Heteromerization of Endogenous Mu and Delta Opioid Receptors Induces Ligand-Selective Co-Targeting to Lysosomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Endogenous Mu–Delta Heteromers Are Present at the Neuronal Surface under Basal Conditions
2.2. CYM51010 Induces Mu–Delta Receptor Co-Internalization and Co-Localization in the Late Endosomal Compartment in Primary Hippocampal Cultures
2.3. CYM51010-Induced Mu–Delta Receptor Co-Internalization Is Blocked by Pretreatment with Mu- or Delta-Selective Antagonists
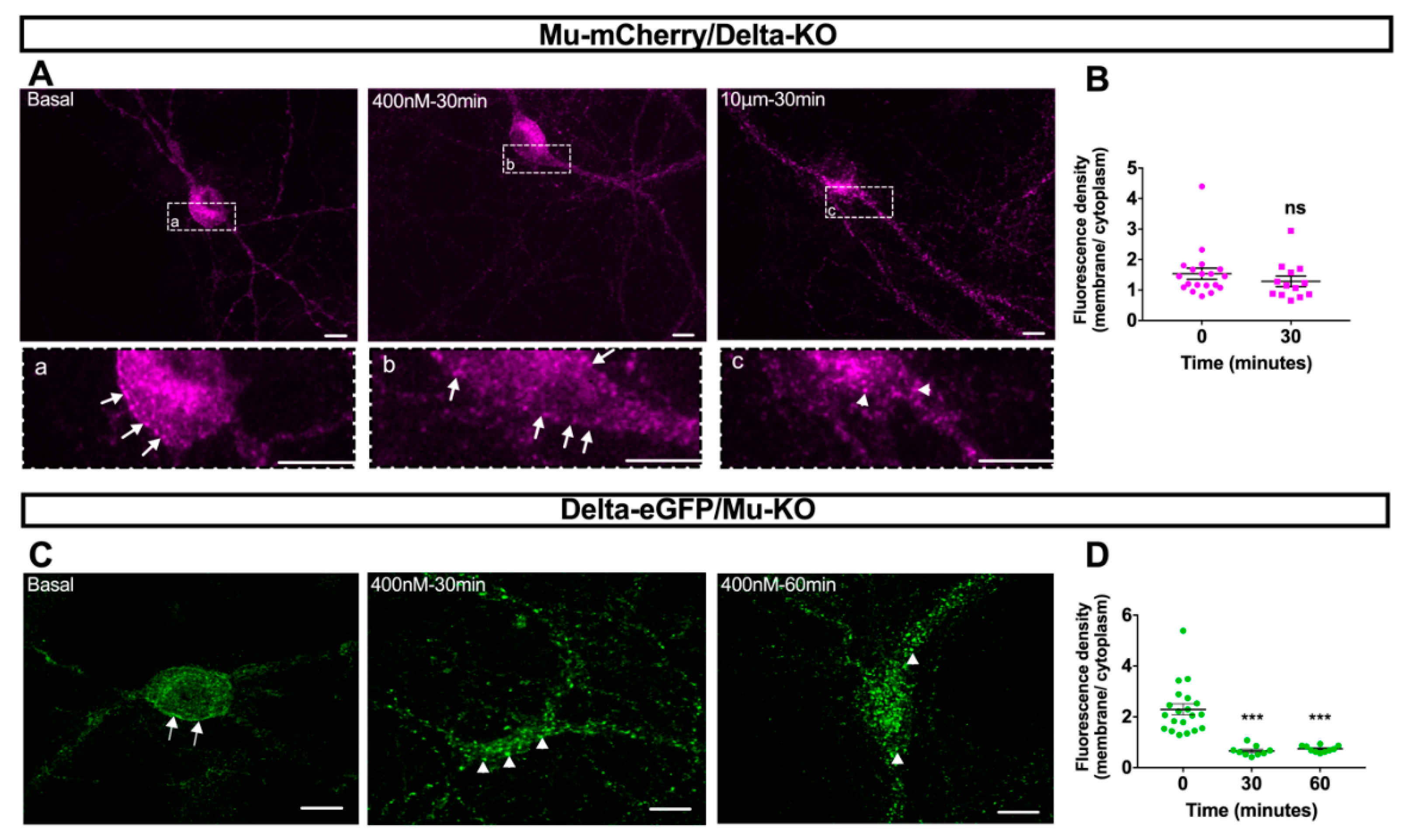
2.4. Mu–Delta Receptor Co-Internalization Is Ligand-Specific
3. Discussion
3.1. Mu–Delta Co-Internalization Is Induced by Different Ligands in Native or Co-Transfected Cells
3.2. CYM51010 Activation Induces Co-Targeting of Mu and Delta Receptors to the Lysosomal Compartment
3.3. Mu and Delta Opioid Receptors Form Functional Heteromers in the Hippocampus
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Drugs
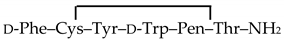 (CTAP) (C-6352), beta-funaltrexamine (β-FNA) (O-003), fentanyl citrate (F3886), naltrindole (N-2893), [d-Ala2, NMe-Phe4, Gly-ol5]enkephalin (DAMGO) (E-7384), and deltorphin II (T-0658) were purchased from Sigma. (+)-4-[(αR)-α-((2S,5R)-4-Allyl-2,5-dimethyl-1-piperazinyl)-3-methoxybenzyl]-N,N-diethylbenzamide (SNC80) (cat n° 0764) was obtained from Tocris bioscience, 1-[[4-(acetylamino)phenyl]methyl]-4-(2-phenylethyl)-4-piperidinecarboxylic acid, ethyl ester (CYM51010) (ML-335) was obtained from Cayman chemical, and tic-deltorphin was synthesized as reported in [42]. Morphine hydrochloride was from Francopia, and methadone (M-0267) was from Sigma.
