20(S)-Protopanaxadiol Phospholipid Complex: Process Optimization, Characterization, In Vitro Dissolution and Molecular Docking Studies
Abstract
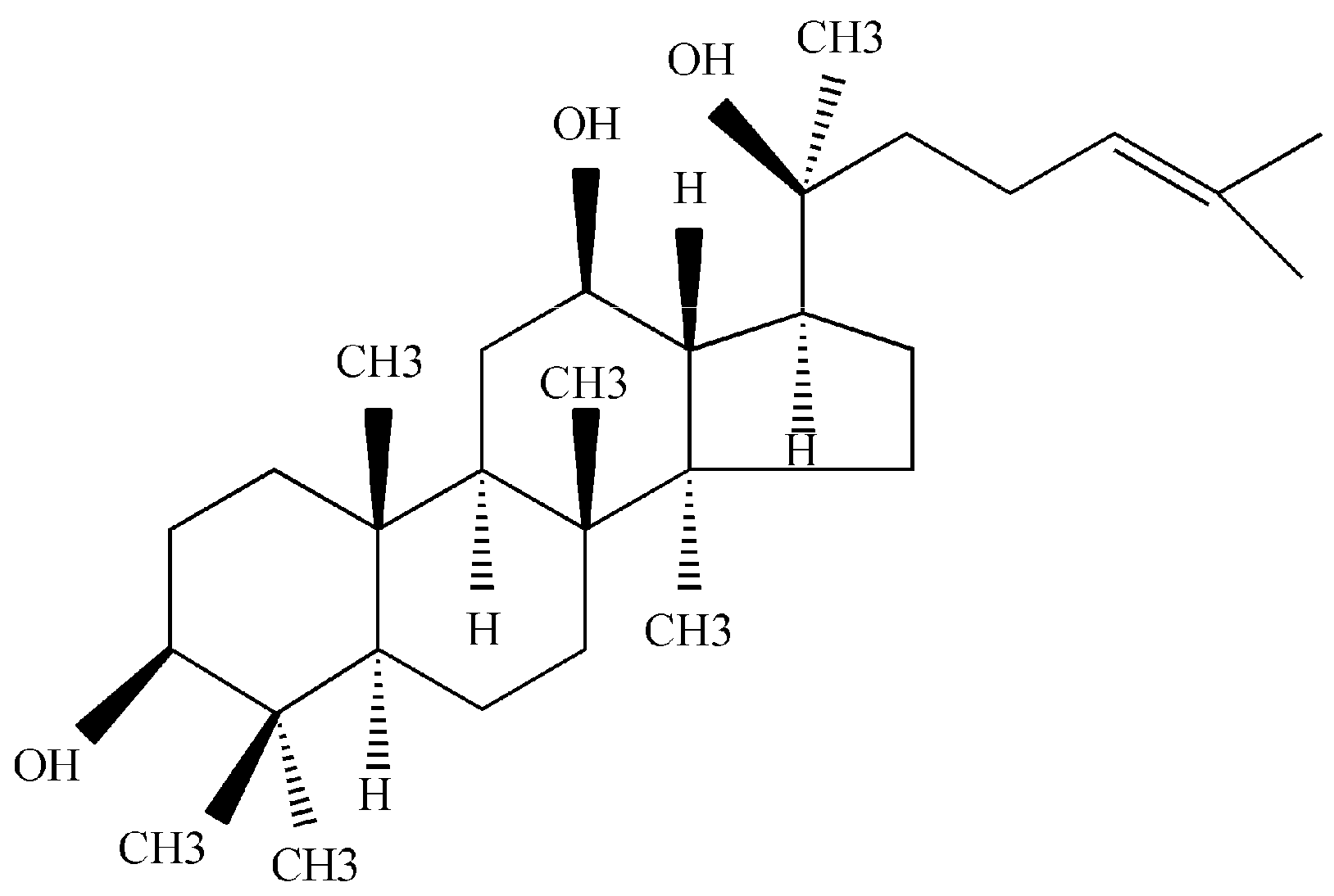
:1. Introduction
2. Results
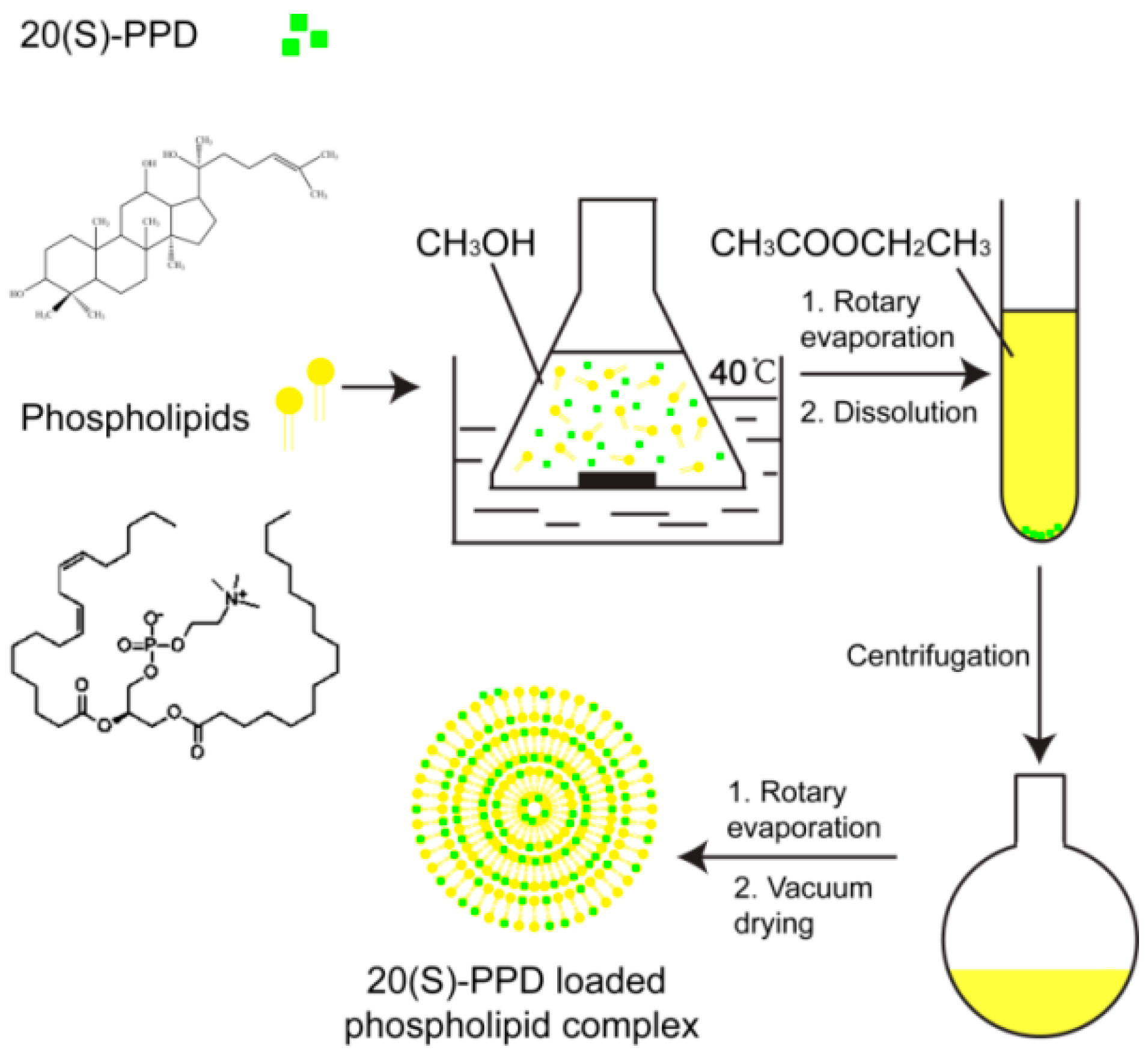
2.1. PPD-PLC Preparation
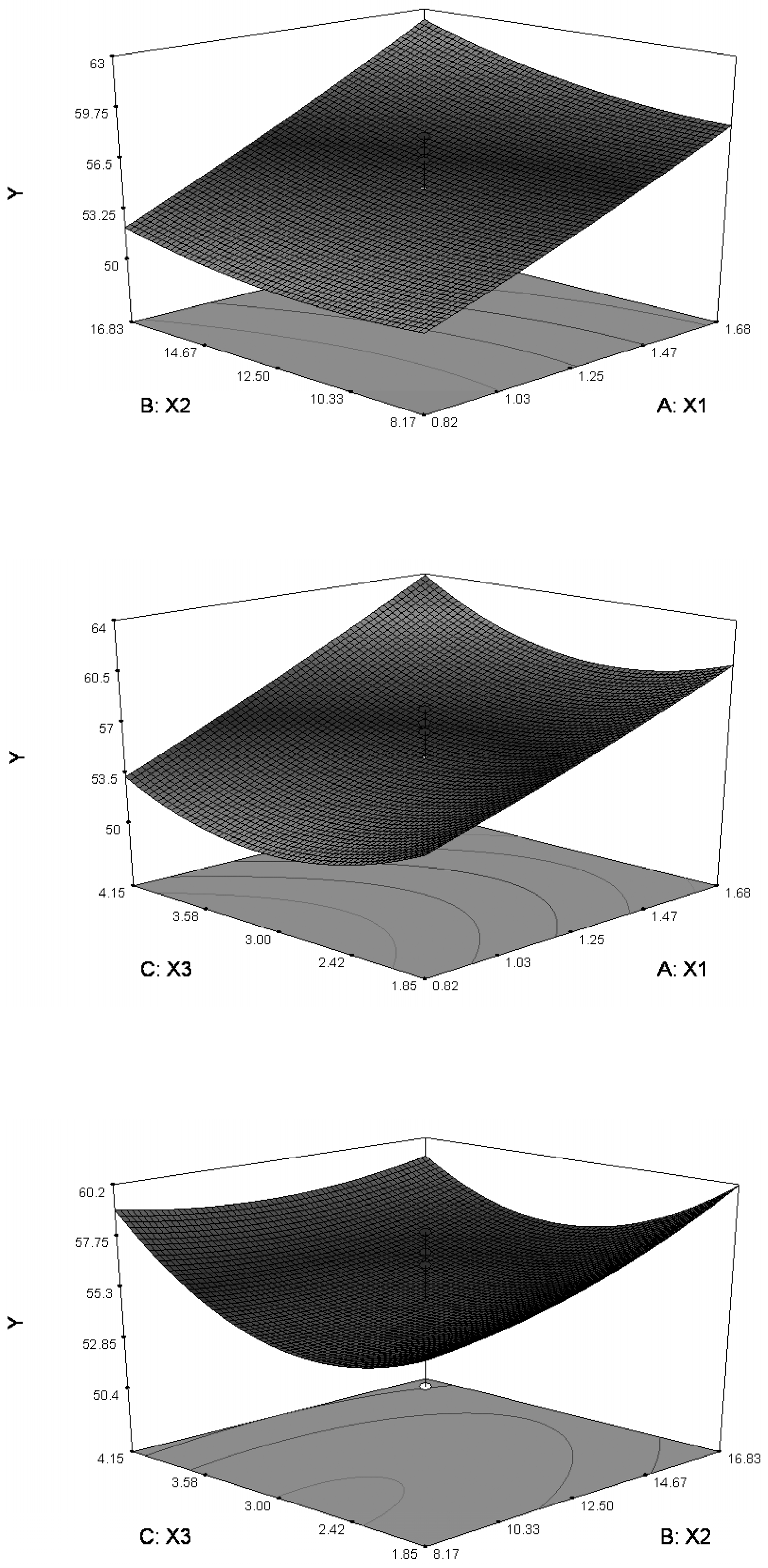
2.1.1. Response Surface Analysis
2.1.2. Validation of Model Optimization
2.1.3. Method Validation of Content Determination
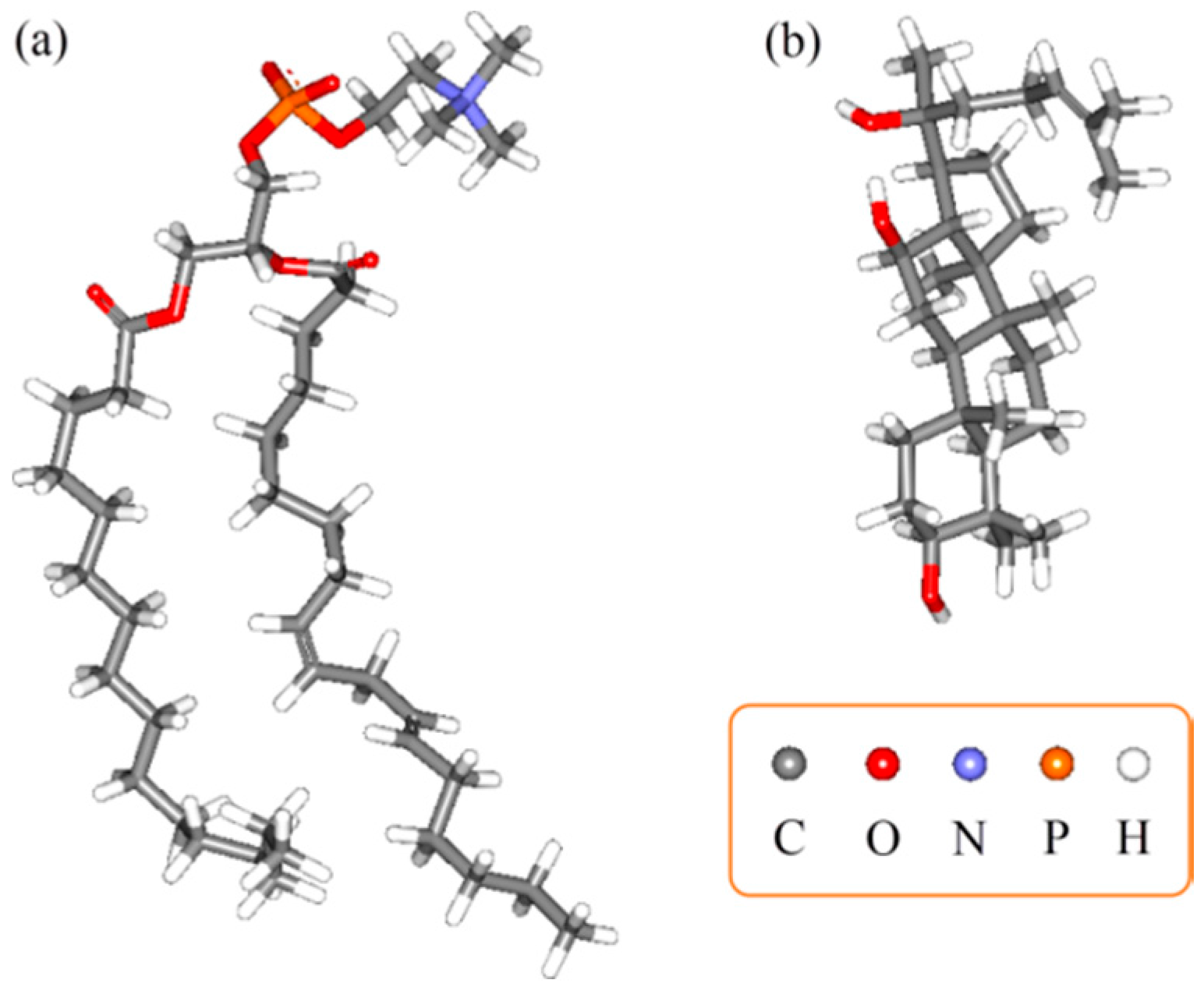
2.2. Physiochemical Characterization of PPD-PLC
2.2.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
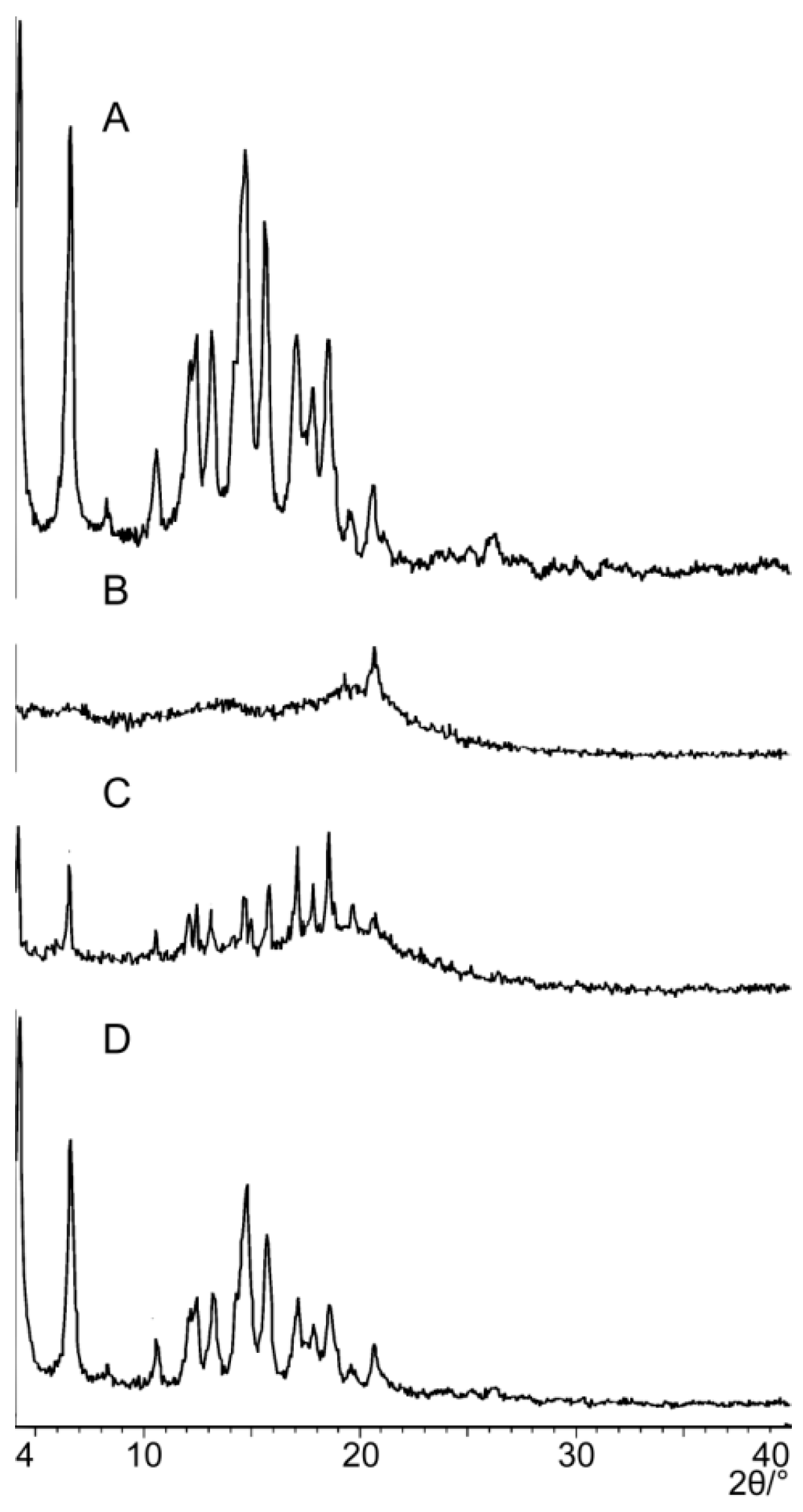
2.2.2. Powder X-ray Diffraction
2.2.3. Fourier-Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy
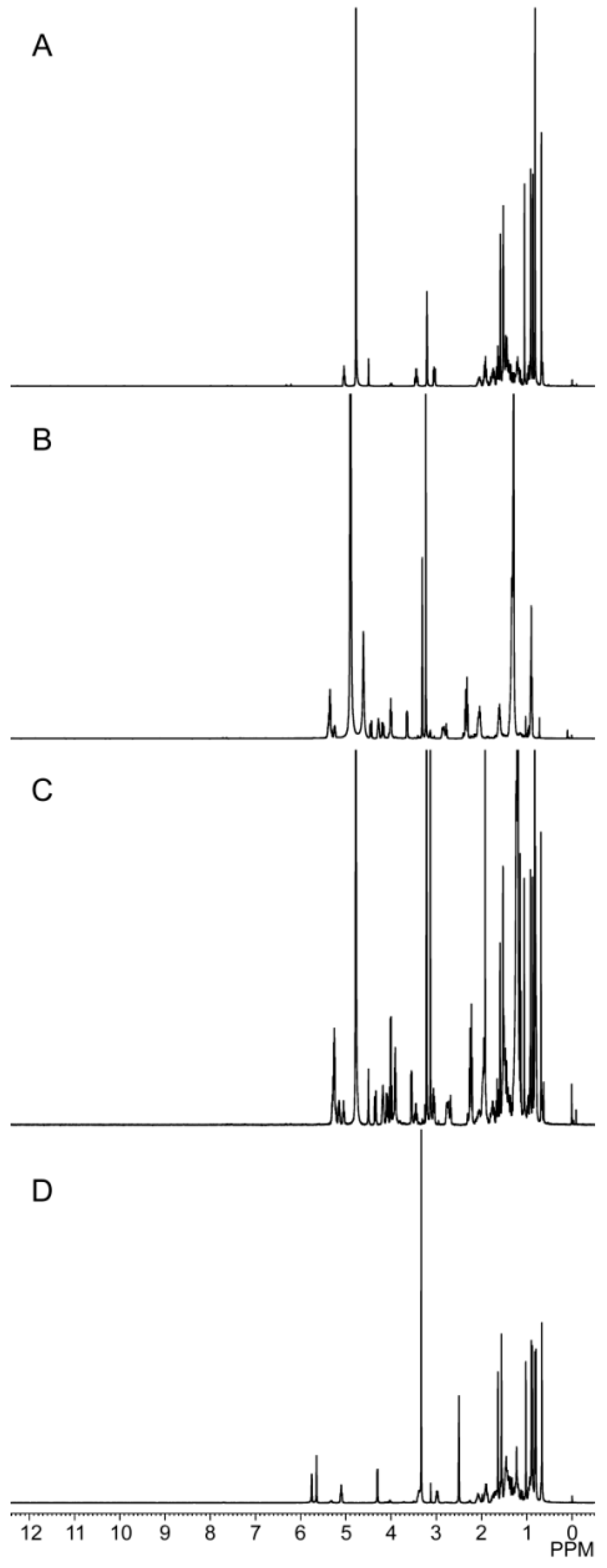
2.2.4. 1H-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
2.3. Molecular Docking
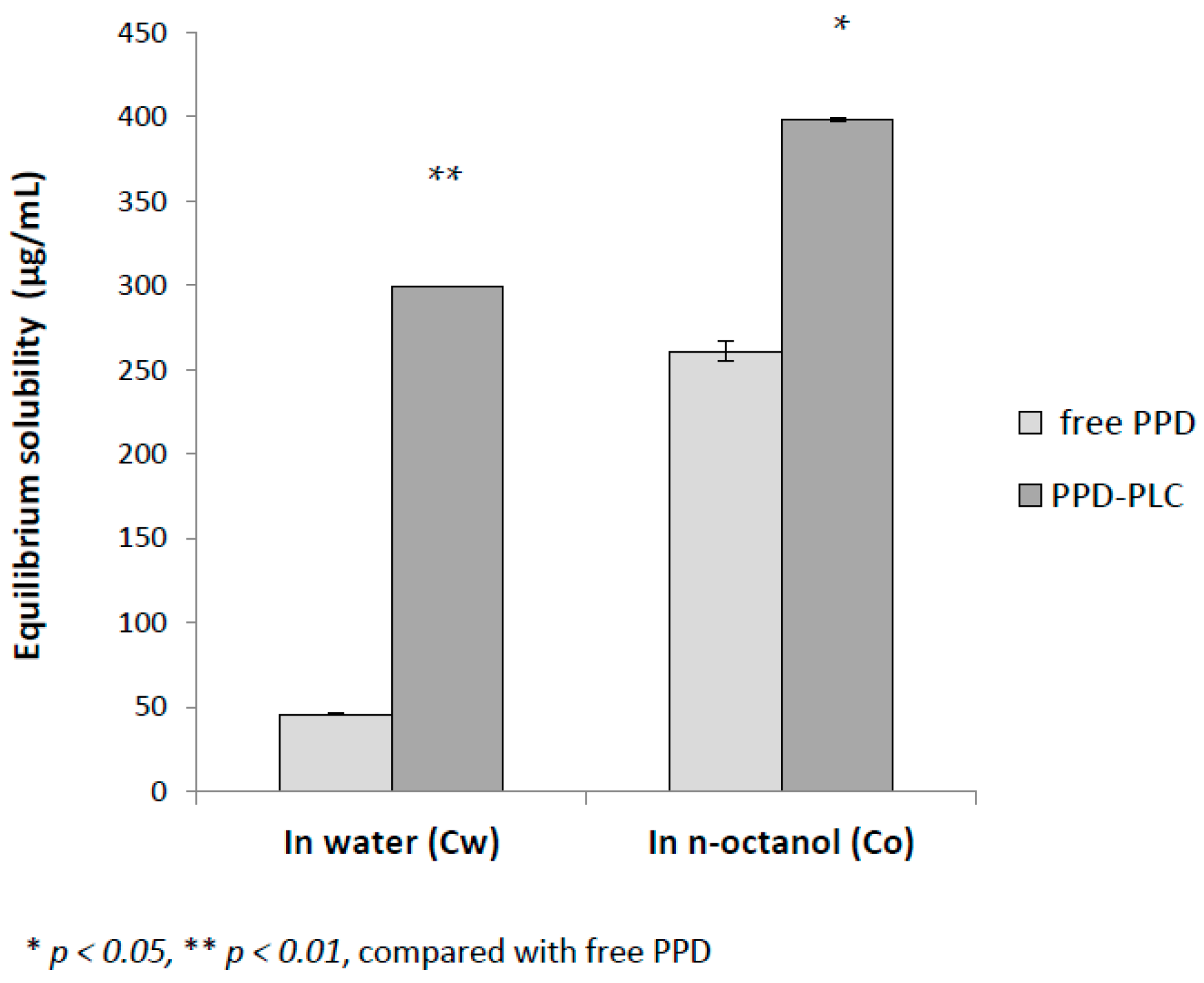
2.4. Equilibrium Solubility Studies
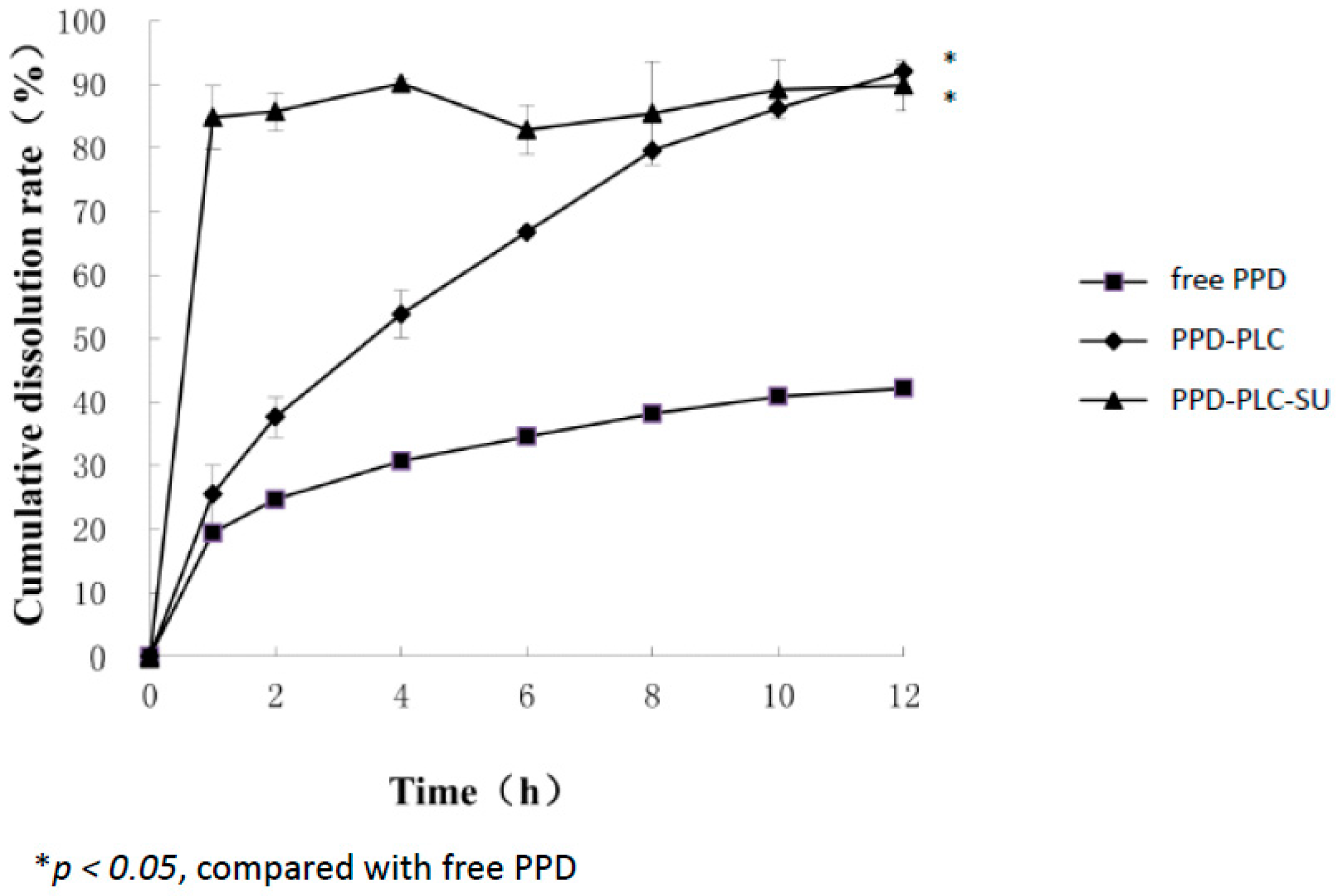
2.5. In Vitro Dissolution Studies
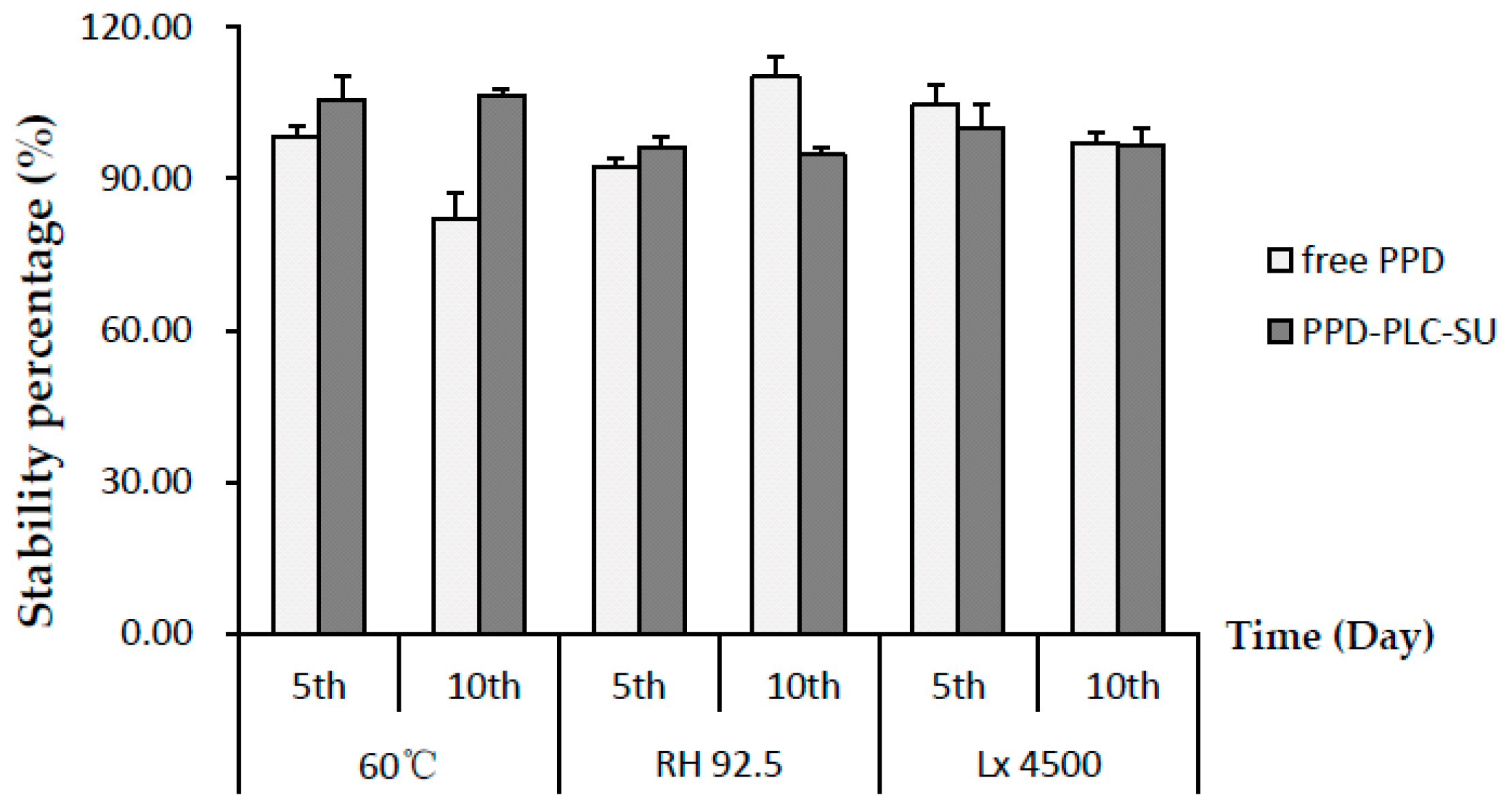
2.6. Stability Investigation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. PPD-PLC Preparation
4.2.1. Process Optimization of PPD-PLC
4.2.2. Validation of Model Optimization
4.2.3. Determination of Entrapment Efficiency
4.2.4. Determination of DL
4.2.5. Method Validation of Content Determination
4.3. Physiochemical Characterization of PPD-PLC
4.3.1. DSC
4.3.2. PXRD
4.3.3. FTIR
4.3.4. 1H-NMR
4.4. Molecular Docking
4.5. Equilibrium Solubility Studies
4.6. PPD-PLC-SU Preparation
4.7. In Vitro Dissolution Studies
4.8. Stability Investigations
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.H.; Ahn, J.Y.; Shin, T.J.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, B.H.; Hwang, S.H.; Kang, J.; Kim, H.J.; Park, C.W.; Nah, S.Y. Effects of Minor Ginsenosides, Ginsenoside Metabolites, and Ginsenoside Epimers on the Growth of Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Ginseng Res. 2011, 35, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.C.; Lee, H.J.; Oh, D.K. Substrate specificity of beta-glucosidase from Gordonia terrae for ginsenosides and its application in the production of ginsenosides Rg3, Rg2, and Rh1 from ginseng root extract. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 119, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Rayburn, E.R.; Hill, D.L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R. In vitro anti-cancer activity and structure-activity relationships of natural products isolated from fruits of Panax ginseng. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabavi, S.F.; Sureda, A.; Habtemariam, S.; Nabavi, S.M. Ginsenoside Rd and ischemic stroke; a short review of literatures. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Yu, X.; Qu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sui, D. In vivo and in vitro cardioprotective effects of Panax quinquefolium 20(S)-protopanaxadiol saponins (PQDS), isolated from Panax quinquefolium. Die Pharm. 2013, 68, 287–292. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Yu, X.; Qu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sui, D. Protective effect of Panax quinquefolium 20(S)-protopanaxadiol saponins, isolated from Panax quinquefolium, on permanent focal cerebral ischemic injury in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 7, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, C.; Lu, M.; Sun, F.; Fu, Y.; Jin, F. Purification and characterization of new special ginsenosidase hydrolyzing multi-glycisides of protopanaxadiol ginsenosides, ginsenosidase type I. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bak, D.H.; Kim, H.D.; Kim, Y.O.; Park, C.G.; Han, S.Y.; Kim, J.J. Neuroprotective effects of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol against glutamate-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in PC12 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Seo, G.S.; Ko, G.; Kim, J.B.; Sohn, D.H. Anti-inflammatory activity of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol: Enhanced heme oxygenase 1 expression in RAW 264.7 cells. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 1167–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, K.W.; Leung, F.P.; Mak, N.K.; Tombran-Tink, J.; Huang, Y.; Wong, R.N. Protopanaxadiol and protopanaxatriol bind to glucocorticoid and oestrogen receptors in endothelial cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 156, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Hang, Y.; Bu, X.; Jia, W. Antiestrogenic effect of 20S-protopanaxadiol and its synergy with tamoxifen on breast cancer cells. Cancer 2007, 109, 2374–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, D.; Kwak, J.Y.; Park, E.H.; Kim, K.H.; Park, H.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Jang, H.J.; Ham, J.; et al. Inhibitory effects of ginseng sapogenins on the proliferation of triple negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 5409–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Eltriki, M.; Deb, S.; Adomat, H.; Tomlinson Guns, E.S. Calcitriol and 20(S)-protopanaxadiol synergistically inhibit growth and induce apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 158, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Qi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, D.; Guo, W.; Zhan, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, A.; Wang, A.R.; et al. 20(S)-protopanaxadiol inhibition of progression and growth of castration-resistant prostate cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Chen, D.; Li, W.; Xiao, D. 20(S)-Protopanaxadiol saponins inhibit SKOV3 cell migration. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 1693–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanderi, C.; Kim, E.; Chang, S.; Choi, C.; Choi, K. Ginsenoside 20(S)-Protopanaxadiol Suppresses Viability of Human Glioblastoma Cells via Down-regulation of Cell Adhesion Proteins and Cell-cycle Arrest. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oh, H.A.; Kim, D.E.