Simultaneous Ultrasound and Heat Enhance Functional Properties of Glycosylated Lactoferrin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of Ultrasound Treatments on the Graft Reaction between LF and BP
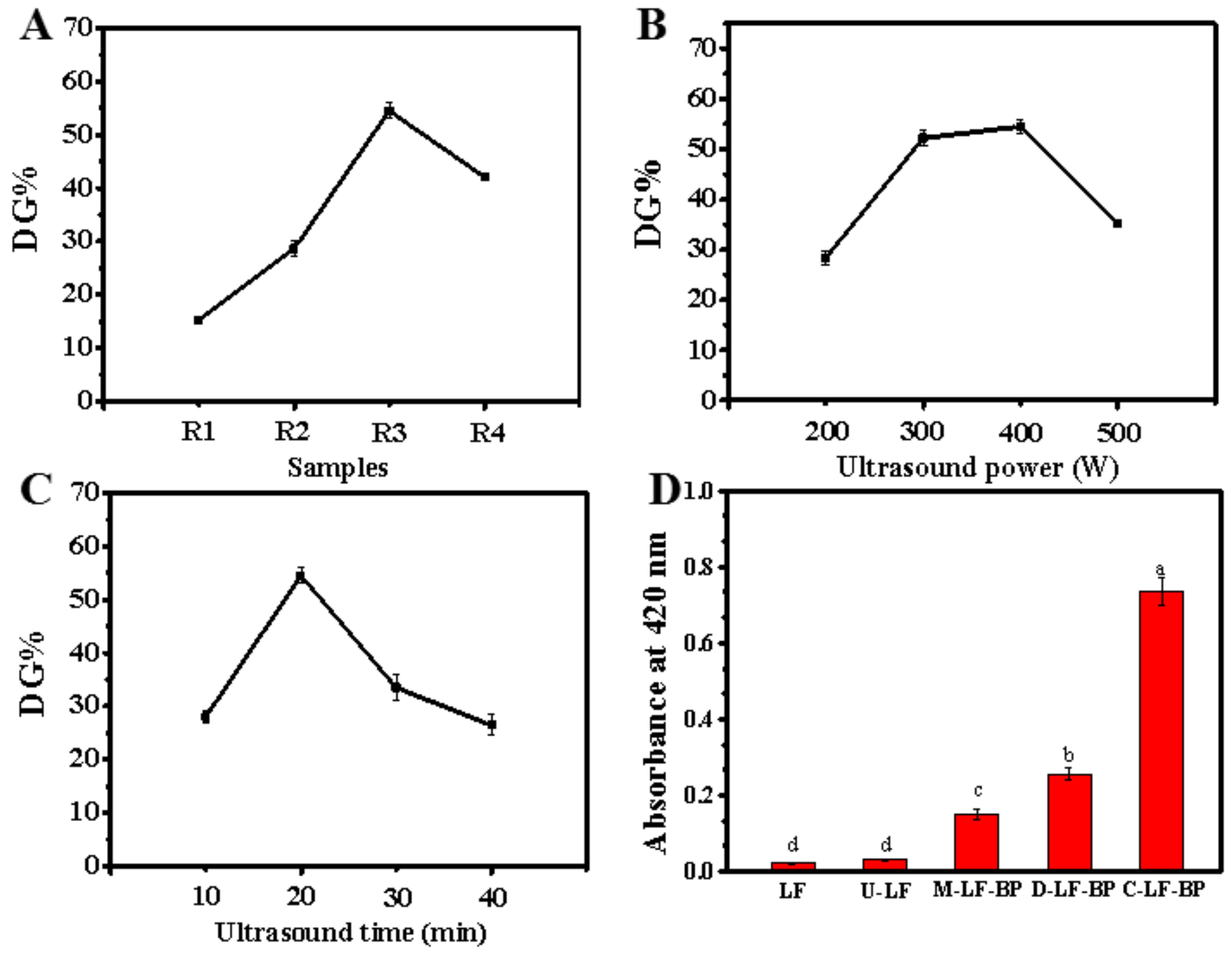
2.1.1. Effects of LF-BP Mass Ratio, Ultrasound Power and Ultrasound Time
2.1.2. Orthogonal Analysis
2.1.3. Confirmation Experiment
2.2. Browning Index
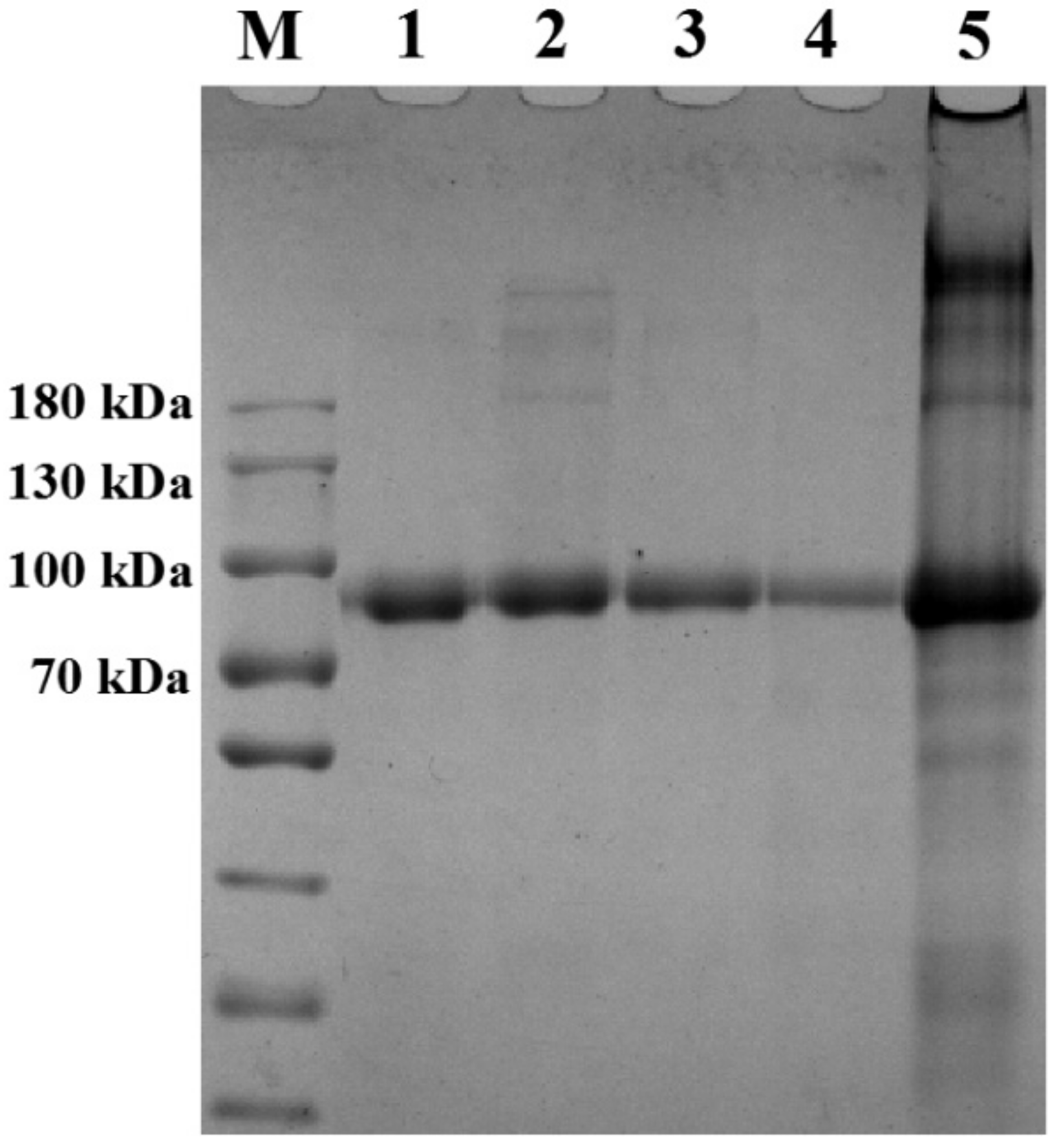
2.3. SDS-PAGE
2.4. Fluorescence Spectra
2.5. FTIR
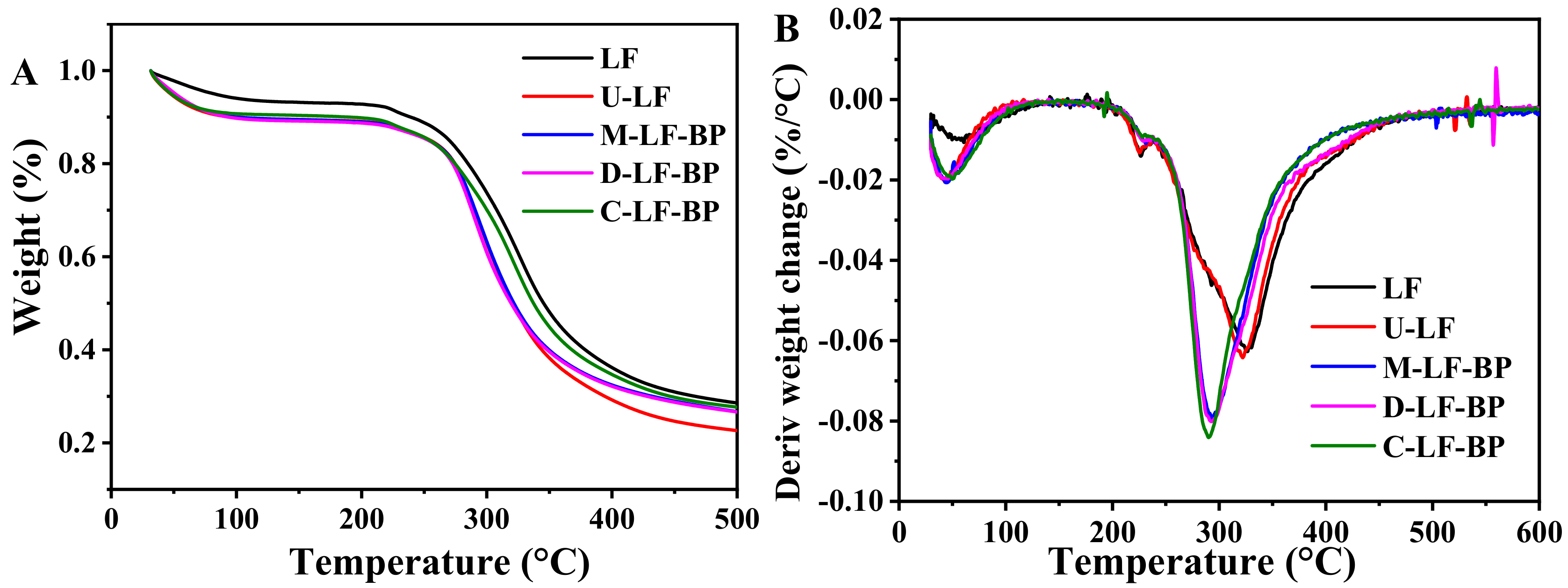
2.6. TGA
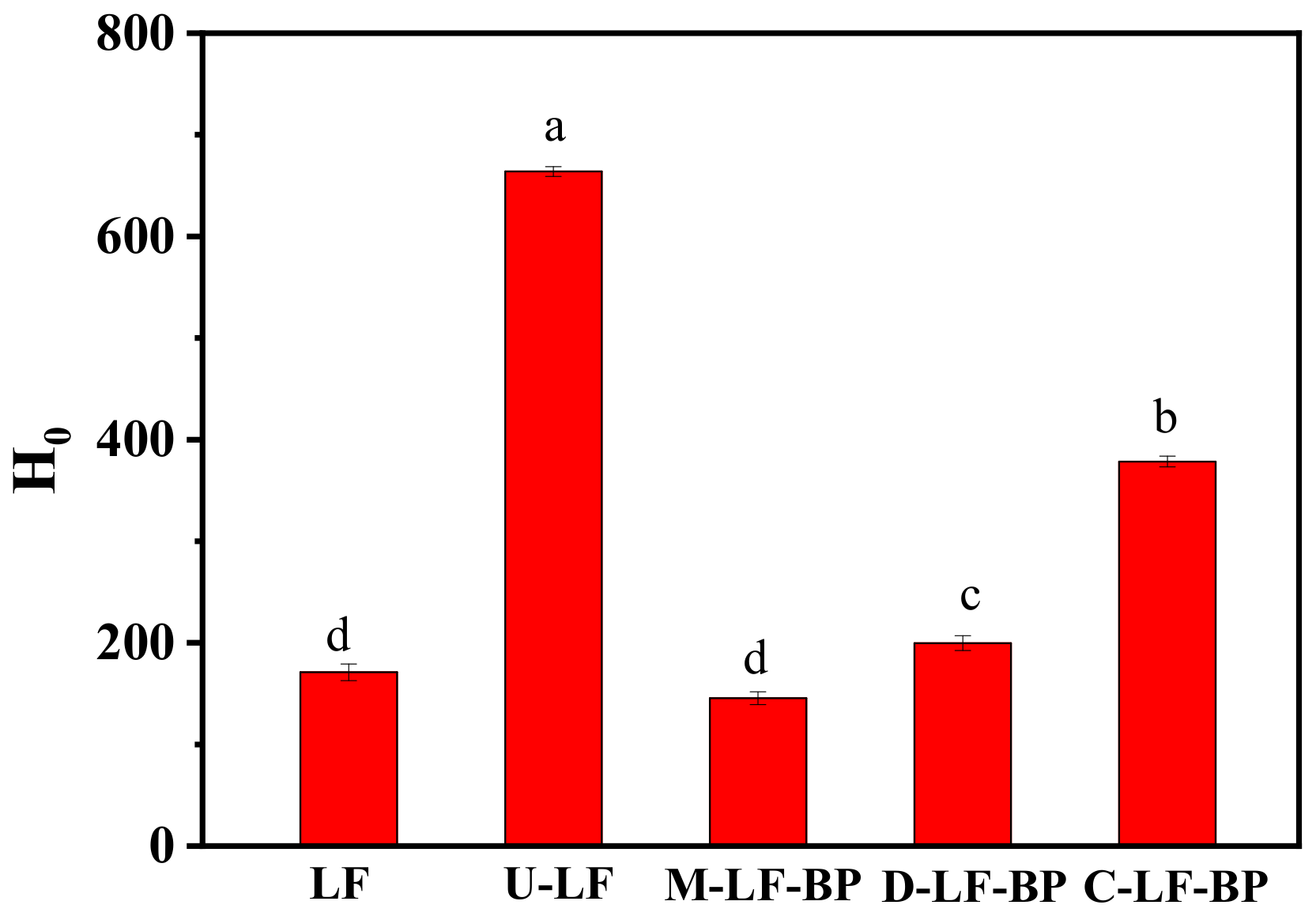
2.7. Surface Hydrophobicity (H0) of Proteins in Conjugates
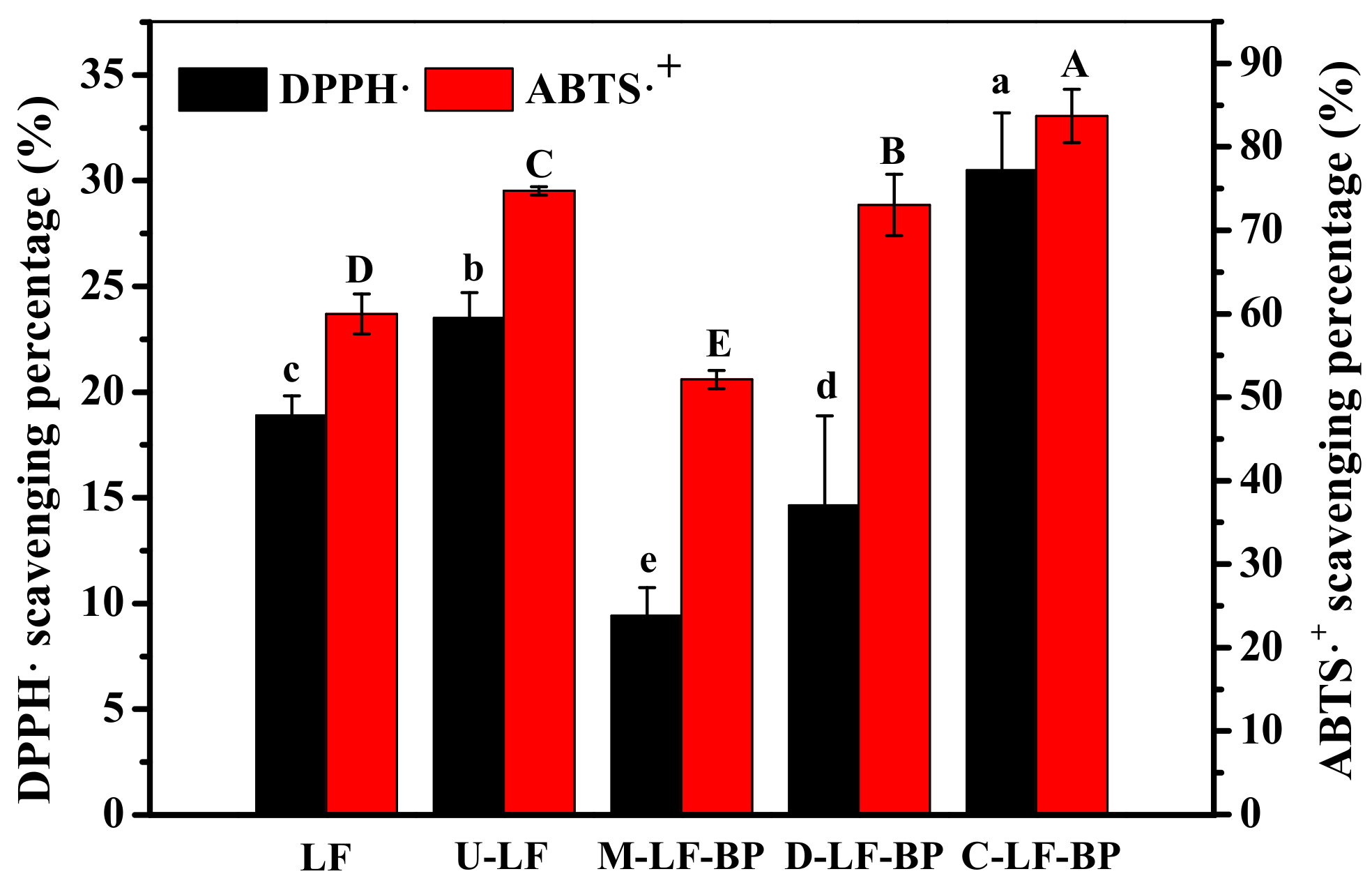
2.8. Antioxidant Activities
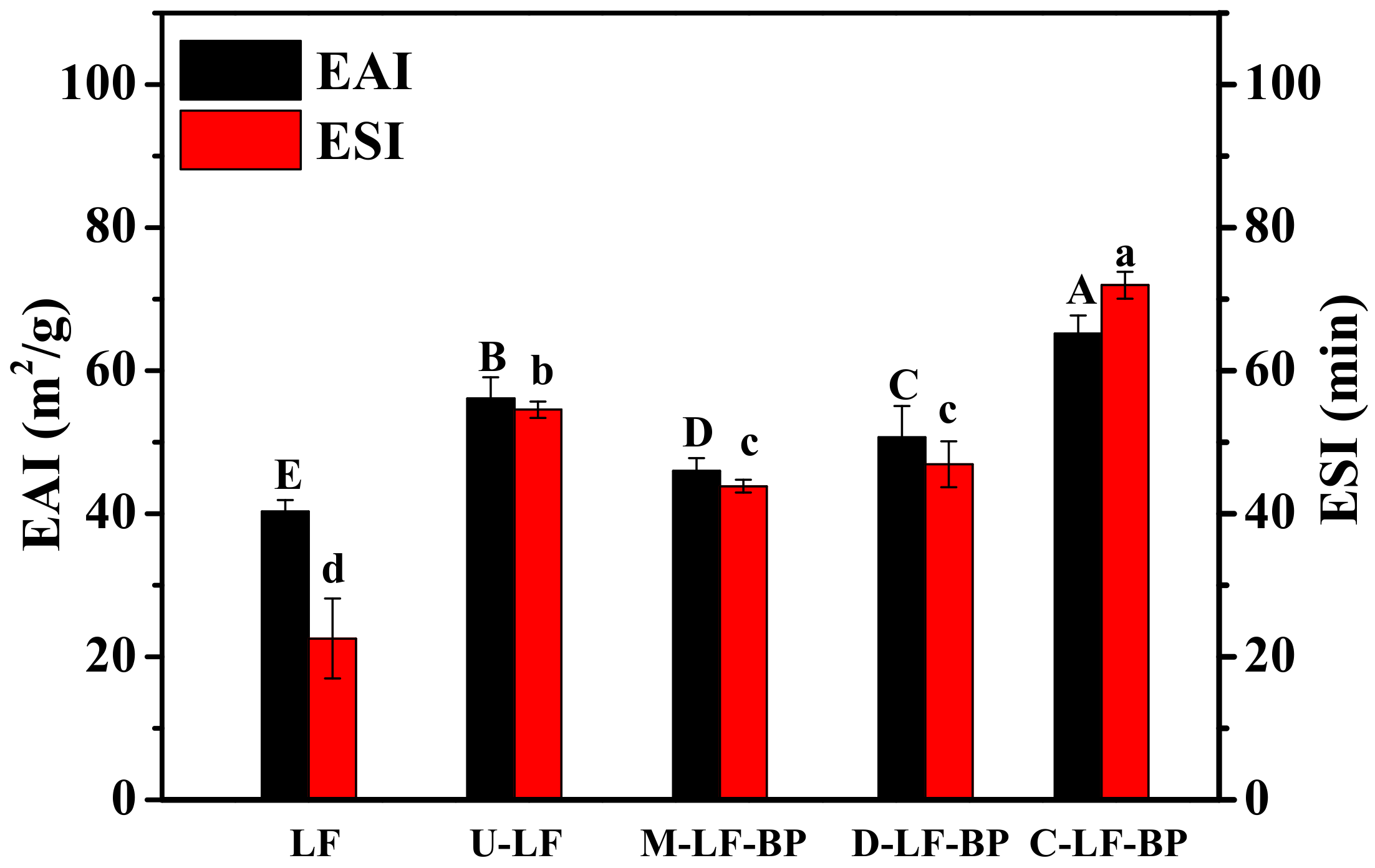
2.9. Emulsion Activity and Stability
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of LF-BP Conjugates
3.3. Measurement of DG
3.4. Browning Index
3.5. Characterization of LF-BP Conjugates
3.5.1. SDS-PAGE
3.5.2. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.5.3. Determination of Intrinsic Fluorescence Emission
3.5.4. Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3.5.5. Surface Hydrophobicity (H0)
3.6. Functional Properties of the Conjugates
3.6.1. DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Activity
3.6.2. ABTS Free Radical Scavenging Activity
3.6.3. Emulsifying Activity and Stability
3.7. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, B.; Timilsena, Y.P.; Blanch, E.; Adhikari, B. Lactoferrin: Structure, function, denaturation and digestion. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2019, 59, 580–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, X. Recent development of lactoferrin-based vehicles for the delivery of bioactive compounds: Complexes, emulsions, and nanoparticles. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 79, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.; Ratcliffe, I.; Williams, P.A. Emulsion stabilisation using polysaccharide-protein complexes. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 18, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, C.M.; Melton, L.D.; Stanley, R.A. Creating proteins with novel functionality via the Maillard reaction: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2006, 46, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, F.C.; dos Reis Coimbra, J.S.; de Oliveira, E.B.; Giraldo Zuniga, A.D.; Garcia Rojas, E.E. Food protein-polysaccharide conjugates obtained via the Maillard reaction: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2016, 56, 1108–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Damodaran, S.; Lucey, J.A. Formation of whey protein isolate (WPI)-dextran conjugates in aqueous solutions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7113–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, T.S.; Moharram, H.A.; Shaltout, O.E.; Asker, D.; Youssef, M.M. Applications of ultrasound in analysis, processing and quality control of food: A review. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 410–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Zill, H.; Khan, M.K. Applications of ultrasound in food technology: Processing, preservation and extraction. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 813–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Han, F.; Sui, X.; Qi, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L. Effect of ultrasound treatment on the wet heating Maillard reaction between mung bean Vigna radiate (L.) protein isolates and glucose and on structural and physico-chemical properties of conjugates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1532–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chi, Y.J.; Li, B. Effect of ultrasound treatment on the wet heating Maillard reaction between beta-conglycinin and maltodextrin and on the emulsifying properties of conjugates. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 238, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.B.; Zhou, L.Y.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, F. Effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on physicochemical characteristics and rheological properties of soy protein/sugar Maillard reaction products. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 2342–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Huang, X.; Peng, Q.; Shan, Y.; Xue, F. Physicochemical properties of peanut protein isolate-glucomannan conjugates prepared by ultrasonic treatment. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 1722–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroux, J.; Langendorff, V.; Schick, G.; Vaishnav, V.; Mazoyer, J. Emulsion stabilizing properties of pectin. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Huan, S.; Li, Z.; McClements, D.J. Comparison of emulsifying properties of food-grade polysaccharides in oil-in-water emulsions: Gum arabic, beet pectin, and corn fiber gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 66, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ma, X.; Wang, W.; Lv, R.; Guo, M.; Ding, T.; Ye, X.; Miao, S.; Liu, D. Preparation of modified whey protein isolate with gum acacia by ultrasound maillard reaction. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 95, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Zhao, M.; Yang, B.; Zhao, H.; Cui, C.; Zhao, Q. Effect of ultrasonic treatment on the graft reaction between soy protein isolate and gum acacia and on the physicochemical properties of conjugates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 58, 4494–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, S.; Jongen, W.M.F.; van Boekel, M. A review of Maillard reaction in food and implications to kinetic modelling. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kitts, D.D. Confirmation that the Maillard reaction is the principle contributor to the antioxidant capacity of coffee brews. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2418–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Ma, N.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ma, G.; Pei, F.; Hu, Q. Characterization and functional evaluation of oat protein isolate-Pleurotus ostreatus β-glucan conjugates formed via Maillard reaction. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.H.; Yu, S.J.; Yang, X.Q.; Qi, J.R.; Lin, H.; Zhao, Z.G. Emulsifying properties and structural characteristics of beta-conglycinin and dextran conjugates synthesised in a pressurised liquid system. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ru, Q.; Ding, Y. Glycation a promising method for food protein modification: Physicochemical properties and structure, a review. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broersen, K.; Voragen, A.G.J.; Hamer, R.J.; de Jongh, H.H.J. Glycoforms of beta-lactoglobulin with improved thermostability and preserved structural packing. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 86, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallares, I.; Vendrell, J.; Aviles, F.X.; Ventura, S. Amyloid fibril formation by a partially structured intermediate state of alpha-chymotrypsin. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 342, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.J.; Kim, H.J.; Park, K.H.; Moon, T.W. Molecular characteristics of ovalbumin-dextran conjugates formed through the Maillard reaction. Food Chem. 2005, 92, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma-Osuna, A.I.; Ramos-Clamont, G.; Guzman-Partida, A.M.; Vazquez-Moreno, L. Conjugates of bovine serum albumin with chitin oligosaccharides prepared through the Maillard reaction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12000–12005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.F.; Huang, Z.; Yuan, X.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, M. Structure and properties of carboxymethyl cellulose/soy protein isolate blend edible films crosslinked by Maillard reactions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, Z.; He, R.; Ma, H. Effects of ultrasonic and graft treatments on grafting degree, structure, functionality, and digestibility of rapeseed protein isolate-dextran conjugates. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 42, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, C.; Duan, X.; McClements, D.; Liu, X.; Liu, F. Formation and characterization of lactoferrin-hyaluronic acid conjugates and their effects on the storage stability of sesamol emulsions. Molecules 2018, 23, 3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, M.; Liu, H.M. Emulsifying and physicochemical properties of soy hull hemicelluloses-soy protein isolate conjugates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 163, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanoop, P.K.; Mahesh, K.V.; Nampoothiri, K.M.; Mangalaraja, R.V.; Ananthakumar, S. Multifunctional ZnO-biopolymer nanocomposite coatings for health-care polymer foams and fabrics. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 126, E232–E243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Ling, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, Y.; Zeng, X.; Sun, R. Maillard reaction products from chitosan-xylan ionic liquid solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Ren, J.; Zhao, M. Effects of ultrasound pretreatment on the enzymatic hydrolysis of soy protein isolates and on the emulsifying properties of hydrolysates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2600–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, J.; Murray, B.; Flynn, C.; Norton, I. The effect of ultrasound treatment on the structural, physical and emulsifying properties of animal and vegetable proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 53, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Villaluenga, C.; Bringe, N.A.; Berhow, M.A.; Mejia, E.G.D. β-Conglycinin embeds active peptides that inhibit lipid accumulation in 3t3-l1 adipocytes in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10533–10543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Muramoto, K.; Yamauchi, F. Structural analysis of antioxidative peptides from soybean beta.-conglycinin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xie, Q.T.; Li, X.M.; Meng, R.; Zhang, B.; Jin, Z.Y. Insight into the stabilization mechanism of emulsions stabilized by Maillard conjugates: Protein hydrolysates-dextrin with different degree of polymerization. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, N.; Raza, A.; Shen, D.; Song, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, P. Sensory attribute and antioxidant capacity of Maillard reaction products from enzymatic hydrolysate of bovine bone marrow extract. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1786–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.T.; Ming, X.W.; Su, P.W.; Ju, Q.K. Effects of ultrasound and additives on the function and structure of trypsin. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2004, 11, 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- Corzo-Martinez, M.; Moreno, F.J.; Villamiel, M.; Harte, F.M. Characterization and improvement of rheological properties of sodium caseinate glycated with galactose, lactose and dextran. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigo, M.S.; Malec, L.S.; Gomez, R.G.; Llosa, R.A. Spectrophotometric assay using o-phthaldialdehyde for determination of reactive lysine in dairy products. Food Chem. 1992, 44, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Li, C.; Zhu, X.W.; Wang, L.F. Comparative studies on the physicochemical properties of soy protein isolate-maltodextrin and soy protein isolate-gum acacia conjugate prepared through Maillard reaction. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Ma, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Fei, M. Synthesis, anti-oxidant activity, and biodegradability of a novel recombinant polysaccharide derived from chitosan and lactose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 118, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.F.; Dai, L.; Sun C., X.; Gao, Y.X. Characterization of curcumin loaded gliadin-lecithin composite nanoparticles fabricated by antisolvent precipitation in different blending sequences. Food Hydrocolloid. 2018, 85, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, N.; Visioli, F.; Buratti, S.; Brighenti, F. Direct analysis of total antioxidant activity of olive oil and studies on the influence of heating. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2532–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |

| Test Number | A: LF to BP | B: Ultrasonic | C: Ultrasonic | Degree of Graft (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass Ratio | Time (Min) | Power (W) | ||
