Inhibition of TGF-β Signaling in Gliomas by the Flavonoid Diosmetin Isolated from Dracocephalum peregrinum L.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
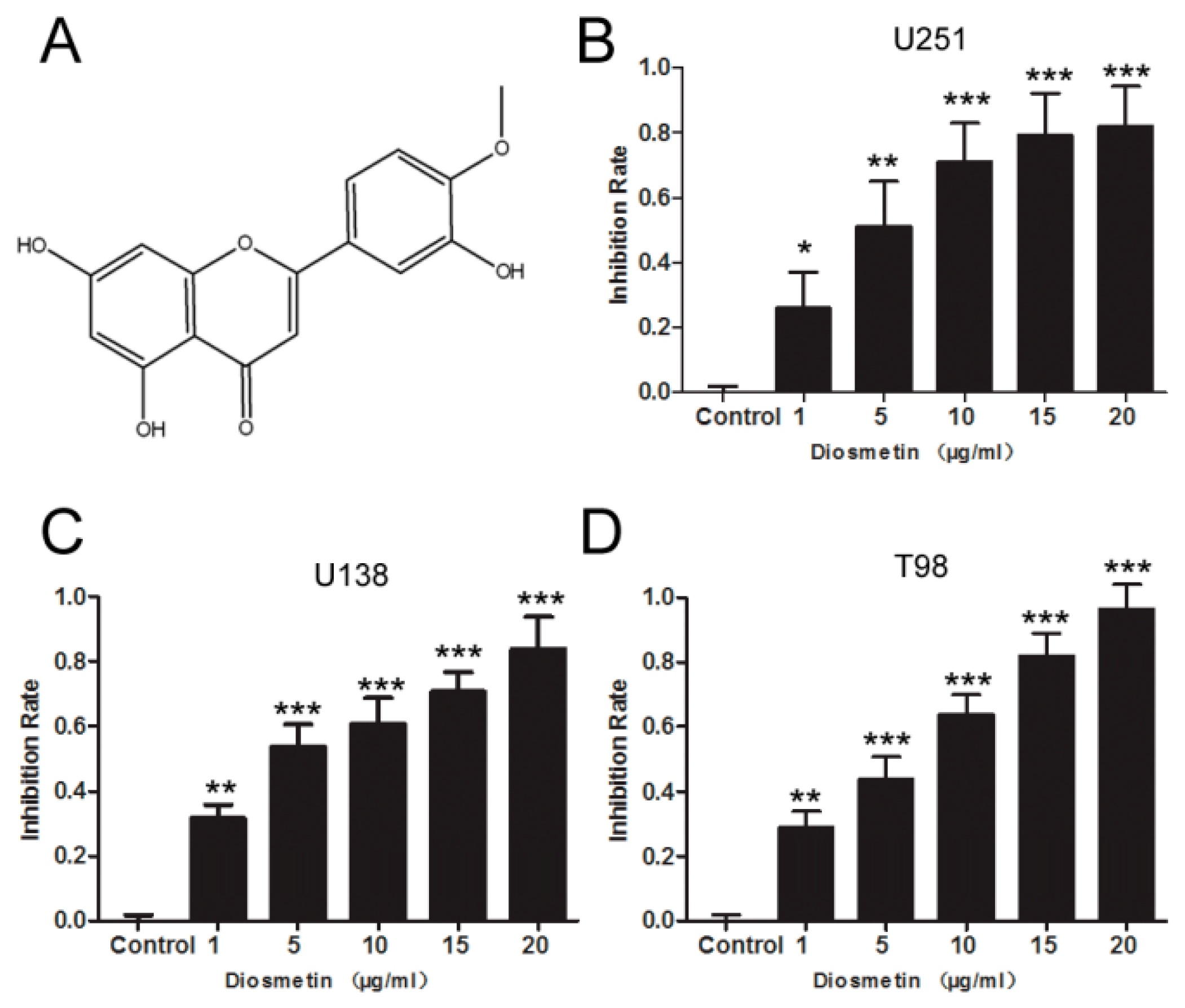
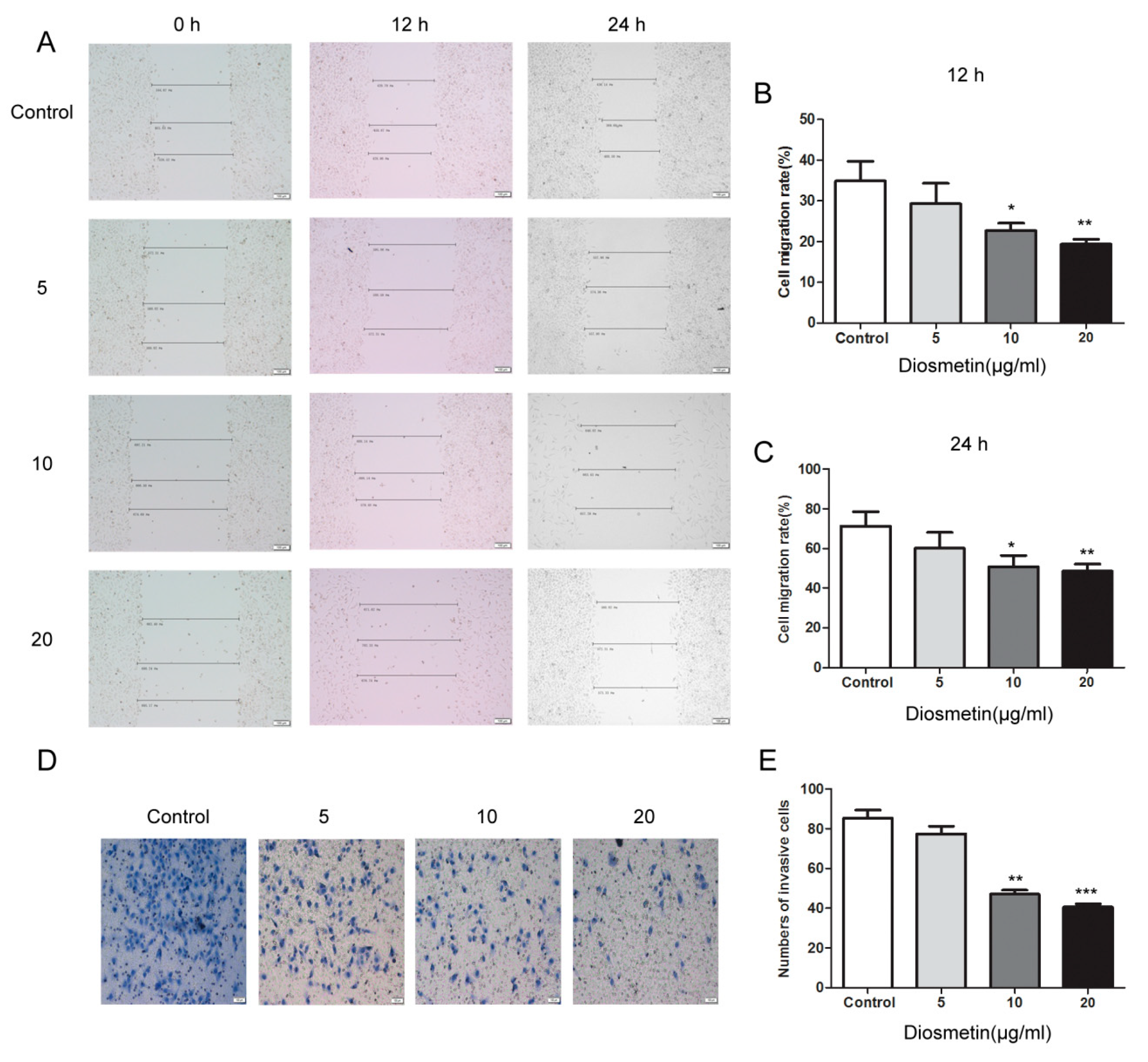
2.1. Diosmetin Inhibits the Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration of Glioma Cells
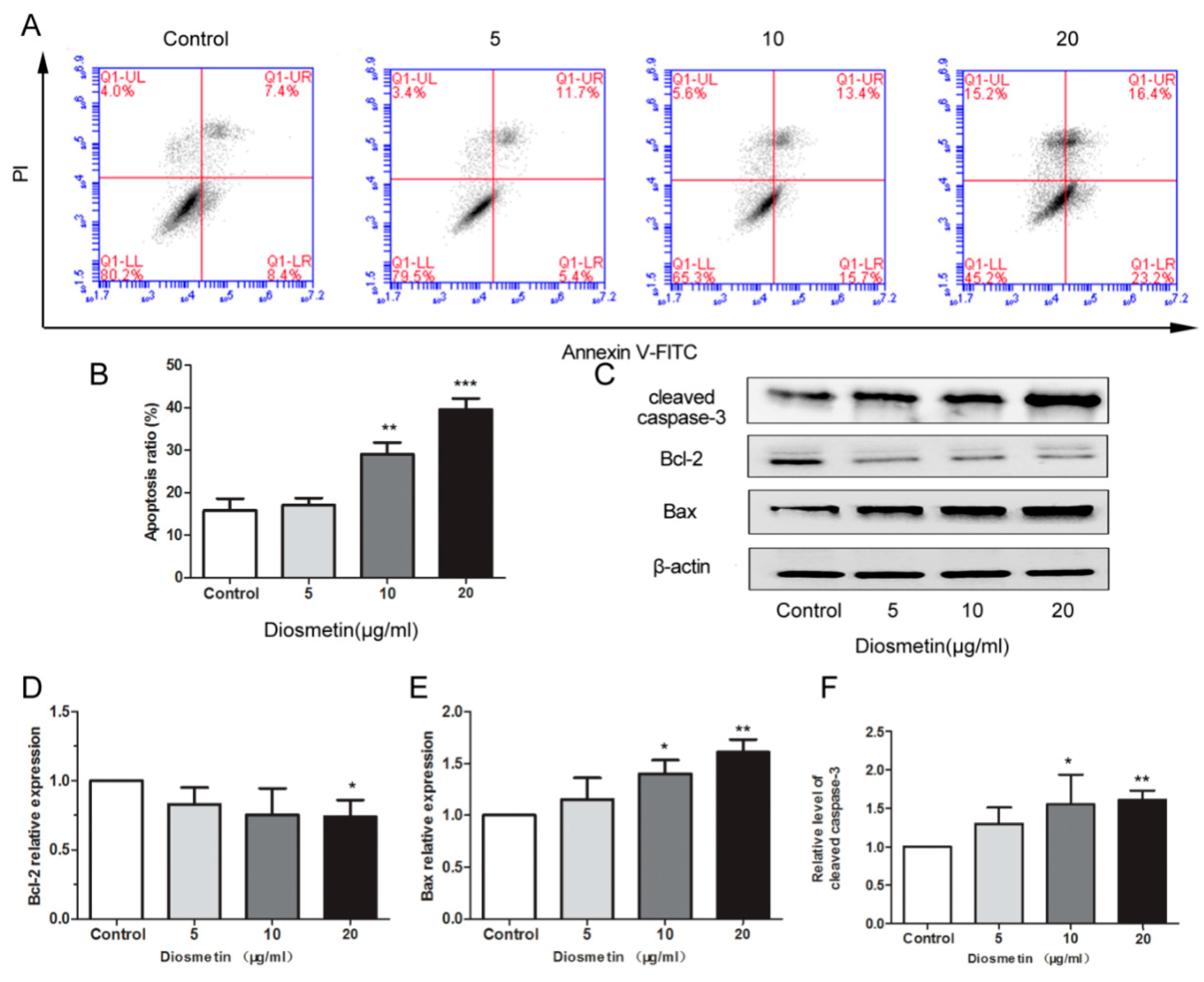
2.2. Diosmetin Induces the Apoptosis of Glioma Cells
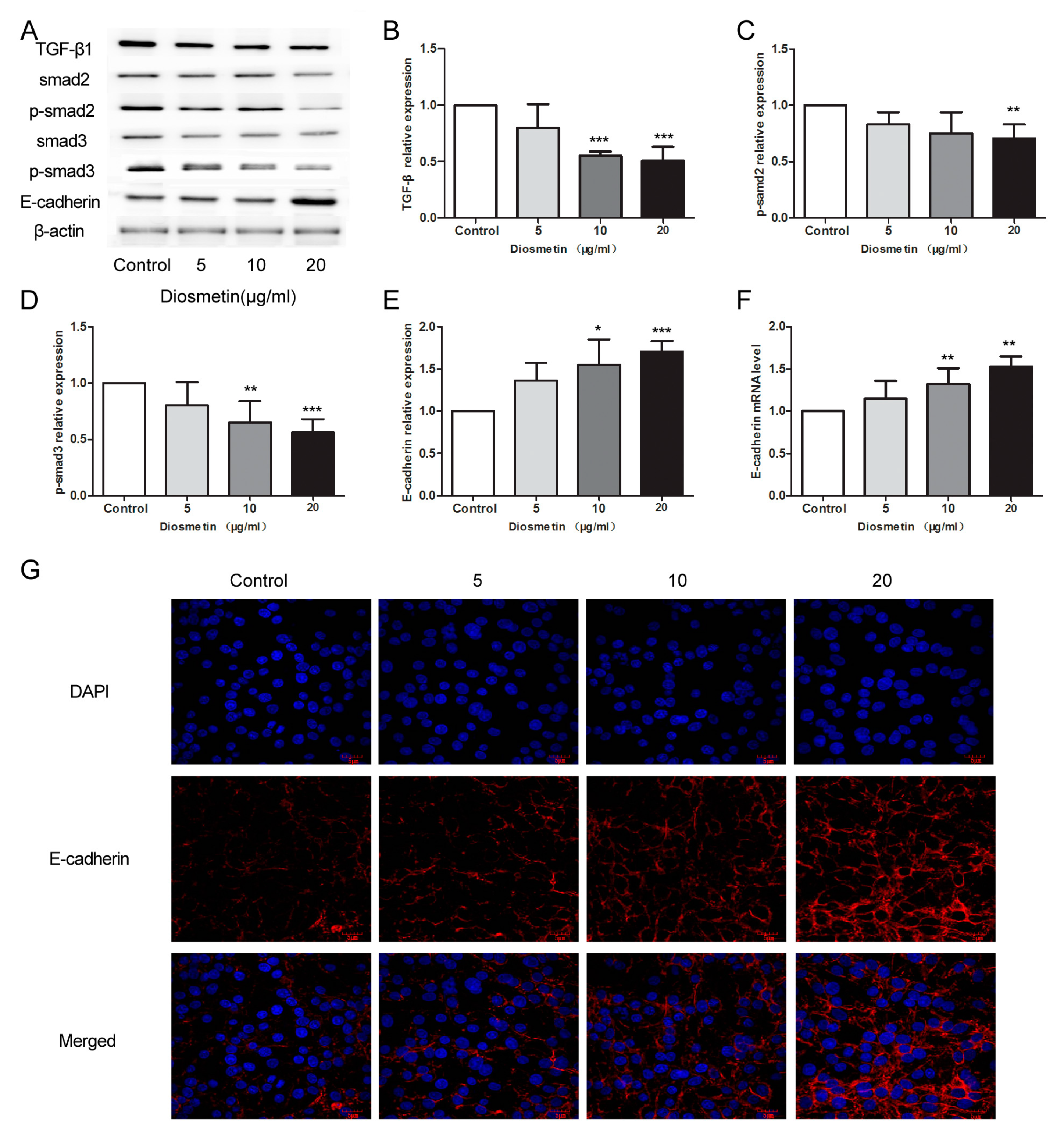
2.3. Diosmetin Leads to Inhibition of the TGF-β Signaling Pathway and Activation of E-Cadherin Expression in Glioma Cells
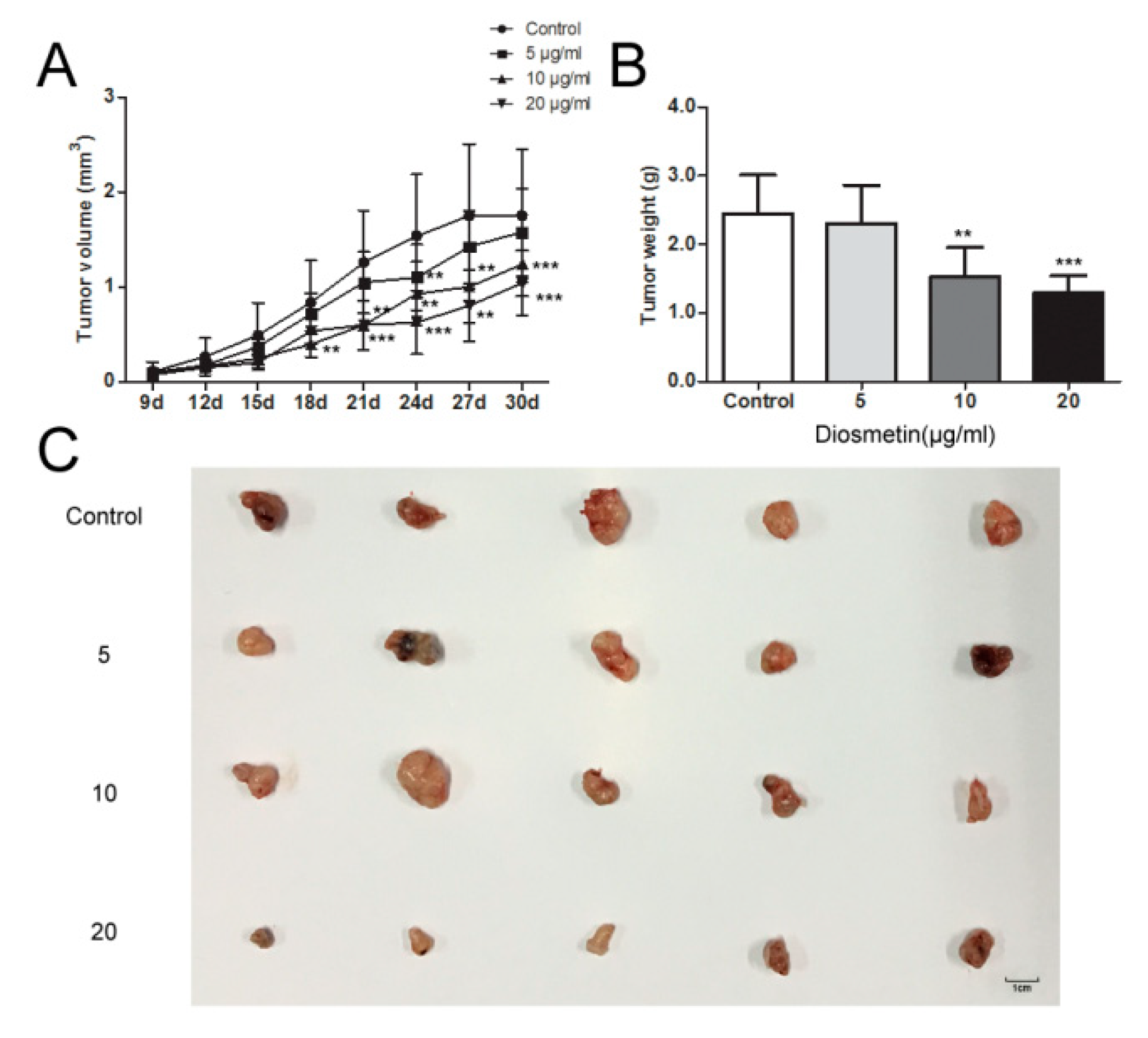
2.4. Diosmetin Inhibits Glioma Tumor Growth In Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Isolation of Diosmetin from D. peregrinum
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. MTT Assay
4.5. Cell Scratch Assay
4.6. Transwell Assay
4.7. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Apoptosis
4.8. Western Blotting
4.9. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.10. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.11. In Vivo Experiments
4.12. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Availability of Data and Materials
Patient Consent for Publication
Abbreviations
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor-β |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-α |
References
- Gladson, C.L.; Prayson, R.A.; Liu, W.M. The pathobiology of glioma tumors. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2010, 5, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, E.M.; Stepien, T.L.; Anderies, B.J.; Plasencia, J.D.; Woolf, E.C.; Scheck, A.C.; Turner, G.H.; Liu, Q.; Frakes, D.; Kodibagkar, V.; et al. Mathematical Analysis of Glioma Growth in a Murine Model. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloughesy, T.F.; Cavenee, W.K.; Mischel, P.S. Glioblastoma: From molecular pathology to targeted treatment. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2014, 9, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X.; Cui, T.; Dai, J. MicroRNA-548c-3p inhibits T98G glioma cell proliferation and migration by downregulating c-Myb. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 3866–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuddapah, V.A.; Robel, S.; Watkins, S.; Sontheimer, H. A neurocentric perspective on glioma invasion. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutwin, M.; Sawosz, E.; Jaworski, S.; Wierzbicki, M.; Strojny, B.; Grodzik, M.; Chwalibog, A. Assessment of the proliferation status of glioblastoma cell and tumour tissue after nanoplatinum treatment. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cockle, J.V.; Bruning-Richardson, A.; Scott, K.J.; Thompson, J.; Kottke, T.; Morrison, E.; Ismail, A.; Carcaboso, A.M.; Rose, A.; Selby, P.; et al. Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Inhibits Pediatric Brain Tumor Migration and Invasion. Mol. Ther. Oncol. 2017, 5, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.J.; Chen, I.L.; Horng, L.Y.; Wu, R.T. Induction of differentiation in rat C6 glioma cells with Saikosaponins. Phytother. Res. 2002, 16, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.C.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Kwon, C.H.; Kim, K.H. Lycii cortex radicis extract inhibits glioma tumor growth in vitro and in vivo through downregulation of the Akt/ERK pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar]
