Acyclic Triterpenoids from Alpinia katsumadai Inhibit IL-6-Induced STAT3 Activation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
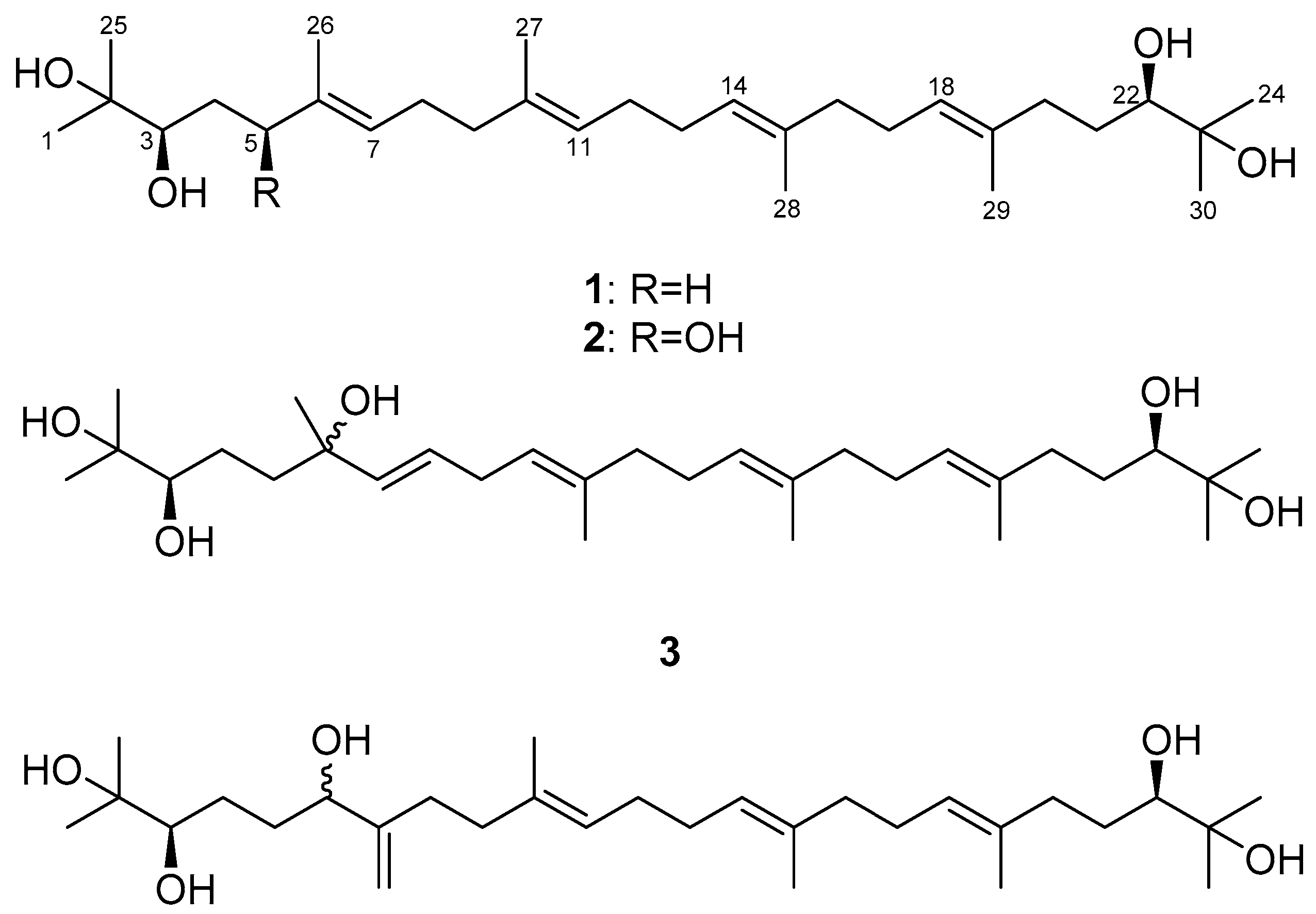
2.1. Isolation of Compounds
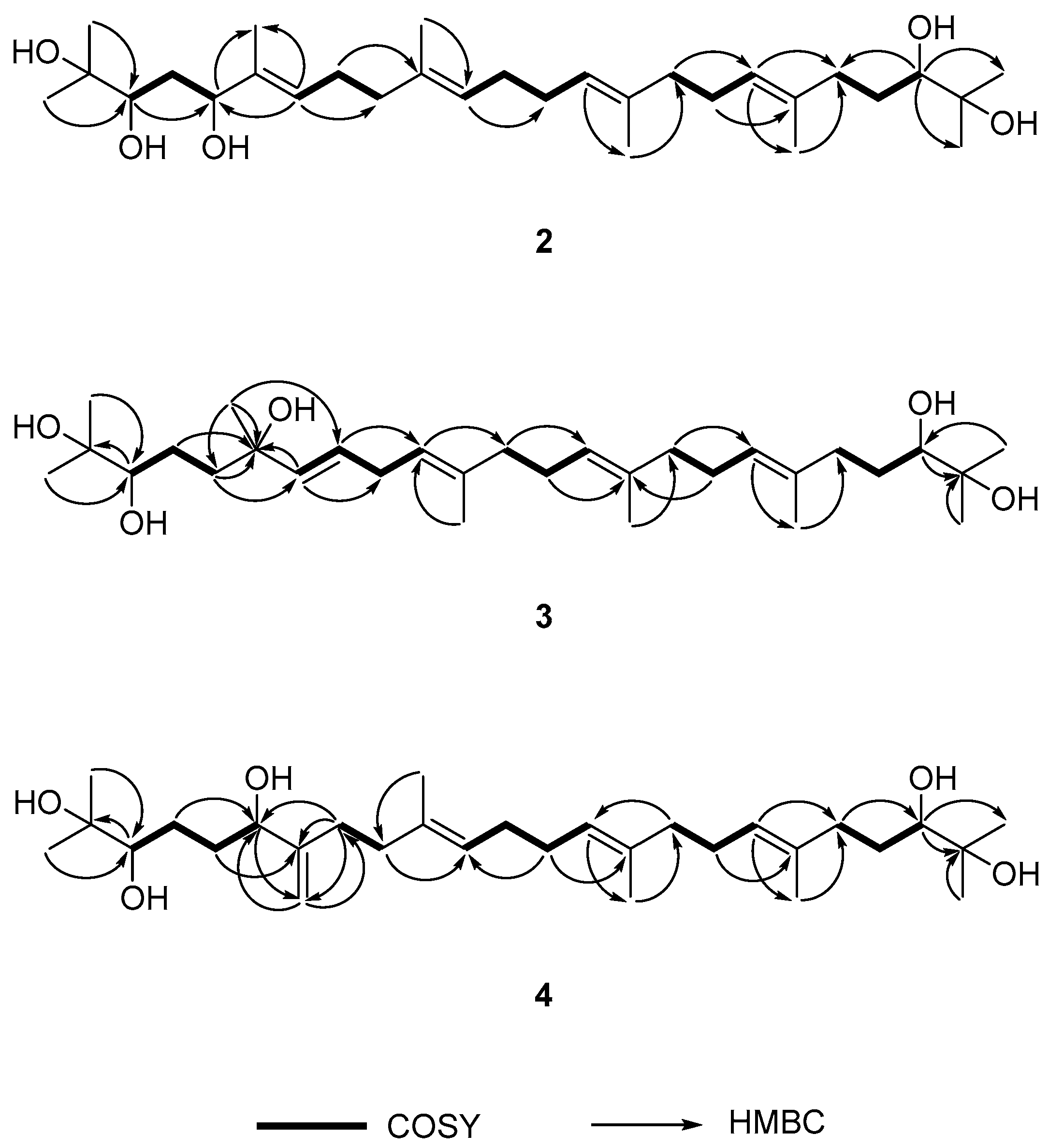
2.2. Determination of the Acyclic Triterpenoids Structure
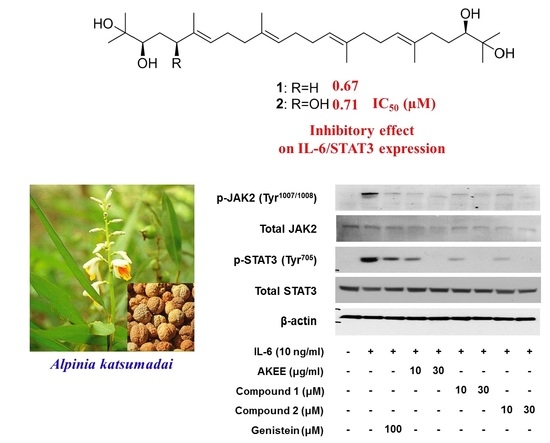
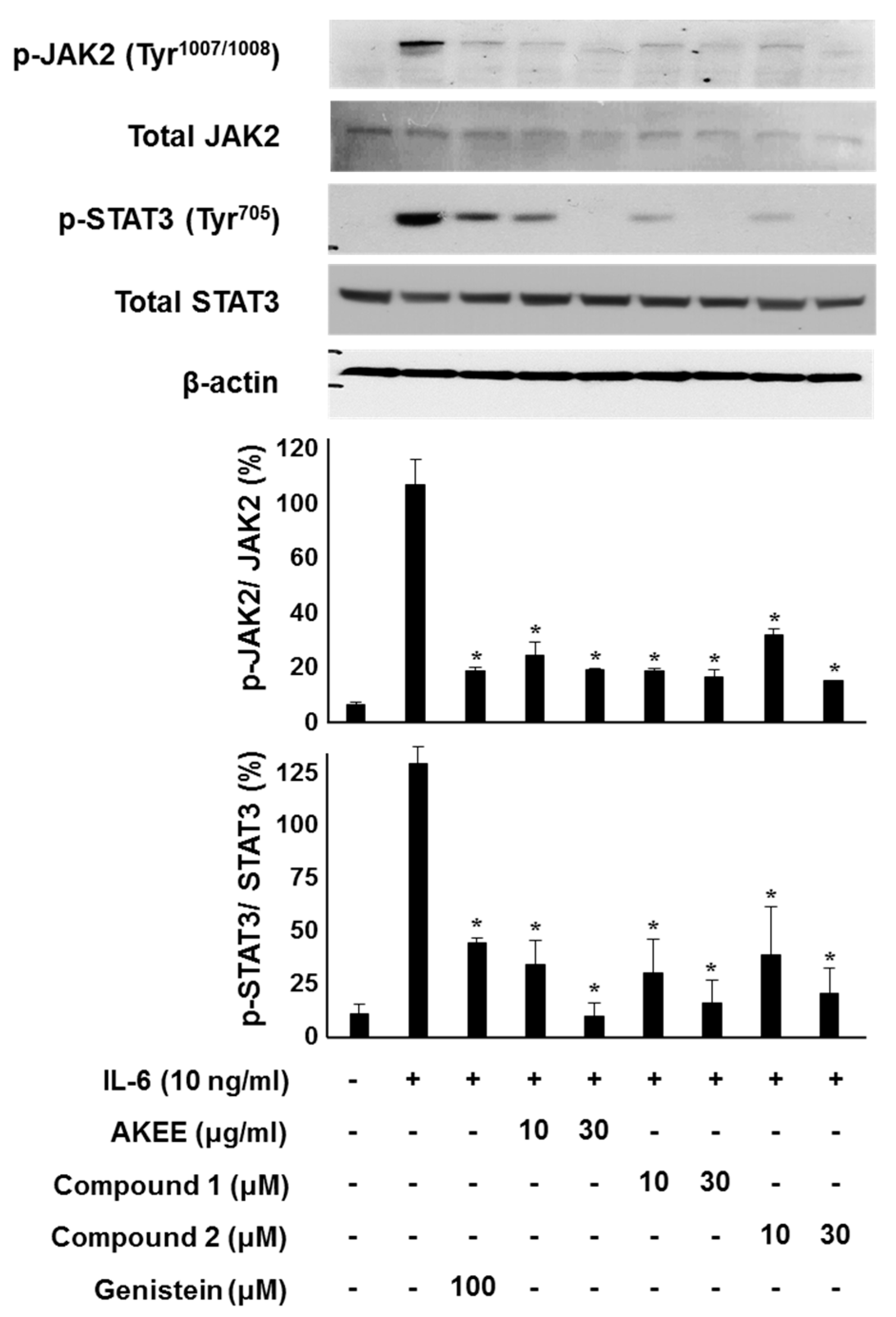
2.3. IL-6/STAT3 Inhibitory Effects of Acyclic Triterpenoids 1–4
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Extraction and Isolation
3.3. (R)- and (S)-MTPA Ester of Compounds 2–3
3.4. Biological Materials and Cell Culture
3.5. Luciferase Assay
3.6. Cell Viability
3.7. Western Blotting Analysis
3.8. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luger, T.A.; Schwarz, T.; Krutmann, J.; Kirnbauer, R.; Neuner, P.; Köck, A.; Urbanski, A.; Borth, W.; Schauer, E. Interleukin-6 is produced by epidermal cells and plays an important role in the activation of human T-lymphocytes and natural killer cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1989, 557, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neveu, W.A.; Allard, J.B.; Dienz, O.; Wargo, M.J.; Ciliberto, G.; Whittaker, L.A.; Rincon, M. IL-6 is required for airway mucus production induced by inhaled fungal allergens. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishima, A.; Marui, A.; Shimamoto, T.; Saji, Y.; Nishina, T.; Komeda, M. A case of interleukin-6-producing cardiac myxoma resembling multicentric Castleman’s disease. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2009, 138, 499–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimoto, N.; Miyasaka, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Kawai, S.; Takeuchi, T.; Azuma, J. Long-term safety and efficacy of tocilizumab, an anti-IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibody, in monotherapy, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (the STREAM study): Evidence of safety and efficacy in a 5-year extension study. Ann. Rheumatol. Dis. 2009, 68, 1580–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernberg, E.; Ulleryd, M.A.; Johansson, M.E.; Bergström, G.M. Social disruption stress increases IL-6 levels and accelerates atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice. Atherosclerosis 2012, 221, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristiansen, O.P.