Cellular Structural Changes in Candida albicans Caused by the Hydroalcoholic Extract from Sapindus saponaria L.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
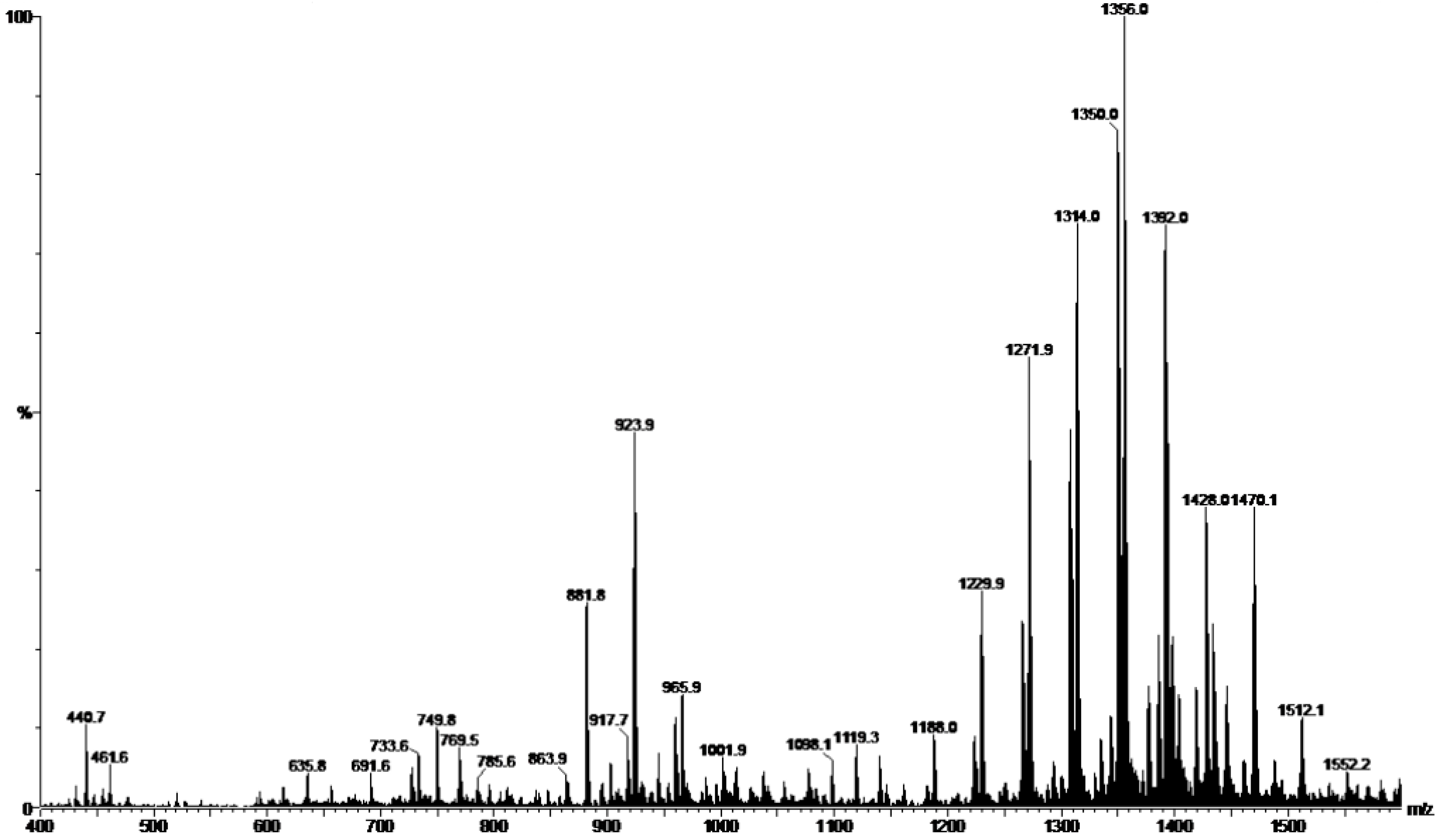
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of HE
2.2. Tests of Susceptibility to Antifungals
| HE | Fluconazole | Nystatin | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC Range | MIC50 | MIC Range | MIC50 | MIC Range | MIC50 | |
| (µg/mL) | ||||||
| Candida albicans | 390–1560 | 1560 | 0.125–1 | 0.125 | 4–8 | 8 |
| Candida glabrata | 97.5–12,500 | 780 | 0.25–64 | 32 | 0.5–8 | 2 |
| Candida tropicalis | 780–3125 | 780 | 0.25–64 | 0.5 | 0.5–4 | 2 |
| Candida parapsilosis | 780–12,500 | 1560 | 1–16 | 2 | 2–4 | 2 |
| Saccharomyces cerevisae | 390–12,500 | 780 | 4–64 | 16 | 2–4 | 2 |
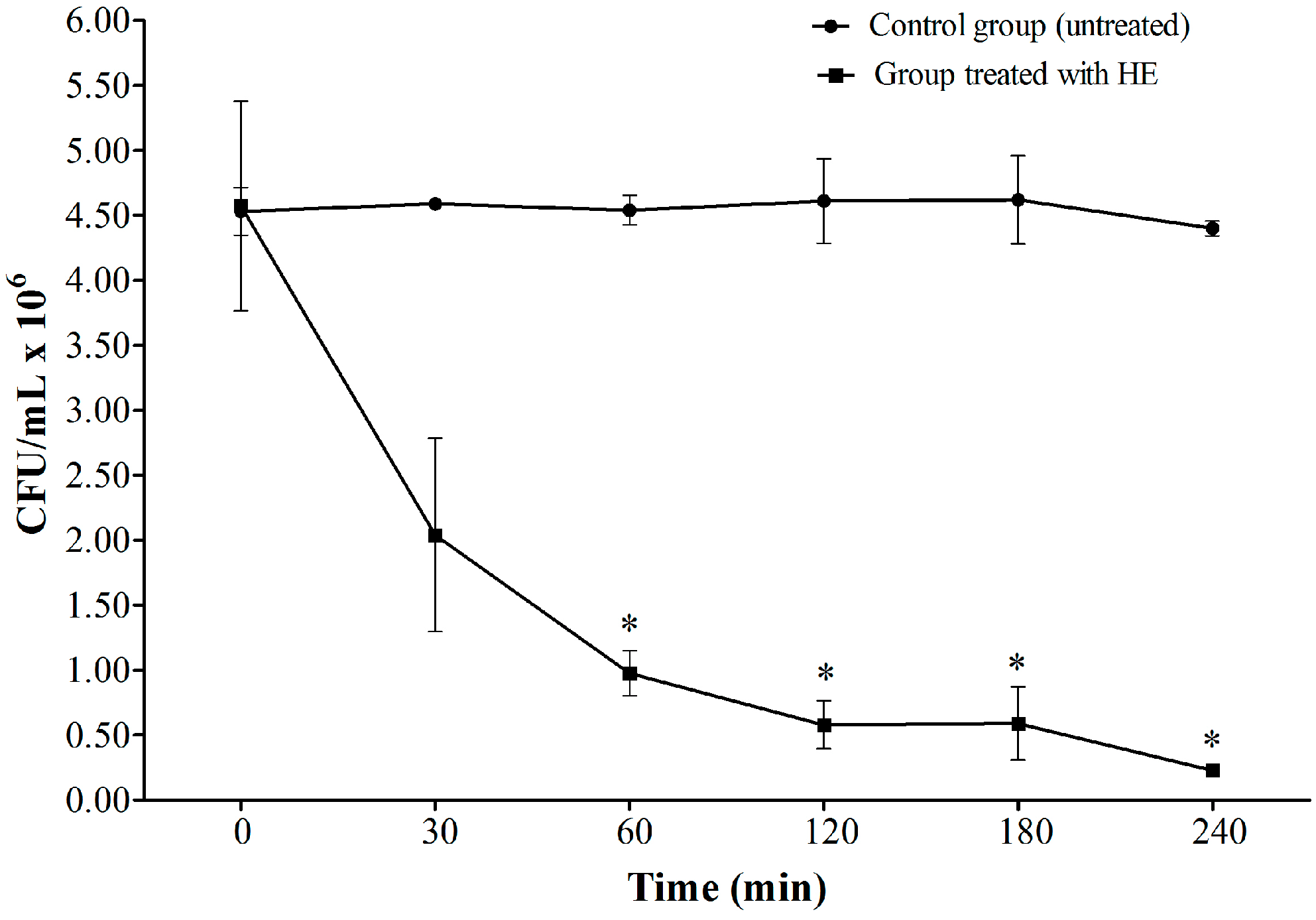
2.3. Time-Kill Assay
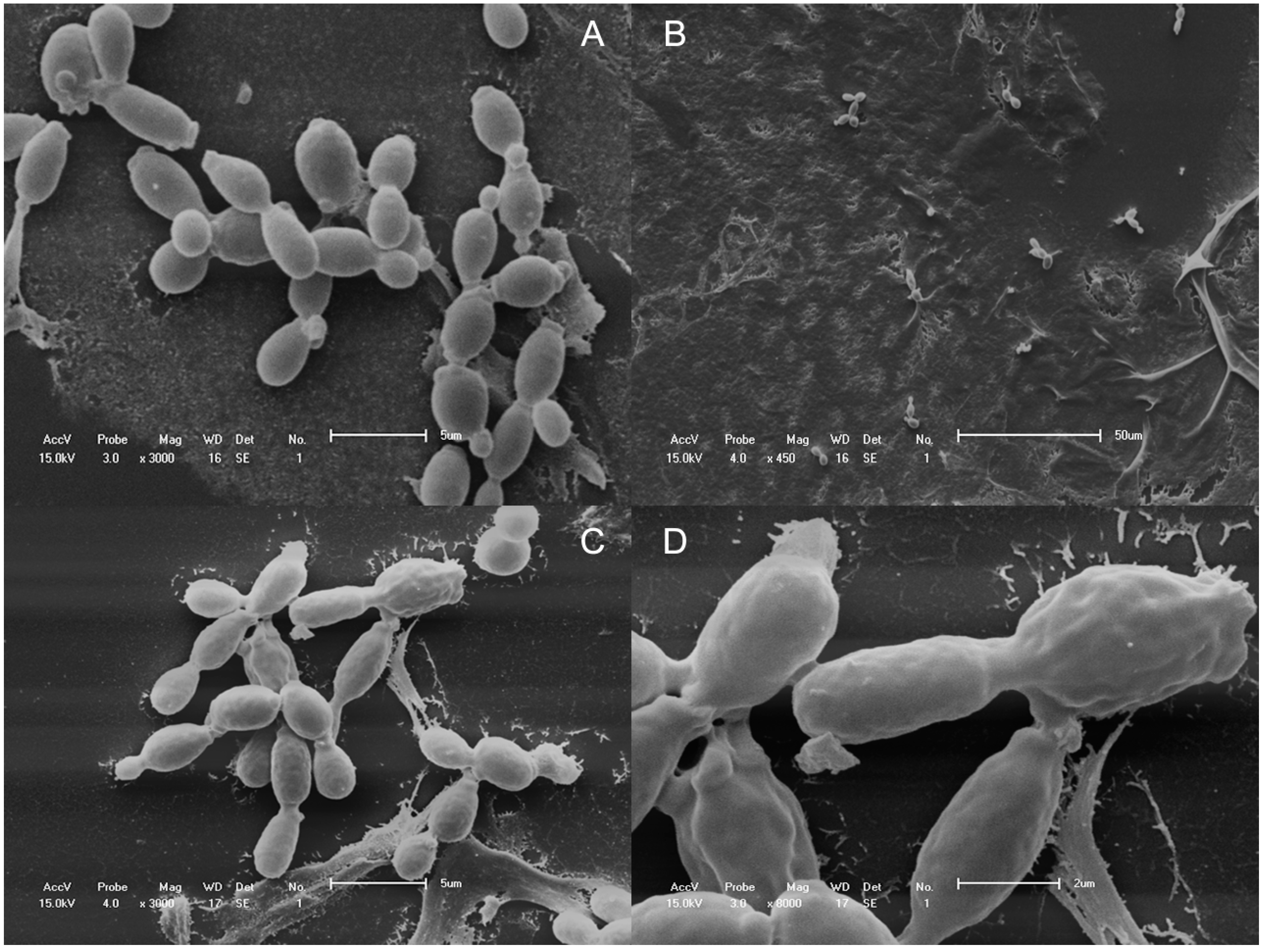
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
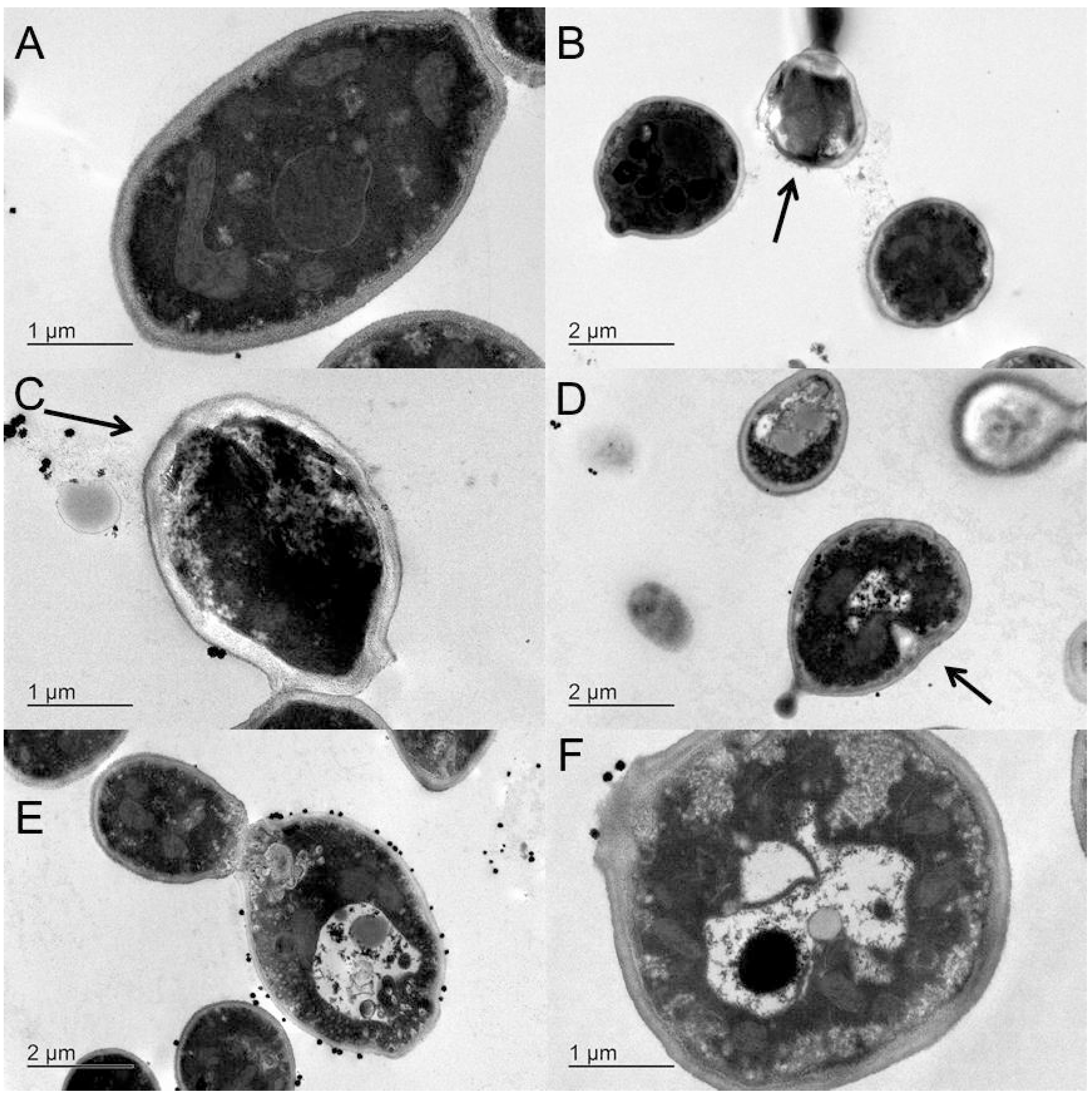
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.6. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Preparation of HE
3.2. Characterization of HE
3.3. Samples
3.4. Tests of Susceptibility to Antifungals
3.5. Time-Kill Assay of C. albicans against HE
3.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sobel, J.D. Vulvovaginal candidosis. Lancet 2007, 369, 1961–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achkar, J.M.; Fries, B.C. Candida infections of the genitourinary tract. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Workowski, K.A.; Berman, S.M. Centers for disease control and prevention. In Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines 2010; Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2010; Volume 59(RR12), pp. 1–110. [Google Scholar]
