Identification of Key Candidate Genes Involved in the Progression of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
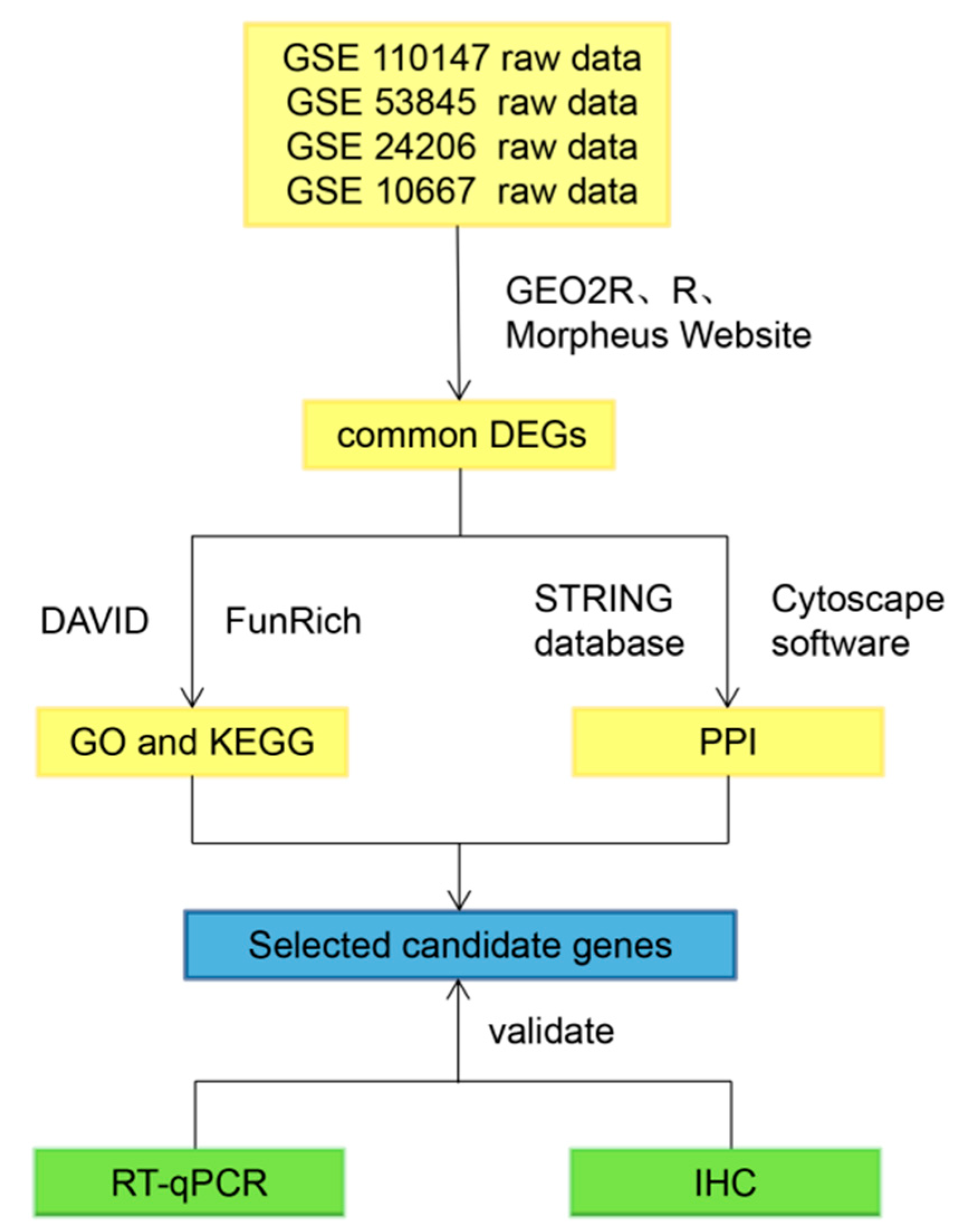
2.1. Identification of the Common DEGs
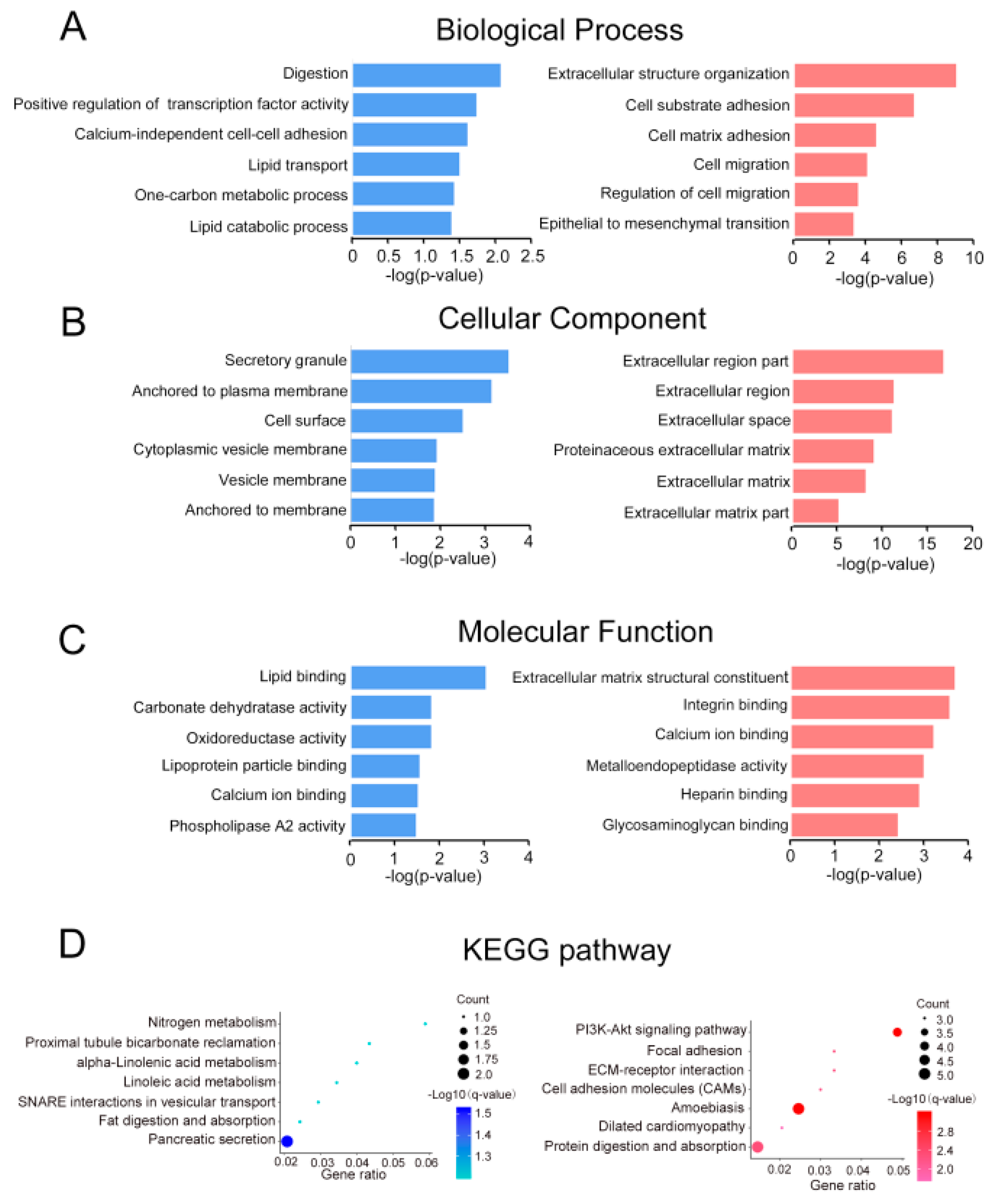
2.2. Gene Ontology and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
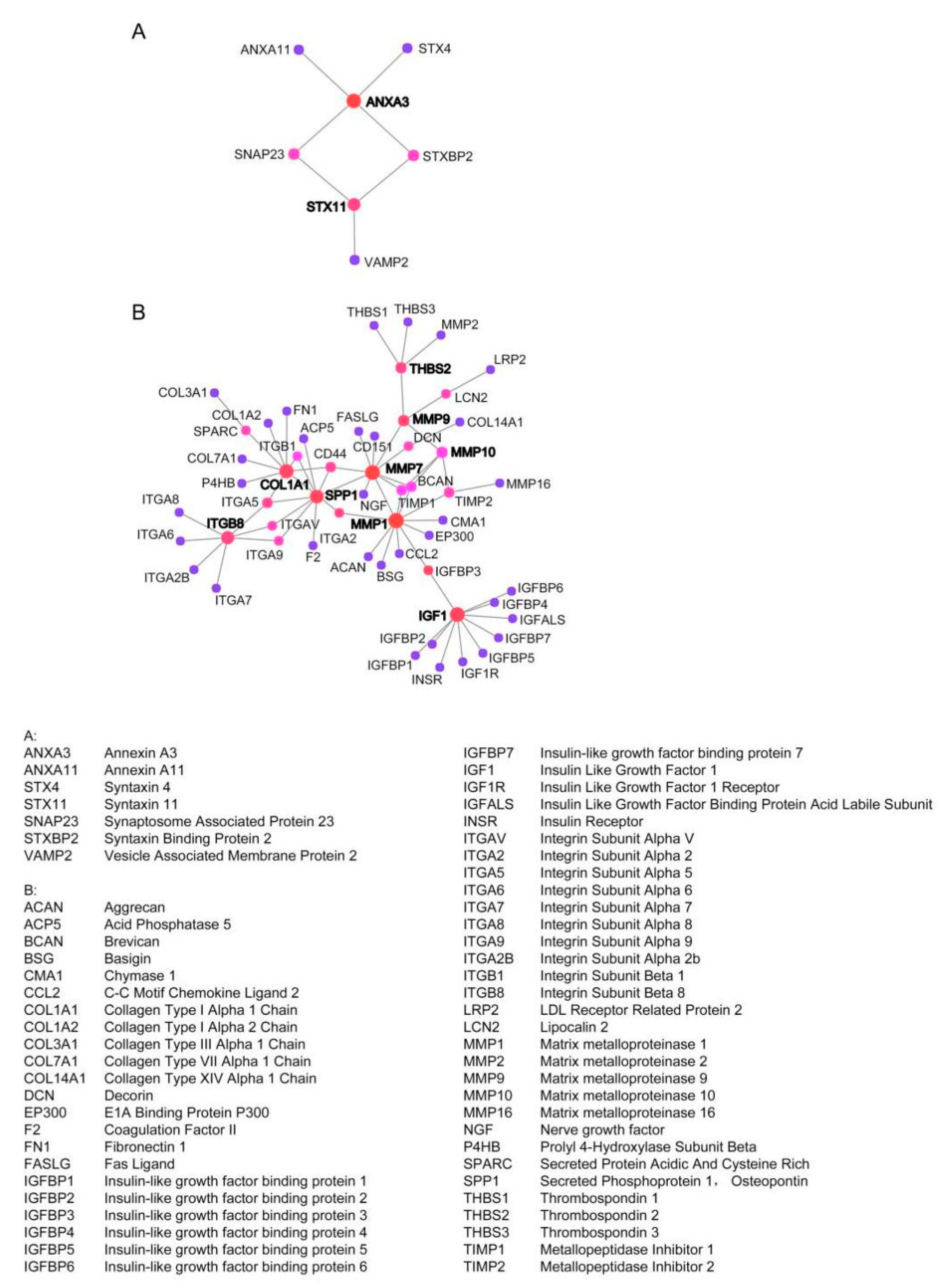
2.3. Establish Protein–Protein International (PPI) Network of the Common DEGs
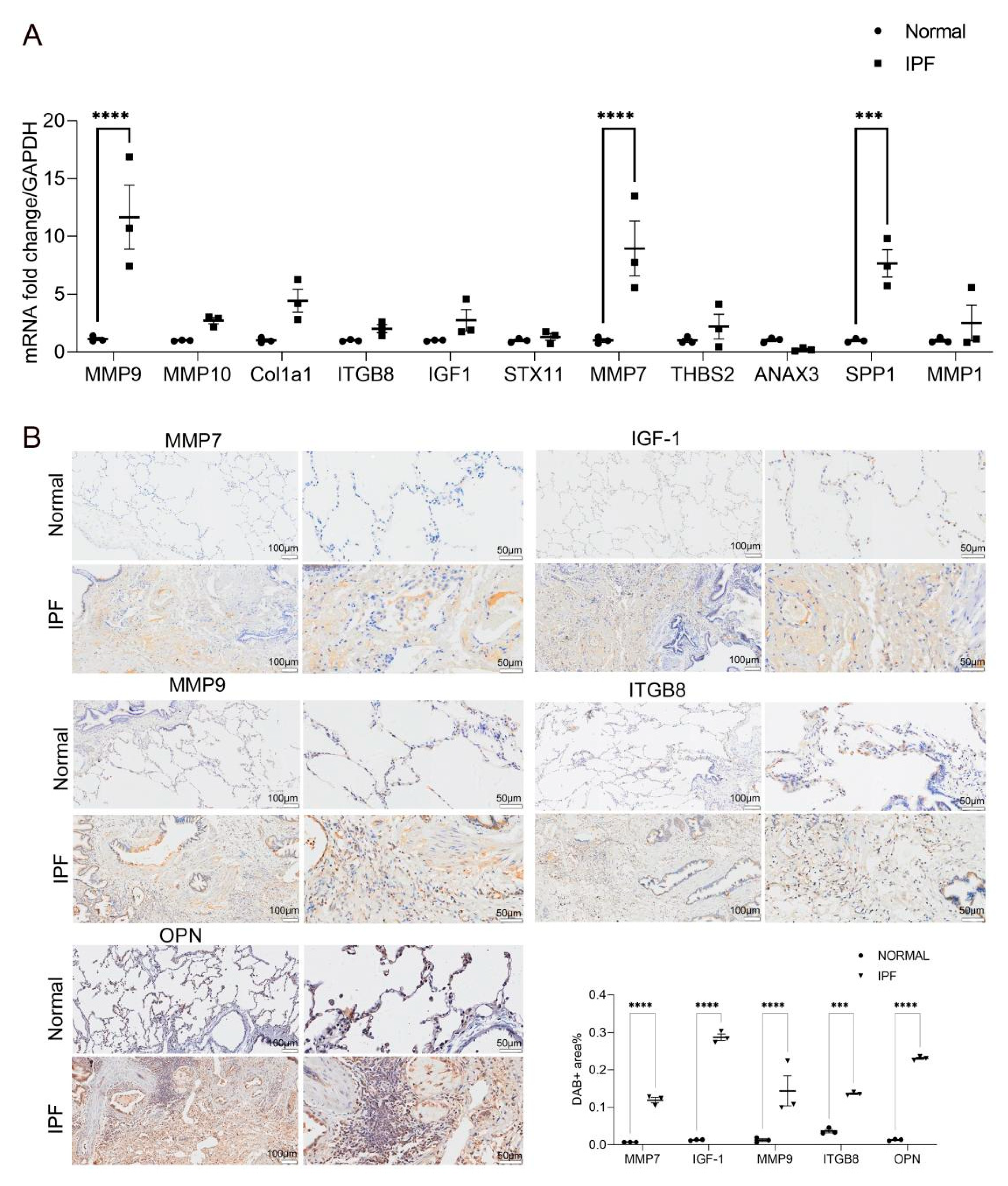
2.4. Validation of the 11 Key DEGs
3. Discussion
3.1. MMP
3.1.1. MMP7
3.1.2. MMP9
3.2. IGF1
3.3. Integrin
3.4. OPN
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Collection and Analysis
4.2. Gene Ontology and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
4.3. Identification of Protein–Protein Interaction Network (PPI)
4.4. Clinical Sample Collection
4.5. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
4.6. Immunohistochemical Staining
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| IPF | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| PF | Pulmonary fibrosis |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| STRING | Search tool for the retrieval of interacting genes |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| IGF | Insulin-like growth factor |
| IGF1R | Insulin Like Growth Factor 1 Receptor |
| OPN | Osteopontin |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-β |
| ANXA3 | Annexin A3 |
| STX11 | Syntaxin 11 |
| THBS2 | Thrombospondin 2 |
| SPP1 | Secreted Phosphoprotein 1 |
| COL1A1 | Collagen Type I Alpha 1 Chain |
| LTBP1 | Latent TGF-β binding protein-1 |
| LAP | Latency-related peptide (LAP) |
| RGD | Arginine−glycine−aspartic acid |
| BLM | Bleomycin |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| PPI | protein–protein interaction network |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| GO | Gene ontology |
| GEO | Gene Expression Omnibus |
| BALF | broncho-alveolar lavage fluid |
