Gold(I)-Catalyzed Domino Reaction for Furopyrans Synthesis
Abstract
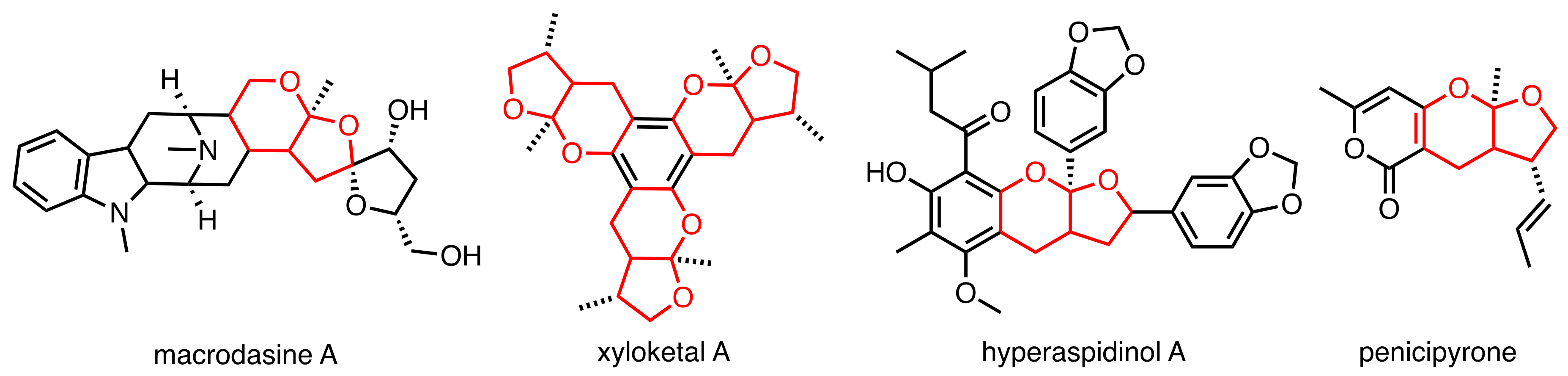
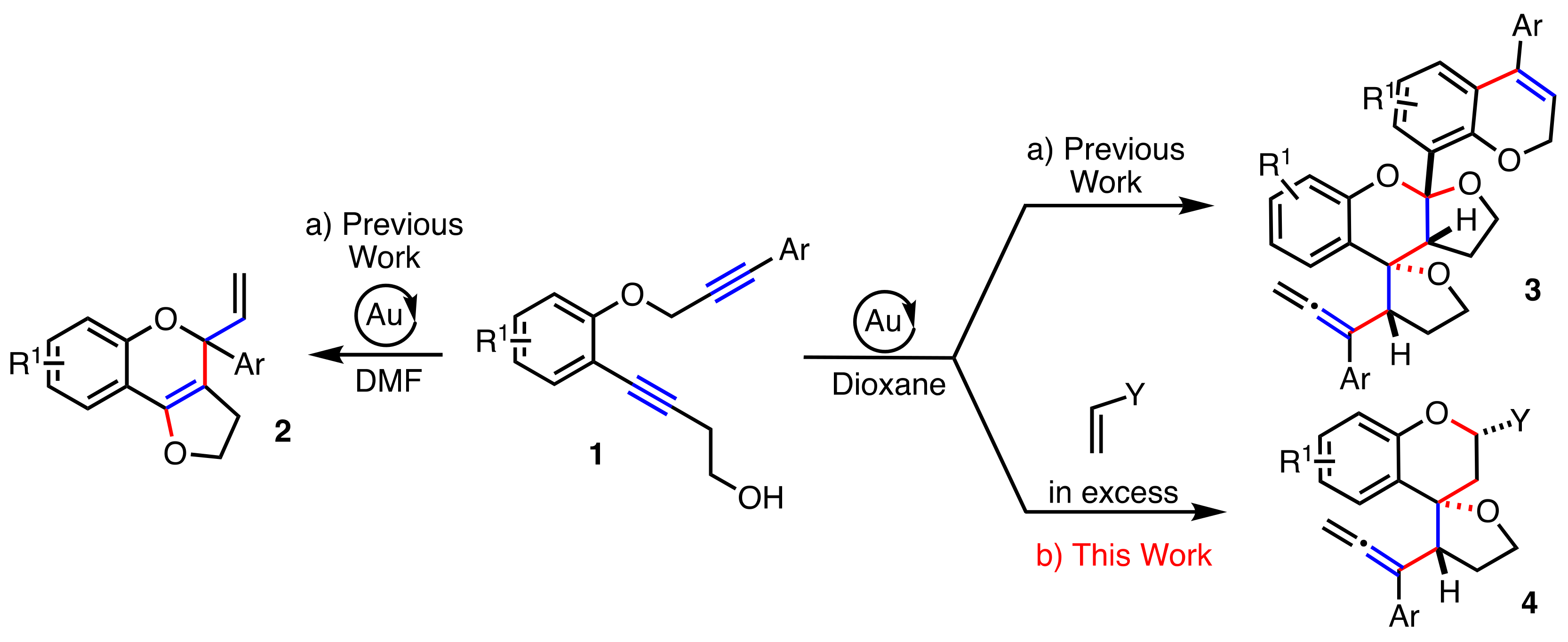
1. Introduction
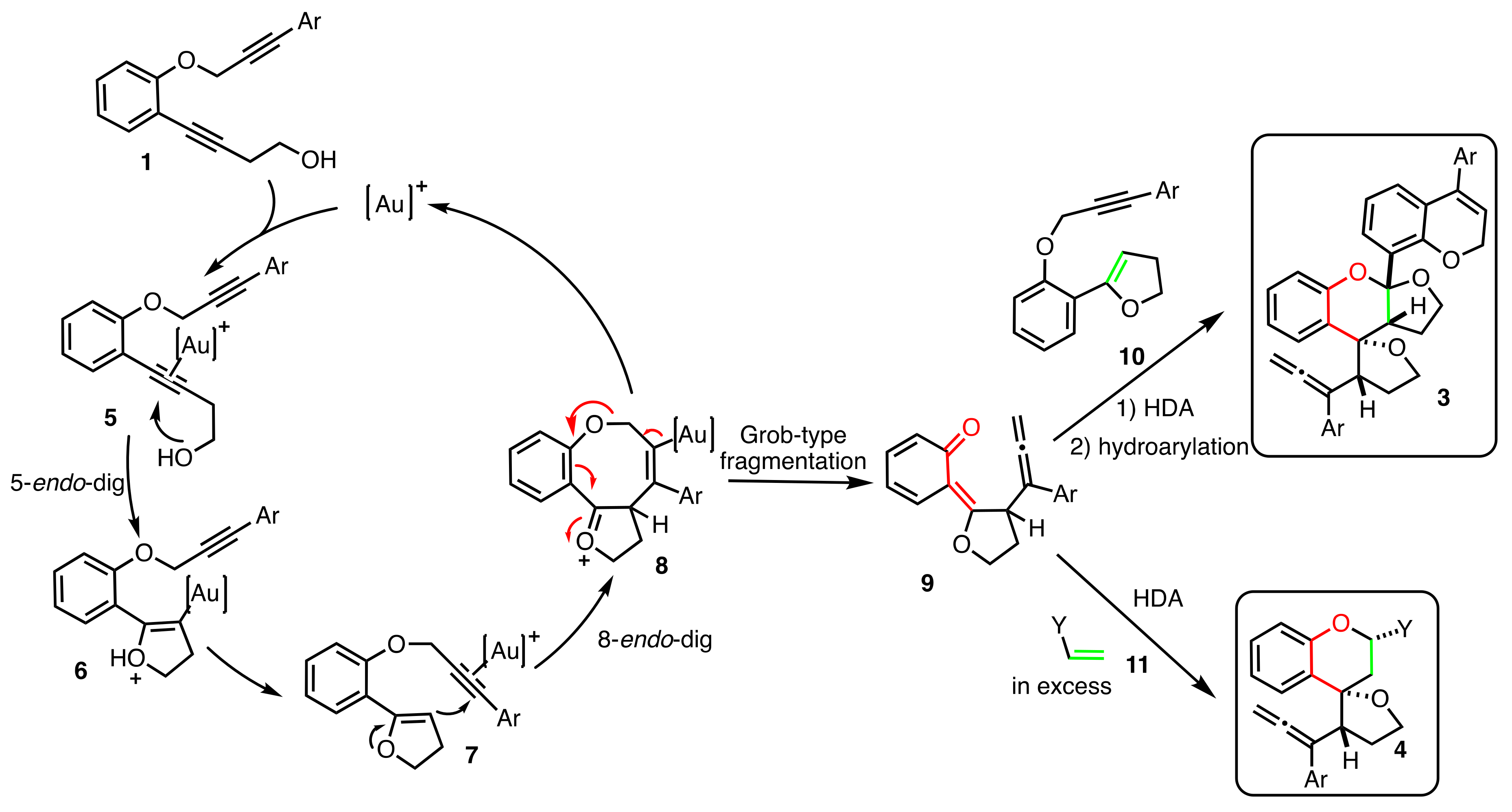
2. Results
2.1. Dienophiles Screening
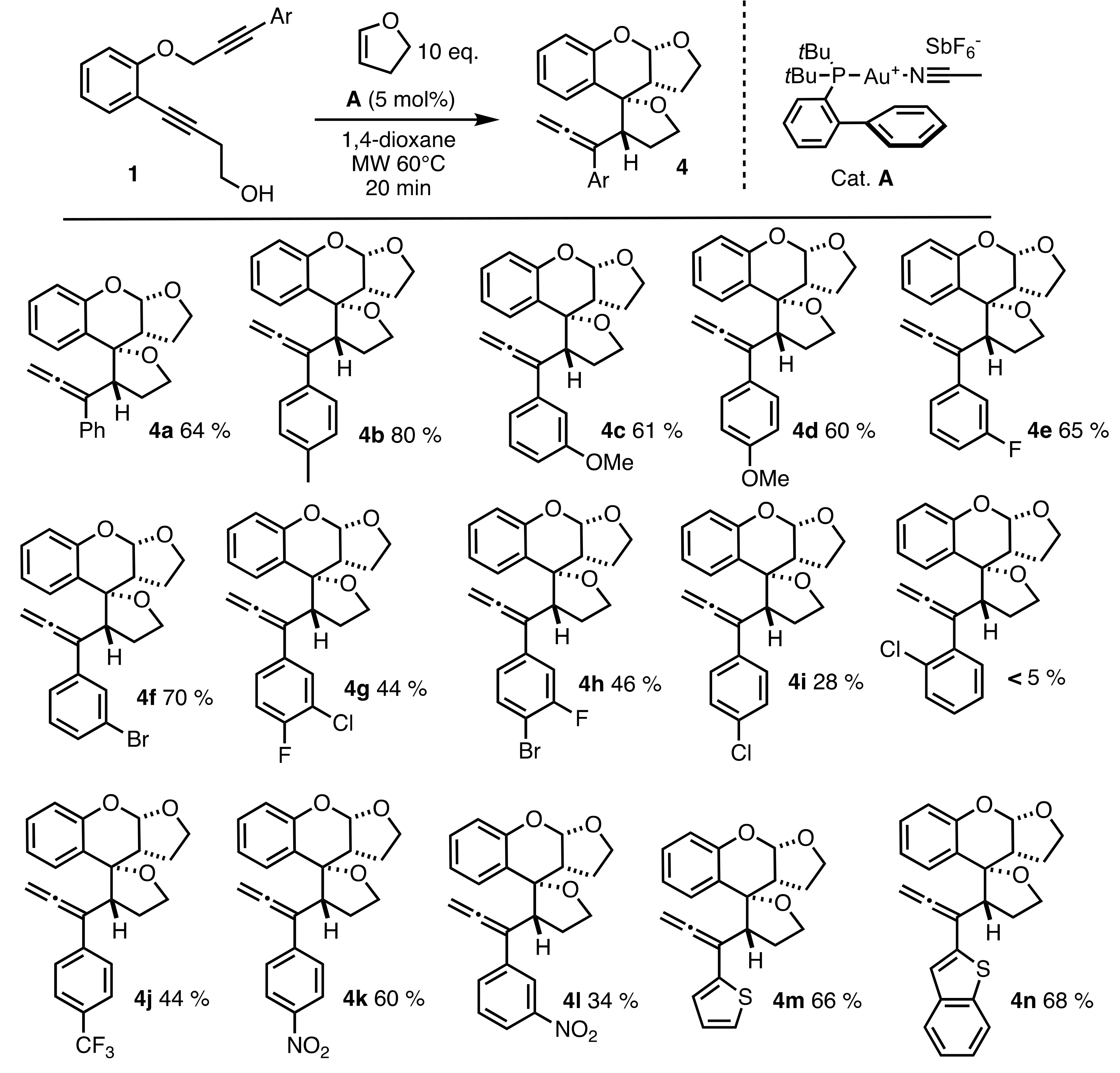
2.2. Scope of the Reaction
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Information
4.2. Synthesis of 1f and 1g
4.2.1. Synthesis of 4-(2-((3-(3-bromophenyl)prop-2-yn-1-yl)oxy)phenyl)but-3-yn-1-ol 1f
4.2.2. 4-(2-((3-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)prop-2-yn-1-yl)oxy)phenyl)but-3-yn-1-ol 1g
4.3. General Procedure for Gold(I) Catalyzed Cascade Reactions: Preparation of 4a–n
4.3.1. Synthesis of (2S,3R,3a′R,9a′S)-3-(1-phenylpropa-1,2-dien-1-yl)-2′,3′,3a′,4,5,9a′-hexahydro-3H-spiro[furan-2,4′-furo[2,3-b]chromene] 4a
4.3.2. Synthesis of (2S,3R,3a′R,9a′S)-3-(1-(p-tolyl)propa-1,2-dien-1-yl)-2′,3′,3a′,4,5,9a′-hexahydro-3H-spiro[furan-2,4′-furo[2,3-b]chromene] 4b
4.3.3. Synthesis of (2S,3R,3a′R,9a′S)-3-(1-(3-methoxyphenyl)propa-1,2-dien-1-yl)-2′,3′,3a′,4,5,9a′-hexahydro-3H-spiro[furan-2,4′-furo[2,3-b]chromene] 4c
4.3.4. Synthesis of (2S,3R,3a′R,9a′S)-3-(1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propa-1,2-dien-1-yl)-2′,3′,3a′,4,5,9a′-hexahydro-3H-spiro[furan-2,4′-furo[2,3-b]chromene] 4d
4.3.5. Synthesis of (2S,3R,3a′R,9a′S)-3-(1-(3-fluorophenyl)propa-1,2-dien-1-yl)-2′,3′,3a′,4,5,9a′-hexahydro-3H-spiro[furan-2,4′-furo[2,3-b]chromene] 4e
4.3.6. Synthesis of (2S,3R,3a′R,9a′S)-3-(1-(3-bromophenyl)propa-1,2-dien-1-yl)-2′,3′,3a′,4,5,9a′-hexahydro-3H-spiro[furan-2,4′-furo[2,3-b]chromene] 4f
4.3.7. Synthesis of (2S,3R,3a′R,9a′S)-3-(1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)propa-1,2-dien-1-yl)-2′,3′,3a′,4,5,9a′-hexahydro-3H-spiro[furan-2,4′-furo[2,3-b]chromene] 4g
