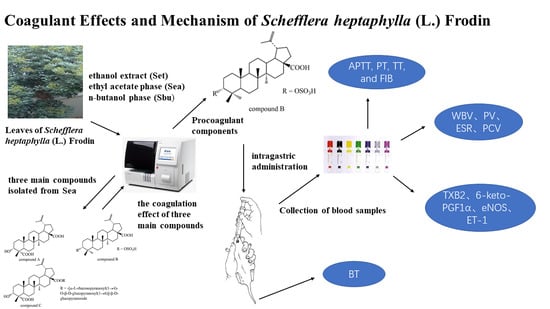
Coagulant Effects and Mechanism of Schefflera heptaphylla (L.) Frodin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
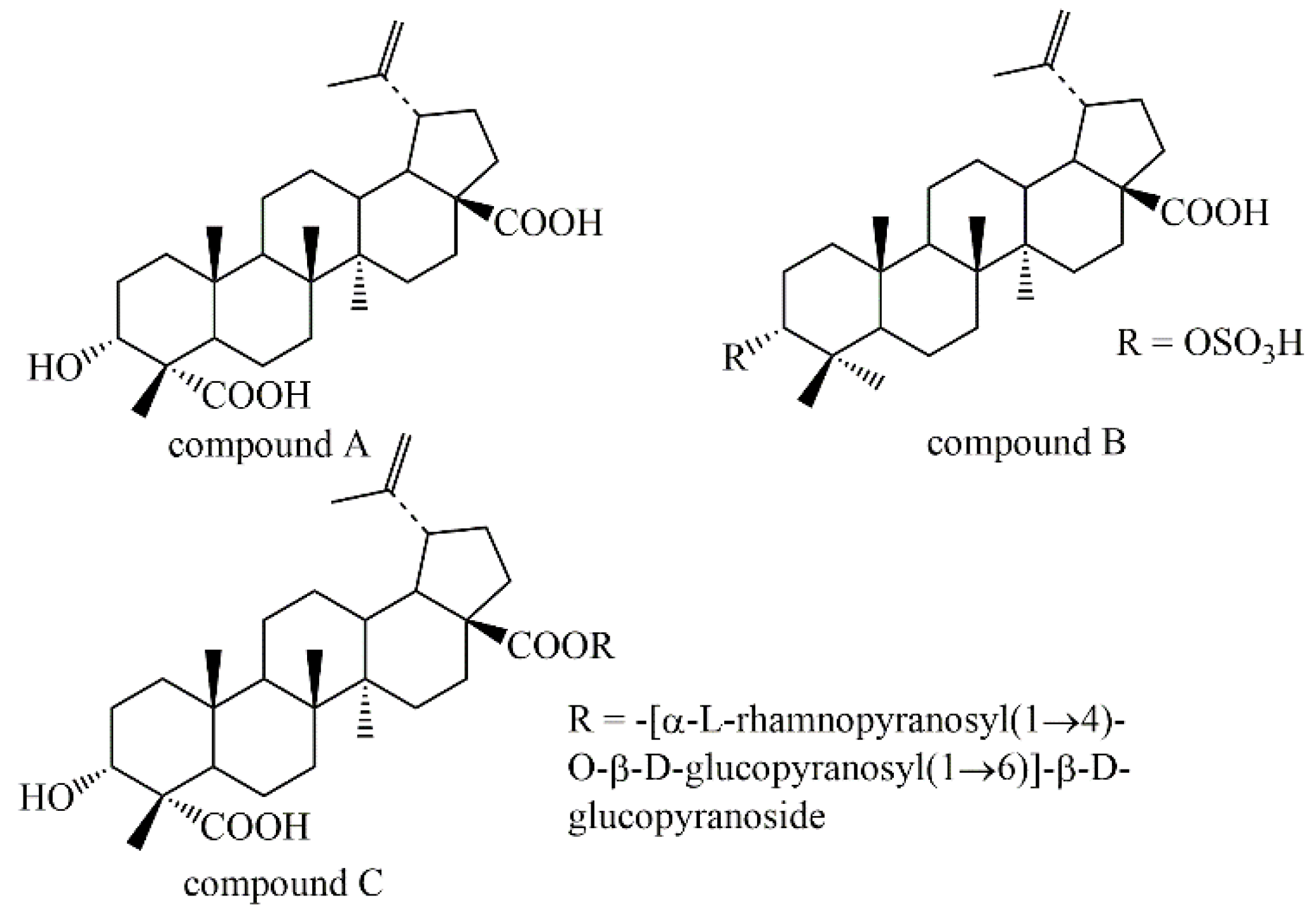
2.1. Isolation and Characterization
2.2. The Pro-Coagulant Effect of S. heptaphylla Extracts In Vitro
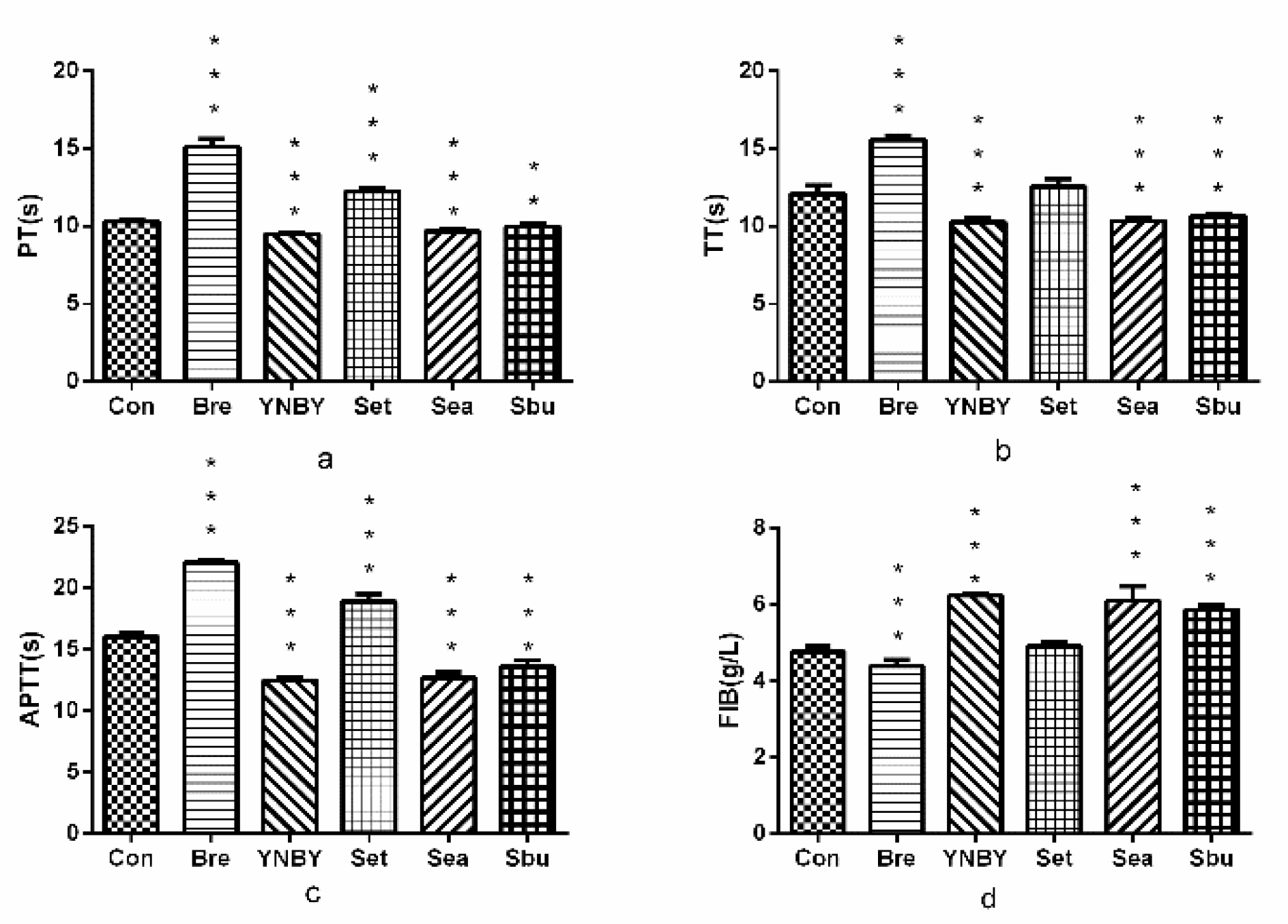
2.2.1. Effects on Plasma Coagulation Parameters In Vitro
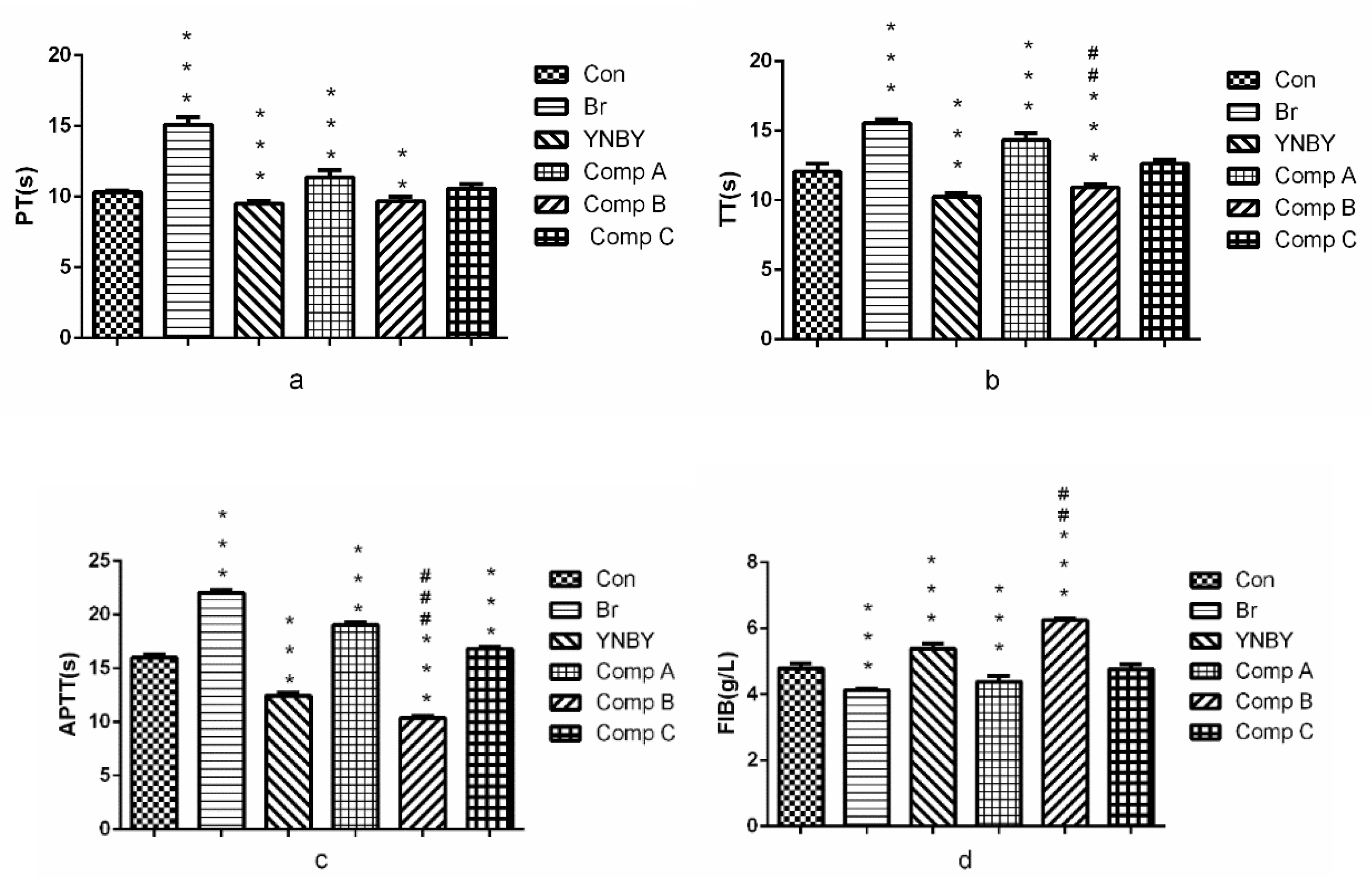
2.2.2. The Coagulation Effect of Compound A–C in vitro
2.3. The Pro-Coagulant Effect of S. heptaphylla Extracts and Compound B In Vivo
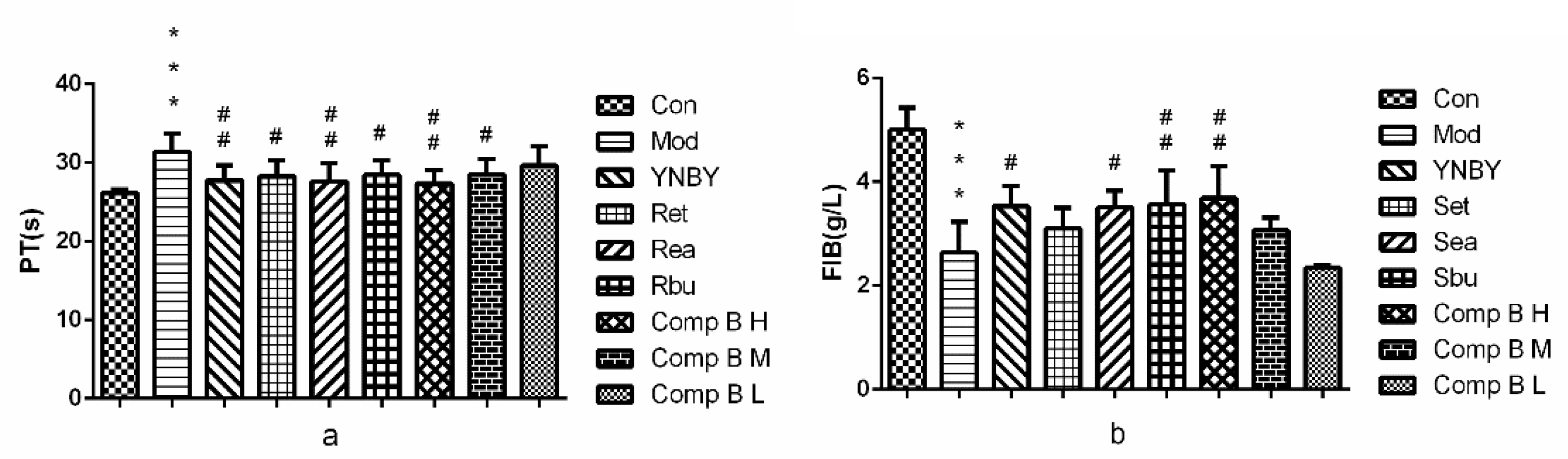
2.3.1. Effects on Plasma Coagulation Parameters
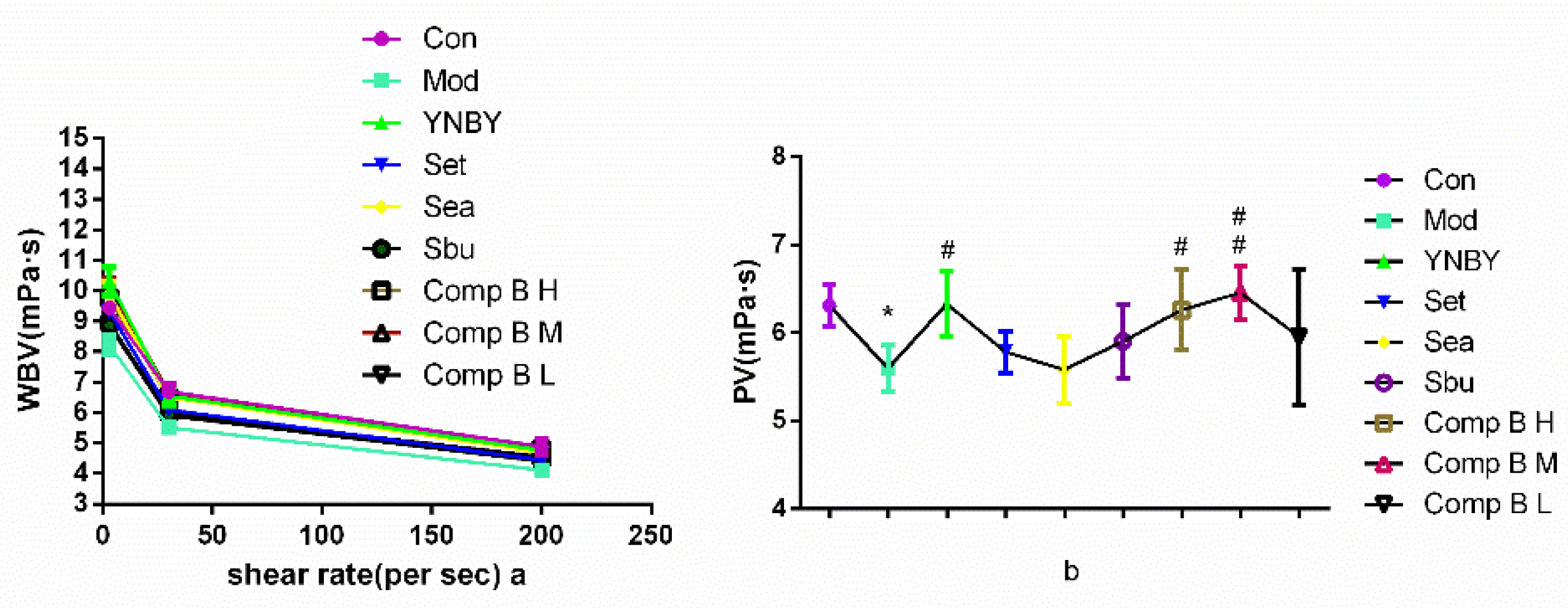
2.3.2. Effects on Whole Blood Viscosity (WBV) and Plasma Viscosity (PV)
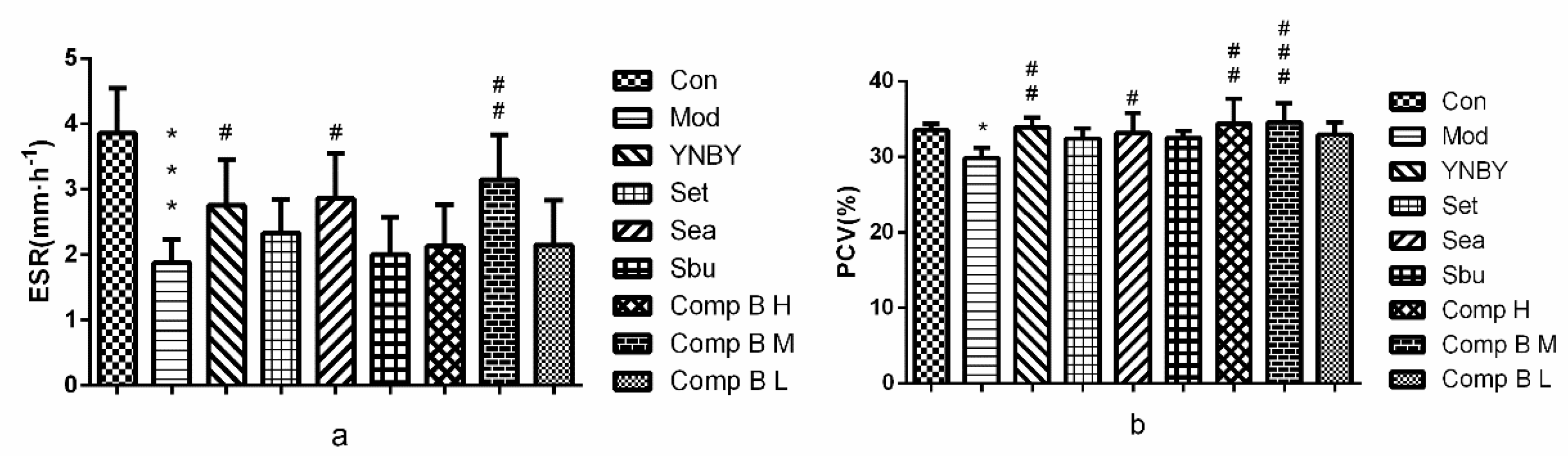
2.3.3. Effects of S. heptaphylla Extracts and Compound B on ESR and PCV
2.3.4. Effects of S. heptaphylla on Tail Bleeding Time
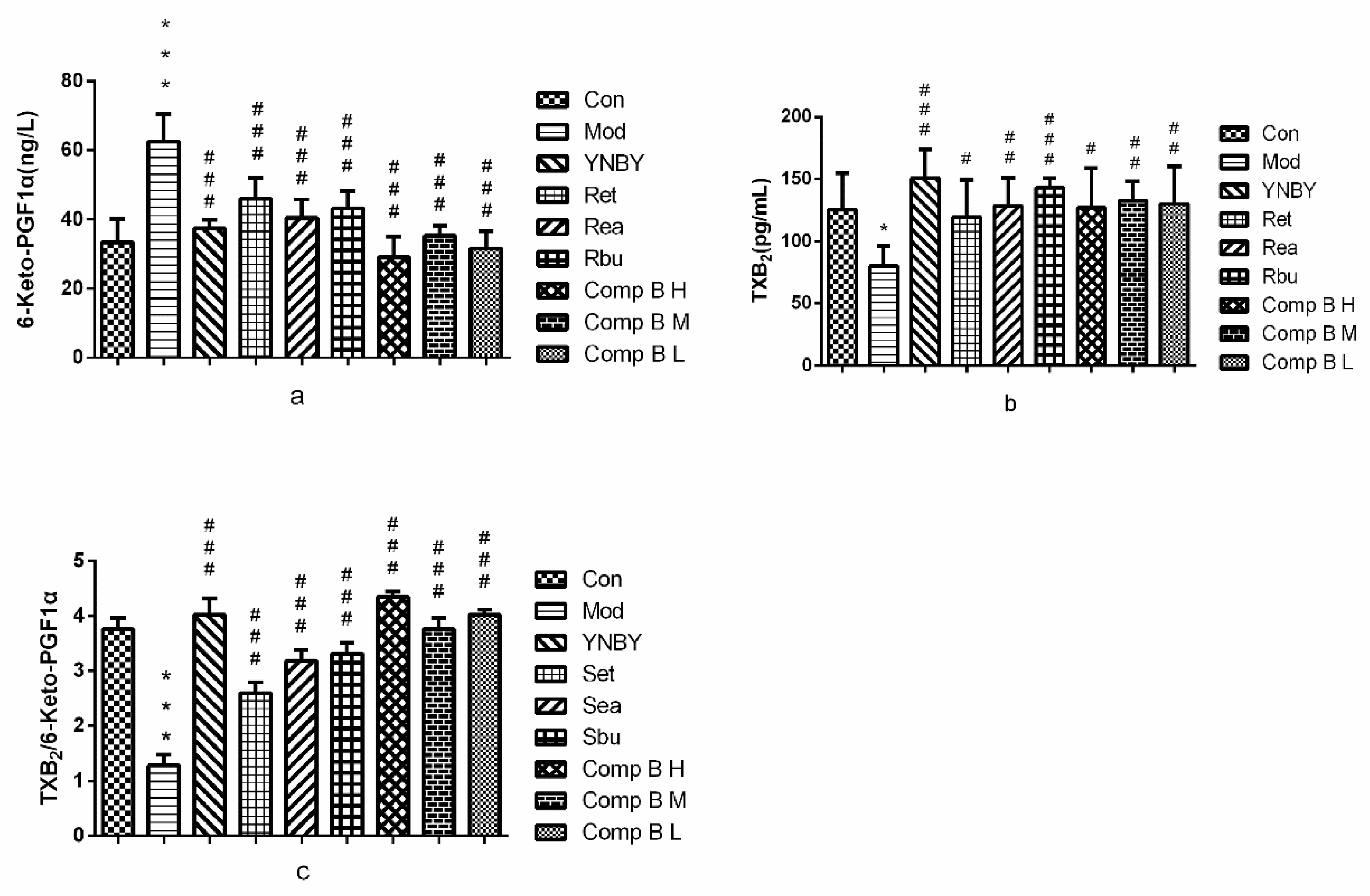
2.3.5. TXB2 and 6-keto-PGF1α in Serum
2.3.6. ET-1 and eNOS In Serum
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.1.1. Drugs and Reagents
3.1.2. Plant Material
3.1.3. Animal
3.2. Experimental
3.2.1. Extraction and Isolation
3.2.2. Plasma Anticoagulation Assay In Vitro
3.2.3. Biological Activity Assays In Vivo
3.2.4. Bleeding Time Assay
3.3. Collection of Blood Samples
