Abstract
The low-molecular-weight fucosylated chondroitin sulfate (LFCS) was prepared from native fucosylated chondroitin sulfate (FCS), which was extracted and isolated from sea cucumber Cucumaria frondosa, and the anti-cancer mechanism of LFCS on mouse Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) was investigated. The results showed that LFCS remarkably inhibited LLC growth and metastasis in a dose-dependent manner. LFCS induced cell cycle arrest by increasing p53/p21 expression and apoptosis through activation of caspase-3 activity in LLC cells. Meanwhile, LFCS suppressed the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), increased the expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) and downregulated the matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) level. Furthermore, LFCS significantly suppressed the activation of ERK1/2/p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway, which played a prime role in expression of MMPs. All of these data indicate LFCS may be used as anti-cancer drug candidates and deserve further study.
1. Introduction
According to World Cancer Report 2014, cancer is the leading cause of mortality and contributes to more than 8.2 million deaths globally in 2012 [1]. Lung cancer remains the most common cancer with the highest incidence rate (12.9%) and mortality rate (19.4%) [2,3,4]. Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for 85% of all cases of lung cancer [5,6]. The high mortality rate is related to the low cure rate as a result of the metastasis, not the primary tumors [7,8].
Metastasis is responsible for 90% of mortality of cancer-associated disease [9]. Tumor metastasis is a complex multi-step process including uncontrolled proliferation of primary tumor, invasion, systemic dissemination, angiogenesis, and colonization. Unlimited proliferation is an acquired capability of cancer cells. p53 is a tumor suppressor transcription factor. Activation of p53 induces the expression of p21, which is a universal inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks), and cell cycle arrest [10,11,12]. Han et al. reported that p21 was required for senescence development of HCT116 cells treated with low concentrations of camptothecin [13]. Caspases work as essential mediators of apoptosis, and caspase-3 is a crucial trigger of apoptosis, which eventually leads to cell death [14,15]. Liu et al. reported that ellagic acid induced G0/G1 arrest through increased p53 level and induced apoptosis through activation of caspase-3 activity in human bladder cancer T24 cells [16]. To invade into the surrounding stroma, tumor cells need to degrade and breach the barrier of basement membranes and the extracellular matrix (ECM). Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are the most important degrading enzymes [17]. MMP-9 is an important gelatinase to degrade ECM components especially Type IV collagen which is the major component of the basement membrane. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) is the natural inhibitor of MMP-9. Wu et al. reported that TIMP-1and MMP-9 may work as biomarkers to predict the progression and prognosis of breast cancer [18]. Angiogenesis primarily regulated by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is one of the critical steps in tumor growth and metastasis [19,20]. Huang et al. reported that fucoidan inhibited lung carcinoma metastasis by down-regulating expression of VEGF and MMPs [21]. Cancer metastasis is a multi-step process regulated by a complex signaling network [8]. The nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) can induce the transcription, expression, and secretion of MMPs [22,23,24], which is regulated by mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPKs) [25,26]. Three distinct MAPKs family members including extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 (ERK1/2), c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase (JNK/SAPK), and p38 play a major role in tumor progression and metastasis by inducing proteolytic enzymes that degrade the basement membrane, enhances cell migration [27,28]. Huang et al. reported that the expression and secretion of MMP-9 protein were induced through the activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) and nuclear factor-kB NF-κB signaling pathways [25].
Fucosylated chondroitin sulfate (FCS) is a heparin-like glycosaminoglycan (GAG) isolated from sea cucumbers. FCS is composed of a backbone consisted of repeating units of →4GlcAβ1→3GalNAcβ1→ with α-fucose branches linked to the O-3 position of GlcA residues. Recent studies have demonstrated that FCS possessed various biological activities, such as anti-coagulant [29], anti-thrombotic [30], and anti-viral effects [31]. Importantly, FCS showed a remarkable function in the inhibition of metastasis and thrombosis by NF-κB/tissue factor/factor Xa pathway in mouse melanoma B16F10 cell [32]. Additionally, FCS was able to suppress metastasis and inflammatory reaction by selectin blocking activity [33]. However, the application of native FCS resulted in an undesirable effect of platelet aggregation [34]. Several studies reported that LFCS exerted anti-thrombotic effect with less bleeding side effect [35], whereas there were scarcely reports about the anti-cancer activity and mechanism of LFCS.
In this study, we evaluated the anti-cancer activity of LFCS derived from sea cucumber Cucumaria frondosa using a mouse Lewis lung carcinoma model. The molecular mechanism of LFCS on tumor growth, invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis were investigated as well. It is demonstrated that LFCS is a potential anti-tumor candidate capable of inhibiting tumor growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis by the MAPK (p38/ERK1/2)/NF-κB pathway.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. LFCS Inhibits LLC Tumor Growth in Vivo
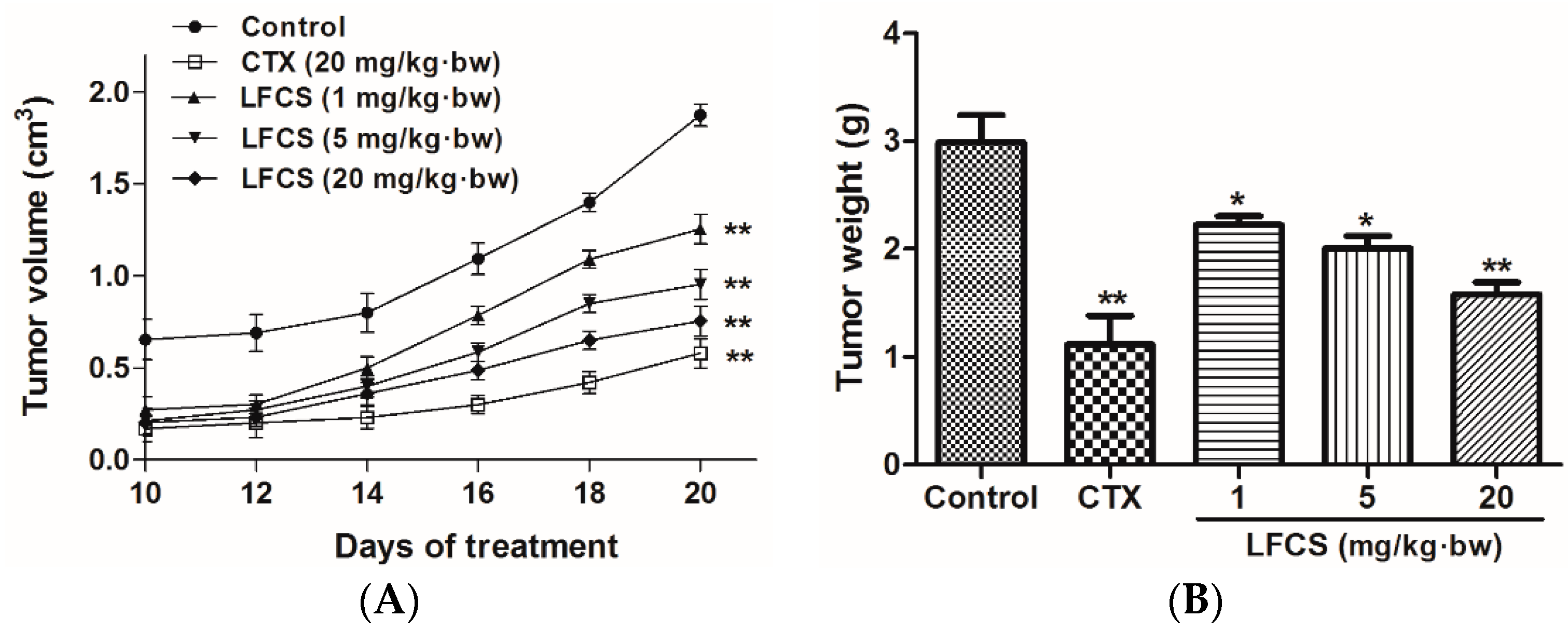
To study the antitumor activity of LFCS in vivo, we set up a mouse LLC metastasis model. A tumor growth curve was constructed as shown in Figure 1A. After 20 days of treatment, the mice were euthanized and the tumors were excised and weighed (Figure 1B). As shown in Figure 1, LFCS significantly reduced the tumor volume (p < 0.01) and weight in a dose-dependent manner in vivo. The inhibition rates of 1, 5, and 20 mg/kg·bw of LFCS were 25.8% (p < 0.05), 33.1% (p < 0.05), and 47.2% (p < 0.01), respectively.