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Interleukin-6 and Diabetes. Diabetes 2005, 54, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulciniti, M.; Hideshima, T.; Vermot-Desroches, C.; Pozzi, S.; Nanjappa, P.; Shen, Z.; Patel, N.; Smith, E.S.; Wang, W.; Prabhala, R.; et al. A high-affinity fully human anti-IL-6 mAb, 1339, for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 7144–7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagat, K.; Vallance, P. Inflammatory cytokines impair endothelium-dependent dilatation in human veins in vivo. Circulation 1997, 96, 3042–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Eisenbrand, G. Chinese Drugs of Plant Origin; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 711–737. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, J.W.; Kang, G.Y.; Han, A.R.; Lee, D.; Lee, Y.S.; Seo, E.K. Diarylheptanoids from the seeds of Alpinia katsumadai as heat shock factor 1 inducers. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2109–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Koyama, K.; Takahashi, K.; Kondo, S.; Watanabe, K. Structure-antiemetic-activity of some diarylheptanoids and their analogues. Phytomedicine 2002, 9, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Koyama, K.; Takahashi, K.; Tai, T.; Nunoura, Y.; Watanabe, K. Two novel anti-emetic principles of Alpinia katsumadai. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1672–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, K.S.; Brown, G.D. Stilbenes, monoterpenes, diarylheptanoids, labdanes and chalcones from Alpinia katsumadai. Phytochemistry 1998, 47, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.Z.; Luo, J.G.; Wang, X.B.; Wang, J.S.; Kong, L.Y. Two novel monoterpene-chalcone conjugates isolated from the seeds of Alpinia katsumadai. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 2728–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, S.Z.; Wang, X.B.; Luo, J.G.; Wang, J.S.; Kong, L.Y. A pair of unique sesquiterpene-chalcone conjugates isolated from the seeds of Alpinia katsumadai. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 5658–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroyanagi, M.; Noro, T.; Fukushima, S.; Aiyama, R.; Ikuta, A.; Itokawa, H.; Morita, M. Studies on the constituents of the seeds of Alpinia katsumadai Hayata. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1983, 31, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Tang, B.; Wang, J.; Sui, H.; Jin, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z. Antiproliferative effect of alpinetin in BxPC-3 pancreatic cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 29, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.H.; Kwon, H.J.; Ryu, Y.B.; Chang, J.S.; Cho, K.O.; Hosmillo, M.D.; Rho, M.C.; Park, S.J.; Lee, W.S. Antiviral activity of Alpinia katsumadai extracts against rotaviruses. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 92, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.J.; Kim, H.H.; Yoon, S.Y.; Ryu, Y.B.; Chang, J.S.; Cho, K.O.; Rho, M.C.; Park, S.J.; Lee, W.S. In vitro inhibitory activity of Alpinia katsumadai extracts against influenza virus infection and hemagglutination. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.Y.; Lee, N.H.; Seo, C.S.; Lee, J.A.; Jung, D.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, H.K. Alpinia katsumadai seed extract attenuate oxidative stress and asthmatic activity in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1746–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y.F.; Huang, W.Z.; Wang, Z.T. Alpinia katsumadai hayata prevents mouse sepsis induced by cecal ligation and puncture through promoting bacterial clearance and downregulating systemic inflammation. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, G.S.; Li, B.; Lee, D.S.; Byun, E.; Kang, D.G.