Innovative “Green” and Novel Strategies for the Extraction of Bioactive Added Value Compounds from Citrus Wastes—A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
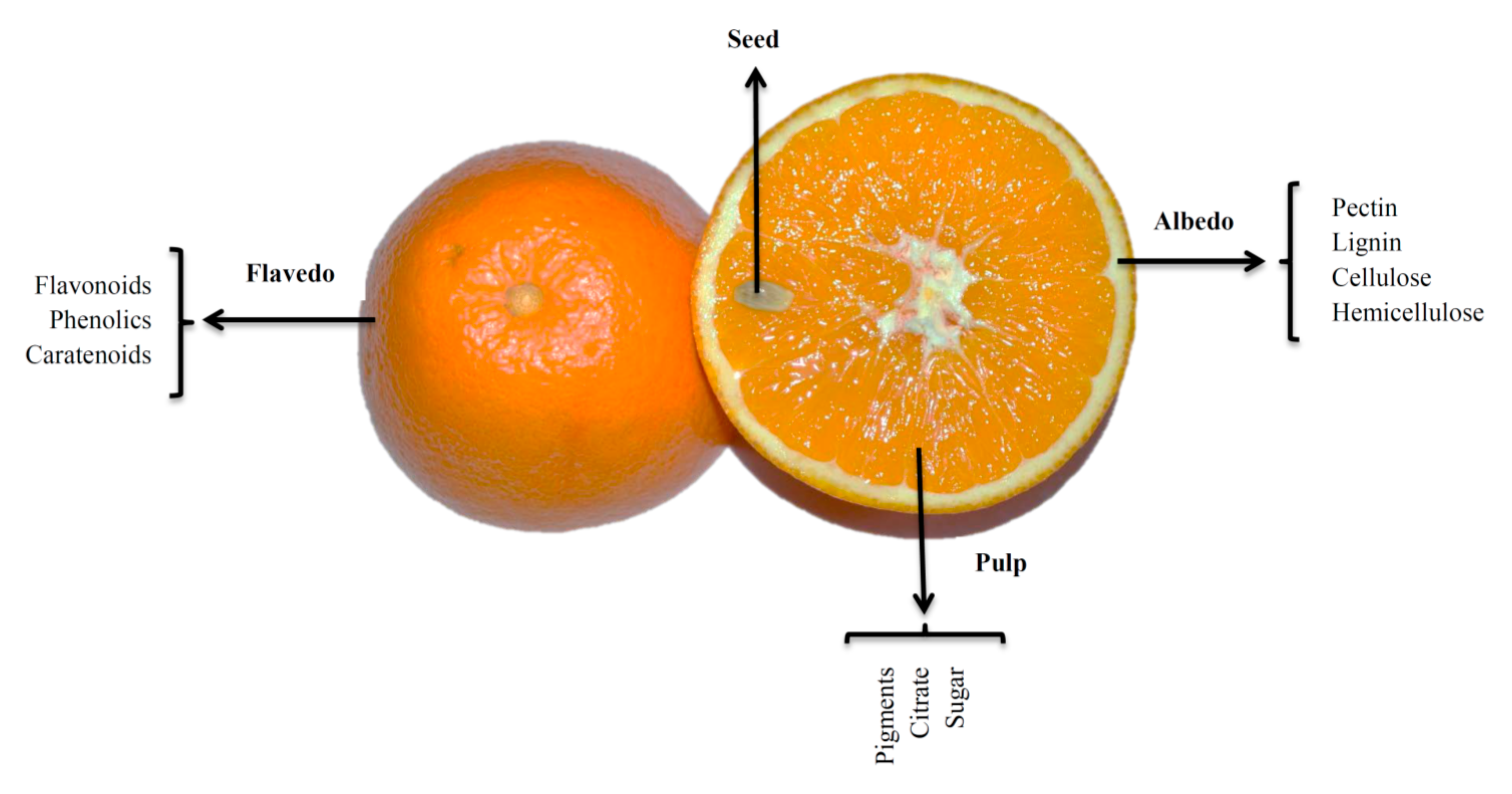
2. Nutritional and Bioactive Composition of Citrus Wastes
2.1. Dietary Fibre
Pectin
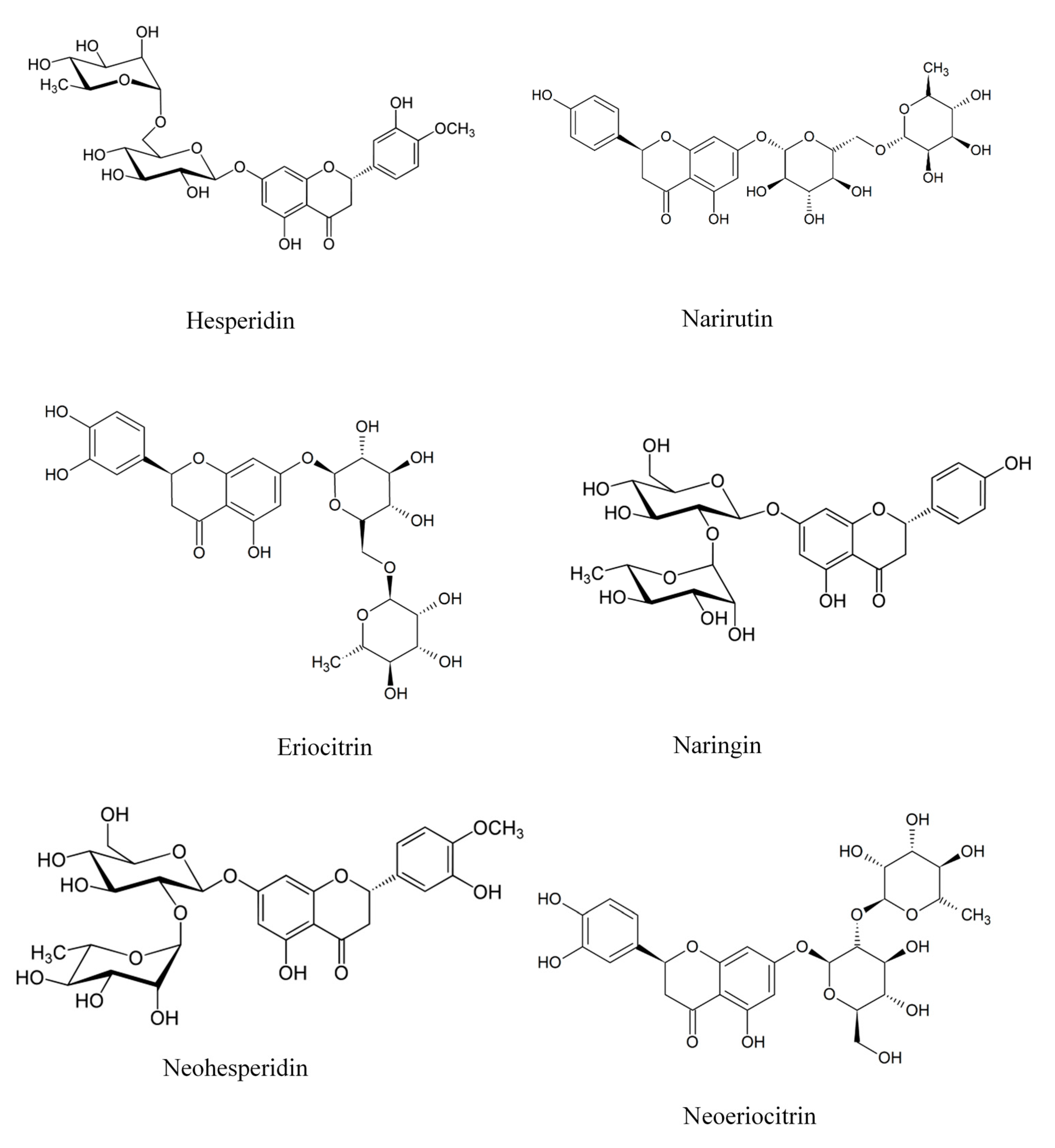
2.2. Polyphenols
2.3. Natural Pigments
2.4. Essential Oils (EOs)
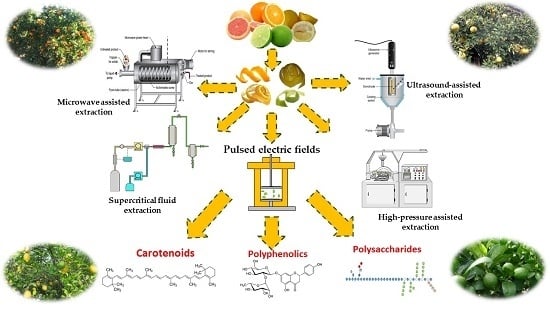
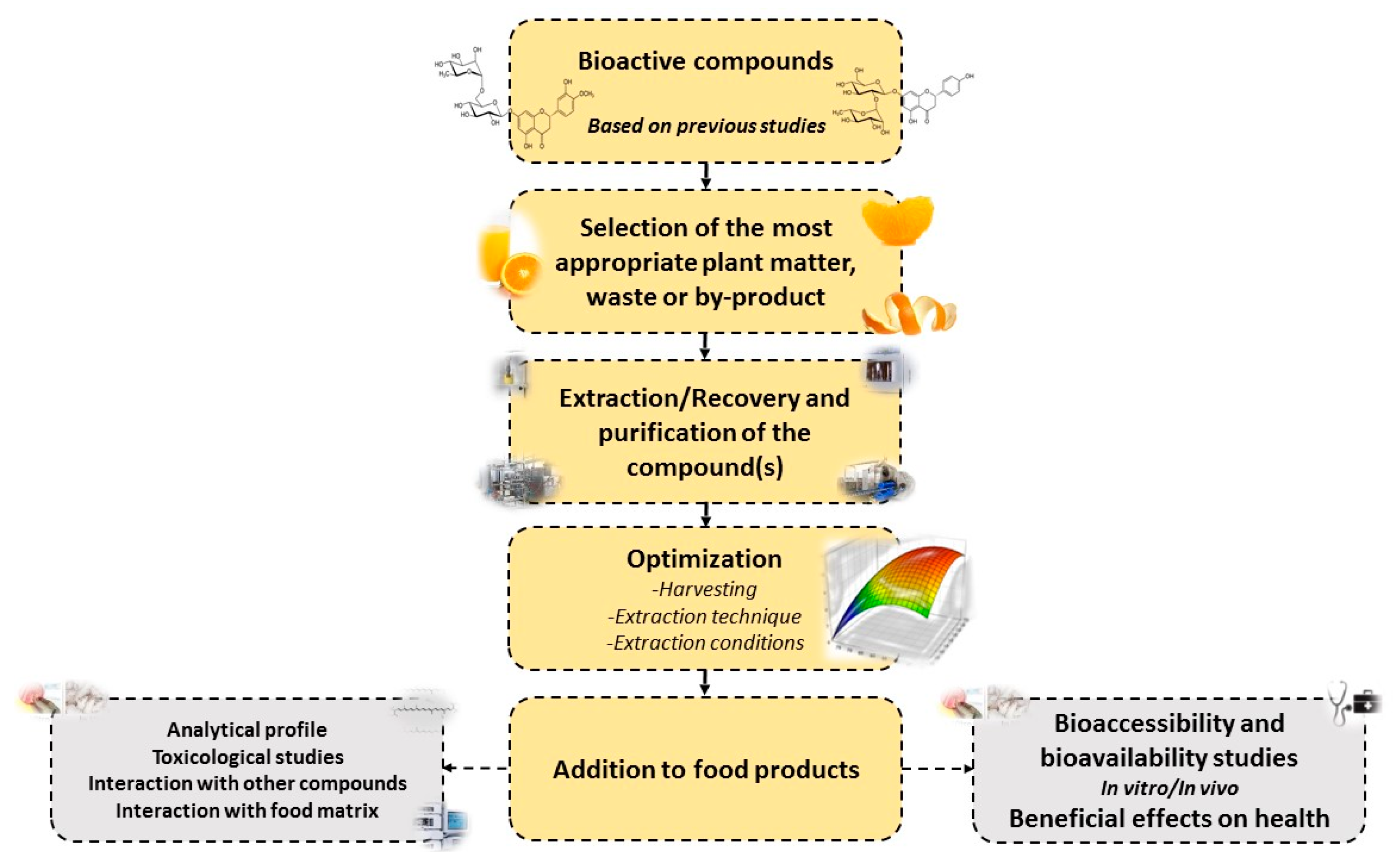
3. Valorisation of Citrus Waste and By-products by Extraction of BACs Using Novel Strategies
3.1. Pectins
3.1.1. Ultrasound
3.1.2. Microwaves
3.1.3. High Pressure
3.2. Antioxidant Bioactive Compounds (Polyphenols, Carotenoids, Vitamin E, etc.)
3.2.1. Pulsed Electric Fields
3.2.2. Ultrasound
3.2.3. Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE)
3.2.4. Pressurized Fluid Extraction
3.2.5. High-Pressure Assisted Extraction (HPE)
3.3. Essential Oils (EOs)
3.3.1. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction
3.3.2. Microwaves
3.3.3. Supercritical Fluid Extraction
3.3.4. Enzyme-Assisted Extraction
3.4. Anaerobic Digestion
4. Challenges and Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ledesma-Escobar, C.A.; Luque de Castro, M.D. Towards a comprehensive exploitation of citrus. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 39, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohrasbi, M.; Pourbafrani, M.; Niklasson, C.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Process design and economic analysis of a citrus waste biorefinery with biofuels and limonene as products. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7382–7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, F.R.; Soler-Rivas, C.; Benavente-Garcia, O.; Castillo, J.; Perez-Alvarez, J.A. By-products from different citrus processes as a source of customized functional fibres. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, M.; Priolo, A.; Biondi, L.; Bella, M.; Salem, H. Ben Replacement of cereal grains by orange pulp and carob pulp in faba bean-based diets fed to lambs: Effects on growth performance and meat quality. Anim. Res. 2001, 50, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazok, A.; Rezaei, M.; Sayyahzadeh, H. Effect of different levels of dried citrus pulp on performance, egg quality, and blood parameters of laying hens in early phase of production. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2010, 42, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, T.C.; Lynch, P.B.; Morrissey, P.A.; O’grady, J.F. Evaluation of citrus pulp in diets for sows and growing pigs. Irish J. Agric. Food Res. 1992, 42, 243–253. [Google Scholar]
