Studying and Modeling of the Extraction Properties of the Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent and Sorbitol-Based Solvents in Regard to Biologically Active Substances from Glycyrrhizae Roots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Solvents
3.2. Methods of Analysis
3.2.1. Reverse Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography Method (RP HPLC)
3.2.2. A Method for Obtaining NADES and Sorbitol-Based Solvents
3.2.3. A method for Extract Preparation
3.2.4. A Method for Thermal Analysis
3.2.5. A Method for Dielectric Constant Analysis
3.3. Theory
- n, n0 are quantity of BAS molecules in the liquid phase and in the extraction system in general, moles;
- C is BAS concentration in the solvent, g/mL;
- V is solvent volume, mL;
- m0 is BAS mass in the extraction system, g;
- Δμ is the change of BAS molecules’ chemical potential at the transition from plant raw material to the solvent, J/mole;
- R is gas constant, 8.314 J/(K·mol);
- T is absolute temperature, K;
- a is constant.
- b, d, f are empirical constants;
- ε is a dielectric constant of the solvent.
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marcus, Y. Deep Eutectic Solvents; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nagarajan, J.; Heng, W.W.; Galanakis, C.M.; Ramanan, R.N.; Raghunandan, M.E.; Sun, J.; Ismail, A.; Beng-Ti, T.; Prasad, K.N. Extraction of phytochemicals using hydrotropic solvents. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1151–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillot, B.; Teychené, S.; Biscans, B. An evaluation of thermodynamic models for the prediction of drug and drug-like molecule solubility in organic solvents. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2011, 309, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.R.A.; Yunus, N.A.; Mustaffa, A.A. Selection of optimum ionic liquid solvents for flavonoid and phenolic acids extraction. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Miri, Malaysia, 1–3 December 2016; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadid, A.; Mokrushina, L.; Minceva, M. Modeling of solid–liquid equilibria in deep eutectic solvents: A parameter study. Molecules 2019, 24, 2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Row, K. Recent developments in deep eutectic solvents in chemical sciences. Mon. Chem. 2013, 144, 1427–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiemenz, P.C.; Rajagopalan, R. Principles of Colloid and Surface Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Boyko, N.N.; Makarevich, N.A.; Pisarev, D.I.; Zhilyakova, E.T. Simplified mathematical modeling of the distribution process of licuroside and glycyram between the extractant and Glycyrrhizae radices. Res. Result. Med. Pharm. 2018, 4, 75–80. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, N.N.; Pisarev, D.I.; Zhilyakova, E.T.; Novikov, O.O. The study of rutin and chlorogenic acid distribution process in the extraction system from the flowers of Calendula officinalis and the extractant. Vestn. Farm. 2018, 81, 52–58. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Boyko, N.; Pisarev, D.; Zhilyakova, E.; Pravlotskaya, A.; Novikov, O.; Makarevich, N.; Kuznietsova, V.; Sushchuk, N. Study and modeling of the distribution process of some phenolic compounds between the solid and liquid phases. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2019, 10, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, N.N.; Pisarev, D.I.; Zhilyakova, E.T.; Malyutina, A.Y.; Novikov, O.O.; Osolodchenko, T.P.; Ghazaryan, M.S. Studies relating to the development of a galenical drug with antimicrobial activity from clove buds. Probl. Biol. Med Pharm. Chem. 2019, 22, 47–52. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, N.N.; Zhilyakova, E.T.; Pisarev, D.I.; Malyutina, A.Y.; Novikov, O.O.; Osolodchenko, T.P. Comprehensive studies for development of galenicals with antimicrobial activity from Hypericum perforatum L. herb. Russ. J. Biopharm. 