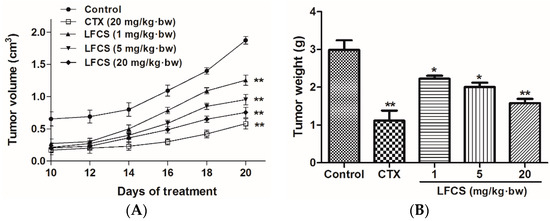
Figure 1.
Anti-tumor effects of LFCS on Lewis lung cancer in vivo. LFCS significantly reduced the tumor volume and weight in C57BL/6 mice. (A) Tumor growth curves and (B) weight of the tumors. Mean weights of the tumors are 2.99 g, 1.12 g, 2.23 g, 2.00 g and 1.58 g, for the control group, CTX group, 1 mg/kg·bw, 5 mg/kg·bw, and 20 mg/kg·bw LFCS group, respectively. Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 8). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, significant difference compared with control group (NS group).
2.2. LFCS Suppressed Lung Metastasis of LLC Cells In Vivo
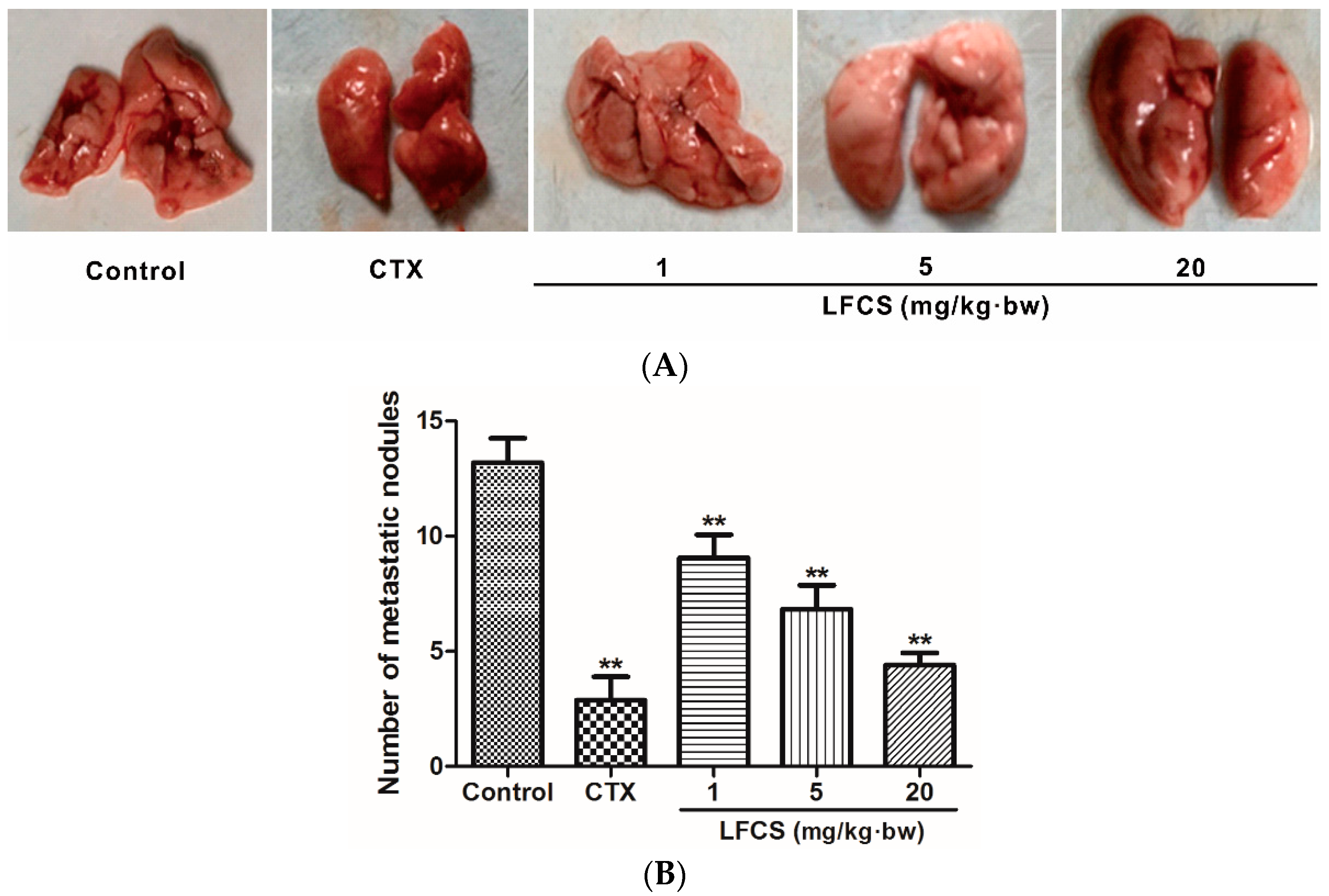
Cancer metastasis is the major cause of mortality in cancer patients. To investigate the anti-metastatic effect of LFCS on LLC cells in vivo, the tumor-bearing mice were euthanized, and the lungs excised and counted the metastatic nodules after LFCS treatment or not (Figure 2). Compared with the control group, LFCS significantly reduced the lung metastasis of LLC cells in dose-dependent manner (p < 0.01). The inhibition rates of 1, 5, and 20 mg/kg·bw of LFCS were 32.4%, 52.2%, and 69.1%, respectively.
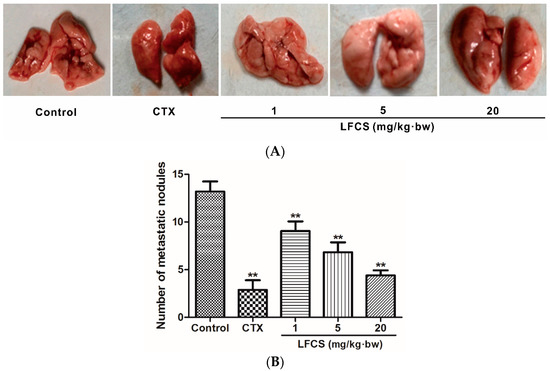
Figure 2.
