Antiviral Activity of a Nanoemulsion of Polyprenols from Ginkgo Leaves against Influenza A H3N2 and Hepatitis B Virus in Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
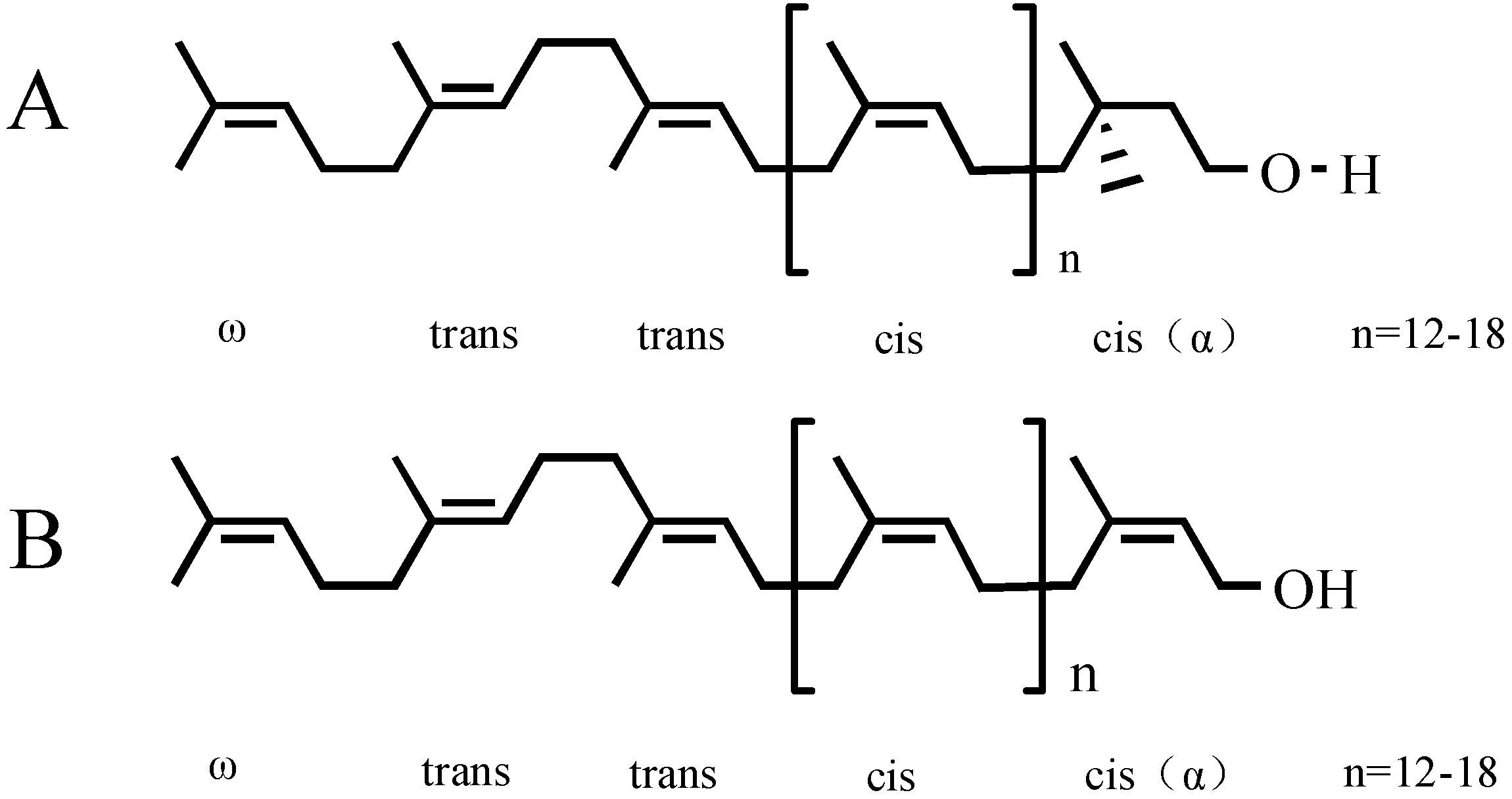
2. Results and Discussion
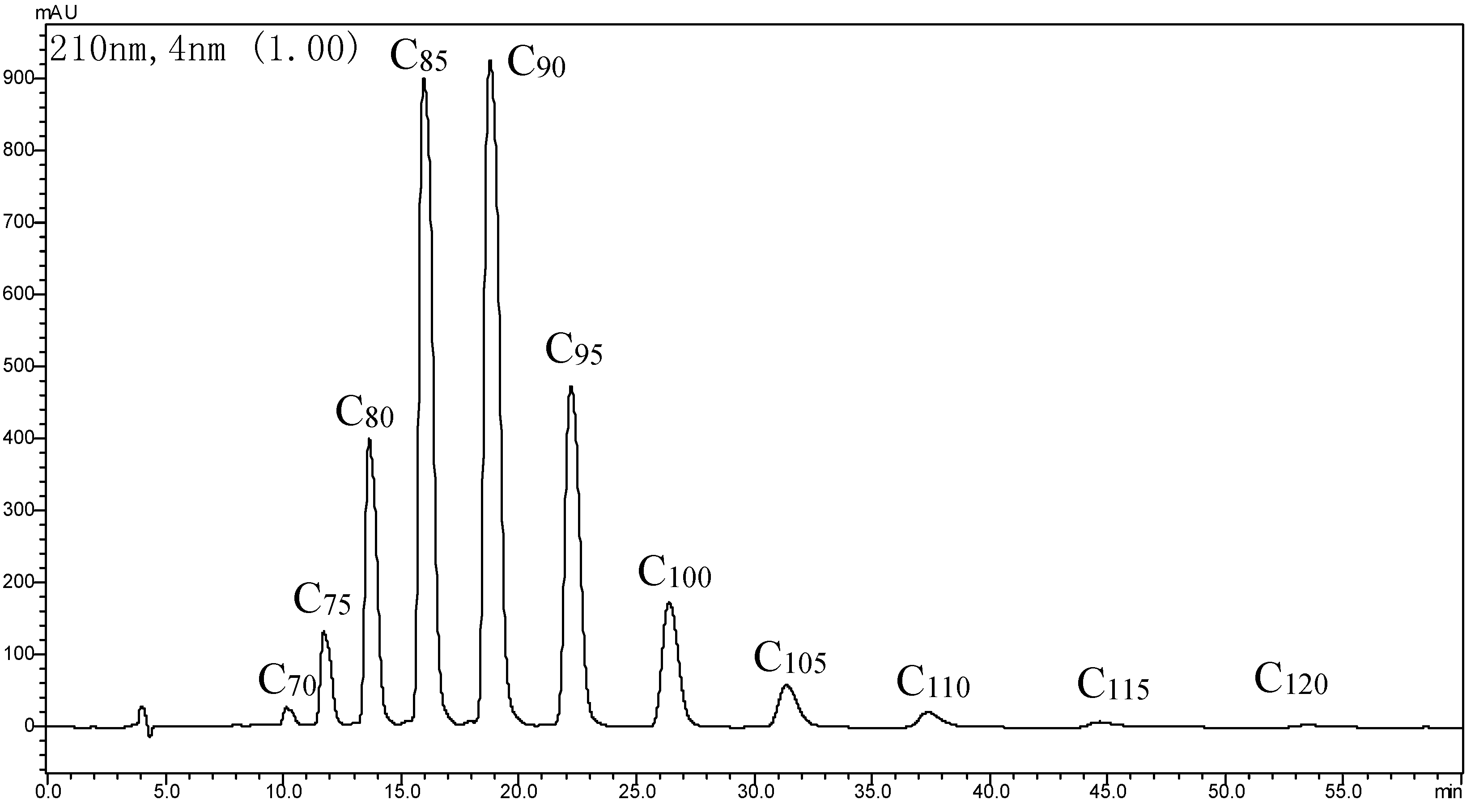
2.1. Determination of GBP
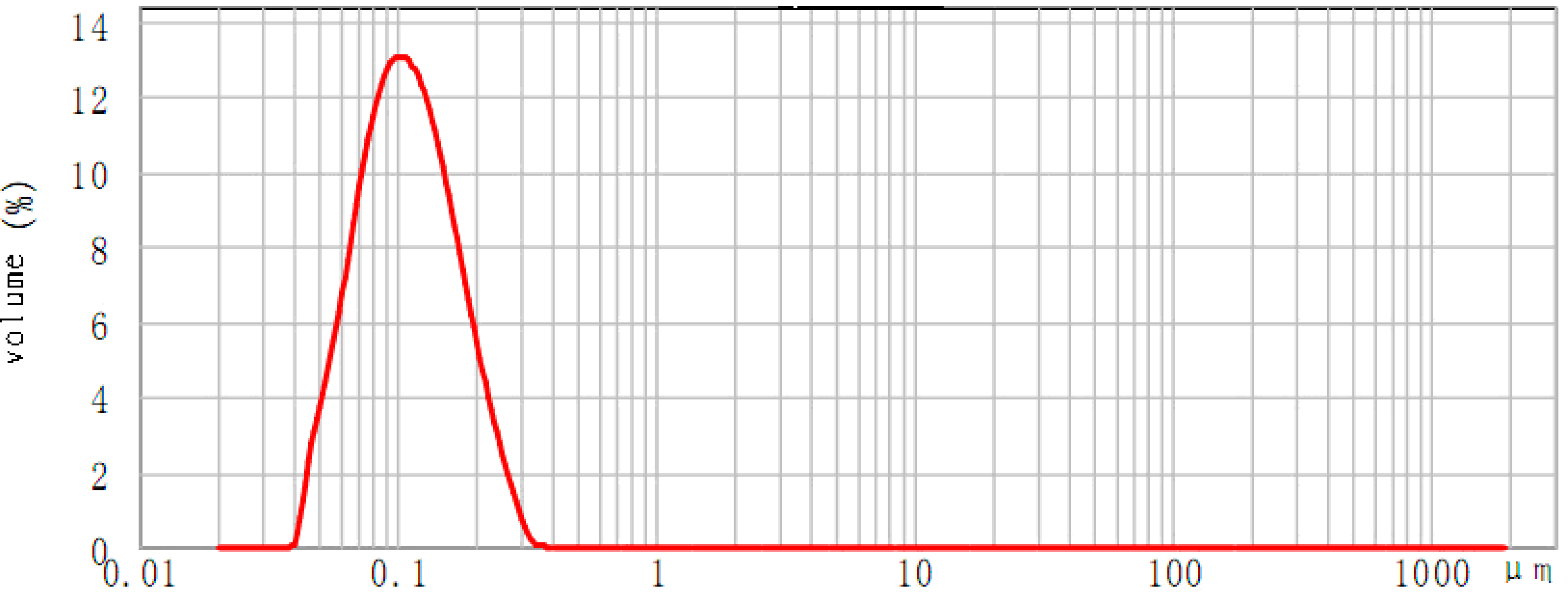
2.2. Physical Properties of GBP Nanoemulsion

2.3. Cellular Toxic Effect of GBP
| GBP Concentration | MDCK Cell | HepG 2215 Cell | IC | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OD570 | cell Breakage Rate | TC | OD570 | Cell Breakage Rate | TC | |||
| 100 μg/mL | 3.214 ± 0.300 | −12.93 | 1.129 | 1.873 ± 0.300 | −1.849 | 1.018 | 0 | >0.05 |
| 10 μg/mL | 3.571 ± 0.067 | −25.48 | 1.255 | 2.111 ± 0.067 | −14.80 | 1.148 | 0 | >0.05 |
| 1 μg/mL | 2.869 ± 0.294 | −0.808 | 1.008 | 1.970 ± 0.294 | −7.127 | 1.071 | 0 | >0.05 |
| 0.1 μg/mL | 3.236 ± 0.164 | −13.71 | 1.137 | 2.139 ± 0.164 | −16.32 | 1.163 | 0 | >0.05 |
| 0.01 μg/mL | 3.675 ± 0.153 | −29.14 | 1.291 | 1.807 ± 0.153 | 1.741 | 0.983 | 0 | >0.05 |
| Control 0 μg/mL | 2.846 ± 0.121 | 1.839 ± 0.121 | / | / | ||||
2.4. Effect of GBP on Influenza Virus and Normal Cells
| Groups | Cons. (μg/mL) | Virucidal Activity | Protecting MDCK Cells | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OD570 | Inhibition Rate (%) | IC50 | OD570 | Protection Rate (%) | IC50 | ||
| GBP+ H3N2 virus | 100 | 1.729 ± 0.238 ** | 70.0 | 1.683 ± 0.201 ** | 74.9 | ||
| GBP+ H3N2 virus | 50 | 1.691 ± 0.192 ** | 65.9 | 1.454 ± 0.142 ** | 60.4 | ||
| GBP+ H3N2 virus | 25 | 1.391 ± 0.271 ** | 49.5 | 3.179 | 1.422 ± 0.302 ** | 58.2 | 1.408 |
| GBP+ H3N2 virus | 12.5 | 0.861 ± 0.318 | 20.5 | 1.103 ± 0.398 * | 37.9 | ||
| GBP+ H3N2 virus | 6.2 | 0.507 ± 0.089 | 1.1 | 0.632 ± 0.223 | 8.0 | ||
| Ribavirin+ H3N2 virus | 10 | 2.267 ± 0.193 *** | 97.4 | 1.957 ± 0.282 *** | 92.3 | ||
| MDCK cell control | – | 2.315 ± 0.213 | 2.078 ± 0.104 | ||||
| H3N2 virus control | – | 0.486 ± 0.098 | 0.507 ± 0.205 | ||||
