Preparation and Evaluation of Antidiabetic Agents of Berberine Organic Acid Salts for Enhancing the Bioavailability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Berberine Organic Acid Salts (BOAs)
2.3. Animals
2.4. Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability
2.4.1. Induction of Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) in Rats
2.4.2. Grouping and Administration
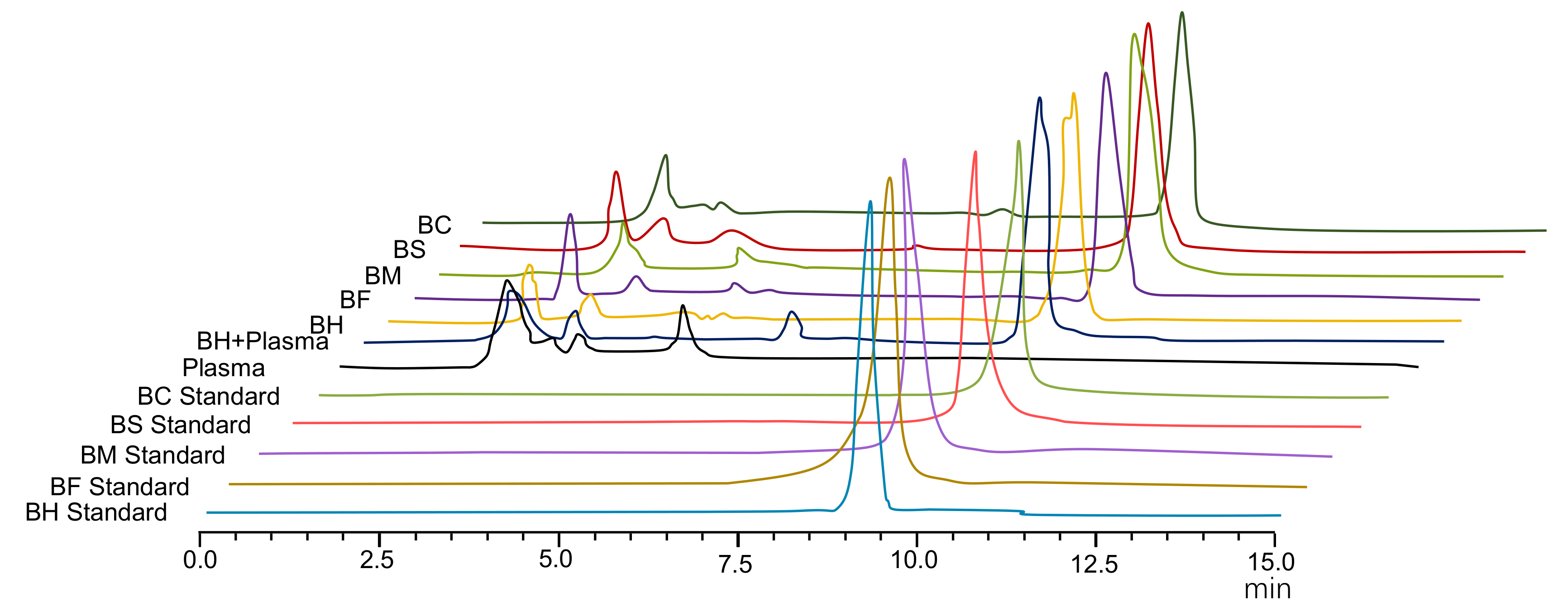
2.4.3. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
2.4.4. Statistics and Analysis
2.5. Tissue Distribution of Berberine Hydrochloride (BH) and Berberine Fumarate (BF)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability of Berberine Hydrochloride (BH) and Berberine Organic Acid Salts (BOAs)
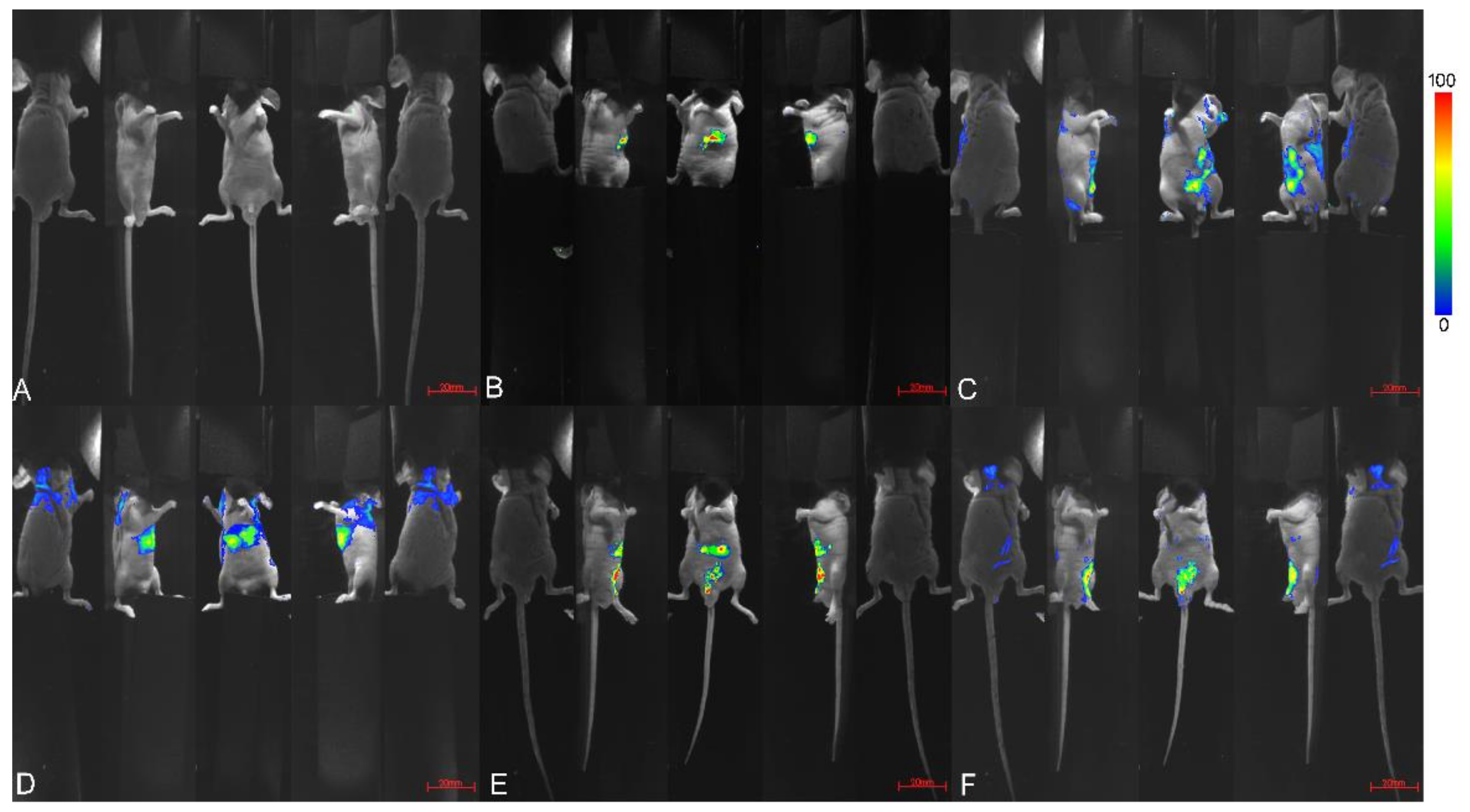
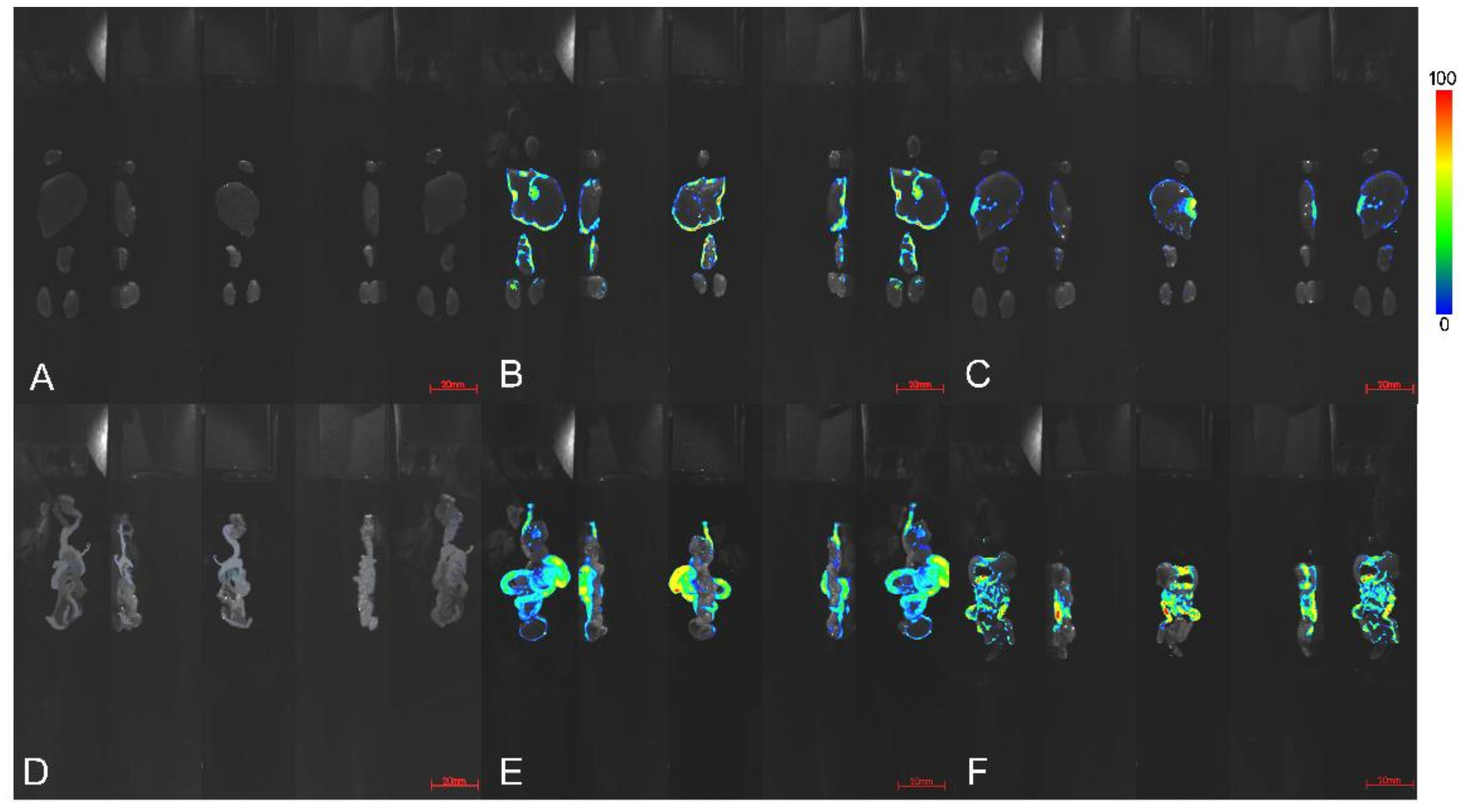
3.2. Tissue Distribution of Berberine Hydrochloride (BH) and Berberine Fumarate (BF)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of interest
References
- Hu, Y.; Davies, G.E. Berberine inhibits adipogenesis in high-fat diet-induced 477 obesity mice. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ye, X.L.; Li, X.G.; Zhen, J.; Zhang, B.S.; Yuan, L.J. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of 8-alkyl Berberine Derivatives with a Long Aliphatic Chain. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 602–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaboli, P.J.; Rahmat, A.; Ismail, P.; Ling, K.H. Targets and mechanisms of berberine, a natural drug with potential to treat cancer with special focus on breast cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 584–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Miao, Y.Q.; Fan, D.J.; Yang, S.S.; Lin, X.; Meng, L.K.; Tang, X. Bioavailability study of berberine and the enhancing effects of TPGS on intestinal absorption in rats. