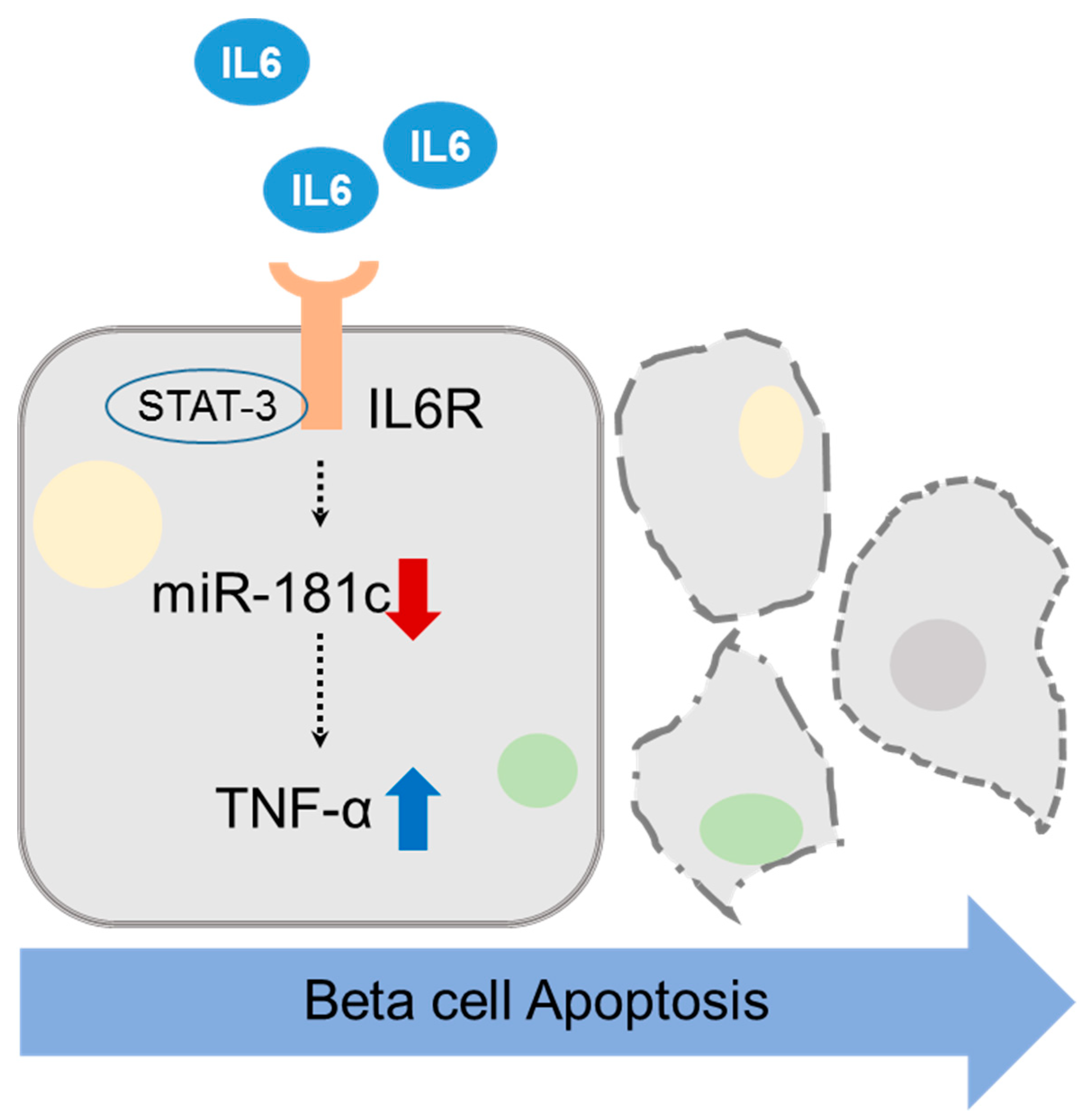
MicroRNA-181c Inhibits Interleukin-6-mediated Beta Cell Apoptosis by Targeting TNF-α Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
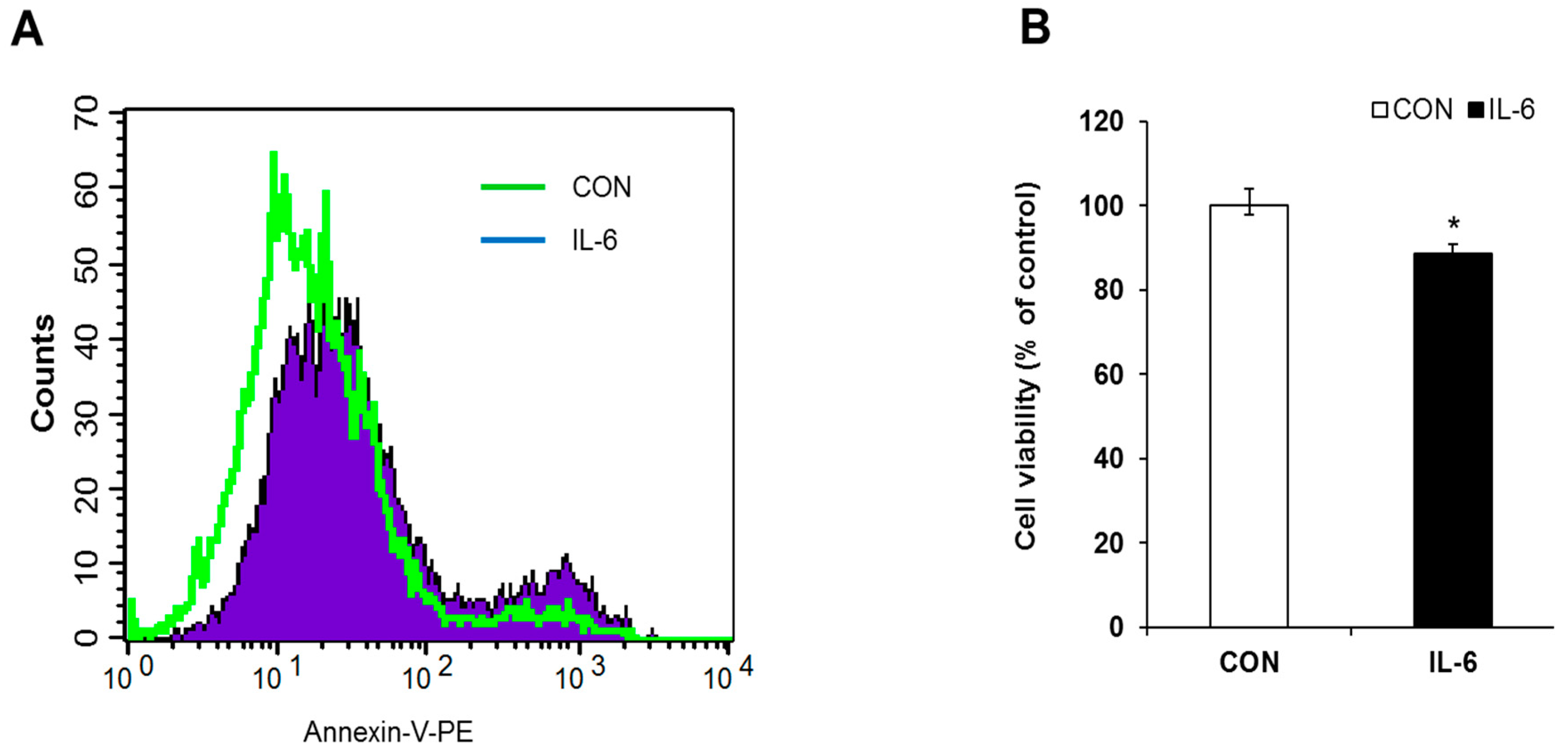
2.1. Induction of Apoptosis in IL-6 Treated Cells
2.2. Differential Gene Expression during Apoptosis in IL-6-Treated Cells
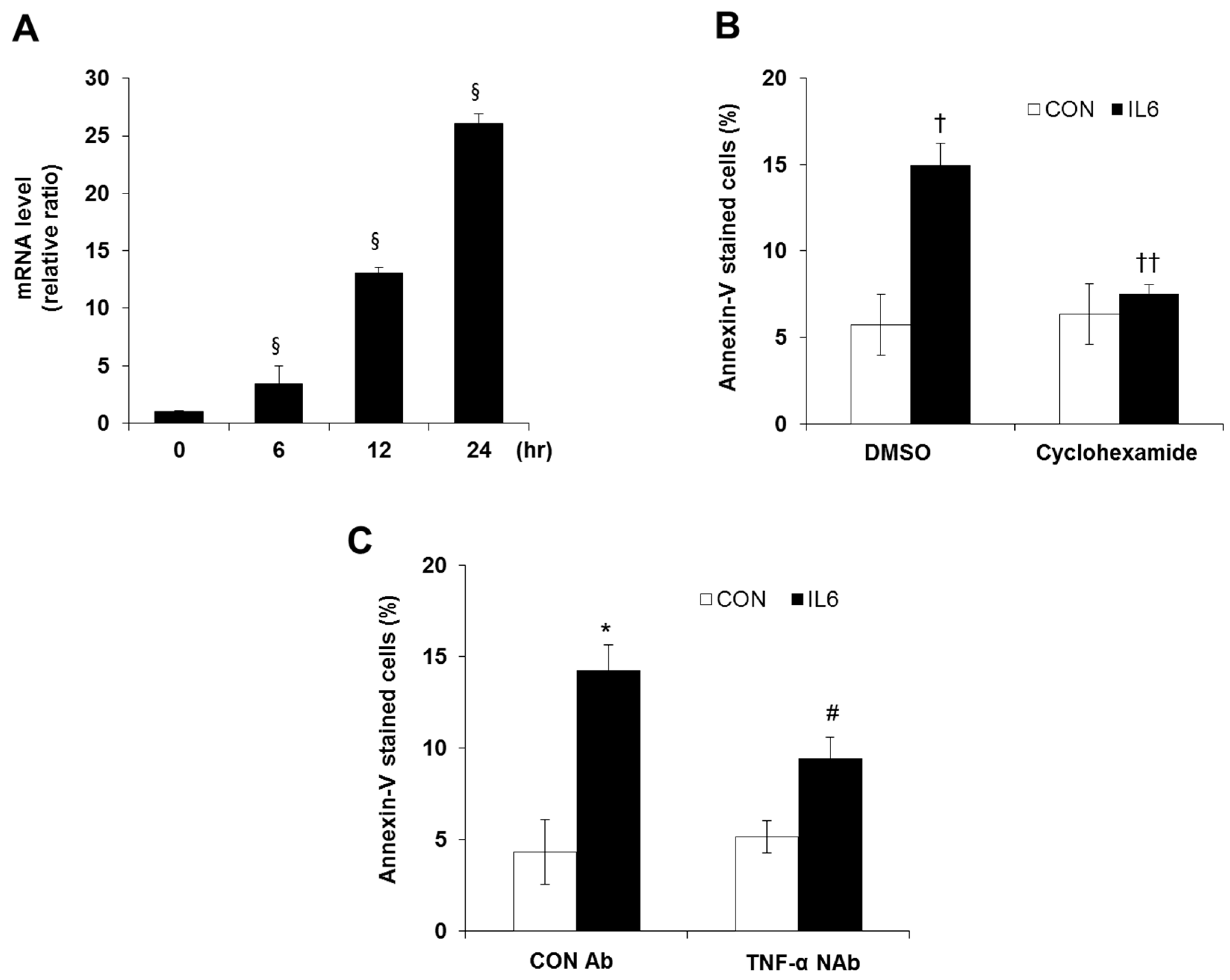
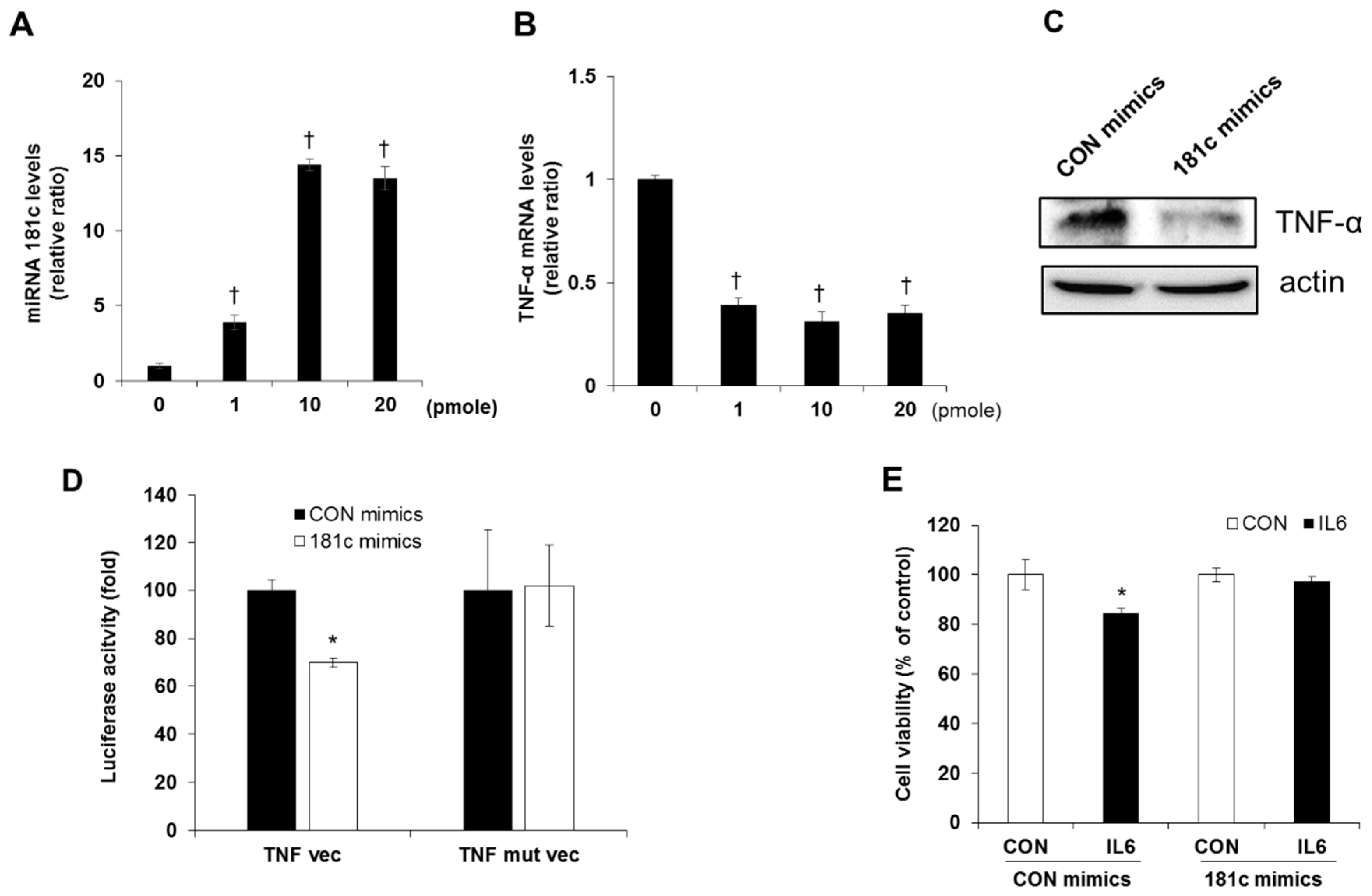
2.3. Involvement of TNF-α Expression Regulation in IL-6-induced Beta Cell Apoptosis
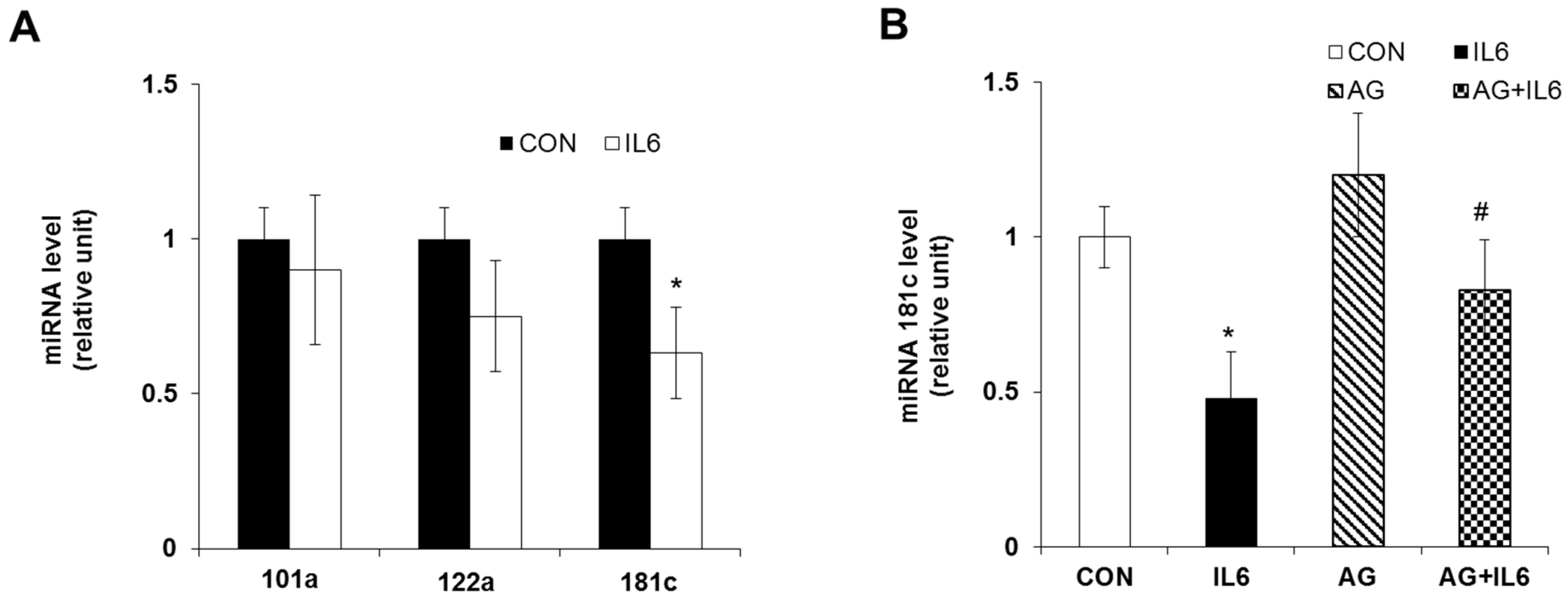
2.4. Downregulation of miR-181c during IL-6-Induced Beta Cell Apoptosis
2.5. Inhibition of IL-6 Induced Beta Cell Cytotoxicity via miR-181c Upregulation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cells
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. RNA Isolation and RT2 Profiler PCR Array
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.6. miRNA Isolation and Quantitative RT-PCR
4.7. Annexin V-PE Staining
4.8. Transfection of MicroRNA Mimics
4.9. Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wellen, K.E.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, L.L.; Garrie, K.; Turner, M.D. Type 2 diabetes - an autoinflammatory disease driven by metabolic stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 3805–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcellini, W.; Rizzardi, G.P.; Borghi, M.O.; Nicoletti, F.; Fain, C.; Del Papa, N.; Meroni, P.L. In vitro type-1 and type-2 cytokine production in systemic lupus erythematosus: Lack of relationship with clinical disease activity. Lupus 1996, 5, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hein, G.E.; Kohler, M.; Oelzner, P.; Stein, G.; Franke, S. The advanced glycation end product pentosidine correlates to il-6 and other relevant inflammatory markers in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2005, 26, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, I.L.; Kay, T.W.; Oxbrow, L.; Harrison, L.C. Essential role for interferon-gamma and interleukin-6 in autoimmune insulin-dependent diabetes in nod/wehi mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 87, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauer, J.; Denson, J.L.; Bruning, J.C. Versatile functions for il-6 in metabolism and cancer. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, A.D.; Manson, J.E.; Rifai, N.; Buring, J.E.; Ridker, P.M. C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 2001, 286, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.L.; Qiao, Y.C.; Pan, Y.H.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Wang, Y.H.; Geng, L.J.; Zhao, H.L.; Zhang, X.X. Correlation between serum interleukin-6 level and type 1 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cytokine 2017, 94, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klover, P.J.; Clementi, A.H.; Mooney, R.A. Interleukin-6 depletion selectively improves hepatic insulin action in obesity. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 3417–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, E.Y.; Jun, H.S. Interleukin-6 treatment induces beta-cell apoptosis via stat-3-mediated nitric oxide production. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2011, 27, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglia, L.A.; Ayres, T.M.; Wong, G.H.; Goeddel, D.V. A novel domain within the 55 kd tnf receptor signals cell death. Cell 1993, 74, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizuka, N.; Yagui, K.; Tokuyama, Y.; Yamada, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Miyazaki, J.; Hashimoto, N.; Makino, H.; Saito, Y.; Kanatsuka, A. Tumor necrosis factor alpha signaling pathway and apoptosis in pancreatic beta cells. Metabolism 1999, 48, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroney, P.A.; Yu, Y.; Fisher, J.; Nilsen, T.W. Evidence that micrornas are associated with translating messenger rnas in human cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006, 13, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.E. Functional aspects of animal micrornas. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Xing, W.; Xie, L. Regulatory roles of micrornas in diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaPierre, M.P.; Stoffel, M. Micrornas as stress regulators in pancreatic beta cells and diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 1010–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filios, S.R.; Shalev, A. Beta-cell micrornas: Small but powerful. Diabetes 2015, 64, 3631–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; You, W.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhan, S.; Zhu, Y.; Han, X. Glucolipotoxicity-inhibited mir-299-5p regulates pancreatic beta-cell function and survival. Diabetes 2018, 67, 2280–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tu, Y.; Shen, H.; Dai, Z.; Lin, J.; Zhou, Z. Mir-101a and mir-30b contribute to inflammatory cytokine-mediated beta-cell dysfunction. Lab. Investig. 2015, 95, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcan, S. Minireview: Microrna function in pancreatic beta cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 28, 1922–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z. Mirnas: Novel regulators of autoimmunity-mediated pancreatic beta-cell destruction in type 1 diabetes. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belgardt, B.F.; Ahmed, K.; Spranger, M.; Latreille, M.; Denzler, R.; Kondratiuk, N.; von Meyenn, F.; Villena, F.N.; Herrmanns, K.; Bosco, D.; et al. The microrna-200 family regulates pancreatic beta cell survival in type 2 diabetes. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.J.; Wu, X.Y.; Hong, Z.; Wei, W.S. Microrna-181c negatively regulates the inflammatory response in oxygen-glucose-deprived microglia by targeting toll-like receptor 4. J. Neurochem. 2015, 132, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cnop, M.; Welsh, N.; Jonas, J.C.; Jorns, A.; Lenzen, S.; Eizirik, D.L. Mechanisms of pancreatic beta-cell death in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: Many differences, few similarities. Diabetes 2005, 54 (Suppl. 2), S97–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donath, M.Y.; Boni-Schnetzler, M.; Ellingsgaard, H.; Ehses, J.A. Islet inflammation impairs the pancreatic beta-cell in type 2 diabetes. Physiology (Bethesda) 2009, 24, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, K.; Nagai, R. Islet inflammation in type 2 diabetes and physiology. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightfoot, Y.L.; Chen, J.; Mathews, C.E. Immune-mediated beta-cell death in type 1 diabetes: Lessons from human beta-cell lines. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 42, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepom, G.T.; Ehlers, M.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Anti-cytokine therapies in t1d: Concepts and strategies. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 149, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, N.; Kishimoto, T. Humanized antihuman il-6 receptor antibody, tocilizumab. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2008, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, C.A.; Jones, S.A. Il-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allocca, M.; Jovani, M.; Fiorino, G.; Schreiber, S.; Danese, S. Anti-il-6 treatment for inflammatory bowel diseases: Next cytokine, next target. Curr. Drug Targets 2013, 14, 1508–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donath, M.Y.; Storling, J.; Maedler, K.