2.5. Inhibition Effect of GBP on HBV Antigen and DNA
| Groups | OD450 | Inhibition Rate (IC), % | IC50, μg/mL | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 3 | Day 6 | Day 9 | Day 3 | Day 6 | Day 9 | Day 3 | |||
| GBP 100 μg/mL | 0.542 ± 0.076 | 0.794 ± 0.510 * | 0.814 ± 0.132 | 41.405 | 52.110 | 38.380 | |||
| GBP 50 μg/mL | 0.678 ± 0.080 | 0.875 ± 0.110 * | 0.634 ± 0.132 | 15.676 | 47.225 | 52.116 | |||
| GBP 25 μg/mL | 0.696 ± 0.030 | 1.057 ± 0.120 * | 0.716 ± 0.167 | 24.756 | 36.248 | 45.798 | 42.71 | 7.450 | 5.531 |
| GBP 12 μg/mL | 0.801 ± 0.108 | 1.311 ± 0.238 | 0.949 ± 0.194 | 13.405 | 20.928 | 28.160 | |||
| GBP 6.2 μg/mL | 0.972 ± 0.195 | 1.416 ± 0.319 | 1.074 ± 0.444 | 5.081 | 14.596 | 18.697 | |||
| 3TC 20 μg/mL | 0.527 ± 0.09 ** | 0.663 ± 0.137 ** | 0.502 ± 0.193 ** | 43.027 | 60.012 | 61.998 | |||
| cell control | 0.925 ± 0.062 | 1.658 ± 0.065 | 1.321 ± 0.073 | – | – | – | |||
| Groups | OD450 | Inhibition Rate (IC), % | IC50, μg/mL | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 3 | Day 6 | Day 9 | Day 3 | Day 6 | Day 9 | Day 3 | |||
| GBP 100 μg/mL | 0.225 ± 0.038 | 0.222 ± 0.194 | 0.493 ± 0.166 * | 48.456 | 48.848 | 67.32 | |||
| GBP 50 μg/mL | 0.356 ± 0.049 | 0.346 ± 0.073 | 0.824 ± 0.131 * | 17.972 | 20.276 | 45.394 | |||
| GBP 25 μg/mL | 0.392 ± 0.029 | 0.382 ± 0.158 | 1.068 ± 0.179 * | 9.677 | 11.981 | 29.225 | 59.02 | 46.55 | 5.349 |
| GBP 12 μg/mL | 0.402 ± 0.044 | 0.392 ± 0.056 | 1.159 ± 0.290 | 7.373 | 9.677 | 23.194 | |||
| GBP 6.2 μg/mL | 0.426 ± 0.037 | 0.416 ± 0.046 | 1.265 ± 0.187 * | 1.843 | 4.147 | 16.170 | |||
| 3TC 20 μg/mL | 0.31 ± 0.035 * | 0.310 ± 0.057 * | 0.483 ± 0.134 ** | 28.571 | 28.571 | 69.992 | |||
| cell control | 0.434 ± 0.040 | 0.434 ± 0.113 | 1.509 ± 0.105 | – | – | – | |||

| Concentrations of Drug | Groups | CT | Copies/μL |
|---|---|---|---|
| GBP 100 μg/mL | F1 | 18.6 | 5.32 × 104 ** |
| GBP 50 μg/mL | F2 | 18.6 | 5.49 × 104 ** |
| GBP 25 μg/mL | F3 | 18.2 | 7.08 × 104 * |