(CTAP) (C-6352), beta-funaltrexamine (β-FNA) (O-003), fentanyl citrate (F3886), naltrindole (N-2893), [d-Ala2, NMe-Phe4, Gly-ol5]enkephalin (DAMGO) (E-7384), and deltorphin II (T-0658) were purchased from Sigma. (+)-4-[(αR)-α-((2S,5R)-4-Allyl-2,5-dimethyl-1-piperazinyl)-3-methoxybenzyl]-N,N-diethylbenzamide (SNC80) (cat n° 0764) was obtained from Tocris bioscience, 1-[[4-(acetylamino)phenyl]methyl]-4-(2-phenylethyl)-4-piperidinecarboxylic acid, ethyl ester (CYM51010) (ML-335) was obtained from Cayman chemical, and tic-deltorphin was synthesized as reported in [42]. Morphine hydrochloride was from Francopia, and methadone (M-0267) was from Sigma.4.3. Primary Neuronal Culture
4.4. Drug Administration and Sample Preparation
4.5. Fluorescent Detection with Antibodies
4.6. Image Acquisition and Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaveriaux-Ruff, C.; Kieffer, B.L. Opioid receptor genes inactivated in mice: The highlights. Neuropeptides 2002, 36, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; He, X.; Yang, Y.; Chao, D.; H Lazarus, L.; Xia, Y. Current research on opioid receptor function. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 230–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charbogne, P.; Kieffer, B.L.; Befort, K. 15 years of genetic approaches in vivo for addiction research: Opioid receptor and peptide gene knockout in mouse models of drug abuse. Neuropharmacology 2014, 76 Pt B, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Pan, Z.Z. Synaptic mechanism for functional synergism between delta- and mu-opioid receptors. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 4735–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gendron, L.; Mittal, N.; Beaudry, H.; Walwyn, W. Recent advances on the delta opioid receptor: From trafficking to function. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, W.; Gomes, I.; Devi, L.A. Revolution in GPCR Signaling: Opioid receptor heteromers as novel therapeutic targets. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 4155–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, B.A.; Devi, L.A. G-protein-coupled receptor heterodimerization modulates receptor function. Nature 1999, 399, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, I.; Jordan, B.A.; Gupta, A.; Trapaidze, N.; Nagy, V.; Devi, L.A. Heterodimerization of mu and delta opioid receptors: A role in opiate synergy. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, W.; Gomes, I.; Devi, L.A. Mu-Delta opioid receptor heteromers: New pharmacology and novel therapeutic possibilities. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trafton, J.A.; Abbadie, C.; Marek, K.; Basbaum, A.I. Postsynaptic signaling via the [mu]-opioid receptor: Responses of dorsal horn neurons to exogenous opioids and noxious stimulation. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 8578–8584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbs, E.; Faget, L.; Scherrer, G.; Matifas, A.; Filliol, D.; Vonesch, J.L.; Koch, M.; Kessler, P.; Hentsch, D.; Birling, M.C.; et al. A mu-delta opioid receptor brain atlas reveals neuronal co-occurrence in subcortical networks. Brain Struct. Funct. 2015, 220, 677–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherrer, G.; Tryoen-Tóth, P.; Filliol, D.; Matifas, A.; Laustriat, D.; Cao, Y.Q.; Basbaum, A.I.; Dierich, A.; Vonesh, J.L.; Gavériaux-Ruff, C.; et al. Knockin mice expressing fluorescent delta-opioid receptors uncover G protein-coupled receptor dynamics in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9691–9696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, A.A.; Becker, J.A.; Scherrer, G.; Tryoen-Toth, P.; Filliol, D.; Matifas, A.; Massotte, D.; Gavériaux-Ruff, C.; Kieffer, B.L. In vivo delta opioid receptor internalization controls behavioral effects of agonists. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whistler, J.L.; Enquist, J.; Marley, A.; Fong, J.; Gladher, F.; Tsuruda, P.; Murray, S.R.; Von Zastrow, M. Modulation of postendocytic sorting of G protein-coupled receptors. Science 2002, 297, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenfeld, R.; Devi, L.A. Receptor heterodimerization leads to a switch in signaling: Beta-arrestin2-mediated ERK activation by mu-delta opioid receptor heterodimers. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasbi, A.; Nguyen, T.; Fan, T.; Cheng, R.; Rashid, A.; Alijaniaram, M.; Rasenick, M.M.; O’Dowd, B.F.; George, S.R. Trafficking of preassembled opioid mu-delta heterooligomer-Gz signaling complexes to the plasma membrane: Coregulation by agonists. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 12997–13009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabli, N.; Martin, N.; Fan, T.; Nguyen, T.; Hasbi, A.; Balboni, G.; O’Dowd, B.F.; George, S.R. Agonists at the delta-opioid receptor modify the binding of micro-receptor agonists to the micro-delta receptor hetero-oligomer. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 161, 1122–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.Q.; Zhang, Z.N.; Guan, J.S.; Liu, H.R.; Zhao, B.; Wang, H.B.; Li, Q.; Yang, H.; Luo, J.; Li, Z.Y.; et al. Facilitation of mu-opioid receptor activity by preventing delta-opioid receptor-mediated codegradation. Neuron 2011, 69, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan-Lobo, L.; Whistler, J.L. Heteromerization of the mu- and delta-opioid receptors produces ligand-biased antagonism and alters mu-receptor trafficking. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 337, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benredjem, B.; Dallaire, P.; Pineyro, G. Analyzing biased responses of GPCR ligands. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 32, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broad, J.; Maurel, D.; Kung, V.W.; Hicks, G.A.; Schemann, M.; Barnes, M.R.; Kenakin, T.P.; Granier, S.; Sanger, G.J. Human native kappa opioid receptor functions not predicted by recombinant receptors: Implications for drug design. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, E.W.; Xue, L.; Olmstead, M.C.; Cahill, C.M. Prolonged morphine treatment alters delta opioid receptor post-internalization trafficking. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierre, F.; Ugur, M.; Faivre, F.; Doridot, S.; Veinante, P.; Massotte, D. Morphine-dependent and abstinent mice are characterized by a broader distribution of the neurons co-expressing mu and delta opioid receptors. Neuropharmacology 2019, 152, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, I.; Fujita, W.; Gupta, A.; Saldanha, S.A.; Negri, A.; Pinello, C.E.; Eberhart, C.; Roberts, E.; Filizola, M.; Hodder, P.; et al. Identification of a mu-delta opioid receptor heteromer-biased agonist with antinociceptive activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12072–12077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, V.; He, S.Q.; Huang, Q.; Liang, L.; Yang, F.; Chen, Z.; Tiwari, V.; Fujita, W.; Devi, L.A.; Dong, X.; et al. Activation of micro-delta opioid receptor heteromers inhibits neuropathic pain behavior in rodents. Pain 2020, 161, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faget, L.; Erbs, E.; Le Merrer, J.; Scherrer, G.; Matifas, A.; Benturquia, N.; Noble, F.; Decossas, M.; Koch, M.; Kessler, P.; et al. In vivo visualization of delta opioid receptors upon physiological activation uncovers a distinct internalization profile. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 7301–7310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbs, E.; Faget, L.; Ceredig, R.A.; Matifas, A.; Vonesch, J.L.; Kieffer, B.L.; Massotte, D. Impact of chronic morphine on delta opioid receptor-expressing neurons in the mouse hippocampus. Neuroscience 2016, 313, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derouiche, L.; Ory, S.; Massotte, D. Double fluorescent knock-in mice to investigate endogenous mu-delta opioid heteromer subscellular distribution. In Receptor-Receptor Interactions in the Central Nervous System; Fuxe, K., Borroto Escuela, D., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Tawfik, V.L.; Corder, G.; Low, S.A.; François, A.; Basbaum, A.I.; Scherrer, G. Functional Divergence of Delta and Mu Opioid Receptor Organization in CNS Pain Circuits. Neuron 2018, 98, 90–108.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charfi, I.; Nagi, K.; Mnie-Filali, O.; Thibault, D.; Balboni, G.; Schiller, P.W.; Trudeau, L.E.; Pineyro, G. Ligand- and cell-dependent determinants of internalization and cAMP modulation by delta opioid receptor (DOR) agonists. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 1529–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thompson, G.L.; Lane, J.R.; Coudrat, T.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A.; Canals, M. Systematic analysis of factors influencing observations of biased agonism at the mu-opioid receptor. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 113, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, I.; Slowe, S.J.; Matthes, H.W.; Kieffer, B. Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of mu-, delta- and kappa-opioid receptors in knockout mice lacking the mu-opioid receptor gene. Brain Res. 1997, 778, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesscher, H.M.; Bailey, A.; Burbach, J.P.H.; Van Ree, J.M.; Kitchen, I.; Gerrits, M.A. Receptor-selective changes in mu-, delta- and kappa-opioid receptors after chronic naltrexone treatment in mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goody, R.J.; Oakley, S.M.; Filliol, D.; Kieffer, B.L.; Kitchen, I. Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of opioid receptors in the brain of delta-opioid receptor gene knockout mice. Brain Res. 2002, 945, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, P.C.S.; Keyworth, H.L.; Martin-Garcia, E.; Charbogne, P.; Darcq, E.; Bailey, A.; Filliol, D.; Matifas, A.; Scherrer, G.; Ouagazzal, A.M.; et al. A novel anxiogenic role for the delta opioid receptor expressed in GABAergic forebrain neurons. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 77, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceredig, R.A.; Massotte, D. Fluorescent knock-in mice to decipher the physiopathological role of G protein-coupled receptors. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceredig, R.A.; Pierre, F.; Doridot, S.; Alduntzin, U.; Salvat, E.; Yalcin, I.; Gaveriaux-Ruff, C.; Barrot, M.; Massotte, D. Peripheral delta opioid receptors mediate duloxetine antiallodynic effect in a mouse model of neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 48, 2231–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertran-Gonzalez, J.; Laurent, V.; Chieng, B.C.; Christie, M.J.; Balleine, B.W. Learning-related translocation of delta-opioid receptors on ventral striatal cholinergic interneurons mediates choice between goal-directed actions. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 16060–16071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, F.A.; Zelnik, J.C.; Traynor, J.R. G protein independent phosphorylation and internalization of the delta-opioid receptor. J. Neurochem. 2009, 109, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, P.Y.; Maestri-El Kouhen, O.; Solberg, J.; Wang, W.; Erickson, L.J.; Loh, H.H. Deltorphin II-induced rapid desensitization of delta-opioid receptor requires both phosphorylation and internalization of the receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 32057–32065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pin, J.P.; Neubig, R.; Bouvier, M.; Devi, L.; Filizola, M.; Javitch, J.A.; Lohse, M.J.; Milligan, G.; Palczewski, K.; Parmentier, M.; et al. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXVII. Recommendations for the recognition and nomenclature of G protein-coupled receptor heteromultimers. Pharmacol. Rev. 2007, 59, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, S.; Guerrini, R.; Balboni, G.; Bianchi, C.; Bryant, S.D.; Cooper, P.S.; Lazarus, L.H. Further studies on the Dmt-Tic pharmacophore: Hydrophobic substituents at the C-terminus endow delta antagonists to manifest mu agonism or mu antagonism. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 5010–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivo-Marin, J.C. Extraction of spots in biological images using multiscale products. Pattern Recogn. 2002, 35, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Derouiche, L.; Pierre, F.; Doridot, S.; Ory, S.; Massotte, D. Heteromerization of Endogenous Mu and Delta Opioid Receptors Induces Ligand-Selective Co-Targeting to Lysosomes. Molecules 2020, 25, 4493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194493
Derouiche L, Pierre F, Doridot S, Ory S, Massotte D. Heteromerization of Endogenous Mu and Delta Opioid Receptors Induces Ligand-Selective Co-Targeting to Lysosomes. Molecules. 2020; 25(19):4493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194493
Chicago/Turabian StyleDerouiche, Lyes, Florian Pierre, Stéphane Doridot, Stéphane Ory, and Dominique Massotte. 2020. "Heteromerization of Endogenous Mu and Delta Opioid Receptors Induces Ligand-Selective Co-Targeting to Lysosomes" Molecules 25, no. 19: 4493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194493
APA StyleDerouiche, L., Pierre, F., Doridot, S., Ory, S., & Massotte, D. (2020). Heteromerization of Endogenous Mu and Delta Opioid Receptors Induces Ligand-Selective Co-Targeting to Lysosomes. Molecules, 25(19), 4493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194493