- Evirgen, O.; Gokce, A.; Ozturk, O.H.; Nacar, E.; Onlen, Y.; Ozer, B.; Motor, V.K. Effect of Thymoquinone on Oxidative Stress in Escherichia coli-Induced Pyelonephritis in Rats. Curr. Ther. Res. Clin. Exp. 2011, 72, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yang, F.; Zhao, H.; Fan, W.; Ge, P. Shikonin kills glioma cells through necroptosis mediated by RIP-1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, A.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Kong, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bai, F.; Huang, M. Effect of diosmetin on airway remodeling in a murine model of chronic asthma. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. Shanghai 2015, 47, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhang, X.Q.; Qi, M.J.; Shi, M.Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, K.Z.; Guo, C.; Han, Y.L. Effects of diosmetin on nine cytochrome P450 isoforms, UGTs and three drug transporters in vitro. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 334, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Jung, T.H.; Kim, H.; Jeong, D.; Choi, G.; Park, W.K.; Kong, J.Y.; Jin, M.H.; Cho, H. Inhibition of c-Kit signaling by diosmetin isolated from Chrysanthemum morifolium. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.; Gadewar, M.; Tahilyani, V.; Patel, D.K. A review on pharmacological and analytical aspects of diosmetin: A concise report. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2013, 19, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poor, M.; Veres, B.; Jakus, P.B.; Antus, C.; Montsko, G.; Zrinyi, Z.; Vladimir-Knezevic, S.; Petrik, J.; Koszegi, T. Flavonoid diosmetin increases ATP levels in kidney cells and relieves ATP depleting effect of ochratoxin A. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2014, 132, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roma, A.; Rota, S.G.; Spagnuolo, P.A. Diosmetin Induces Apoptosis of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wan, R.; Yin, G.; Xiong, J.; Hu, Y.; Xing, M.; Cang, X.; Fan, Y.; Xiao, W.; Qiu, L.; et al. Diosmetin ameliorates the severity of cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in mice by inhibiting the activation of the nuclear factor-kappaB. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 2133–2142. [Google Scholar]
- Androutsopoulos, V.P.; Mahale, S.; Arroo, R.R.; Potter, G. Anticancer effects of the flavonoid diosmetin on cell cycle progression and proliferation of MDA-MB 468 breast cancer cells due to CYP1 activation. Oncol. Rep. 2009, 21, 1525–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Li, W.F.; Yu, J.F.; Yi, C.; Huang, W.F. Diosmetin protects against ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury in mice. J. Surg. Res. 2017, 214, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Jia, K.; Yang, Y.; Hao, S.; Lu, C.; Xu, F.; Feng, D.; Zhu, R. Diosmetin Induces Cell Apoptosis by Regulating CYP1A1/CYP1A2 Due to p53 Activation in HepG2 Cells. Protein. Pept. Lett. 2017, 24, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Gong, X.B.; Huang, L.G.; Wang, Z.X.; Wan, R.Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, B.S. Diosmetin exerts anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects to protect against endotoxin-induced acute hepatic failure in mice. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30723–30733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ren, H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Zhu, R. Diosmetin inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by regulating autophagy via the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 4385–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, A.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Kong, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bai, F.; Huang, M. Diosmetin prevents TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via ROS/MAPK signaling pathways. Life Sci. 2016, 153, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oak, C.; Khalifa, A.O.; Isali, I.; Bhaskaran, N.; Walker, E.; Shukla, S. Diosmetin suppresses human prostate cancer cell proliferation through the induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonberg, D.L.; Lubelski, D.; Miller, T.E.; Rich, J.N. Brain tumor stem cells: Molecular characteristics and their impact on therapy. Mol. Asp. Med. 2014, 39, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Liu, J.; Jia, K.; Li, N.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, R. Diosmetin triggers cell apoptosis by activation of the p53/Bcl-2 pathway and inactivation of the Notch3/NF-kappaB pathway in HepG2 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 5122–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschella, G.; Melino, G.; Gambacurta, A. Cell death in cancer in the era of precision medicine. Genes Immun. 2018, 20, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarnescu, O.; Brehar, F.M.; Chivu, M.; Ciurea, A.V. Immunohistochemical localization of caspase-3, caspase-9 and Bax in U87 glioblastoma xenografts. J. Mol. Histol. 2008, 39, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, M.; Acharya, S.; Ghosh, A.; Sarkar, P.; Chatterjee, S.; Kumar, P.; Chaudhuri, S. Bax and Bid act in synergy to bring about T11TS-mediated glioma apoptosis via the release of mitochondrial cytochrome c and subsequent caspase activation. Int. Immunol. 2008, 20, 1489–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja-Khan, N. The role of TGF-beta in polycystic ovary syndrome. Reprod. Sci. 2014, 21, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, S.; Lin, R.; Yi, X. Pttg1 inhibits TGFbeta signaling in breast cancer cells to promote their growth. Tumour. Biol. 2015, 36, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araz, O.; Demirci, E.; Ucar, E.Y.; Calik, M.; Karaman, A.; Durur-Subasi, I.; Orsal, E.; Subasi, M.; Daloglu, F.; Akgun, M. Roles of Ki-67, p53, transforming growth factor-beta and lysyl oxidase in the metastasis of lung cancer. Respirology 2014, 19, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drabsch, Y.; Ten Dijke, P. TGF-beta signalling and its role in cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012, 31, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Dai, Q.; Min, Z.; Zhang, M. [Transforming growth factor beta1 enhances the invasiveness of human glioma cell line via ERK/MAPK pathway]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2013, 33, 1744–1747. [Google Scholar]
