; Reinhold, G.; Oliver, K.; Mike, M.; Klaus, M.; Matthias, M.G.; Jurjen, S.; Mathias, B.; Jana, L.; Wernner, H. Procede de Preparation de 4-{4-[({[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino}carbonyl)amino]phenoxy}-n-methylpyridine-2-carboxa-mide. PCT Int. Appl. WO 2006034796 A1, 6 April 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bankston, D.; Dumas, J.; Natero, R.; Riedl, B.; Monahan, M.K.; Sibley, R. A scaleable synthesis of BAY 43-9006: A potent Raf kinase inhibitor for the treatment of cancer. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2002, 6, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zhen, R.; Lin, H.; Luo, S.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Mao, Y.; et al. SKLB610: A Novel Potential Inhibitor of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Inhibits Angiogenesis and Tumor Growth in Vivo. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 27, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
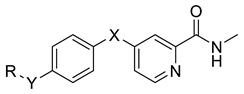
| Compound | X | Y | R | IC50(μM) 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HepG2 | HCT116 | ||||
| 5a | NH | NHCONH | Ph- | 48.4 ± 2.5 | 28.2 ± 1.6 |
| 5b | NH | NHCONH | 3-CF3-Ph- | 16.8 ± 2.0 | 14.9 ± 1.1 |
| 5c | NH | NHCONH | 3-F-Ph- | 40.0 ± 3.1 | 18.1 ± 1.0 |
| 5d | NH | NHCONH | 3-Cl-Ph- | 22.4 ± 1.4 | 21.0 ± 1.1 |
| 5e | NH | NHCONH | 3-Br-Ph- | 18.0 ± 1.2 | 17.2 ± 1.2 |
| 5f | NH | NHCONH | 3-NO2-Ph- | 24.1 ± 1.3 | 27.6 ± 1.6 |
| 5g | NH | NHCONH | 3-MeO-Ph- | 27.6 ± 1.7 | 17.1 ± 0.8 |
| 5h | NH | NHCONH | 4-Cl-3-CF3-Ph- | 25.2 ± 1.3 | 29.2 ± 1.3 |
| 5i | NH | NHCONH | cyclohexane- | 17.3 ± 1.0 | 12.1 ± 0.7 |
| 5j | NH | CONH | 3-CF3-Ph- | 16.8 ± 1.1 | 31.5 ± 1.9 |
| 5k | NH | CONH | 3-F-Ph- | 60.2 ± 3.4 | 17.9 ± 1.2 |
| 5l | NH | CONH | 3-Cl-Ph- | 94.4 ± 3.9 | 25.6 ± 1.4 |
| 5m | NH | CONH | 3-NO2-Ph- | >100 | >100 |
| 5n | NH | CONH | 3-MeO-Ph- | 32.2 ± 2.0 | 29.2 ± 1.9 |
| 5o | O | CONH | Ph- | 55.1 ± 3.2 | 61.6 ± 3.1 |
| 5p | O | CONH | 2-CF3-Ph- | >100 | 98.0 ± 4.2 |
| 5q | O | CONH | 3-CF3-Ph- | 6.6 ± 0.3 | 5.3 ± 0.3 |
| 5r | O | CONH | 4-CF3-Ph- | 51.4 ± 2.8 | 48.8 ± 3.2 |
| 5s | O | CONH | 3-F-Ph- | >100 | 56.2 ± 3.8 |
| 5t | O | CONH | 3-Cl-Ph- | 68.2 ± 31 | 30.6 ± 2.8 |
| 5u | O | CONH | 3-NO2-Ph- | >100 | >100 |
| 5v | O | CONH | cyclohexane- | >100 | 55.8 ± 4.1 |
| Sorafenib 2 | 15.3 ± 0.8 | 13.1 ± 0.7 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, N.; Zhou, S.; Hu, M.; Xu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zeng, X.; Yu, L. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel 4-(4-Formamidophenylamino)-N-methylpicolinamide Derivatives as Potential Antitumor Agents. Molecules 2021, 26, 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26041150
Meng N, Zhou S, Hu M, Xu Y, Xia Y, Zeng X, Yu L. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel 4-(4-Formamidophenylamino)-N-methylpicolinamide Derivatives as Potential Antitumor Agents. Molecules. 2021; 26(4):1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26041150
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Nana, Shuyan Zhou, Min Hu, Youzhi Xu, Yong Xia, Xiuxiu Zeng, and Luoting Yu. 2021. "Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel 4-(4-Formamidophenylamino)-N-methylpicolinamide Derivatives as Potential Antitumor Agents" Molecules 26, no. 4: 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26041150
APA StyleMeng, N., Zhou, S., Hu, M., Xu, Y., Xia, Y., Zeng, X., & Yu, L. (2021). Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel 4-(4-Formamidophenylamino)-N-methylpicolinamide Derivatives as Potential Antitumor Agents. Molecules, 26(4), 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26041150