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.X. Pharmacokinetics of three alkaloids in Huanglianjiedu Decoction in diabetic rats. Master’s Thesis, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China, June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, W. Non-coding RNAs and Berberine: A new mechanism of its anti-diabetic activities. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 795, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.W.; Yuan, K.; Shang, S.C.; Guo, Y. A safer hypoglycemic agent for type 2 diabetes—Berberine organic acid salt. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.X.; Yao, M. In Vivo Imaging Technology in Small Animal. Chin J. Comparative Med. 2011, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Pamela, R.C. Whole-animal celluar and molecular imaging to accelerate drug development. Res. Focus 2002, 7, 555–557. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, N.C.; Egen, J.G.; Secundino, N.; Debrabant, A.; Kimblin, N.; Kamhawi, S.; Lawyer, P.; Fay, M.P.; Germain, R.N.; Sacks, D. In vivo imaging reveals an essential role for neutrophils in leishmaniasis transmitted by sand flies. Science 2008, 321, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, B.; Pittman, K.; Menezes, G.B. Intravascular danger signals guide neutrophils to sites of sterile inflammation. Science 2010, 330, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.D.; Xin, K.; Dou, H.F.; Yin, G.; Quan, Y.W.; Wang, R.Y. A fast-responsive mitochondria-targeted fluorescent probe detecting endogenous hypochlorite in living RAW 264.7 cells and nude mouse. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 1442–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, P.F.; Gao, C.; Cheng, P.P.; Li, J.L.; Huang, X.; Lin, Y.Y.; Li, Q.; Peng, Y.Z.; Cai, M.C.; Wei, S.; et al. Immunosuppressive Effect of Compound K on Islet Transplantation in an STZ-Induced Diabetic Mouse Model. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3458–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.R.; Zhou, J.P.; Xie, S.F. PKSolver: An add-in program for pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data analysis in Microsoft Excel. