Cordycepin Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Proliferation of Human Lung Cancer Cell Line H1975 via Inhibiting the Phosphorylation of EGFR
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
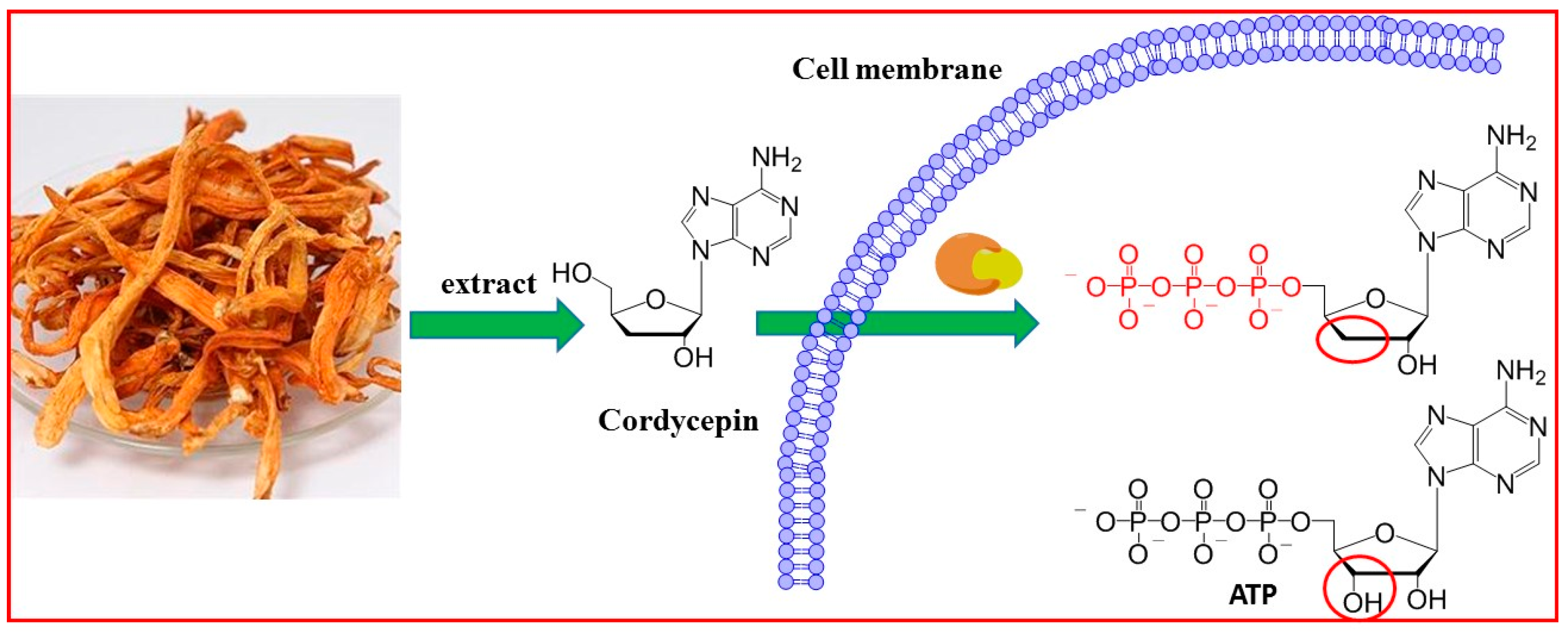
2.1. Cordycepin Extraction and Purification
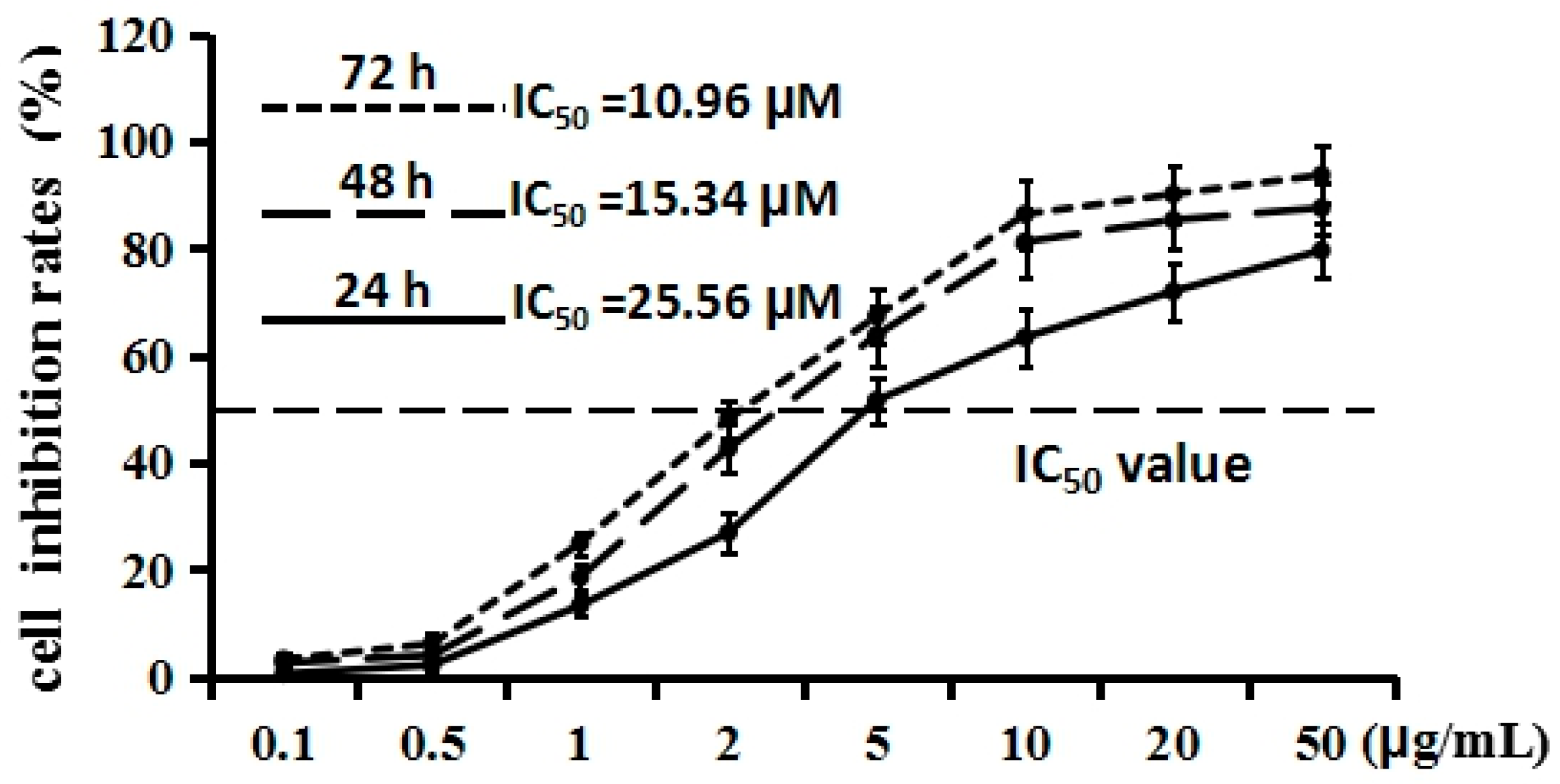
2.2. Cordycepin Inhibits H1975 Cell Proliferation
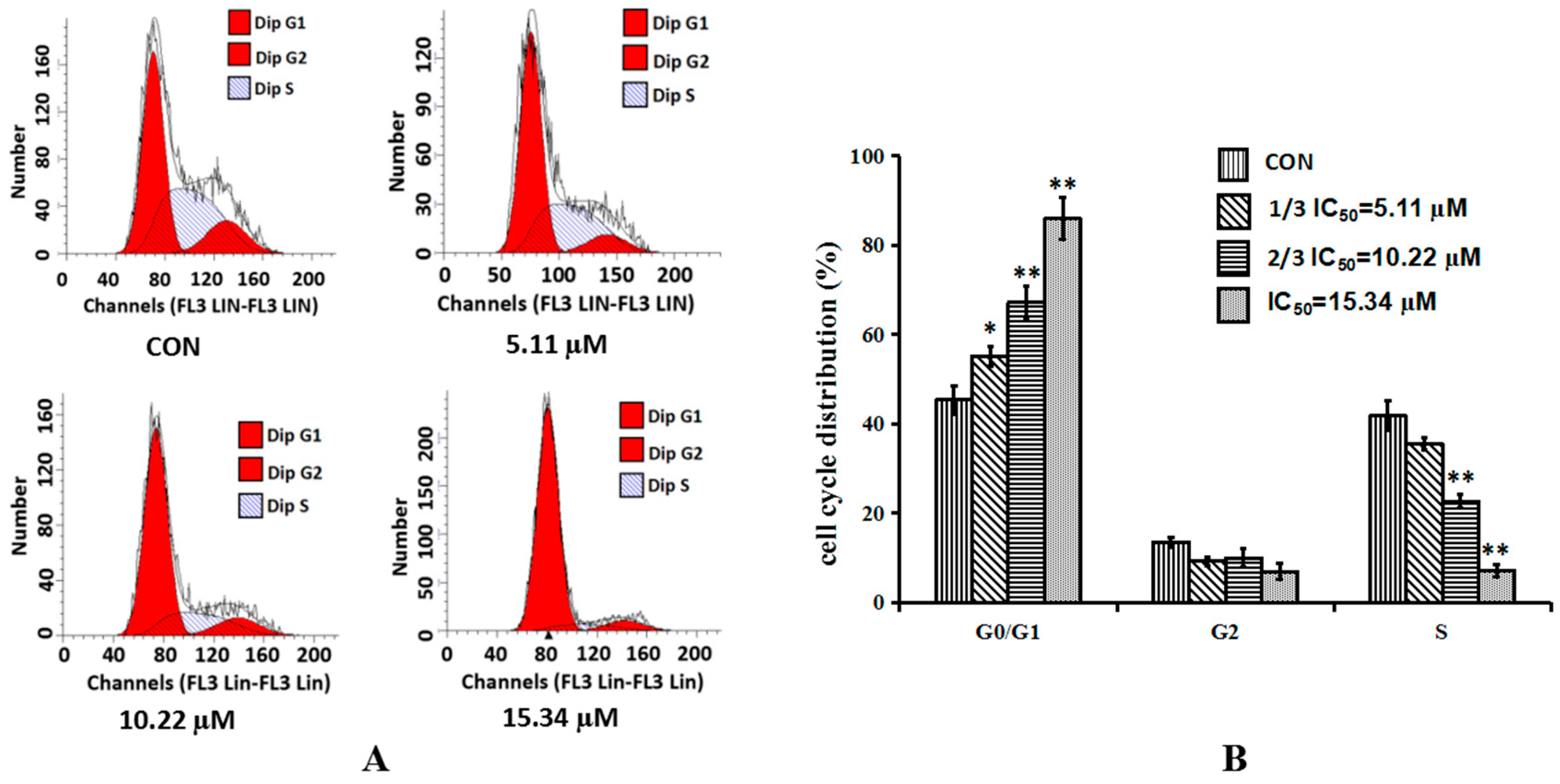
2.3. Cordycepin Induces G0/G1 Phase Arrest in H1975 Cells
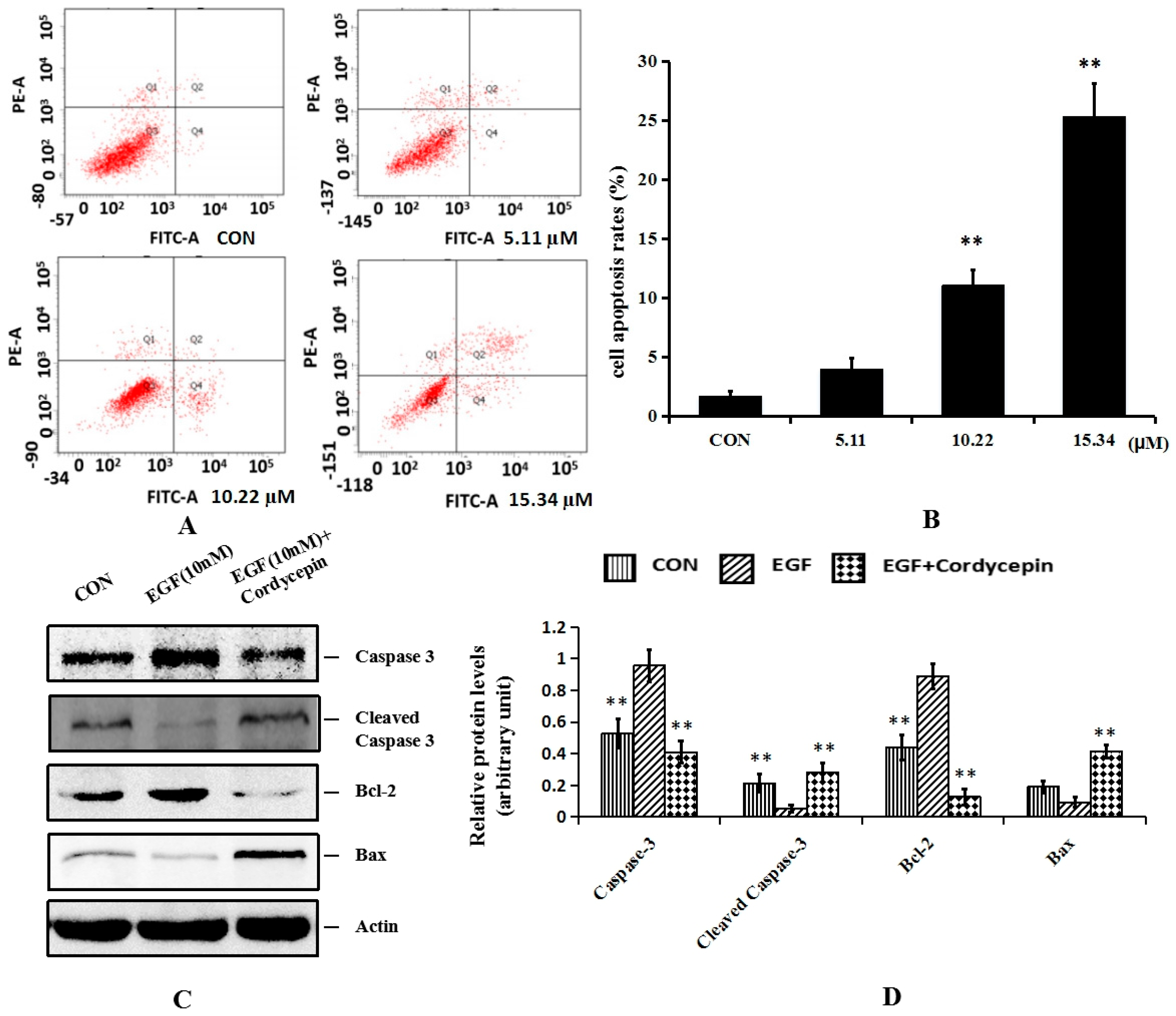
2.4. Cordycepin Induces Apoptosis and Regulates Apoptosis-Related Proteins Bcl-2 and Caspase-3 in H1975 Cells
2.5. Cordycepin Inhibits the Phosphorylation of EGFR, AKT and ERK1/2 in H1975 Cells
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cordycepin Extraction and Purification
3.2. Cell Culture and MTT Assay
3.3. Flow Cytometry Analysis
3.4. Western Blot Analysis
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Cang, S.; Liu, D. Third-generation inhibitors targeting EGFR T790M mutation in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, R.; Liu, B.; Wang, L. EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment in a patient with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and concurrent exon 19 and 21 EGFR mutations: A case report and review of the literature. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 3546–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J. A novel strategy to the synthesis of 4-anilinoquinazoline derivatives. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, J.; Averbuch, S.D. ZD1839 (‘Iressa’) as an anticancer agent. Drugs 2000, 60, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, A.J.; Wedge, S.R. ZD6474—A novel inhibitor of VEGFR and EGFR tyrosine kinase activity. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, S6–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Song, Z.; Tang, Z. Facile and efficient synthesis and biological evaluation of 4-anilinoquinazoline derivatives as EGFR inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 2589–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.M. Update of epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2013, 76, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequist, L.V.; Waltman, B.A.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Digumarthy, S.; Turke, A.B.; Fidias, P.; Bergethon, K.; Shaw, A.T.; Gettinger, S.; Cosper, A.K.; et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, C.H.; Mengwasser, K.E.; Toms, A.V.; Woo, M.S.; Greulich, H.; Wong, K.K.; Meyerson, M.; Eck, M.J. The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Boggon, T.J.; Dayaram, T.; Janne, P.A.; Kocher, O.; Meyerson, M.; Johnson, B.E.; Eck, M.J.; Tenen, D.G.; Halmos, B. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Ercan, D.; Chen, L.; Yun, C.H.; Li, D.; Capelletti, M.; Cortot, A.B.; Chirieac, L.; Iacob, R.E.; Padera, R.; et al. Novel mutant-selective EGFR kinase inhibitors against EGFR T790M. Nature 2009, 462, 1070–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, A.O.; Sjin, R.T.; Haringsma, H.J.; Ohashi, K.; Sun, J.; Lee, K.; Dubrovskiy, A.; Labenski, M.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Z.; et al. Discovery of a mutant-selective covalent inhibitor of EGFR that overcomes T790M-mediated resistance in NSCLC. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 1404–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuli, H.S.; Sharma, A.K.; Sandhu, S.S.; Kashyap, D. Cordycepin: A bioactive metabolite with therapeutic potential. Life Sci. 2013, 93, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Liu, J.L.; Tang, Z.S. Advances in research on Antitumor Activities of Cordycepin. Chin. Pharm. J. 2015, 50, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Vodnala, S.K.; Lundback, T.; Yeheskieli, E.; Sjoberg, B.; Gustavsson, A.L.; Svensson, R.; Olivera, G.C.; Eze, A.A.; de Koning, H.P.; Hammarstrom, L.G.; et al. Structure-activity relationships of synthetic cordycepin analogues as experimental therapeutics for African trypanosomiasis. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9861–9873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Nakagome, L.; Hirono, S.; Itoh, T.; Fujiwara, R. Inhibition of adenosine deaminase (ADA)-mediated metabolism of cordycepin by natural substances. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomadaki, H.; Tsiapalis, C.M.; Scorilas, A. The effect of the polyadenylation inhibitor cordycepin on human Molt-4 and Daudi leukaemia and lymphoma cell lines. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2008, 61, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Yoshikawa, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kagota, S.; Shinozuka, K.; Kunitomo, M. Antitumor effect of cordycepin (3′-deoxyadenosine) on mouse melanoma and lung carcinoma cells involves adenosine A3 receptor stimulation. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.L.; Ko, B.S.; Liu, T.A.; Liang, S.M.; Liu, C.C.; Lu, Y.J.; Tzean, S.S.; Shen, T.L.; Liou, J.Y. Cordycepin suppresses integrin/FAK signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.H.; Park, C.; Jeong, J.W.; Kim, M.J.; Seo, M.J.; Kang, B.W.; Park, J.U.; Kim, G.Y.; Choi, B.T.; Choi, Y.H.; et al. Apoptosis induction of human prostate carcinoma cells by cordycepin through reactive oxygen species mediated mitochondrial death pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, S.H.; Hueng, D.Y.; Syu, J.P.; Liao, C.C.; Wu, Y.C. Cordycepin induces apoptosis of C6 glioma cells through the adenosine 2A receptor-p53-caspase-7-PARP pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 216, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, W.E.; Seibert, G.; Beyer, R.; Breter, H.J.; Maidhof, A.; Zahn, R.K. Effect of cordycepin on nucleic acid metabolism in L5178Y cells and on nucleic acid-synthesizing enzyme systems. Cancer Res. 1977, 37, 3824–3833. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodman, L.E.; Farnell, D.R.; Coyne, J.M.; Allan, P.W.; Hill, D.L.; Duncan, K.L.; Tomaszewski, J.E.; Smith, A.C.; Page, J.G. Toxicity of cordycepin in combination with the adenosine deaminase inhibitor 2′-deoxycoformycin in beagle dogs. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1997, 147, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C.L.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, N.; Sun, Y.N.; Liu, Z.L.; Tang, Z.S.; Liu, J.L. Synthesis of new 4-anilinoquinazoline analogues and evaluation of their EGFR inhibitor activity. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2015, 50, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.A.; Xiang, S.S.; Li, H.F.; Wu, X.S.; Li, M.L.; Shu, Y.J.; Zhang, F.; Cao, Y.; Ye, Y.Y.; Bao, R.F.; et al. Cordycepin induces S phase arrest and apoptosis in human gallbladder cancer cells. Molecules 2014, 19, 11350–11365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds cordycepin are available from the authors.

© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Liang, Y.-N.; Wang, L.; Song, Z.-X.; Liu, J.-L.; Tang, Z.-S. Cordycepin Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Proliferation of Human Lung Cancer Cell Line H1975 via Inhibiting the Phosphorylation of EGFR. Molecules 2016, 21, 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101267
Wang Z, Wu X, Liang Y-N, Wang L, Song Z-X, Liu J-L, Tang Z-S. Cordycepin Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Proliferation of Human Lung Cancer Cell Line H1975 via Inhibiting the Phosphorylation of EGFR. Molecules. 2016; 21(10):1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101267
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zheng, Xue Wu, Yan-Ni Liang, Li Wang, Zhong-Xing Song, Jian-Li Liu, and Zhi-Shu Tang. 2016. "Cordycepin Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Proliferation of Human Lung Cancer Cell Line H1975 via Inhibiting the Phosphorylation of EGFR" Molecules 21, no. 10: 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101267
APA StyleWang, Z., Wu, X., Liang, Y.-N., Wang, L., Song, Z.-X., Liu, J.-L., & Tang, Z.-S. (2016). Cordycepin Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Proliferation of Human Lung Cancer Cell Line H1975 via Inhibiting the Phosphorylation of EGFR. Molecules, 21(10), 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101267