| GBP 12.5 μg/mL | F4 | 18.1 | 7.60 × 104 * |
| GBP 6.2 μg/mL | F5 | 17.7 | 1.46 × 104 * |
| 3TC 20 μg/mL | F6 | 22.9 | 5.04 × 104 ** |
| No Treatment | F7 | 16.4 | 2.28 × 104 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals and Instruments
3.2. Viruses, Cells and Positive Control Compounds
3.3. Nanoemulsion and HPLC of GBP
3.4. Cellular Toxicity Test
3.5. Virucidal Activity and Protecting Cells Tests
3.6. Hepatitis B Virus Antigen Inhibition Test
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, J.; Huang, P.; Wen, M.H.; Liang, L.J.; Zhang, X.; Tan, S.N.; Zhu, X.L. Antigenic epitope peptides of influenza H3N2 virus neuraminidase gene based on experiments. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 2908–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ooi, E.V.; Ang, P.O., Jr. Antiviral activities of extracts from Hong Kong seaweeds. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2008, 9, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, S.W.; Chan, H.L.; Leung, N.W.; Chau, T.N.; Lai, S.T.; Chan, F.K.; Sung, J.J. Lamivudine treatment for fulminant hepatic failure due to acute exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 15, 1737–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tziomalos, K. Effect of antiviral treatment on the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B. World J. Hepatol. 2010, 2, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roslinska, M.; Walinska, K.; Swiezewska, E.; Chojnacki, T. Plant Long-chain Polyprenols as Chemotaxonomic Markers. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2001, 6, 228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chojnacki, T.; Jankowski, W.; Swiezewska, E. Dolichols and Polyprenols; Elements of Membranes, Coenzymes and Secondary Metabolites. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2001, 6, 192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Swiezewskae, E.; Danikiewiczb, W. Polyisoprenoids: Structure, biosynthesis and function. Prog. Lipid Res. 2005, 44, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; Yu, Q.; Tan, W.H. Purification of Flavonol Glycosides from Ginkgo biloba L. Leaves. Chin. J. Pharm 1998, 29, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Z.; Shen, Z.B.; Chen, X. Polyprenols from Ginkgo biloba Leaves. Chem. Ind. For. Prod. 1992, 12, 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Shishkina, L.N.; Safatov, A.S.; Sergeev, A.N.; P’iankov, O.V.; Poryvaev, V.D.; Bulychev, L.E.; Petrishchenko, V.A.; P’iankova, O.G.; Zhukov, V.A.; Ryzhikov, A.B.; et al. Mechanisms of mice resistance to influenza virus A/AICHI/2/68 after preventive injection with polyprenols. Vopr. Virusol. 2001, 46, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Danilov, L.L.; Maltsev, S.D.; Deyeva, A.V.; Narovlyansky, A.N.; Sanin, A.V.; Ozherelkov, S.V.; Pronin, A.V. Phosprenyl: A novel drug with antiviral and immunomodulatory activity. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 1995, 44, 395–400. [Google Scholar]
- Pronin, A.V.; Grigorieva, E.A.; Sanin, A.V.; Narovlyansky, A.N.; Ozherelkov, S.V.; Deyeva, A.V.; Danilov, L.L.; Maltsev, S.D.; Najid, A. Polyprenols as possible factors that determine an instructive role of the innate immunity in the acquired immune response. Russ. J. Immunol. 2002, 7, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Safatov, A.S.; Boldyrev, A.N.; Bulychev, L.E. A prototype prophylactic anti-influenza preparation in aerosol form on the basis of abies sibirica polyprenols. J. Aerosol Med. 2005, 18, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergeev, A.N.; Safatov, A.S.; P’iankov, O.V. Prophylactic efficacy of aerosol preparations based on Abies siberica polyprenols in experimental influenza infection. Vopr. Virusol. 2001, 46, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shishkina, L.N.; Safatov, A.S.; Sergeev, A.N.; Zhukov, V.A.; Bulychev, L.E.; P’iankov, O.V.; Poryvaev, V.D.; P’iankova, O.G.; Buriak, G.A.; Goncharova, E.P. Mechanisms of action of aerosol preparations based on abies siberica polyprenols in experimental influenza infection. Vopr. Virusol. 