Discriminative Analysis of Different Grades of Gaharu (Aquilaria malaccensis Lamk.) via 1H-NMR-Based Metabolomics Using PLS-DA and Random Forests Classification Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of Gaharu Metabolites
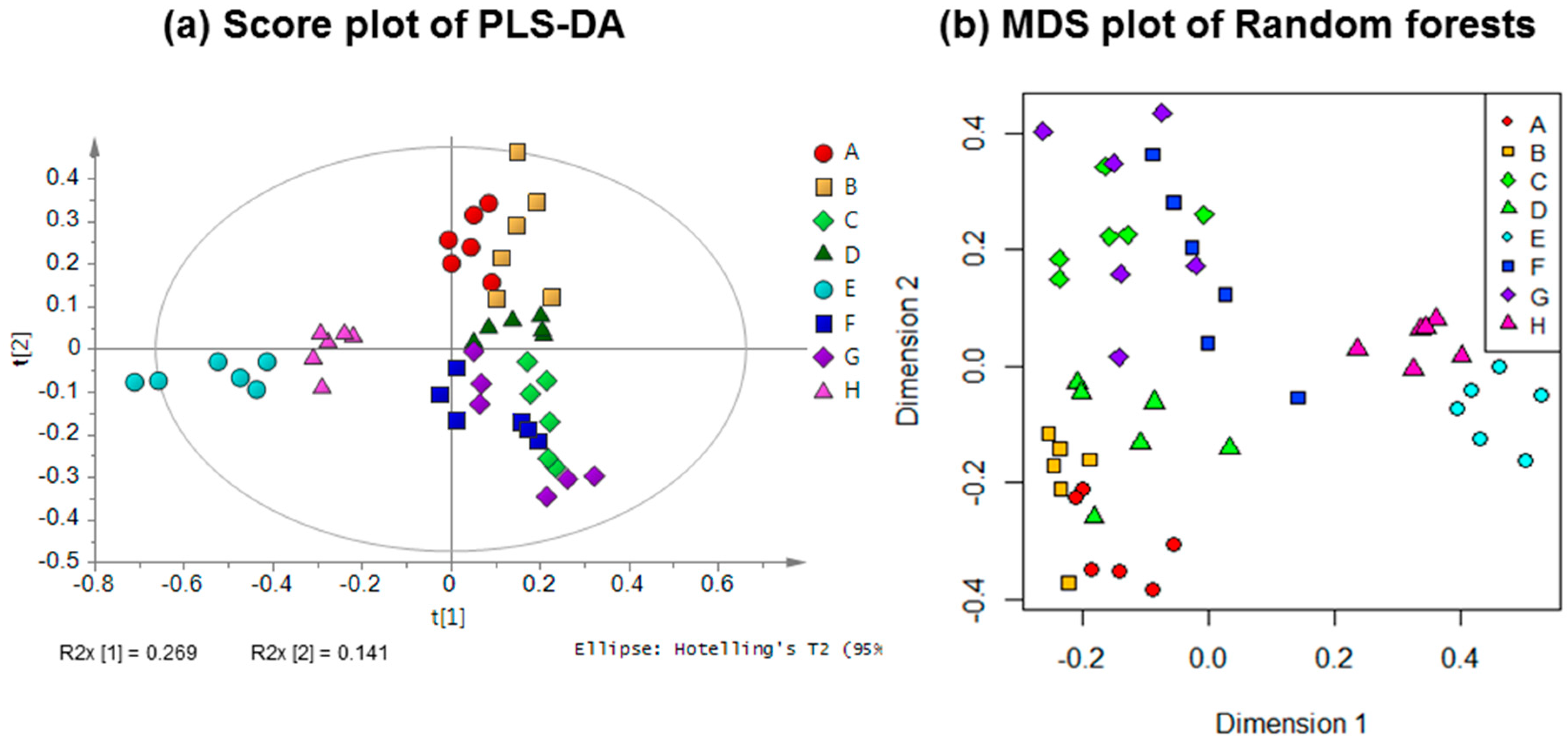
2.2. Discriminative Analysis of Gaharu Samples
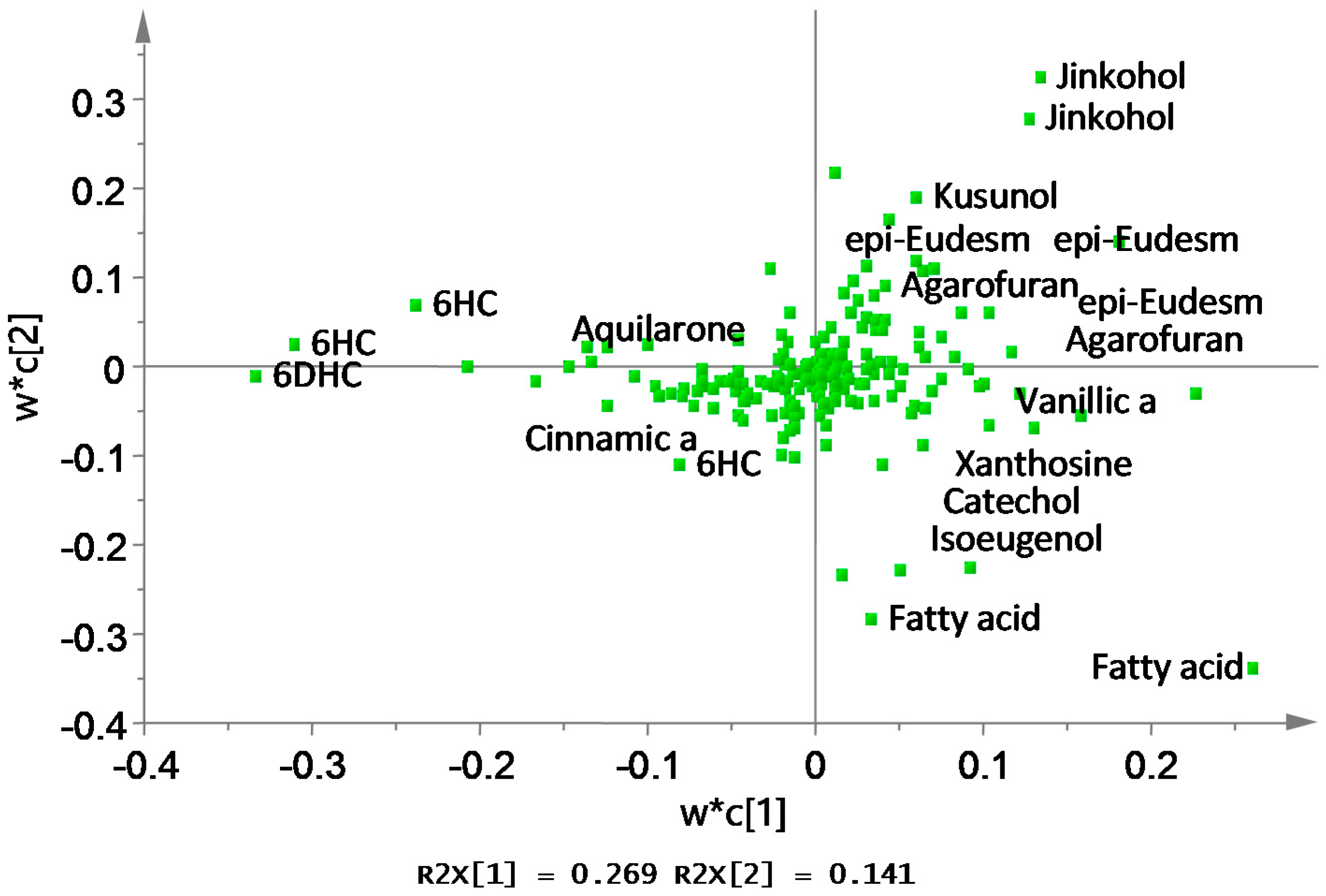
2.3. Identification of Discriminating Metabolites
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Samples and Chemicals
3.2. 1H-NMR Sample Preparation
3.3. 1H-NMR Data Acquisition and Data Preprocessing
3.4. Metabolite Assignment
3.5. Development of PLS-DA and Random Forests Models
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Plant List. Version 1.1. 2013. Available online: http://www.theplantlist.org/ (accessed on 2 February 2017).
