LC–MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Determination of Linarin and Its Metabolites in Rat Plasma and Liver Tissue Samples: Application to Pharmacokinetic and Liver Tissue Distribution Study After Oral Administration of Linarin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Method Development
2.2. Method Validation
2.2.1. Selectivity
2.2.2. Analytical Curve and Lower Limit of Quantification
2.2.3. Accuracy and Precision
2.2.4. Extraction Recovery and Matrix Effects
2.2.5. Stability
2.3. Application
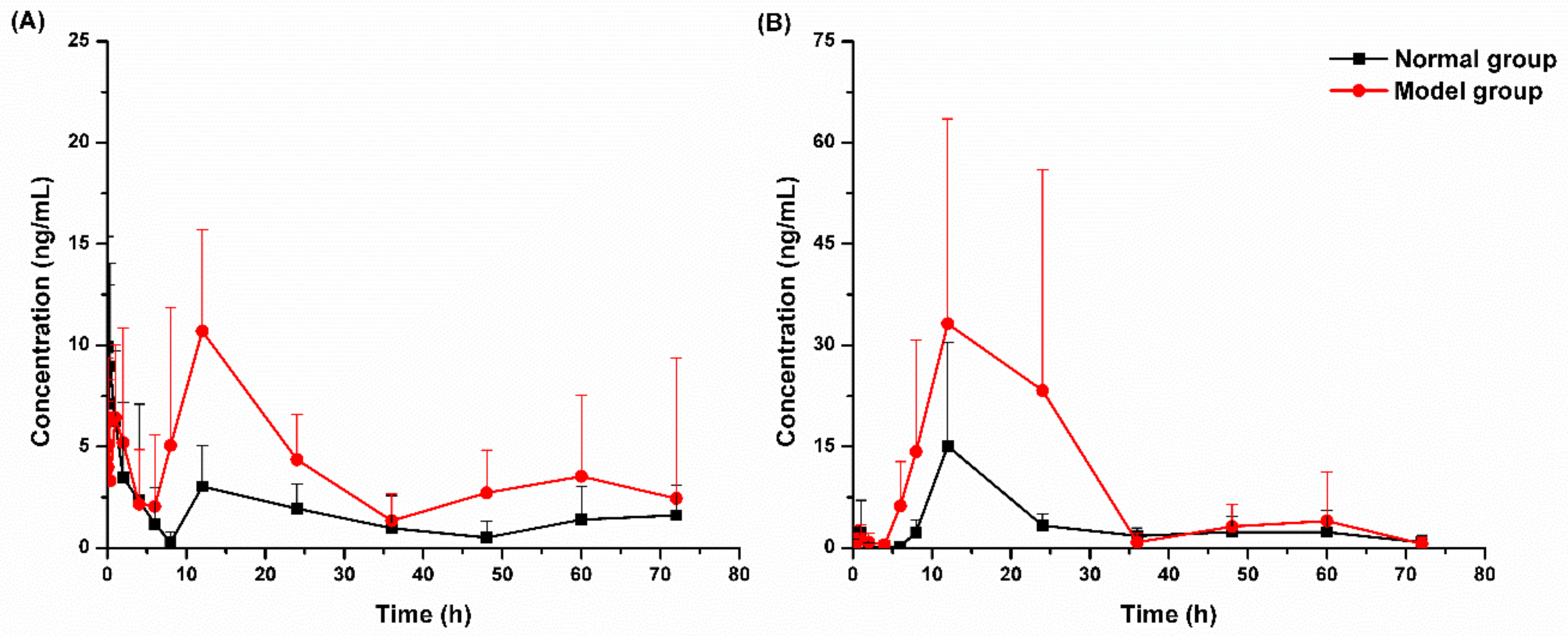
2.3.1. Pharmacokinetic Study
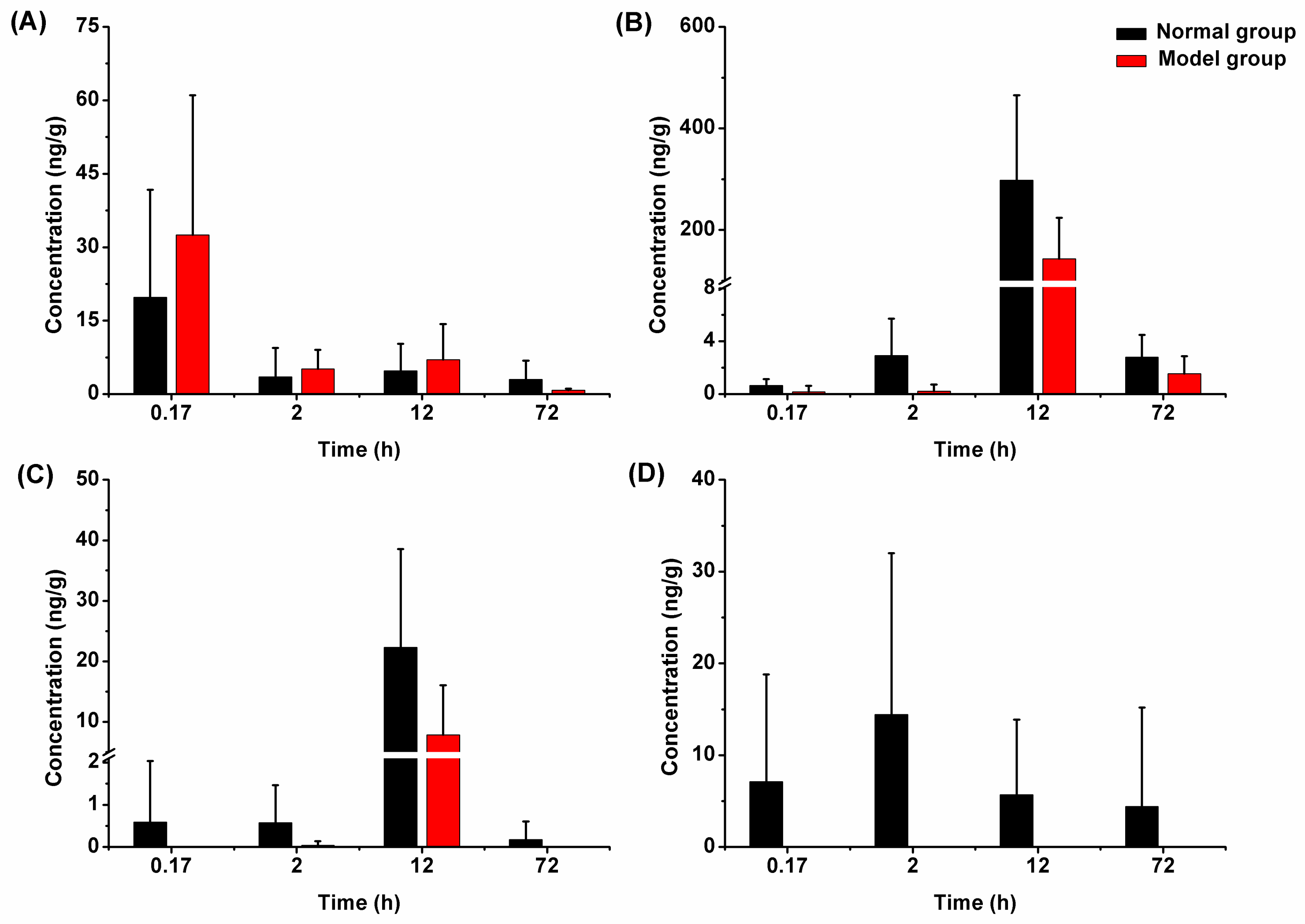
2.3.2. Liver Tissue Distribution
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Animals
3.3. Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometry Conditions
3.4. Preparation of Calibration Standard and Quality Control Samples
3.5. Sample Preparation
3.6. Method Validation
3.7. Pharmacokinetic and Tissue Distribution
3.7.1. Pharmacokinetic Study
3.7.2. Liver Tissue Distribution Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martínez-Vázquez, M.; Ramírez Apan, T.O.; Lastra, A.L.; Bye, R. A comparative study of the analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of pectolinarin isolated from Cirsium subcoriaceum and linarin isolated from Buddleia cordata. Planta Med. 1998, 64, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, H.Y.; Fan, P.H.; Perez, R.G.; Lou, H.Y. Neuroprotective effects of linarin through activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway in amyloid-β-induced neuronal cell death. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 4021–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Sung, K.H.; Yim, D.; Lee, S.; Lee, C.K.; Ha, N.J.; Kim, K. The effect of linarin on LPS-induced cytokine production and nitric oxide inhibition in murine macrophages cell line RAW264.7. Arch. Pharm Res. 2002, 25, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, S.; Wasowski, C.; Paladini, A.C.; Marder, M. Sedative and sleep-enhancing properties of linarin, a flavonoid-isolated from Valeriana officinalis. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2004, 77, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oinonen, P.P.; Jokela, J.K.; Hatakka, A.I.; Vuorela, P.M. Linarin, a selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitor from Mentha arvensis. Fitoterapia 2006, 77, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.H.; Kang, S.S.; Seo, E.A.; Shin, S.W. Isolation of aldose reductase inhibitors from the flowers of Chrysanthemum boreale. Arch. Pharm. Res. 1995, 18, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.H.; Hay, A.E.; Marston, A.; Hostettmann, K. Acetylcholinesterase-inhibitory activity of linarin from Buddleja davidii, structure–activity relationships of related flavonoids, and chemical investigation of Buddleja nitida. Pharm. Biol. 2008, 46, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.J.; Shan, C.W.; Li, B.; Pang, M.X.; Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Song, Y.; Wang, N.N.; Chen, S.H.; et al. Linarin enriched extract attenuates liver injury and inflammation induced by high fat high-cholesterol diet in rats. Evid. -Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Cho, H.I.; Kim, S.J.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, S.K.; Kwak, J.H.; Lee, S.M. Protective effect of linarin against D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide-induced fulminant hepatic failure. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 738, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.X.; Meng, X.S.; Tong, J.; Ge, L.L.; Zhou, G.; Wang, Y.W. Protective effects of Coptis chinensis inflorescence extract and linarin against carbon tetrachloride-induced damage in HepG2 cells through the MAPK/Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 2353–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Di, X. A rapid and sensitive LC-MS/MS method for the determination of linarin in small-volume rat plasma and tissue samples and its application to pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution study. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2016, 30, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Li, Y.; Guang, C.; Qiao, M.; Wang, T.; Chai, L.; Qiu, F. Characterization of the in vivo and in vitro metabolites of linarin in rat biosamples and intestinal flora using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. Molecules 2018, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Li, Y.J.; Tan, X.J.; Li, Q.; Bi, K.S. RP-HPLC determination of linarin in beagle dog plasma after administration of Yejuhua injection. Chromatographia 2006, 64, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Liu, H.J.; Lin, L. Rapid LC-MS/MS determination and pharmacokinetic application of linarin in rat plasma. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2013, 27, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Jia, P.P.; Zhang, X.X.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Yang, H.T.; Shi, H.; Zhang, L. LC-MS/MS determination and pharmacokinetic study of seven flavonoids in rat plasma after oral administration of Cirsium japonicum DC. extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 158, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.P.; Dong, L.H.; Yan, W.Y.; Wei, J.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.J. Simultaneous determination of linarin, naringenin and formononetin in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS and its application to a pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of Bushen Guchi Pill. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nicolò, A.; Cantù, M.; D’Avolio, A. Matrix effect management in liquid chromatography mass spectrometry: The internal standard normalized matrix effect. Bioanalysis 2017, 9, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical Method Validation. 2001. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/guidanceComplianceregulatoryInformation/guidances/UCM070107.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2018).