4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APTT | activated partial thromboplastin time |
| PT | prothrombin time |
| TT | thrombin time |
| FIB | plasma fibrinogen |
| 6-keto-PGF1α | 6-keto prostaglandin F1α |
| eNOS | nitric oxide synthase |
| TXB2 | thromboxane B2 |
| ET-1 | endothelin-1 |
| ESR | blood sedimentation |
| PCV | hematocrit |
| WBV | whole blood viscosity |
| PV | plasma viscosity |
References
- Zolotukhin, K.N.; Krüger, P.h.; Samorodov, A.V. Low level of antithrombin III as a warning sign for developing trombotic complications in surgical patients. Creat. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 1, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Lin, C.; Li, A.; Wei, B.; Teng, J.; Li, L. Pro-coagulant Activity of Phenolic Acids Isolated from Blumea riparia. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Chen, T.; Yin, H.; Lin, J.; Zhang, H. In Vitro Effects on Thrombin of Paris Saponins and In Vivo Hemostatic Activity Evaluation of Paris fargesii var. brevipetala. Molecules 2019, 24, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butenas, S.; Mann, K.G. Blood coagulation. Biochemistry 2002, 67, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.L.; Hu, M.Y.; Cao, P.R.; Niu, Y.Y.; Li, C.Q.; Liu, Z.H.; Kang, W.Y. Chemical constituents and coagulation activity of Syringa oblata Lindl flowers. BMC Chem. 2019, 13, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carville, D.G.M.; Guyer, K.E. Coagulation testing (part 1): Current methods and challenges. IVD Technol. 