| 1 | 1 (2:0.3) | 1 (10) | 1 (300) | 13.46 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 (20) | 2 (400) | 15.24 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 (30) | 3 (500) | 15.71 |
| 4 | 2 (2:0.6) | 1 | 2 | 27.6 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 36.15 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 36.82 |
| 7 | 3 (2:0.9) | 1 | 3 | 34.52 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 52.22 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 33.48 |
| K1 | 44.41 | 75.68 | 102.50 | |
| K2 | 100.66 | 103.62 | 76.41 | |
| K3 | 120.23 | 86.00 | 86.38 | |
| k1 | 14.80 | 25.23 | 34.17 | |
| k2 | 33.55 | 34.54 | 25.47 | |
| k3 | 40.08 | 28.67 | 28.79 | |
| R | 25.27 | 9.31 | 8.70 | |
| Factors | A3 | B2 | C1 | |
| Optimal condition | A3B2C1 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Ma, D.; He, Y.; Guo, S.; Liu, F.; Liu, X. Simultaneous Ultrasound and Heat Enhance Functional Properties of Glycosylated Lactoferrin. Molecules 2020, 25, 5774. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235774
Li Z, Ma D, He Y, Guo S, Liu F, Liu X. Simultaneous Ultrasound and Heat Enhance Functional Properties of Glycosylated Lactoferrin. Molecules. 2020; 25(23):5774. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235774
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhipeng, Dexue Ma, Yiyang He, Siqi Guo, Fuguo Liu, and Xuebo Liu. 2020. "Simultaneous Ultrasound and Heat Enhance Functional Properties of Glycosylated Lactoferrin" Molecules 25, no. 23: 5774. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235774
APA StyleLi, Z., Ma, D., He, Y., Guo, S., Liu, F., & Liu, X. (2020). Simultaneous Ultrasound and Heat Enhance Functional Properties of Glycosylated Lactoferrin. Molecules, 25(23), 5774. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235774