Sample Availability: Not available. |
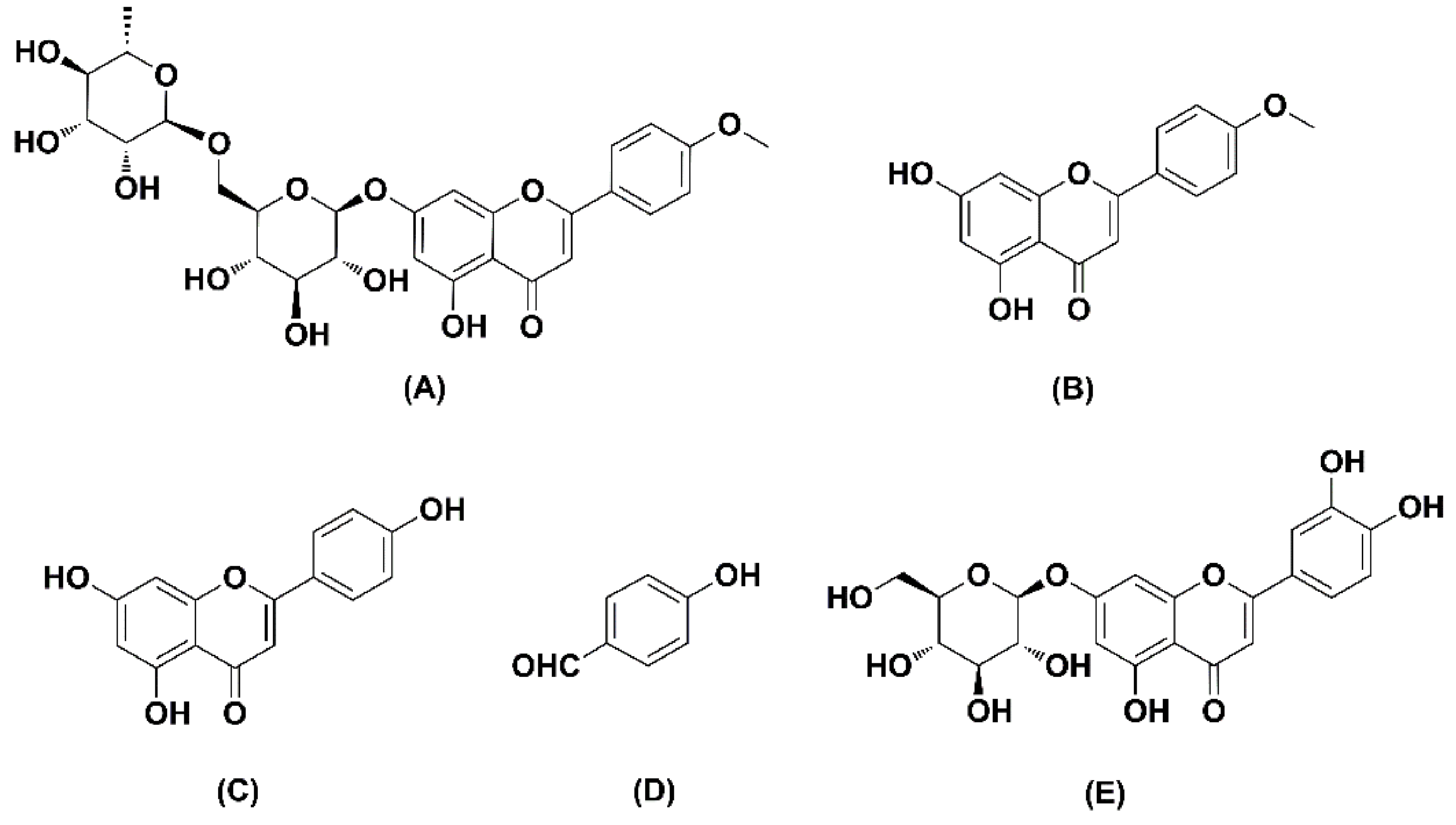
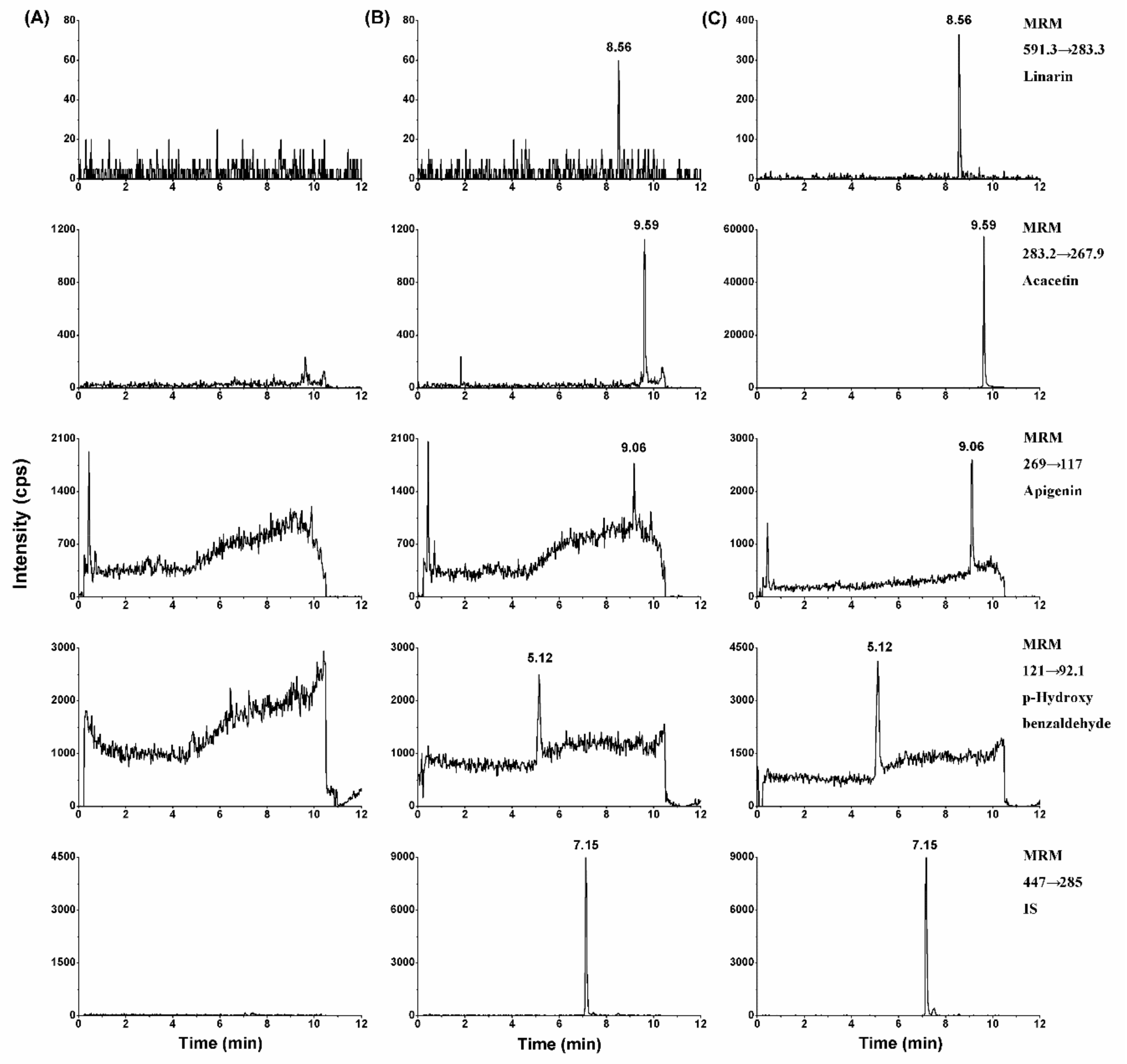
| Compounds | Q1 | Q3 | DP (V) | EP (V) | CE (V) | CXP (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linarin | 591.3 | 283.3 | −120 | −10 | −22 | −17 |
| Acacetin | 283.2 | 267.9 | −100 | −10 | −30 | −17 |
| Apigenin | 269 | 117 | −45 | −10 | −45 | −17 |
| p-Hydroxy benzaldehyde | 121 | 92.1 | −108 | −10 | −35 | −17 |
| Luteolin-7-O-glucopyranoside (IS) | 447 | 285 | −40 | −10 | −37 | −17 |
| Compounds | Analytical Curves | r | Linear Range (ng/mL) | LLOQ (ng/mL) | RSD (%) | RE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linarin | y = 0.00116x + 0.0011 | 0.9966 | 1.00–200 | 1.00 | 9.1 | −4.1 |
| Acacetin | y = 0.171x + 0.0921 | 0.9951 | 1.00–200 | 1.00 | 3.6 | 5.2 |
| Apigenin | y = 0.0875x + 0.0366 | 0.9974 | 1.00–200 | 1.00 | 6.4 | −0.6 |
| p-Hydroxy benzaldehyde | y = 0.0767x + 0.1950 | 0.9955 | 1.00–200 | 1.00 | 7.2 | 3.1 |
| Compounds | Added Concentration | Found Concentration | Intra-Day | Inter-Day | Accuracy | Recovery | Matrix Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ng/mL) | (ng/mL) | RSD (%) | RSD (%) | RE (%) | (%) | (%) | |
| Linarin | 3.00 | 2.97 ± 0.29 | 9.3 | 13.3 | −0.9 | 60.9 ± 8.3 | 88.1 ± 7.8 |
| 25.0 | 24.3 ± 2.35 | 8.0 | 14.6 | −2.9 | 62.0 ± 6.8 | 102.8 ± 3.3 | |
