Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction: From Homogeneous Catalysts to Heterogeneous-Based Reticular Chemistry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Discussion
2.1. Homogeneous Catalyst for CO2 Reduction
2.2. Heterogeneous-Based MOFs Catalyst for CO2 Reduction
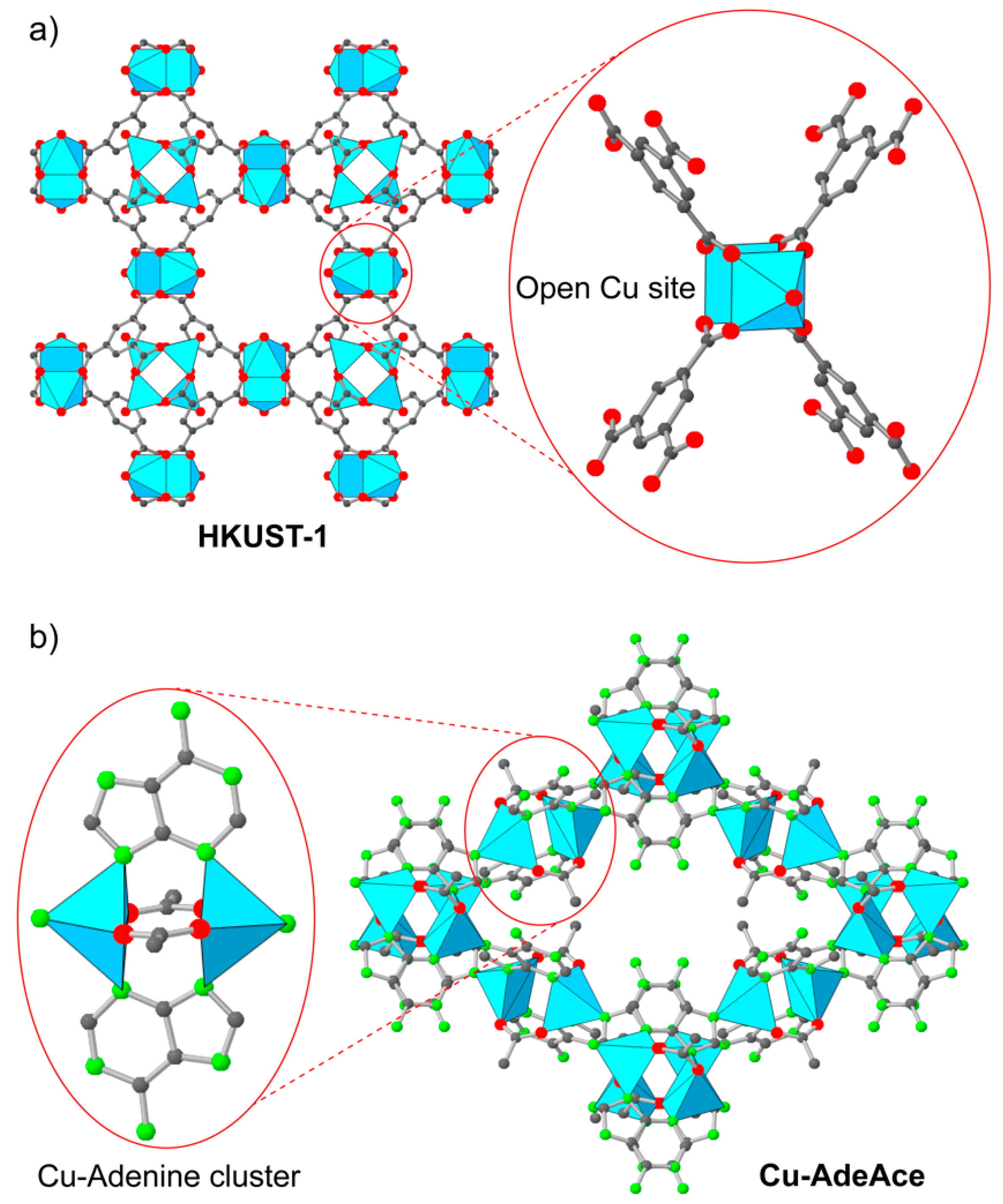