2001, 46, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Safaov, A.S.; Sergeev, A.N.; Shishkina, L.N.; Pyankov, O.V.; Poryvaev, V.D.; Bulychev, L.E.; Petrishchenko, V.A.; Pyankova, O.G.; Zhukov, V.A.; Ryzhikov, A.B.; et al. Effect of intramuscularly injected polyprenols on influenza virus infection in mice. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2010, 11, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sviderskii, V.; Khovanskikh, A.; Rozengart, E.; Moralev, S.N.; Yagodina, O.V.; Gorelkin, V.S.; Basova, I.N.; Kormilitsyn, B.N.; Nikitina, T.V.; Roshchin, V.I.; et al. A comparative study of the effect of the polyprenol preparation ropren from coniferous plants on the key enzymes of the cholinergic and monoaminergic types of nervous transmission. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2006, 408, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, R.; Wang, C.Z.; Kong, Z.W. Antibacterial/Antifungal Activity and Synergistic Interactions between Polyprenols and Other Lipids Isolated from Ginkgo biloba L. Leaves. Molecules 2013, 18, 2166–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, R.; Wang, C.Z.; Kong, Z.W. Antibacterial activity of polyprenols and other lipids from Ginkgo biloba L. Leaves. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Applied Biotechnology (ICAB 2012), Tianjin, China, 18–19 October, 2012; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 251, pp. 1581–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Z.; Zheng, G.Y.; Chen, W.Y.; Shen, Z.B. Protection of GP soft capsules on acute liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride and d-galactosamine. Pharm. Clin. Chin. Mater. Med. 2007, 23, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Z.; Chen, W.Y.; Zheng, G.Y.; Shen, Z.B. Study on the protective effect of GP on acute liver injury induced by alcohol in mice. Chin. J. Biolchem. Pharm. 