| 160 | 155 ± 12.1 | 7.9 | 7.3 | −3.2 | 60.5 ± 4.7 | 94.1 ± 2.0 | |
| Acacetin | 3.00 | 2.87 ± 0.18 | 6.6 | 4.2 | −4.5 | 76.1 ± 3.6 | 106.8 ± 5.5 |
| 25.0 | 24.8 ± 0.94 | 3.3 | 6.4 | −0.8 | 72.7 ± 1.3 | 104.1 ± 3.1 | |
| 160 | 163 ± 5.30 | 3.3 | 2.9 | 2.0 | 73.9 ± 1.6 | 104.1 ± 1.0 | |
| Apigenin | 3.00 | 2.89 ± 0.22 | 8.0 | 4.3 | −3.8 | 71.3 ± 3.8 | 105.4 ± 6.5 |
| 25.0 | 24.4 ± 1.06 | 2.6 | 10.6 | −2.5 | 72.4 ± 1.3 | 104.1 ± 1.9 | |
| 160 | 161 ± 7.86 | 3.1 | 11.4 | 0.4 | 74.0 ± 1.8 | 102.6 ± 1.7 | |
| p-Hydroxy benzaldehyde | 3.00 | 2.97 ± 0.23 | 7.2 | 6.8 | −0.9 | 61.0 ± 2.4 | 107.9 ± 7.8 |
| 25.0 | 24.9 ± 1.39 | 4.8 | 9.8 | −0.4 | 68.3 ± 2.7 | 101.9 ± 3.0 | |
| 160 | 166 ± 10.9 | 4.0 | 14.5 | 3.7 | 63.6 ± 1.0 | 104.3 ± 7.2 | |
| Luteolin-7-O-glucopyranoside (IS) | 50.0 | - | - | - | - | 48.9 ± 1.4 | 108.4 ± 3.1 |
| Compounds | Added Concentration | Post-Preparative Stability | Short-Term Stability | Freeze-Thaw Stability | Long-Term Stability | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ng/mL) | RE (%) | RSD (%) | RE (%) | RSD (%) | RE (%) | RSD (%) | RE (%) | RSD (%) | |
| Linarin | 3.00 | 7.0 | 3.7 | 5.3 | 8.9 | −7.3 | 7.9 | 9.7 | 4.6 |
| 160 | −8.5 | 5.8 | −8.5 | 1.5 | −3.5 | 9.1 | 2.3 | 4.8 | |
| Acacetin | 3.00 | −7.0 | 3.9 | −8.0 | 7.6 | −1.3 | 5.7 | −5.0 | 2.5 |