| DAVID | The Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery |
| GAPDH | glyseraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| PCNA | proliferating cell nuclear antigen |
References
- King, T.; Pardo, A.; Selman, M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2011, 378, 1949–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishaba, T. Evaluation and management of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respir. Investig. 2019, 57, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, V.J.; Zhang, L.; Hagood, J.S. Matrix metalloproteinases as therapeutic targets for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 53, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, G. The complex biology of the receptor for the insulin-like growth factor-1. Drug News Perspect. 2003, 16, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Dong, X.; Zhao, B. Atypical interactions of integrin alphaV beta8 with pro-TGF-beta1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E4168–E4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, J.S.; Serlin, D.; Li, X.; Whitley, G.; Hayes, J.; Rishikof, D.C.; Ricupero, D.A.; Liaw, L.; Goetschkes, M.; O’Regan, A.W. Altered bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in osteopontin-deficient mice. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2004, 286, L1311–L1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barratt, S.L.; Creamer, A.; Hayton, C.; Chaudhuri, N. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF): An Overview. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeown, S.; Richter, A.G.; O’Kane, C.; McAuley, D.F.; Thickett, D.R. MMP expression and abnormal lung permeability are important determinants of outcome in IPF. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 33, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalanobish, S.; Saha, S.; Dutta, S.; Sil, P.C. Matrix metalloproteinase: An upcoming therapeutic approach for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 152, 104591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, K.J.; Reikvam, H.; Bruserud, O. The crosstalk between the matrix metalloprotease system and the chemokine network in acute myeloid leukemia. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 4448–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-De-Alba, C.; Becerril, C.; Ruiz, V.; González, Y.; Reyes, S.; García-Alvarez, J.; Selman, M.; Pardo, A. Expression of Matrix Metalloproteases by Fibrocytes: Possible role in migration and homing. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 1144–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dancer, R.C.A.; Wood, A.M.; Thickett, D.R. Metalloproteinases in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmasheva, R.T.; Houghton, P.J. IGF-I mediated survival pathways in normal and malignant cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg. 2006, 1766, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, J.H.; Larsen, L.; Dasgupta, B.; Brodmerkel, C.; Curran, M.; Karsdal, M.; Sand, J.; Willumsen, N.; Knox, A.; Bolton, C.; et al. Levels of circulating MMP-7 degraded elastin are elevated in pulmonary disorders. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Park, P.W.; Wilson, C.L.; Parks, W.C. Matrilysin Shedding of Syndecan-1 Regulates Chemokine Mobilization and Transepithelial Efflux of Neutrophils in Acute Lung Injury. Cell 2002, 111, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.; McMahon, K.; Mackarel, A.; Prikk, K.; Sorsa, T.; Maisi, P.; Sepper, R.; Fitzgerald, M.; O’Connor, C. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in sarcoidosis and IPF. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 20, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Stamenkovic, I. Cell surface-localized matrix metalloproteinase-9 proteolytically activates TGF-beta and promotes tumor invasion and angiogenesis. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pardo, A.; Selman, M.; Kaminski, N. Approaching the degradome in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis☆. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 1141–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroith, D.; Roberts, C.T. The insulin-like growth factor system and cancer. Cancer Lett. 2003, 195, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.I.; Clemmons, D.R. Insulin-Like Growth Factors and Their Binding Proteins: Biological Actions. Endocr. Rev. 1995, 16, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, R.H.; Poliks, C.F.; Pilch, P.; Smith, B.D.; Fine, A. Stimulation of Collagen Formation by Insulin and Insulin-Like Growth Factor I in Cultures of Human Lung Fibroblasts. Endocrinology 1989, 124, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rom, W.N.; Basset, P.; A Fells, G.; Nukiwa, T.; Trapnell, B.C.; Crysal, R.G. Alveolar macrophages release an insulin-like growth factor I-type molecule. J. Clin. Investig. 1988, 82, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, A.; Hiyama, K.; Yamakido, H.; Ishioka, S.; Yamakido, M. Increased Expression of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor A and Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I in BAL Cells During the Development of Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice. Chest 1996, 109, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krein, P.M.; Sabatini, P.J.B.; Tinmouth, W.; Green, F.H.Y.; Winston, B.W. Localization of Insulin-like Growth Factor-I in Lung Tissues of Patients with Fibroproliferative Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-E.; Lee, S.-S.; Sunde, D.A.; Huizar, I.; Haugk, K.L.; Thannickal, V.J.; Vittal, R.; Plymate, S.R.; Schnapp, L.M. Insulin-like Growth Factor-I Receptor Blockade Improves Outcome in Mouse Model of Lung Injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtrum, D.