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Inflammatory mediators and islet beta-cell failure: A link between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. J. Mol. Med. (Berl.) 2003, 81, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.A.; Lee, M.S. Recent progress in research on beta-cell apoptosis by cytokines. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2009, 14, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappell, V.L.; Le, L.X.; LaGrone, L.; Mileski, W.J. Stat proteins play a role in tumor necrosis factor alpha gene expression. Shock 2000, 14, 400–402; discussion 402–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastiani, G.; Po, A.; Miele, E.; Ventriglia, G.; Ceccarelli, E.; Bugliani, M.; Marselli, L.; Marchetti, P.; Gulino, A.; Ferretti, E.; et al. Microrna-124a is hyperexpressed in type 2 diabetic human pancreatic islets and negatively regulates insulin secretion. Acta Diabetol. 2015, 52, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roggli, E.; Britan, A.; Gattesco, S.; Lin-Marq, N.; Abderrahmani, A.; Meda, P.; Regazzi, R. Involvement of micrornas in the cytotoxic effects exerted by proinflammatory cytokines on pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 2010, 59, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Wu, Y.; Ye, S. Mir-181c restrains nitration stress of endothelial cells in diabetic db/db mice through inhibiting the expression of foxo1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 486, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, S.; Yuan, S.; Yun, C.; Hui, H.; Mao, P.; Wen, F.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Q. Serum mirna biomarkers serve as a fingerprint for proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 1733–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, G.; Guo, D.; Bai, X. Mir-181c-3p and -5p promotes high-glucose-induced dysfunction in human umbilical vein endothelial cells by regulating leukemia inhibitory factor. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.; Shrivastava, S.; Bhanja Chowdhury, J.; Ray, R.; Ray, R.B. Transcriptional suppression of mir-181c by hepatitis c virus enhances homeobox a1 expression. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7929–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulos, D.; Jaeger, S.A.; Hirsch, H.A.; Bulyk, M.L.; Struhl, K. Stat3 activation of mir-21 and mir-181b-1 via pten and cyld are part of the epigenetic switch linking inflammation to cancer. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schonrock, N.; Humphreys, D.T.; Preiss, T.; Gotz, J. Target gene repression mediated by mirnas mir-181c and mir-9 both of which are down-regulated by amyloid-beta. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 46, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguibneva, I.; Ameyar-Zazoua, M.; Polesskaya, A.; Ait-Si-Ali, S.; Groisman, R.; Souidi, M.; Cuvellier, S.; Harel-Bellan, A. The microrna mir-181 targets the homeobox protein hox-a11 during mammalian myoblast differentiation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Wang, L.; Li, F.; Gao, X.; Wei, X.; Liu, Z. Mir181c inhibits ovarian cancer metastasis and progression by targeting prkcd expression. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 15198–15205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Dong, L.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Hong, Z.; Wei, W.S. The microrna mir-181c controls microglia-mediated neuronal apoptosis by suppressing tumor necrosis factor. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, P.; Agirre, X.; Garate, L.; Banos, R.; Alvarez, L.; San Jose-Eneriz, E.; Badell, I.; Casado, J.A.; Garin, M.; Prosper, F.; et al. Down-regulated expression of hsa-mir-181c in fanconi anemia patients: Implications in tnfalpha regulation and proliferation of hematopoietic progenitor cells. Blood 2012, 119, 3042–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |
| Gene Symbol | Name of Gene | Fold Up-Regulation (IL-6-Treated vs. Control) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor (TNF superfamily, member 2) | 92.7929 | 0.001 |
| Tlr2 | Toll-like receptor 2 | 21.3735 | 0.009 |
| Ltb | Lymphotoxin beta (TNF superfamily, member 3) | 17.7839 | 0.003 |
| Birc3 | Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 3 | 11.4395 | 0.016 |
| Socs3 | Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 | 9.4656 | 0.01 |
| Casp4 | Caspase 4, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase | 7.9376 | 0.009 |
| Igf1r | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor | 5.9825 | 0.004 |
| Plg | Plasminogen | 4.1543 | 0.001 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, Y.S.; Bae, G.D.; Park, E.-Y.; Jun, H.-S. MicroRNA-181c Inhibits Interleukin-6-mediated Beta Cell Apoptosis by Targeting TNF-α Expression. Molecules 2019, 24, 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071410
Oh YS, Bae GD, Park E-Y, Jun H-S. MicroRNA-181c Inhibits Interleukin-6-mediated Beta Cell Apoptosis by Targeting TNF-α Expression. Molecules. 2019; 24(7):1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071410
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Yoon Sin, Gong Deuk Bae, Eun-Young Park, and Hee-Sook Jun. 2019. "MicroRNA-181c Inhibits Interleukin-6-mediated Beta Cell Apoptosis by Targeting TNF-α Expression" Molecules 24, no. 7: 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071410
APA StyleOh, Y. S., Bae, G. D., Park, E.-Y., & Jun, H.-S. (2019). MicroRNA-181c Inhibits Interleukin-6-mediated Beta Cell Apoptosis by Targeting TNF-α Expression. Molecules, 24(7), 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071410