LFCS suppressed lung metastasis of LLC cells in vivo. (A) Representative photos of lungs with the metastatic colonies after treatment with LFCS or not. Tumor-bearing mice were euthanized, and the lungs excised and counted the metastatic nodules (B) Lung metastatic nodules. Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 8). ** p < 0.01, significant difference compared with control group (NS group).
2.3. LFCS Inhibited LLC Cell Proliferation and Cell Migration
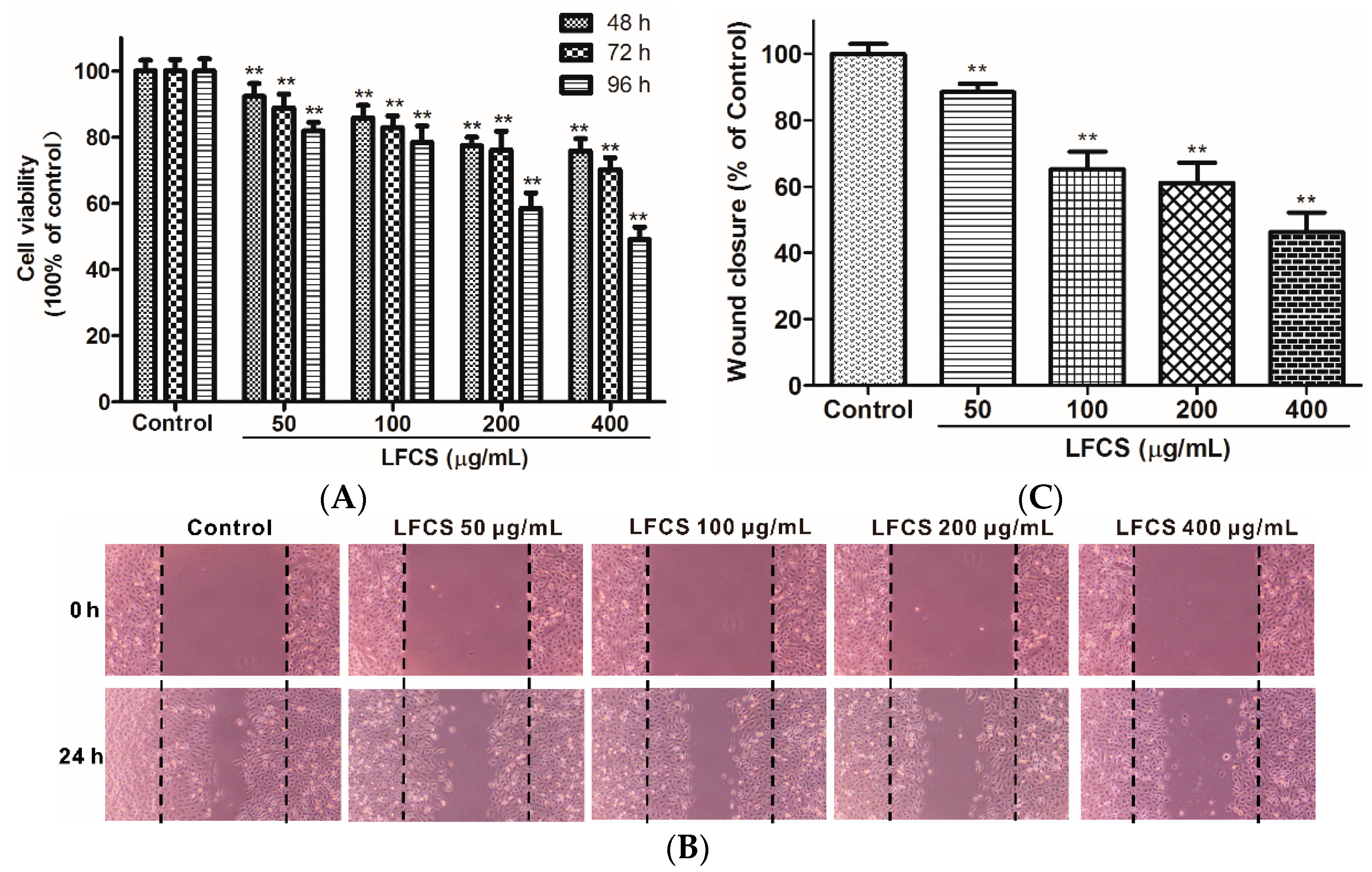
Clearly, the in vivo data described above demonstrated significant inhibitory effects of LFCS on tumor growth and metastasis. Since tumor cell proliferation and migration play critical roles in the process of tumor development [36,37], we then examined the effects of LFCS on LLC cell proliferation and migration by MTT assay and wound healing assay, respectively. For the MTT assay, LLC cells were incubated and treated with LFCS (50 μg/mL, 100 μg/mL, 200 μg/mL, and 400 μg/mL) for 48 h, 72 h, and 96 h. As shown in Figure 3A, LFCS decreased LLC cell viability in dose- and time-dependent manners (p < 0.01). After treatment for 96 h, 400 μg/mL LFCS decreased viable LLC cell number by 50.9% as compared with untreated control group. In the wound healing assay, the chemotactic motility of LLC cells were investigated after treatment with or without LFCS (50 μg/mL, 100 μg/mL, 200 μg/mL, and 400 μg/mL) for 24 h. As shown in Figure 3B, untreated cells migrated into the wounded area of the cell monolayer, whereas LFCS remarkably inhibited the LLC cells migration in a dose-dependent manner. The inhibition effects were measured to be 11.5%, 34.7%, 38.8%, and 53.7% for 50, 100, 200, and 400 μg/mL LFCS, respectively (Figure 3C).
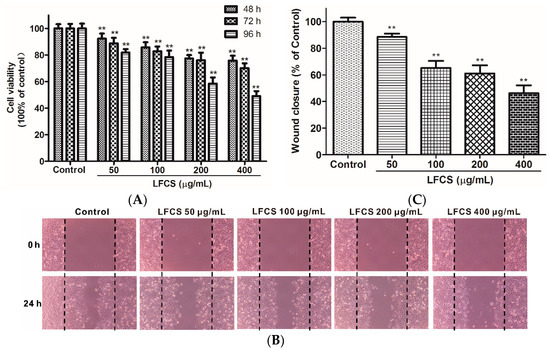
Figure 3.
LFCS inhibited LLC cell proliferation and cell migration. (A) Inhibitory effect of LFCS on LLC cell proliferation. LLC cells were treated with 50, 100, 200, and 400 μg/mL LFCS separately for 48 h, 72 h and 96 h and measured for viability by MTT assay. Values relative to that of control group (in which cell viability is set as 100%) were shown; (B) inhibitory effect of LFCS on LLC cell migration. Representative photos of wound closures after treatment with LFCS or not (40× magnification). Black dotted lines indicate the wound edge; and (C) quantification of the effect of LFCS on LLC cell migration in the wound healing assay. Wound closure relative to that of control group (in which wound closure is set as 100%) was determined. Data were derived from three independent experiments and presented as mean ± SD. ** p < 0.01, significant difference compared with control group.