2.2.1. Early State: Cu-MOFs and Open Metal Sites (OMS) Utilization
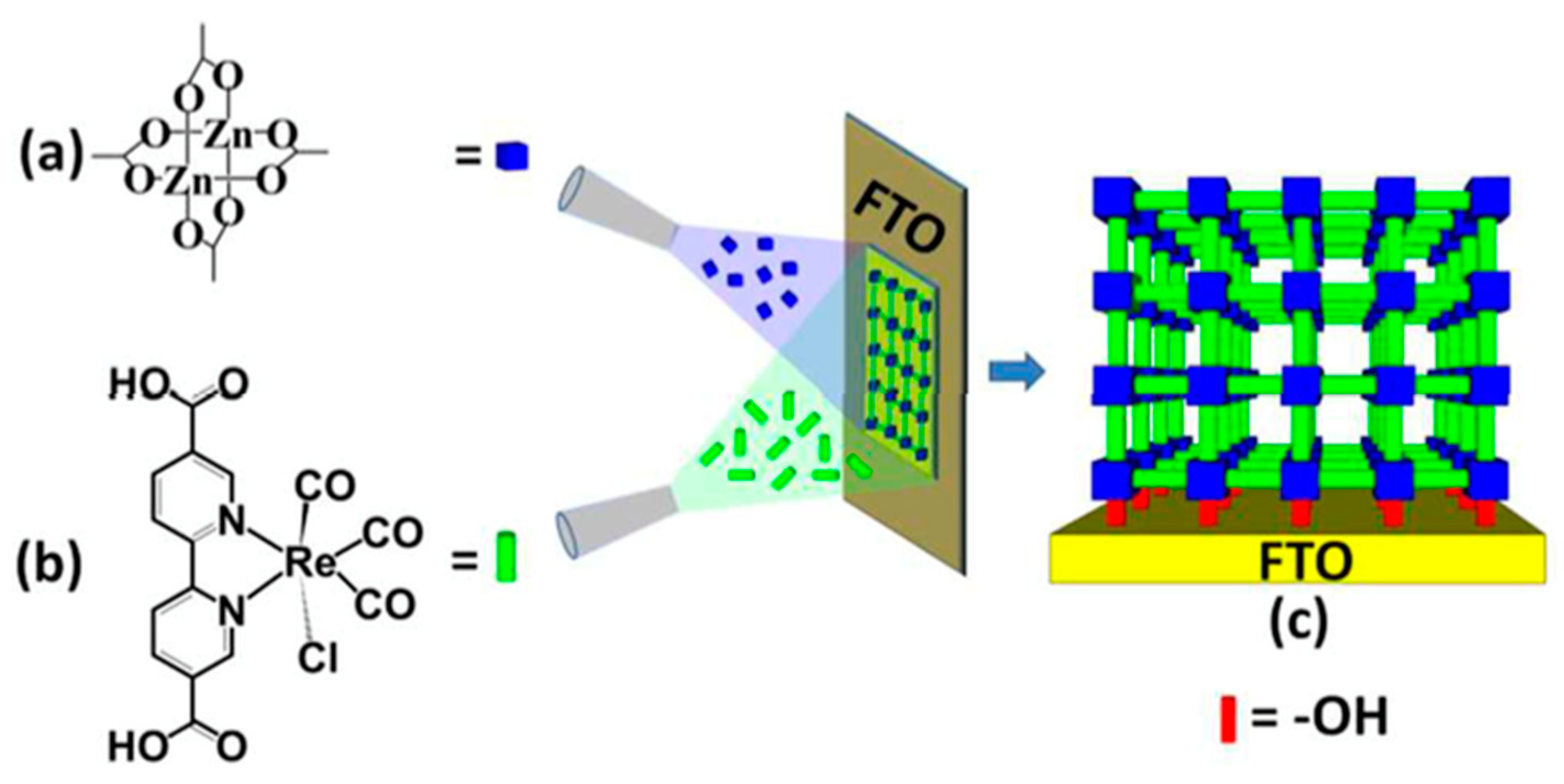
2.2.2. Functional Incorporation into MOFs
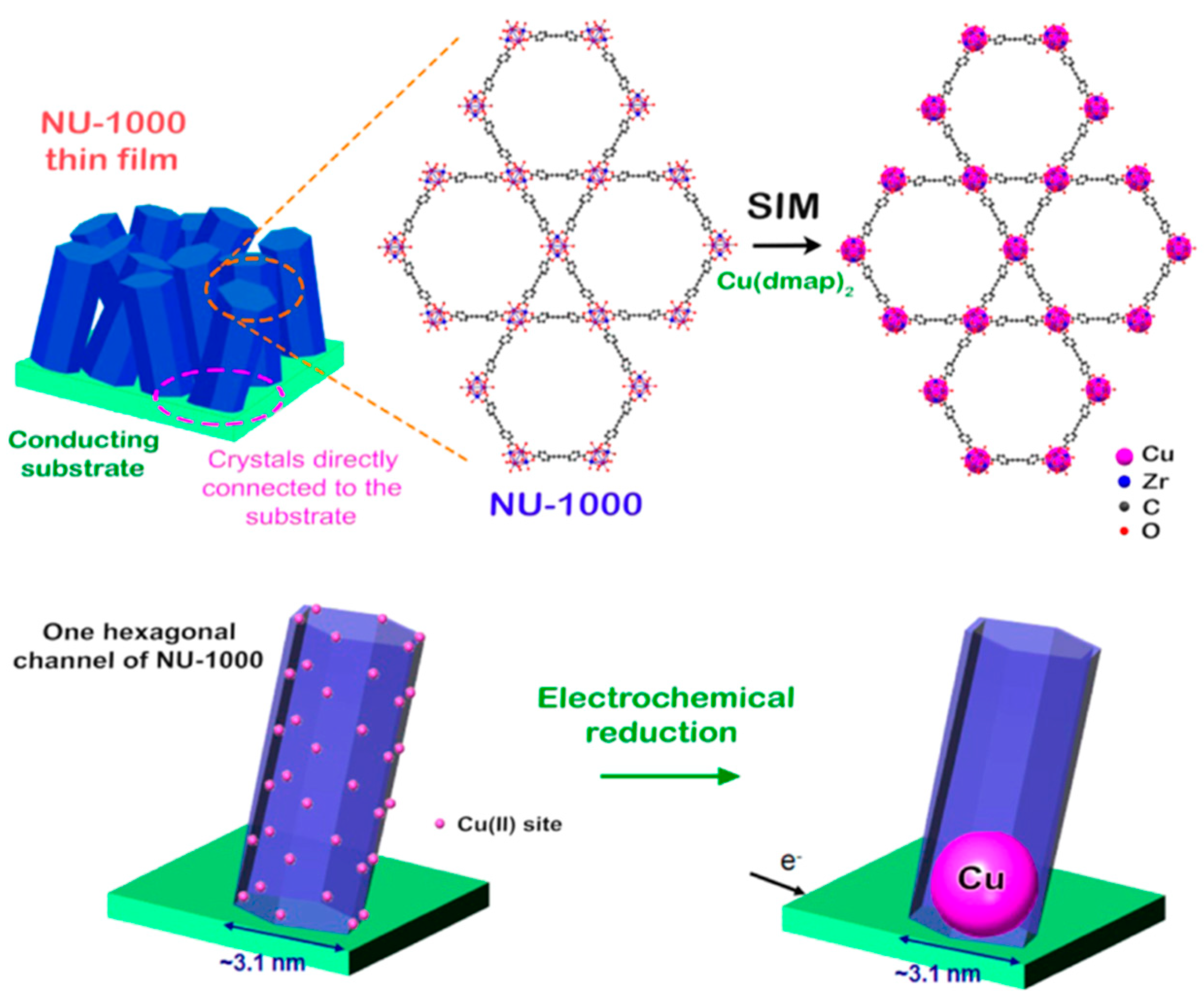
2.2.3. Next Generation: Enhancing the Charge Carrier Mobility
3. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.R.; Ma, Y.; McCarthy, M.C.; Sculley, J.; Yu, J.; Jeong, H.K.; Balbuena, P.B.; Zhou, H.C. Carbon dioxide capture-related gas adsorption and separation in metal-organic frameworks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 1791–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Paris Agreement. Available online: https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/the-paris-agreement/the-paris-agreement (accessed on 3 July 2018).
