Association, Distribution, Liberation, and Rheological Balances of Alkyldimethylbenzylammonium Chlorides (C12–C16) †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Association Properties
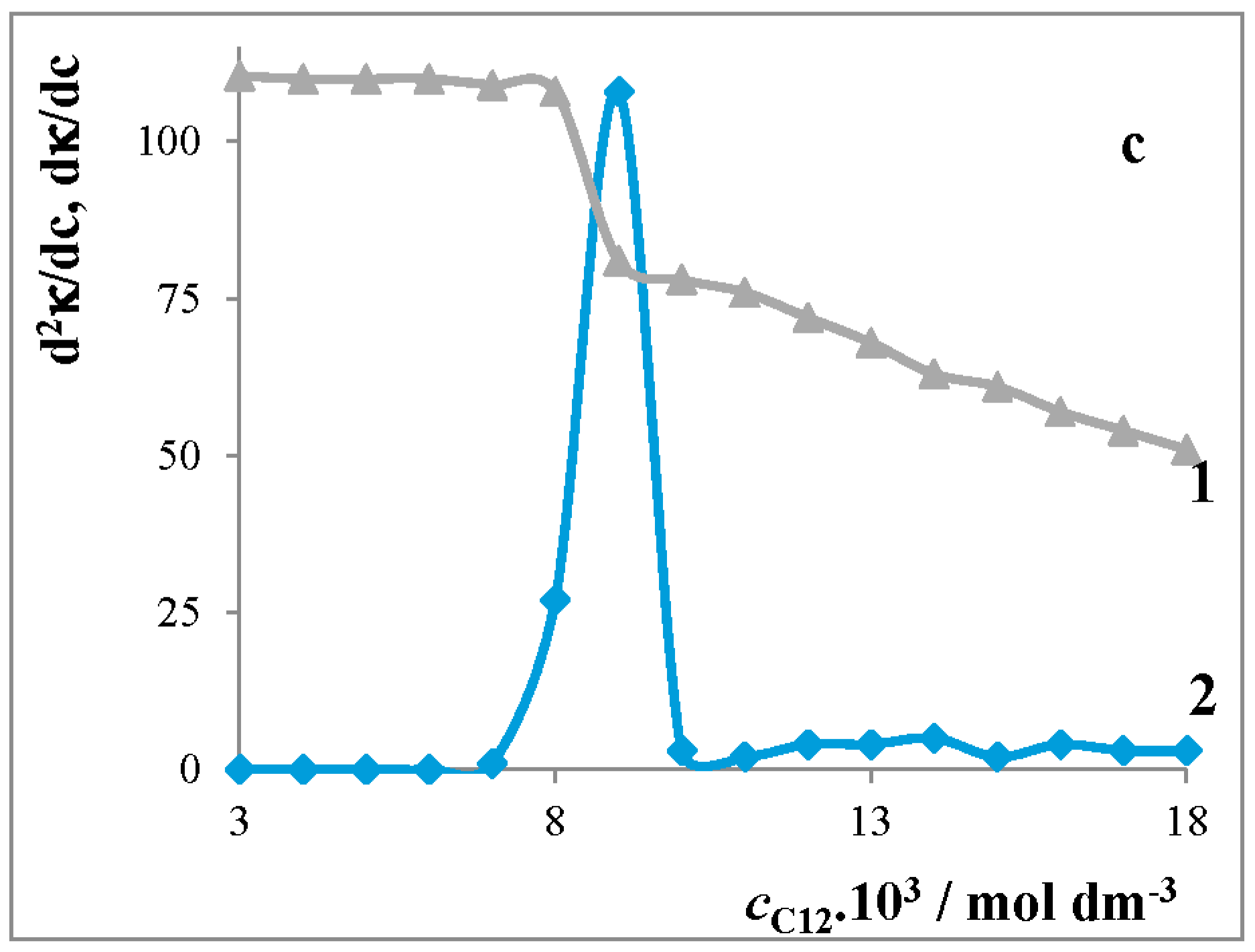
Critical Micelle Concentration of Surfactants
2.2. Partition Balances
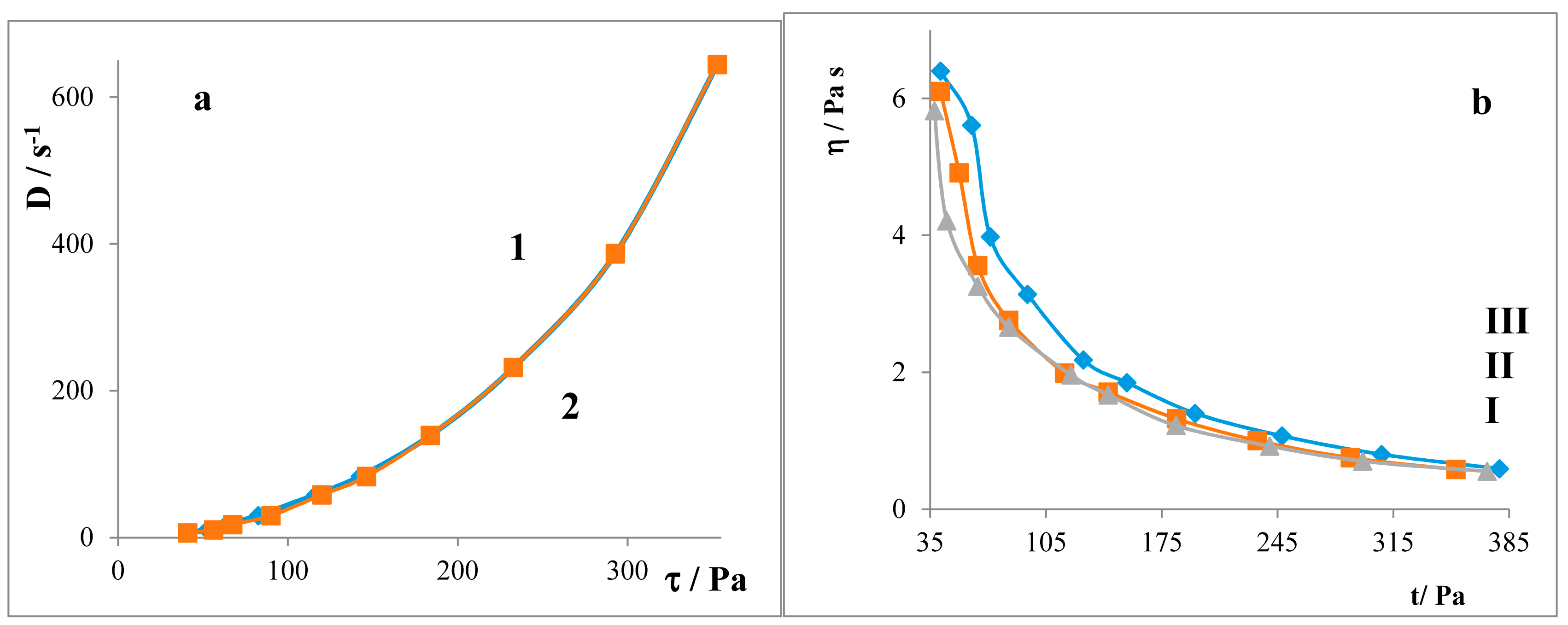
2.3. Liberation Balances
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Drug
3.2. Auxiliary Substance
- As a solvent there was used redistilled water with conductivity κ <1.5 μS cm−1.
- Pyrene (abbreviation Pyr)—fenantrene—Mr = 202.25 and density ρ = 1.271 g mol−1 (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany).
- Universal buffer, 1000 mL of it contains 0.04 mol dm−3 H3PO4 (4.9 g 80% dm−3 H3PO4), 0.04 mol dm−3 CH3COOH (2.4 g CH3COOH), 0.04 mol dm−3 H3BO3 (2.474 g H3BO3), was mixed with a mL 0.2 mol dm−3 of solution of NaOH. The value of pH was within the interval 11.98–2.09. All used chemicals were of purity p.a.
- Chitosan—medium (abbreviation CHIT)—Mr = 190.000–375.000) was obtained from Sigma Aldrich Chemie GmbH, Steinheim, Germany.
- Lactic acid solution (abbreviation LA) was supplied by Merck Chemical Company, (Germany).
- The 1-octanol for UV–VIS was supplied by Merck Chemical Company, (Germany).