4.3.8. Synthesis of (2S,3R,3a′R,9a′S)-3-(1-(4-bromo-3-fluorophenyl)propa-1,2-dien-1-yl)-2′,3′,3a′,4,5,9a′-hexahydro-3H-spiro[furan-2,4′-furo[2,3-b]chromene] 4h
4.3.9. Synthesis of (2S,3R,3a′R,9a′S)-3-(1-(4-chlorophenyl)propa-1,2-dien-1-yl)-2′,3′,3a′,4,5,9a′-hexahydro-3H-spiro[furan-2,4′-furo[2,3-b]chromene] 4i
4.3.10. Synthesis of (2S,3R,3a′R,9a′S)-3-(1-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)propa-1,2-dien-1-yl)-2′,3′,3a′,4,5,9a′-hexahydro-3H-spiro[furan-2,4′-furo[2,3-b]chromene] 4j
4.3.11. Synthesis of (2S,3R,3a′R,9a′S)-3-(1-(4-nitrophenyl)propa-1,2-dien-1-yl)-2′,3′,3a′,4,5,9a′-hexahydro-3H-spiro[furan-2,4′-furo[2,3-b]chromene] 4k
4.3.12. Synthesis of (2S,3R,3a′R,9a′S)-3-(1-(3-nitrophenyl)propa-1,2-dien-1-yl)-2′,3′,3a′,4,5,9a′-hexahydro-3H-spiro[furan-2,4′-furo[2,3-b]chromene] 4l
4.3.13. Synthesis of (2S,3R,3a′R,9a′S)-3-(1-(thiophen-2-yl)propa-1,2-dien-1-yl)-2′,3′,3a′,4,5,9a′-hexahydro-3H-spiro[furan-2,4′-furo[2,3-b]chromene] 4m
4.3.14. Synthesis of (2S,3R,3a′R,9a′S)-3-(1-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)propa-1,2-dien-1-yl)-2′,3′,3a′,4,5,9a′-hexahydro-3H-spiro[furan-2,4′-furo[2,3-b]chromene] 4n
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kam, T.-S.; Choo, Y.-M. Macrodasine A, a Novel Macroline Derivative Incorporating Fused Spirocyclic Tetrahydrofuran Rings Containing a Spiroacetal Moiety. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 8787–8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.-J.; Robinson, W.T.; Komiyama, K.; Kam, T.-S. Macrodasines A–G, Macroline Indole Alkaloids Incorporating Fused Spirocyclic Tetrahydrofuran–Tetrahydrofuran and Tetrahydrofuran–Tetrahydropyran Rings. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 3830–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wu, X.; Feng, S.; Jiang, G.; Luo, J.; Zhou, S.; Vrijmoed, L.L.P.; Jones, E.B.G.; Krohn, K.; Steingröver, K.; et al. Five Unique Compounds: Xyloketals from Mangrove Fungus Xylaria Sp. from the South China Sea Coast. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 6252–6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zeng, Y.H.; Osman, K.; Shinde, K.; Rahman, M.; Gibbons, S.; Mu, Q. Norlignans, Acylphloroglucinols, and a Dimeric Xanthone from Hypericum Chinense. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1815–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisuwan, K.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Sukpondma, Y.; Phongpaichit, S.; Preedanon, S.; Sakayaroj, J. Lactone Derivatives from the Marine-Derived Fungus Penicillium Sp. PSU-F44. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 1100–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blond, G.; Gulea, M.; Mamane, V. Recent Contributions to Hetero Diels-Alder Reactions. Curr. Org. Chem. 2016, 20, 2161–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachet, E.; Belmont, P. Inverse Electron Demand Diels-Alder (IEDDA) Reactions: Synthesis of Heterocycles and Natural Products Along with Bioorthogonal and Material Sciences Applications. COC 2016, 20, 2136–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pałasz, A. Recent Advances in Inverse-Electron-Demand Hetero-Diels–Alder Reactions of 1-Oxa-1,3-Butadienes. Top. Curr. Chem. 2016, 374, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ishihara, K.; Sakakura, A. 5.10 Hetero-Diels–Alder Reactions. In Comprehensive Organic Synthesis II; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 409–465. [Google Scholar]
- Sogani, N.; Bansal, R. Catalytic Hetero-Diels-Alder Reaction of the Carbonyl Compounds. CCAT 2017, 6, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzyńska, A.; Frankowski, S.; Albrecht, Ł. Cyclic 1-Azadienes in the Organocatalytic Inverse-Electron-Demand Aza-Diels-Alder Cycloadditions. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.-Y.; Chen, D.-F.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Guo, R.; Wang, P.-S.; Wang, C.; Gong, L.-Z. Hybrid Metal/Organo Relay Catalysis Enables Enynes To Be Latent Dienes for Asymmetric Diels–Alder Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6532–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Tay, G.L.; Neo, C.; Lee, B.R.; Chan, P.W.H. Gold-Catalyzed Cycloisomerization and Diels–Alder Reaction of 1,6-Diyne Esters with Alkenes and Diazenes to Hydronaphthalenes and -Cinnolines. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 4176–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.-L.; Zhao, F.; Han, Z.-Y.; Gong, L.-Z. Chiral Gold Complex Catalyzed Tandem Dehydrative Cyclization/Hetero-Diels–Alder Reaction. Synthesis 2016, 49, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yao, Z.; Dong, S.; Wei, F.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z. Synthesis of Fused Bicyclic Aminals through Sequential Gold/Lewis Acid Catalysis. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 2234–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Dong, S.; Yao, Z.; Feng, L.; Daka, P.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z. Synthesis of Spiroaminals and Spiroketals with Bimetallic Relay Catalysis. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, Z.; Jia, J.; Tung, C.-H.; Xu, Z. Synthesis of Spiroaminals by Bimetallic Au/Sc Relay Catalysis: TMS as a Traceless Controlling Group. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 12084–12087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, L.; Hu, B.; Lian, X.