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, N.J.; Kim, D.H. Anti-stress Effects of 20(S)-Protopanaxadiol and 20(S)-Protopanaxatriol in Immobilized Mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Pu, Y.; Xu, B.; Tao, J.; Zhang, T. Apparent Oil/water Partition Coefficient of 20(S)-PPD and Its Intestinal Absorption in Rats. Chin. J. Inform. TCM 2011, 18, 50–61. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, Z.H.; Sun, E.; Tan, X.B.; Xia, H.J.; Liu, Q.Y.; Jia, X.B. Polybasic research on the biopharmaceutical characteristics of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol. Yao Xue Xue Bao/Acta Pharm. Sin. 2013, 48, 411–416. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, X. Development of a UPLC-ESI-MS/MS assay for 20(S)-protopanaxadiol and pharmacokinetic application of its two formulations in rats. Anal. Sci. Int. J. Jpn. Soc. Anal. Chem. 2010, 26, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, L.; Cao, F.; Miao, X.; Chen, T.; Chang, Q.; Zheng, Y. Formulation of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol nanocrystals to improve oral bioavailability and brain delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 497, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, Z.H.; Li, S.L.; Sun, E.; Tan, X.B.; Song, J.; Jia, X.B. A nanostructured liquid crystalline formulation of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol with improved oral absorption. Fitoterapia 2013, 84, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Ma, L.; Yu, X.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X. A nanoparticulate drug-delivery system for 20(S)-protopanaxadiol: Formulation, characterization, increased oral bioavailability and anti-tumor efficacy. Drug Deliv. 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Jin, X.; Hu, Q.; Chen, X.Y.; Jia, X.B. A novel drug-phospholipid complex enriched with micelles: Preparation and evaluation in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Pu, Y.; Xu, B.; Tao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wu, P. Self-Microemulsifying Drug Delivery System Improved Oral Bioavailability of 20(S)-Protopanaxadiol: From Preparation to Evaluation. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 63, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Pu, Y.; Tao, J.; Xu, B.; Zhang, T. Determination and in vitro evaluation of 20(S)-PPD tablets. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formul. 2011, 17, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, K.X.; Chen, Y.X.; Zhang, T.; Tao, J.S.; Wang, B. Study on praparation and release in vitro of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol complex microspheres. J. Math. Med. 2015, 28, 813–815. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Pu, Y.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, T. Preparation of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol polylactic acid-glycolic acid sustained release microspheres. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formula 2013, 19, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Zang, C.Q.; Chen, Y.X.; Tao, J.S.; Zhang, T. Preparation of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol-phospholipid complex HAP assemblies. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2014, 37, 2282–2285. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Lin, J.; Wang, Y.; Cui, F.; Zhou, S.; Jia, M.; Ye, S.; Zhang, Q. Phytosomes loaded with mitomycin C-soybean phosphatidylcholine complex developed for drug delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lin, J.; Wu, H.; Chang, Y.; Yuan, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Hou, Z.; Dai, L. Orthogonally functionalized nanoscale micelles for active targeted codelivery of methotrexate and mitomycin C with synergistic anticancer effect. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lin, J.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, S.; Huang, Y.; Ye, S.; Xie, L.; Dai, L.; Hou, Z. Self-Assembled Nanoparticles Based on Amphiphilic Anticancer Drug-Phospholipid Complex for Targeted Drug Delivery and Intracellular Dual-Controlled Release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 17573–17581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Yang, X.; Jia, M.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lin, J.; Wu, S.; Hou, Z. Mitomycin C-soybean phosphatidylcholine complex-loaded self-assembled PEG-lipid-PLA hybrid nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and dual-controlled drug release. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 2915–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, L.; Guo, S.; Meng, Z.; Cui, J.; Xue, M.; et al. Monodisperse microparticles loaded with the self-assembled berberine-phospholipid complex-based phytosomes for improving oral bioavailability and enhancing hypoglycemic efficiency. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 103, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Gu, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Bi, K.; Chen, X. Preparation and evaluation of kaempferol-phospholipid complex for pharmacokinetics and bioavailability in SD rats. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 114, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.-R.; Yu, H.-T.; Yang, Y.; Hang, L.; Yang, X.-W.; Ding, S.-H. Quercetin phospholipid complex significantly protects against oxidative injury in ARPE-19 cells associated with activation of Nrf2 pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 770, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Teng, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, T.; Tang, X.; Cai, C. A highly stable norcantharidin loaded lipid microspheres: Preparation, biodistribution and targeting evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Xu, P.H.; Shen, B.D.; Shen, G.; Li, J.J.; Qiu, L.; Liu, C.Y.; Yuan, H.L.; Han, J. Improve bile duct-targeted drug delivery and therapeutic efficacy for cholangiocarcinoma by cucurbitacin B loaded phospholipid complex modified with berberine hydrochloride. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 489, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damle, M.; Mallya, R. Development and Evaluation of a Novel Delivery System Containing Phytophospholipid Complex for Skin Aging. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, P.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, C. Phospholipid complex as an approach for bioavailability enhancement of echinacoside. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Application of phospholipid complex technique to improve the dissolution and pharmacokinetic of probucol by solvent-evaporation and co-grinding methods. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 474, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalita, B.; Das, M.K.; Sarma, M.; Deka, A. Sustained Anti-inflammatory Effect of Resveratrol-Phospholipid Complex Embedded Polymeric Patch. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, S.K.; Singh, C.; Dora, C.P.; Suresh, S. Development of tamoxifen-phospholipid complex: Novel approach for improving solubility and bioavailability. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Xiang, N.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Fu, Y.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Z. Encapsulation of teniposide into albumin nanoparticles with greatly lowered toxicity and enhanced antitumor activity. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 487, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, C.; Xia, X.; Liu, Y. Self-assembled lecithin/chitosan nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery: Preparation and functional evaluation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Chen, D.; Jiang, R.; Tan, Q.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, J. Improved absorption and in vivo kinetic characteristics of nanoemulsions containing evodiamine-phospholipid nanocomplex. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 4411–4420. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Tan, A.; Prestidge, C.A.; Nielsen, H.M.; Mullertz, A. Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems for oral insulin delivery: In vitro and in vivo evaluations of enteric coating and drug loading. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 477, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, M.R.; Bhingole, R.C. Nanosponge-based pediatric-controlled release dry suspension of Gabapentin for reconstitution. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 2029–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, B.; Tao, J. Prescription of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol for suspension. Chin. Tradit. Patent Med. 2012, 34, 1680–1684. [Google Scholar]