- Gorinstein, S.; Martı́n-Belloso, O.; Park, Y.-S.; Haruenkit, R.; Lojek, A.; Ĉı́ž, M.; Caspi, A.; Libman, I.; Trakhtenberg, S. Comparison of some biochemical characteristics of different citrus fruits. Food Chem. 2001, 74, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.; Yáñez, R.; Alonsó, J.L.; Parajó, J.C. Chemical production of pectic oligosaccharides from orange peel wastes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 8470–8476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casquete, R.; Castro, S.M.; Villalobos, M.C.; Serradilla, M.J.; Queirós, R.P.; Saraiva, J.A.; Córdoba, M.G.; Teixeira, P. High pressure extraction of phenolic compounds from citrus peels. High Press. Res. 2014, 34, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Mahato, N.; Cho, M.H.; Lee, Y.R. Converting citrus wastes into value-added products: Economic and environmently friendly approaches. Nutrition 2017, 34, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangoni, A.G. Editorial overview: Food chemistry and biochemistry. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 7, iv–v. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, A. Side streams of plant food processing as a source of valuable compounds: Selected examples. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostopoulou, M.A.; Kefalas, P.; Papageorgiou, V.P.; Assimopoulou, A.N.; Boskou, D. Radical scavenging activity of various extracts and fractions of sweet orange peel (Citrus sinensis). Food Chem. 2006, 94, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levaj, B.; Dragović-Uzelac, V.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; Krasnići, N. Determination of flavonoids in pulp and peel of mandarin fruits. Agric. Conspec. Sci. 2009, 74, 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Bursać Kovačević, D.; Gajdoš Kljusurić, J.; Putnik, P.; Vukušić, T.; Herceg, Z.; Dragović-Uzelac, V. Stability of polyphenols in chokeberry juice treated with gas phase plasma. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bursać Kovačević, D.; Putnik, P.; Dragović-Uzelac, V.; Pedisić, S.; Režek Jambrak, A.; Herceg, Z. Effects of cold atmospheric gas phase plasma on anthocyanins and color in pomegranate juice. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bursać Kovačević, D.; Putnik, P.; Dragović-Uzelac, V.; Vahčić, N.; Babojelić, M.S.; Levaj, B. Influences of organically and conventionally grown strawberry cultivars on anthocyanins content and color in purees and low-sugar jams. Food Chem. 2015, 181, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Giampieri, F.; Gasparrini, M.; Mazzoni, L.; Quiles, J.L.; Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Battino, M. The effects of bioactive compounds from plant foods on mitochondrial function: A focus on apoptotic mechanisms. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 154–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Londono-Londono, J.; Lima, V.R.; Lara, O.; Gil, A.; Pasa, T.B.C.; Arango, G.J.; Pineda, J.R.R. Clean recovery of antioxidant flavonoids from citrus peel: Optimizing an aqueous ultrasound-assisted extraction method. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Guerrini, A.; Maietti, S.; Bruni, R.; Paganetto, G.; Poli, F.; Scalvenzi, L.; Radice, M.; Saro, K.; Sacchetti, G. Chemical fingerprinting and bioactivity of Amazonian Ecuador Croton lechleri Müll. Arg. (Euphorbiaceae) stem bark essential oil: A new functional food ingredient? Food Chem. 2011, 126, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-Q.; Lei, J.-C.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Yu, H.-D.; Tian, D.-Z.; Liao, Z.-X.; Zou, G.-L. Anticancer, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of the essential oil of Lycopus lucidus Turcz. var. hirtus Regel. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1593–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakkali, F.; Averbeck, S.; Averbeck, D.; Idaomar, M. Biological effects of essential oils—A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 446–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putnik, P.; Bursac Kovacevc, D. Fresh-cut apples spoilage and predictive microbial growth under modified atmosphere packaging. In Food Safety and Protection; Rai, R., Aswathanarayan, J.B., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; p. 504. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Citrus and Subtropical Products Research Laboratory. Available online: http://www.ars-grin.gov/ars/SoAtlantic/Winter_Haven/uscsprl/ (accessed on 29 March 2017).