- Dalben Dota, K.F.; Shinobu, C.S.; Patussi, E.V.; Lopes Consolaro, M.E.; Estivalet Svidzinski, T.I. Susceptibilidad de levaduras vaginales a los antifúngicos más utilizados en Maringá, Paraná, Brasil. Acta Bioquím. Clin. Latinoam. 2008, 42, 561–566. [Google Scholar]
- Ragunathan, L.; Poongothai, G.K.; Sinazer, A.R.; Kannaiyan, K.; Gurumurthy, H.; Jaget, N.; Kuthalaramalingam, S. Phenotypic characterization and antifungal susceptibility pattern to fluconazole in Candida species isolated from vulvovaginal candidiasis in a tertiary care hospital. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, DC01–DC04. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumari, V.; Banerjee, T.; Kumar, P.; Pandey, S.; Tilak, R. Emergence of non-albicans Candida among candidal vulvovaginitis cases and study of their potential virulence factors, from a tertiary care center, North India. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2013, 56, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.P.; Fan, S.R.; Peng, Y.T.; Zhang, H.P. Species distribution and susceptibility of Candida isolates from patient with vulvovaginal candidiasis in Southern China from 2003 to 2012. J. Med. Mycol. 2014, 24, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinel-Ingroff, A.; Canton, E. Comparison of neo-sensitabs tablet diffusion assay with CLSI broth microdilution M38-A and disk diffusion methods for testing susceptibility of filamentous fungi with amphotericin B, caspofungin, itraconazole, posaconazole, and voriconazole. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1793–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghannoum, M.A.; Rice, L.B. Antifungal agents: Mode of action, mechanisms of resistance, and correlation of these mechanisms with bacterial resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iavazzo, C.; Gkegkes, I.D.; Zarkada, I.M.; Falagas, M.E. Boric acid for recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis: The clinical evidence. J. Women’s Health 2011, 20, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dota, K.F.D.; Consolaro, M.E.L.; Svidzinski, T.I.E.; Bruschi, M.L. Antifungal activity of brazilian propolis microparticles against yeasts isolated from vulvovaginal candidiasis. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, Article ID 201953. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer Albiero, A.L.; Aboin Sertié, J.A.; Bacchi, E.M. Antiulcer activity of Sapindus saponaria L. in the rat. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 82, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgu, M.; Rodrigues-Filho, E. Dereplication of glycosides from Sapindus saponaria using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2006, 17, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, K.N.; Ćirić, A.; Glamočlija, J.; Calhelha, R.C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Soković, M. Antimicrobial activity, growth inhibition of human tumour cell lines, and phytochemical characterization of the hydromethanolic extract obtained from Sapindus saponaria L. aerial parts. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzuki, J.K.; Svidzinski, T.I.; Shinobu, C.S.; Silva, L.F.; Rodrigues-Filho, E.; Cortez, D.A.; Ferreira, I.C. Antifungal activity of the extracts and saponins from Sapindus saponaria L. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2007, 79, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damke, E.; Tsuzuki, J.K.; Cortez, D.A.; Ferreira, I.C.; Bertoni, T.A.; Batista, M.R.; Donati, L.; Svidzinski, T.I.; Consolaro, M.E. In vivo activity of Sapindus saponaria against azole-susceptible and resistant human vaginal Candida species. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, M.C.T.; Figueira, G.M.; Sartoratto, A.; Rehder, V.L.G.; Delarmelina, C. Anti-Candida activity of brazilian medicinal plants. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 97, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Arellano, A.; López-Villegas, E.O.; Rodríguez-Tovar, A.V.; Zamilpa, A.; Jiménez-Ferrer, E.; Tortoriello, J.; Martínez-Rivera, M.A. Use of antifungal saponin SC-2 of Solanum chrysotrichum for the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis: In vitro studies and clinical experiences. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 10, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goswami, D.; Goswami, R.; Banerjee, U.; Dadhwal, V.; Miglani, S.; Lattif, A.A.; Kochupillai, N. Pattern of Candida species isolated from patients with diabetes mellitus and vulvovaginal candidiasis and their response to single dose oral fluconazole therapy. J. Infect. 2006, 52, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermitsky, J.-P.; Edlind, T.D. Azole resistance in Candida glabrata: Coordinate upregulation of multidrug transporters and evidence for a PDR1-like transcription factor. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3773–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, J. Vaginal candidosis: Epidemiological and etiological factors. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2000, 71, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalben-Dota, K.F.; Faria, M.G.I.; Bruschi, M.L.; Pelloso, S.M.; Lopes-Consolaro, M.E.; Svidzinski, T.I.E. Antifungal activity of propolis extract against yeasts isolated from vaginal exudates. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2010, 16, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barchiesi, F.; Calabrese, D.; Sanglard, D.; di Francesco, L.F.; Caselli, F.; Giannini, D.; Giacometti, A.; Gavaudan, S.; Scalise, G. Experimental induction of fluconazole resistance in Candida tropicalis ATCC 750. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damke, E.; Tsuzuki, J.K.; Chassot, F.; Cortez, D.A.G.; Ferreira, I.C.P.; Mesquita, C.S.S.; da-Silva, V.R.S.; Svidzinski, T.I.E.; Consolaro, M.E.L. Spermicidal and anti-Trichomonas vaginalis activity of brazilian Sapindus saponaria. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, G.; Kerem, Z.; Makkar, H.P.S.; Becker, K. The biological action of saponins in animal systems: A review. Br. J. Nutr. 2002, 88, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, M.; Salci, T.P.; Shinobu-Mesquita, C.S.; Capoci, I.R.G.; Svidzinski, T.I.E.; Kioshima, E.S. Early state research on antifungal natural products. Molecules 2014, 19, 2925–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgu, M.; Santos, L.F.A.; Souza, G.D.D.; Daolio, C.; Schneider, B.; Ferreira, A.G.; Rodrigues-Filho, E. Hydroxylation of a hederagenin derived saponin by a Xylareaceous fungus found in fruits of Sapindus saponaria. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2008, 19, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Zhu, N.; Ze-Ren-Wang-Mu, N.; Shen, Y. Two new antifungal saponins from the tibetan herbal medicine Clematis tangutica. Planta Medica 2003, 69, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escalante, A.M.; Santecchia, C.B.; López, S.N.; Gattuso, M.A.; Gutiérrez Ravelo, A.; Delle Monache, F.; Gonzalez Sierra, M.; Zacchino, S.A. Isolation of antifungal saponins from Phytolacca tetramera, an argentinean species in critic risk. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 82, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larone, D.H. Medically Important Fungi: A Guide to Identification, 5th ed.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts, Approved Standard—3rd ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: 940 West Valley Road, Suite 1400, Wayne, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shinobu-Mesquita, C.S.; Bonfim-Mendonça, P.S.; Moreira, A.L.; Ferreira, I.C.P.; Donatti, L.; Fiorini, A.; Svidzinski, T.I.E. Cellular Structural Changes in Candida albicans Caused by the Hydroalcoholic Extract from Sapindus saponaria L. Molecules 2015, 20, 9405-9418. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20059405
Shinobu-Mesquita CS, Bonfim-Mendonça PS, Moreira AL, Ferreira ICP, Donatti L, Fiorini A, Svidzinski TIE. Cellular Structural Changes in Candida albicans Caused by the Hydroalcoholic Extract from Sapindus saponaria L. Molecules. 2015; 20(5):9405-9418. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20059405
Chicago/Turabian StyleShinobu-Mesquita, Cristiane S., Patricia S. Bonfim-Mendonça, Amanda L. Moreira, Izabel C. P. Ferreira, Lucelia Donatti, Adriana Fiorini, and Terezinha I. E. Svidzinski. 2015. "Cellular Structural Changes in Candida albicans Caused by the Hydroalcoholic Extract from Sapindus saponaria L." Molecules 20, no. 5: 9405-9418. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20059405
APA StyleShinobu-Mesquita, C. S., Bonfim-Mendonça, P. S., Moreira, A. L., Ferreira, I. C. P., Donatti, L., Fiorini, A., & Svidzinski, T. I. E. (2015). Cellular Structural Changes in Candida albicans Caused by the Hydroalcoholic Extract from Sapindus saponaria L. Molecules, 20(5), 9405-9418. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20059405