| 160 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 7.9 | 6.4 | 4.4 | 2.4 | 2.9 | 2.3 | |
| Apigenin | 3.00 | 6.0 | 11.0 | −10.0 | 0.7 | −7.0 | 3.9 | −3.3 | 4.8 |
| 160 | −4.8 | 3.5 | 10.6 | 6.7 | 6.0 | 1.4 | 4.2 | 0.7 | |
| p-Hydroxy | 3.00 | 7.7 | 4.0 | 11.3 | 3.3 | −4.3 | 9.1 | −7.0 | 3.2 |
| benzaldehyde | 160 | 0.4 | 6.1 | 7.3 | 4.2 | 11.5 | 3.7 | 9.4 | 3.0 |
| Parameters | Linarin | Acacetin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Rats | Model Rats | Normal Rats | Model Rats | |
| t1/2z (h) | 36.9 ± 21.8 | 37.4 ± 27.9 | 16.5 ± 3.7 | 11.0 ± 6.1 |
| Tmax (h) | 0.12 ± 0.10 | 8.65 ± 5.17 | 15.13 ± 13.83 | 12.25 ± 5.28 |
| Cmax (μg/L) | 14.40 ± 4.37 | 13.85 ± 4.47 | 16.78 ± 14.30 | 41.65 ± 30.77 |
| AUC0–t (μg/L·h) | 174 ± 54 | 352 ± 99 | 282 ± 116 | 839 ± 682 |
| AUC0–∞ (μg/L·h) | 250 ± 52 | 367 ± 51 | 340 ± 128 | 919 ± 658 |
| Vz/F (L/kg) | 22517 ± 14103 | 9077 ± 4335 | 11233 ± 7029 | 2595 ± 2117 |
| CLz/F (L/h/kg) | 335 ± 145 | 225 ± 77 | 322 ± 187 | 149 ± 91 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Guang, C.; Zhao, N.; Feng, X.; Qiu, F. LC–MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Determination of Linarin and Its Metabolites in Rat Plasma and Liver Tissue Samples: Application to Pharmacokinetic and Liver Tissue Distribution Study After Oral Administration of Linarin. Molecules 2019, 24, 3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183342
Li Y, Guang C, Zhao N, Feng X, Qiu F. LC–MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Determination of Linarin and Its Metabolites in Rat Plasma and Liver Tissue Samples: Application to Pharmacokinetic and Liver Tissue Distribution Study After Oral Administration of Linarin. Molecules. 2019; 24(18):3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183342
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yang, Chenxi Guang, Na Zhao, Xinchi Feng, and Feng Qiu. 2019. "LC–MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Determination of Linarin and Its Metabolites in Rat Plasma and Liver Tissue Samples: Application to Pharmacokinetic and Liver Tissue Distribution Study After Oral Administration of Linarin" Molecules 24, no. 18: 3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183342
APA StyleLi, Y., Guang, C., Zhao, N., Feng, X., & Qiu, F. (2019). LC–MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Determination of Linarin and Its Metabolites in Rat Plasma and Liver Tissue Samples: Application to Pharmacokinetic and Liver Tissue Distribution Study After Oral Administration of Linarin. Molecules, 24(18), 3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183342