2019, 11, 89–96. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Boyko, N.N.; Zhilyakova, E.T.; Malyutina, A.Y.; Naplekov, D.K.; Shestopalova, N.N.; Martceva, D.S.; Novikov, O.O.; Pisarev, D.I.; Mizina, P.G. Study of distribution of biologically active substances from flowers of Helichrysum arenarium between phases of the extraction system. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 7, 271–278. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, N.N.; Pisarev, D.I.; Zhilyakova, E.T.; Novikov, O.O. Study and modeling of solvent influence on isosalipurposide extraction from Helichrysi arenarii flowers. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 6, 340–350. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, N.N.; Pisarev, D.I.; Zhilyakova, E.T.; Novikov, O.O.; Tsvetkova, Z.E.; Kuznietsova, V.Y.; Sushchuk, N.A. The role of solvent dielectric constant in modeling of the extraction process of phenolic compounds from Silybum marianum L. fruits. J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 12, 440–445. [Google Scholar]
- Boyko, N.; Pisarev, D.; Zhilyakova, E.; Novikov, O.; Kuznietsova, V.; Sushchuk, N. Modeling of solvent effects on phytocompounds’ extraction from Glycyrrhizae radix. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2018, 9, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlfarth, C. Static Dielectric Constants of Pure Liquids and Binary Liquid Mixtures; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sorby, D.L.; Liu, G.; Horowitz, K.N. Dielectric constants of complex pharmaceutical solvent systems II. Water-ethanol-sucrose and water-ethanol-sorbitol. J. Pharm. Sci. 1965, 54, 1811–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, H. Effective extraction of flavonoids from Lycium barbarum L. fruits by deep eutectic solvents-based ultrasound-assisted extraction. Talanta 2019, 203, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Wang, M.; Guo, H.; Xu, J.; Ye, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, L. Ultrasound-assisted deep eutectic solvent as green and efficient media for the extraction of flavonoids from Radix scutellariae. New J. Chem 2019, 43, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.-M.; Wang, L.-J.; Gao, Z.; Zhuang, B.; Yin, Q.; Liu, E.-H. Green and efficient extraction of different types of bioactive alkaloids using deep eutectic solvents. Microchem. J. 2019, 145, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Rozema, E.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Application of natural deep eutectic solvents to the extraction of anthocyanins from Catharanthus roseus with high extractability and stability replacing conventional organic solvents. J. Chromatogr. A. 2016, 1434, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, C.G.; Mustafa, N.R.; Wilson, E.G.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Application of natural deep eutectic solvents for the “green” extraction of vanillin from vanilla pods. Flavour Fragr. J. 2017, 33, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, B.D.; Coelho, M.A.Z.; Marrucho, I.M. Extraction of saponins from sisal (Agave sisalana) and juá (Ziziphusjoazeiro) with cholinium-based ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2013, 237, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espino, M.; Fernández, M.; Gomez, F.; Silva, M. Natural designer solvents for greening analytical chemistry. Trac Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 76, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reregister of Medicines of Russia. Available online: https://www.rlsnet.ru/tn_index_id_5789.htm (accessed on 23 December 2019). (In Russian).
- Electronic Medicines Compendium UK. Natures aid Herbal Mucus Cough Syrup. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/7984/smpc#companyDetails (accessed on 23 December 2019).