- Mabberley, D.J. Mabberley’s Plant-Book: A Portable Dictionary of Plants, Their Classifications, and Uses; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Xu, Z.; Chai, X.; Zeng, K.; Jia, Y.; Bi, D.; Ma, Z.; Tu, P. Nine 2-(2-phenylethyl)chromone derivatives from the resinous wood of Aquilaria sinensis and their inhibition of LPS-induced NO production in RAW 264.7 cells. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 27, 5389–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barden, A.; Anak, N.A.; Mulliken, T.; Song, M. Heart of the Matter: Agarwood Use and Trade and CITES Implementation for Aquilaria Malaccensis; TRAFFIC International: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bhore, S.J.; Preveena, J.; Kandasamy, K.I. Isolation and identification of bacterial endophytes from pharmaceutical agarwood-producing Aquilaria species. Pharmacogn. Res. 2013, 5, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Wei, J.; Chen, H.; Gao, Z.; Sui, C.; Luo, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; et al. Identification of genes related to agarwood formation: Transcriptome analysis of healthy and wounded tissues of Aquilaria sinensis. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkill, I.H. A Dictionary of the Economic Products of the Malay Peninsula; Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1935.
- Kim, Y.C.; Lee, E.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, H.K.; Song, B.K.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, H.M. The effect of the aqueous extract of Aquilaria agallocha stems on the immediate hypersensitivity reactions. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1997, 58, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.T.; Chang, Y.S.; Kadir, A.A. A review on agar (gaharu) producing Aquilaria species. J. Trop. For. Prod. 1997, 2, 272–285. [Google Scholar]
- Antonopoulou, M.; Compton, J.; Perry, L.S.; Al-Mubarak, R. The Trade and Use of Agarwood (Oudh) in the United Arab Emirates; TRAFFIC Southeast Asia: Selangor, Malaysia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, T.W.; Anak, N.A. Wood for Trees: A Review of the Agarwood (Gaharu) Trade in Malaysia; TRAFFIC Southeast Asia: Petaling Jaya, Malaysia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, N.; Ali, N.A.M.; Jamil, M.; Rahiman, M.H.F.; Tajuddin, S.N.; Tai, M.N. A Review study of agarwood oil and its quality analysis. J. Teknol. 2014, 1, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.; Rahiman, M.H.F.; Taib, M.N.; Ibrahim, M.; Zareen, S.; Tajuddin, S. A review on agarwood and its quality determination. In Proceedings of the IEEE 6th Control and System Graduate Research Colloquium (ICSGRC), Shah Alam, Malaysia, 10–11 August 2015; pp. 