Simultaneous Optimization for Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction and Antioxidant Activity of Flavonoids from Sophora flavescens Using Response Surface Methodology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
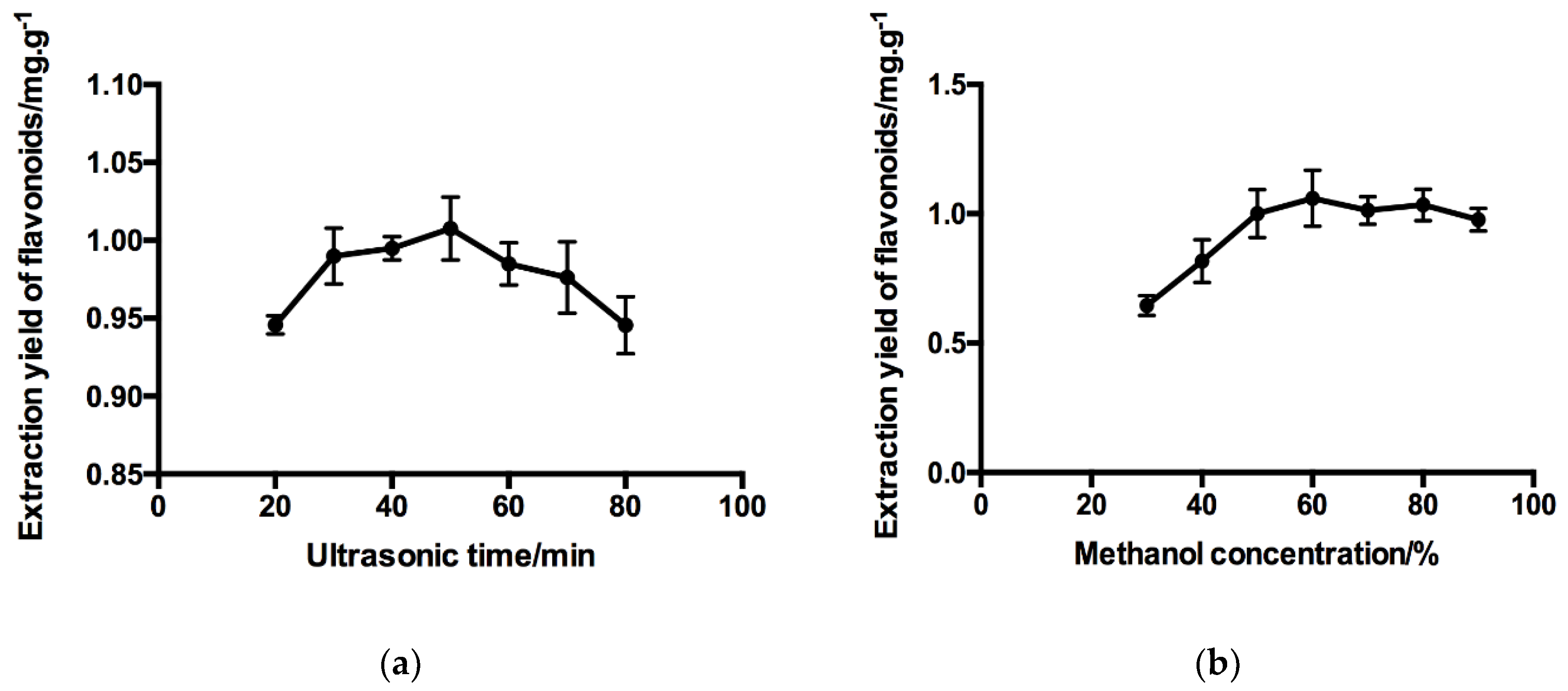
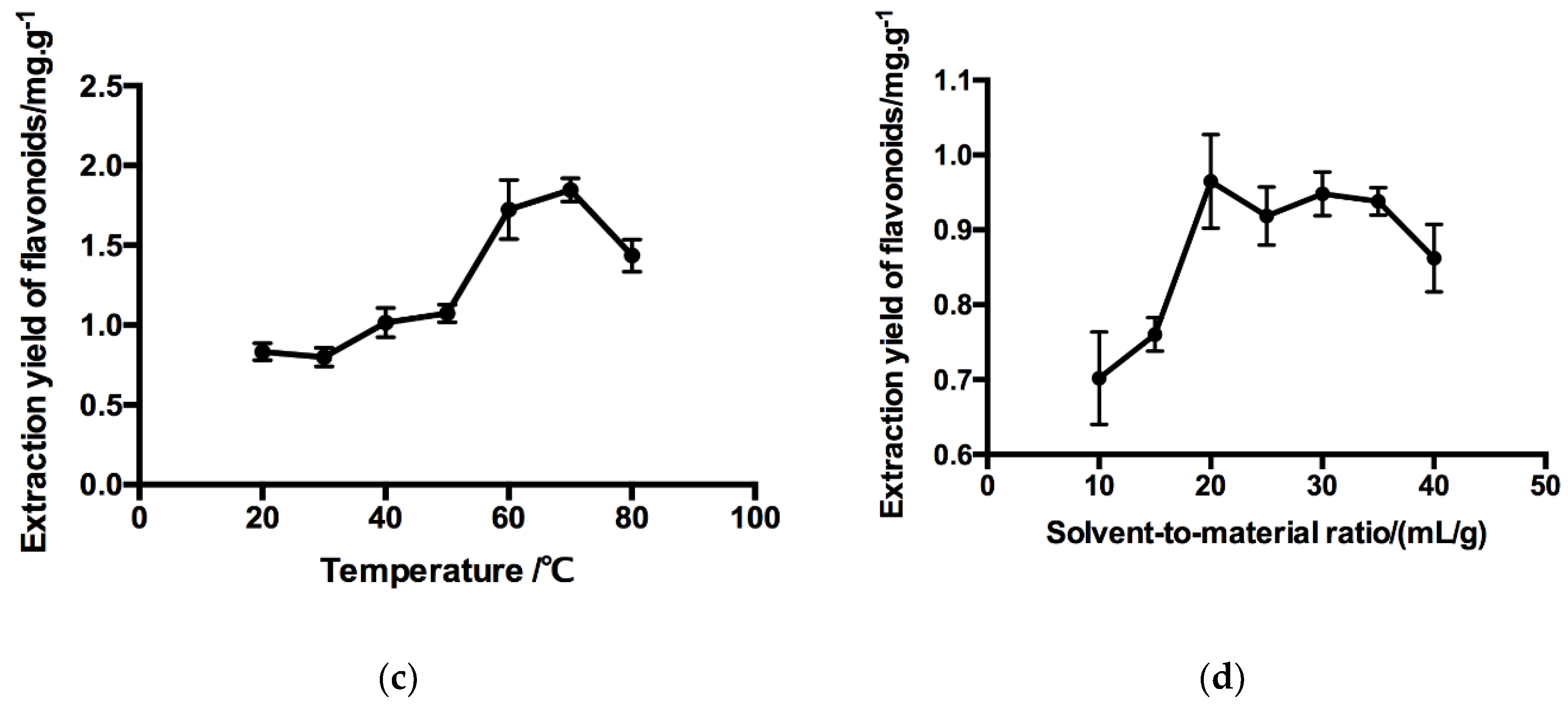
2.1. Single-Factor Experiment of Flavonoids Extraction
2.1.1. Effect of Ultrasonic Time
2.1.2. Effect of Solvent
2.1.3. Effect of Temperature
2.1.4. Effect of Liquid-to-Material Ratio
2.2. Model Fitting
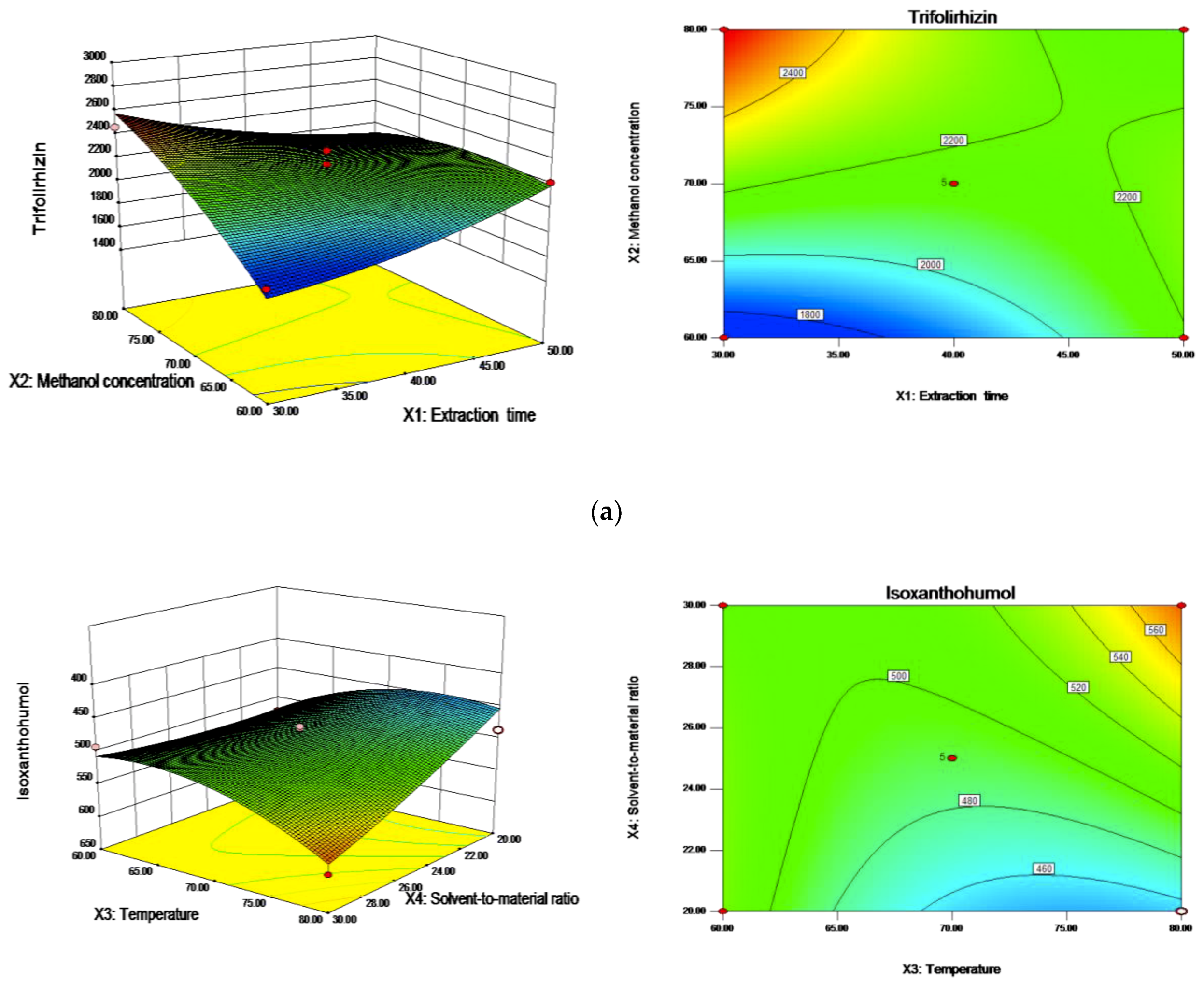
2.3. Effect of the Variables on the Extraction Yield of Flavonoids
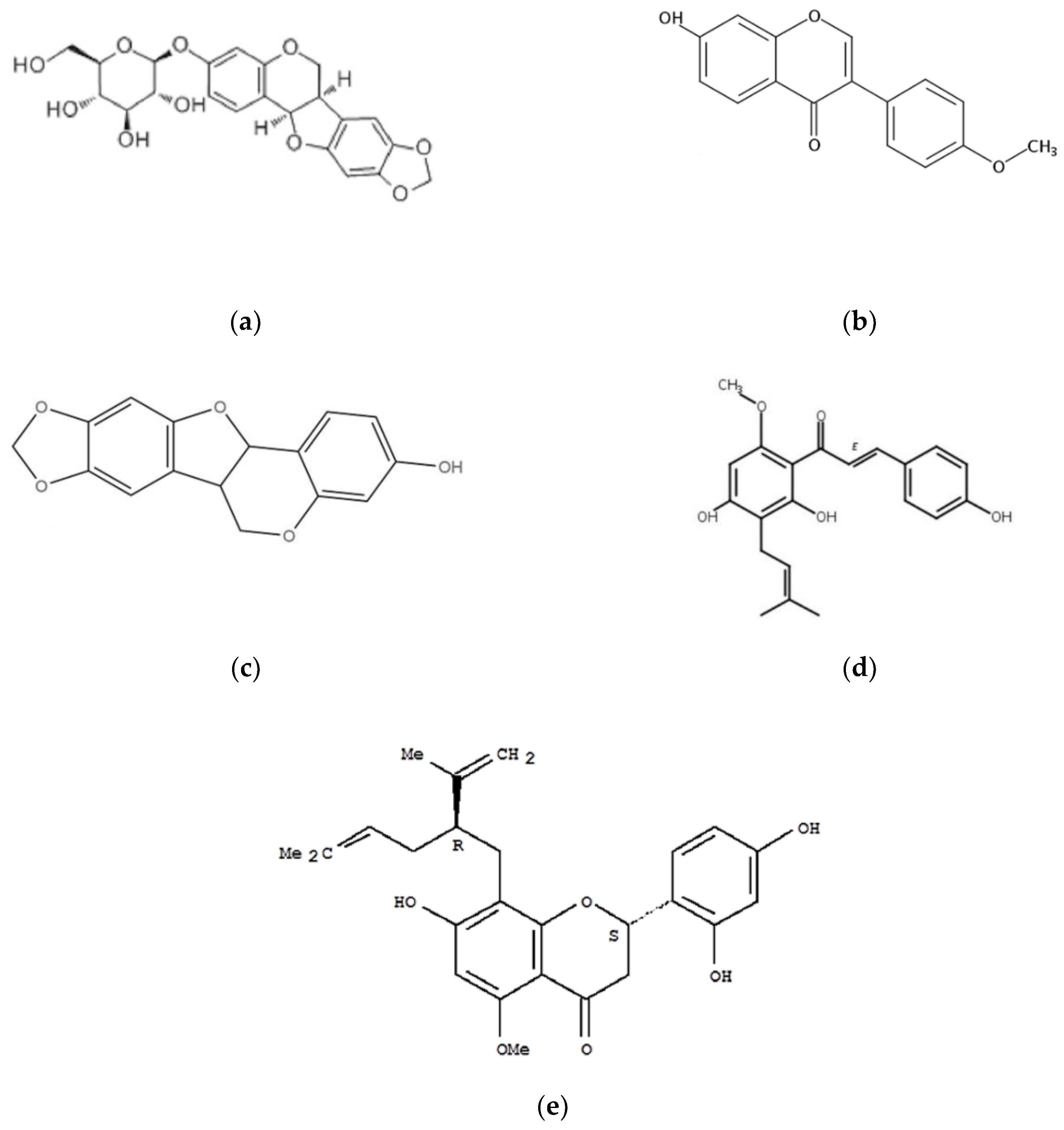
2.3.1. Trifolirhizin
32.12X2X3 + 14.6X2X4 − 103.3X3X4 + 75.39X12 − 86.69X22 + 90.78X32 + 26.23X42
2.3.2. Formononetin
16.75X2X4 − 8.68X3X4 + 9.63X12 − 4.26X22 + 16.32X32 − 23.93X42
2.3.3. Isoxanthohumol
2.3.4. Maackiain
13.43X2X3 − 60.72X2X4 + 37.21X3X4 − 5.72X12 − 9.61X22 − 7.62X32 − 24.05X42
2.3.5. Kurarinone
70X2X3 − 33.67X2X4 + 70.7X3X4 + 194.62X12 − 83.15X22 + 51.19X32 + 61.22X42
2.4. Optimal Processing Conditions and Model Verification
2.5. Antioxidant Activity In Vitro
2.5.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
2.5.2. Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Activity
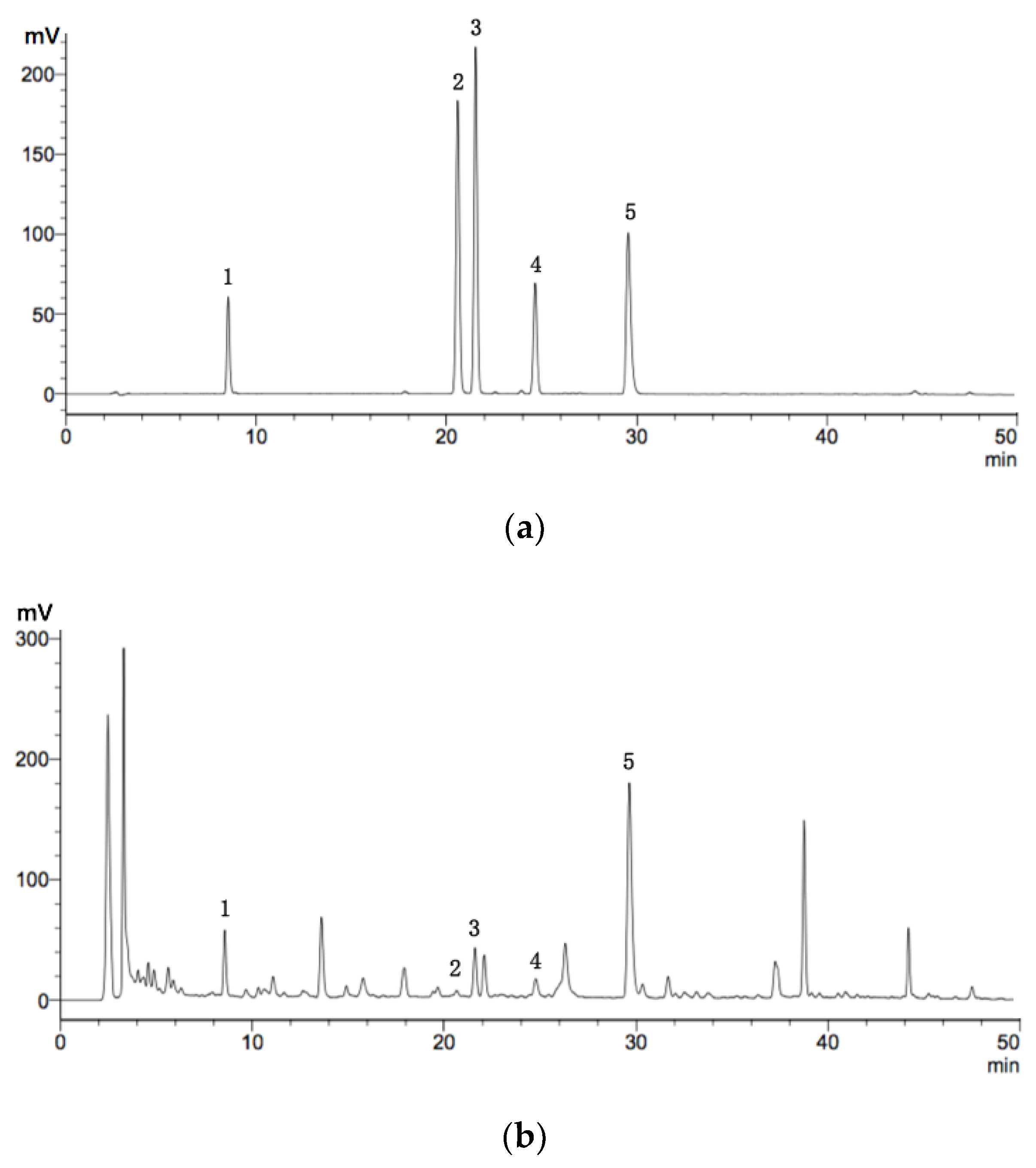
2.6. HPLC Analysis of Flavonoids
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Materials
3.2. Chemicals and Reagents
3.3. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (UAE) of Flavonoids
3.4. Determination of Flavonoids
3.5. Selection of Experimental Factors and Levels
3.6. BBD Experimental Design
3.7. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) analysis
3.8. Determination of Antioxidant Activities
3.8.1. Assay of DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
3.8.2. Assay of Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Activity