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, D.; Anderson, D.M.; Prewett, M.; Pereira, D.S.; Bassi, R.; Abdullah, R.; Hooper, A.T.; Koo, H.; et al. A fully human monoclonal antibody to the insulin-like growth factor I receptor blocks ligand-dependent signaling and inhibits human tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8912–8921. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anderson, N.A.; Campos, S.; Butler, S.; Copley, R.C.B.; Duncan, I.; Harrison, S.; Le, J.; Maghames, R.; Pastor-Garcia, A.; Pritchard, J.M.; et al. Discovery of an Orally Bioavailable Pan αv Integrin Inhibitor for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 8796–8808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatler, A.L.; Jenkins, G. TGF-β activation and lung fibrosis. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2012, 9, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Zhu, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, X.; Mi, L.; Walz, T.; Springer, T.A. Latent TGF-β structure and activation. Nature 2011, 474, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, D.; Cambier, S.; Fjellbirkeland, L.; Baron, J.L.; Munger, J.S.; Kawakatsu, H.; Sheppard, D.; Broaddus, V.C.; Nishimura, S.L. The integrin αvβ8 mediates epithelial homeostasis through MT1-MMP–dependent activation of TGF-β1. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 157, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minagawa, S.; Lou, J.; Seed, R.I.; Cormier, A.; Wu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Murray, L.; Tsui, P.; Connor, J.; Herbst, R.; et al. Selective Targeting of TGF-β Activation to Treat Fibroinflammatory Airway Disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 241ra79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denhardt, D.T.; Guo, X. Osteopontin: A protein with diverse functions. FASEB J. 1993, 7, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinholt, F.P.; Hultenby, K.; Oldberg, A.; Heinegard, D. Osteopontin—A possible anchor of osteoclasts to bone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 4473–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, G.F.; Ashkar, S.; Glimcher, M.J.; Cantor, H. Receptor-ligand interaction between CD44 and osteopontin (Eta-1). Science 1996, 271, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denhardt, D.T.; Noda, M.; O’Regan, A.W.; Pavlin, D.; Berman, J.S. Osteopontin as a means to cope with environmental insults: Regulation of inflammation, tissue remodeling, and cell survival. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Regan, A.; Berman, J.S. Osteopontin: A key cytokine in cell-mediated and granulomatous inflammation. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2001, 81, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo, A.; Gibson, K.; Cisneros, J.; Richards, T.J.; Yang, Y.; Becerril, C.; Yousem, S.; Herrera, I.; Ruiz, V.; Selman, M.; et al. Up-Regulation and Profibrotic Role of Osteopontin in Human Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, M.; Ruiz, V.; Cabrera, S.; Segura, L.; Ramírez, R.; Barrios, R.; Pardo, A. TIMP-1, -2, -3, and -4 in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. A prevailing nondegradative lung microenvironment? Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2000, 279, L562–L574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brabletz, T.; Jung, A.; Dag, S.; Hlubek, F.; Kirchner, T. β-Catenin Regulates the Expression of the Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 in Human Colorectal Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tanani, M.; Platt-Higgins, A.; Rudland, P.S.; Campbell, F.C. Ets Gene PEA3 Cooperates with β-Catenin-Lef-1 and c-Jun in Regulation of Osteopontin Transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 