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Naef, R. The volatile and semi-volatile constituents of agarwood, the infected heartwood of Aquilaria species: A review. Flavour Fragr. J. 2011, 26, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azah, M.A.N.; Husni, S.S.; Mailina, J.; Sahrim, L.; Majid, J.A.; Faridz, Z.M. Classification of agarwood (gaharu) by resin content. J. Trop. For. Sci. 2013, 25, 213–219. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.Y.; Ng, W.L.; Mahat, M.N.; Nazre, M.; Mohamed, R. DNA barcoding of the endangered Aquilaria (Thymelaeaceae) and its application in species authentication of agarwood products traded in the market. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidayat, W.; Shakaff, A.Y.M.; Ahmad, M.N.; Adom, A.H. Classification of agarwood oil using an electronic nose. Sensors 2010, 10, 4675–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najib, M.S.; Ali, N.A.M.; Arip, M.N.M.; Jalil, A.M.; Taib, M.N. Classification of agarwood region using ANN. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Control and System Graduate Research Colloquium (ICSGRC 2010), Shah Alam, Malaysia, 22 June 2010; pp. 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Najib, M.S.; Ahmad, M.U.; Funk, P.; Taib, M.N.; Ali, N.A.M. Agarwood classification: A case-based reasoning approach based on E-nose. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 8th International Colloquium on Signal Processing and Its Applications, Melaka, Malaysia, 23–25 March 2012; pp. 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, N.; Rahiman, M.H.F.; Taib, M.N.; Ali, N.A.M.; Jamil, M.; Tajuddin, S.N. Application of ANN in agarwood oil grade classification. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 10th International Colloquium on Signal Processing and Its Applications, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 7–9 March 2014; pp. 216–220. [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara, M.; Tsuneya, T.; Uneyama, K. Components of the agarwood smoke on heating. J. Essent. Oil Res. 1993, 5, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pripdeevech, P.; Khummueng, W.; Park, S.K. Identification of odor-active components of agarwood essential oils from Thailand by solid phase microextraction-GC/MS and GC-O. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2011, 23, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wei, J.H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, J.Q.; Chen, H.Q.; Liu, Y.J. Production of high-quality agarwood in Aquilaria sinensis trees via whole-tree agarwood-induction technology. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2012, 23, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.; Azah, M.A.N.; Jamil, M.; Rahiman, M.H.F.; Tajuddin, S.N.; Taib, M.N. Analysis of high quality agarwood oil chemical compounds by means of SPME/GC-MS and Z-score technique. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2013, 17, 403–413. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, N.; Rahiman, M.H.F.; Taib, M.N.; Ali, N.A.M.; Jamil, M.; Tajuddin, S.N. Analysis of chemical compounds of agarwood oil based on headspace-solid phase microextraction combined with gas chromatography mass-spectrometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE 9th International Colloquium on Signal Processing and Its Applications, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 8–10 March 2013; pp. 215–218. [Google Scholar]
