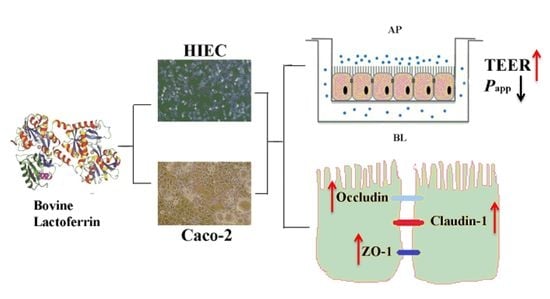
The In Vitro Protective Role of Bovine Lactoferrin on Intestinal Epithelial Barrier
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
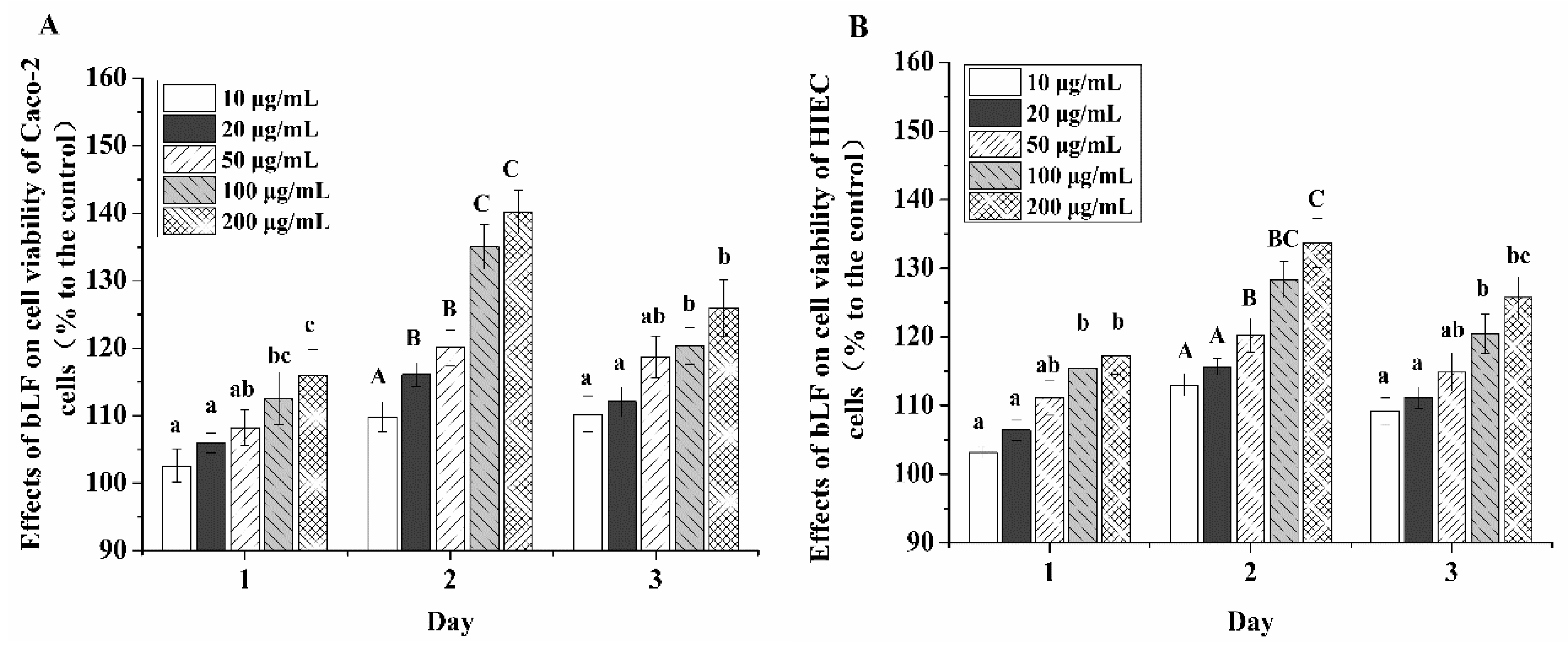
2.1. Growth Promotion Effect of bLF on the Two Cell Lines
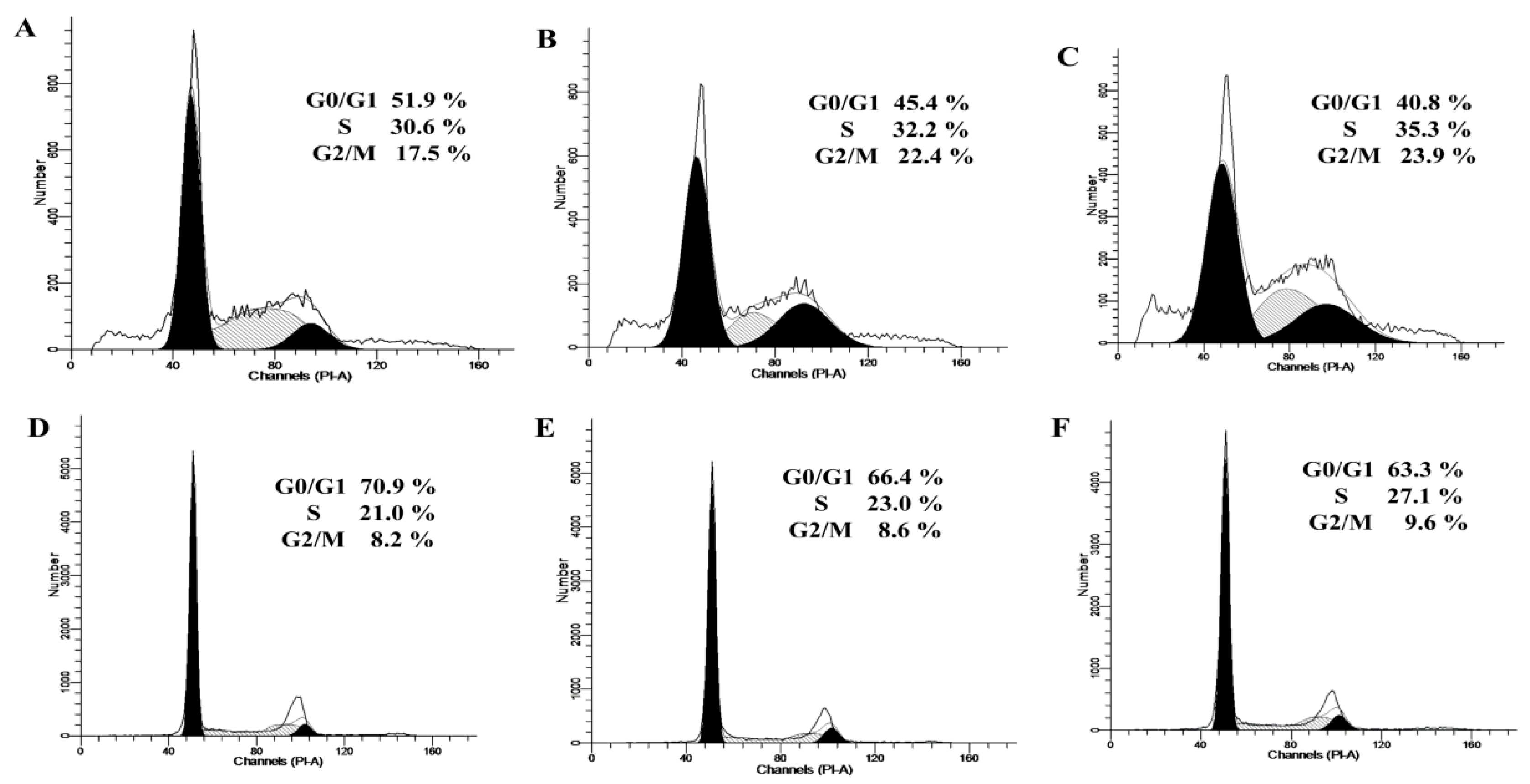
2.2. Cell-Cycle Distribution in the Two Cell Lines Treated with bLF
2.3. Cell Differentiation of the Two Cell Lines Treated with bLF
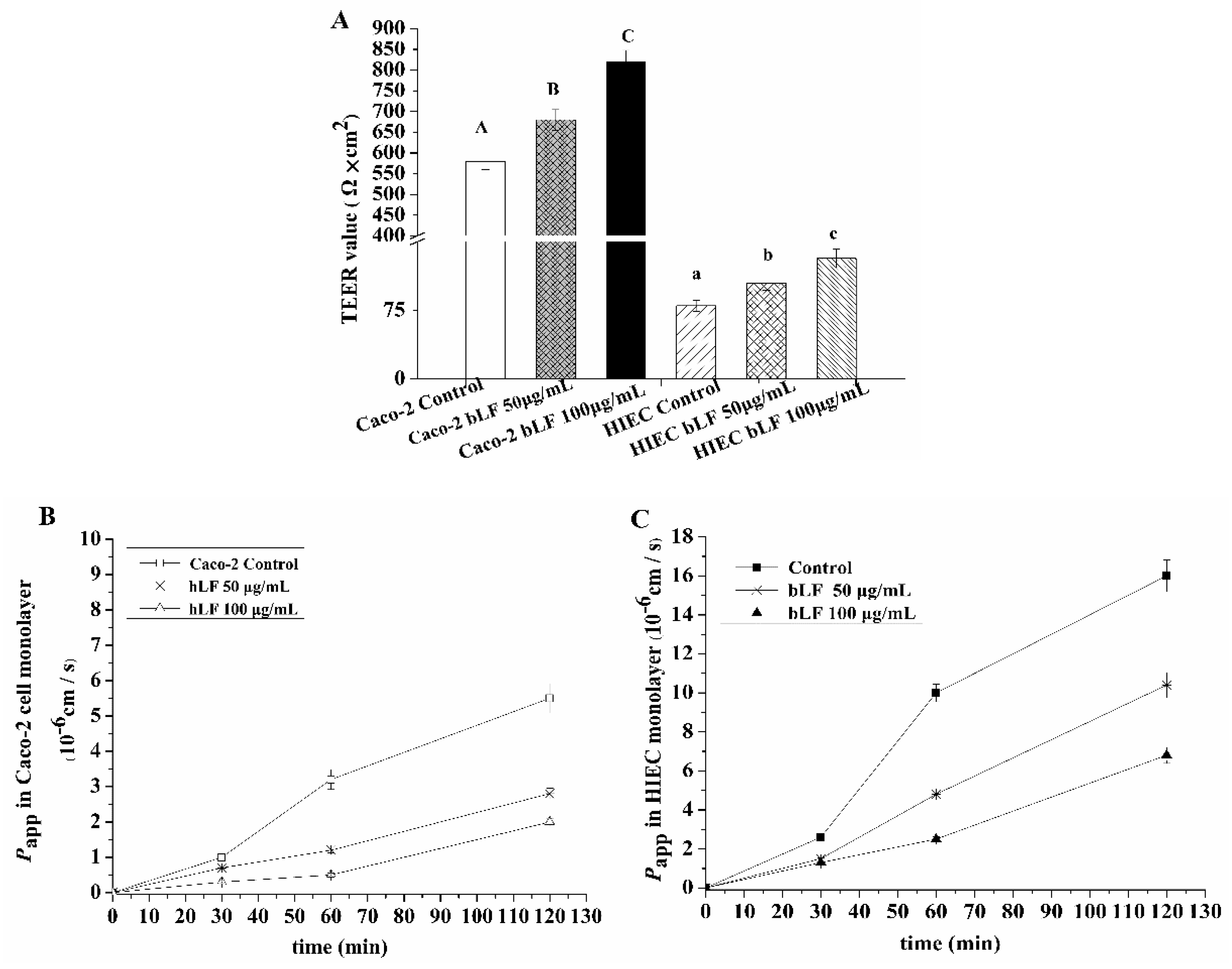
2.4. Effects of bLF on Epithelial Monolayer Resistance and Permeability of Two Cell Lines
2.5. Effect of bLF on Expression of TJ Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
4.3. Measurement of Cell Viability
4.4. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.5. Cell Differentiation Assay
4.6. Transepithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER) Measurement
4.7. Determination of Epithelial Monolayer Permeability
4.8. Immunofluorescence Analysis
4.9. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) Analysis
4.10. WB Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, S.Y.; Hur, S.J. Antihypertensive peptides from animal products, marine organisms, and plants. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, M.; Karboune, S. Natural Antimicrobial/Antioxidant Agents in Meat and Poultry Products as Well as Fruits and Vegetables: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2017, 58, 486–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halim, N.R.A.; Yusof, H.M.; Sarbon, N.M. Functional and bioactive properties of fish protein hydolysates and peptides: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Te. 2016, 51, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; Fitzgerald, R.J. The scientific evidence for the role of milk protein-derived bioactive peptides in humans: A Review. J. Funct Foods. 2015, 17, 640–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, P.; Rinaldi, M.; Cattani, S.; Pugni, L.; Romeo, M.G.; Messner, H.; Stoblfi, I.; Decembrino, L.; Laforgia, N.; Vagnarelli, F. Bovine Lactoferrin supplementation for prevention of late-onset sepsis in very Low-Birth-Weight neonates: A Randomized Trial. JAMA 2009, 302, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Montoya, I.A.; Cendón, T.S.; Arévalo-Gallegos, S.; Rascón-Cruz, Q. Lactoferrin a multiple bioactive protein: An overview. BBA 2012, 1820, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, N.A.; Luettig, J.; Krug, S.M.; Wiegand, S.; Gross, G.; Van Tol, E.A.; Schulzke, J.D.; Rosenthal, R. Lactoferrin protects against intestinal inflammation and bacteria-induced barrier dysfunction in vitro. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2017, 1405, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotani, Y.; Ikeda, K.; Kato, R.; Myotoku, M.; Umeda, T.; Ijiri, Y.; Tanaka, K. Protective effects of lactoferrin against intestinal mucosal damage induced by lipopolysaccharide in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Yakugaku Zasshi 2008, 128, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, W.; Shi, J.; Zhong, Y.; van Tol, E.A.; Tang, Q.; Cai, W. Enteral supplementation of bovine lactoferrin improves gut barrier function in rats after massive bowel resection. Brit. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, N.A.; Andres, S.; Fromm, A.; van Tol, E.A.; Amasheh, M.; Mankertz, J.; Fromm, M.; Schulzke, J.D. Transforming growth factor-β, a whey protein component, strengthens the intestinal barrier by upregulating claudin-4 in HT-29/B6 cells. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madara, J.L. Regulation of the movement of solutes across tight junctions. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 1998, 60, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.C.; Bassett, S.A.; Haggarty, N.W.; Gopal, P.K.; Armstrong, K.M.; Roy, N.C. Short communication: Early-lactation, but not mid-lactation, bovine lactoferrin preparation increases epithelial barrier integrity of caco-2 cell layers. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnott, I.D.; Kingstone, K.; Ghosh, S. Abnormal intestinal permeability predicts relapse in inactive Crohn disease. Scand. J. Gastroent. 2000, 35, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koch, S.; Nusrat, A. Dynamic regulation of epithelial cell fate and barrier function by intercellular junctions. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2009, 1165, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, C.R. Dynamic properties of the tight junction barrier. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2012, 1257, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhold, A.K.; Rittner, H.L. Barrier function in the peripheral and central nervous system—A review. Eur. J. Physiol. 2017, 469, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmeyer, C.; Schulzke, J.D.; Fromm, M. Claudin-related intestinal diseases. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 42, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, B.; Kolli, A.R.; Esch, M.B.; Abaci, H.E.; Shuler, M.L.; Hickman, J.J. TEER measurement techniques for in vitro barrier model systems. JALA J. Lab. Autom. 2015, 20, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.R. Molecular basis of epithelial barrier regulation: From basic mechanisms to clinical application. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 1901–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuse, M.; Hirase, T.; Itoh, M.; Nagafuchi, A.; Yonemura, S.; Tsukita, S.; Tsukita, S. Occludin: A novel integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 123, 1777–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-sad, R.I.; Khatib, K.; Guo, S.; Ye, D.; Youssef, M.; Ma, T. Occludin regulates macromolecule flux across the intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier. Am. J. Physiol. Gastr. L 2011, 300, G1054–G1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itallie, C.M.V.; Anderson, J.M. Claudins and epithelial paracellular transport. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2006, 68, 403–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuse, M.; Sasaki, H.; Tsukita, S. Manner of interaction of heterogeneous claudin species within and between tight junction strands. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 147, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H. Intestinal permeability regulation by tight junction: Implication on inflammatory bowel diseases. Intest. Res. 2015, 13, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T. Regulation of intestinal epithelial permeability by tight junctions. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 631–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpern, M.D.; Denning, P.W. The role of intestinal epithelial barrier function in the development of NEC. Tissue Barriers 2015, 3, 1000707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macedo, M.H.; Araújo, F.; Martínez, E.; Barrias, C.; Sarmento, B. iPSC-Derived enterocyte-like cells for drug absorption and metabolism studies. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 696–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pageot, L.P.; Perreault, N.; Basora, N.; Francoeur, C.; Magny, P.; Beaulieu, J.F. Human cell models to study small intestinal functions: Recapitulation of the crypt-villus axis. Microsc. Res. Techni. 2000, 49, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guezguez, A.; Paré, F.; Benoit, Y.D.; Basora, N.; Beaulieu, J.F. Modulation of stemness in a human normal intestinal epithelial crypt cell line by activation of the WNT signaling pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 322, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, T.; Harada, N.; Kuze, J.; Chiba, M.; Iwao, T.; Matsunaga, T. Application of a human intestinal epithelial cell monolayer to the prediction of oral drug absorption in humans as a superior alternative to the Caco-2 cell monolayer. J. Pharm. Sci. US 2016, 105, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Du, X.; Li, J.; Lönnerdal, B. Human milk exosomes and their microRNAs survive digestion in vitro and are taken up by human intestinal cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lönnerdal, B. Infant formula and infant nutrition: Bioactive proteins of human milk and implications for composition of infant formulas. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 712S–717S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hering, N.A.; Fromm, M.; Schulzke, J.D. Determinants of colonic barrier function in inflammatory bowel disease and potential therapeutics. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadi, N.; Klems, M.; Untersmayr, E. The role of gastrointestinal permeability in food allergy. Ann. Allergy Asthma Im. 2018, 121, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaldaferri, F.; Pizzoferrato, M.; Gerardi, V.; Lopetuso, L.; Gasbarrini, A. The gut barrier: New acquisitions and therapeutic approaches. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 46, S12–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andre, C.; Andre, F.; Colin, L.; Cavagna, S. Measurement of intestinal permeability to mannitol and lactulose as a means of diagnosing food allergy and evaluating therapeutic effectiveness of disodium cromoglycate. Ann. Allergy 1987, 59, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Järvinen, K.M.; Konstantinou, G.N.; Pilapil, M.; Arrieta, M.C.; Noone, S.; Sampson, H.A.; Meddings, J.; Nowak-Węgrzyn, A. Intestinal permeability in children with food allergy on specific elimination diets. Pediatr. Allergy Imm. 2013, 24, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, C.; Magnusson, K.E.; Sundqvist, T.; Stenling, R.; Björkstén, B. Intestinal permeability as qssessed with polyethyleneglycols in birch pollen allergic children undergoing oral immunotherapy. Allergy 1986, 41, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamacchia, C.; Musaico, D.; Henderson, M.E.; Bergillos-Meca, T.; Roul, M.; Landriscina, L.; Decina, I.; Corona, G.; Costabile, A. Temperature-treated gluten proteins in Gluten-Friendly™ bread increase mucus production and gut-barrier function in human intestinal goblet cells. J. Funct. Foods. 2018, 48, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amasheh, M.; Schlichter, S.; Amasheh, S.; Mankertz, J.; Zeitz, M.; Fromm, M.; Schulzke, J.D. Quercetin enhances epithelial barrier function and increases claudin-4 expression in Caco-2 cells. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, Y.Y.; Ha, C.W.Y.; Hoffmann, J.M.A.; Oscarsson, J.; Dinudom, A.; Mather, T.J.; Cook, D.I.; Hunt, N.H.; Caterson, I.D.; Holmes, A.J.; et al. Effects of dietary fat profile on gut permeability and microbiota and their relationships with metabolic changes in mice. Obesity 2015, 23, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, P.S.; Caria, C.R.P.; Gotardo, E.M.F.; Ribeiro, M.L.; Pedrazzoli, J.J.; Gambero, A. Artificial sweetener saccharin disrupts intestinal epithelial cells’ barrier function in vitro. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 3815–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.H.; Xiao, K.; Song, J.; Luan, Z.S. Effects of zinc oxide supported on zeolite on growth performance, intestinal microflora and permeability, and cytokines expression of weaned pigs. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2013, 181, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, N.; Li, J. The study of n-3PUFAs protecting the intestinal barrier in rat HS/R model. Lipids Health Dis. 2014, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; He, P.; Tan, L.; Ma, X. Dietary grape-seed procyanidins decreased postweaning diarrhea by modulating intestinal permeability and suppressing oxidative stress in rats. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 6227–6232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, J.; Wang, A.; Shang, H.; Liu, C.; Bao, C.; Wu, L.; Yin, S. Herb-partitioned moxibustion upregulated the expression of colonic epithelial tight junction-related proteins in Crohn’s disease model rats. Chin. Med. UK 2016, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, L.A.; Lönnerdal, B. Persistence of human milk proteins in the breast-fed infant. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 1987, 76, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lönnerdal, B.; Jiang, R.; Du, X. Bovine lactoferrin can be taken up by the human intestinal lactoferrin receptor and exert bioactivities. J. Pediatr. Gastr. Nut. 2011, 53, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blais, A.; Fan, C.; Voisin, T.; Aattouri, N.; Dubarry, M.; Blachier, F.; Tome, D. Effects of lactoferrin on intestinal epithelial cell growth and differentiation: An in vivo and in vitro study. Biometals 2014, 27, 857–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusup, A.; Upur, H.; Umar, A.; Berke, B.; Moore, N. Ethanol extract of abnormal savda munziq, a herbal preparation of traditional uighur medicine, inhibits caco-2 cells proliferation via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Evid. Based Compl. Alt. 2012, 2012, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, M.; Mackman, N. Lps induction of gene expression in human monocytes. Cell Signal. 2001, 13, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, I.J.; Raub, T.J.; Borchardt, R.T. Characterization of the human colon carcinoma cell line (Caco-2) as a model system for intestinal epithelial permeability. Gastroenterology 1989, 96, 736–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, J.F.; Quaroni, A. Clonal analysis of sucrase-isomaltase expression in the human colon adenocarcinoma Caco-2 cells. Biochem. J. 1991, 280, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.J.; Miller, P.; Shuler, M.L. A pumpless body-on-a-chip model using a primary culture of human intestinal cells and a 3D culture of liver cells. Lab. Chip. 2018, 18, 2036–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balimane, P.V.; Chong, S. Cell culture-based models for intestinal permeability: A critique. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Zhao, X.H. The growth proliferation, apoptotic prevention, and differentiation induction of the gelatin hydrolysates from three sources to human fetal osteoblasts (hFOB 1.19 Cells). Molecules 2018, 23, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, S.; Feighery, L.; Brayden, D.J.; Mcclean, S. Melittin as an epithelial permeability enhancer I: Investigation of its mechanism of action in Caco-2 monolayers. Pharm. Res. Dordr. 2007, 24, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Ding, X.; Shang, L.; Zeng, X.; Liu, H.; Li, N.; Huang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Cai, S. Protective ability of biogenic antimicrobial peptide microcin J25 against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia Coli-induced intestinal epithelial dysfunction and inflammatory responses IPEC-J2 cells. Front. Cell Infect. Mi. 2018, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.C.; MacGibbon, A.K.; Haggarty, N.; Armstrong, K.M.; Roy, N.C. Bovine dairy complex lipids improve in vitro measures of small intestinal epithelial barrier integrity. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Gillingham, T.; Guo, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhu, W.; Walker, W.A.; Ganguli, K. Secretions of Bifidobacterium infantis and Lactobacillus acidophilus protect intestinal epithelial barrier function. J. Pediatr. Gastr. Nutr. 2017, 64, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |



| Gene Name | NCBI Reference Sequence | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CLDN-1 | 9076 | GCGACAACATCGTGACCG | CCAACCACCATCAAGGCAC |
| OCLN | 100506658 | CCCCATCTGACTATGTGGAAAG | CAGGCGAAGTTAATGGAAGC |
| TJP-1 | 7082 | GAGTGAACCACGAGACGCTG | TTCCGAGATTCTGGACATAACC |
| ACTB | 60 | TGACGTGGACATCCGCAAAG | CTGGAAGGTGGACAGCGAGG |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Xu, X.-X.; Liu, Y.; Xi, E.-Z.; An, J.-J.; Tabys, D.; Liu, N. The In Vitro Protective Role of Bovine Lactoferrin on Intestinal Epithelial Barrier. Molecules 2019, 24, 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010148
Zhao X, Xu X-X, Liu Y, Xi E-Z, An J-J, Tabys D, Liu N. The In Vitro Protective Role of Bovine Lactoferrin on Intestinal Epithelial Barrier. Molecules. 2019; 24(1):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010148
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xiao, Xiao-Xi Xu, Yang Liu, En-Ze Xi, Jing-Jing An, Dina Tabys, and Ning Liu. 2019. "The In Vitro Protective Role of Bovine Lactoferrin on Intestinal Epithelial Barrier" Molecules 24, no. 1: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010148
APA StyleZhao, X., Xu, X.-X., Liu, Y., Xi, E.-Z., An, J.-J., Tabys, D., & Liu, N. (2019). The In Vitro Protective Role of Bovine Lactoferrin on Intestinal Epithelial Barrier. Molecules, 24(1), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010148