2.4. LFCS Suppressed Proliferation and Migration of HUVEC
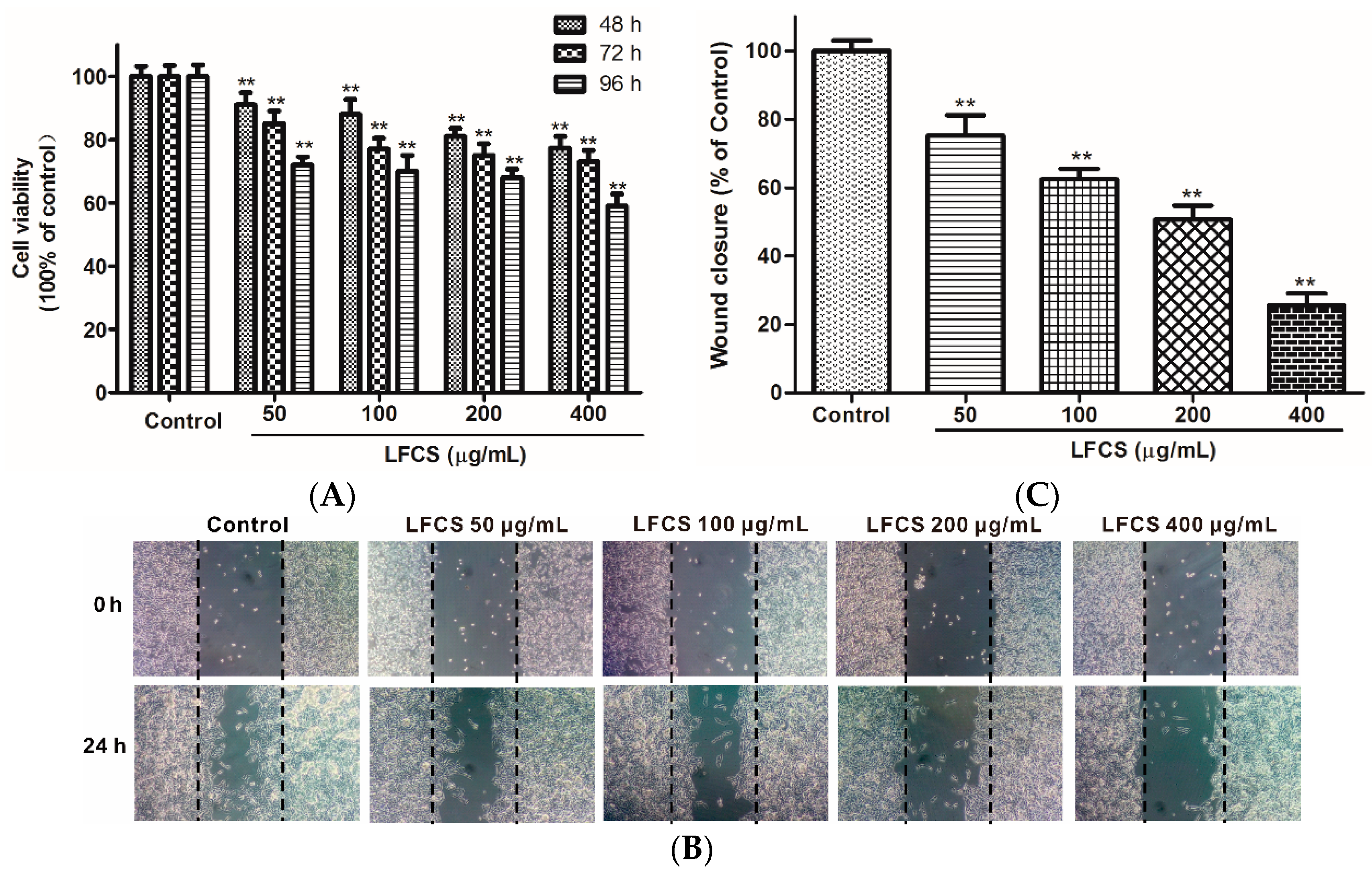
Angiogenesis plays an important role in the growth, progression, and metastasis of a tumor by providing oxygen and nutrients to the tumor cells and also removing waste products, whereas endothelial cell migration is essential for angiogenesis [38]. LFCS demonstrated significant anti-tumor efficacy in LLC-bearing mice, and we next examined whether LFCS could affect angiogenesis by investigating its effects on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) migration using wound healing assays. The chemotactic motility of HUVEC were investigated after treatment with or without LFCS (50 μg/mL, 100 μg/mL, 200 μg/mL, and 400 μg/mL) for 24 h. As shown in Figure 4A, cells in control group migrated into the wounded area of the cell monolayer, whereas HUVEC with LFCS treatment migrated remarkably slowly. It demonstrated that LFCS inhibited HUVEC migration in a dose-dependent manner by 24.8%, 37.5%, 49.3%, and 74.4% for 50, 100, 200, and 400 μg/mL LFCS, respectively (Figure 4B). Then, we determined the viability of HUVEC by a MTT assay to assess whether the inhibitory ability of LFCS on HUVEC migration was a result of the inhibition on HUVEC proliferation. HUVEC were treated with 50, 100, 200, and 400 μg/mL LFCS for 48 h, 72 h and 96 h separately. As shown in Figure 4C, LFCS reduced HUVEC viability in dose- and time-dependent manners (p < 0.01). After treatment for 96 h, 400 μg/mL LFCS decreased viable HUVEC number by 41.0% as compared with vehicle control. Thus, LFCS inhibited angiogenesis by suppressing migration and proliferation of endothelial cells.
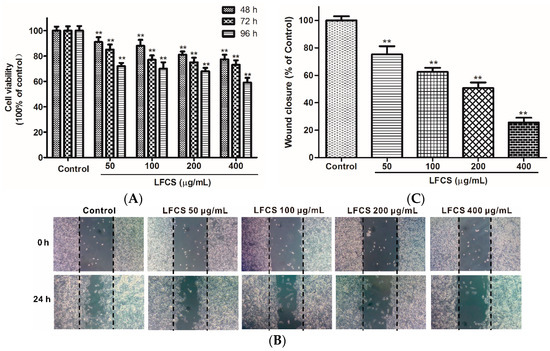
Figure 4.
LFCS suppressed proliferation and cell migration of HUVEC. (A) Inhibitory effect of LFCS on HUVEC proliferation. HUVEC were treated with 50, 100, 200, and 400 μg/mL LFCS separately for 48 h, 72 h, and 96 h and measured for viability by MTT assay. Values relative to that of control group (in which cell viability is set as 100%) were shown; (B) inhibitory effect of LFCS on HUVEC migration. Representative photos of wound closures after treatment with LFCS or not (10× magnification); and (C) quantification of the effect of LFCS on HUVEC migration. Wound closure relative to that of control group (in which wound closure is set as 100%). Data were derived from three independent experiments and presented as mean ± SD. ** p < 0.01, significant difference compared with control group.