- Chemat, F.; Vian, M.A.; Cravotto, G. Green extraction of natural products: Concept and principles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 8615–8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerton, F.M. Alternative Solvents for Green Chemistry; Kerton, F.M., Ed.; RSC Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Thuy Pham, T.P.; Cho, C.-W.; Yun, Y.-S. Environmental fate and toxicity of ionic liquids: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 352–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bursać Kovačević, D.; Putnik, P.; Pedisić, S.; Dragović-Uzelac, V. High hydrostatic pressure extraction of flavonoids from freeze-dried red grape skin as winemaking by-product. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 67, 521–522. [Google Scholar]
- Goiris, K.; Muylaert, K.; Fraeye, I.; Foubert, I.; de Brabanter, J.; de Cooman, L. Antioxidant potential of microalgae in relation to their phenolic and carotenoid content. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabella, N.; Castellani, V.; Sala, S. Current options for the valorization of food manufacturing waste: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamma, D.; Christakopoulos, P. Biotransformation of citrus by-products into value added products. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2014, 5, 529–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’hiri, N.; Ioannou, I.; Ghoul, M.; Boudhrioua, N.M. Extraction methods of citrus peel phenolic compounds. Food Rev. Int. 2014, 30, 265–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’hiri, N.; Ioannou, I.; Ghoul, M.; Boudhrioua, N.M. Phytochemical characteristics of citrus peel and effect of conventional and nonconventional processing on phenolic compounds: A review. Food Rev. Int. 2017, 33, 587–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, F.J.; Parniakov, O.; Pereira, S.A.; Wiktor, A.; Grimi, N.; Boussetta, N.; Saraiva, J.A.; Raso, J.; Martin-Belloso, O.; Witrowa-Rajchert, D.; et al. Current applications and new opportunities for the use of pulsed electric fields in food science and industry. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 773–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertolas, E.; Barba, F.J. Electrotechnologies applied to valorization of by-products from food industry: Main findings, energy and economic cost of their industrialization. Food Bioprod. Process. 2016, 100, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Weller, C.L. Recent advances in extraction of nutraceuticals from plants. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, F.J.; Zhu, Z.; Koubaa, M.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Orlien, V. Green alternative methods for the extraction of antioxidant bioactive compounds from winery wastes and by-products: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 49, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levaj, B.; Putnik, P.; Linardić, I.; Herceg, Z.; Režek-Jambrak, A.; Kovačević-Bursać, D. Influence of pre-treatment on yield and quality of mandarin juices. In 6th Central European Congress; Matica Srpska: Novi Sad, Serbia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Wang, L.; Walzem, R.L.; Miller, E.G.; Pike, L.M.; Patil, B.S. Antioxidant activity of citrus limonoids, flavonoids, and coumarins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2009–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo, J.; Mahecha, L.; Yepes, S.A.; Yepes, A.M.; Bustamante, G.; Jaramillo, H.; Valencia, E.; Villamil, T.; Gallo, J. Quantitative and nutritional characterization of fruit and vegetable waste from marketplace: A potential use as bovine feedstuff? J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 95, S203–S209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, I.S.; Kim, J.-H.; Wi, S.G.; Kim, K.H.; Bae, H.-J. Bioethanol production from mandarin (Citrus unshiu) peel waste using popping pretreatment. Appl. Energy 2013, 102, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, S.R.; Sanromán, M.Á. Application of solid-state fermentation to food industry—A review. J. Food Eng. 2006, 76, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, M.L.; Chau, H.K.; Hoagland, P.; Ayyad, K. Characterization of pectin, flash-extracted from orange albedo by microwave heating, under pressure. Carbohydr. Res. 1999, 323, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ginés, J.M.; Fernández-López, J.; Sayas-Barberá, E.; Sendra, E.; Pérez-Alvarez, J.A. Effect of storage conditions on quality characteristics of Bologna sausages made with citrus fiber. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáyago-Ayerdi, S.G.; Brenes, A.; Goñi, I. Effect of grape antioxidant dietary fiber on the lipid oxidation of raw and cooked chicken hamburgers. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moraes Crizel, T.; Jablonski, A.; de Oliveira Rios, A.; Rech, R.; Flôres, S.H. Dietary fiber from orange byproducts as a potential fat replacer. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 53, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.; Ahlawat, S.S.; Sharma, D.P.; Dabur, R.S. Novel trends in development of dietary fiber rich meat products—A critical review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngouémazong, E.D.; Christiaens, S.; Shpigelman, A.; van Loey, A.; Hendrickx, M. The emulsifying and emulsion-stabilizing properties of pectin: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriminna, R.; Fidalgo, A.; Delisi, R. Pectin production and global market. Agro Food Ind. Hi-Tech 2016, 27, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Tasneem, M.; Siddique, F.; Ahmad, A.; Farooq, U. Stabilizers: Indispensable substances in dairy products of high rheology. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Sinha, A.K.; Makkar, H.P.S.; de Boeck, G.; Becker, K. Dietary roles of non-starch polysachharides in human nutrition: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 899–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Fishman, M.L.; Hicks, K.B. Pectin in controlled drug delivery—A review. Cellulose 2006, 14, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, C.D. Industrial pectins: Sources, production and applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 1990, 12, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staunstrup, J. The waht if you Can! Company. Proceedings of The International Citrus & Beverge Conference, Gainesville, FL, USA, 15–18 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pourbafrani, M.; Forgács, G.; Horváth, I.S.; Niklasson, C.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Production of biofuels, limonene and pectin from citrus wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4246–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, E.G.; Belshaw, N.J.; Waldron, K.W.; Morris, V.J. Pectin—An emerging new bioactive food polysaccharide. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 24, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripoli, E.; La Guardia, M.; Giammanco, S.; Di Majo, D.; Giammanco, M. Citrus flavonoids: Molecular structure, biological activity and nutritional properties: A review. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ahmedna, M.; Bansode, R.R. Agricultural by-products as important food sources of polyphenols. In Polyphenols : Food Sources, Bioactive Properties, and Antioxidant Effects; Cobb, D.T., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Hsu, H.-W. The flavonoid, carotenoid and pectin content in peels of citrus cultivated in Taiwan. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandalari, G.; Bennett, R.N.; Bisignano, G.; Saija, A.; Dugo, G.; Lo Curto, R.B.; Faulds, C.B.; Waldron, K.W. Characterization of flavonoids and pectins from bergamot (Citrus bergamia Risso) peel, a major byproduct of essential oil extraction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocco, A.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Richard, H.; Berset, C. Antioxidant activity and phenolic composition of citrus peel and seed extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 2123–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawalha, S.M.S.; Arráez-Román, D.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A. Quantification of main phenolic compounds in sweet and bitter orange peel using CE-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Guan, Y.; Ye, J. Determination of flavonoids and ascorbic acid in grapefruit peel and juice by capillary electrophoresis with electrochemical detection. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y. Comprehensive Utilization of Citrus By-products; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Burt, S. Essential oils: Their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods—A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.I.; Anwar, F.; Hussain Sherazi, S.T.; Przybylski, R. Chemical composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of basil (Ocimum basilicum) essential oils depends on seasonal variations. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, B.; Marques, A.; Ramos, C.; Neng, N.R.; Nogueira, J.M.F.; Saraiva, J.A.; Nunes, M.L. Chemical composition and antibacterial and antioxidant properties of commercial essential oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 43, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valgimigli, L. Essential Oils as Natural Food Additives Composition, Applications, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bayala, B.; Bassole, I.H.; Scifo, R.; Gnoula, C.; Morel, L.; Lobaccaro, J.-M.A.; Simpore, J. Anticancer activity of essential oils and their chemical components—A review. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2014, 4, 591–607. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raut, J.S.; Karuppayil, S.M. A status review on the medicinal properties of essential oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 62, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astani, A.; Reichling, J.; Schnitzler, P. Screening for antiviral activities of isolated compounds from essential oils. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 253643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, H.-F.; Hsieh, C.-T.; Hsieh, T.-J.; Chang, F.-R.; Wang, C.-K. In vitro anti-diabetic effect and chemical component analysis of 29 essential oils products. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015, 23, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, M.G. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of essential oils: A short review. Molecules 2010, 15, 9252–9287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabassum, N.; Vidyasagar, G.M. Antifungal investigations on plant essential oils. A review. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 5, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zoubiri, S.; Baaliouamer, A. Potentiality of plants as source of insecticide principles. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2014, 18, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thormar, H. Lipids and Essential Oils as Antimicrobial Agents; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Oprean, R.; Tamas, M.; Sandulescu, R.; Roman, L. Essential oils analysis. I. Evaluation of essential oils composition using both GC and MS fingerprints. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1998, 18, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapo, B.; Koffi, K. Extraction and characterization of highly gelling low methoxy pectin from cashew apple pomace. Foods 2013, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yapo, B.M. Pectin quantity, composition and physicochemical behaviour as influenced by the purification process. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, L.R.; Adekunle, A.; Orsat, V.; Raghavan, V. Advances in the pectin production process using novel extraction techniques: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 62, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maran, J.P.; Sivakumar, V.; Thirugnanasambandham, K.; Sridhar, R. Optimization of microwave assisted extraction of pectin from orange peel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 97, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagherian, H.; Zokaee Ashtiani, F.; Fouladitajar, A.; Mohtashamy, M. Comparisons between conventional, microwave- and ultrasound-assisted methods for extraction of pectin from grapefruit. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2011, 50, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ma, X.; Xu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Ding, T.; Ye, X.; Liu, D. Ultrasound-assisted heating extraction of pectin from grapefruit peel: Optimization and comparison with the conventional method. Food Chem. 2015, 178, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghshineh, M.; Olsen, K.; Georgiou, C.A. Sustainable production of pectin from lime peel by high hydrostatic pressure treatment. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Han, D.; Xi, H.; Rao, L.; Liao, X.; Hu, X.; Wu, J. Extraction of pectin from navel orange peel assisted by ultra-high pressure, microwave or traditional heating: A comparison. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Q.; Lü, X. Pectin extracted from apple pomace and citrus peel by subcritical water. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 38, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominiak, M.; Søndergaard, K.M.; Wichmann, J.; Vidal-Melgosa, S.; Willats, W.G.T.; Meyer, A.S.; Mikkelsen, J.D. Application of enzymes for efficient extraction, modification, and development of functional properties of lime pectin. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 40, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouambia, Y.; Youcef Ettoumi, K.; Krea, M.; Moulai-Mostefa, N. A new approach for pectin extraction: Electromagnetic induction heating. Arab. J. Chem. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamsazzadeh Kermani, Z.; Shpigelman, A.; Kyomugasho, C.; Van Buggenhout, S.; Ramezani, M.; van Loey, A.M.; Hendrickx, M.E. The impact of extraction with a chelating agent under acidic conditions on the cell wall polymers of mango peel. Food Chem. 2014, 161, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, A.; Dominiak, M.; Vidal-Melgosa, S.; Willats, W.G.T.; Søndergaard, K.M.; Hansen, P.W.; Meyer, A.S.; Mikkelsen, J.D. Prediction of pectin yield and quality by FTIR and carbohydrate microarray analysis. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyomugasho, C.; Christiaens, S.; Shpigelman, A.; van Loey, A.M.; Hendrickx, M.E. FT-IR spectroscopy, a reliable method for routine analysis of the degree of methylesterification of pectin in different fruit- and vegetable-based matrices. Food Chem. 2015, 176, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Bailina, Y.; Ge, Z.; Ding, T.; Ye, X.; Liu, D. Effects of ultrasound and/or heating on the extraction of pectin from grapefruit peel. J. Food Eng. 2014, 126, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qiao, L.; Yang, F.; Gu, H.; Yang, L. Brönsted acidic ionic liquid based ultrasound-microwave synergistic extraction of pectin from pomelo peels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 94, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukroufa, M.; Boutekedjiret, C.; Petigny, L.; Rakotomanomana, N.; Chemat, F. Bio-refinery of orange peels waste: A new concept based on integrated green and solvent free extraction processes using ultrasound and microwave techniques to obtain essential oil, polyphenols and pectin. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 24, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratchanova, M.; Pavlova, E.; Panchev, I. The effect of microwave heating of fresh orange peels on the fruit tissue and quality of extracted pectin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 56, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Khodaiyan, F.; Yarmand, M.S. Optimization of microwave assisted extraction of pectin from sour orange peel and its physicochemical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 140, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guolin, H.; Jeffrey, S.; Kai, Z.; Xiaolan, H. Application of ionic liquids in the microwave-assisted extraction of pectin from lemon peels. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2012, 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balu, A.M.; Budarin, V.; Shuttleworth, P.S.; Pfaltzgraff, L.A.; Waldron, K.; Luque, R.; Clark, J.H. Valorisation of orange peel residues: Waste to biochemicals and nanoporous materials. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidalgo, A.; Ciriminna, R.; Carnaroglio, D.; Tamburino, A.; Cravotto, G.; Grillo, G.; Ilharco, L.M.; Pagliaro, M. Eco-friendly extraction of pectin and essential oils from orange and lemon peels. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2243–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shpigelman, A.; Kyomugasho, C.; Christiaens, S.; van Loey, A.M.; Hendrickx, M.E. Thermal and high pressure high temperature processes result in distinctly different pectin non-enzymatic conversions. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 39, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roeck, A.; Duvetter, T.; Fraeye, I.; Van der Plancken, I.; Sila, D.N.; van Loey, A.; Hendrickx, M. Effect of high-pressure/high-temperature processing on chemical pectin conversions in relation to fruit and vegetable texture. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shpigelman, A.; Kyomugasho, C.; Christiaens, S.; van Loey, A.M.; Hendrickx, M.E. The effect of high pressure homogenization on pectin: Importance of pectin source and pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-L.; Yang, D.-J.; Liu, S.-C. Effects of drying temperature on the flavonoid, phenolic acid and antioxidative capacities of the methanol extract of citrus fruit (Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck) peels. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shofinita, D.; Feng, S.; Langrish, T.A.G. Comparing yields from the extraction of different citrus peels and spray drying of the extracts. Adv. Powder Technol. 2015, 26, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidrianny, I.; Sari, E.; Ruslan, K. Phytochemical content and antioxidant activities in different organs of pomelo (Citrus maxima [Burm.] Merr.) using 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl and phosphomolybdenum assays. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2016, 9, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-M.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, D.-R.; Jo, S.-C.; Nam, K.C.; Ahn, D.U.; Lee, S.-C. Effect of heat treatment on the antioxidant activity of extracts from citrus peels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3389–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luengo, E.; Álvarez, I.; Raso, J. Improving the pressing extraction of polyphenols of orange peel by pulsed electric fields. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 17, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselló-Soto, E.; Galanakis, C.M.; Brnčić, M.; Orlien, V.; Trujillo, F.J.; Mawson, R.; Knoerzer, K.; Tiwari, B.K.; Barba, F.J. Clean recovery of antioxidant compounds from plant foods, by-products and algae assisted by ultrasounds processing. Modeling approaches to optimize processing conditions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 42, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-Q.; Chen, J.-C.; Liu, D.-H.; Ye, X.-Q. Simultaneous extraction of phenolic compounds of citrus peel extracts: Effect of ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2009, 16, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.K.; Abert-Vian, M.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.-S.; Dangles, O.; Chemat, F. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of polyphenols (flavanone glycosides) from orange (Citrus sinensis L.) peel. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singanusong, R.; Nipornram, S.; Tochampa, W.; Rattanatraiwong, P. Low power ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from mandarin (Citrus reticulata Blanco cv. Sainampueng) and lime (Citrus aurantifolia) peels and the antioxidant. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 8, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Castello, E.M.; Rodriguez-Lopez, A.D.; Mayor, L.; Ballesteros, R.; Conidi, C.; Cassano, A. Optimization of conventional and ultrasound assisted extraction of flavonoids from grapefruit (Citrus paradisi L.) solid wastes. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 1114–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Sun, Y.; Chen, R.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Shen, Y.; Ye, X. Sonochemical Effects on 14 flavonoids common in citrus: Relation to stability. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Ye, X.; Yu, D. Effects of different factors of ultrasound treatment on the extraction yield of the all-trans-β-carotene from citrus peels. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, K.; Hussain, S.; Abbas, S.; Farooq, U.; Ding, B.; Xia, S.; Jia, C.; Zhang, X.; Xia, W. Optimized microwave-assisted extraction of phenolic acids from citrus mandarin peels and evaluation of antioxidant activity in vitro. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 70, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Langrish, T.A.G. Optimisation of total phenolic acids extraction from mandarin peels using microwave energy: The importance of the Maillard reaction. J. Food Eng. 2012, 109, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, B.; Dahmoune, F.; Moussi, K.; Remini, H.; Dairi, S.; Aoun, O.; Khodir, M. Comparison of microwave, ultrasound and accelerated-assisted solvent extraction for recovery of polyphenols from Citrus sinensis peels. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahmoune, F.; Boulekbache, L.; Moussi, K.; Aoun, O.; Spigno, G.; Madani, K. Valorization of Citrus limon residues for the recovery of antioxidants: Evaluation and optimization of microwave and ultrasound application to solvent extraction. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 50, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’hiri, N.; Ioannou, I.; Mihoubi Boudhrioua, N.; Ghoul, M. Effect of different operating conditions on the extraction of phenolic compounds in orange peel. Food Bioprod. Process. 2015, 96, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’hiri, N.; Ioannou, I.; Paris, C.; Ghoul, M.; Boudhrioua, M.N. Comparison of the efficiency of different extraction methods on antioxidants of maltease orange peel. Int. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2016, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Min, K.Y.; Lee, K.A.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.-T.; Chung, M.-S.; Chang, P.-S.; Park, H.; Paik, H.-D. Antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activities of Citrus unshiu peel extracts using a combined process of subcritical water extraction and acid hydrolysis. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W.; Nagaoka, T.; Ishida, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Kitagawa, K.; Lee, S.-C. Subcritical water extraction of nutraceutical compounds from citrus pomaces. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 2598–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, F.J.; Terefe, N.S.; Buckow, R.; Knorr, D.; Orlien, V. New opportunities and perspectives of high pressure treatment to improve health and safety attributes of foods. A review. Food Res. Int. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, F.J.; Puértolas, E.; Brnčić, M.; Panchev, I.N.; Dimitrov, D.A.; Athés-Dutour, V.; Mousaa, M.; Souchon, I. Food Waste Recovery Processing Technologies and Industrial Techniques; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 249–272. [Google Scholar]
- Doernenburg, H.; Knorr, D. Cellular permeabilization of cultured plant tissues by high electric field pulses or ultra high pressure for the recovery of secondary metabolites. Food Biotechnol. 1993, 7, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toepfl, S.; Mathys, A.; Heinz, V.; Knorr, D. Review: Potential of high hydrostatic pressure and pulsed electric fields for energy efficient and environmentally friendly food processing. Food Rev. Int. 2006, 22, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casquete, R.; Castro, S.M.; Martín, A.; Ruiz-Moyano, S.; Saraiva, J.A.; Córdoba, M.G.; Teixeira, P. Evaluation of the effect of high pressure on total phenolic content, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of citrus peels. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 31, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahlou, M. Methods to study the phytochemistry and bioactivity of essential oils. Phyther. Res. PTR 2004, 18, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asikin, Y.; Taira, I.; Inafuku, S.; Sumi, H.; Sawamura, M.; Takara, K.; Wada, K. Volatile aroma components and antioxidant activities of the flavedo peel extract of unripe shiikuwasha (Citrus depressa Hayata). J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, C469–C475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitiku, S.B.; Sawamura, M.; Itoh, T.; Ukeda, H. Volatile components of peel cold-pressed oils of twocultivars of sweet orange (Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck) fromEthiopia. Flavour Fragr. J. 2000, 4, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanciullino, A.L.; Tomi, F.; Luro, F.; Desjobert, J.M.; Casanova, J. Chemical variability of peel and leaf oils of mandarins. Flavour Fragr. J. 2006, 21, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, M.-C.; Liu, Y.-H.; Sun, Y.-W.; Chan, C.-F. The Composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of cold-pressed and distilled essential oils of Citrus paradisi and Citrus grandis (L.) Osbeck. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.S.; Lan Phi, N.T.; Park, Y.H.; Sawamura, M. Volatile profiles in cold-pressed peel oil from Korean and Japanese Shiranui (Citrus unshiu Marcov. × C. sinensis Osbeck × C. reticulata Blanco). Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 737–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombaut, N.; Tixier, A.-S.; Bily, A.; Chemat, F. Green extraction processes of natural products as tools for biorefinery. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2014, 8, 530–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmortazavi, S.M.; Hajimirsadeghi, S.S. Supercritical fluid extraction in plant essential and volatile oil analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1163, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinatoru, M. An overview of the ultrasonically assisted extraction of bioactive principles from herbs. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2001, 8, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso-Ugarte, G.A.; Juárez-Becerra, G.P.; Sosa-Morales, M.E.; López-Malo, A. Microwave-assisted extraction of essential oils from herbs. J. Microw. Power Electromagn. Energy A Publ. Int. Microw. Power Inst. 2013, 47, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingret, D.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.-S.; Chemat, F. An improved ultrasound Clevenger for extraction of essential oils. Food Anal. Methods 2013, 7, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, T.; Chemat, F.; Vinatoru, M. The extraction of natural products using ultrasound andmicrowaves. Curr. Org. Chem. 2011, 15, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.; Chemat, F. Essential Oils: From Conventional to Green Extraction. In Essential Oils as Reagents in Green Chemistry; Li, Y., Fabiano-Tixier, A., Chemat, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Tylewicz, U.; Inchingolo, R.; Rodriguez-Estrada, M. Food aroma compounds. In Nutraceutical and Functional Food Components: Effects of Innovative Processing Techniques; Galanakis, C., Ed.; Elsevier-Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 297–334. [Google Scholar]