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2010, 21, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battu, S.K.; Repka, M.A.; Maddineni, S.; Chittiboyina, A.G.; Avery, M.A.; Majumdar, S. Physicochemical characterization of berberine chloride: A perspective in the development of a solution dosage form for oral delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, F.; Nakamura, N.; Akao, T. Pharmacokinetics of berberine and its main metabolites in conventional and pseudo germ-free rats determind by liquid chromatography/ion trap mass spectrometry. Drug Dispos. 2006, 34, 2064–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Q.M.; Zhang, M.F. The pharmacokinetics of berberine. Chin. Acad. Med. Mag. Org. 2002, 12, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, G.Y.; Wang, G.J.; Liu, X.D.; Fawcett, J.P.; Xie, Y.Y. The involvement of P-glycoprotein in berberine absorption. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2002, 91, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.L.; Tsai, T.H. Simultaneous determination of berberine in rat blood, liver and bile using microdialysis coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 961, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.L.; Tsai, T.H. Hepatobiliary excretion of berberine. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Ma, Y.; Shi, R.; Wang, T. Simultaneous quantification of three alkaloids of Coptidis Rhizoma in rat urine by high-performance liquid chromatography: application to pharmacokinetic study. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2007, 28, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, W.X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.L.; Liu, J. Determination of berberine hydrochloride by fluorescent spectrometry with sodium dodecyl sulfates sensitizer. Phys. Test. Chem. Anal. 2015, 10, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.S.; Ma, J.Y.; Feng, R.; Ma, C.; Chen, W.J.; Sun, Y.P.; Fu, J.; Huang, M.; He, C.Y.; Shou, J.W. Tissue Distribution of Berberine and Its Metabolites after Oral Administration in Rats. Plos ONE 2013, 8, e77969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, C.Y.; Shi, X.B.; Dai, Z.S. Pharmacokinetic study of 3H-berberine in rabbits and mouse. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 1989, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Xing, D.; Su, H.; Ma, C. Kinetic difference of berberine between hippocampus and plasma in rat after intravenous administration of Coptidis rhizome extract. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 3058–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Qian, C. Berberine chloride can ameliorate the spatial memory impairment and increase the expression of interleukin-1beta and inducible nitric oxide synthase in the rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Neurosci. 2006, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, B.W.; Nam, E.; Org, E.; Kostem, E.; Norheim, F.; Hui, S.T.; Pan, C.; Civelek, M.C.D.; Rau, B.J.; Bennett, M.; et al. Genetic control of obesity and gut microbiota composition in response to high-fat, high-sucrose diet in mice. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.H.; Zhang, M.H.; Wang, S.Y.; Han, R.J.; Cao, Y.F.; Hua, W.Y.; Mao, Y.J.; Zhang, X.J.; Pang, X.Y.; Wei, C.C.; et al. Interactions between gut microbiota, host genetics and diet relevant to development of metabolic syndromes in mice. ISME J. 2010, 4, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.H.; Zhang, M.H.; Pang, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.F.; Wang, L.H.; Zhao, L.P. Structural resilience of the gut microbiota in adult mice under high-fat dietary perturbations. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1848–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaret, M.N. Are biologists in “future shock”? Symbiosis integrates biology across domains. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 789–92. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, R.J.; Peng, L.; Barry, N.A.; Cline, G.W.; Zhang, D.Y.; Cardone, R.L.; Petersen, K.F.; Kibbey, R.G.; Goodman, A.L.; Shulman, G.I. Acetate mediates a microbiome-brain-β-cell axis to promote metabolic syndrome. Nature 2016, 534, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpal, D.K.; Klein, J.L.; Mayhew, D.; Boucheron, J.; Spivak, A.T.; Kumar, V.; Ingraham, K.; Paulik, M.; Chen, L.H.; Horn, S.V.; et al. Selective Spectrum Antibiotic Modulation of the Gut Microbiome in Obesity and Diabetes Rodent Models. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, R.; Shou, J.; Zhao, Z.; He, C.; Ma, C.; Huang, M.; Fu, J.; Tan, X.S.; Li, X.Y.; Wen, B.Y. Transforming berberine into its intestine-absorbable form by the gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.C.; Dong, S.; Xu, L.J.; Zhang, C.Y. Intestinal absorption of berberine and 8-hydroxy dihydroberberine and their effects on sugar absorption in rat small intestine. J Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technolog. Med. Sci. 2014, 34, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delzenne, N.M.; Cani, P.D. Nutritional modulation of gut microbiota in the context of obesity and insulin resistance: Potential interestof perbiotics. Int. Dairy J. 2010, 20, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; He, S.; Selko, E.T. Control of Salmonella typhimurium using organic acids. Pigs Poult. 2016, 8, 1–3. Available online: http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/GWXM201608001.htm (accessed on 7 August 2016).
- André, M.; Kuang, Y.W. Utilization of Organic Acids to Optimize Microecological Balance of Digestive Tract. Feed Husb. 2012, 7, 20–23. Available online: http://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=e9bcaaff47a8542abb834e7f1f691c48&site=xueshu_se (accessed on 12 July 2012).