- ICH Q2B Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology; Consensus Guideline; The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- Maiti, K.; Mukherjee, K.; Gantait, A.; Ahamed, H.N.; Saha, B.P.; Mukherjee, P.K. Enhanced therapeutic benefit of quercetin phospholipid complex carbon tetrachlorideinduced acute liver injury in rats: A comparative study. Iran. J. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 4, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, C.; Bhatt, T.D.; Gill, M.S.; Suresh, S. Novel rifampicin-phospholipid complex for tubercular therapy: Synthesis, physicochemical characterization and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 460, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Began, G.; Sudharshan, E.; Udaya Sankar, K.; Appu Rao, A.G. Interaction of curcumin with phosphatidylcholine: A spectrofluorometric study. J. Agric. Food chem. 1999, 47, 4992–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jin, W.; Yan, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, C. Development of intravenous lipid emulsion of vinorelbine based on drug-phospholipid complex technique. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 454, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, L.; Hu, G.; Chen, X.; Jia, J. Development of quercetin-phospholipid complex to improve the bioavailability and protection effects against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in SD rats. Fitoterapia 2016, 113, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidd, P.M. Bioavailability and activity of phytosome complexes from botanical polyphenols: The silymarin, curcumin, green tea, and grape seed extracts. Altern. Med. Rev. J. Clin. Ther. 2009, 14, 226–246. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, Z.H.; Sun, E.; Tan, X.B.; Zhu, F.X.; Jia, X.B. A novel drug-phospholipid complex loaded micelle for baohuoside I enhanced oral absorption: In vivo and in vivo evaluations. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolson, G.L.; Ash, M.E. Lipid Replacement Therapy: A natural medicine approach to replacing damaged lipids in cellular membranes and organelles and restoring function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 1657–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, J.; Alexander, A.; Ajazuddin; Saraf, S.; Saraf, S. Recent advances and future prospects of phyto-phospholipid complexation technique for improving pharmacokinetic profile of plant actives. J. Control. Release 2013, 168, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, J.; Liu, J.; Zhu, D.; Gong, T.; Yang, F.; Hao, X.; Zhang, Z. Preparation and evaluation of self-nanoemulsified drug delivery systems (SNEDDSs) of matrine based on drug-phospholipid complex technique. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 386, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Long, X.; Yuan, F.; Chen, L.; Pan, S.; Liu, Y.; Stowell, Y.; Li, X. Combined use of phospholipid complexes and self-emulsifying microemulsions for improving the oral absorption of a BCS class IV compound, baicalin. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 4, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.P.; Sun, J.; Chen, H.X.; Xiao, Y.Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Cai, H.; Cai, B.C. Comparative pharmacokinetics and bioavailability studies of quercetin, kaempferol and isorhamnetin after oral administration of Ginkgo biloba extracts, Ginkgo biloba extract phospholipid complexes and Ginkgo biloba extract solid dispersions in rats. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, P.; Liu, J.P.; Yang, J.K.; Zhang, W.L.; Fan, Y.Q.; Kan, S.L.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, W.J. Bioavailability and foam cells permeability enhancement of Salvianolic acid B pellets based on drug-phospholipids complex technique. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 83, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Luan, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Song, A.; Shao, W.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Z. Huperzine A-phospholipid complex-loaded biodegradable thermosensitive polymer gel for controlled drug release. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 433, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Kirsch, L.E. Correlation of the thermal stability of phospholipid-based emulsions and the microviscosity measurements using fluorescence polarization. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2004, 9, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Sun, X.; Gong, T.; Wu, C.Y.; Zhang, T.; Tan, J.; Zhang, Z.R. Injectable and biodegradable thermosensitive hydrogels loaded with PHBHHx nanoparticles for the sustained and controlled release of insulin. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 5063–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, S.; Qin, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y. Investigation of the mechanisms of improved oral bioavailability of bergenin using bergenin-phospholipid complex. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, P.F.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, B.; Yang, M.; Wang, M.S.; Zhang, H.Y.; Hu, P.Y.; Wu, Z.F. Process optimization by response surface design and characterization study on geniposide pharmacosomes. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2012, 17, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiti, K.; Mukherjee, K.; Gantait, A.; Saha, B.P.; Mukherjee, P.K. Curcumin-phospholipid complex: Preparation, therapeutic evaluation and pharmacokinetic study in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 330, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Q.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Wu, M.; Wang, H.; Yin, H.; He, D.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, J. Design and evaluation of a novel evodiamine-phospholipid complex for improved oral bioavailability. AAPS PharmSciTech 2012, 13, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, J.; Marsili, M. Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity—A rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron 1980, 36, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Not available.



| No. | X1 | X2 | X3 | Y/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 53.77 ± 0.46 |
| 2 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 60.37 ± 5.00 |