2.5. LFCS Induced Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis by Uprgulating Protein Expression of p53, p21, and Caspase-3
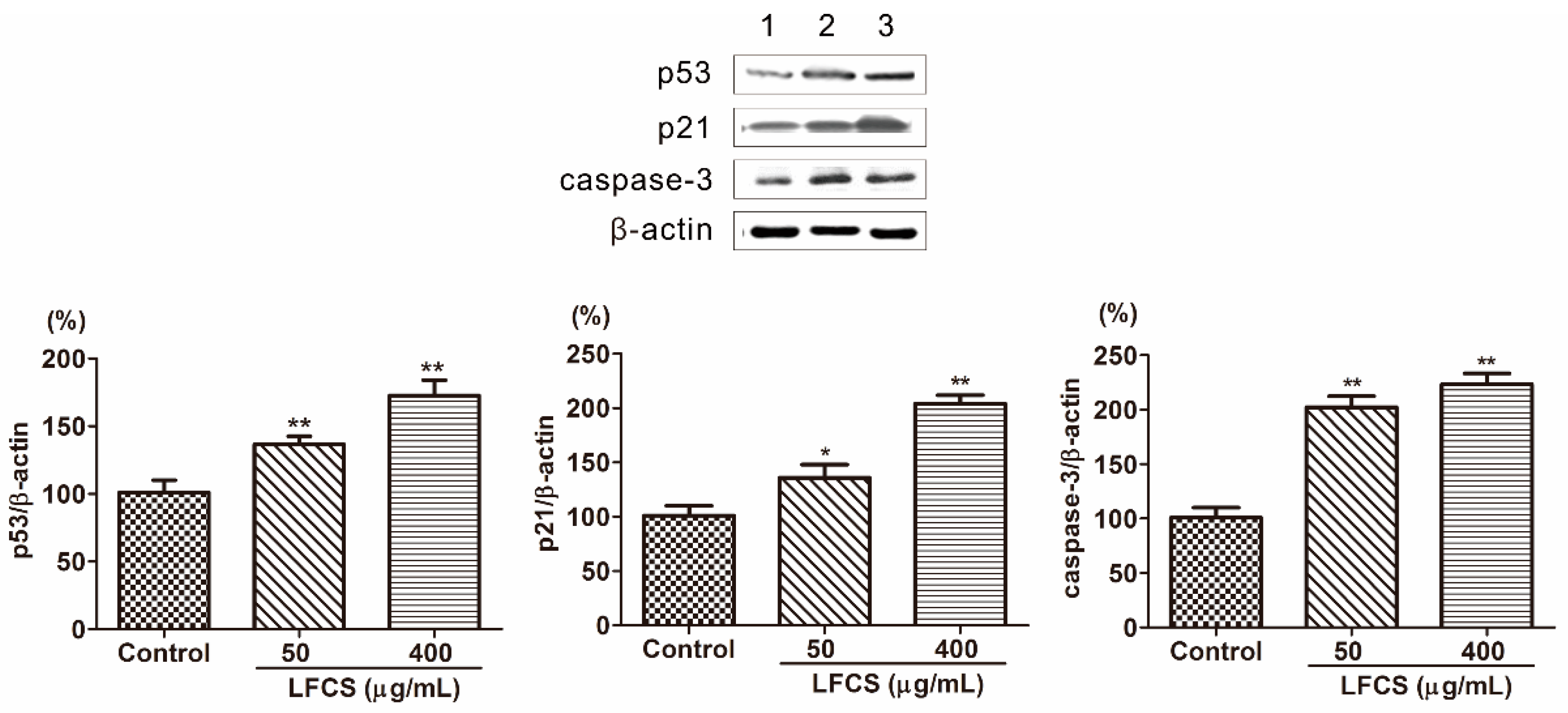
Tumor occurrence is a result of deviant of cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Tumors display six essential characteristics of self-sufficiency in growth signals, insensitivity to antigrowth signals, evasion of apoptosis, limitless replicative potential, sustained angiogenesis and tissue invasion, and metastasis [36,39]. To investigate the mechanism that LFCS inhibits tumor growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis, we examined protein expression in the molecular pathways induced by LFCS. p53 is a tumor suppressor transcription factor, and induces transcription of p21 and inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases by p21 resulting in cell cycle arrest [10,11,12]. As shown in Figure 5, the expression of p53 and p21 were significantly increased by LFCS (Figure 5). The result indicated that LFCS increased the expression of p53 to upregulate the expression of p21 resulting in cell cycle arrest. Apoptosis is a process of programmed cell death requiring activation of several signaling cascades. Caspases are essential mediators of apoptosis, and caspase-3 is crucial for cell death and some certain biochemical events associated with apoptosis [14,15]. After LFCS treatment, the level of caspase-3 increased (Figure 5) and demonstrated that LFCS induced a caspase-3-dependent apoptotic pathway in LLC cells consistent with effect of fucoidan on breast cancer [40].
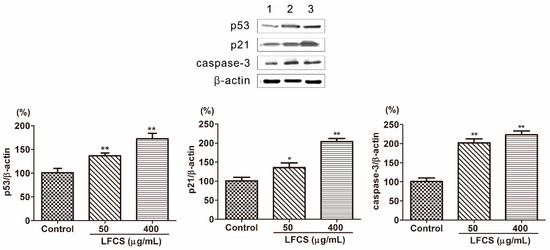
Figure 5.
LFCS increased protein expression of p53, p21, and caspase-3 in LLC cells after 72 h treatment of LFCS detected by Western blot. Expression of the β-actin was used as internal control. Lane 1: vehicle-treated cells; Lane 2: 50 μg/mL LFCS-treated cells; Lane 3: 400 μg/mL LFCS-treated cells. Data were presented as mean ± SD and derived from one representative experiment performed in triplicate. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, significant difference compared with control group.