1998, 4, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.L.; Xing, M.M.; Xu, L.T.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Ma, C.Y.; Kang, W.Y. Antithrombotic components of Malus halliana Koehne flowers. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 119, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J. Clinical application of coagulation four indices. Lab. Med. Clin. 2013, 10, 450–452. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, P.P.; Zhu, L.S.; Ma, Q.; Ai, B.; Tian, T. The relationship of HCT between age and ESR. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2017, 38, 209–213. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, P.Y.; Cui, L.L.; Shan, Y.; Kang, W.Y. Antithrombotic effect and mechanism of radix paeoniae rubra. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Wang, P.Y.; Niu, Y.Y.; Chen, J.Q.; Li, C.Q.; Kang, W.Y. Evaluation antithrombotic activity and action mechanism of myricitrin. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 129, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.S.; Lim, K.M.; Kang, S.; Noh, J.Y.; Kim, K.; Bae, O.N.; Chung, J.H. Procoagulant and prothrombotic effects of the herbal medicine, Dipsacus asper and its active ingredient, dipsacus saponin C., on human platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.B.; Wei, J.F.; Kang, W.Y. Antithrombotic effect and mechanism of Rubus spp. Blackberry. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 2000–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homo-Delarche, F.; Bach, J.F.; Dardenne, M. In vitro inhibition of prostaglandin production by azathioprine and 6-merchaptopurine. Prostaglandins 1988, 35, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forstermann, U.; Sessa, W.C. Nitric oxide synthases: Regulation and function. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Förstermann, U. Nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of vascular disease. J. Pathol. 2000, 190, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wallerath, T.; Förstermann, U. Physiological mechanisms regulating the expression of endothelial-type NO synthase. Nitric Oxide 2002, 7, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förstermann, U.; Münzel, T. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular disease: From marvel to menace. Circulation 2006, 113, 13, 1708–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.L.; Huang, Z.; Mashimo, H.; Bloch, K.D.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Bevan, J.A.; Fishman, M.C. Hypertension in mice lacking the gene for endothelial nitric oxide. Nature 1995, 377, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.W. Effect of endothelin receptors, endotheline receptor antagonist on cardiovascular disease. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 2014, 31, 376–380. [Google Scholar]