| 3 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 59.87 ± 3.01 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 65.73 ± 6.93 |
| 5 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 54.81 ± 2.36 |
| 6 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 61.44 ± 6.13 |
| 7 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 53.42 ± 4.62 |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 65.21 ± 7.05 |
| 9 | −1.732 | 0 | 0 | 45.33 ± 2.08 |
| 10 | 1.732 | 0 | 0 | 64.22 ± 2.98 |
| 11 | 0 | −1.732 | 0 | 55.46 ± 0.77 |
| 12 | 0 | 1.732 | 0 | 57.54 ± 2.32 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | −1.732 | 58.24 ± 0.40 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 1.732 | 66.55 ± 4.58 |
| 15–20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 54.90 ± 2.83 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 459.36 | 9 | 51.04 | 5.35 | 0.0075 | significant |
| X1 | 288.91 | 1 | 288.91 | 30.26 | 0.0003 | |
| X2 | 21.73 | 1 | 21.73 | 2.28 | 0.1623 | |
| X3 | 6.49 | 1 | 6.49 | 0.68 | 0.4288 | |
| X1 X2 | 2.44 | 1 | 2.44 | 0.26 | 0.6240 | |
| X1 X3 | 4.44 | 1 | 4.44 | 0.47 | 0.5107 | |
| X2 X3 | 10.31 | 1 | 10.31 | 1.08 | 0.3233 | |
| X12 | 0.86 | 1 | 0.86 | 0.090 | 0.7701 | |
| X22 | 10.30 | 1 | 10.30 | 1.08 | 0.3233 | |
| X32 | 121.18 | 1 | 121.18 | 12.69 | 0.0052 | |
| Residual | 95.47 | 10 | 9.55 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 55.50 | 5 | 11.10 | 1.39 | 0.3638 | not significant |
| Pure Error | 39.97 | 5 | 7.99 | |||
| Corrected Total | 554.83 | 19 |
| Factors | Level | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1.732 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 1.732 | |
| X1 (g/g) | 0.5 | 0.82 | 1.25 | 1.68 | 2 |
| X2 (mg/mL) | 5 | 8.17 | 12.5 | 16.83 | 20 |
| X3 (h) | 1 | 1.85 | 3 | 4.15 | 5 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Zang, C.; Wang, Y.; Dong, T.T.-X.; Zhang, T. 20(S)-Protopanaxadiol Phospholipid Complex: Process Optimization, Characterization, In Vitro Dissolution and Molecular Docking Studies. Molecules 2016, 21, 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101396
Pu Y, Zhang X, Zhang Q, Wang B, Chen Y, Zang C, Wang Y, Dong TT-X, Zhang T. 20(S)-Protopanaxadiol Phospholipid Complex: Process Optimization, Characterization, In Vitro Dissolution and Molecular Docking Studies. Molecules. 2016; 21(10):1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101396
Chicago/Turabian StylePu, Yiqiong, Xitong Zhang, Qi Zhang, Bing Wang, Yuxi Chen, Chuanqi Zang, Yuqin Wang, Tina Ting-Xia Dong, and Tong Zhang. 2016. "20(S)-Protopanaxadiol Phospholipid Complex: Process Optimization, Characterization, In Vitro Dissolution and Molecular Docking Studies" Molecules 21, no. 10: 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101396
APA StylePu, Y., Zhang, X., Zhang, Q., Wang, B., Chen, Y., Zang, C., Wang, Y., Dong, T. T.-X., & Zhang, T. (2016). 20(S)-Protopanaxadiol Phospholipid Complex: Process Optimization, Characterization, In Vitro Dissolution and Molecular Docking Studies. Molecules, 21(10), 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101396