4. Methods and Computational Procedures
4.1. Determination of the CMC Value
4.1.1. Conductivity
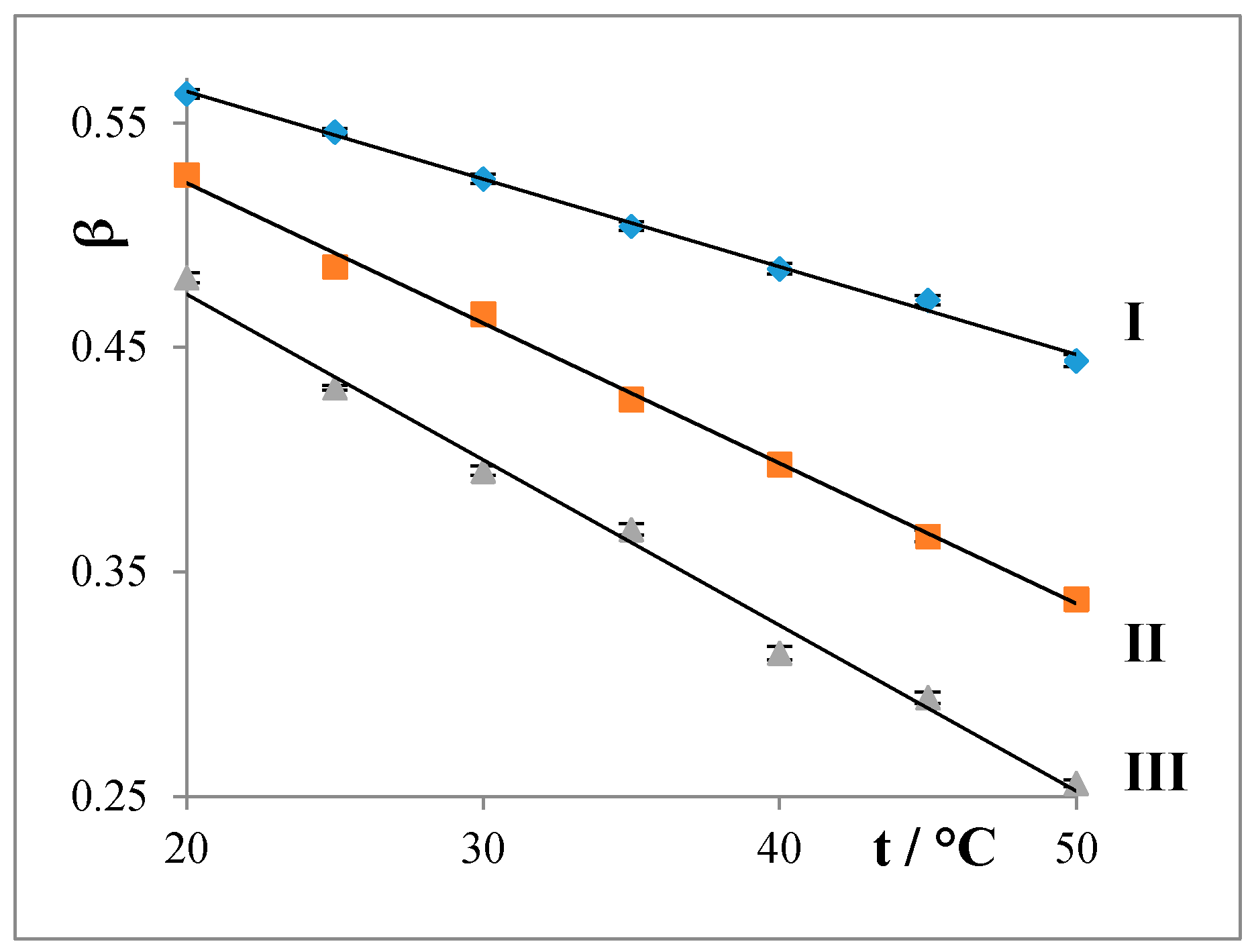
4.1.2. Degree of Counterion Binding (β)
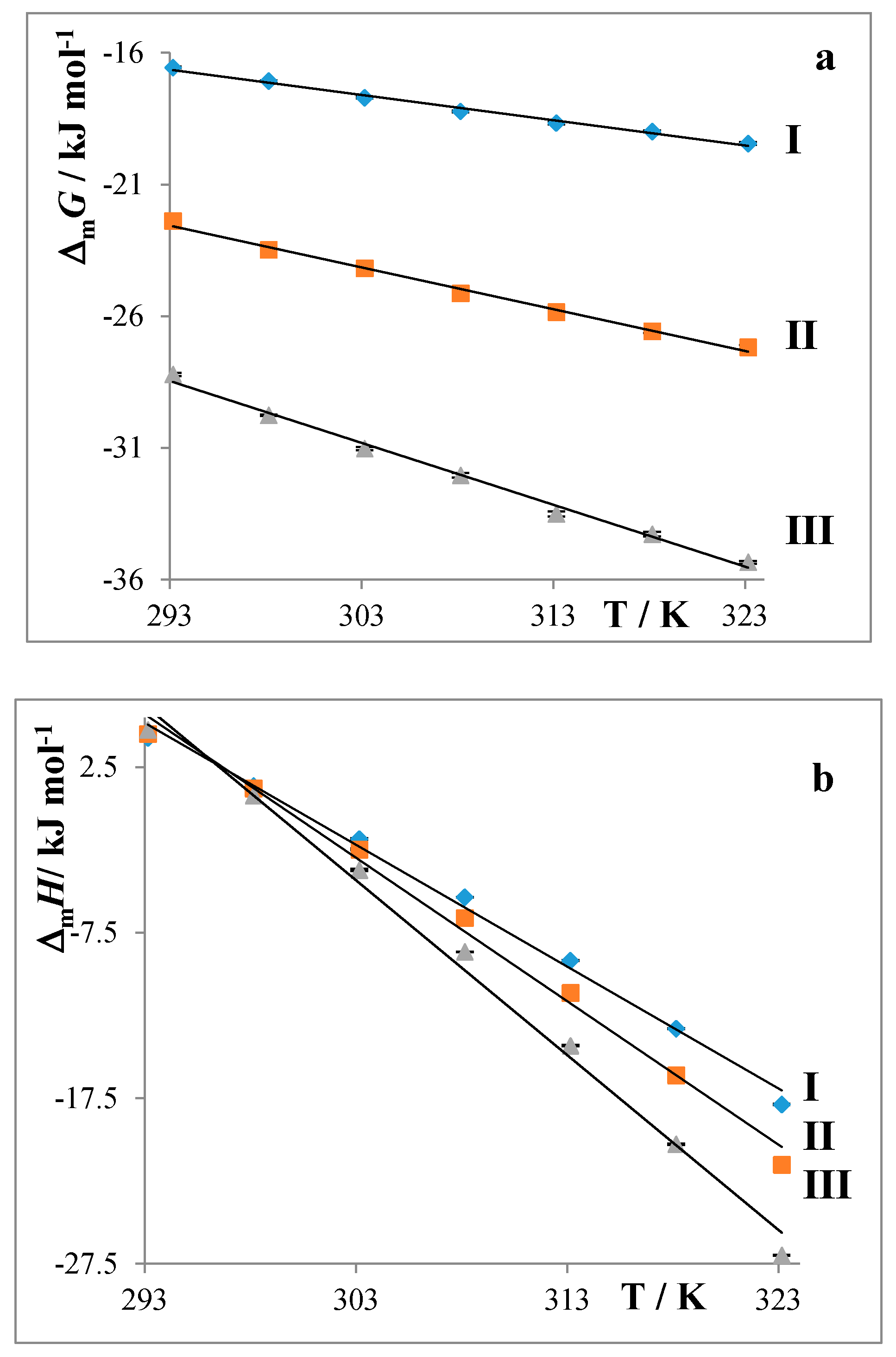
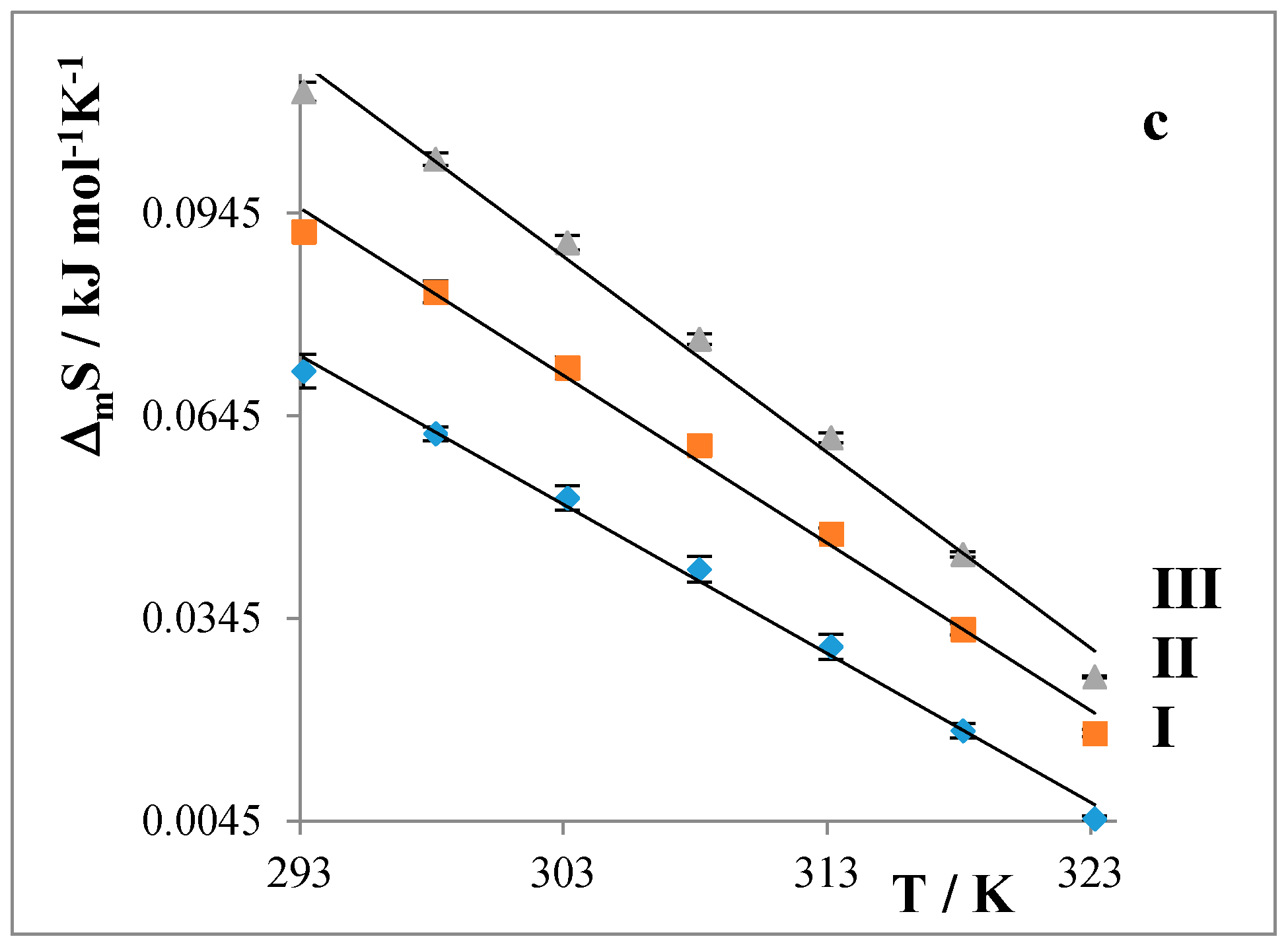
4.1.3. Thermodynamic Parameters of Micellization
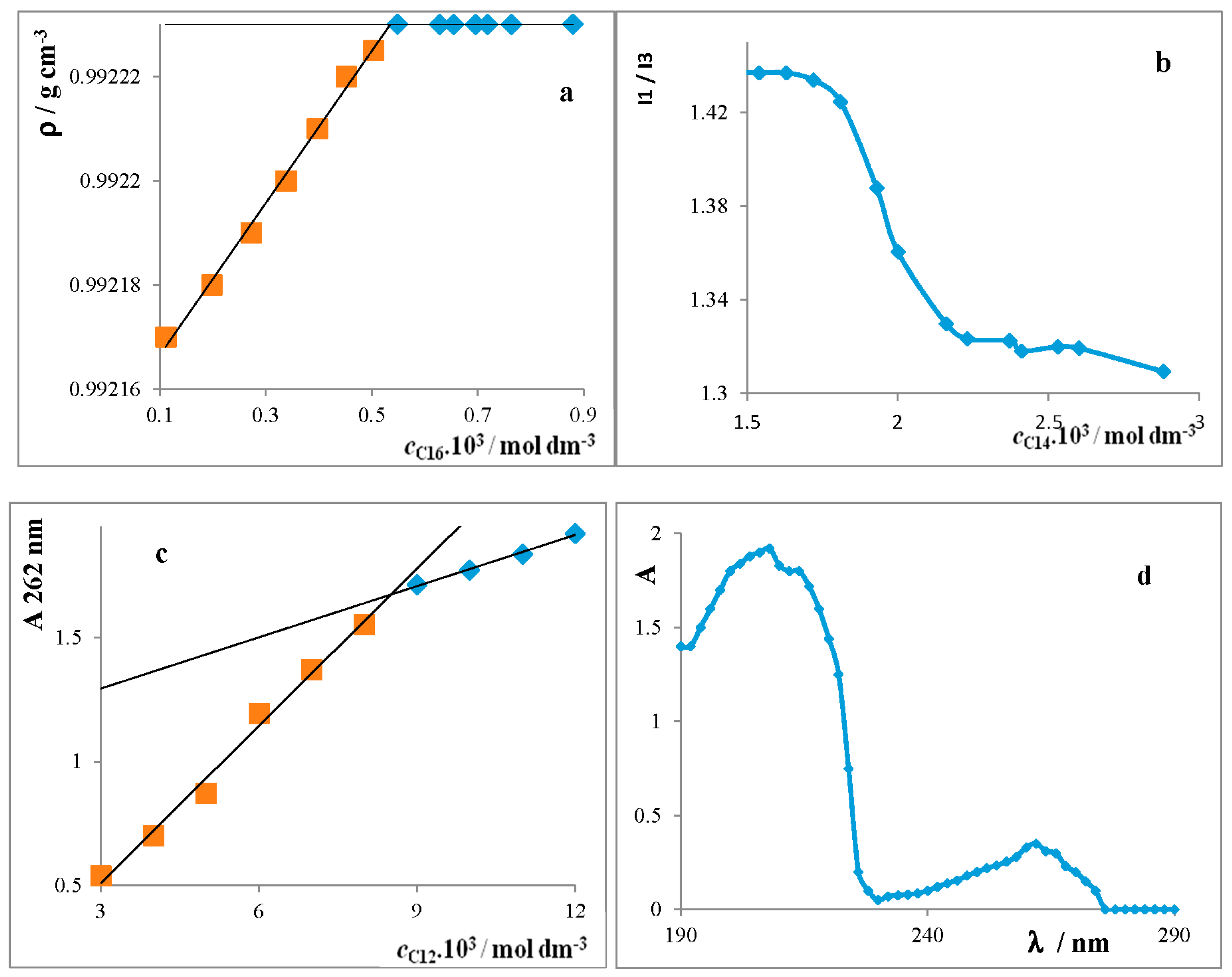
4.1.4. Spectrophotometry
4.1.5. Densitometry
4.1.6. Spectrofluorimetry
4.1.7. Determination of Partition Coefficients
- m0: mass of sample (surfactants) (kg).
- cW: molarity of surfactant in water phase (mol m−3).
- M: molar mass of surfactant (kg mol−1).
- VW: volume of water phase (m3).
- VO: volume of octanol phase (m3).
4.1.8. Preparation of Hydrogels
4.1.9. Preparation of Dosage Form
4.1.10. In Vitro Release
4.2. Drug Release Rate Constants
Measurement of pH
5. Conclusions
The Conclusions Derived from Association Measurements
- The values of CMC increase with an increasing temperature of the micellization process. The curves of CMC = f(t) reach a shallow minimum at a temperature of about 30 °C. The values of CMC of the studied surfactants are decrease in the order C12 > C14 > C16, which is caused by increasing lipophility, i.e., the prolongation of the alkyl chain in the molecule of the surfactant.
- For verification of the determined CMC from conductivity measurements were used another three experimental methods: densitometry, spectrofluorimetry, and UV–VIS spectrophotometry. All methods are suitable for the study of the formation of micelles.
- The degrees of counterion bindings (β) of the studied water systems linearly decrease with both increasing temperature and prolongation of the alkyl chain of the surfactant.
- For the thermodynamic parameters of micellization:
- Partition balances