- Kamato, D.; Burch, M.L.; Piva, T.J.; Rezaei, H.B.; Rostam, M.A.; Xu, S.; Zheng, W.; Little, P.J.; Osman, N. Transforming growth factor-beta signalling: Role and consequences of Smad linker region phosphorylation. Cell Signal. 2013, 25, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Lee, M.; Jang, S.W. Celastrol inhibits TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by inhibiting Snail and regulating E-cadherin expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 437, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Miyajima, M.; Jiang, C.; Arai, H. Expression of TGF-betas and TGF-beta type II receptor in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 413, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, M.; Hirai, S.; Yasumoto, M.; Nishikawa, K.; Nagata, S.; Otsuka, M.; Kamihagi, K.; Kato, I. Soluble fragments of e-cadherin cell-adhesion molecule increase in urinary-excretion of cancer-patients, potentially indicating its shedding from epithelial tumor-cells. Int. J. Oncol. 1994, 5, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Kitajima, Y.; Edakuni, G.; Sato, S.; Miyazaki, K. Abnormal expression of E-cadherin and beta-catenin may be a molecular marker of submucosal invasion and lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2002, 89, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Min, S.; Xiaoyan, X.; Fanghui, P.; Yamei, W.; Xiaoli, Y.; Feng, W. The glioma-associated oncogene homolog 1 promotes epithelial--mesenchymal transition in human esophageal squamous cell cancer by inhibiting E-cadherin via Snail. Cancer Gene. Ther. 2013, 20, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Not available. |
| Pos. | δH (mult., J in Hz) | δC |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | - | 163.50 |
| 3 | 6.73 (s) | 103.72 |
| 4 | - | 181.66 |