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Xiao, S.S.; Liao, Q.F.; Li, Q.; Liang, J.; Chen, X.H.; Bi, K.S. Characterization of flavonoids in the extract of Sophora flavescens Ait. by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode-array detector and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 44, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.L.; Liao, Z.X.; Huang, H.; Zhou, P.; Chen, D.F. (+)-12α-Hydroxysophocarpine, a new quinolizidine alkaloid and related anti-HBV alkaloids from Sophora flavescens. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 1231–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Henderson, G. Antifeedant activity and acute and residual toxicity of alkaloids from Sophora flavescens (Leguminosae) against formosan subterranean termites (isoptera: rhinotermitidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2007, 100, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Guo, Y.J.; Yang, X.L.; Ou, Z.L. Anti-cervical cancer role of matrine, oxymatrine and Sophora flavescens alkaloid gels and its mechanism. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Chen, W.; Jin, Y. Effect of Sophora flavescens alkaloid on aerobic vaginitis in gel form for local treatment. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 37, 314–320. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.L.; Chen, X.X.; Wang, F.; Cai, W.; Chen, L. A new flavonoid from Sophora flavescens Ait. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Xin, X.; Su, D.H.; Liu, J.; Wei, Q.; Li, B.; Cui, J. Two new lavandulyl flavonoids from Sophora flavescens. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 1889. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, S.Y.; Choi, S.U.; Kim, S.K.; No, Z.; Lee, C.O.; Ahn, J.W.; Kim, S.H. In vitro antitumour activity of flavonoids from Sophora flavescens. Phytother. Res. 2015, 11, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.M.; Oak, M.H. Vasorelaxant prenylated flavonoids from the roots of Sophora flavescens. J. Agri. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2013, 77, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kang, S.S.; Son, K.H.; Chang, H.W.; Kim, H.P. Anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic activity of total flavonoids of the roots of Sophora flavescens. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 127, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Yu, G.; Zhu, C.; Qiao, J. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) of flavonoids compounds (FC) from hawthorn seed (HS). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang-Liang, J.; Xiao-Fang, D.; Jian-Ming, T. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of flavonoid compounds and antioxidants from alfalfa using response surface method. Molecules 2015, 20, 15550–15571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.L.; Yu, C.H.; Chen, J.; Li, X.X.; Wang, W.; Li, S.Q. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction optimized by response surface methodology, chemical composition and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Tremella mesenterica. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Zheng, N.; Qu, B. An improved ultrasonic-assisted extraction method by optimizing the ultrasonic frequency for enhancing the extraction efficiency of lycopene from tomatoes. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 2288–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhu, J.; Diao, W.; Wang, C. Ultrasound-assisted enzymatic extraction and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata). Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 113, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, S.; Fernandes, F.A.N. Ultrasound-assisted extraction. Stewart Postharvest Rev. 2009, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Manson, A.R. Response surface methodology. Technometrics 2010, 15, 936–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.A.; Santelli, R.E.; Oliveira, E.P.; Villar, L.S.; Escaleira, L.A. Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 2008, 76, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Su, W. Selective extraction of flavonoids from Sophora flavescens Ait. by mechanochemistry. Molecules 2016, 21, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.H.; Dong, C.J.; Nie, S.P.; Li, F.; Wang, Z.J.; Shen, M.Y.; Xie, M.Y. Extraction, chemical composition and antioxidant activity of flavonoids from Cyclocarya paliurus (Batal.) Iljinskaja leaves. Food Chem. 2015, 186, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.X.; Wang, H.W.; Zhang, W.J.; Xie, G.L.; Wang, Q.R.; Feng, Y.F.; Wang, Y.H. Optimization of content determination method of total flavonoids from Sophora flavescens. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2017, 39, 946–951. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Xie, L. Optimization of extraction process for flavonoid from Soutellaria barbata by response surface methodology and evaluation of its antioxidant activity. Food Sci. 2016, 37, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zeng, Z.; Hu, N.; Bai, B.; Wang, H.; Suo, Y. Simultaneous optimization of the ultrasound-assisted extraction for phenolic compounds content and antioxidant activity of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. fruit using response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammi, K.M.; Jdey, A.; Abdelly, C.; Majdoub, H.; Ksouri, R. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of antioxidant compounds from Tunisian Zizyphus lotus fruits using response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2015, 184, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Cai, J.; Wang, S.; Hu, L.; Yang, X. Effect of Radix Sophorae flavescentis on activity of CYP450 isoforms in rats. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 21365–21371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Guo, J.; Yan, Y.; Heshui, Y.U.; Wei, L.I.; Zhang, L.; Song, X. Study on the chemical constituents and antibacterial activity of Radix Sophora flavescens. J. Liaoning Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 19, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.P.; Son, K.H.; Chang, H.W.; Kang, S.S. Anti-inflammatory plant flavonoids and cellular action mechanisms. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 96, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.C. Antioxidant activity of flavonoids from sweet potato vines in vitro. Adv. Mat. Res. 2011, 236–238, 2634–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Xia, X.; Dai, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Q.; Andraemarobela, K.; Okatch, H. Flavonoids profiles, antioxidant, acetylcholinesterase inhibition activities of extract from Dryoathyrium boryanum (Willd.) Ching. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 55, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.M.; Shen, L.L. Extraction and antioxidant activity of flavoniods from Sophora flavescens. Food Sci. 2009, 30, 137–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zamri, N.; Abdullah, L. A new linguistic variable in interval type-2 fuzzy entropy weight of a decision making method. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2013, 24, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jia, X.; Zhang, C.; Hu, J.; He, M.; Bao, J.; Wang, K.; Li, P.; Chen, M.; Wan, J.; Su, H. Ultrasound-assisted extraction, antioxidant and anticancer activities of the polysaccharides from Rhynchosia minima root. Molecules 2015, 20, 20901–20911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Li, X.; Jiao, Y.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, L.; Fan, B.; Zhang, Q. Optimization for ultrasound-assisted extraction of polysaccharides with antioxidant activity in vitro from the aerial root of Ficus microcarpa. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 110, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
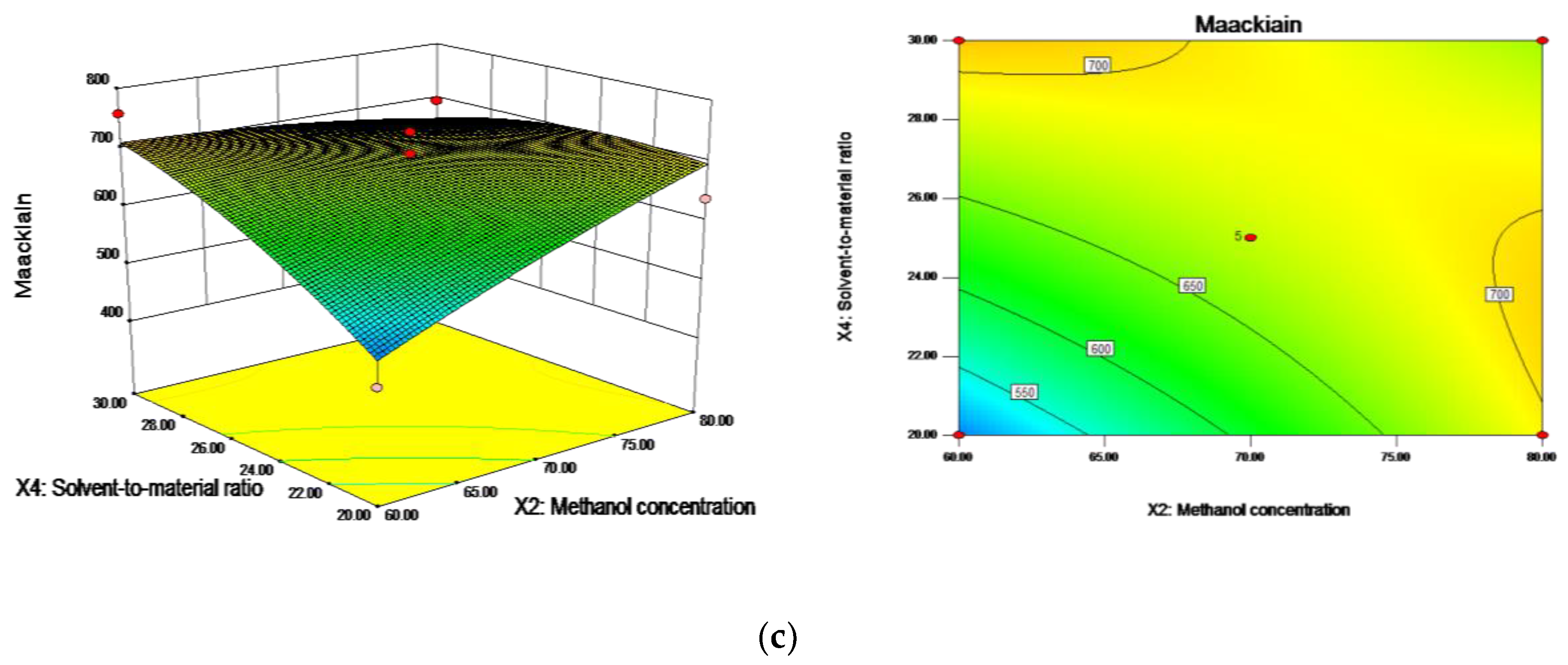

| Factor | Trifolirhizin | Formononetin | Isoxanthohumol | Maackiain | Kurarinone |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F Value (Model) | 2.68 * | 3 * | 2.9 * | 2.76 * | 2.63 * |