- Gómez, A.V.; Biswas, A.; Tadini, C.C.; Furtado, R.F.; Alves, C.R.; Cheng, H.N. Use of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for Polymerization and Polymer Reactions. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2019, 30, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; van Spronsen, J.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural deep eutectic solvents as new potential media for green technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 766, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraz, V.R.; Pegashkin, V.F. Using the MS Excel for the Statistical Analysis of Data; NTI (filial) UrFU: Nizhny Tagil, Russia, 2014. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zhilyakova, E.T.; Novikov, O.O.; Pisarev, D.I.; Malyutina, A.Y.; Boyko, N.N. Studying the polyphenolic structure of Laurus Nobilis L. leaves. Indoam J. Pharmsci. 2017, 4, 3066–3074. [Google Scholar]
- State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation, XIVth ed.; Ministry of Healthcare of Russian Federation: Moscow, Russia, 2018; Volume I. (In Russian)
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
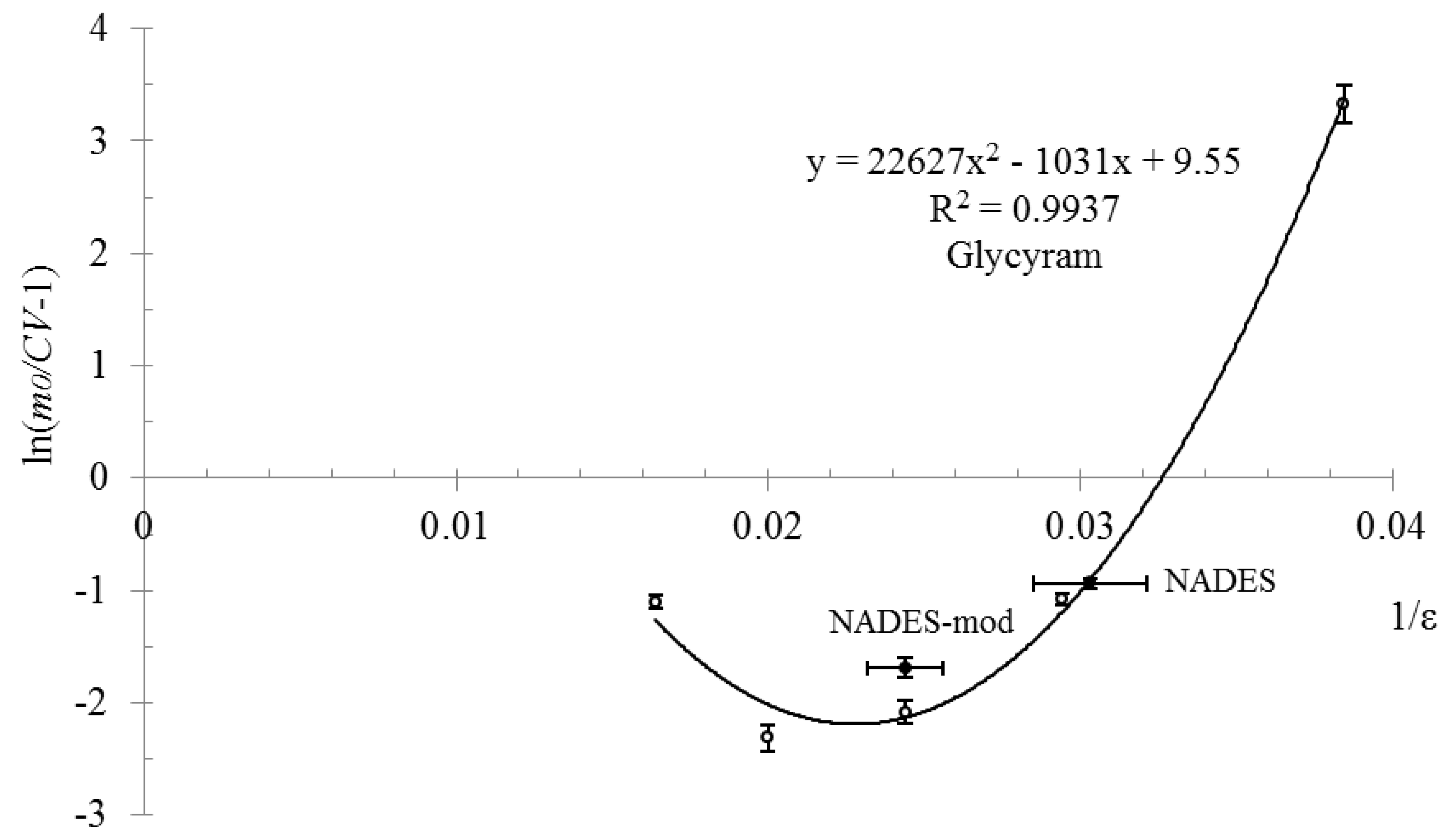
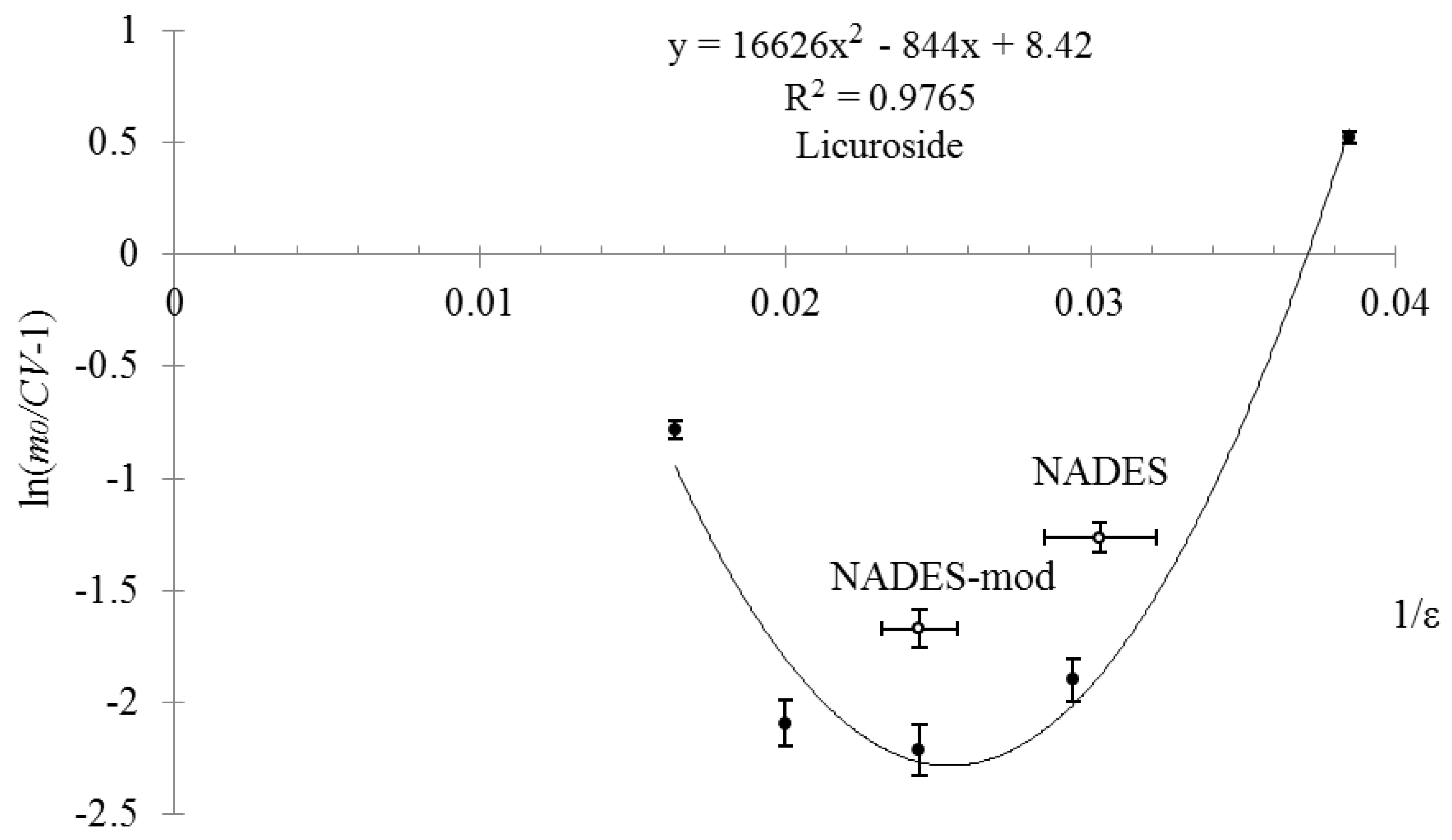
| Compound | Mole Ratio | Tm, °C | Tg, °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Sorbitol | - | 97.3 ± 0.5 | - |
| 2. Malic acid | - | 130.1 ± 0.5 | - |
| 3. Sorbitol-based NADES (sorbitol:malic acid:water) | 1:1:3 | - | −55.9 ± 1.5 |
| Parameter | Pharmacopoeia Limit [32] | Licuroside * | Glycyram * |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Retention time, min | - | 24.2 ± 0.2 | 37.3 ± 0.3 and 37.9 ± 0.3 |