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, Y.C. Cytoprotective constituents of Alpinia katsumadai seeds against glutamate-induced oxidative injury in HT22 cells. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2007, 13, 268–271. [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama, Y.; Moriyasu, M.; Ichimaru, M.; Tachibana, Y.; Kato, A.; Mathenge, S.G.; Nganga, J.N.; Juma, F.D. Acyclic triterpenoids from Ekebergia capensis. Phytochemistry 1996, 42, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, Y.; Moriyasu, M.; Ichimaru, M.; Kato, A.; Mathenge, S.G.; Naganga, J.N.; Juma, F.D. Absolute configurations of two acyclic triterpenoids from Ekebergia capensis. Phytochemistry 1999, 52, 1593–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, M.C.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, H.S.; Jun, C.D.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.W.; Choi, J.H.; Song, G.Y. New Acyclic Triterpenoids Compound, and Pharmaceutical Composition Comprising Alpinia katsumadai Extract or Acyclic Triterpenoids Compounds Isolated from the Same. World Patent WO2008133387, 6 November 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kouda, K.; Ooi, T.; Kusumi, T. Application of the modified Mosher’s method to linear 1, 3-diols. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 3005–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, T.; Fukushima, T.; Ohtani, I.; Kakisawa, H. Elucidation of the absolute configurations of amino acids and amines by the modified Mosher’s method. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991, 32, 2939–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, F.; Seco, J.M.; Quiñoá, E.; Riguera, R. Determining the absolute stereochemistry of secondary/secondary diols by 1H-NMR: Basis and applications. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 3778–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.W.; Yun, B.R.; Kim, M.H.; Park, C.S.; Lee, W.S.; Oh, H.M.; Rho, M.C. Phenolic compounds isolated from Psoralea corylifolia inhibit IL-6-induced STAT3 activation. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanada, T.; Yoshimura, A. Regulation of cytokine signaling and inflammation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002, 13, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, D.; Ishihara, K.; Hirano, T. IL-6 signal transduction and its physiological roles: The signal orchestration model. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 149, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.S.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, M.S.; Yun, B.R.; Park, M.H.; Lee, S.G.; Park, S.J.; Lee, W.S.; Rho, M.C. Manassantin A and B from Saururus chinensis inhibit interleukin-6–induced signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation in Hep3B Cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 115, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Jang, H.J.; Kim, Y.; Oh, H.M.; Lee, S.; Jung, K.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, W.S.; Lee, S.W.; Rho, M.C. Inhibitory effects of IL-6-induced STAT3 activation of bio-active compounds derived from Salvia plebeia R. Br. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 2222–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Compounds 1 and 2 are available from the authors. |


| Position | 2 a | 3 b | 4 b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | |
| 1 | 1.20, s | 24.0 | 1.19, s | 26.4 | 1.15, s | 26.4 |
| 2 | - | 73.3 | - | 73.1 | - | 73.0 |
| 3 | 3.62, dd (8.4, 3.6) | 78.5 | 3.35, dd (10.8, 1.8) | 48.2 | 3.34, d (9.6) | 78.1 |
| 4 | 1.63, m | 36.1 | 2.03, m | 22.9 | 1.40, 1.58, m | 29.5 |
| 5 | 4.26, dd (7.6, 4.8) | 78.6 | 1.55, m | 42.4 | 2.01, m | 24.3 |
| 6 | - | 134.9 | - | 73.0 | 4.09, m | 75.1 |
| 7 | 5.43, t (6.4) | 126.6 | 5.50, dd (15.6, 1.2) | 136.7 | - | 151.3 |
| 8 | 2.13, m | 26.6 | 5.58, dt (15.6, 6.0) | 126.7 | 2.01, 2.19, m | 31.0 |
| 9 | 2.05, m | 39.4 | 2.74, t (6.6) | 30.8 | 1.58, 1.65, m | 35.3 |
| 10 | - | 135.1 | 5.14, td (7.2, 1.2) | 122.2 | - | 135.9 |
| 11 | 5.14, m | 124.7 | - | 135.0 | 5.22, t (6.6) | 125.1 |
| 12 | 1.41, m | 29.8 | 2.03, 2.10, m | 39.5 | 1.58, m | 29.6 |
| 13 | 1.59, m | 39.8 | 1.40, 1.58, m | 29.5 | 2.10, m | 29.4 |