- Liberation balances
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vitková, Z.; Herdová, P.; Vitko, A. Farmakokinetics and Pharmakodynamics from the Perspective of Pharmaceutical Technology, 1st ed.; FELIA s.r.o.: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2016; p. 219. ISBN 978-80-89824-03-8. (In Slovak) [Google Scholar]
- Baroncini, S.; Villani, A.; Serfini, J.-P. Anestesia Neonataly Pediátricá; Elsevier: Espaňa, Barcelona, 2006; p. 19. ISBN 84-458-1569-5. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, M.J. Characteristic Features of Surfactants. In Surfactant and International Phenomena, 3th ed.; Willey-Interscience Publication: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- McBain, J.W. Mobility of Highly Charged Micelles. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1913, 9, 99–101. [Google Scholar]
- Tanford, C. The Hydrophobic Effect: Formation of Micelles and Biological Membranes, 2nd ed.; John Willey and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Elworthy, P.H.; Mysels, K.J. The Surface tension of Sodium Dodecylsulphate Phase Solutions and Phase Separation Model of Micelle Formation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1966, 21, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroi, Y.; Nishikido, N.; Uehara, H.; Matuura, R. An Interelationship between Heat of Micelle Formation an Critical Micelle Concentration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1975, 50, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, V.; del Rio, J.M.; Attwood, D.; Garcia, M.; Jones, M.N.; Prieto, G.; Suarez, M.J.; Sarmiento, F. Study of the Aggregation Behavior og Hexyltrimethylammonium Bromide in Aqueous Solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 206, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitková, Z.; Oremusová, J.; Vitko, A.; Bezáková, Ž. Influence of Surfactants on Release of Chlorhexidine from Hydrogels. Tenside Surf. Det. 2011, 48, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchař, M.; Rejholec, V. Evaluation of Lipophilicity in Quantitative Structure-biological Activity Relations. I. Distribution Coefficient. Česk. Farm. 1979, 28, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oremusová, J.; Greksáková, O. Effect of Counterions Binding on the Association and Partition Balances of Hexadecylpyridinium Halides in Aqueous Solutions. Tenside Surf. Det. 2005, 4, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, J.; Varade, J.; Bahadur, P. Aggregtion Behavior of Quarternary Salt Based Cationic Surfactants. Thermochim. Acta 2005, 428, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.-K.; Bhasin, K.K.; Chauhan, R.; Dham, S. Effect of Temperature on Critical Concentration and Thermodynamic Behavior of Dodecyldimethyl-ammonium Bromide and Dodecyltrimethylammonium Chloride in Aqueous Media. Colloid Surf. A Phys.Chem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 255, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.S.; Jamroz, N.U.; Sharif, O.M. Micellization Parameters and Electrostatic Interaction in Micellar Solution of Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate (SDS) at Different Temperature. Colloids Surf. A Phys.-Chem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 178, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, M.S. Micelle Formation by Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate in Water additive system. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1996, 69, 2723–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitková, Z.; Oremusová, J.; Herdová, P.; Vitko, A.; Ivánková, O. Model Based Approach to Study of Release Kinetics of the Drug Chlorhexidine from Hydrogels. Tenside Surfactants Deterg. 2015, 52, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Z.; Malik, M.A.; Al-Thabaiti, S.A.; Alsehri, A.; Nabi, F. Micellization and Thermodynamic Properties of Cationic Surfactant Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide in non-Aqueous Mixture of Lauric Acid. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12, 4528–4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitková, Z.; Oremusová, J.; Herdová, P.; Kodadová, A. Release and Reological Properties of Topical Drugs. Tenside Surfactants Deterg. 2013, 50, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitková, Z.; Herdová, P. Dermal Semisolid Drugs, 1st ed.; FELIA s.r.o.: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2017; p. 129. ISBN 978-80-89824-07-6. (In Slovak) [Google Scholar]
- Sklenář, Z.; Vitková, Z.; Herdová, P.; Horáčková, K.; Šimunková, V. Formulation and Release of Alaptide from Cellulose-based Hydrogels. Acta Vet. 2012, 81, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |



| CMC.103/mol dm−3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surfactant | t/°C | Methode | (CMC ± sCMC).103/mol dm−3 | |||
| κ *1 | ρ *2 | A *3 | I1/I3 *4 | |||
| C12 | 20 | 8.84 | 8.83 | 8.83 | 8.86 | 8.837 ± 0.014 |
| 25 | 8.77 | 8.71 | 8.740 ± 0.032 | |||
| 30 | 8.55 | 8.65 | 8.600 ± 0.059 | |||
| 35 | 8.61 | 8.70 | 8.655 ± 0.045 | |||
| 40 | 8.81 | 8.90 | 8.855 ± 0.045 | |||
| 45 | 9.14 | 9.22 | 9.180 ± 0.040 | |||
| 50 | 9.65 | 9.84 | 9.62 | 9.703 ± 0.118 | ||
| C14 | 20 | 1.96 | 1.98 | 1.95 | 1.99 | 1.970 ± 0.009 |
| 25 | 1.94 | 1.96 | 1.950 ± 0.010 | |||