2.6. LFCS Suppressed Metastasis and Angiogenesis by Regulating Protein Expression of MMP-9, TIMP-1, VEGF, p38, ERK1/2, and NF-κB
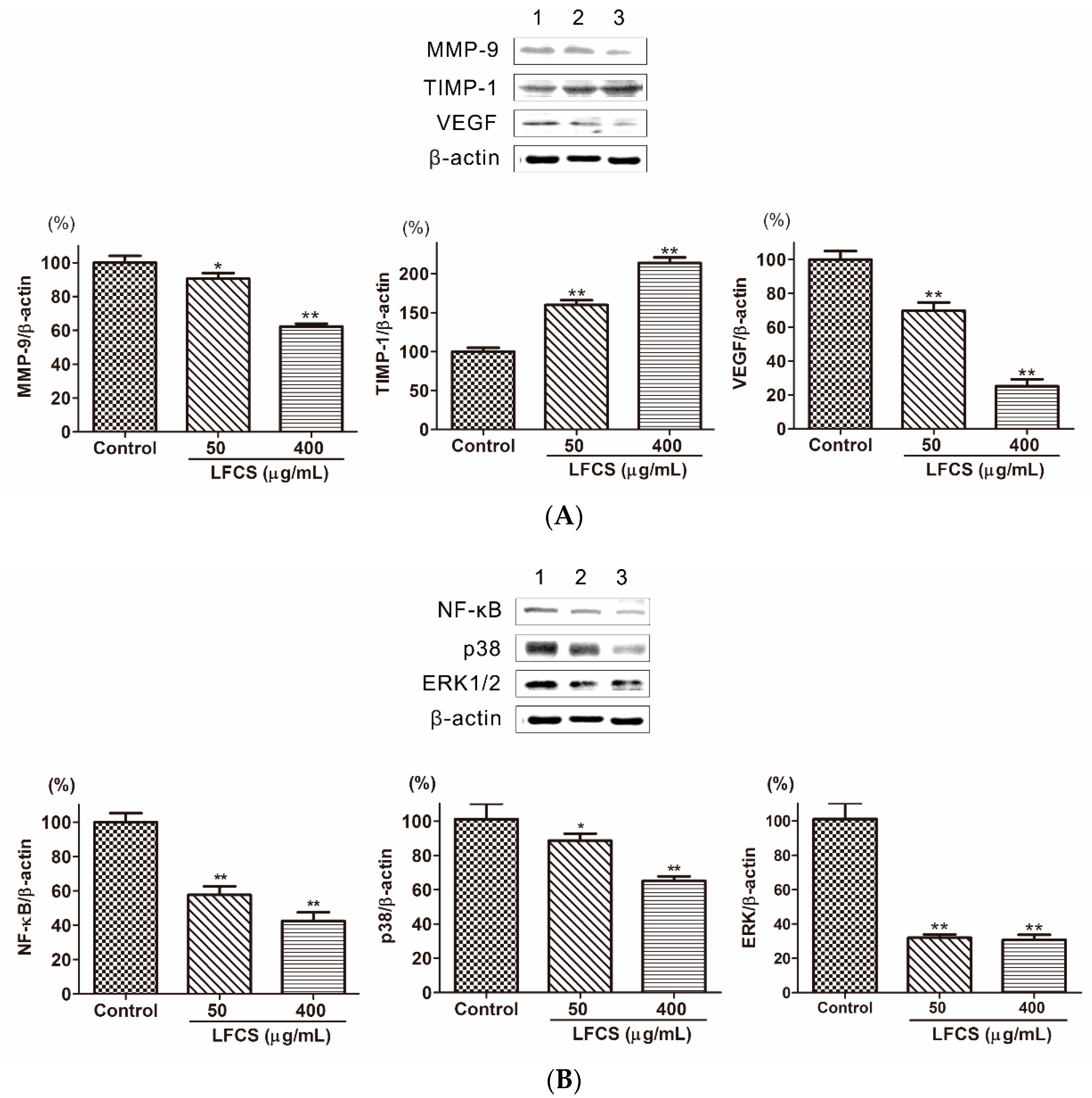
Cancer metastasis is a multi-step process regulated by a complex signaling network [8]. In order to invade into the surrounding stroma, tumor cells need to breach the basement membrane barrier by secreting proteinases to degrade the extracellular matrix (ECM). Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are the most important degrading enzymes [17]. MMP-9 is an important gelatinase to degrade ECM components especially Type IV collagen which is the major component of the basement membrane. As shown in Figure 6A, the level of MMP-9 was decreased in LLC cells treated with LFCS. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) is the natural inhibitor of MMP-9, and it can suppress MMP-9 to inhibit tumor cell invasion and migration [18]. Then we determined the protein level of TIMP-1 by Western blot to assess whether the inhibitory ability of LFCS on MMP-9 protein expression was a result of the inhibition on TIMP-1. The result showed that LFCS up-regulated TIMP-1 level in LLC cells (Figure 6A). Thus LFCS inhibited degradation effect of MMP-9 by directly decreasing expression of MMP-9 and indirectly increasing level of TIMP-1. Angiogenesis plays a critical role in tumor growth and metastasis. The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is one of representative proangiogenic factors and promotes vascular endothelial growth and mitosis to form vascular plexus [41]. To investigate whether LFCS suppresses the expression of VEGF to inhibit angiogenesis, we examined the VEGF expression in LLC cells after treatment with LFCS. As shown in Figure 6A, the level of VEGF increased. The result demonstrated that LFCS inhibited tumor metastasis by increasing TIMP-1 and decreasing MMP-9 expression, and suppressing VEGF to inhibit angiogenesis.
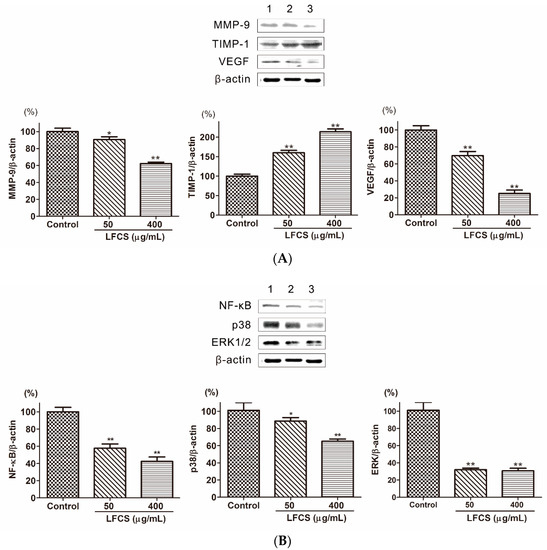
Figure 6.
LFCS suppressed metastasis and angiogenesis by regulating protein expression of MMP-9, TIMP-1, VEGF, p38, ERK1/2, and NF-κB in LLC cells after 72 h treatment of LFCS detected by Western blot. (A) LFCS increased TIMP-1, and decreased MMP-9 and VEGF expression; (B) LFCS suppressed NF-κB, p38 and ERK1/2 expression. Expression of the β-actin was used as internal control. Lane 1: vehicle-treated cells; Lane 2: 50 μg/mL LFCS-treated cells; Lane 3: 400 μg/mL LFCS-treated cells. Data were presented as mean ± SD and derived from one representative experiment performed in triplicate. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, significant difference compared with control group.