| Intercept | 2156.02 | 191.81 | 490.11 | 675.45 | 2632.55 |
| X1 (Time) | 7.09 | −1.37 | 1.97 | −14.06 | 38.28 |
| X2 (Methanol concentration) | 203.12 ** | 3.89 | 4.90 | 37.05 * | 116.87 * |
| X3 (Temperature) | −30.26 | −7.30 | 2.44 | −35.14 * | 68.12 |
| X4 (Solvent-to-sample ratio) | 107.87 * | 16.56 * | 28.77 ** | 44.03 ** | 113.83 * |
| X1X2 | −238.19 * | −12.30 | −15.68 | −45.85 | 72.16 |
| X1X3 | 38.95 | −1.05 | −12.42 | −31.24 | −61.74 |
| X1X4 | 61.92 | 18.71 | 1.01 | 24.88 | −243.38 |
| X2X3 | 32.12 | 13.57 | 19.25 | 13.43 | 70.00 |
| X2X4 | 14.60 | −16.75 | −17.01 | −60.72 * | −33.67 |
| X3X4 | −103.30 | −8.68 | 34.37 * | 37.21 | 70.70 |
| X12 | 75.39 | 9.63 | 2.36 | −5.72 | 194.62 |
| X22 | −86.69 | −4.26 | −16.77 | −9.61 | −83.15 |
| X32 | 90.78 | 16.32 | 31.07 * | −7.62 | 51.19 |
| X42 | 26.23 | −23.93 * | −6.43 | −24.05 | 61.22 |
| R2 | 0.728 | 0.7501 | 0.7434 | 0.7339 | 0.7244 |
| Adj. R2 | 0.456 | 0.5001 | 0.4679 | 0.4868 | 0.4488 |
| F Value (Lack of Fit) | 1.44 | 1.69 | 3.71 | 1.28 | 2.11 |
| Varication Experiment | Trifolirhizin (mg/g) | Formononetin (mg/g) | Isoxanthohumol (mg/g) | Maackiain (mg/g) | Kurarinone (mg/g) | Comprehensive Evaluation Value | Predicted Value | Relative Error/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.696 | 0.225 | 0.561 | 0.870 | 3.004 | 1.341 | 1.345 | 2.55 |
| 2 | 2.520 | 0.204 | 0.523 | 0.769 | 3.022 | 1.279 | ||
| 3 | 2.445 | 0.218 | 0.531 | 0.812 | 3.230 | 1.316 | ||
| 4 | 2.555 | 0.207 | 0.524 | 0.765 | 2.976 | 1.278 | ||
| 5 | 2.633 | 0.208 | 0.533 | 0.767 | 3.224 | 1.338 | ||
| Mean ± SD | 2.570 ± 0.098 | 0.213 ± 0.009 | 0.534 ± 0.015 | 0.797 ± 0.046 | 3.09± 0.125 | 1.311 ± 0.031 |
| Runs | Time (X1)/min | Methanol Concentration (X2)/% | Temperature (X3)/°C | Solvent-to-Material Ratio (X4)/(mL/g) | Extraction Yield/mg.g−1 | Comprehensive Evaluation Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trifolirhizin | Formononetin | Isoxanthohumol | Maackiain | Kurarinone | ||||||