| 30 | 1.92 | 1.91 | 1.915 ± 0.005 | |||
| 35 | 1.96 | 1.97 | 1.965 ± 0.005 | |||
| 40 | 2.04 | 2.04 | 2.040 ± 0.000 | |||
| 45 | 2.14 | 2.16 | 2.150 ± 0.010 | |||
| 50 | 2.27 | 2.33 | 2.25 | 2.283 ± 0.042 | ||
| C16 | 20 | 0.49 | 0.50 | 0.48 | 0.50 | 0.493 ± 0.010 |
| 25 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.473 ± 0.000 | |||
| 30 | 0.46 | 0.47 | 0.468 ± 0.005 | |||
| 35 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.472 ± 0.005 | |||
| 40 | 0.48 | 0.48 | 0.486 ± 0.003 | |||
| 45 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.515 ± 0.001 | |||
| 50 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.539 ± 0.008 | ||
| Sample | Hydrogel | k.103/min−1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | without surfactants | 6.90 ± 0.29 |
| 2 | C12 below CMC | 9.09 ± 0.33 |
| 3 | C12 above CMC | 6.70 ± 0.33 |
| 4 | C14 below CMC | 7.99 ± 0.41 |
| 5 | C14 above CMC | 7.69 ± 0.51 |
| 6 | C16 below CMC | 5.56 ± 0.62 |
| 7 | C16 above CMC | 2.40 ± 0.16 |
| Sample | Hydrogels | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | Hydrogel | ||
| 1 | without surfactant | 6.25 | 6.06 |
| 2 | C12 below CMC | 6.20 | 6.13 |
| 3 | C12 above CMC | 6.16 | 6.05 |
| 4 | C14 below CMC | 6.03 | 6.06 |
| 5 | C14 above CMC | 6.00 | 6.02 |
| 6 | C16 below CMC | 5.98 | 6.03 |
| 7 | C16 above CMC | 6.09 | 6.35 |
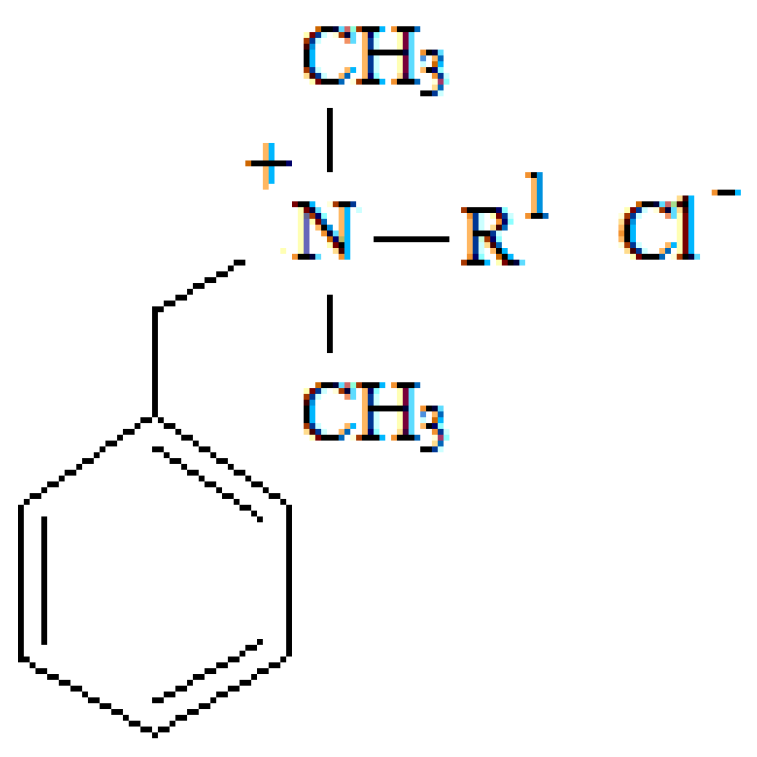
| Surfactant | Formula | Mr | m.p. (°C) | R1 | Purity (%) | Supplier |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C12 | C21H38NCl | 339.99 | 60–61 | dodecyl-(CH2)11-CH3 | 99 | FLUKA |
| C14 | C23H42NCl | 368.05 | 53–56 | tetradecyl-(CH2)13-CH3 | 99 | FLUKA |
| C16 | C25H46rNCl | 396.10 | 55–69 | hexadecyl-(CH2)15-CH3 | 97 | FLUKA |