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Feng, X. Bimetallic Gold(I)/Chiral N,N′-Dioxide Nickel(II) Asymmetric Relay Catalysis: Chemo- and Enantioselective Synthesis of Spiroketals and Spiroaminals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6075–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Wan, Q.; Kang, Q. Gold(I)/Chiral Rh(III) Lewis Acid Relay Catalysis Enables Asymmetric Synthesis of Spiroketals and Spiroaminals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 360, 4031–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Li, J.; Cao, W.; Lin, Q.; Yang, J.; Lin, L.; Liu, X.; Feng, X. Asymmetric Synthesis of Fused Bicyclic N,O- and O,O-Acetals via Cascade Reaction by Gold(I)/N,N′-Dioxide-Nickel(II) Bimetallic Relay Catalysis. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2018, 360, 2831–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-S.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Zhou, J.; Mei, G.-J.; Wang, S.-L.; Shi, F. Metal-Catalyzed Oxa-[4+2] Cyclizations of Quinone Methides with Alkynyl Benzyl Alcohols. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 13861–13873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liang, M.; Tang, J.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Sun, H.; Tung, C.-H.; Jia, J.; Xu, Z. Gold/Lewis Acid Catalyzed Cycloisomerization/Diastereoselective [3 + 2] Cycloaddition Cascade: Synthesis of Diverse Nitrogen-Containing Spiro Heterocycles. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 4614–4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arto, T.; Fañanás, F.J.; Rodríguez, F. Gold(I)-Catalyzed Generation of the Two Components of a Formal [4 + 2] Cycloaddition Reaction for the Synthesis of Tetracyclic Pyrano[2,3,4-de ]Chromenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 7218–7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertschi, R.; Wagner, P.; Ghosh, N.; Gandon, V.; Blond, G. Gold(I)-Catalyzed Synthesis of Furopyrans: Insight into Hetero-Diels–Alder Reactions. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 6084–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, P.; Ghosh, N.; Gandon, V.; Blond, G. Solvent Effect in Gold(I)-Catalyzed Domino Reaction : Access to Furopyrans. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 7333–7337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 4a–4n and 5a are available from the authors. |
| Entry | Dienophile | Product | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 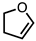 | 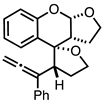 | 4a 64% |
| 2 | 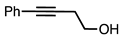 | 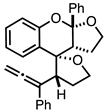 | 5a 7% |
| 3 | 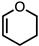 |  | 6 20% |
| 4 |  | CM 2 | - |
| 5 | 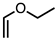 | CM 2 | - |
| 6 | 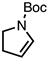 | CM 2 | - |
| 7 | 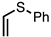 | CM 2 | - |
| 8 | 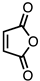 | CM 2 | - |
Publisher′s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruch, M.; Brach, N.; Galéa, R.; Wagner, P.; Blond, G. Gold(I)-Catalyzed Domino Reaction for Furopyrans Synthesis. Molecules 2020, 25, 4976. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25214976
Ruch M, Brach N, Galéa R, Wagner P, Blond G. Gold(I)-Catalyzed Domino Reaction for Furopyrans Synthesis. Molecules. 2020; 25(21):4976. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25214976
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuch, Marie, Nicolas Brach, Roméric Galéa, Patrick Wagner, and Gaëlle Blond. 2020. "Gold(I)-Catalyzed Domino Reaction for Furopyrans Synthesis" Molecules 25, no. 21: 4976. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25214976
APA StyleRuch, M., Brach, N., Galéa, R., Wagner, P., & Blond, G. (2020). Gold(I)-Catalyzed Domino Reaction for Furopyrans Synthesis. Molecules, 25(21), 4976. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25214976