| 2. Asymmetry parameter | 0.8–1.5 | 0.82 | 0.84 |
| 3. Resolution between the peaks | ≥1.5 | 2.5 | 1.7 and 1.5 |
| 4. Relative standard deviation, RSD, % | ≤2.0 | 1.6 | 1.9 and 1.9 |
| 5. LOD, g/mL | - | 2.0·10−5 | 8.9·10−5 |
| 6. LOQ, g/mL | - | 6.1·10−5 | 2.7·10−4 |
| 7. Determination coefficient, r2 | ≥0.98 | 0.9999 | 0.9997 |
| 8. Linear regression equation, C(g/mL) = f(S(mAU·s)) | - | C = (3.36 ± 0.04)·10−7·S | C = (1.77 ± 0.06)·10−6·S |
| No. | Content, % wt. * | Density, g/mL * | Dielectric Constant (ε) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sorbitol | Ethanol | Water | Malic Acid | Glycerin | |||
| 1 | 2.00 ± 0.01 | 91.0 ± 0.5 | 7.00 ± 0.04 | 0 | 0 | 0.815 ± 0.006 | 26 |
| 2 | 14.0 ± 0.1 | 66.0 ± 0.3 | 20.0 ± 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0.900 ± 0.006 | 34 |
| 3 | 34.0 ± 0.2 | 42.0 ± 0.2 | 24.0 ± 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 1.018 ± 0.006 | 41 |
| 4 | 51.0 ± 0.3 | 22.0 ± 0.1 | 27.0 ± 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 1.130 ± 0.006 | 50 |
| 5 | 72.0 ± 0.4 | 0 | 28.0 ± 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 1.298 ± 0.006 | 61 |
| 6 ** | 49.0 ± 0.3 | 0 | 15.0 ± 0.1 | 36.0 ± 0.2 | 0 | 1.404 ± 0.006 | 33 ± 2 *** |
| 7 ** | 42.7 ± 0.3 | 0 | 4.20 ± 0.03 | 31.5 ± 0.2 | 21.6 ± 0.1 | 1.381 ± 0.006 | 41 ± 2 *** |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boyko, N.; Zhilyakova, E.; Malyutina, A.; Novikov, O.; Pisarev, D.; Abramovich, R.; Potanina, O.; Lazar, S.; Mizina, P.; Sahaidak-Nikitiuk, R. Studying and Modeling of the Extraction Properties of the Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent and Sorbitol-Based Solvents in Regard to Biologically Active Substances from Glycyrrhizae Roots. Molecules 2020, 25, 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071482