| % (w/w) | msurf/g | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | CHIT | LA | CHX | C12 | C14 | C16 |
| 1 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 0.1 | - | - | - |
| 2 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.015 | - | - |
| 3 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.222 | - | - |
| 4 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 0.1 | - | 0.004 | - |
| 6 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 0.1 | - | 0.361 | - |
| 6 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 0.1 | - | - | 0.010 |
| 7 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 0.1 | - | - | 0.015 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vitková, Z.; Oremusová, J.; Herdová, P.; Ivánková, O.; Vitko, A. Association, Distribution, Liberation, and Rheological Balances of Alkyldimethylbenzylammonium Chlorides (C12–C16). Molecules 2017, 22, 1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101802
Vitková Z, Oremusová J, Herdová P, Ivánková O, Vitko A. Association, Distribution, Liberation, and Rheological Balances of Alkyldimethylbenzylammonium Chlorides (C12–C16). Molecules. 2017; 22(10):1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101802
Chicago/Turabian StyleVitková, Zuzana, Jarmila Oremusová, Petra Herdová, Oľga Ivánková, and Anton Vitko. 2017. "Association, Distribution, Liberation, and Rheological Balances of Alkyldimethylbenzylammonium Chlorides (C12–C16)" Molecules 22, no. 10: 1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101802
APA StyleVitková, Z., Oremusová, J., Herdová, P., Ivánková, O., & Vitko, A. (2017). Association, Distribution, Liberation, and Rheological Balances of Alkyldimethylbenzylammonium Chlorides (C12–C16). Molecules, 22(10), 1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101802