20794–20806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilosi, M.; Poletti, V.; Zamò, A.; Lestani, M.; Montagna, L.; Piccoli, P.; Pedron, S.; Bertaso, M.; Scarpa, A.; Murer, B.; et al. Aberrant Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Activation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, F.; Takahashi, K.; Okazaki, T.; Maeda, K.; Ienaga, H.; Maeda, M.; Kon, S.; Uede, T.; Fukuchi, Y. Role of Osteopontin in the Pathogenesis of Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2001, 24, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, R.H.; Fine, A. Fibrotic Reactions in the Lung: The Activation of the Lung Fibroblast. Exp. Lung Res. 1986, 11, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Mo, L.; Feng, X.; Huang, M.; Li, L. Using bioinformatics approach identifies key genes and pathways in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Medicine 2020, 99, e22099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Ma, T.; Cao, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Xiang, Z.; Han, X. TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation promotes myofibroblast differentiation of LR-MSCs and exacerbates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 2409–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
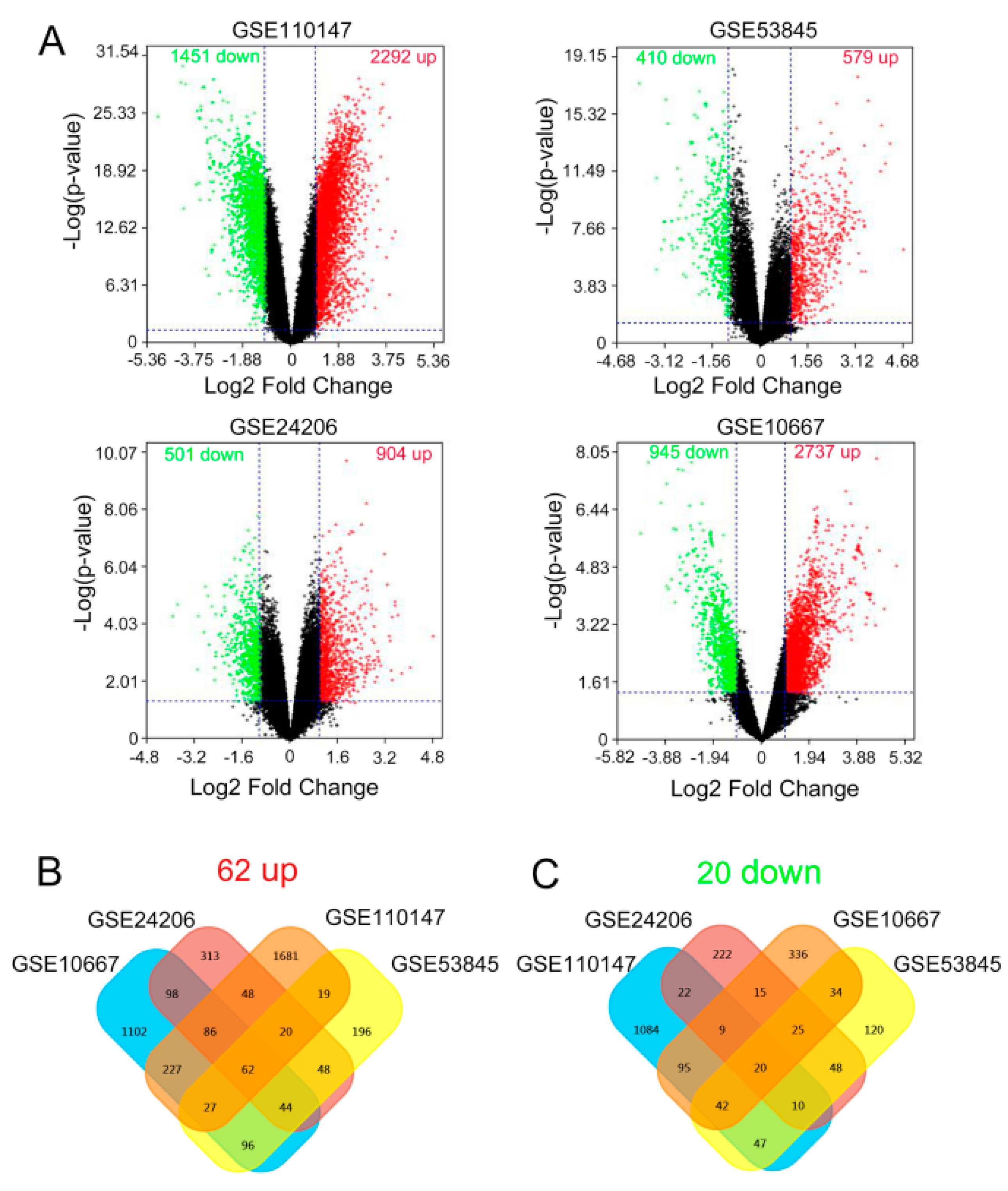
| Accession | Year | Area | Platform | Number of Samples | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | IPF | ||||
| GSE10667 | 2008 | USA | GPL4133 | 15 | 8 |
| GSE24206 | 2010 | USA | GPL570 | 6 | 17 |
| GSE110147 | 2018 | Canada | GPL6244 | 11 | 22 |
| GSE53845 | 2014 | USA | GPL6480 | 8 | 40 |
| Primer | |
|---|---|
| Homo mmp1R | GTTGTCCCGATGATCTCCCC |
| Homo mmp7 F | GTCTCTGGACGGCAGCTATG |
| Homo mmp7 R | GATAGTCCTGAGCCTGTTCCC |
| Homo anxa3 F | CCTTCGCTCGCAGTTTGTTC |
| Homo anxa3 R | TCGGTGTCCAACCCAGATAGA |
| Homo stx11 F | TGAATCGGGTCATGGAAGGTT |
| Homo stx11 R | CTTGAGGCTGCTCCATGTCT |
| Homo thbs2 F | TTGGCAAACCAGGAGCTCAG |