2007, 28, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Wang, C.Z.; Ye, J.Z.; Li, H.T. Hepatoprotective effects of polyprenols from Ginkgo biloba L. leaves on CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; Shen, Z.B. The effects on transplanted Heps and EC tumors in mouse for polyprenols in combination with chemotherapeutic drugs. Chin. J. Biolchem. Pharm. 2003, 24, 113–115. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Z.; Shen, Z.B. The effect of 60Co radiotherapy in combination with Ginkgo biloba polyprenols in mice transplanted heps. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2004, 11, 329–331. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Z.; Shen, Z.B.; Zheng, G.Y. Study on effect of polyprenols from leaves of Ginkgo biloba L on prolonging the life of cancer-bearing mice. Chem. Ind. For. Prod. 2008, 27, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Van Meerloo, J.; Kaspers, G.J.L.; Cloos, J. Cell sensitivity assays: The MTT assay. In Cancer Cell Culture; Humana Press: Clifton, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.-Y.; Wei, L.-W.; Zhang, X.-Z. In vitro anti-hepatitis B virus activity screening of Gankang granule prescriptions. China J. Mod. Med. 2011, 21, 709–717. [Google Scholar]
- Tolo, F.M.; Rukunga, G.M.; Muli, F.W.; Njagi, E.N.; Njue, W.; Kumon, K.; Mungai, G.M.; Muthaura, C.N.; Muli, J.M.; Keter, L.K.; et al. Antiviral activity of the extracts of a Kenyan medicinal plant Carissa edulis against herpes simplex virus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 104, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.L.; Shen, W.Z.; Rui, W.; Ma, X.J.; Cen, Y.Z. Antiviral activity of a sulfoquinovosy diacylglycerol (SQDG) compound isolated from the green alga Caulerpa racemosa. Botanica Marina 2007, 50, 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamini, E.; Bizzarri, R.; Cavallini, G.; Cerbai, B.; Chiellini, E.; Donati, A.; Gori, Z.; Manfrini, A.; Parentini, I.; Signori, F.; et al. Ageing and oxidative stress: A role for dolichol in the antioxidant machinery of cell membranes. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2004, 6, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walinska, K. Comparison of the influence of the polyprenol structure on model membranes. Desalination 2004, 163, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krystyna, W.; Tadeuse, J. The effect of phosphate ester derivates of polyprenol on model membrane stability. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2001, 6, 426. [Google Scholar]
- Janas, T.; Nowotarski, K. Monolayer and bilayer studies on the effect of polyprenols on phospholipid model membranes. Curr. Top. Biophys. 2001, 25, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.-Z.; Li, W.-J.; Tao, R.; Ye, J.-Z.; Zhang, H.-Y. Antiviral Activity of a Nanoemulsion of Polyprenols from Ginkgo Leaves against Influenza A H3N2 and Hepatitis B Virus in Vitro. Molecules 2015, 20, 5137-5151. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20035137
Wang C-Z, Li W-J, Tao R, Ye J-Z, Zhang H-Y. Antiviral Activity of a Nanoemulsion of Polyprenols from Ginkgo Leaves against Influenza A H3N2 and Hepatitis B Virus in Vitro. Molecules. 2015; 20(3):5137-5151. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20035137
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Cheng-Zhang, Wen-Jun Li, Ran Tao, Jian-Zhong Ye, and Hong-Yu Zhang. 2015. "Antiviral Activity of a Nanoemulsion of Polyprenols from Ginkgo Leaves against Influenza A H3N2 and Hepatitis B Virus in Vitro" Molecules 20, no. 3: 5137-5151. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20035137
APA StyleWang, C.-Z., Li, W.-J., Tao, R., Ye, J.-Z., & Zhang, H.-Y. (2015). Antiviral Activity of a Nanoemulsion of Polyprenols from Ginkgo Leaves against Influenza A H3N2 and Hepatitis B Virus in Vitro. Molecules, 20(3), 5137-5151. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20035137