Tumor metastasis is a complex multistep process modulated by signaling pathways. The nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) is highly activated in diverse cancers and plays a critical role in tumor cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and metastasis, resulting in aggressiveness of tumors [42]. NF-κB can induce transcription, expression, and secretion of MMPs [22,23,24], and this progress is regulated by mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPKs) [25,26]. Three distinct MAPKs family members, including extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 (ERK1/2), c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase (JNK/SAPK), and p38, play major roles in tumor progression and metastasis by inducing proteolytic enzymes that degrade the basement membrane, enhances cell migration [27,28]. The expression and secretion of MMP-9 protein were induced through the activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathways [24]. To elucidate whether LFCS regulates these signaling pathways in LLC cells, we examined the expression of NF-κB, p38 and ERK1/2 in LLC cells after treatment with LFCS. As shown in Figure 6B, the level of NF-κB, p38 and ERK1/2 were decreased by LFCS. The result demonstrated that LFCS inhibited tumor metastasis by activated MAPKs (p38 and ERK1/2)/NF-κB pathway.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
The low-molecular-weight fucosylated chondroitin sulfate (LFCS) was a depolymerized fragment of native fucosylated chondroitin sulfate (FCS), which was isolated from the body walls of the sea cucumbers C. frondosa purchased in the Nanshan market of Qingdao City, China. LFCS contained GlcA, GalN, Fuc, and sulfate in molar ratios of 1.0:1.0:1.1:3.2 with a molecular weight of 12.0 kDa. LFCS mainly composed of a chondroitin sulfate-like backbone of →4GlcAβ1→3GalNAc6Sβ1→ with sulfated α-Fuc branches linked to the O-3 position of GlcA residues was characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analysis (Figure S1). Normal salt (NS) was purchased from Cisen Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Jining, Shandong, China). Cyclophosphamide for injection (CTX) was purchased from Hengrui Medicine Co., Ltd. (Lianyungang, Jiangsu, China). 5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Anti-p53, p21, caspase-3, MMP-9, TIMP-1, VEGF, p38, ERK1/2, NF-κB, and β-actin antibodies were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). All other chemicals and solvents used were of analytical grade unless otherwise specified.
3.2. Cells and Cell Culture
Lewis lung carcinoma cells (LLC) and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were purchased from the Cell Bank of the Type Culture Collection Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Shanghai, China. These cells were maintained in DMEM culture medium (Gino Biological Medicine Technology Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (v/v), 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin, and cultured in an incubator at 37 °C under a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2.
3.3. Animals and Ethical Approval
Male C57BL/6 mice (6–8 weeks old) were purchased from Experimental Animals and Animal Experiments Center (Qingdao, China). The animals were maintained in a climate controlled room (12:12 dark-light cycle with a constant room temperature of 21 ± 1 °C) and fed standard rodent chow and water ad libitum. Mice were acclimatized for at least one week. All experiments were performed in accordance to internationally-accepted guidelines on laboratory animal use.
3.4. In Vivo LLC Cells Metastasis Model
To study the antitumor activity of LFCS in vivo, approximately 2 × 106 log growth-phase LLC cells in 0.2 mL NS were injected through subcutaneous injection to the right armpit of male C57BL/6 mice on day one. One day after the tumor cell inoculation, a volume of 0.2 mL of NS (as blank control), CTX (20 mg/kg, as a positive reference) and LFCS (1, 5 and 20 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to the mice (n = 8) once a day for 20 days, respectively. After 10 days, tumors were visible at the inoculated sites, and their sizes were measured in two perpendicular dimensions (a = length, b = width) with a vernier caliper and recorded as a volume (cm3) as calculated by a × b2/2 every two days. Then a tumor growth curve was constructed. After 20 days of treatment, the mice were euthanized, and the lungs and tumors were excised and weighted. The number of lung metastatic foci was counted.
3.5. Cell Proliferation Assays
Cell proliferation was measured by using the MTT assay based on the ability of viable cells to change from soluble yellow tetrazolium salt to blue formazan crystals. Briefly, LLC cells/HUVECs (1 × 104 cells/mL) were seeded in 96-well plates and treated with or without LFCS (50 μg/mL, 100 μg/mL, 200 μg/mL, and 400 μg/mL). After 48 h, 72 h and 96 h, the cells were treated with 20 μL MTT (5 mg/mL) and re-incubated for 4 h. After removal of the supernatant, 150 μL of DMSO was added to dissolve the blue crystals. The absorbance was recorded at 490 nm by a Bio-Tek Elx 808 microplate reader (BioTek China Shanghai Office, Shanghai, China).
3.6. Cell Migration Assays
Cell migration was determined using the wound healing assays. Briefly, LLC cells/HUVECs (1 × 105 cells/well) were seeded in 24-well plates and grown as monolayer cells at 90%–95% confluence. Then the monolayer was carefully wounded by sterile pipette tips (t = 0 h). After removal of the detached cells, the cells were treated with or without LFCS (50 μg/mL, 100 μg/mL, 200 μg/mL and 400 μg/mL) for 24 h and photographed by a microscope (Olympus, CKX41, Tokyo, Japan) immediately (t = 24 h).
3.7. Western Blot Analysis
LLC cells were seeded in six-well plates and treated with LFCS (50 μg/mL and 400 μg/mL) for 72 h. After removal of the supernatant, the cells were washed twice with ice-cold PBS and lysed in 50 μL RIPA lysis buffer (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, Beijing, China) on ice for 30 min with sonication for 10 s every 10 min. Protein concentrations were measured using a BCA protein assay kit (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, Beijing, China). Equal amounts of protein were fractionated by SDS-PAGE and then transferred to PVDF membranes. After blocking with 5% non-fat milk in TBST buffer for 1 h, the membranes were incubated with various primary antibodies against p53, p21, caspase-3, MMP-1, TIMP-1, VEGF, p38, ERK1/2, NF-κB, and β-actin at 4 °C overnight. After washing, the membranes were incubated with alkaline phosphatase-labeled secondary antibodies (Boster, Wuhan, China) for 2 h. The proteins were then detected using a BCIP/NBT Alkaline Phosphatase Color Development Kit (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, Beijing, China).
3.8. Statistical Analysis
Results were expressed as mean ± SD. Data were analyzed by ANOVA and statistical significance was considered at p < 0.05 in all cases.
4. Conclusions
In this study, LFCS was demonstrated to have remarkable inhibition on Lewis lung carcinoma growth and metastasis in a dose-dependent manner in vivo. The anticancer activity was related to p53/p21-induced cell cycle arrest, caspase-3-induced apoptosis, VEGF-mediated angiogenesis, and TIMP/MMPs-mediated metastasis by the ERK1/2/p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Our studies suggest that LFCS may be an anti-tumor drug candidate that deserves further research.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials can be accessed at: http://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/21/5/625/s1.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by NSFC-Shandong Joint Fund for Marine Science Research Centers (U1406402), National Science & Technology Support Program of China (2013BAB01B02), Major Science and Technology Projects of Shandong Province (2015ZDJS04002), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, and Taishan Scholars Project Special Funds (G. Yu).