- Azah, M.A.N.; Ismail, N.; Mailina, J.; Taib, M.N.; Rahiman, M.H.F.; Hafizi, Z.M. Chemometric study of selected agarwood oils by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Trop. For. Sci. 2014, 26, 382–388. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, N.A.M.; Ismail, N.; Jamil, M.; Aziz, A.; Lias, S.; Rahiman, M.H.F.; Taib, M.N. Identification of odor components of agarwood. J. Teknol. 2015, 77, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, C.H.; Lee, C.Y.; Yang, C.L.; Lee, M.R. Classification and differentiation of agarwoods by using non-targeted HS-SPME-GC/MS and multivariate analysis. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 7449–7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromski, P.S.; Correa, E.; Vaughan, A.A.; Wedge, D.C.; Turner, M.L.; Goodacre, R. A comparison of different chemometrics approaches for the robust classification of electronic nose data. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7581–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromski, P.S.; Muhamadali, H.; Ellis, D.I.; Xu, Y.; Correa, E.; Turner, M.L.; Goodacre, R. A tutorial review: Metabolomics and partial least squares-discriminant analysis—A marriage of convenience or a shotgun wedding. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 879, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromski, P.S.; Xu, Y.; Correa, E.; Ellis, D.I.; Turner, M.L.; Goodacre, R. A comparative investigation of modern feature selection and classification approaches for the analysis of mass spectrometry data. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 829, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromski, P.S.; Xu, Y.; Hollywood, K.A.; Turner, M.L.; Goodacre, R. The influence of scaling metabolomics data on model classification accuracy. Metabolomics 2014, 11, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xie, M.; Liu, S.; Guo, X.; Chen, X.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W. Chromatographic fingerprint analysis of metabolites in natural and artificial agarwood using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry combined with chemometric methods. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 967, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, S.; Talukdar, N.C.; Khan, M. A simple metabolite profiling approach reveals critical biomolecular linkages in fragrant agarwood oil production from Aquilaria malaccensis—A traditional agro-based industry in North East India. Curr. Sci. 2015, 108, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Jayachandran, K.; Sekar, I.; Parthiban, K.T.; Amirtham, D.; Suresh, K.K. Analysis of different grades of agarwood (Aquilaria malaccensis Lamk.) oil through GC-MS. Indian J. Nat. Prod. Resour. 2014, 5, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, Y.F.; Chin, S.T.; Perlmutter, P.; Marriott, P.J. Evaluation of comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography with accurate mass time-of-flight mass spectrometry for the metabolic profiling of plant-fungus interaction in Aquilaria malaccensis. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1387, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooy, F.V.D.; Maltese, F.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, H.K.; Verpoorte, R. Quality control of herbal material and phytopharmaceuticals with MS- and NMR-based metabolic fingerprinting. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. NMR-based metabolomic analysis of plants. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konishi, T.; Konoshima, T.; Shimada, Y.; Kiyosawa, S. Six new 2-(2-phenylethyl)chromones from agarwood. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Q.; Wei, J.H.; Yang, J.S.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Z.H.; Sui, C.; Gong, B. Chemical constituents of agarwood originating from the endemic genus Aquilaria plants. Chem. Biodivers. 2012, 9, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, K.; Yamagata, E.; Nakanishi, T.; Nagashima, T.; Kawasaki, I.; Yoshida, T.; Mori, H.; Miura, I. Sesquiterpenoids in two different kinds of agarwood. Phytochemistry 1984, 23, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, T.; Yamagata, E.; Yoneda, K.; Miura, I.; Mori, H. Jinkoh-eremol and jinkohol II, two new sesquiterpene alcohols from agarwood. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1983, 1, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, T.; Yamagata, E.; Yoneda, K.; Nagashima, T.; Kawasaki, I.; Yoshida, T.; Mori, H.; Miura, I. Three fragrant sesquiterpenes of agarwood. Phytochemistry 1984, 23, 2066–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Package ‘randomForests’. Breiman and Cutler’s Random Forests for Classification and Regression. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/randomForest/randomForest.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2017).
- Xia, J.; Psychogios, N.; Young, N.; Wishart, D.S. MetaboAnalyst: A web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalivodová, A.; Hron, K.; Filzmoser, P.; Najdekr, L.; Janečková, H.; Adam, T. PLS-DA for compositional data with application to metabolomics. J. Chemom. 2015, 29, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, E.; Saccenti, E.; Smilde, A.K.; Westerhuis, J.A. Double-check: Validation of diagnostic statistics for PLS-DA models in metabolomics studies. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