- Duncan, S.H.; Belenguer, A.; Holtrop, G.; Johnstone, A.M.; Flint, H.J.; Lobley, G.E. Reduced dietary intake of carbohydrates by obese subjects results in decreased concentrations of butyrate and butyrate-producing bacteria in feces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 7, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, B.S.; Shaito, A.; Motoike, T.; Rey, F.E.; Backhed, F.; Manchester, J.K.; Hammer, R.E.; Williams, S.C.; Crowley, J.; Yanagsawa, M.; et al. Effects of the gut microbiota on host adiposity are modulated by the short-chain fatty-acid binding G protein-coupled receptor, Gpr41. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16767–16772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds not are available from the authors. |
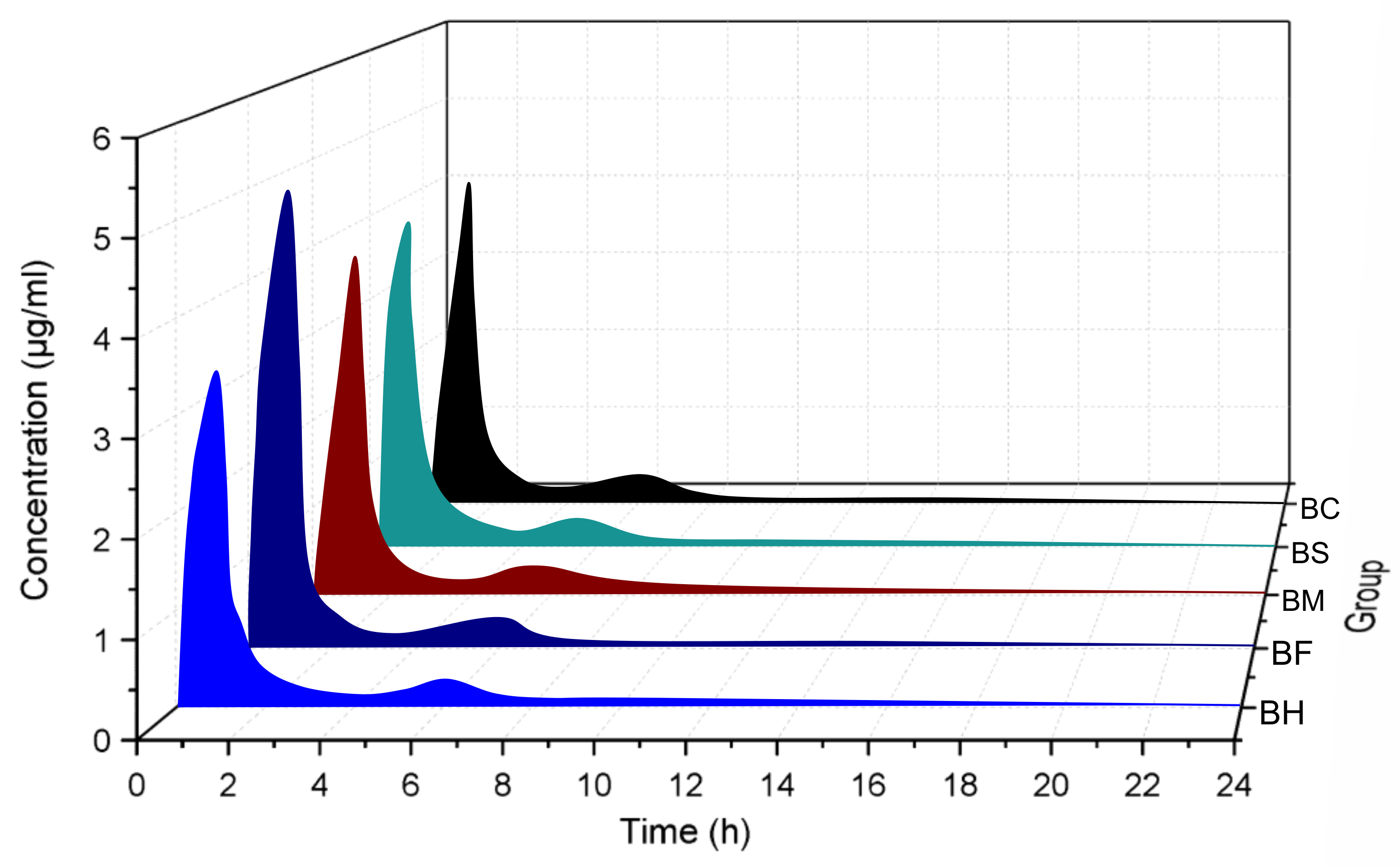
| Parameter | BH | BF | BM | BS | BC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t1/2 (h) | 11.79 ± 3.51 | 9.02 ± 1.46 | 12.13 ± 7.38 | 15.31 ± 15.50 | 16.94 ± 4.66 |
| Tmax (h) | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.90 ± 0.22 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.90 ± 0.22 | 1.00 ± 0.00 |
| Cmax (μg/mL) | 4.22 ± 0.87 | 5.47 ± 0.51 | 4.54 ± 0.82 | 4.39 ± 1.25 | 4.30 ± 1.56 |
| AUC0-t (μg mL/h) | 7.21 ± 0.65 | 9.51 ± 1.72 * | 8.77 ± 1.65 | 8.86 ± 1.29 | 7.60 ± 0.94 |
| AUC0-∞ (μg mL/h) | 8.29 ± 0.78 | 10.60 ± 1.68 * | 10.31 ± 1.34 * | 10.89 ± 1.95 * | 9.89 ± 1.28 |
| AUC0-∞ (iv) (μg mL/h) | 14.05 ± 0.22 | 10.26 ± 0.28 | 11.74 ± 0.50 | 10.27 ± 0.52 | 11.83 ± 0.36 |