| 5 | 12.91 | 157.29 |
| 6 | 6.18 (d, 2.0 Hz) | 98.84 |
| 7 | 10.80 | 164.17 |
| 8 | 6.45(d, 1.6 Hz) | 93.87 |
| 9 | - | 161.43 |
| 10 | - | 103.50 |
| 1′ | - | 118.68 |
| 2′ | 7.41 (d, 2.4 Hz) | 112.93 |
| 3′ | 9.41 | 146.76 |
| 4′ | - | 151.11 |
| 5′ | 7.07 (1 H, d, 8.4 Hz) | 112.14 |
| 6′ | 7.53 (1 H, dd, 2.0, 8.4 Hz) | 122.98 |
| -OCH3 | 3.85 (3 H, s) | 55.74 |
| Primer Name | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| E-cadherin F | ATGCCGCCATCGCTTACAC |
| E-cadherin R | CGACGTTAGCCTCGTTCTCA |
| β-actin F | CTTAGTTGCGTTACACCCTTTCTTG |
| β-actin R | CTGTCACCTTCACCGTTCCAGTTT |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Y.; Liu, X.; Gao, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Inhibition of TGF-β Signaling in Gliomas by the Flavonoid Diosmetin Isolated from Dracocephalum peregrinum L. Molecules 2020, 25, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010192
Yan Y, Liu X, Gao J, Wu Y, Li Y. Inhibition of TGF-β Signaling in Gliomas by the Flavonoid Diosmetin Isolated from Dracocephalum peregrinum L. Molecules. 2020; 25(1):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010192
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Yuli, Xingyu Liu, Jie Gao, Yin Wu, and Yuxin Li. 2020. "Inhibition of TGF-β Signaling in Gliomas by the Flavonoid Diosmetin Isolated from Dracocephalum peregrinum L." Molecules 25, no. 1: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010192
APA StyleYan, Y., Liu, X., Gao, J., Wu, Y., & Li, Y. (2020). Inhibition of TGF-β Signaling in Gliomas by the Flavonoid Diosmetin Isolated from Dracocephalum peregrinum L. Molecules, 25(1), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010192