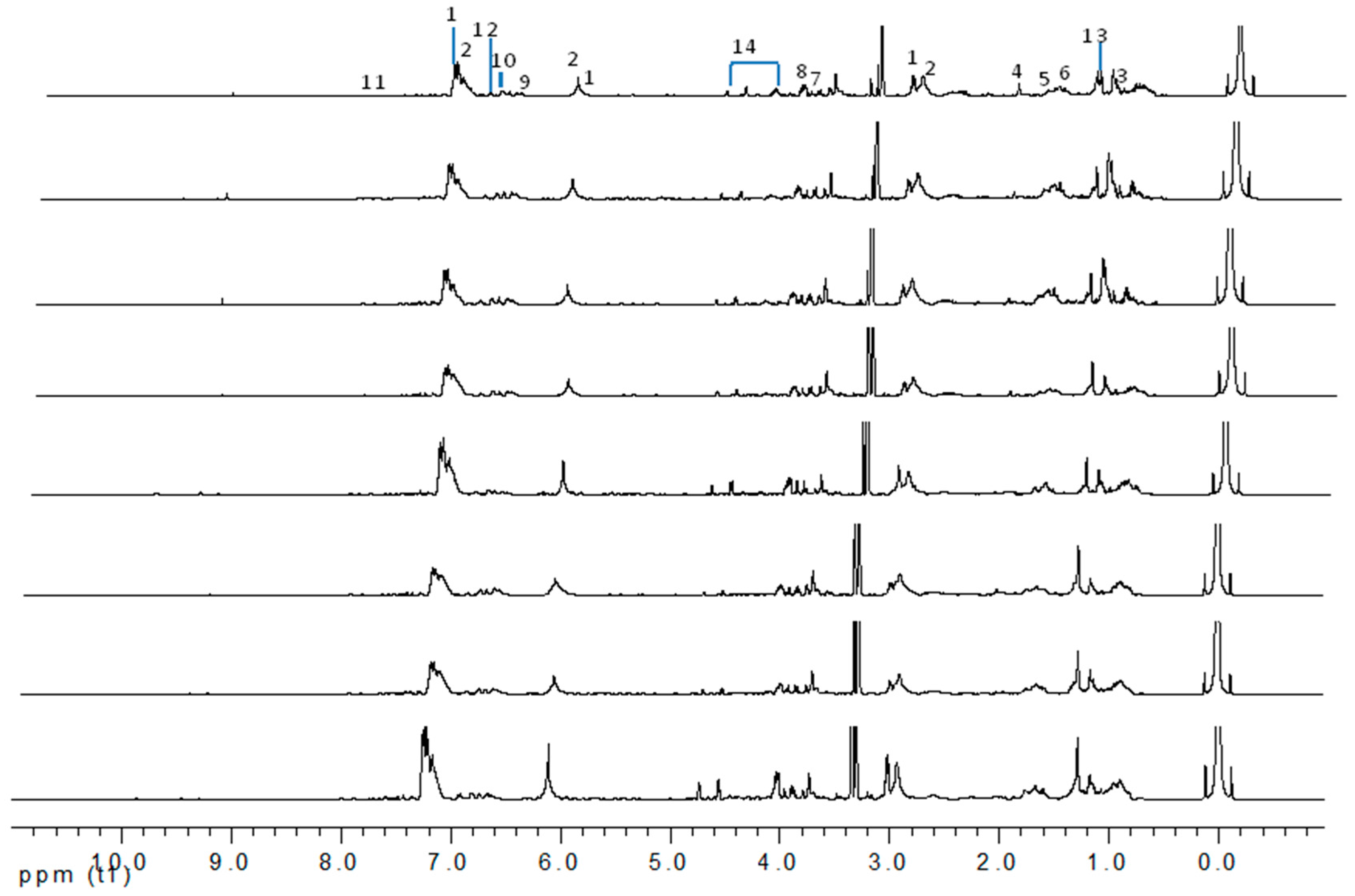
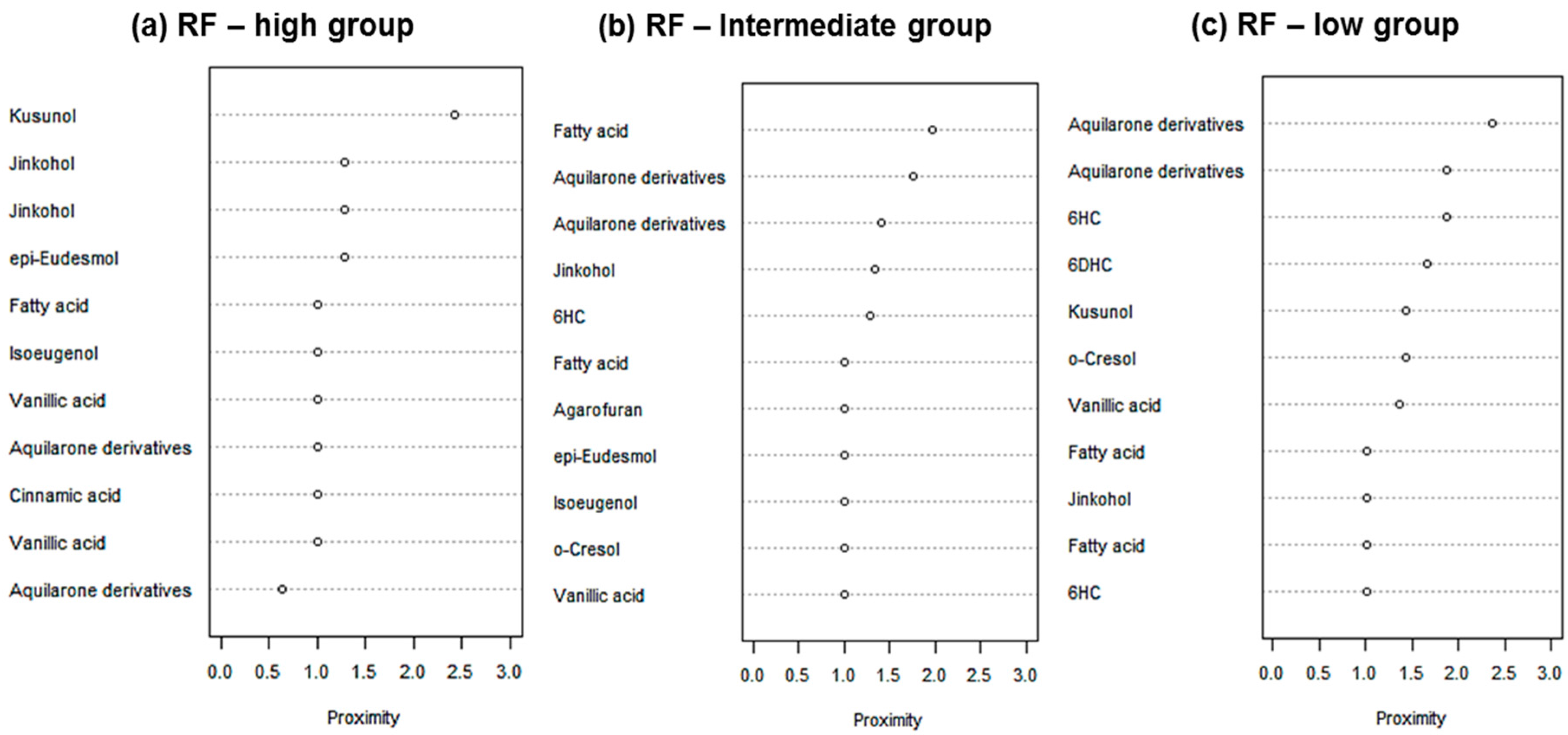
| Tentative Compound | Chemical Shifts |
|---|---|
6-Hydroxy-2-(2-phenylethyl)chromone (1) | 8.09 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, H-5); 7.26–7.19 (m, H-2′-H-6′); 7.14 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, H-8);6.10 (s, H-3); 3.02–2.99 (m, H-7′); 2.92–2.90 (m, H-8′) |
6-Hydroxy-2-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]chromone (2)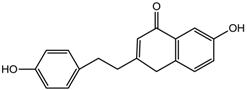 | 7.98 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, H-5); 7.21 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-2′); 7.17 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-6′); 6.73 (dd, J = 8.0, 2.5 Hz, H-7); 6.11 (s, H-3); 2.95 (m, H-7'); 2.87 (m, H-8') |
Jinkohol (3)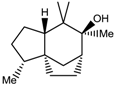 | 2.01 (dd, J = 4.9, 4.4 Hz, H-8); 1.86 (m, H-3); 1.80 (m, H-2); 1.69 (dd, J = 9.8 Hz, H-5); 1.56 (ddd, J = 10.6, 1.5 Hz, H-11); 1.38 (dd, J = 10.6, 4.4 Hz, H-11); 0.90 (s, 6-Me); 0.84 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 2-Me) |
usunol (4)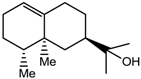 | 5.32 (ddd, J = 5.7, 2.2 Hz, H-1); 2.27 (dddd, J = 13.8, 12.4, 3.3 Hz, H-9); 1.62 (dddd, J = 12.4, 3.3 Hz, H-7); 1.41 (m, H-4) |
α-Agarofuran (5)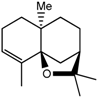 | 5. 59 (s, H-3); 2.22 (dd, J = 12.5, 4.0 Hz, H-9); 1.72 (s, H-12); 1.23 (s, H-14); 0.91 (s, H-13) |
10-epi-γ-Eudesmol (6)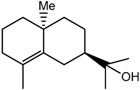 | 2.12 (d, J = 15.8 Hz, H-3); 1. 68 (s, H-12); 1.19 (s, H-13); 1.09 (s, H-11) |
Isoeugenol (7)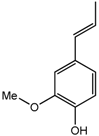 | 7.09 (dd, J = 1.9, 0.5 Hz, H-5); 3.79 (s, H-10); 1.55 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, H-9); 6.32 (d, J = 16.9 Hz, H-7); 6.29 (dq, J = 16.9, 6.9 Hz, H-8); 7.40 (dd, J = 8.6, 1.9 Hz, H-3) |
Vanillic acid (8)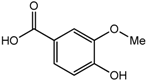 | 3.94 (s, H-8); 6.92 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, H-3); 7.43 (dd, J = 8.2, 1.7 Hz, H-4); 7.52 (d, J = 1.7 Hz, H-6) |
Cinnamic acid (9)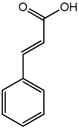 | 7.60 (dd, J = 7.9, 1.1 Hz, H-6); 7.45 (m, H-5); 7.40 (d, trans, J = 16.0 Hz, H-7); 6.54 (d, trans, J = 16.0 Hz, H-8) |
o-Cresol (10)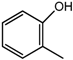 | 2.29 (s, H-8); 6.82 (m, H-4, H-6); 7.14 (m, H-5); 7.20 (m, H-3) |
Xanthosine (11)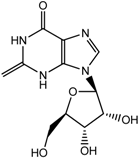 | 7.88 (s, H-7); 5.85 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, H-2); 4.69 (t, J = 5.7 Hz, H-3); 4.25 (q, J = 2.7 Hz, H-5); 3.89 (m, H-17) |
Catechol (12) | 6.87 (m, H-4, H-5); 6.94 (m, H-3, H-6) |
| Fatty acid: (13) | 1.28 (m) |
Aquilarone derivatives (14)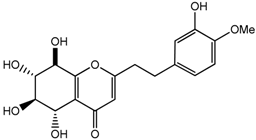 | 4.72 (d, J = 2.7 Hz, H-5); 4.55 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, H-8); 4.29 (m, H-6); 3.99 (dd, J = 6.2, 2.4 Hz, H-7); 2.70–2.80 (m, 2H) |