| MRT0-t (h) | 5.02 ± 0.31 | 5.36 ± 0.66 | 6.08 ± 0.59 | 5.80 ± 0.72 | 5.88 ± 0.70 |
| MRT0-∞ (h) | 9.86 ± 2.75 | 8.72 ± 1.34 | 12.17 ± 5.19 | 15.29 ± 13.55 | 15.89 ± 2.72 |
| Vz/F (L/kg) | 1022.22 ± 262.73 | 631.42 ± 161.00 | 875.12 ± 586.36 | 940.58 ± 777.81 | 1235.01 ± 296.39 |
| Cl/F (L/h/kg) | 60.72 ± 6.00 | 48.10 ± 7.44 * | 49.15 ± 6.46 * | 47.26 ± 9.56 * | 51.12 ± 5.84 * |
| Fr (%) | 127.80 | 124.30 | 131.27 | 119.31 | |
| Fa (%) | 0.708 | 0.970 | 0.848 | 0.968 | 0.841 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, H.-X.; Hu, Y.-N.; Li, J.-W.; Yuan, K.; Guo, Y. Preparation and Evaluation of Antidiabetic Agents of Berberine Organic Acid Salts for Enhancing the Bioavailability. Molecules 2019, 24, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010103
Cui H-X, Hu Y-N, Li J-W, Yuan K, Guo Y. Preparation and Evaluation of Antidiabetic Agents of Berberine Organic Acid Salts for Enhancing the Bioavailability. Molecules. 2019; 24(1):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010103
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Hong-Xin, Ya-Nan Hu, Jing-Wan Li, Ke Yuan, and Ying Guo. 2019. "Preparation and Evaluation of Antidiabetic Agents of Berberine Organic Acid Salts for Enhancing the Bioavailability" Molecules 24, no. 1: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010103
APA StyleCui, H.-X., Hu, Y.-N., Li, J.-W., Yuan, K., & Guo, Y. (2019). Preparation and Evaluation of Antidiabetic Agents of Berberine Organic Acid Salts for Enhancing the Bioavailability. Molecules, 24(1), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010103