| 14 | 5.14, m | 124.9 | 5.18, t (6.6) | 124.9 | 5.14, q (6.6) | 124.3 |
| 15 | - | 135.2 | - | 135.2 | - | 135.0 |
| 16 | 2.02, m | 28.4 | 2.03, m | 36.8 | 2.02, m | 39.5 |
| 17 | 2.10, m | 26.6 | 2.10, m | 26.1 | 2.01, 2.10, m | 26.4 |
| 18 | 5.19, t (6.4) | 125.3 | 5.23, td (6.6, 1.2) | 125.5 | 5.14, q (6.6) | 124.9 |
| 19 | - | 137.3 | - | 135.9 | - | 135.1 |
| 20 | 2.23, m | 37.0 | 2.02, 2.22, m | 36.8 | 2.03, 2.21, m | 36.7 |
| 21 | 2.09, m | 26.2 | 1.58, m | 29.6 | 1.40, 1.58, m | 29.5 |
| 22 | 3.35, d (10.4) | 78.9 | 3.35, dd (10.8, 1.8) | 78.2 | 3.34, d (9.6) | 78.1 |
| 23 | - | 72.8 | - | 73.1 | - | 73.0 |
| 24 | 1.19, s | 23.5 | 1.15, s | 23.4 | 1.19, s | 23.4 |
| 25 | 1.17, s | 26.4 | 1.15, s | 23.3 | 1.19, s | 23.3 |
| 26 | 1.63, s | 11.9 | 1.26, s | 28.1 | 4.87, 5.05, br s | 109.9 |
| 27 | 1.62, s | 16.1 | 1.60, s | 16.0 | 1.60, s | 15.9 |
| 28 | 1.61, s | 16.2 | 1.61, s | 15.9 | 1.62, s | 16.0 |
| 29 | 1.60, s | 16.2 | 1.61, s | 15.9 | 1.61, s | 15.9 |
| 30 | 1.15, s | 26.6 | 1.19, s | 26.5 | 1.15, s | 26.4 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, H.-J.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, S.; Jung, K.; Lee, S.W.; Rho, M.-C. Acyclic Triterpenoids from Alpinia katsumadai Inhibit IL-6-Induced STAT3 Activation. Molecules 2017, 22, 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101611
Jang H-J, Lee S-J, Lee S, Jung K, Lee SW, Rho M-C. Acyclic Triterpenoids from Alpinia katsumadai Inhibit IL-6-Induced STAT3 Activation. Molecules. 2017; 22(10):1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101611
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Hyun-Jae, Seung-Jae Lee, Soyoung Lee, Kyungsook Jung, Seung Woong Lee, and Mun-Chual Rho. 2017. "Acyclic Triterpenoids from Alpinia katsumadai Inhibit IL-6-Induced STAT3 Activation" Molecules 22, no. 10: 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101611
APA StyleJang, H.-J., Lee, S.-J., Lee, S., Jung, K., Lee, S. W., & Rho, M.-C. (2017). Acyclic Triterpenoids from Alpinia katsumadai Inhibit IL-6-Induced STAT3 Activation. Molecules, 22(10), 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101611