| Random Forests Class | Producer Accuracy | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | Total | Percent Correct | Omission Error (%) | ||
| Reference class | A | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 67 | 33 |
| B | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 50 | 50 | |
| C | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 83 | 17 | |
| D | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 50 | 50 | |
| E | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 100 | 0 | |
| F | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 83 | 17 | |
| G | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 6 | 50 | 50 | |
| H | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 6 | 100 | 0 | |
| Total | 6 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 4 | 6 | 48 | |||
| Users accuracy | ||||||||||||
| Percent correct | 67 | 43 | 83 | 50 | 100 | 71 | 75 | 100 | 72.92 | |||
| Commission error (%) | 33 | 57 | 17 | 50 | 0 | 29 | 25 | 0 | ||||
| Agreement | 4 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 35 | |||
| By chance | 0.75 | 0.88 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.875 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 6.00 | |||
| Kappa | 0.69 | |||||||||||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ismail, S.N.; Maulidiani, M.; Akhtar, M.T.; Abas, F.; Ismail, I.S.; Khatib, A.; Ali, N.A.M.; Shaari, K. Discriminative Analysis of Different Grades of Gaharu (Aquilaria malaccensis Lamk.) via 1H-NMR-Based Metabolomics Using PLS-DA and Random Forests Classification Models. Molecules 2017, 22, 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101612
Ismail SN, Maulidiani M, Akhtar MT, Abas F, Ismail IS, Khatib A, Ali NAM, Shaari K. Discriminative Analysis of Different Grades of Gaharu (Aquilaria malaccensis Lamk.) via 1H-NMR-Based Metabolomics Using PLS-DA and Random Forests Classification Models. Molecules. 2017; 22(10):1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101612
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsmail, Siti Nazirah, M. Maulidiani, Muhammad Tayyab Akhtar, Faridah Abas, Intan Safinar Ismail, Alfi Khatib, Nor Azah Mohamad Ali, and Khozirah Shaari. 2017. "Discriminative Analysis of Different Grades of Gaharu (Aquilaria malaccensis Lamk.) via 1H-NMR-Based Metabolomics Using PLS-DA and Random Forests Classification Models" Molecules 22, no. 10: 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101612
APA StyleIsmail, S. N., Maulidiani, M., Akhtar, M. T., Abas, F., Ismail, I. S., Khatib, A., Ali, N. A. M., & Shaari, K. (2017). Discriminative Analysis of Different Grades of Gaharu (Aquilaria malaccensis Lamk.) via 1H-NMR-Based Metabolomics Using PLS-DA and Random Forests Classification Models. Molecules, 22(10), 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101612