| 1 | 40(0) | 70(0) | 70(0) | 25(0) | 2.117 | 0.172 | 0.432 | 0.574 | 2.428 | 1.040 |
| 2 | 40(0) | 60(−1) | 80(1) | 25(0) | 1.784 | 0.168 | 0.437 | 0.552 | 2.323 | 0.954 |
| 3 | 50(1) | 80(1) | 70(0) | 25(0) | 1.955 | 0.180 | 0.468 | 0.608 | 2.584 | 1.051 |
| 4 | 40(0) | 70(0) | 80(1) | 30(1) | 2.050 | 0.159 | 0.496 | 0.632 | 2.683 | 1.087 |
| 5 | 50(1) | 70(0) | 70(0) | 20(−1) | 1.901 | 0.136 | 0.457 | 0.585 | 2.556 | 1.015 |
| 6 | 40(0) | 60(−1) | 70(0) | 30(1) | 1.975 | 0.207 | 0.517 | 0.757 | 2.706 | 1.120 |
| 7 | 40(0) | 70(0) | 70(0) | 25(0) | 2.010 | 0.192 | 0.475 | 0.738 | 2.644 | 1.102 |
| 8 | 30(−1) | 70(0) | 70(0) | 20(−1) | 2.158 | 0.171 | 0.439 | 0.673 | 2.482 | 1.078 |
| 9 | 40(0) | 70(0) | 80(1) | 20(−1) | 2.277 | 0.179 | 0.487 | 0.709 | 2.709 | 1.155 |
| 10 | 40(0) | 70(0) | 60(−1) | 20(−1) | 2.195 | 0.200 | 0.522 | 0.666 | 2.948 | 1.183 |
| 11 | 30(−1) | 70(0) | 80(1) | 25(0) | 2.288 | 0.221 | 0.550 | 0.717 | 3.049 | 1.238 |
| 12 | 30(−1) | 60(−1) | 70(0) | 25(0) | 1.863 | 0.197 | 0.471 | 0.606 | 2.548 | 1.032 |
| 13 | 50(1) | 70(0) | 70(0) | 30(1) | 2.498 | 0.216 | 0.524 | 0.672 | 2.896 | 1.237 |
| 14 | 40(0) | 70(0) | 60(−1) | 30(1) | 1.980 | 0.214 | 0.493 | 0.640 | 2.639 | 1.085 |
| 15 | 40(0) | 70(0) | 70(0) | 25(0) | 2.036 | 0.198 | 0.500 | 0.624 | 2.748 | 1.107 |
| 16 | 40(0) | 70(0) | 70(0) | 25(0) | 2.364 | 0.163 | 0.495 | 0.641 | 2.718 | 1.154 |
| 17 | 40(0) | 60(−1) | 70(0) | 20(−1) | 1.809 | 0.114 | 0.416 | 0.457 | 2.414 | 0.936 |
| 18 | 30(−1) | 80(1) | 70(0) | 25(0) | 2.459 | 0.203 | 0.514 | 0.771 | 2.804 | 1.229 |
| 19 | 40(0) | 80(1) | 60(−1) | 25(0) | 2.489 | 0.208 | 0.522 | 0.782 | 2.926 | 1.260 |
| 20 | 50(1) | 70(0) | 60(−1) | 25(0) | 2.357 | 0.213 | 0.515 | 0.770 | 2.689 | 1.193 |
| 21 | 30(−1) | 70(0) | 60(−1) | 25(0) | 2.232 | 0.204 | 0.483 | 0.633 | 2.559 | 1.112 |
| 22 | 40(0) | 60(−1) | 60(−1) | 25(0) | 2.540 | 0.216 | 0.536 | 0.698 | 2.824 | 1.239 |
| 23 | 50(1) | 70(0) | 80(1) | 25(0) | 2.569 | 0.227 | 0.531 | 0.719 | 2.933 | 1.270 |