- Kawanabe, Y.; Nauli, S.M. Endothelin. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, G.; Lischewski, M.; Phiet, H.V.; Preiss, A.; Schmidt, J.; Sung, T.V. 3α-Hydroxy-lup-20(29)-ene-23,28-dioic acid from Schefflera octophylla. Phytochemistry 1982, 21, 1385–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Jiang, R.W.; Ooi, L.S.; But, P.P.; Ooi, V.E. Antiviral triterpenoids from the medicinal plant Schefflera heptaphylla. Phytother Res. 2007, 21, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KITAJIMA, J.; Shindo, M.; Tanako, Y. Two new triterpenoid sulfates from the leaves of Schefflera octophylla. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 714–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.C. Herbal Medicines and Teas of Hong Kong; Commercial Press: Hong Kong, Chnia, 2000; pp. 90–91. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, J.; Lin, R. Chemical constituents and biological activity of Schefflera plant. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2002, 25, 363. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, T.V.; Katalinic, P.; Adam, G. A bidesmosidic triterpenoid saponin from Schefflera octophylla. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 3717–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lischewski, M.; Ty, P.D.; Schmidt, J.; Preiss, A.; Phiet, H.V.; Adam, G. 3α,11α-Dihydroxylup-20(29)-ene-23,28-dioic acid from Schefflera octophylla. Phytochemistry 1984, 23, 1695–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.; Nam, V.V.; Lischewski, M.; Phiet, H.V.; Kuhnt, C.; Adam, G. Long-chain fatty acid esters of 3α-hydroxylup-20(29)-ene-23,28-dioic acid and other triterpenoid constituents from the bark of Schefflera octophylla. Phytochemistry 1984, 23, 2081–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KITAJIMA, J.; Tanako, Y. Two new triterpenoid glycosides from the leaves of Schefflera octophylla. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1989, 37, 2727–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, C.; Ohtani, K.; Kasai, R.; Yamasaki, K. Oleanane and ursane glycosides from Schefflera octophylla. Phytochemistry 1994, 37, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Yang, S.L.; Phillipson, J.D.; Greengrass, P.M.; Bowery, N.G. Four new triterpenoid glycosides from Schefflera bodinieri roots. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.X.; Duan, Y.H.; Dai, Y.; Jiang, R.W.; Ye, W.C.; Li, Y.L. A new ursane-type triterpenoid from Schefflera heptaphylla (L.) Frodin. J. Asian. Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 13, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Tao, S.H.; Zeng, F.L.; Xie, L.W.; Shen, Z.B. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of Schefflera octophylla extracts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 171, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.L.; Yeung, C.M.; Chiu, L.C.; Cen, Y.Z.; Ooi, V.E. Chemical composition and antiproliferative activity of essential oil from the leaves of a medicinal herb, Schefflera heptaphylla. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Ooi, L.S.; Wang, H.; But, P.P.; Ooi, V.E. Antiviral activities of medicinal herbs traditionally used in southern mainland china. Phytother. Res. 2004, 18, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.L.; But, P.P.; Ooi, V.E. Antiviral activity and mode of action of caffeoylquinic acids from Schefflera heptaphylla (L.) Frodin. Antivir. Res. 2005, 68, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.J. Antioxidant activities of extracts from Schefflera. Chin. J. Trop. Crops. 2009, 30, 500–504. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.P.; Dou, D.Q.; Smith, D.C. Studies on chemical constituents of ginseng leaves in North America. Mod. Chin. Med. 2010, 12, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, T.V.; Steglich, W.; Adam, G. Triterpene glycosides from Schefflera octophylla. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Lian, P.L.; Yu, Q.; Wei, J.F.; Kang, W.Y. Antithrombotic mechanism of polysaccharides in Blackberry (Rubus spp.) seeds. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, P.E.; Barrie, R.J.; Pestina, T.I.; Steward, S.A.; Arnold, J.T.; Murti, A.K.; Hutson, N.K.; Jackson, C.W. Prolonged bleeding time with defective platelet filopodia formation in the Wistar Furth rat. Blood 1998, 91, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds A–C are available from the authors. |


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Dong, J.; Liang, Q.; Wang, H.-m.D.; Liu, Z.; Xu, R.; Kang, W. Coagulant Effects and Mechanism of Schefflera heptaphylla (L.) Frodin. Molecules 2019, 24, 4547. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244547
Liu X, Dong J, Liang Q, Wang H-mD, Liu Z, Xu R, Kang W. Coagulant Effects and Mechanism of Schefflera heptaphylla (L.) Frodin. Molecules. 2019; 24(24):4547. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244547
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xuqiang, Jing Dong, Qiongxin Liang, Hui-min David Wang, Zhenhua Liu, Ruian Xu, and Wenyi Kang. 2019. "Coagulant Effects and Mechanism of Schefflera heptaphylla (L.) Frodin" Molecules 24, no. 24: 4547. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244547
APA StyleLiu, X., Dong, J., Liang, Q., Wang, H.-m. D., Liu, Z., Xu, R., & Kang, W. (2019). Coagulant Effects and Mechanism of Schefflera heptaphylla (L.) Frodin. Molecules, 24(24), 4547. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244547