| Homo thbs2 R | GGTCTTGCGGTTGATGTTGC |
| Homo mmp9 F | CTTTGAGTCCGGTGGACGAT |
| Homo mmp9 R | TCGCCAGTACTTCCCATCCT |
| Homo mmp10 F | GACAGAAGATGCATCAGGCAC |
| Homo mmp10 R | GGCGAGCTCTGTGAATGAGT |
| Homo col1a1 F | GGACACAGAGGTTTCAGTGGT |
| Homo col1a1 R | GCACCATCATTTCCACGAGC |
| Homo itgb8 F | AAAGTGCTGAGTAGAGGGCG |
| Homo itgb8 R | TATTGTCTTCTGGCCGGGATG |
| Homo igf1 F | TGCTCTCAACATCTCCCATCTC |
| Homo igf1 R | CATGGTGTGCATCTTCACCTTC |
| Homo Spp1 F | GCAGCTTTACAACAAATACCCAGAT |
| Homo Spp1 R | TGGACTTACTTGGAAGGGTCTGTG |
| Antibody | Company | Catalog | Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-MMP-7 | Proteintech | 10374-2-AP | 1:100 |
| Anti-MMP-9 | Proteintech | 10375-2-AP | 1:100 |
| Anti-SPP1 | Proteintech | 11952-1-AP | 1:100 |
| Anti-IGF-1 Anti-ITGB8 | Santa Cruz Santa Cruz | sc-74116 sc-514150 | 1:50 1:50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, Y.; Ji, J.; Hou, J.; Tan, Y.; Han, X. Identification of Key Candidate Genes Involved in the Progression of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Molecules 2021, 26, 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26041123
Cui Y, Ji J, Hou J, Tan Y, Han X. Identification of Key Candidate Genes Involved in the Progression of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Molecules. 2021; 26(4):1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26041123
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Yu, Jie Ji, Jiwei Hou, Yi Tan, and Xiaodong Han. 2021. "Identification of Key Candidate Genes Involved in the Progression of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis" Molecules 26, no. 4: 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26041123
APA StyleCui, Y., Ji, J., Hou, J., Tan, Y., & Han, X. (2021). Identification of Key Candidate Genes Involved in the Progression of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Molecules, 26(4), 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26041123