Boyko N, Zhilyakova E, Malyutina A, Novikov O, Pisarev D, Abramovich R, Potanina O, Lazar S, Mizina P, Sahaidak-Nikitiuk R. Studying and Modeling of the Extraction Properties of the Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent and Sorbitol-Based Solvents in Regard to Biologically Active Substances from Glycyrrhizae Roots. Molecules. 2020; 25(7):1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071482
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoyko, Nikolay, Elena Zhilyakova, Anastasiya Malyutina, Oleg Novikov, Dmitriy Pisarev, Rimma Abramovich, Olga Potanina, Simon Lazar, Praskovia Mizina, and Rita Sahaidak-Nikitiuk. 2020. "Studying and Modeling of the Extraction Properties of the Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent and Sorbitol-Based Solvents in Regard to Biologically Active Substances from Glycyrrhizae Roots" Molecules 25, no. 7: 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071482
APA StyleBoyko, N., Zhilyakova, E., Malyutina, A., Novikov, O., Pisarev, D., Abramovich, R., Potanina, O., Lazar, S., Mizina, P., & Sahaidak-Nikitiuk, R. (2020). Studying and Modeling of the Extraction Properties of the Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent and Sorbitol-Based Solvents in Regard to Biologically Active Substances from Glycyrrhizae Roots. Molecules, 25(7), 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071482