| 24 | 50(1) | 60(−1) | 70(0) | 25(0) | 2.212 | 0.204 | 0.488 | 0.627 | 2.539 | 1.104 |
| 25 | 30(−1) | 70(0) | 70(0) | 30(1) | 2.507 | 0.187 | 0.502 | 0.581 | 2.996 | 1.225 |
| 26 | 40(0) | 80(1) | 80(1) | 25(0) | 2.362 | 0.214 | 0.500 | 0.669 | 2.706 | 1.174 |
| 27 | 40(0) | 80(1) | 70(0) | 20(−1) | 2.266 | 0.151 | 0.443 | 0.637 | 2.441 | 1.077 |
| 28 | 40(0) | 70(0) | 70(0) | 25(0) | 2.654 | 0.214 | 0.638 | 0.801 | 1.579 | 1.076 |
| 29 | 40(0) | 80(1) | 70(0) | 30(1) | 2.490 | 0.177 | 0.476 | 0.695 | 2.597 | 1.170 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Jin, W.; Chen, W.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y. Simultaneous Optimization for Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction and Antioxidant Activity of Flavonoids from Sophora flavescens Using Response Surface Methodology. Molecules 2019, 24, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010112
Zhou J, Zhang L, Li Q, Jin W, Chen W, Han J, Zhang Y. Simultaneous Optimization for Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction and Antioxidant Activity of Flavonoids from Sophora flavescens Using Response Surface Methodology. Molecules. 2019; 24(1):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010112
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jing, Lincheng Zhang, Qinping Li, Weifeng Jin, Weiyan Chen, Jin Han, and Yuyan Zhang. 2019. "Simultaneous Optimization for Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction and Antioxidant Activity of Flavonoids from Sophora flavescens Using Response Surface Methodology" Molecules 24, no. 1: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010112
APA StyleZhou, J., Zhang, L., Li, Q., Jin, W., Chen, W., Han, J., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Simultaneous Optimization for Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction and Antioxidant Activity of Flavonoids from Sophora flavescens Using Response Surface Methodology. Molecules, 24(1), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010112