Author Contributions
Xiaoxiao Liu, Lijuan Zhang and Guangli Yu conceived and designed the experiments. Xiaoxiao Liu performed the extraction, structural analysis and bioactivity experiments and drafted the manuscript. Yong Liu, Jiejie Hao, Fei Fan and Yinzhi Lang participated in the bioactivity experiments. Xiaoliang Zhao, Chao Cai and Guoyun Li participated in writing the paper. Guangli Yu comprehensively revised the manuscript and approved the final version for submission to the target journal.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Stewart, W.B.; Wild, P.C. World Cancer Report 2014; International Agency for Research on Cancer, WHO Press: Lyon, France, 2014; ISBN 9789283204329. [Google Scholar]
- Travis, W.D.; Elisabeth, B.; Nicholson, A.G.; Yasushi, Y.; Austin, J.H.M.; Mary Beth, B.; Chirieac, L.R.; Sanja, D.; Edwina, D.; Flieder, D.B. The 2015 world health organization classification of lung tumors: Impact of genetic, clinical and radiologic advances since the 2004 classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Gómez, M.; Malmierca, E.; de Górgolas, M.; Casado, E. Cancer in developing countries: The next most preventable pandemic. The global problem of cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2013, 88, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, J.E.; Cascone, T.; Gerber, D.E.; Heymach, J.V.; Minna, J.D. Targeted therapies for lung cancer. Cancer J. 2011, 17, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, I.; Planchard, D. ALK inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: The latest evidence and developments. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2016, 8, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meoni, G.; Cecere, F.L.; Lucherini, E.; di Costanzo, F. Medical treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer in elderly patients: A review of the role of chemotherapy and targeted agents. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2013, 4, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valastyan, S.; Weinberg, R.A. Tumor metastasis: Molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell 2011, 147, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaffer, C.L.; Weinberg, R.A. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science 2011, 331, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millau, J.F.; Bastien, N.; Drouin, R. P53 transcriptional activities: A general overview and some thoughts. Mutat. Res. 2009, 681, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, R.A.; Mclure, K.G.; Lees-Miller, S.P.; Rancourt, D.E.; Lee, P.W. DNA-dependent protein kinase acts upstream of p53 in response to DNA damage. Nature 1998, 394, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Hannon, G.J.; Zhang, H.; Casso, D.; Kobayashi, R.; Beach, D. p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature 1993, 366, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhiyong, R.E.H.; Wei, W.; Stephen, D.; Jamesw, D.; Paul, C.; John, S.; Erica, H.; Kannanv, B.; Panayotis, P.; Jamesh, W. Role of p21 in apoptosis and senescence of human colon cancer cells treated with camptothecin. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 17154–17160. [Google Scholar]
- Stennicke, H.R.; Salvesen, G.S. Properties of the caspases. Cell Death Differ. 1999, 6, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, G. Caspases: The executioners of apoptosis. Biochem. J. 1997, 326, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.M.; Chen, G.C.; Lin, J.G.; Yeh, C.C.; Cheng, K.C.; Chung, J.G. Ellagic acid induced p53/p21 expression, G1 arrest and apoptosis in human bladder cancer T24 cells. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stamenkovic, I. Matrix metalloproteinases in tumor invasion and metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2001, 10, 415–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Ding, X.; Yang, F.; Xu, X. Prognostic significance of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 serum and tissue expression in breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 2050–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D Amore, P.A. Vascular endothelial cell growth factor-A. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaranta, M.; Daniele, A.; Coviello, M.; Venneri, M.T.; Abbate, I.; Caringella, M.E.; Di, T.S.; Divella, R.; Trerotoli, P.; Di, G.M. MMP-2, MMP-9, VEGF and CA 15.3 in breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 3593–3600. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.H.; Chiu, Y.H.; Chan, Y.L.; Chiu, Y.H.; Wang, H.; Huang, K.C.; Li, T.L.; Hsu, K.H.; Wu, C.J. Prophylactic administration of fucoidan represses cancer metastasis by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in Lewis tumor-bearing mice. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1882–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, H.S.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, E. Piceatannol suppresses breast cancer cell invasion through the inhibition of MMP-9: Involvement of PI3K/AKT and NF-κB pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 4083–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Pina, V.; Martinez, E.; Fernandez-Ruiz, I.; Del, F.C.; Soares-Schanoski, A.; Jurado, T.; Siliceo, M.; Toledano, V.; Fernandez-Palomares, R.; Garcia-Rio, F.; et al. Role of MMPs in orchestrating inflammatory response in human monocytes via a TREM-1-PI3K-NF-κB pathway. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 91, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Tsai, C. CCL2 increases MMP-9 expression and cell motility in human chondrosarcoma cells via the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biochem. Pharmcol. 2012, 83, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.J.; Huang, S.S.; Deng, J.S. Anti-inflammatory activities of inotilone from Phellinus linteus through the inhibition of MMP-9, NF-κB, and MAPK activation in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babykutty, S.; Priya, P.S.; Nandini, R.J.; Kumar, M.A.S.; Nair, M.S.; Srinivas, P.; Gopala, S. Nimbolide retards tumor cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis by downregulating MMP-2/9 expression via inhibiting ERK1/2 and reducing DNA-binding activity of NF-κB in colon cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2012, 51, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al, S.S.; Sharaf, L.H.; Luqmani, Y.A. Signalling pathways involved in endocrine resistance in breast cancer and associations with epithelial to mesenchymal transition (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 38, 1197–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, K.B.; Nabha, S.M.; Atanaskova, N. Role of MAP kinase in tumor progression and invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Lv, Z. Novel branch patterns and anticoagulant activity of glycosaminoglycan from sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Wen, D.; Gao, N.; Xiao, C.; Yang, L.; Xu, L.; Lian, W.; Peng, W.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, J. Anticoagulant and antithrombotic evaluation of native fucosylated chondroitin sulfates and their derivatives as selective inhibitors of intrinsic factor Xase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 92, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, W.; Wu, M.; Huang, N.; Gao, N.; Xiao, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Peng, W.; Zhao, J. Anti-HIV-1 activity and structure-activity-relationship study of a fucosylated glycosaminoglycan from an echinoderm by targeting the conserved CD4 induced epitope. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 4681–4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Tao, L.; Wang, A.; Chen, W.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, S.; Gao, X.; Lu, Y. Holothurian glycosaminoglycan inhibits metastasis and thrombosis via targeting of nuclear factor-κB/tissue factor/Factor Xa pathway in melanoma B16F10 cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsig, L.; Wang, L.; Cavalcante, M.C.; Cardilo-Reis, L.; Ferreira, P.L.; Mourao, P.A.; Esko, J.D.; Pavao, M.S. Selectin blocking activity of a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycan from sea cucumber. Effect on tumor metastasis and neutrophil recruitment. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 14984–14991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Z.; Lian, E.C. Aggregation of human platelets by acidic mucopolysaccharide extracted from Stichopus japonicus Selenka. Thromb. Haemost. 1988, 59, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kitazato, K.; Kitazato, K.T.; Nagase, H.; Minamiguchi, K. DHG, a new depolymerized holothurian glycosaminoglycan, exerts an antithrombotic effect with less bleeding than unfractionated or low molecular weight heparin, in rats. Thromb. Res. 1996, 84, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Seedi, H.R.; Burman, R.; Mansour, A.; Turki, Z.; Boulos, L.; Gullbo, J.; Göransson, U. The traditional medical uses and cytotoxic activities of sixty-one Egyptian plants: Discovery of an active cardiac glycoside from Urginea maritima. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 145, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makrilia, N.; Lappa, T.; Xyla, V.; Nikolaidis, I.; Syrigos, K. The role of angiogenesis in solid tumours: An overview. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2009, 20, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Hou, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, Q. Anticancer properties and mechanisms of fucoidan on mouse breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimberger, P.; Chebouti, I.; Kasimir-Bauer, S.; Lachmann, R.; Kuhlisch, E.; Kimmig, R.; Süleyman, E.; Kuhlmann, J.D. Explorative investigation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor expression in primary ovarian cancer and its clinical relevance. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 133, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeel, Z.; Marianne, F. Role of nuclear factor-κB in breast and colorectal cancer. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2013, 13, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).