- Attard, T.M.; Watterson, B.; Budarin, V.L.; Clark, J.H.; Hunt, A.J. Microwave assisted extraction as an important technology for valorising orange waste. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 2278–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, J.; van Stempvoort, S.; García-Gallarreta, M.; Houghton, J.A.; Briers, H.K.; Budarin, V.L.; Matharu, A.S.; Clark, J.H. Microwave assisted hydro-distillation of essential oils from wet citrus peel waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atti-Santos, A.C.; Rossato, M.; Serafini, L.A.; Cassel, E.; Moyna, P. Extraction of essential oils from lime (Citrus latifolia Tanaka) by hydrodistillation and supercritical carbon dioxide. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2005, 48, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.C.; Hoshino, M.; Ueno, H.; Sasaki, M.; Goto, M. Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of the volatiles from the peel of Japanese citrus fruits. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2007, 19, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-H.; Huang, T.-C. Volatile and nonvolatile constituents and antioxidant capacity of oleoresins in three Taiwan citrus varieties as determined by supercritical fluid extraction. Molecules 2016, 21, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.-Z.; Shao, P.; Liu, J.-H.; Ru, Q.-M. Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of flavonoids from pomelo (Citrus grandis (L.) osbeck) peel and their antioxidant activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 13065–13078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndayishimiye, J.; Getachew, A.T.; Chun, B.S. Comparison of characteristics of oils extracted from a mixture of citrus seeds and peels using hexane and supercritical carbon dioxide. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2016, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-González, M.L.; López-López, L.I.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R.; Contreras-Esquivel, J.C.; Aguilar, C.N. Enzyme-assisted extraction of citrus essential oil. Chem. Pap. 2016, 70, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowbhagya, H.B.; Chitra, V.N. Enzyme-assisted extraction offlavorings and colorants from plant materials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 50, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, D.; Shukla, A.K.; Dixit, A.K.; Singh, K. Aqueous enzymaticextraction of oil from mandarin peels. J. Oleo Sci. 2005, 54, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Alisaraei, A.; Hosseini, S.H.; Ghobadian, B.; Motevali, A. Biofuel production from citrus wastes: A feasibility study in Iran. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 1100–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boluda-Aguilar, M.; López-Gómez, A. Production of bioethanol by fermentation of lemon (Citrus limon L.) peel wastes pretreated with steam explosion. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 41, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, M.; Panno, D.; Volpe, R.; Messineo, A. Upgrade of citrus waste as a biofuel via slow pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 115, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negro, V.; Mancini, G.; Ruggeri, B.; Fino, D. Citrus waste as feedstock for bio-based products recovery: Review on limonene case study and energy valorization. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, B.; Flotats, X. Effect of limonene on batch anaerobic digestion of citrus peel waste. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 109, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppar, A.; Pullammanappallil, P. Anaerobic digestion of peel waste and wastewater for on site energy generation in a citrus processing facility. Energy 2013, 60, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, B.; Flotats, X. Citrus essential oils and their influence on the anaerobic digestion process: An overview. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2063–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Citrus Waste | Pectin | Lignin | Cellulose | Hemicellulose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lemon peels | 13.00 ± 1.06 | 7.56 ± 0.54 | 23.06 ± 2.11 | 8.09 ± 0.81 |
| Lemon pulp | 22.53 ± 1.95 | 7.55 ± 0.66 | 36.22 ± 3.24 | 11.05 ± 1.09 |
| Orange peels | 23.02 ± 2.12 | 7.52 ± 0.59 | 37.08 ± 3.1 | 11.04 ± 1.05 |
| Orange pulp | 12.07 ± 1.12 | 7.51 ± 0.62 | 24.52 ± 2.0 | 7.57 ± 0.66 |
| Type | Basic Structure |
|---|---|
| α-Carotene |  |
| β-Carotene |  |
| Lutein |  |
| Zeaxanthin |  |
| β-Cryptoxanthin |  |
| Plant Material | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasound-assisted extraction | |||||||||
| Treatment conditions | Ethanol/Water Ratio (v/v) | Extraction yield | Reference | ||||||
| kHz | W | °C | min | ||||||
| Orange peel | 25 | 150 | 30 | 15 | 50:50 | Polyphenols (caffeic (207%), p-coumaric (180%), ferulic (192%), sinapic acid (66%), p-hydroxybenzoic (94%)) | [110] | ||
| 25 | 50–150 | 10–40 | 60 | 20–80:80–20 | Polyphenols (naringin (38%), Hesperidin (42%), total phenolic compounds (31%)) | [111] | |||
| - | 125 | 35 | 30 | 80:20 | - | [120] | |||
| Microwave-assisted extraction | |||||||||
| Treatment conditions | Extraction yield | ||||||||
| W | °C | s | Liquid-to solid ratio | ||||||
| Orange peels | 500 | <135 | 122 | 25 mL·g−1 | Polyphenol content (12.20 mg/GAE g−1 DW) | [118] | |||
| 200 | - | 180 | - | - | [120] | ||||
| Lemon peels | 400 | 123 | 28:1 mL | Polyphenol content (15.74 mg/GAE g−1 DW) | [119] | ||||
| Mandarin peels | 400 | <135 | 180 | 1:2 | - | [117] | |||
| 152 | 49 | 16 | - | [116] | |||||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Putnik, P.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; Režek Jambrak, A.; Barba, F.J.; Cravotto, G.; Binello, A.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Shpigelman, A. Innovative “Green” and Novel Strategies for the Extraction of Bioactive Added Value Compounds from Citrus Wastes—A Review. Molecules 2017, 22, 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050680
Putnik P, Bursać Kovačević D, Režek Jambrak A, Barba FJ, Cravotto G, Binello A, Lorenzo JM, Shpigelman A. Innovative “Green” and Novel Strategies for the Extraction of Bioactive Added Value Compounds from Citrus Wastes—A Review. Molecules. 2017; 22(5):680. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050680
Chicago/Turabian StylePutnik, Predrag, Danijela Bursać Kovačević, Anet Režek Jambrak, Francisco J. Barba, Giancarlo Cravotto, Arianna Binello, Jose Manuel Lorenzo, and Avi Shpigelman. 2017. "Innovative “Green” and Novel Strategies for the Extraction of Bioactive Added Value Compounds from Citrus Wastes—A Review" Molecules 22, no. 5: 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050680
APA StylePutnik, P., Bursać Kovačević, D., Režek Jambrak, A., Barba, F. J., Cravotto, G., Binello, A., Lorenzo, J. M., & Shpigelman, A. (2017). Innovative “Green” and Novel Strategies for the Extraction of Bioactive Added Value Compounds from Citrus Wastes—A Review. Molecules, 22(5), 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050680