- Nguyen, P.T.; Nguyen, H.T.; Nguyen, H.N.; Trickett, C.A.; Ton, Q.T.; Gutiérrez-Puebla, E.; Monge, M.A.; Cordova, K.E.; Gándara, F. New metal-organic frameworks for chemical fixation of CO2. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 10, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kattel, S.; Ramírez, P.J.; Chen, J.G.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Liu, P. Active sites for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol on Cu/ZnO catalysts. Science 2017, 355, 1296–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zou, Z. Photocatalytic conversion of CO2 into renewable hydrocarbon fuels: state-of-the-art accomplishment, challenges, and prospects. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4607–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K.E.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks. Science 2013, 341, 1230444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, L.; Jackstell, R.; Beller, M. Using carbon dioxide as a building block in organic synthesis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, P.Q.; Shen, J.Q.; Zhang, J.P. Metal–organic frameworks for electrocatalysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 373, 22–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maina, J.W.; Pozo-Gonzalo, C.; Kong, L.; Schütz, J.; Hill, M.; Dumée, L.F. Metal-organic framework based catalysts for CO2 conversion. Mater. Horiz. 2017, 4, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, C.A.; Marinescu, S.C. Electrocatalytic metal-organic frameworks for energy applications. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 4374–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diercks, C.S.; Liu, Y.; Cordova, K.E.; Yaghi, O.M. The role of reticular chemistry in the design of CO2 reduction catalysts. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, D.M.; Zhu, Y.P.; Chen, P.; Ma, T.Y. Recent advances in transition-metal-mediated electrocatalytic CO2 reduction: from homogeneous to heterogeneous systems. Catalysts 2017, 7, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, E.E.; Kubiak, C.P.; Sathrum, A.J.; Smieja, J.M. Electrocatalytic and homogeneous approaches to conversion of CO2 to liquid fuels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francke, R.; Schille, B.; Roemelt, M. Homogeneously catalyzed electroreduction of carbon dioxide—methods, mechanisms, and catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 4631–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshitsuka, S.; Ichikawa, M.; Tamaru, K. Electrocatalysis by metal phthalocyanines in the reduction of carbon dioxide. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1974, 0, 158–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, B.J.; Eisenberg, R. Electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide by using macrocycles of nickel and cobalt. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 7361–7363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beley, M.; Collin, J.P.; Ruppert, R.; Sauvage, J.P. Electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide by nickel cyclam2+ in water: study of the factors affecting the efficiency and the selectivity of the process. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 7461–7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, J.P.; Jouaiti, A.; Sauvage, J.P. Electrocatalytic properties of (tetraazacyclotetradecane) nickel (2+) and Ni2 (biscyclam) 4+ with respect to carbon dioxide and water reduction. Inorg. Chem. 1988, 27, 1986–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammouche, M.; Lexa, D.; Momenteau, M.; Savéant, J.M. Chemical catalysis of electrochemical reactions. Homogeneous catalysis of the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide by iron (“0”) porphyrins. Role of the addition of magnesium cations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 8455–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhugun, I.; Lexa, D.; Savéant, J.M. Catalysis of the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide by iron (0) porphyrins: Synergystic effect of weak Brönsted acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 1769–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costentin, C.; Drouet, S.; Robert, M.; Savéant, J.-M. A local proton source enhances CO2 electroreduction to CO by a molecular fe catalyst. Science 2012, 338, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costentin, C.; Passard, G.; Robert, M.; Savéant, J.M. Ultraefficient homogeneous catalyst for the CO2-to-CO electrochemical conversion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14990–14994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raciti, D.; Wang, C. Recent advances in CO2 reduction electrocatalysis on copper. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 1545–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, M.B.; Church, T.L.; D’Alessandro, D.M. Perspectives on metal-organic frameworks with intrinsic electrocatalytic activity. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 4049–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diercks, C.S.; Kalmutzki, M.J.; Yaghi, O.M. Covalent organic frameworks–organic chemistry beyond the molecule. Molecules 2017, 22, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoedel, A.; Ji, Z.; Yaghi, O.M. The role of metal-organic frameworks in a carbon-neutral energy cycle. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinogami, R.; Yotsuhashi, S.; Deguchi, M.; Zenitani, Y.; Hashiba, H.; Yamada, Y. Electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide using a copper rubeanate metal organic framework. ECS Electrochem. Lett. 2012, 1, H17–H19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.S.; Kumar, S.S.; Kulandainathan, M.A. Highly selective electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide using Cu based metal organic framework as an electrocatalyst. Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 25, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo, J.; Vallejo, D.; Beobide, G.; Castillo, O.; Castaño, P.; Irabien, A. Copper-based metal-organic porous materials for CO2 electrocatalytic reduction to alcohols. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.M. Postsynthetic methods for the functionalization of metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 970–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Cohen, S.M. Postsynthetic modification of metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1315–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, T.N.; Nguyen, M.V.; Nguyen, H.L.; Yuliarto, B.; Cordova, K.E.; Demir, S. Designing bipyridine-functionalized zirconium metal-organic frameworks as a platform for clean energy and other emerging applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 364, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Gong, C.; Addicoat, M.; Heine, T.; Wöll, C.; Sun, L. Highly oriented MOF thin film-based electrocatalytic device for the reduction of CO2 to CO exhibiting high faradaic efficiency. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 15320–15326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wächter, T.; Irmler, A.; Weidler, P.G.; Gliemann, H.; Pauly, F.; Mugnaini, V.; Zharnikov, M.; Wöll, C. Electric transport properties of surface-anchored metal-organic frameworks and the effect of ferrocene loading. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 9824–9830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, C.W.; Audu, C.O.; Peters, A.W.; Noh, H.; Farha, O.K.; Hupp, J.T. Copper nanoparticles installed in metal-organic framework thin films are electrocatalytically competent for CO2 reduction. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 2394–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrenholtz, S.R.; Epley, C.C.; Morris, A.J. Solvothermal preparation of an electrocatalytic metalloporphyrin MOF thin film and its redox hopping charge-transfer mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 2464–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hod, I.; Sampson, M.D.; Deria, P.; Kubiak, C.P.; Farha, O.K.; Hupp, J.T. Fe-porphyrin-based metal-organic framework films as high-surface concentration, heterogeneous catalysts for electrochemical reduction of CO2. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 6302–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costentin, C.; Drouet, S.; Robert, M.; Savéant, J.M. Turnover numbers, turnover frequencies, and overpotential in molecular catalysis of electrochemical reactions. Cyclic voltammetry and preparative-scale electrolysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11235–11242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornienko, N.; Zhao, Y.; Kley, C.S.; Zhu, C.; Kim, D.; Lin, S.; Chang, C.J.; Yaghi, O.M.; Yang, P. Metal-organic frameworks for electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14129–14135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Diercks, C.S.; Zhang, Y.B.; Kornienko, N.; Nichols, E.M.; Zhao, Y.; Paris, A.R.; Kim, D.; Yang, P.; Yaghi, O.M.; Chang, C.J. Covalent organic frameworks comprising cobalt porphyrins for catalytic CO2 reduction in water. Science 2015, 349, 1208–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diercks, C.S.; Lin, S.; Kornienko, N.; Kapustin, E.A.; Nichols, E.M.; Zhu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Chang, C.J.; Yaghi, O.M. Reticular electronic tuning of porphyrin active sites in covalent organic frameworks for electrocatalytic carbon dioxide reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Omari, A.A.; Yamani, Z.H.; Nguyen, H.L. Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction: From Homogeneous Catalysts to Heterogeneous-Based Reticular Chemistry. Molecules 2018, 23, 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112835
Al-Omari AA, Yamani ZH, Nguyen HL. Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction: From Homogeneous Catalysts to Heterogeneous-Based Reticular Chemistry. Molecules. 2018; 23(11):2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112835
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Omari, Abdulhadi A., Zain H. Yamani, and Ha L. Nguyen. 2018. "Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction: From Homogeneous Catalysts to Heterogeneous-Based Reticular Chemistry" Molecules 23, no. 11: 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112835
APA StyleAl-Omari, A. A., Yamani, Z. H., & Nguyen, H. L. (2018). Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction: From Homogeneous Catalysts to Heterogeneous-Based Reticular Chemistry. Molecules, 23(11), 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112835




